Botulinum Toxin Therapy: A Comprehensive Review on Clinical and Pharmacological Insights
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Botulinum Toxin History
1.2. The Structure of Botulinum Toxin

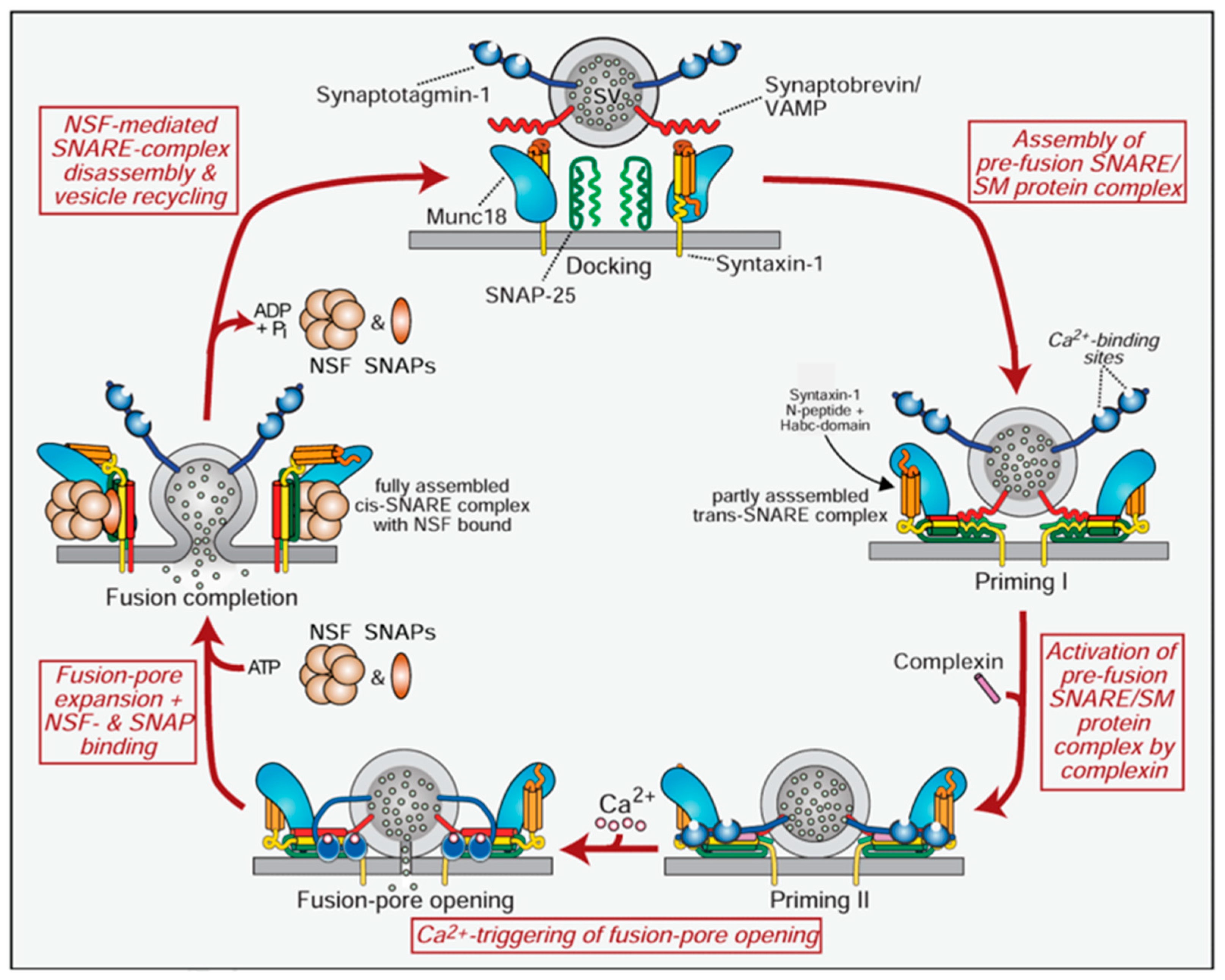
1.3. Botulinum Neurotoxin Mechanism of Action
1.4. Duration of Action
1.5. Long-Distance Effects of Botulinum Neurotoxins
2. Results
2.1. Therapeutic Uses of Botulinum Toxin in Clinical Practice
2.1.1. Botulinum Toxin in Dystonia
- Cervical Dystonia
2.1.2. Botulinum Toxin in Spasticity
- Multiple sclerosis (MS)
- Cerebral Palsy (CP)
- Stroke
- Traumatic brain injury (TBI)
2.1.3. Botulinum Toxin in Pain Management
2.1.4. Botulinum Toxin in Overactive Bladder (OAB)
2.1.5. Botulinum Toxin in Chronic Migraine
2.1.6. Botulinum Toxin in Strabismus
2.1.7. Botulinum Toxin in Primary Axillary Hyperhidrosis
2.1.8. Botulinum Toxin in Blepharospasm
2.1.9. Botulinum Toxin in Hemifacial Spasm
2.2. Botulinum Toxins and COVID
2.3. Botulinum Toxin and Immunogenicity
2.4. Adverse Events of Botulinum Toxin Treatment
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Methodology
5.1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
5.2. Study Selection Process
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Declaration of Generative AI and AI-Assisted Technologies in the Writing Process
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AE | Adverse Event |
| AUR | Acute Urinary Retention |
| BoNT | Botulinum Neurotoxin |
| BTX | Botulinum Toxin |
| COL-CAP | Classification System for Cervical Dystonia |
| CGRP | Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide |
| CPM | Conditioned Pain Modulation |
| GMFCS | Gross Motor Function Classification System |
| MFP | Myofascial Pain (Syndrome) |
| NTNH | Stands for Non-Toxic Non-Hemagglutinin |
| NAbs | Neutralizing Antibodies |
| OAB | Overactive Bladder |
| PREEMPT | Phase III Research Evaluating Migraine Prophylaxis Therapy |
| SNARE | Soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor Attachment Protein Receptor |
| RCT | Randomized Controlled Trial |
| SV2 | Synaptic Vesicle Protein 2 |
| TeNT | Tetanus Neurotoxin |
| UTIs | Urinary Tract Infections |
References
- Simpson, L.L. The origin, structure, and pharmacological activity of botulinum toxin. Pharmacol. Rev. 1981, 33, 155–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erbguth, F.J.; Naumann, M. On the first systematic descriptions of botulism and botulinum toxin by Justinus Kerner (1786–1862). J. Hist. Neurosci. 2000, 9, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbguth, J.F.; Naumann, M. Historical aspects of botulinum toxin: Justinus Kerner (1786–1862) and the “sausage poison”. Neurology 1999, 53, 1850–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitcup, M.S.; Hallett, M. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology Botulinum Toxin Therapy; Barrett, J.E., Ed.; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; p. 289. [Google Scholar]
- van Ermengem, E. Originally published as “Ueber einen neuen anaëroben Bacillus und seine Beziehungen zum Botulismus” in Zeitschrift für Hygiene und Infektionskrankheiten. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1897, 26, 701–719. [Google Scholar]
- Devriese, P.P. On the discovery of Clostridium botulinum. J. Hist. Neurosci. 1999, 8, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, G. The occurrence of Bacillus botulinus in nature. J. Bacteriol. 1919, 4, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snipe, P.T.; Sommer, H. Studies on botulinus toxin. 3. Acid precipitation of botulinus toxin. J. Infect. Dis. 1928, 43, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmunds, C.; Keiper, G. Further studies on the action of botulinus toxin. JAMA 1924, 83, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovic, J.; Brin, M.F. Botulinum toxin: Historical perspective and potential new indications. Muscle Nerve Off. J. Am. Assoc. Electrodiagn. Med. 1997, 20, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevdakh, I.A.; Toth, B.A.; Daane, S.P. Botulinum Toxin: BOTOX®. In International Textbook of Aesthetic Surgery; Scuderi, N., Toth, B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. Clinical uses of botulinum neurotoxins: Current indications, limitations and future developments. Toxins 2012, 4, 913–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiri Nawrocki, J.C. The etiology, diagnosis, and management of hyperhidrosis: A comprehensive review: Therapeutic options. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 81, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, D.; Brodsky, M.; Lew, M.; Brashear, A.; Jankovic, J.; Molho, E.; Orlova, O.; Timerbaeva, S. Long-term efficacy and safety of botulinum toxin type A (Dysport) in cervical dystonia. Park. Relat. Disord. 2010, 16, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergfeldt, U.; Borg, K.; Kullander, K.; Julin, P. Focal spasticity therapy with botulinum toxin: Effects on function, activities of daily living and pain in 100 adult patients. J. Rehabil. Med. 2006, 38, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raciti, L.; Raciti, G.; Militi, D.; Casella, C.; Calabrò, R.S. Chronic Migraine: A Narrative Review on the Use of Botulinum Toxin with Clinical Indications and Future Directions. