The Link Between Sleep-Related Breathing Disorders and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Treatment Options—A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sleep Architecture in IPF
3. IPF and Obstructive Sleep Apneas
3.1. Recurring Alveolar Microdamage
3.2. Intermittent Night-Time Hypoxemia and Systemic Inflammation
3.3. Vascular Alterations
3.4. Reduction of Lung Volumes
3.5. High Loop Gain
3.6. Low Arousal Threshold
4. IPF and Nocturnal Hypoxemia
5. IPF and Central Sleep Apneas
6. IPF Associated with Emphysema and SBD
7. Biomarkers
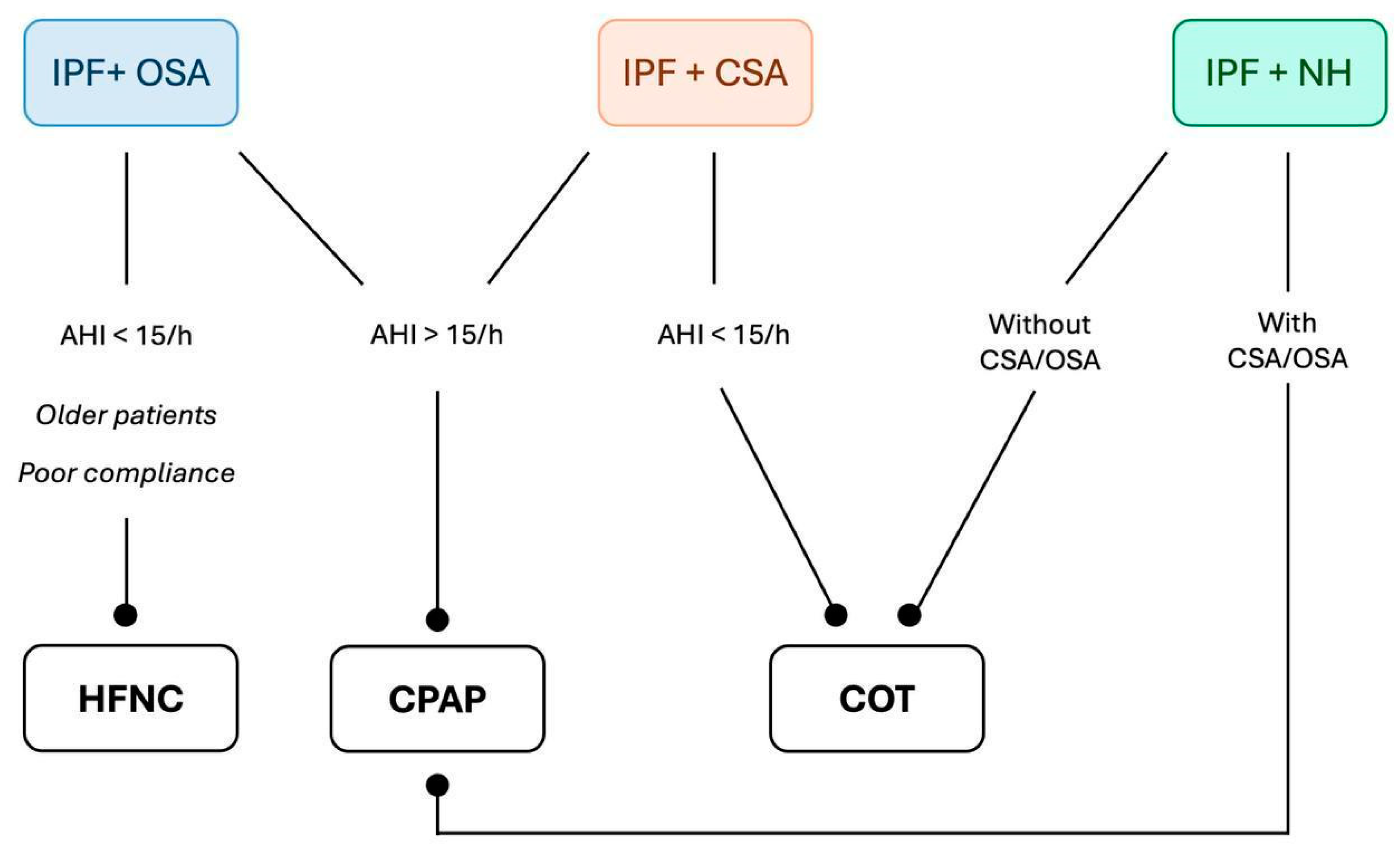
8. IPF and SBDs: Treatment Options
8.1. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure
8.2. High-Flow Nasal Cannula
8.3. Conventional Oxygen Therapy
9. Future Perspectives
9.1. Artificial Intelligence
9.2. Radiological Features
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AHI | Apnea-Hypopnea Index |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| ALP | Alkaline Phosphatase |
| ARF | Acute Respiratory Failure |
| ASV | Adaptive Servo-ventilation |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| BiPAP | Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure |
| CCL | Chemokine Ligand |
| CINC | Cytokine-induced Neutrophil Chemoattractant |
| COPD | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease |
| CPAP | Continuous Positive Airway Pressure |
| CPET | Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing |
| CPFE | Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema |
| CRP | C-Reactive Protein |
| CSA | Central Sleep Apnea |
| COT | Conventional Oxygen Therapy |
| DLCO | Diffusion capacity for carbon monoxide |
| ER | Endoplasmic Reticulum |
| FVC | Forced Vital Capacity |
| FEV1 | Forced Expiratory Volume in the first second |
| FOSQ | Functional Outcomes of Sleep Questionnaire |
| GERD | Gastroesophageal reflux disease |
| HAA | High-attenuation Areas |
| HFNC | High-flow Nasal Cannula |
| HIF | Hypoxia-inducible Factor |
| IL | Interleukin |
| ILD | Interstitial Lung Disease |
| IPF | Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis |
| LDH | Lactate Dehydrogenase |
| LIX | Lipopolysaccharide-induced CXC chemokine |
| MIG | Monokine Induced by interferon γ |
| MIP | Macrophage Inflammatory Proteins |
| MMP-1 | Matrix Metalloproteinase-1 |
| miRNA | microRNA |
| MV | Mechanical Ventilation |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| NH | Nocturnal Hypoxemia |
| NIV | Non-invasive Ventilation |
| N 1 | stage 1 sleep |
| N2 | stage 2 sleep |
| OSA | Obstructive Sleep Apnea |
| PEEP | Positive end-Expiratory Pressure |
| PI3k-Akt | Phosphatidylinositol 3 Kinase/Protein Kinase B |
| PH | Pulmonary Hypertension |
| PSG | Polysomnography |
| REM | Rapid Eye Movement Sleep |
| QoL | Quality Of Life |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| SBDs | Sleep-related Breathing Disorders |
| SND | Significant Nocturnal Desaturation |
| SSH | Sleep-sustained Hypoxemia |
| TIMP | Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase |
| TNF | Tumor Necrosis Factor |
| WASO | Wake time After Sleep Onset |
References
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Richeldi, L.; Thomson, C.C.; Inoue, Y.; Johkoh, T.; Kreuter, M.; Lynch, D.A.; Maher, T.M.; Martinez, F.J.; et al. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (an Update) and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis in Adults: An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, e18–e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spagnolo, P.; Tonelli, R.; Cocconcelli, E.; Stefani, A.; Richeldi, L. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Diagnostic pitfalls and therapeutic challenges. Multidiscip. Respir. Med. 2012, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caminati, A.; Lonati, C.; Cassandro, R.; Elia, D.; Pelosi, G.; Torre, O.; Zompatori, M.; Uslenghi, E.; Harari, S. Comorbidities in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: An underestimated issue. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2019, 28, 190044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuga, F.F.; Kaczmarski, P.; Szmyd, B.; Białasiewicz, P.; Sochal, M.; Gabryelska, A. The Association between Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Jang, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Ko, J.; Jung, S.Y.; Kim, D.W.; Hong, S.; Jang, H.J. Prevalence and clinical impacts of obstructive sleep apnea in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A single-center, retrospective study. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0291195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, L.H.; Mason, W.R.; Parnell, J.A.; Rice, T.W.; Loyd, J.E.; Milstone, A.P.; Collard, H.R.; Malow, B.A. Obstructive sleep apnea is common in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 2009, 136, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Park, C.S.; Song, J.W. Obstructive sleep apnea in patients with interstitial lung disease: Prevalence and predictive factors. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermigkis, C.; Bouloukaki, I.; Schiza, S. Obstructive sleep apnea in patients with interstitial lung diseases: Past and future. Sleep Breath. 