Radiographic and Clinical Comparison of Polyetheretherketone Versus 3D-Printed Titanium Cages in Lumbar Interbody Fusion—A Single Institution’s Experience
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Radiographic Assessment
2.3. Patient-Reported Outcomes Measures
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Demographics
3.2. Perioperative Analyses
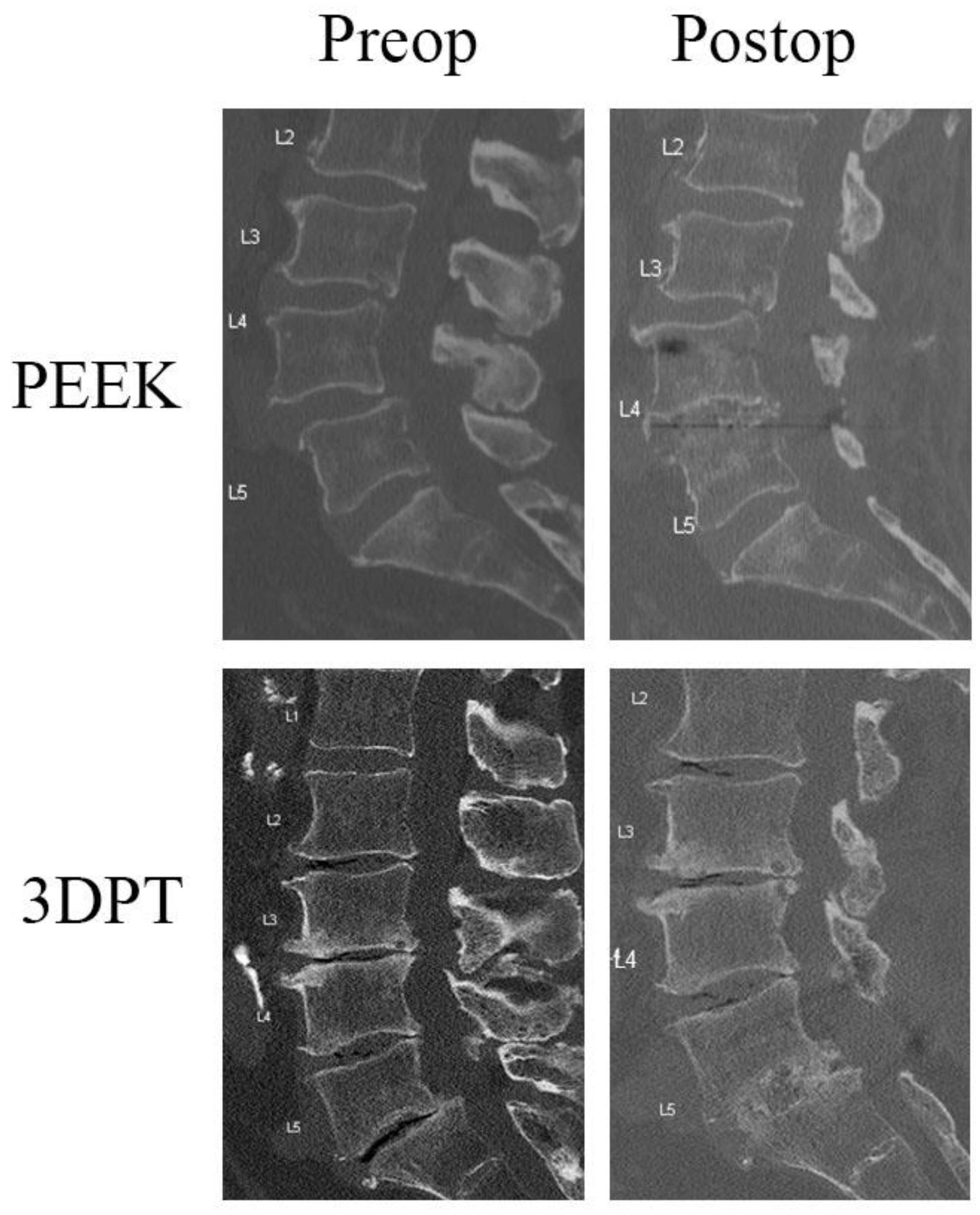
3.3. Radiographic Analysis
3.4. Patient Reported Outcomes
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALIF | Anterior lumbar interbody fusion |
| BMP | Bone morphogenetic protein |
| EQ-5D | EuroQol-5D |
| GPa | Gigapascal |
| LLIF | Lateral lumbar interbody fusion |
| ODI | Oswestry Disability Index |
| PEEK | Polyetheretherketone |
| PLIF | Posterior lumbar interbody fusion |
| PROM | Patient reported outcome measure |
| TLIF | Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion |
| US | United States |
| VAS | Visual analog scale |
| 3DPT | 3D-printed titanium |
References
- Ravindra, V.M.; Senglaub, S.S.; Rattani, A.; Dewan, M.C.; Härtl, R.; Bisson, E.; Park, K.B.; Shrime, M.G. Degenerative Lumbar Spine Disease: Estimating Global Incidence and Worldwide Volume. Glob. Spine J. 2018, 8, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidhu, G.S.; Henkelman, E.; Vaccaro, A.R.; Albert, T.J.; Hilibrand, A.; Anderson, G.D.; Rihn, J.A. Minimally Invasive versus Open Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Systematic Review. Clin Orthop Relat. Res. 2014, 472, 1792–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heemskerk, J.L.; Akinduro, O.O.; Clifton, W.; Quiñones-Hinojosa, A.; Abode-Iyamah, K.O. Long-term clinical outcome of minimally invasive versus open single-level transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar diseases: A meta-analysis. Spine J. 2021, 21, 2049–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenz, M.; Mohamud, K.; Bredow, J.; Oikonomidis, S.; Eysel, P.; Scheyerer, M.J. Comparison of Different Approaches in Lumbosacral Spinal Fusion Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Asian Spine J. 2022, 16, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, F.B.; Hansen, E.S.; Eiskjær, S.P.; Høy, K.; Helmig, P.; Neumann, P.; Niedermann, B.; Bünger, C.E. Circumferential Lumbar Spinal Fusion With Brantigan Cage Versus Posterolateral Fusion With Titanium Cotrel–Dubousset Instrumentation: A prospective, randomized clinical study of 146 patients. Spine 2002, 27, 2674–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.M.; Devine, J.N. PEEK biomaterials in trauma, orthopedic, and spinal implants. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 4845–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sul, Y.-T.; Johansson, C.; Byon, E.; Albrektsson, T. The bone response of oxidized bioactive and non-bioactive titanium implants. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6720–6730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, P.J.; Lehman, R.A. Optimizing the Spinal Interbody Implant: Current Advances in Material Modification and Surface Treatment Technologies. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2020, 13, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Jiang, W.; Yan, J.; Hu, K.; Han, Z.; Wang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, G.; Wang, Z.; Mao, K.; et al. A novel 3D printed cage with microporous structure and in vivo fusion function. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2019, 107, 1386–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Easley, K.; Lee, J.-S.; Hong, J.-Y.; Virk, M.; Hsieh, P.C.; Yoon, S.T. Comparison of Minimally Invasive Versus Open Transforaminal Interbody Lumbar Fusion. Glob. Spine J. 2020, 10, 143S–150S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.J.; Kim, D.-M.; Park, S. Comparison of Fusion, Subsidence, and Clinical Results Between 3D-Printed Porous Titanium Cage and Polyetheretherketone Cage in Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Minimum of 2 Years Follow-Up. World Neurosurg. 2023, 177, e732–e741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, D.A.; Okano, I.; Oezel, L.; Zhu, J.; Chiapparelli, E.; Shue, J.; Sama, A.A.; Cammisa, F.P.; Girardi, F.P.; Hughes, A.P. Evaluation of cage subsidence in standalone lateral lumbar interbody fusion: Novel 3D-printed titanium versus polyetheretherketone (PEEK) cage. Eur. Spine J. 2021, 30, 2377–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogel, G.; Martin, N.; Lynch, K.; Pelletier, M.H.; Wills, D.; Wang, T.; Walsh, W.R.; Williams, G.M.; Malik, J.; Peng, Y.; et al. Subsidence and fusion performance of a 3D-printed porous interbody cage with stress-optimized body lattice and microporous endplates—A comprehensive mechanical and biological analysis. Spine J. 2022, 22, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toop, N.; Dhaliwal, J.; Grossbach, A.; Gibbs, D.; Reddy, N.; Keister, A.; Mallory, N.; Xu, D.; Viljoen, S. Subsidence Rates Associated With Porous 3D-Printed Versus Solid Titanium Cages in Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion. Glob. Spine J. 2023, 14, 1889–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, O.; Asazuma, T.; Yato, Y.; Imabayashi, H.; Yasuoka, H.; Fujikawa, A. Comparison of fusion rates following transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion using polyetheretherketone cages or titanium cages with transpedicular instrumentation. Eur. Spine J. 2014, 23, 2150–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, L.; Abdala, N.; Oliveira, L.; Amaral, R.; Coutinho, E.; Pimenta, L. Radiographic and clinical evaluation of cage subsidence after stand-alone lateral interbody fusion. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2013, 19, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, S.L.; Adogwa, O.; Paul, A.R.; Anderson, W.N.; Aaronson, O.; Cheng, J.S.; McGirt, M.J. Utility of minimum clinically important difference in assessing pain, disability, and health state after transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2011, 14, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgstaller, J.M.; Wertli, M.M.; Ulrich, N.H.; Pichierri, G.; Brunner, F.; Farshad, M.; Porchet, F.; Steurer, J.; Gravestock, I. Evaluating the Minimal Clinically Important Difference of EQ-5D-3L in Patients With Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Swiss Prospective Multicenter Cohort Study. Spine 2020, 45, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posit Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R; Posit Software P.: Boston, MA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.-H.; Cheong, C.K.; Hey, H.W.D. Titanium (Ti) cages may be superior to polyetheretherketone (PEEK) cages in lumbar interbody fusion: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical and radiological outcomes of spinal interbody fusions using Ti versus PEEK cages. Eur. Spine J. 2021, 30, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaman, S.; Kerezoudis, P.; Bydon, M.; Torner, J.C.; Hitchon, P.W. Titanium vs. polyetheretherketone (PEEK) interbody fusion: Meta-analysis and review of the literature. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 44, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaad, E.; Fatima, N.; Kiapour, A.; Hadzipasic, M.; Shankar, G.M.; Shin, J.H. Polyetheretherketone Versus Titanium Cages for Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Meta-Analysis and Review of the Literature. Neurospine 2020, 17, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelletier, M.H.; Cordaro, N.; Punjabi, V.M.; Waites, M.; Lau, A.; Walsh, W.R. PEEK Versus Ti Interbody Fusion Devices: Resultant Fusion, Bone Apposition, Initial and 26-Week Biomechanics. Clin. Spine Surgery: A Spine Publ. 2016, 29, E208–E214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahill, K.S.; Chi, J.H.; Day, A.; Claus, E.B. Prevalence, Complications, and Hospital Charges Associated With Use of Bone-Morphogenetic Proteins in Spinal Fusion Procedures. JAMA 2009, 302, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safaee, M.M.; Ore, C.L.D.; Zygourakis, C.C.; Deviren, V.; Ames, C.P. Estimating a price point for cost-benefit of bone morphogenetic protein in pseudarthrosis prevention for adult spinal deformity surgery. J. Neurosurgery: Spine 2019, 30, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Nandyala, S.V.B.; Marquez-Lara, A.; Fineberg, S.J. Epidemiological Trends in the Utilization of Bone Morphogenetic Protein in Spinal Fusions From 2002 to 2011. Spine 2014, 39, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrastil, J.; Low, J.B.; Whang, P.G.; Patel, A.A. Complications Associated With the Use of the Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Proteins for Posterior Interbody Fusions of the Lumbar Spine. Spine 2013, 38, E1020–E1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helgeson, M.D.; Lehman, R.A.; Patzkowski, J.C.; Dmitriev, A.E.; Rosner, M.K.; Mack, A.W. Adjacent vertebral body osteolysis with bone morphogenetic protein use in transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Spine J. 2011, 11, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, M.C.; Brown, J.V.; Heirs, M.K.; Higgins, J.P.; Mannion, R.J.; Rodgers, M.A.; Stewart, L.A. Safety and Effectiveness of Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 for Spinal Fusion: A meta-analysis of individual-participant data. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Selph, S.; McDonagh, M.; Peterson, K.; Tiwari, A.; Chou, R.; Helfand, M. Effectiveness and Harms of Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 in Spine Fusion: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 890–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hikata, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Ishihara, S.; Shinozaki, Y.; Nimoniya, K.; Konomi, T.; Fujii, T.; Funao, H.; Yagi, M.; Hosogane, N.; et al. Risk factors for early reoperation in patients after posterior lumbar interbody fusion surgery. A propensity-matched cohort analysis. J. Orthop. Sci. 2022, 29, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Yang, S.; Wei, Z.; Cai, C.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, H.; Chu, T. Incidence and Risk Factors for Adjacent Segment Disease After Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Patients with Lumbar Degenerative Diseases. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, ume 14, 8185–8192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, S.; Yamashita, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Nagamoto, Y.; Sugiura, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Maeno, T.; Iwasaki, M. Adjacent Segment Disease After Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Case Series of 1000 Patients. Glob. Spine J. 2018, 8, 722–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Li, X.; Bai, X.; Wang, Y.; Han, P.; Li, H. Titanium-coated polyetheretherketone cages vs. polyetheretherketone cages in lumbar interbody fusion: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2023, 25, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokawem, M.; Katzouraki, G.; Harman, C.L.; Lee, R. Lumbar interbody fusion rates with 3D-printed lamellar titanium cages using a silicate-substituted calcium phosphate bone graft. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 68, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.K.; Bydon, M.; Bisson, E.F.; Glassman, S.D.; Foley, K.T.; Shaffrey, C.I.; Potts, E.A.; Shaffrey, M.E.; Coric, D.; Knightly, J.J.; et al. Minimally invasive versus open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for grade I lumbar spondylolisthesis: 5-year follow-up from the prospective multicenter Quality Outcomes Database registry. Neurosurg. Focus 2023, 54, E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, S.L.; Adogwa, O.; Mendenhall, S.K.; Shau, D.N.; Anderson, W.N.; Cheng, J.S.; Devin, C.J.; McGirt, M.J. Determination of minimum clinically important difference (MCID) in pain, disability, and quality of life after revision fusion for symptomatic pseudoarthrosis. Spine J. 2012, 12, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beighley, A.; Zhang, A.; Huang, B.; Carr, C.; Mathkour, M.; Werner, C.; Scullen, T.; Kilgore, M.D.; Maulucci, C.M.; Dallapiazza, R.F.; et al. Patient-reported outcome measures in spine surgery: A systematic review. J. Craniovertebral Junction Spine 2022, 13, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Grade | Description |
|---|---|
| I | Fusion with remodeling and trabeculae |
| II | Graft intact without full incorporation or remodeling, but no lucency present. |
| III | Graft intact, potential lucency above and below implant |
| IV | No fusion, implant collapse and/or resorption |
| PEEK (N = 49) | 3DPT (N = 42) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | ||
| Age (years) | 59.67 (11.07) | 64.26 (10.60) | 0.047 * (1) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 30.68 (7.07) | 32.23 (5.75) | 0.259 (1) |
| Sex | No (%) | No (%) | |
| Male | 23 (46.9%) | 27 (64.3%) | 0.139 (2) |
| Female | 26 (53.1%) | 15 (35.7%) | |
| Comorbidity | |||
| Diabetes Mellitus | 6 (12.2%) | 5 (11.9%) | 1.000 (2) |
| Coronary Artery Disease | 2 (4.1%) | 2 (4.8%) | 1.000 (2) |
| Hypertension | 3 (6.1%) | 28 (66.7%) | <0.001 * (2) |
| Smoking Status (+nicotine level) | 3 (6.1%) | 2 (4.8%) | 1.000 (2) |
| History of Spine Surgery | 10 (20.4%) | 6 (14.3%) | 0.583 (2) |
| Presenting Symptom | |||
| Back Pain | 46 (93.9%) | 35 (83.3%) | 0.178 (2) |
| Leg Pain | 43 (87.8%) | 36 (85.7%) | 1.000 (2) |
| Numbness/Tingling | 8 (16.3%) | 5 (11.9%) | 0.765 (2) |
| Weakness | 6 (12.2%) | 3 (7.1%) | 0.498 (2) |
| Spondylolisthesis | |||
| Grade 1 | 40 (81.6%) | 33 (78.5%) | 0.70 (2) |
| Grade 2 | 3 (6.1%) | 5 (11.9%) | 0.33 (2) |
| Number of Surgical Levels | |||
| 1 | 35 (71.4%) | 31 (73.8%) | 0.819 (2) |