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2022, 21, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, R.; Fink, H.A.; Huckabay, C.; Monga, M.; Wilt, T.J. Botulinum toxin for treatment of urinary incontinence due to detrusor overactivity: A systematic review of effectiveness and adverse effects. Spinal Cord 2007, 45, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, D.M.; Alexander, D.N.; O’Brien, C.F.; Tagliati, M.; Aswad, A.S.; Leon, J.M.; Gibson, J.; Mordaunt, J.M.; Monaghan, E.P. Botulinum toxin type A in the treatment of upper extremity spasticity. Neurology 1996, 46, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessy, L.A.; Fallico, N.; Mazzocchi, M.; Scuderi, N. Botulinum toxin for glabellar lines: A review of the efficacy and safety of currently available products. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2011, 12, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poewe, W.; Deuschl, G.; Nebe, A.; Feifel, E.; Wissel, J.; Benecke, R.; Kessler, K.R.; Ceballos-Baumann, A.O.; Ohly, A.; Oertel, W.; et al. What is the optimal dose of botulinum toxin A in the treatment of cervical dystonia? Results of a double blind, placebo controlled, dose ranging study using Dysport®. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1998, 64, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizo, J.; Südhof, T.C. Mechanics of membrane fusion. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1998, 5, 839–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitcup, S.M.; Hallett, M. (Eds.) Botulinum Toxin Therapy. In Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2004; Volume 263. [Google Scholar]
- Lacy, D.B.; Tepp, W.; Cohen, A.C.; DasGupta, B.R.; Stevens, R.C. Crystal structure of botulinum neurotoxin type A and implications for toxicity. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1998, 10, 898–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Carranza, M.; Škerlová, J.; Lee, P.G.; Zhang, J.; Burgin, D.; Elliott, M.; Philippe, J.; Donald, S.; Hornby, F.; Henriksson, L.; et al. Structure and activity of botulinum neurotoxin X. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rossetto, O.; Pirazzini, M.; Montecucco, C. Botulinum neurotoxins: Genetic, structural and mechanistic insights. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, M.; Masuyer, G.; Stenmark, P. Botulinum and Tetanus Neurotoxins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2019, 88, 811–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogolari, F.; Tosatto, S.C.; Muraro, L.; Montecucco, C. Electric dipole reorientation in the interaction of botulinum neurotoxins with neuronal membranes. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 2321–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuemket, N.; Tanaka, Y.; Tsukamoto, K.; Tsuji, T.; Nakamura, K.; Kozaki, S.; Yao, M.; Tanaka, I. Structural and mutational analyses of the receptor binding domain of botulinum D/C mosaic neurotoxin: Insight into the ganglioside binding mechanism. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 411, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Berntsson, R.P.; Tepp, W.H.; Tao, L.; Johnson, E.A.; Stenmark, P.; Dong, M. Structural basis for the unique ganglioside and cell membrane recognition mechanism of botulinum neurotoxin DC. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, D.; Weisemann, J.; Le Blanc, A.; von Berg, L.; Mahrhold, S.; Piesker, J.; Laue, M.; Luppa, P.B.; Dorner, M.B.; Dorner, B.G.; et al. A lipid-binding loop of botulinum neurotoxin serotypes B, DC and G is an essential feature to confer their exquisite potency. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanaday, N.L.; Cousin, M.A.; Milosevic, I.; Watanabe, S.; Morgan, J.R. The Synaptic Vesicle Cycle Revisited: New Insights into the Modes and Mechanisms. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 8209–8216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirazzini, M.; Azarnia Tehran, D.; Leka, O.; Zanetti, G.; Rossetto, O.; Montecucco, C. On the translocation of botulinum and tetanus neurotoxins across the membrane of acidic intracellular compartments. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1858, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirazzini, M.; Azarnia Tehran, D.; Zanetti, G.; Megighian, A.; Scorzeto, M.; Fillo, S.; Shone, C.C.; Binz, T.; Rossetto, O.; Lista, F.; et al. Thioredoxin and its reductase are present on synaptic vesicles, and their inhibition prevents the paralysis induced by botulinum neurotoxins. Cell Rep. 2014, 8, 1870–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanetti, G.; Tehran, D.A.; Pirazzini, M.; Binz, T.; Shone, C.C.; Fillo, S.; Lista, F.; Rossetto, O.; Montecucco, C. Inhibition of botulinum neurotoxins interchain disulfide bond reduction prevents the peripheral neuroparalysis of botulism. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 98, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossetto, O.; Pirazzini, M.; Lista, F.; Montecucco, C. The role of the single interchains disulfide bond in tetanus and botulinum neurotoxins and the development of antitetanus and antibotulism drugs. Cell. Microbiol. 