2013, 17, 1127–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Troy, L.K.; Young, I.H.; Lau, E.M.T.; Wong, K.K.H.; Yee, B.J.; Torzillo, P.J.; Corte, T.J. Nocturnal hypoxaemia is associated with adverse outcomes in interstitial lung disease. Respirology 2019, 24, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordas-Martinez, J.; Salord, N.; Vicens-Zygmunt, V.; Pérez, S.; Prado, E.; Calvo, M.; Blavia, R.; Bermudo, G.; Montes-Worboys, A.; Santos, S.; et al. Characterization of Sleep-Disordered Breathing in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2023, 59, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagmeyer, L.; Herkenrath, S.D.; Treml, M.; Pietzke-Calcagnile, A.; Anduleit, N.; Randerath, W. Sleep-related breathing disorders in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis are frequent and may be associated with pulmonary vascular involvement. Sleep Breath. 2023, 27, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadogiannis, G.; Bouloukaki, I.; Mermigkis, C.; Michelakis, S.; Ermidou, C.; Mauroudi, E.; Moniaki, V.; Tzanakis, N.; Antoniou, K.M.; Schiza, S.E. Patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with and without obstructive sleep apnea: Differences in clinical characteristics, clinical outcomes, and the effect of PAP treatment. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2021, 17, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolilekas, L.; Manali, E.; Vlami, K.A.; Lyberopoulos, P.; Triantafillidou, C.; Kagouridis, K.; Baou, K.; Gyftopoulos, S.; Vougas, K.N.; Karakatsani, A.; et al. Sleep oxygen desaturation predicts survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2013, 9, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosi, M.; Milioli, G.; Parrino, L.; Fanfulla, F.; Tomassetti, S.; Melpignano, A.; Trippi, I.; Vaudano, A.E.; Ravaglia, C.; Mascetti, S.; et al. OSA and Prolonged Oxygen Desaturation During Sleep are Strong Predictors of Poor Outcome in IPF. Lung 2017, 195, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosi, M.; Milioli, G.; Parrino, L.; Fanfulla, F.; Tomassetti, S.; Melpignano, A.; Trippi, I.; Vaudano, A.E.; Ravaglia, C.; Mascetti, S.; et al. Quality of life in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: The impact of sleep disordered breathing. Respir. Med. 2019, 147, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, V.; McCormack, M.C.; Mathai, S.C.; Agarwal, S.; Richardson, B.; Horton, M.R.; Polito, A.J.; Collop, N.A.; Danoff, S.K. Sleep quality and health-related quality of life in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 2008, 134, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valecchi, D.; Bargagli, E.; Pieroni, M.G.; Refini, M.R.; Sestini, P.; Rottoli, P.; Melani, A.S. Prognostic Significance of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in a Population of Subjects with Interstitial Lung Diseases. Pulm. Ther. 2023, 9, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermigkis, C.; Chapman, J.; Golish, J.; Mermigkis, D.; Budur, K.; Kopanakis, A.; Polychronopoulos, V.; Burgess, R.; Foldvary-Schaefer, N. Sleep-related breathing disorders in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lung 2007, 185, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermigkis, C.; Stagaki, E.; Amfilochiou, A.; Polychronopoulos, V.; Korkonikitas, P.; Mermigkis, D.; Bregou, M.; Kouris, N.; Bouros, D. Sleep quality and associated daytime consequences in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Med. Princ. Pract. 2009, 18, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermigkis, C.; Stagaki, E.; Tryfon, S.; Schiza, S.; Amfilochiou, A.; Polychronopoulos, V.; Panagou, P.; Galanis, N.; Kallianos, A.; Mermigkis, D.; et al. How common is sleep-disordered breathing in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? Sleep Breath. 2010, 14, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonson, J.L.; Pandya, D.; Khan, S.; Verma, S.; Greenberg, H.E.; Talwar, A. Sleep architecture in patients with interstitial lung disease with and without pulmonary hypertension. Sleep Breath. 2022, 26, 1711–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, W.D.; Costabel, U.; Hansell, D.M.; King, T.E., Jr.; Lynch, D.A.; Nicholson, A.G.; Ryerson, C.J.; Ryu, J.H.; Selman, M.; Wells, A.U.; et al. ATS/ERS Committee on Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: Update of the international multidisciplinary classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 733–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Yang, N.; Fiore, V.F.; Barker, T.H.; Sun, Y.; Morris, S.W.; Ding, Q.; Thannickal, V.J.; Zhou, Y. Matrix stiffness-induced myofibroblast differentiation is mediated by intrinsic mechanotransduction. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 47, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sateia, M.J. International classification of sleep disorders-third edition: Highlights and modifications. Chest 2014, 146, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonaglia, C.; Citton, G.M.; Soave, S.; Salton, F.; Ruaro, B.; Confalonieri, P.; Confalonieri, M. Deciphering loop gain complexity: A primer for understanding a pathophysiological trait of obstructive sleep apnea patients. Respir. Med. 2024, 234, 107820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gille, T.; Didier, M.; Boubaya, M.; Moya, L.; Sutton, A.; Carton, Z.; Baran-Marszak, F.; Sadoun-Danino, D.; Israël-Biet, D.; Cottin, V.; et al. Obstructive sleep apnoea and related comorbidities in incident idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1601934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, N.; Cardoso, A.V.; Mota, P.C.; Santos, A.C.; Melo, N.; Morais, A.; Drummond, M. Predictive factors of obstructive sleep apnoea in patients with fibrotic lung diseases. Sleep Med. 2019, 56, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.R.; Jalali, I.; Singh, J.; Nagaraj, A.; Dari, M.A.; Mekonen Gdey, M.; Bai, M.; Palleti, S.K. Exploring the Prevalence and Characteristics of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Among Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cureus 2024, 16, e54562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, K.O. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis may be a disease of recurrent, tractional injury to the periphery of the aging lung: A unifying hypothesis regarding etiology and pathogenesis. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2012, 136, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lederer, D.J.; Jelic, S.; Bhattacharya, J.; Basner, R.C. Is obstructive sleep apnea a cause of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2012, 136, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, B.G.; Kato, M.; Narkiewicz, K.; Choe, I.; Somers, V.K. Increases in leptin levels, sympathetic drive, and weight gain in obstructive sleep apnea. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 279, H234–H237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-García, E.; García-Tovar, S.; Alfaro, E.; Jaureguizar, A.; Casitas, R.; Sánchez-Sánchez, B.; Zamarrón, E.; Fernández-Lahera, J.; López-Collazo, E.; Cubillos-Zapata, C.; et al. Inflammasome Activation: A Keystone of Proinflammatory Response in Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, 1337–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinovitch, M. Molecular pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 4306–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwara, M.I.; Green, N.J.; Borthwick, L.A.; Mann, J.; Mayer-Barber, K.D.; Barron, L.; Corris, P.A.; Farrow, S.N.; Wynn, T.A.; Fisher, A.J.; et al. DAIL-1a released from damaged epithelial cells is sufficient and essential to trigger inflammatory responses in human lung fibroblasts. Mucosal Immunol. 2014, 7, 684–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozo Vukovac, E.; Lozo, M.; Mise, K.; Gudelj, I.; Puljiz, Ž.; Jurcev-Savicevic, A.; Bradaric, A.; Kokeza, J.; Mise, J. Bronchoalveolar pH and inflammatory biomarkers in newly diagnosed IPF and GERD patients: A case-control study. Med. Sci. Monit. 2014, 20, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.G.; Morgenthaler, T.I.; Katzka, D.A. Sleep and Nocturnal Gastroesophageal Reflux: An Update. Chest 2018, 154, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.B.; Seo, B.S.; Kim, J.H. Effect of arousal on sympathetic overactivity in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Med. 2019, 62, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adir, Y.; Humbert, M.; Chaouat, A. Sleep-related breathing disorders and pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2002258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haine, L.; Bravais, J.; Yegen, C.H.; Bernaudin, J.F.; Marchant, D.; Planès, C.; Voituron, N.; Boncoeur, E. Sleep Apnea in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Molecular Investigation in an Experimental Model of Fibrosis and Intermittent Hypoxia. Life 2021, 11, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trakada, G.; Nikolaou, E.; Pouli, A.; Tsiamita, M.; Spiropoulos, K. Endothelin-1 levels in interstitial lung disease patients during sleep. Sleep Breath. 2003, 7, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kairaitis, K.; Byth, K.; Parikh, R.; Stavrinou, R.; Wheatley, J.R.; Amis, T.C. Tracheal traction effects on upper airway patency in rabbits: The role of tissue pressure. Sleep 2007, 30, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khor, Y.H.; Ryerson, C.J.; Landry, S.A.; Howard, M.E.; Churchward, T.J.; Edwards, B.A.; Hamilton, G.S.; Joosten, S.A. Interstitial lung disease and obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Med. Rev. 2021, 58, 101442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, C.G.; Valente, C.; Serino, M.; Rodrigues, I.; Carvalho, A.; Coelho, D.B.; Bastos, H.N.; Mota, P.C.; Morais, A.; Drummond, M. Obstructive sleep apnea in patients with fibrotic interstitial lung disease (non-idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis): What should be offered? J. Bras. Pneumol. 2024, 50, e20240058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon-Diaz, N.L.; Sands, S.A.; McEvoy, R.D.; Catcheside, P.G. Daytime loop gain is elevated in obstructive sleep apnea but not reduced by CPAP treatment. J. Appl. Physiol. 2018, 125, 1490–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, J.A.; Veasey, S.C.; Morgan, B.J.; O’Donnell, C.P. Pathophysiology of sleep apnea. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 47–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joosten, S.A.; Landry, S.A.; Mann, D.L.; Sands, S.A.; Ryerson, C.J.; Sidhu, C.; Hamilton, G.S.; Howard, M.E.; Edwards, B.A.; Khor, Y.H. Understanding the Physiological Endotypes Responsible for Comorbid Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 208, 624–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gries, R.E.; Brooks, L.J. Normal oxyhemoglobin saturation during sleep. How low does it go? Chest 1996, 110, 1489–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilwan, F.N.; Escourrou, P.; Garcia, G.; Jaïs, X.; Humbert, M.; Roisman, G. High occurrence of hypoxemic sleep respiratory disorders in precapillary pulmonary hypertension and mechanisms. Chest 2013, 143, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, Y.; Nagano, T.; Izumi, S.; Yasuda, M.; Tsuruno, K.; Tobino, K.; Nakata, K.; Okamura, K.; Nishiuma, T.; Takatsuki, K.; et al. Analysis of nocturnal desaturation waveforms using algorithms in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sleep Breath. 