Brain Atrophy Is Associated with Hematoma Expansion in Intracerebral Hemorrhage, Depending on Coagulation Status
Abstract
:1. Introduction
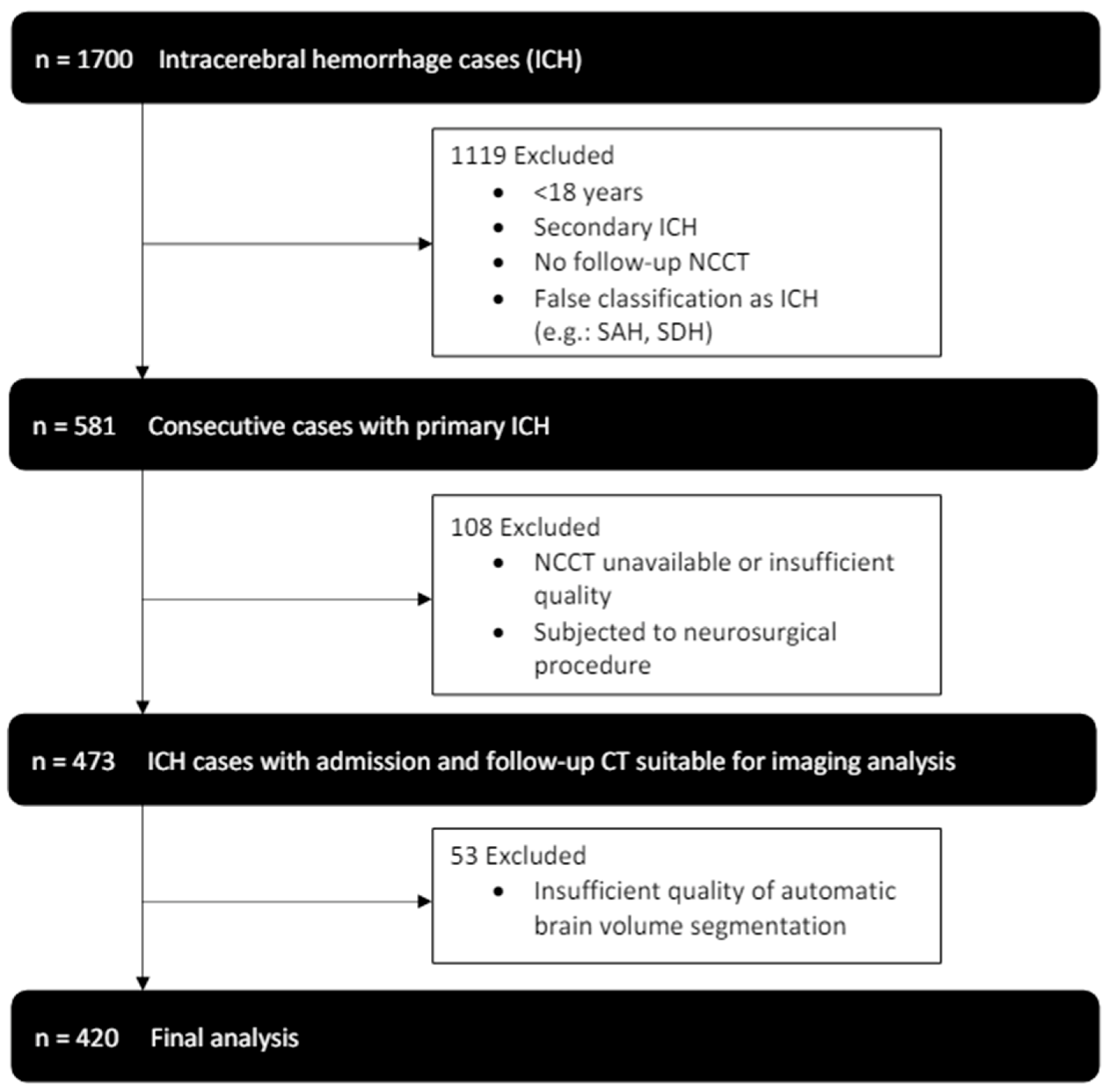
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Image Acquisition
2.3. Image Analysis—ICH Volume
2.4. Image Analysis—Brain Volume
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Participants and CT Data
3.2. NBV and Hematoma Growth
3.3. NBV, Hematoma Growth, and Neurological Outcome
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morotti, A.; Goldstein, J.N. Diagnosis and Management of Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Emerg. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 34, 883–899. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, C.M. Pathological Observations in Hypertensive Cerebral Hemorrhage. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1971, 30, 536–550. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, A.I.; Tuhrim, S.; Broderick, J.P.; Batjer, H.H.; Hondo, H.; Hanley, D.F. Spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1450–1460. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schlunk, F.; Böhm, M.; Boulouis, G.; Qin, T.; Arbel, M.; Tamim, I.; Fischer, P.; Bacskai, B.J.; Frosch, M.P.; Endres, M.; et al. Secondary Bleeding During Acute Experimental Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stroke 2019, 50, 1210–1215. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, S.A. Ultra-Early Hemostatic Therapy for Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stroke 2003, 34, 224–229. [Google Scholar]
- Vychopen, M.; Wach, J.; Lampmann, T.; Asoglu, H.; Borger, V.; Hamed, M.; Vatter, H.; Güresir, E. Postoperative Hematoma Expansion in Patients Undergoing Decompressive Hemicraniectomy for Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, M.S.; Shanbhag, N.C.; Shukla, D.P.; Konar, S.K.; Bhat, D.I.; Devi, B.I. Complications of Decompressive Craniectomy. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 977. [Google Scholar]
- Flaherty, M.L.; Tao, H.; Haverbusch, M.; Sekar, P.; Kleindorfer, D.; Kissela, B.; Khatri, P.; Stettler, B.; Adeoye, O.; Moomaw, C.J.; et al. Warfarin use leads to larger intracerebral hematomas. Neurology 2008, 71, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar]
- Massaro, A.R.; Sacco, R.L.; Mohr, J.P.; Foulkes, M.A.; Tatemichi, T.K.; Price, T.R.; Hier, D.B.; Wolf, P.A. Clinical discriminators of lobar and deep hemorrhages: The Stroke Data Bank. Neurology 1991, 41, 1881–1885. [Google Scholar]
- Kurogi, R.; Nishimura, K.; Nakai, M.; Kada, A.; Kamitani, S.; Nakagawara, J.; Toyoda, K.; Ogasawara, K.; Ono, J.; Shiokawa, Y.; et al. Comparing Intracerebral Hemorrhages Associated with Direct Oral Anticoagulants or Warfarin. Neurology 2018, 90, e1143–e1149. [Google Scholar]