2019, 21, e13037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantano, S.; Montecucco, C. The blockade of the neurotransmitter release apparatus by botulinum neurotoxins. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 793–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirazzini, M.; Rossetto, O.; Eleopra, R.; Montecucco, C. Botulinum Neurotoxins: Biology, Pharmacology, and Toxicology. Pharmacol. Rev. 2017, 69, 200–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Rumpel, S.; Zhou, J.; Strotmeier, J.; Bigalke, H.; Perry, K.; Shoemaker, C.B.; Rummel, A.; Jin, R. Botulinum neurotoxin is shielded by NTNHA in an interlocked complex. Science 2012, 335, 977–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossetto, O.; Pirazzini, M.; Fabris, F.; Montecucco, C. Botulinum Neurotoxins: Mechanism of Action Botulinum Toxin Therapy. In Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 263. [Google Scholar]
- Südhof, T.C. Neurotransmitter Release: The Last Millisecond in the Life of a Synaptic Vesicle. Neuron 2013, 80, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, B.; Buhr, N.; Bigalke, H.; Krampfl, K.; Dengler, R.; Kollewe, K. A long-term follow-up of botulinum toxin A in cervical dystonia. Neurol. Res. 2009, 31, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restani, L.; Giribaldi, F.; Manich, M.; Bercsenyi, K.; Menendez, G.; Rossetto, O.; Caleo, M.; Schiavo, G. Botulinum neurotoxins A and E undergo retrograde axonal transport in primary motor neurons. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1003087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonucci, F.; Rossi, C.; Gianfranceschi, L.; Rossetto, O.; Caleo, M. Long-distance retrograde effects of botulinum neurotoxin A. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 3689–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzocchio, R.; Caleo, M. More than at the Neuromuscular Synapse: Actions of Botulinum Neurotoxin A in the Central Nervous System. Neuroscientist 2015, 21, 44–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hok, P.; Veverka, T.; Hlustik, P.; Nevrly, M.; Kanovsky, P. The Central Effects of Botulinum Toxin in Dystonia and Spasticity. Toxins 2021, 13, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luvisetto, S. Botulinum Toxin and Neuronal Regeneration after Traumatic Injury of Central and Peripheral Nervous System. Toxins 2020, 12, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.H.; Jhang, J.F.; Chen, S.F.; Kuo, H.C. Real-Life Treatment Outcome of Botulinum Toxin A Injection on Overactive Bladder and Voiding Dysfunction in Patients with Central Nervous System Lesions. Toxins 2024, 16, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowson, A.J.; Kilminster, S.G.; Salt, R. Clinical profile of botulinum toxin A in patients with chronic headaches and cervical dystonia: A prospective, open-label, longitudinal study conducted in a naturalistic clinical practice setting. Drugs 2008, 9, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiple, D.; Strano, S.; Colosimo, C.; Fabbrini, G.; Calcagnini, G.; Prencipe, M.; Berardelli, A. Autonomic cardiovascular function and baroreflex sensitivity in patients with cervical dystonia receiving treatment with botulinum toxin type A. J. Neurol. 2008, 255, 843–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comella, C.L.; Jankovic, J.; Truong, D.D.; Hanschmann, A.; Grafe, S.; US XEOMIN Cervical Dystonia Study Group. Efficacy and safety of incobotulinumtoxinA (NT 201, XEOMIN®, botulinum neurotoxin type A, without accessory proteins) in patients with cervical dystonia. J. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 308, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, R.E.; Duarte, G.S.; Rodrigues, F.B.; Castelão, M.; Ferreira, J.; Sampaio, C.; Moore, A.P.; Costa, J. Botulinum toxin type B for cervical dystonia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 2016, CD004315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallett, M.; Albanese, A.; Dressler, D.; Segal, K.R.; Simpson, D.M.; Truong, D.; Jankovic, J. Evidence-based review and assessment of botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of movement disorders. Toxicon 2013, 67, 94–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, P.; Kang, U.; Fahn, S.; Brin, M.; Moskowitz, C.; Flaster, E. Double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of botulinum toxin injections for the treatment of spasmodic torticollis. Neurology 1990, 40, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brans, J.W.; Lindeboom, R.; Aramideh, M.; Speelman, J.D. Long-term effect of botulinum toxin on impairment and functional health in cervical dystonia. Neurology 1998, 50, 1461–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezaki, T.; Kaji, R.; Hamano, T.; Nagamine, T.; Shibasaki, H.; Shimizu, T.; Kimura, J. Optimisation of botulinum treatment for cervical and axial dystonias: Experience with a Japanese type A toxin. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1994, 57, 1535–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovic, J.; Schwartz, K. Botulinum toxin injections for cervical dystonia. Neurology 1990, 40, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankovic, J. Treatment of cervical dystonia with botulinum toxin. Mov. Disord. 