Glycemic Variability and Its Association with Traditional Glycemic Control Biomarkers in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional, Multicenter Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patients
2.2. Anthropometrical, Clinical and Laboratory Assessments
2.3. Glycemic Variability Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GV | Glycemic variability |
| TIR | Time in range |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| T1DM | Type 1 diabetes mellitus |
| BG | Blood glucose |
| HbA1c | Hemoglobin A1c |
| CGMS | Continuous glucose monitor system |
| CV | Coefficient of variability |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes management |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| CVR | Cardiovascular risk |
| CVE | Cardiovascular event |
References
- Roep, B.O.; Thomaidou, S.; van Tienhoven, R.; Zaldumbide, A. Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus as a Disease of the β-Cell (Do Not Blame the Immune System?). Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zajec, A.; Trebušak Podkrajšek, K.; Tesovnik, T.; Šket, R.; Čugalj Kern, B.; Jenko Bizjan, B.; Šmigoc Schweiger, D.; Battelino, T.; Kovač, J. Pathogenesis of Type 1 Diabetes: Established Facts and New Insights. Genes 2022, 13, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, B.; Dey, S.; Das, T.; Sarkar, M.; Banerjee, J.; Dash, S.K. Chronic Hyperglycemia Mediated Physiological Alteration and Metabolic Distortion Leads to Organ Dysfunction, Infection, Cancer Progression and Other Pathophysiological Consequences: An Update on Glucose Toxicity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 306–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, I.C.; Ahmadizadeh, I.; Randell, J.; Younk, L.; Davis, S.N. Understanding the Impact of Hypoglycemia on the Cardiovascular System. Expert Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 12, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergès, B. Cardiovascular Disease in Type 1 Diabetes, an Underestimated Danger: Epidemiological and Pathophysiological Data. Atherosclerosis 2024, 394, 117158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butalia, S.; Chu, L.M.; Dover, D.C.; Lau, D.; Yeung, R.O.; Eurich, D.T.; Senior, P.; Kaul, P. Association Between Hemoglobin A1c and Development of Cardiovascular Disease in Canadian Men and Women Without Diabetes at Baseline: A Population-Based Study of 608 474 Adults. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2024, 13, e031095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colom, C.; Rull, A.; Sanchez-Quesada, J.L.; Pérez, A. Cardiovascular Disease in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: Epidemiology and Management of Cardiovascular Risk. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, N.; Mitchell, P.; Wong, T.Y. Diabetic Retinopathy. Lancet 2010, 376, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The Effect of Intensive Treatment of Diabetes on the Development and Progression of Long-Term Complications in Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, M.; Sundkvist, G.; Arnqvist, H.J.; Björk, E.; Blohmé, G.; Bolinder, J.; Henricsson, M.; Nyström, L.; Torffvit, O.; Waernbaum, I.; et al. Signs of Nephropathy May Occur Early in Young Adults With Diabetes Despite Modern Diabetes Management. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 2903–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, B.S.; Sjølie, A.K.; Hougaard, P.; Johannesen, J.; Marinelli, K.; Jacobsen, B.B.; Mortensen, H.B. The Significance of the Prepubertal Diabetes Duration for the Development of Retinopathy and Nephropathy in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2004, 18, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costacou, T.; Orchard, T.J. Cumulative Kidney Complication Risk by 50 Years of Type 1 Diabetes: The Effects of Sex, Age, and Calendar Year at Onset. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfannkuche, A.; Alhajjar, A.; Ming, A.; Walter, I.; Piehler, C.; Mertens, P.R. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in a Diabetics Cohort: Register Initiative “Diabetes and Nerves”. Endocr. Metab. Sci. 2020, 1, 100053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braffett, B.H.; El ghormli, L.; Albers, J.W.; Feldman, E.L.; Herman, W.H.; Gubitosi-Klug, R.A.; Martin, C.L.; Orchard, T.J.; White, N.H.; Lachin, J.M.; et al. Neuropathic Pain With and Without Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, 1559–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, L.; Jaiswal, M.; Martin, C.; Pop-Busui, R. Glucose Control and Diabetic Neuropathy: Lessons from Recent Large Clinical Trials. Curr. Diab Rep. 2014, 14, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrashali, S.B.; Madhu, B.; Sree, M.M.; Chaithra, M.; Sahana, K.S.; Nagendra, K. Relationship between the Cost of Illness and Quality of Life among Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes—A Mixed Method Study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sussman, M.; Benner, J.; Haller, M.J.; Rewers, M.; Griffiths, R. Estimated Lifetime Economic Burden of Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2020, 22, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. 5. Lifestyle Management: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2019. Diabetes Care 2019, 42 (Suppl. S1), S46–S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschner, P.; Horton, E.; Leiter, L.A.; Munro, N.; Skyler, J.S. Practical Steps to Improving the Management of Type 1 Diabetes: Recommendations from the Global Partnership for Effective Diabetes Management. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2010, 64, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, D.B.; Kirkman, M.S.; Little, R.R. Point-of-Care HbA1c in Clinical Practice: Caveats and Considerations for Optimal Use. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, R.W.; Connor, C.G.; Mullen, D.M.; Wesley, D.M.; Bergenstal, R.M. The Fallacy of Average: How Using HbA1c Alone to Assess Glycemic Control Can Be Misleading. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 994–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, S.; Kim, J.H. Glycemic Variability: How Do We Measure It and Why Is It Important? Diabetes Metab. J. 2015, 39, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyser, T.A.; Balo, A.K.; Buckingham, B.A.; Hirsch, I.B.; Garcia, A. Glycemic Variability Percentage: A Novel Method for Assessing Glycemic Variability from Continuous Glucose Monitor Data. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2018, 20, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belli, M.; Bellia, A.; Sergi, D.; Barone, L.; Lauro, D.; Barillà, F. Glucose Variability: A New Risk Factor for Cardiovascular Disease. Acta Diabetol. 2023, 60, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodbard, D. Glucose Variability: A Review of Clinical Applications and Research Developments. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2018, 20, S2-5–S2-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnier, L.; Mas, E.; Ginet, C.; Michel, F.; Villon, L.; Cristol, J.-P.; Colette, C. Activation of Oxidative Stress by Acute Glucose Fluctuations Compared With Sustained Chronic Hyperglycemia in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. JAMA 2006, 295, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceriello, A.; Esposito, K.; Piconi, L.; Ihnat, M.A.; Thorpe, J.E.; Testa, R.; Boemi, M.; Giugliano, D. Oscillating Glucose Is More Deleterious to Endothelial Function and Oxidative Stress Than Mean Glucose in Normal and Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1349–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papachristoforou, E.; Lambadiari, V.; Maratou, E.; Makrilakis, K. Association of Glycemic Indices (Hyperglycemia, Glucose Variability, and Hypoglycemia) with Oxidative Stress and Diabetic Complications. J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 2020, 7489795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risso, A.; Mercuri, F.; Quagliaro, L.; Damante, G.; Ceriello, A. Intermittent High Glucose Enhances Apoptosis in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells in Culture. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 281, E924–E930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saisho, Y. Glycemic Variability and Oxidative Stress: A Link between Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 18381–18406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.-M.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, H.-M.; Su, Q. Effects of Intermittent High Glucose on Oxidative Stress in Endothelial Cells. Acta Diabetol. 