- Morotti, A.; Boulouis, G.; Dowlatshahi, D.; Li, Q.; Shamy, M.; Salman, R.A.-S.; Rosand, J.; Cordonnier, C.; Goldstein, J.N.; Charidimou, A. Intracerebral Haemorrhage Expansion: Definitions, Predictors and Prevention. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 22, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purrucker, J.C.; Haas, K.; Rizos, T.; Khan, S.; Wolf, M.; Hennerici, M.G.; Poli, S.; Kleinschnitz, C.; Steiner, T.; Heuschmann, P.U.; et al. Early Clinical and Radiological Course, Management, and Outcome of Intracerebral Hemorrhage Related to New Oral Anticoagulants. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouvent, E.; Viswanathan, A.; Chabriat, H. Cerebral Atrophy in Cerebrovascular Disorders. J. Neuroimaging 2010, 20, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, T.C.; de Rooij, R.; Kuhl, E. The Shrinking Brain: Cerebral Atrophy Following Traumatic Brain Injury. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 47, 1941–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethlehem, R.A.I.; Seidlitz, J.; White, S.R.; Vogel, J.W.; Anderson, K.M.; Adamson, C.; Adler, S.; Alexopoulos, G.S.; Anagnostou, E.; Areces-Gonzalez, A.; et al. Brain charts for the human lifespan. Nature 2022, 604, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adduru, V.; Baum, S.; Zhang, C.; Helguera, M.; Zand, R.; Lichtenstein, M.; Griessenauer, C.; Michael, A. A Method to Estimate Brain Volume from Head CT Images and Application to Detect Brain Atrophy in Alzheimer Disease. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburner, J.; Friston, K.J. Unified segmentation. Neuroimage 2005, 26, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakae, R.; Sekine, T.; Tagami, T.; Murai, Y.; Kodani, E.; Warnock, G.; Sato, H.; Morita, A.; Yokota, H.; Yokobori, S. Rapidly progressive brain atrophy in septic ICU patients: A retrospective descriptive study using semiautomatic CT volumetry. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luijten, S.P.; Compagne, K.C.; van Es, A.C.; Roos, Y.B.; Majoie, C.B.; van Oostenbrugge, R.J.; van Zwam, W.H.; Dippel, D.W.; Wolters, F.J.; van der Lugt, A.; et al. Brain atrophy and endovascular treatment effect in acute ischemic stroke: A secondary analysis of the MR CLEAN trial. Int. J. Stroke 2021, 17, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwers, H.B.; Greenberg, S.M. Hematoma Expansion following Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2013, 35, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlunk, F.; Greenberg, S.M. The Pathophysiology of Intracerebral Hemorrhage Formation and Expansion. Transl. Stroke Res. 2015, 6, 257–263. [Google Scholar]
- Boulouis, G.; Dumas, A.; Betensky, R.A.; Brouwers, H.B.; Fotiadis, P.; Vashkevich, A.; Ayres, A.; Schwab, K.; Romero, J.M.; Smith, E.E.; et al. Anatomic pattern of intracerebral hemorrhage expansion: Relation to CT angiography spot sign and he-matoma center. Stroke 2014, 45, 1154–1156. [Google Scholar]
- Falcone, G.J.; Biffi, A.; Brouwers, H.B.; Anderson, C.D.; Battey, T.W.K.; Ayres, A.M.; Vashkevich, A.; Schwab, K.; Rost, N.S.; Goldstein, J.N.; et al. Predictors of Hematoma Volume in Deep and Lobar Supratentorial Intracerebral Hemorrhage. JAMA Neurol. 2013, 70, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.; Ahmed, R.; Ali, S.S.; Patel, U.; Shahid, I.; Zafar, M.; Sharma, A.; Ashraf, A.; Jani, V. Intracerebral hemorrhage outcomes in patients using direct oral anticoagulants versus vitamin K antagonists: A meta-analysis. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2020, 198, 106146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.S.; Marsh, E.B.; Ali, H.; Nyquist, P.A.; Hanley, D.F.; Ziai, W.C. Comparison of Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage Expansion and Outcomes Among Patients on Direct Oral Anticoagulants Versus Vitamin k Antagonists. Neurocrit. Care 2020, 32, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lauer, A.; Cianchetti, F.A.; Van Cott, E.M.; Schlunk, F.; Schulz, E.; Pfeilschifter, W.; Steinmetz, H.; Schaffer, C.B.; Lo, E.H.; Foerch, C. Anticoagulation With the Oral Direct Thrombin Inhibitor Dabigatran Does Not Enlarge Hematoma Volume in Experimental Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Circulation 2011, 124, 1654–1662. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, J.H.; Leung, W.; Wu, L.; Van Cott, E.M.; Lok, J.; Whalen, M.; van Leyen, K.; Lauer, A.; van Ryn, J.; Lo, E.H.; et al. Translational Insights into Traumatic Brain Injury Occurring during Dabigatran or Warfarin Anticoagulation. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 34, 870–875. [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg, S.M.; Bacskai, B.J.; Hernandez-Guillamon, M.; Pruzin, J.; Sperling, R.; van Veluw, S.J. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy and Alzheimer disease—One peptide, two pathways. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 30–42. [Google Scholar]
- Vollhardt, A.; Frölich, L.; Stockbauer, A.C.; Danek, A.; Schmitz, C.; Wahl, A.-S. Towards a better diagnosis and treatment of dementia: Identifying common and distinct neuropathological mechanisms in Alzheimer’s and vascular dementia. Neurobiol. Dis. 2025, 208, 106845. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, G.; Keep, R.F.; Hoff, J.T. Mechanisms of brain injury after intracerebral haemorrhage. Lancet Neurol. 2006, 5, 53–63. [Google Scholar]
- Herweh, C.; Prager, E.; Sykora, M.; Bendszus, M. Cerebral Atrophy is an Independent Risk Factor for Unfavorable Outcome After Spontaneous Supratentorial Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stroke 2013, 44, 968–971. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sato, S.; Delcourt, C.; Heeley, E.; Arima, H.; Zhang, S.; Salman, R.A.-S.; Stapf, C.; Woo, D.; Flaherty, M.L.; Vagal, A.; et al. Significance of Cerebral Small-Vessel Disease in Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stroke 2016, 47, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.M.; Choi, K.-S.; Yi, H.-J.; Ko, Y.; Kim, Y.-S.; Bak, K.-H.; Chun, H.-J.; Lee, Y.-J.; Lee, J.Y. Impact of brain atrophy on 90-day functional outcome after moderate-volume basal ganglia hemorrhage. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4819. [Google Scholar]
- Venema, S.M.U.; Marini, S.; Brouwers, H.B.; Morotti, A.; Woo, D.; Anderson, C.D.; Rosand, J. Associations of Radiographic Cerebral Small Vessel Disease with Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage Volume, Hematoma Expansion, and Intraventricular Hemorrhage. Neurocrit. Care 2019, 32, 383–391. [Google Scholar]


| Variable | Total (n = 420) |
|---|---|
| Age, median (IQR), y | 72 (61–79) |
| Female sex, No. (%) | 184 (44) |
| Hypertension, No. (%) | 345 (82) |
| Diabetes, No. (%) | 70 (17) |
| Antiplatelet therapy, No. (%) | 100 (24) |
| Anticoagulation therapy, No. (%) | 123 (29) |
| 45 47 31 |
| Glasgow Coma Scale score, median (IQR) | 12 (8–14) |
| NIHSS admission, median (IQR) | 10 (5–15) |
| mRS discharge, median (IQR) | 5 (4–6) |
| Bleeding location, No. (%) | |
| 198 (47) 160 (38) 31 (7) 29 (7) |