2004, 19, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyslerowicz, M.; Kiedrzynska, W.; Adamkiewicz, B.; Jost, W.H.; Slawek, J. Cervical dystonia—Improving the effectiveness of botulinum toxin therapy. Neurol. Neurochir. Pol. 2020, 54, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brashear, A.; Lew, M.; Dykstra, D.; Comella, C.; Factor, S.; Rodnitzky, R.; Trosch, R.; Singer, C.; Brin, M.; Murray, J.; et al. Safety and efficacy of NeuroBloc (botulinum toxin type B) in type A—Responsive cervical dystonia. Neurology 1999, 53, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, M.F.; Adornato, B.T.; Dykstra, D.D.; Factor, S.A.; Massey, J.M.; Brin, M.F.; Jankovic, J.; Rodnitzky, R.L.; Singer, C.; Swenson, M.R.; et al. Botulinum toxin type B: A double-blind, placebo-controlled, safety and efficacy study in cervical dystonia. Neurology 1997, 49, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figgitt, D.P.; Noble, S. Botulinum Toxin B. Drugs 2002, 62, 705–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comella, C.L.; Jankovic, J.; Shannon, K.M.; Tsui, J.; Swenson, M.; Leurgans, S.; Fan, W.; The Dystonia Study Group. Comparison of botulinum toxin serotypes A and B for the treatment of cervical dystonia. Neurology 2005, 65, 1423–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comella, C.L.; Tanner, C.M.; DeFoor-Hill, L.; Smith, C. Dysphagia after botulinum toxin injections for spasmodic torticollis: Clinical and radiologic findings. Neurology 1992, 42, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, D.M.; Hallett, M.; Ashman, E.J.; Comella, C.L.; Green, M.W.; Gronseth, G.S.; Armstrong, M.J.; Gloss, D.; Potrebic, S.; Jankovic, J.; et al. Practice guideline update summary: Botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of blepharospasm, cervical dystonia, adult spasticity, and headache: Report of the Guideline Development Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2016, 19, 1818–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedlaya, D.; Reynolds, L.W.; Strum, S.R.; Waldman, S.D. Effective treatment of cervical dystonia with botulinum toxin: Review. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 1999, 3, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorentz, I.T.; Subramaniam, S.S.; Yiannikas, C. Treatment of idiopathic spasmodic torticollis with botulinum toxin A: A double-blind study on twenty-three patients. Mov. Disord. 1991, 6, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brin, M.; Lew, M.; Adler, C.; Comella, C.; Factor, S.; Jankovic, J.; O’brien, C.; Murray, J.; Wallace, J.; Willmer–Hulme, A.; et al. Safety and efficacy of NeuroBloc (botulinum toxin type B) in type A—Resistant cervical dystonia. Neurology 1999, 53, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dressler, D.; Altavista, M.C.; Altenmueller, E.; Bhidayasiri, R.; Bohlega, S.; Chana, P.; Chung, T.M.; Colosimo, C.; Fheodoroff, K.; Garcia-Ruiz, P.J.; et al. Consensus guidelines for botulinum toxin therapy: General algorithms and dosing tables for dystonia and spasticity. J. Neural Transm. 2021, 128, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiegel, L.L.; Ostrem, J.L.; Bledsoe, I.O. FDA Approvals and Consensus Guidelines for Botulinum Toxins in the Treatment of Dystonia. Toxins 2020, 12, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erro, R.; Picillo, M.; Pellecchia, M.T.; Barone, P. Improving the Efficacy of Botulinum Toxin for Cervical Dystonia: A Scoping Review. Toxins 2023, 15, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.W. Basis of movement control in dystonia and why botulinum toxin should influence it? Toxicon 2024, 237, 107251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza, J.C.C.; Falcone, A.C.M.; Barbosa, R.M.G.; Soares, M.C.; Munhoz, R.; Farah, M.; Capato, T.; Casagrande, S.C.B.; Cordellini, M.F.; de Castro Micheli, G.; et al. Botulinum Toxin and Deep Brain Stimulation in Dystonia. Toxins 2024, 16, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safarpour, Y.; Mousavi, T.; Jabbari, B. Botulinum Toxin Treatment in Multiple Sclerosis-a Review. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2017, 19, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habek, M.; Karni, A.; Balash, Y.; Gurevich, T. The place of the botulinum toxin in the management of multiple sclerosis. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2010, 112, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, W.H. Botulinum toxin in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2006, 253 (Suppl. 1), i16–i20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baccouche, I.; Bensmail, D.; Leblong, E.; Fraudet, B.; Aymard, C.; Quintaine, V.; Pottier, S.; Lansaman, T.; Malot, C.; Gallien, P.; et al. Goal-Setting in Multiple Sclerosis-Related Spasticity Treated with Botulinum Toxin: The GASEPTOX Study. Toxins 2022, 14, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dressler, D.; Bhidayasiri, R.; Bohlega, S.; Chahidi, A.; Chung, T.M.; Ebke, M.; Jacinto, L.J.; Kaji, R.; Koçer, S.; Kanovsky, P.; et al. Botulinum toxin therapy for treatment of spasticity in multiple sclerosis: Review and recommendations of the IAB-Interdisciplinary Working Group for Movement Disorders task force. J. Neurol. 