| 2 | 14 (28.6%) | 11 (26.2%) | |
| Interbody Fusion Level | |||
| L3–4 | 3 (6.1%) | 11 (26.2%) | 0.010 * (2) |
| L4–5 | 39 (79.6%) | 26 (61.9%) | 0.102 (2) |
| L5–S1 | 21 (42.9%) | 16 (38.1%) | 0.674 (2) |
| Interbody Placement | |||
| PLIF | 32 (65.3%) | 20 (47.6%) | 0.096 (2) |
| TLIF | 17 (34.7%) | 22 (52.4%) | |
| Open | 27 (55.1%) | 32 (76.2%) | |
| Mini-open | 22 (44.9%) | 10 (23.8%) | 0.048 * (2) |
| MIS-tubular | 4 (8.2%) | 4 (9.5%) | 1.000 (2) |
| Bone Morphogenetic Protein | 38 (80.9%) | 23 (54.8%) | 0.012 * (2) |
| Cellular Allograft | 6 (12.8%) | 19 (45.2%) | <0.001 * (2) |
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | ||
| Estimated Blood Loss (mL) | 525.00 (394.84) | 227.38 (153.40) | <0.001 * (1) |
| Length of Stay (days) | 4.35 (2.99) | 4.26 (2.91) | 0.883 (1) |
| PEEK (N = 49) | 3DPT (N = 42) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Return to OR | No (%) | No (%) | |
| 1-year | 1 (2.0%) | 0 | 1.000 (1) |
| 2-year | 2 (4.1%) | 2 (4.8%) | 1.000 (1) |
| Cumulative 2-year | 3 (6.1%) | 2 (4.8%) | 1.000 (1) |
| Fusion | 47 (95.9%) | 41 (97.6%) | 1.000 (1) |
| ODI MCID 1-year (14.9) | 31 (73.8%) | 9 (64.3%) | 0.511 (1) |
| ODI MCID 2-year (14.9) | 22 (84.6%) | 13 (68.4%) | 0.281 (1) |
| EQ-5D MCID 1-year (0.19) | 22 (52.4%) | 10 (71.4%) | 0.350 (1) |
| EQ-5D MCID 2-year (0.19) | 14 (53.8%) | 11 (57.9%) | 1.000 (1) |
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | ||
| ODI Change 1-year | 24.45 (17.03) | 18.22 (14.32) | 0.224 (2) |
| ODI Change 2-year | 25.69 (13.39) | 19.37 (19.78) | 0.208 (2) |
| EQ-5D Change 1-year | −0.22 (0.22) | −0.22 (0.17) | 0.927 (2) |
| EQ-5D Change 2-year | −0.22 (0.24) | −0.19 (0.24) | 0.658 (2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, D.; Chan, J.L.; Eleanore, A.; DeCost, K.; Luk, J.; Neukam, L.C.; Rizvi, T.Z.; Lin, Z.; Ghogawala, Z.; Magge, S.N.; et al. Radiographic and Clinical Comparison of Polyetheretherketone Versus 3D-Printed Titanium Cages in Lumbar Interbody Fusion—A Single Institution’s Experience. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1813. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061813
Liu D, Chan JL, Eleanore A, DeCost K, Luk J, Neukam LC, Rizvi TZ, Lin Z, Ghogawala Z, Magge SN, et al. Radiographic and Clinical Comparison of Polyetheretherketone Versus 3D-Printed Titanium Cages in Lumbar Interbody Fusion—A Single Institution’s Experience. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(6):1813. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061813
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Diang, Julie L. Chan, Art Eleanore, Kristin DeCost, Justin Luk, Lissette C. Neukam, Tasneem Zaihra Rizvi, Zhibang Lin, Zoher Ghogawala, Subu N. Magge, and et al. 2025. "Radiographic and Clinical Comparison of Polyetheretherketone Versus 3D-Printed Titanium Cages in Lumbar Interbody Fusion—A Single Institution’s Experience" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 6: 1813. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061813
APA StyleLiu, D., Chan, J. L., Eleanore, A., DeCost, K., Luk, J., Neukam, L. C., Rizvi, T. Z., Lin, Z., Ghogawala, Z., Magge, S. N., Yew, A. Y., & Whitmore, R. G. (2025). Radiographic and Clinical Comparison of Polyetheretherketone Versus 3D-Printed Titanium Cages in Lumbar Interbody Fusion—A Single Institution’s Experience. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(6), 1813. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14061813