| Intraventricular hemorrhage, No. (%) | 181 (43) |
| Baseline ICH volume, median (IQR), mL | 19 (7–41) |
| Follow ICH volume, median (IQR), mL | 23 (8–46) |
| Time to admission CT scan, median (IQR), min | 135 (73–459) |
| Time CT admission to follow up, median (IQR), min | 975 (365–1525) |
| No OAT | VKAs | DOACs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Covariate | ß | p Value | ß | p Value | ß | p Value |
| Age | −0.135 | 0.1 | −0.486 | 0.031 * | 0.209 | 0.276 |
| Sex (male) | −0.08 | 0.281 | −0.063 | 0.771 | 0.095 | 0.627 |
| NBV | −0.159 | 0.032 * | −0.667 | 0.006 * | −0.159 | 0.436 |
| Hypertension | −0.055 | 0.454 | −0.182 | 0.439 | −0.371 | 0.082 |
| Diabetes | −0.07 | 0.327 | 0.09 | 0.691 | −0.444 | 0.041 * |
| Antiplatelet therapy | 0.156 | 0.032 * | 0.125 | 0.504 | −0.014 | 0.952 |
| Initial hematoma vol. | 0.331 | <0.001 *** | 0.399 | 0.056 | 0.317 | 0.1 |
| Intracerebral Hemorrhage | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deep | Lobar | |||||||
| HE > 0 mL | HE > 6 mL or 33% | HE > 0 mL | HE > 6 mL or 33% | |||||
| Covariate | ß | p Value | ß | p Value | ß | p Value | ß | p Value |
| Age | −0.085 | 0.49 | −0.440 | 0.08 | −0.289 | 0.049 * | −0.471 | 0.008 ** |
| Sex (male) | −0.136 | 0.24 | −0.267 | 0.27 | −0.028 | 0.83 | −0.176 | 0.35 |
| NBV | −0.053 | 0.64 | −0.152 | 0.55 | −0.226 | 0.081 | −0.14 | 0.39 |
| Hypertension | 0.094 | 0.39 | 0.024 | 0.92 | −0.093 | 0.49 | −0.295 | 0.07 |
| Diabetes | −0.049 | 0.66 | −0.115 | 0.64 | −0.086 | 0.5 | −0.22 | 0.18 |
| Antiplatelet therapy | 0.103 | 0.34 | 0.084 | 0.73 | 0.246 | 0.06 | 0.501 | 0.016 * |
| Initial hematoma vol. | 0.286 | 0.007 ** | −0.048 | 0.832 | 0.276 | 0.03 * | 0.121 | 0.43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Speth, A.; Dell’Orco, A.; Kleine, J.F.; Güttler, C.; Morotti, A.; Urbach, H.; Bohner, G.; Scheel, M.; Nawabi, J.; Schlunk, F. Brain Atrophy Is Associated with Hematoma Expansion in Intracerebral Hemorrhage, Depending on Coagulation Status. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2227. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072227
Speth A, Dell’Orco A, Kleine JF, Güttler C, Morotti A, Urbach H, Bohner G, Scheel M, Nawabi J, Schlunk F. Brain Atrophy Is Associated with Hematoma Expansion in Intracerebral Hemorrhage, Depending on Coagulation Status. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(7):2227. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072227
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpeth, Anna, Andrea Dell’Orco, Justus F. Kleine, Christopher Güttler, Andrea Morotti, Horst Urbach, Georg Bohner, Michael Scheel, Jawed Nawabi, and Frieder Schlunk. 2025. "Brain Atrophy Is Associated with Hematoma Expansion in Intracerebral Hemorrhage, Depending on Coagulation Status" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 7: 2227. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072227
APA StyleSpeth, A., Dell’Orco, A., Kleine, J. F., Güttler, C., Morotti, A., Urbach, H., Bohner, G., Scheel, M., Nawabi, J., & Schlunk, F. (2025). Brain Atrophy Is Associated with Hematoma Expansion in Intracerebral Hemorrhage, Depending on Coagulation Status. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(7), 2227. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072227