2017, 264, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novarella, F.; Carotenuto, A.; Cipullo, P.; Iodice, R.; Cassano, E.; Spiezia, A.L.; Capasso, N.; Petracca, M.; Falco, F.; Iacovazzo, C.; et al. Persistence with Botulinum Toxin Treatment for Spasticity Symptoms in Multiple Sclerosis. Toxins 2022, 14, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedroff, K.; Granath, F.; Forssberg, H.; Haglund-Akerlind, Y. Long-term effects of botulinum toxin A in children with cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2009, 51, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multani, I.; Manji, J.; Hastings-Ison, T.; Khot, A.; Graham, K. Botulinum Toxin in the Management of Children with Cerebral Palsy. Paediatr. Drugs 2019, 21, 261–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, H.; Aoki, K.; Autti-Rämö, I.; Boyd, R.N.; Delgado, M.R.; Gaebler-Spira, D.J.; E Gormley, M.; Guyer, B.M.; Heinen, F.; Holton, A.F.; et al. Recommendations for the use of botulinum toxin type A in the management of cerebral palsy. Gait Posture 2000, 11, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picelli, A.; Santamato, A.; Cosma, M.; Baricich, A.; Chisari, C.; Millevolte, M.; Prete, C.D.; Mazzu, I.; Girardi, P.; Smania, N. Early Botulinum Toxin Type A Injection for Post-Stroke Spasticity: A Longitudinal Cohort Study. Toxins 2021, 13, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varvarousis, D.N.; Martzivanou, C.; Dimopoulos, D.; Dimakopoulos, G.; Vasileiadis, G.I.; Ploumis, A. The effectiveness of botulinum toxin on spasticity and gait of hemiplegic patients after stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Toxicon 2021, 203, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Liu, Y.; Shen, L.; Liang, X.; Xu, X.; Wei, Y. Botulinum Toxin Type A for Upper Limb Spasticity in Poststroke Patients: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29, 104682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.C.; Chang, K.V.; Chiu, Y.H.; Wu, W.T.; Ozcakar, L. Comparative Effectiveness of Botulinum Toxin Injections and Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy for Post-Stroke Spasticity: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. EClinicalMedicine 2022, 43, 101222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palazon-Garcia, R.; Benavente-Valdepenas, A.M. Botulinum Toxin: From Poison to Possible Treatment for Spasticity in Spinal Cord Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.M.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wei, C.J.; Jiang, Y.J. Can Botulinum Toxin Type A effectively treat neuropathic pain in spinal cord injury?: A protocol of systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e20702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacca, V.; Madaro, L.; De Angelis, F.; Proietti, D.; Cobianchi, S.; Orsini, T.; Puri, P.L.; Luvisetto, S.; Pavone, F.; Marinelli, S. Revealing the Therapeutic Potential of Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A in Counteracting Paralysis and Neuropathic Pain in Spinally Injured Mice. Toxins 2020, 12, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baricich, A.; Battaglia, M.; Cuneo, D.; Cosenza, L.; Millevolte, M.; Cosma, M.; Filippetti, M.; Dalise, S.; Azzollini, V.; Chisari, C.; et al. Clinical efficacy of botulinum toxin type A in patients with traumatic brain injury, spinal cord injury, or multiple sclerosis: An observational longitudinal study. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1133390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łuczak, B.; Nowińska, B.; Słychan, K.; Hądzlik, I.; Piotrowski, J.; Biały-Karbowniczek, J.; Bulska, K.; Brzozowska, P.; Piela, A.; Sławek, K. Botulinum toxin in management of back pain. Qual. Sport 2024, 15, 51889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta Gupta, A.; Edwards, S.; Smith, J.; Snow, J.; Visvanathan, R.; Tucker, G.; Wilson, D. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Efficacy of Botulinum Toxin A for Neuropathic Pain. Toxins 2022, 14, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luis, J.V.; Cordeiro, D.; e Pereira, G.M.; Pinheiro, F.; Antunes, S.; Lorga, S.; Almeida, S. Pain and Botulinum Toxin—Two Off-Label Botulinum Toxin Uses. Toxicon 2024, 237, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, K.M.; Barreto, E.S.R.; Alencar, V.B.; Lins-Kusterer, L.E.F.; Azi, L.M.T.d.A.; Kraychete, D.C. The efficacy of botulinum toxin in neuropathic pain: A systematic review. Br. J. Pain 2024, 18, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poenaru, D.; Sandulescu, M.I.; Cinteza, D. Pain Modulation in Chronic Musculoskeletal Disorders: Botulinum Toxin, a Descriptive Analysis. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Kuo, H.C. Clinical application of intravesical botulinum toxin type A for overactive bladder and interstitial cystitis. Investig. Clin. Urol. 2020, 61 (Suppl. 