2022, 26, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, S.; Nagano, T.; Yoshizaki, A.; Nishimura, Y. Classification Algorithm for Nocturnal Hypoxemia Using Nocturnal Pulse Oximetry. In Proceedings of the 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 3662–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myall, K.J.; West, A.G.; Martinovic, J.L.; Lam, J.L.; Roque, D.; Wu, Z.; Maher, T.M.; Molyneaux, P.L.; Suh, E.S.; Kent, B.D. Nocturnal Hypoxemia Associates with Symptom Progression and Mortality in Patients with Progressive Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Disease. Chest 2023, 164, 1232–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margaritopoulos, G.A.; Proklou, A.; Trachalaki, A.; Badenes Bonet, D.; Kokosi, M.; Kouranos, V.; Chua, F.; George, P.; Renzoni, E.A.; Devaraj, A.; et al. Overnight desaturation in interstitial lung diseases: Links to pulmonary vasculopathy and mortality. ERJ Open Res. 2024, 10, 00740–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, R.K.; Smith, B.; Perlman, C.E.; Schwartz, D.A. Is Progression of Pulmonary Fibrosis due to Ventilation-induced Lung Injury? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryerson, C.J.; Vahidy, S. Nocturnal hypoxaemia in interstitial lung disease: An easy target to treat? Respirology 2019, 24, 930–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, J.E.; Malhotra, A.; Sands, S.A. Pathogenesis of central and complex sleep apnoea. Respirology 2017, 22, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plantier, L.; Cazes, A.; Dinh-Xuan, A.T.; Bancal, C.; Marchand-Adam, S.; Crestani, B. Physiology of the lung in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2018, 27, 170062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yegen, C.H.; Marchant, D.; Bernaudin, J.F.; Planes, C.; Boncoeur, E.; Voituron, N. Chronic pulmonary fibrosis alters the functioning of the respiratory neural network. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1205924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, J.A. Crossing the apnoeic threshold: Causes and consequences. Exp. Physiol. 2005, 90, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.J.; Overholt, J.L.; Kline, D.; Kumar, G.K.; Prabhakar, N.R. Induction of sensory long-term facilitation in the carotid body by intermittent hypoxia: Implications for recurrent apneas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 10073–10078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitrascu, R.; Tiede, H.; Eckermann, J.; Mayer, K.; Reichenberger, F.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Seeger, W.; Heitmann, J.; Schulz, R. Sleep apnea in precapillary pulmonary hypertension. Sleep Med. 2013, 14, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canora, A.; Nicoletta, C.; Ghinassi, G.; Bruzzese, D.; Rea, G.; Capaccio, A.; Castaldo, S.; Coppola, A.; Polistina, G.E.; Sanduzzi, A.; et al. First Description of the Hyperpnea-Hypopnea Periodic Breathing in Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease-Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Treatment Implications in a Real-Life Setting. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivali, N.; Thongprayoon, C.; Tangpanithandee, S.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Won, C. The use of continuous positive airway pressure in COPD-OSA overlap syndrome: A systematic review. Sleep Med. 2023, 108, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottin, V.; Selman, M.; Inoue, Y.; Wong, A.W.; Corte, T.J.; Flaherty, K.R.; Han, M.K.; Jacob, J.; Johannson, K.A.; Kitaichi, M.; et al. Syndrome of Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema: An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Research Statement. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 206, e7–e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangani, R.; Ghio, A.; Culp, S.; Patel, Z.; Sharma, S. Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis Emphysema: Role of Cigarette Smoking and Pulmonary Hypertension in a Rural Cohort. Int. J. Chron. Obs. Pulmon Dis. 2021, 16, 1873–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Snyder, L.D.; Neely, M.L.; Hellkamp, A.S.; Hotchkin, D.L.; Morrison, L.D.; Bender, S.; Leonard, T.B.; Culver, D.A.; IPF-PRO™ Registry Investigators. Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Combined Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema in the IPF-PRO Registry. Lung 2022, 200, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiza, S.; Mermigkis, C.; Margaritopoulos, G.A.; Daniil, Z.; Harari, S.; Poletti, V.; Renzoni, E.A.; Torre, O.; Visca, D.; Bouloukaki, I.; et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and sleep disorders: No longer strangers in the night. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2015, 24, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.N.; Kelly, E.; Nolan, G.; Eigenheer, S.; Boylan, D.; Murphy, D.; Dodd, J.D.; Keane, M.P.; McNicholas, W.T. Disordered breathing during sleep and exercise in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and the role of biomarkers. QJM Mon. J. Assoc. Physicians 2015, 108, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasse, A.; Probst, C.; Bargagli, E.; Zissel, G.; Toews, G.B.; Flaherty, K.R.; Olschewski, M.; Rottoli, P.; Müller-Quernheim, J. Serum CC-chemokine ligand 18 concentration predicts outcome in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 179, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizaka, A.; Matsuda, T.; Albertine, K.H.; Koh, H.; Tasaka, S.; Hasegawa, N.; Kohno, N.; Kotani, T.; Morisaki, H.; Takeda, J.; et al. Elevation of KL-6, a lung epithelial cell marker, in plasma and epithelial lining fluid in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2004, 286, L1088–L1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathani, N.; Perkins, G.D.; Tunnicliffe, W.; Murphy, N.; Manji, M.; Thickett, D.R. Kerbs von Lungren 6 antigen is a marker of alveolar inflammation but not of infection in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit. Care 2008, 12, R12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Callister, M.E.; Mumby, S.; Quinlan, G.J.; Welsh, K.I.; duBois, R.M.; Evans, T.W. KL-6 levels are elevated in plasma from patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Eur. Respir. J. 2004, 23, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, A.; Kohno, N.; Hamada, H.; Sakatani, M.; Ueda, E.; Kondo, K.; Hirasawa, Y.; Hiwada, K. Circulating KL-6 predicts the outcome of rapidly progressive idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 158, 1680–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouloukaki, I.; Michelakis, S.; Tsitoura, E.; Vasarmidi, E.; Koutoulaki, C.; Tzanakis, N.; Schiza, S.; Antoniou, K.M. KL-6, ET-1 and S100A9 levels in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and obstructive sleep apnea. Exp. Ther. Med. 2024, 29, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, H.; Yokoyama, A.; Kondo, K.; Hamada, H.; Abe, M.; Nishimura, K.; Hiwada, K.; Kohno, N. Comparative study of KL-6, surfactant protein-A, surfactant protein-D, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 as serum markers for interstitial lung diseases. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lederer, D.J.; Jelic, S.; Basner, R.C.; Ishizaka, A.; Bhattacharya, J. Circulating KL-6, a biomarker of lung injury, in obstructive sleep apnoea. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 33, 793–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aihara, K.; Oga, T.; Harada, Y.; Chihara, Y.; Handa, T.; Tanizawa, K.; Watanabe, K.; Tsuboi, T.; Hitomi, T.; Mishima, M.; et al. Comparison of biomarkers of subclinical lung injury in obstructive sleep apnea. Respir. Med. 2011, 105, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Bhattacharjee, R.; Khalyfa, A.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; Capdevila, O.S.; Wang, Y.; Gozal, D. DNA methylation in inflammatory genes among children with obstructive sleep apnea. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 185, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; Khalyfa, A.; Gozal, D.; Bhattacharjee, R.; Wang, Y. Endothelial dysfunction in children with obstructive sleep apnea is associated with epigenetic changes in the eNOS gene. Chest 2013, 143, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, A.S.; McSharry, D.G.; Malhotra, A. Adult obstructive sleep apnoea. Lancet 2014, 383, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Kondoh, Y. The clinical impact of major comorbidities on idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Investig. 2017, 55, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchioni, A.; Tonelli, R.; Cerri, S.; Castaniere, I.; Andrisani, D.; Gozzi, F.; Bruzzi, G.; Manicardi, L.; Moretti, A.; Demurtas, J.; et al. Pulmonary Stretch and Lung Mechanotransduction: Implications for Progression in the Fibrotic Lung. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, R.; Castaniere, I.; Cortegiani, A.; Tabbì, L.; Fantini, R.; Andrisani, D.; Gozzi, F.; Moretti, A.; Bruzzi, G.; Manicardi, L.; et al. Inspiratory Effort and Respiratory Mechanics in Patients with Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary fibrosis: A Preliminary Matched Control Study. Pulmonology 2023, 29, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchioni, A.; Tonelli, R.; Rossi, G.; Spagnolo, P.; Luppi, F.; Cerri, S.; Cocconcelli, E.; Pellegrino, M.R.; Fantini, R.; Tabbì, L.; et al. Ventilatory support and mechanical properties of the fibrotic lung acting as a “squishy ball”. Ann. Intensive Care 2020, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediano, O.; González Mangado, N.; Montserrat, J.M.; Alonso-Álvarez, M.L.; Almendros, I.; Alonso-Fernández, A.; Barbé, F.; Borsini, E.; Caballero-Eraso, C.; Cano-Pumarega, I.; et al. International Consensus Document on Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Documento internacional de consenso sobre apnea obstructiva del sueño. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2022, 58, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.P.; Ayappa, I.A.; Caples, S.M.; Kimoff, R.J.; Patel, S.R.; Harrod, C.G. Treatment of Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea with Positive Airway Pressure: An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2019, 15, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermigkis, C.; Bouloukaki, I.; Antoniou, K.M.; Mermigkis, D.; Psathakis, K.; Giannarakis, I.; Varouchakis, G.; Siafakas, N.; Schiza, S.E. CPAP therapy in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and obstructive sleep apnea: Does it offer a better quality of life and sleep? Sleep Breath. 2013, 17, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermigkis, C.; Bouloukaki, I.; Antoniou, K.; Papadogiannis, G.; Giannarakis, I.; Varouchakis, G.; Siafakas, N.; Schiza, S.E. Obstructive sleep apnea should be treated in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sleep Breath. 2015, 19, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegunsoye, A.; Neborak, J.M.; Zhu, D.; Cantrill, B.; Garcia, N.; Oldham, J.M.; Noth, I.; Vij, R.; Kuzniar, T.J.; Bellam, S.K.; et al. CPAP Adherence, Mortality, and Progression-Free Survival in Interstitial Lung Disease and OSA. Chest 2020, 158, 1701–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzouvelekis, A.; Voulgaris, A.; Steiropoulos, P. Obstructive sleep apnea in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Pulmonary hypertension could be the missing link for the diagnosis and different positive airway pressure treatment outcomes. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2021, 17, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordas-Martinez, J.; Salord, N.; Vicens-Zygmunt, V.; Carmezim, J.; Pérez, S.; Prado, E.; Calvo, M.; Blavia, R.; Bermudo, G.; Santos, S.; et al. Treating sleep-disordered breathing of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients with CPAP and nocturnal oxygen treatment. A pilot study: Sleep-disordered breathing treatment in IPF. Respir. Res. 2024, 25, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franquet, T.; Giménez, A.; Torrubia, S.; Sabaté, J.M.; Rodriguez-Arias, J.M. Spontaneous pneumothorax and pneumomediastinum in IPF. Eur. Radiol. 2000, 10, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimoto, K.; Fujisawa, T.; Yoshimura, K.; Enomoto, Y.; Enomoto, N.; Nakamura, Y.; Inui, N.; Sumikawa, H.; Johkoh, T.; Colby, T.V.; et al. The prognostic significance of pneumothorax in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respirology 2018, 23, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasawa, T.; Ogura, T.; Takahashi, H.; Asakura, A.; Gotoh, T.; Yazawa, T.; Inoue, T. Pneumothorax and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2010, 28, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langner, S.; Kolditz, M.; Kleymann, J.; Tausche, K.; Almeida, A.B.; Schweigert, M.; Koschel, D. Großer. Large pneumothorax in a sleep apnea patient with CPAP without previously known lung and thoracic diseases—A case report. Pneumologie 2020, 74, 217–221. [Google Scholar]
- Herrejón Silvestre, A.; Inchaurraga Alvarez, I.; Marín González, M. Neumotórax espontáneo asociado al uso de BiPAP nocturno con mascarilla nasal. Arch. Bronconeumol. 1998, 34, 512. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.T.; Bernabei, A.; Cutrufello, N.; Kern, J.D. Spontaneous pneumothorax caused by excessive positive airway pressure therapy for obstructive sleep apnea, in D36. Pleural Disease: Case Reports II. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, A6682. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez, E.C.; Carpintero, M.A.; GonzálezCastro, A. Edema pulmonar ex vacuo tras drenaje de neumotórax. Med. Intensiv. 2018, 42, e24–e25. [Google Scholar]
- Rajdev, K.; Idiculla, P.S.; Sharma, S.; Von Essen, S.G.; Murphy, P.J.; Bista, S. Recurrent Pneumothorax with CPAP Therapy for Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Case Rep. Pulmonol. 2020, 2020, 8898621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randerath, W.; Verbraecken, J.; Andreas, S.; Arzt, M.; Bloch, K.E.; Brack, T.; Buyse, B.; De Backer, W.; Eckert, D.J.; Grote, L.; et al. Definition, discrimination, diagnosis and treatment of central breathing disturbances during sleep. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1600959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoletini, G.; Alotaibi, M.; Blasi, F.; Hill, N.S. Heated Humidified High-Flow Nasal Oxygen in Adults: Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Implications. Chest 2015, 148, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, J.V., Jr.; Gardner, M.T.; Walenga, R.; Hosseini, S.; Longest, P.W.; Golshahi, L. Mechanistic Understanding of High Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy and Pressure Support with an In Vitro Infant Model. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 48, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dysart, K.; Miller, T.L.; Wolfson, M.R.; Shaffer, T.H. Research in high flow therapy: Mechanisms of action. Respir. Med. 2009, 103, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, F.; Gu, Y.H.; He, Y.C.; Deng, W.F.; Liu, Z.Z. High-flow nasal cannula therapy for pediatric obstructive sleep apnea: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 4583–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishman, H.; Al-Shamli, N.; Sunkonkit, K.; Maguire, B.; Selvadurai, S.; Baker, A.; Amin, R.; Propst, E.J.; Wolter, N.E.; Eckert, D.J.; et al. Heated humidified high flow nasal cannula therapy in children with obstructive sleep apnea: A randomized cross-over trial. Sleep Med. 2023, 107, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Qinghua, L.; Mengyuan, P.; Yaoyu, C.; Long, Z.; Mengjie, L.; Xiaosong, D.; Fang, H. High flow nasal cannula therapy for obstructive sleep apnea in adults. Sleep Breath. 