1), S33–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, P.F.; Chiu, H.C.; Chen, K.C.; Chang, C.H.; Chou, E.C. Botulinum toxin A for the Treatment of Overactive Bladder. Toxins 2016, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orasanu, B.; Mahajan, S.T. The use of botulinum toxin for the treatment of overactive bladder syndrome. Indian J. Urol. 2013, 29, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepczynska, K.; Domitrz, I. Botulinum Toxin-A Current Place in the Treatment of Chronic Migraine and Other Primary Headaches. Toxins 2022, 14, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herd, C.P.; Tomlinson, C.L.; Rick, C.; Scotton, W.J.; Edwards, J.; Ives, N.; Clarke, C.E.; Sinclair, A. Botulinum toxins for the prevention of migraine in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 6, CD011616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escher, C.M.; Paracka, L.; Dressler, D.; Kollewe, K. Botulinum toxin in the management of chronic migraine: Clinical evidence and experience. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2017, 10, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, F.J.; Noonan, C.P. Botulinum toxin for the treatment of strabismus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 3, CD006499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bort-Marti, A.R.; Rowe, F.J.; Ruiz Sifre, L.; Ng, S.M.; Bort-Marti, S.; Ruiz Garcia, V. Botulinum toxin for the treatment of strabismus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 3, CD006499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglione, L.; Murariu, M.; Boeriu, E.; Enatescu, I. Assessing Botulinum Toxin Effectiveness and Quality of Life in Axillary Hyperhidrosis: A One-Year Prospective Study. Diseases 2024, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grove, G.L.; Togsverd-Bo, K.; Zachariae, C.; Haedersdal, M. Botulinum toxin A versus microwave thermolysis for primary axillary hyperhidrosis: A randomized controlled trial. JAAD Int. 2024, 15, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton Andres, M.J.; Candau Perez, E.D.; Bermejo de la Fuente, M.P. Treatment of Primary Axillary Hyperhidrosis with Two Doses of Botulinum Toxin A-Observational Study. Toxins 2024, 16, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlak, I.; Perkowska, K.; Kaźmierczak, A.; Izdebska, W.; Sornek, P.; Borkowska, A.; Kiełb, A.; Mich, A.; Ciesielski, R.; Stanek, J. Variety of therapeutic approaches to primary hyperhidrosis (HH) and botulinum toxin priority over other treatment options in this condition—A review. Qual. Sport 2024, 25, 54770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, R.O.; Shaarawi, E.; Hegazy, R.A.; Hafez, V. Long-term efficacy of fractional microneedle radiofrequency versus botulinum toxin-A in primary axillary hyperhidrosis: A randomized controlled trial. Lasers Med. Sci. 2024, 39, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanati, A.; Diotallevi, F.; Radi, G.; Martina, E.; Marconi, B.; Bobyr, I.; Offidani, A. Efficacy and Safety of Botulinum Toxin B in Focal Hyperhidrosis: A Narrative Review. Toxins 2023, 15, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodan-Barbulescu, C.; Castiglione, L.; Burtic, S.R.; Murariu, M.; Reddy, S.; Rosca, O.; Bratosin, F.; Melania Fizedean, C.; Krupyshev, P.; Enatescu, I. Longitudinal Assessment of Facial Hyperhidrosis Management: Evaluating the Utility and Quality of Life Improvements following Botulinum Toxin Injection. Toxins 2024, 16, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eilertsen, T.; Kvammen, B.O.; Grimstad, O. Botulinum Toxin A and B for Palmoplantar Hyperhidrosis. Dermatol. Ther. 2024, 14, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hast, M.A.; Kong, A.M.; Desai, S.; Back, S.; Syed, S.; Holmes, J. Patient Characteristics and Real-World Use of Botulinum Toxins for the Treatment of Cervical Dystonia, Blepharospasm, and Hemifacial Spasm. Toxins 2024, 16, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colorado-Ochoa, H.J.; Tenorio-González, V.G. 12-year effectiveness and safety of botulinum toxin type A for the treatment of blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm. Rev. Mex. Neurocienc. 2024, 25, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, B.; Couesnon, A.; Girard, E.; Molgó, J. Stable Convergent Polyneuronal Innervation and Altered Synapse Elimination in Orbicularis oculi Muscles from Patients with Blepharospasm Responding Poorly to Recurrent Botulinum Type-A Neurotoxin Injections. Toxins 2024, 16, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wabbels, B.; Liebertz, R. Depressive symptoms and quality of life in patients with benign essential blepharospasm under long-term therapy with botulinum toxin. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2025, 125, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thitiwichienlert, S.; Sirikietsoong, P.; Lolekha, P.; Sapthanakorn, W. Efficacy and Complications of Full Dose versus Half Dose of Botulinum Toxin Type A Injection in Benign Essential Blepharospasm. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 2024, 107, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wei, X.; Qi, H.; Bao, X.; Hu, M.; Ma, J. Efficacy and safety of botulinum neurotoxin in the treatment of hemifacial spasms: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Neurol. 2024, 24, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Zheng, H.; Wu, L.; Wu, W. Factors influencing short-term prognosis after botulinum toxin type A treatment for hemifacial spasm: A retrospective study. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubaisi, T.; Sharquie, K. The impact of COVID-19 infection on botulinum toxin hypersensitivity: Case report and literature review. J. Pak. Assoc. Dermatol. 2023, 33, 1762–1766. [Google Scholar]