2022, 26, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Hua, C.C.; Wu, H.P. High-flow nasal cannula compared with continuous positive airway pressure in the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath. 2022, 26, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, J.; Nagata, K.; Morimoto, T.; Kogo, M.; Fujimoto, D.; Nakagawa, A.; Otsuka, K.; Tomii, K. Respiratory management of acute exacerbation of interstitial pneumonia using high-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy: A single center cohort study. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyauchi, T.; Hasegawa, H.; Kanata, K.; Kakutani, T.; Amano, Y.; Ozawa, Y.; Matsui, T.; Yokomura, K.; Suda, T. Efficacy and Tolerability of High-Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy for Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure in Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease with Do-Not-Intubate Orders: A Retrospective Single-Center Study. Respiration 2018, 96, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frat, J.P.; Thille, A.W.; Mercat, A.; Girault, C.; Ragot, S.; Perbet, S.; Prat, G.; Boulain, T.; Morawiec, E.; Cottereau, A.; et al. REVA Network. High-flow oxygen through nasal cannula in acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2185–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, J.; Nagata, K.; Morimoto, T.; Iwata, K.; Matsunashi, A.; Sato, Y.; Tachikawa, R.; Ishikawa, A.; Tomii, K. Effect of high-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy on exercise tolerance in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A randomized crossover trial. Respirology 2022, 27, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badenes-Bonet, D.; Cejudo, P.; Rodó-Pin, A.; Martín-Ontiyuelo, C.; Chalela, R.; Rodríguez-Portal, J.A.; Vázquez-Sánchez, R.; Gea, J.; Duran, X.; Caguana, O.A.; et al. Impact of high-flow oxygen therapy during exercise in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A pilot crossover clinical trial. BMC Pulm. Med. 2021, 21, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narang, I.; Carberry, J.C.; Eckert, D.J. Central apnea and decreased drive to upper airway motoneurons during high flow nasal cannula therapy. Sleep Med. 2020, 69, 98–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Guo, H.J.; Wang, Y.; Cao, J.; Chen, B.Y. Treatment-emergent central sleep apnea: A unique sleep-disordered breathing. Chin. Med. J. 2020, 133, 2721–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeineddine, S.; Rowley, J.A.; Chowdhuri, S. Oxygen Therapy in Sleep-Disordered Breathing. Chest 2021, 160, 701–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, H.F.; Polo, O.; McNamara, S.G.; Berthon-Jones, M.; Sullivan, C.E. Effect of different levels of hyperoxia on breathing in healthy subjects. J. Appl. Physiol. 1996, 81, 1683–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, V.; Vasu, T.S.; Phillips, B.; Chung, F. Obstructive sleep apnea and oxygen therapy: A systematic review of the literature and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2013, 9, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sands, S.A.; Edwards, B.A.; Terrill, P.I.; Butler, J.P.; Owens, R.L.; Taranto-Montemurro, L.; Azarbarzin, A.; Marques, M.; Hess, L.B.; Smales, E.T.; et al. Identifying obstructive sleep apnoea patients responsive to supplemental oxygen therapy. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1800674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, A.; Skatrud, J.B.; Puleo, D.S.; Dempsey, J.A. Influence of arterial O2 on the susceptibility to posthyperventilation apnea during sleep. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 100, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khor, Y.H.; Ng, Y.; Sweeney, D.; Ryerson, C.J. Nocturnal hypoxaemia in interstitial lung disease: A systematic review. Thorax 2021, 76, 1200–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, J.C.; Pérez-Padilla, R. Effect of oxygen on sleep and breathing in patients with interstitial lung disease at moderate altitude. Respiration 2001, 68, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Aghbari, J.; Wong, K.; Lau, E. Supplemental oxygen improves sleep disordered breathing but not quality of life in patients with interstitial lung disease. Respirology 2016, 21, 147. [Google Scholar]
- Molnár, V.; Kunos, L.; Tamás, L.; Lakner, Z. Evaluation of the Applicability of Artificial Intelligence for the Prediction of Obstructive Sleep Apnoea. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapur, V.K.; Auckley, D.H.; Chowdhuri, S.; Kuhlmann, D.C.; Mehra, R.; Ramar, K.; Harrod, C.G. Clinical Practice Guideline for Diagnostic Testing for Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea: An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2017, 13, 479–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Sanford, L.D.; Ren, R.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X. Multiple Machine Learning Methods Reveal Key Biomarkers of Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Treatment. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 927545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederberg, K.L.J.; Hanif, U.; Peris Sempere, V.; Hédou, J.; Leary, E.B.; Schneider, L.D.; Lin, L.; Zhang, J.; Morse, A.M.; Blackman, A.; et al. Proteomic Biomarkers of the Apnea Hypopnea Index and Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Insights into the Pathophysiology of Presence, Severity, and Treatment Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Azarbarzin, A.; Podolanczuk, A.J.; Anderson, M.R.; Cade, B.E.; Kawut, S.M.; Wysoczanski, A.; Laine, A.F.; Hoffman, E.A.; Gottlieb, D.J.; et al. Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Longitudinal Changes in Interstitial Lung Imaging and Lung Function: The MESA Study. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2023, 20, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Author | Cohort | Modifications in Sleep Organization | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mermigkis et al. 2007 [18] | 18 patients with IPF | Reduction of sleep efficiency, REM sleep and slow-wave sleep, and increased arousal index. AHI positively correlated with BMI and negatively correlated with FEV1. | small-sized simple retrospective study |
| Mermigkis et al. 2009 [19] | 15 patients with IPF compared with 15 controls | Decrease in sleep efficiency and slow-wave sleep. Increase in N1 sleep and arousal index. Daytime tachypnea persisted during sleep in patients with IPF. | small-sized simple patients not receiving any treatment excluding the advanced forms |
| Lancaster et al. 2009 [6] | 50 patients with IPF | Reduction of sleep efficiency, slow-wave sleep, and REM sleep. Increased arousals, which correlated with the severity of OSA. | unselected sample: patients with prior diagnosis of OSA were included lack of a control group |
| Mermigkis et al. 2010 [20] | 34 patients with IPF treatment naive | Decreased sleep efficiency and REM sleep. Increased N1 stage and arousal index. | small-sized simple lack of a control group patients not receiving any treatment excluding the advanced forms |
| Kolilekas et al. 2013 [13] | 31 patients with IPF treatment naive | Decreased REM sleep. Increased arousal index and N2 stage. Sleep oxygen desaturation indices correlated with the right ventricular systolic pressure providing the link between intermittent oxygen desaturation and PH. | limited-sized simple lack of a control group |
| Simonson et al. 2022 [21] | 24 patients with ILD and PH compared with 25 patients with ILD without PH | Reduced total sleep time, a decreased proportion of stage N2. Increased proportion of stage N1 and wake after sleep onset (WASO) and poor sleep quality. | small-sized sample retrospective study lack of data measuring arousals |
| Author | Cohort | Intervention | Main Findings | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mermigkis et al. 2013 [86] | 12 IPF patients | CPAP for 6 months | Significant improvement in quality of life (measured by FOSQ) | First study demonstrating CPAP benefit in IPF patients |
| Mermigkis et al. 2015 [87] | 92 IPF patients (45 on CPAP) | CPAP, stratified by compliance | Good compliance group (n = 37) had significant QOL and sleep improvement, survival benefit over 24 months | Consistent CPAP use may improve survival |
| Papadogiannis et al. 2021 [12] | 45 IPF patients (29 on CPAP) | CPAP, adherence stratified | Improvements in sleepiness, fatigue, sleep quality; better survival with ≥6 h adherence | CPAP adherence impacts both QoL and survival |
| Bordas-Martinez et al. 2024 [90] | 50 IPFpatients | CPAP | Optimal adherence (6.74 h/night); no significant pulmonary or QoL changes, but reduced MMP-1 levels | CPAP may reduce profibrotic markers |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patsoura, A.; Baldini, G.; Puggioni, D.; Delle Vergini, M.; Castaniere, I.; Andrisani, D.; Gozzi, F.; Samarelli, A.V.; Raineri, G.; Michelacci, S.; et al. The Link Between Sleep-Related Breathing Disorders and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Treatment Options—A Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2205. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072205
Patsoura A, Baldini G, Puggioni D, Delle Vergini M, Castaniere I, Andrisani D, Gozzi F, Samarelli AV, Raineri G, Michelacci S, et al. The Link Between Sleep-Related Breathing Disorders and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Treatment Options—A Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(7):2205. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072205
Chicago/Turabian StylePatsoura, Athina, Giulia Baldini, Daniele Puggioni, Matteo Delle Vergini, Ivana Castaniere, Dario Andrisani, Filippo Gozzi, Anna Valeria Samarelli, Giulia Raineri, Sofia Michelacci, and et al. 2025. "The Link Between Sleep-Related Breathing Disorders and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Treatment Options—A Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 7: 2205. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072205
APA StylePatsoura, A., Baldini, G., Puggioni, D., Delle Vergini, M., Castaniere, I., Andrisani, D., Gozzi, F., Samarelli, A. V., Raineri, G., Michelacci, S., Ruini, C., Carzoli, A., Cuculo, A., Marchioni, A., Beghè, B., Clini, E., Cerri, S., & Tonelli, R. (2025). The Link Between Sleep-Related Breathing Disorders and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Treatment Options—A Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(7), 2205. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072205