- Hamed Azzam, S.; Mukari, A.; Hamed, M.; Kridin, K. Influence of COVID-19 mRNA vaccination on the efficacy and safety of Botulinum toxin type A injections. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 3663–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teuschl, Y.; Pinter, M. Impact of COVID-19 related delays of botulinum toxin injections on the quality of life of patients with dystonia or spasticity. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 429, 119610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avasilichioaiei, M.; Bajenaru, O.-L.; Blidaru, N.; Neculai, S.; Cozma, L.; Mitrea, I.; Tulba, D.; Popescu, B.O. The COVID-19 Pandemic a Study on Its Impact on Patients with Dystonia and Related Conditions Treated with Botulinum Toxin in a Tertiary Centre in Romania. Mod. Med. 2022, 29, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavikatte, G.; Jacinto, J.; Deltombe, T.; Wissel, J. Botulinum Toxin Services for Neurorehabiliation: Recommendations for Challenges and Opportunities during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Toxins 2021, 13, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellows, S.; Jankovic, J. Immunogenicity Associated with Botulinum Toxin Treatment. Toxins 2019, 11, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benecke, R. Clinical Relevance of Botulinum Toxin Immunogenicity. Curr. Opin. 2012, 26, e1–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, S.Y.; Park, E.S. Immunogenicity of botulinum toxin. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2022, 49, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naumann, M.; Boo, L.M.; Ackerman, A.H.; Gallagher, C.J. Immunogenicity of botulinum toxins. J. Neural Transm. 2013, 120, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, E.; Carruthers, J.D.A. Immunogenicity of Botulinum Toxin A: Insights. Dermatol. Surg. 2024, 50, S117–S126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.W.A.; Chan, L.K.W.; Lee, A.W.K.; Lee, C.H.; Wan, J.; Yi, K.H. Immunogenicity of Botulinum Toxin Type A in Different Clinical and Cosmetic Treatment, a Literature Review. Life 2024, 14, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.U.; Frevert, J.; Tay, C.M. Complexing Protein-Free Botulinum Neurotoxin A Formulations: Implications of Excipients for Immunogenicity. Toxins 2024, 16, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coté, T.R.; Mohan, A.K.; Polder, J.A.; Walton, M.K.; Braun, M.M. Botulinum toxin type A injections: Adverse events reported to the US Food and Drug Administration in therapeutic and cosmetic cases. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2005, 53, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidu, K.; Smith, K.; Sheedy, M.; Adair, B.; Yu, X.; Graham, H.K. Systemic adverse events following botulinum toxin A therapy in children with cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2010, 52, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Flaherty, S.J.; Janakan, V.; Morrow, A.M.; Scheinberg, A.M.; Waugh, M.C. Adverse events and health status following botulinum toxin type A injections in children with cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2011, 53, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinney, C.M.; Bau, K.; Burton, K.L.O.; O’Flaherty, S.J.; Bear, N.L.; Paget, S.P. Severity of cerebral palsy and likelihood of adverse events after botulinum toxin A injections. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2018, 60, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaszczyk, I.; Foumani, N.P.; Ljungberg, C.; Wiberg, M. Questionnaire about the adverse events and side effects following botulinum toxin A treatment in patients with cerebral palsy. Toxins 2015, 7, 4645–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollina, U.; Konrad, H. Managing Adverse Events Associated with Botulinum Toxin Type A. Am. J. Clin. Derm. 2005, 16, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, N.F.; Burke, J.P.; Redmond, E.J.; Elamin, S.; Brady, C.M.; Flood, H.D. Trigonal versus extratrigonal botulinum toxin-A: A systematic review and meta-analysis of efficacy and adverse events. Int. Urogynecology J. 2015, 26, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranowska, A.; Baranowska, K.; Czyżewski, F.; Filipek, K.; Kawka, J.; Maciek, M.; Mrugała, S.; Mrugała, W.; Skierkowski, B.; Zalewska, N. Botulinum toxin type A in scar treatment: Review article. Med. Sci. 2024, 28, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmatipour, H.; Shabestari, S.M.; Benisi, S.Z.; Samadikhah, H. Pioneering Pain Management with Botulinum Toxin Type A: From Anti-Inflammation to Regenerative Therapies. Heliyon 2025, 11, e42350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michon, A. Botulinum toxin for cosmetic treatments in young adults: An evidence-based review and survey on current practice among aesthetic practitioners. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashied, R.; Gold, M. Innovation in Botulinum Toxins. Dermatol. Clin. 2025, 43, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papagni, M.; Renga, M.; Mogavero, S.; Veronesi, P.; Cavallini, M. The Esthetic Use of Botulinum Toxins in Cancer Patients: Providing a Foundation for Future Indications. Toxins 2025, 17, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, W.W.; Jain, N.; Sublett, J.W. Immunogenicity of Botulinum Toxin Formulations: Potential Therapeutic Implications. Adv. Ther. 2021, 38, 5046–5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, E.; Alhitmi, H.K.; Mosahebi, A. Immunogenicity to Botulinum Toxin Type A: A Systematic Review With Meta-Analysis Across Therapeutic Indications. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2022, 42, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.W.S.; Albrecht, P.; Calderon, P.E.; Corduff, N.; Loh, D.; Martin, M.U.; Park, J.Y.; Suseno, L.S.; Tseng, F.W.; Vachiramon, V.; et al. Emerging Trends in Botulinum Neurotoxin A Resistance: An International Multidisciplinary Review and Consensus. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2022, 10, e4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siongco, P.R.L.; Rosales, R.L.; Moore, A.P.; Freynhagen, R.; Arimura, K.; Kanovsky, P.; Kaji, R.; Fernandez, H.H.; Dressler, D. Botulinum neurotoxin injections for muscle-based (dystonia and spasticity) and non-muscle-based (neuropathic pain) pain disorders: A meta-analytic study. J. Neural Transm. 2020, 127, 935–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohn, E.; Goren, K.; Switzer, L.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Fehlings, D. Pharmacological and neurosurgical interventions for individuals with cerebral palsy and dystonia: A systematic review update and meta-analysis. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2021, 63, 1038–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasera, A.; Squintani, G.M.; Cerruto, M.A. A Systematic Review of Botulinum Toxin Injection in Pediatric Dystonia. Toxins 2024, 16, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brideau-Andersen, A.; Dolly, J.O.; Brin, M.F. Botulinum neurotoxins: Future innovations. Medicine 2023, 102, e32378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brin, M.F.; Nelson, M.; Ashourian, N.; Brideau-Andersen, A.; Maltman, J. Update on Non-Interchangeability of Botulinum Neurotoxin Products. Toxins 2024, 16, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Singh, B.R. Botulinum Toxin: A Comprehensive Review of Its Molecular Architecture and Mechanistic Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonfria, E.; Elliott, M.; Beard, M.; Chaddock, J.A.; Krupp, J. Engineering Botulinum Toxins to Improve and Expand Targeting and SNARE Cleavage Activity. Toxins 2018, 10, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Year | FDA Approval |
|---|---|
| 12/1989 | FDA approval for strabismus, blepharospasm, and hemifacial spasm (used in eye muscle disorders and facial spasms). |
| 12/2000 | FDA approval for cervical dystonia (a condition that causes abnormal head positioning and neck pain due to muscle spasms). |
| 4/2002 | FDA approval for glabellar lines (frown lines between the eyebrows, for cosmetic use). |
| 7/2004 | FDA approval for severe primary axillary hyperhidrosis (excessive underarm sweating). |
| 3/2010 | FDA approval for upper limb spasticity in adults (muscle stiffness in the arm and hand muscles). |
| 10/2010 | FDA approval for chronic migraine (headaches occurring on 15 or more days a month, lasting 4 h or more per day). |
| 8/2011 | FDA approval for a specific form of urinary incontinence (due to neurogenic detrusor overactivity). |
| 1/2013 | FDA approval for overactive bladder symptoms in adults (for reducing bladder muscle activity that leads to incontinence). |
| 9/2013 | FDA approval for severe lateral canthal lines (crow’s feet, for cosmetic purposes). |
| 1/2016 | FDA approval for pediatric patients with upper limb spasticity (muscle stiffness in children’s arms and hands). |
| 10/2019 | FDA approval for lower limb spasticity, excluding spasticity caused by cerebral palsy (muscle stiffness in legs). |
| 7/2020 | FDA approval for pediatric patients with spasticity (muscle stiffness conditions). |
| 2/2021 | FDA approval for pediatric detrusor overactivity associated with neurologic conditions (bladder overactivity in children). |
| 7/2021 | FDA approval to include eight new muscles to treat adults with upper limb spasticity (expanding treatment options). |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ayoub, N. Botulinum Toxin Therapy: A Comprehensive Review on Clinical and Pharmacological Insights. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14062021
Ayoub N. Botulinum Toxin Therapy: A Comprehensive Review on Clinical and Pharmacological Insights. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(6):2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14062021
Chicago/Turabian StyleAyoub, Nahla. 2025. "Botulinum Toxin Therapy: A Comprehensive Review on Clinical and Pharmacological Insights" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 6: 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14062021
APA StyleAyoub, N. (2025). Botulinum Toxin Therapy: A Comprehensive Review on Clinical and Pharmacological Insights. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(6), 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14062021