2010, 47, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, M.; Hayashi, T.; Mizuno, N.; Hattori, Y.; Kuzuya, M. Intermittent High Glucose Implements Stress-Induced Senescence in Human Vascular Endothelial Cells: Role of Superoxide Production by NADPH Oxidase. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinman, B.; Marso, S.P.; Poulter, N.R.; Emerson, S.S.; Pieber, T.R.; Pratley, R.E.; Lange, M.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Moses, A.; Ocampo Francisco, A.M.; et al. Day-to-Day Fasting Glycaemic Variability in DEVOTE: Associations with Severe Hypoglycaemia and Cardiovascular Outcomes (DEVOTE 2). Diabetologia 2018, 61, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceriello, A.; Monnier, L.; Owens, D. Glycaemic Variability in Diabetes: Clinical and Therapeutic Implications. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehregosha, H.; Khamseh, M.E.; Malek, M.; Hosseinpanah, F.; Ismail-Beigi, F. A View Beyond HbA1c: Role of Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Diabetes Ther. 2019, 10, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urakami, T.; Terada, H.; Tanabe, S.; Mine, Y.; Aoki, M.; Aoki, R.; Suzuki, J.; Morioka, I. Clinical Significance of Coefficient of Variation in Continuous Glucose Monitoring for Glycemic Management in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes. J. Diabetes Investig. 2024, 15, 1669–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSayed, N.A.; McCoy, R.G.; Aleppo, G.; Balapattabi, K.; Beverly, E.A.; Early, B.; Bruemmer, D.; Echouffo-Tcheugui, J.B.; Ekhlaspour, L.; Garg, R.; et al. 6. Glycemic Goals and Hypoglycemia: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2025. Diabetes Care 2025, 48, S128–S145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVries, J.H. Glucose Variability: Where It Is Important and How to Measure It. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1405–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliasson, B.; Allansson Kjölhede, E.; Salö, S.; Fabrin Nielsen, N.; Eeg-Olofsson, K. Associations Between HbA1c and Glucose Time in Range Using Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Type 1 Diabetes: Cross-Sectional Population-Based Study. Diabetes Ther. 2024, 15, 1301–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Sun, B.; Huang, S.; Zhu, C.; Bian, M. Glycemic Variability: Adverse Clinical Outcomes and How to Improve It? Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartore, G.; Chilelli, N.C.; Burlina, S.; Di Stefano, P.; Piarulli, F.; Fedele, D.; Mosca, A.; Lapolla, A. The Importance of HbA1c and Glucose Variability in Patients with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes: Outcome of Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM). Acta Diabetol. 2012, 49, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stem, M.S.; Dunbar, G.E.; Jackson, G.R.; Farsiu, S.; Pop-Busui, R.; Gardner, T.W. Glucose Variability and Inner Retinal Sensory Neuropathy in Persons with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Eye 2016, 30, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Malahi, A.; Van Elsen, M.; Charleer, S.; Dirinck, E.; Ledeganck, K.; Keymeulen, B.; Crenier, L.; Radermecker, R.; Taes, Y.; Vercammen, C.; et al. Relationship Between Time in Range, Glycemic Variability, HbA1c, and Complications in Adults With Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, e570–e581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartore, G.; Ragazzi, E.; Caprino, R.; Lapolla, A. Long-Term HbA1c Variability and Macro-/Micro-Vascular Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis Update. Acta Diabetol. 2023, 60, 721–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorst, C.; Kwok, C.S.; Aslam, S.; Buchan, I.; Kontopantelis, E.; Myint, P.K.; Heatlie, G.; Loke, Y.; Rutter, M.K.; Mamas, M.A. Long-Term Glycemic Variability and Risk of Adverse Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 2354–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilpatrick, E.S.; Rigby, A.S.; Atkin, S.L. A1C Variability and the Risk of Microvascular Complications in Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 2198–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, I.B. Glycemic Variability and Diabetes Complications: Does It Matter? Of Course It Does! Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 1610–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šoupal, J.; Škrha, J.; Fajmon, M.; Horová, E.; Mráz, M.; Škrha, J.; Prázný, M. Glycemic Variability Is Higher in Type 1 Diabetes Patients with Microvascular Complications Irrespective of Glycemic Control. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2014, 16, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Li, Y.; Guo, K.; Wu, X.; Chen, C.; Lin, X. Association of Glycemic Variability with Death and Severe Consciousness Disturbance among Critically Ill Patients with Cerebrovascular Disease: Analysis of the MIMIC-IV Database. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besch, G.; Pili-Floury, S.; Morel, C.; Gilard, M.; Flicoteaux, G.; Salomon du Mont, L.; Perrotti, A.; Meneveau, N.; Chocron, S.; Schiele, F.; et al. Impact of Post-Procedural Glycemic Variability on Cardiovascular Morbidity and Mortality after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation: A Post Hoc Cohort Analysis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; He, L.; Cao, S.; Yang, Q.; Yang, S.; Zhou, Y. Effect of Glycemic Variability on Short Term Prognosis in Acute Myocardial Infarction Subjects Undergoing Primary Percutaneous Coronary Interventions. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2014, 6, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Xu, J.; Li, B.; Liu, Z.; Hao, H.; Yin, C.; Xu, D. Association between Glycemic Variability and Major Adverse Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Events (MACCE) in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome during 30-Day Follow-Up. Clin. Chim. Acta 2017, 466, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, G.; Mi, S.; Tao, H.; Li, Z.; Yang, H.; Zheng, H.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, C. Association of Glycemic Variability and the Presence and Severity of Coronary Artery Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2011, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roussel, R.; Steg, P.G.; Mohammedi, K.; Marre, M.; Potier, L. Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease through Reduction of Glycaemic Exposure in Type 2 Diabetes: A Perspective on Glucose-lowering Interventions. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tateishi, K.; Saito, Y.; Kitahara, H.; Kobayashi, Y. Impact of Glycemic Variability on Coronary and Peripheral Endothelial Dysfunction in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. J. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farabi, S.S.; Quinn, L.; Phillips, S.; Mihailescu, D.; Park, C.; Ali, M.; Martyn-Nemeth, P. Endothelial Dysfunction Is Related to Glycemic Variability and Quality and Duration of Sleep in Adults With Type 1 Diabetes. J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 2018, 33, E21–E25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Alexanian, A.; Ying, R.; Kizhakekuttu, T.J.; Dharmashankar, K.; Vasquez-Vivar, J.; Gutterman, D.D.; Widlansky, M.E. Acute Exposure to Low Glucose Rapidly Induces Endothelial Dysfunction and Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress: Role for AMP Kinase. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacco, F.; Brownlee, M. Oxidative Stress and Diabetic Complications. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 1058–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Shen, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Han, P. Acute Blood Glucose Fluctuation Enhances Rat Aorta Endothelial Cell Apoptosis, Oxidative Stress and pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Expression in Vivo. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2016, 15, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceriello, A. Glucose Variability and Diabetic Complications: Is It Time to Treat? Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1169–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Sun, B.; Zhu, C. Perspectives of Glycemic Variability in Diabetic Neuropathy: A Comprehensive Review. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Long, D.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Q. Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy and Glycemic Variability Assessed by Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2024, 213, 111757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
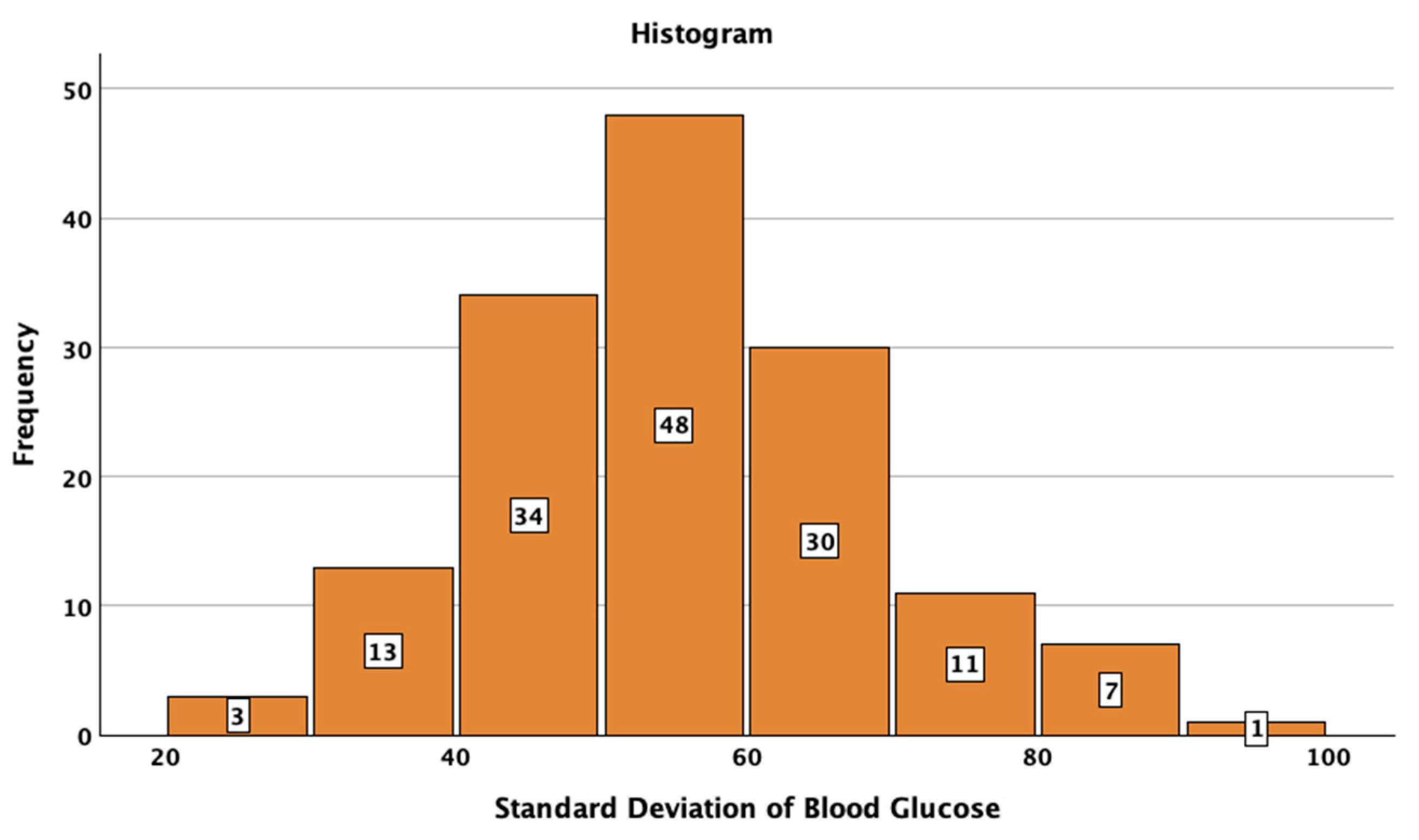



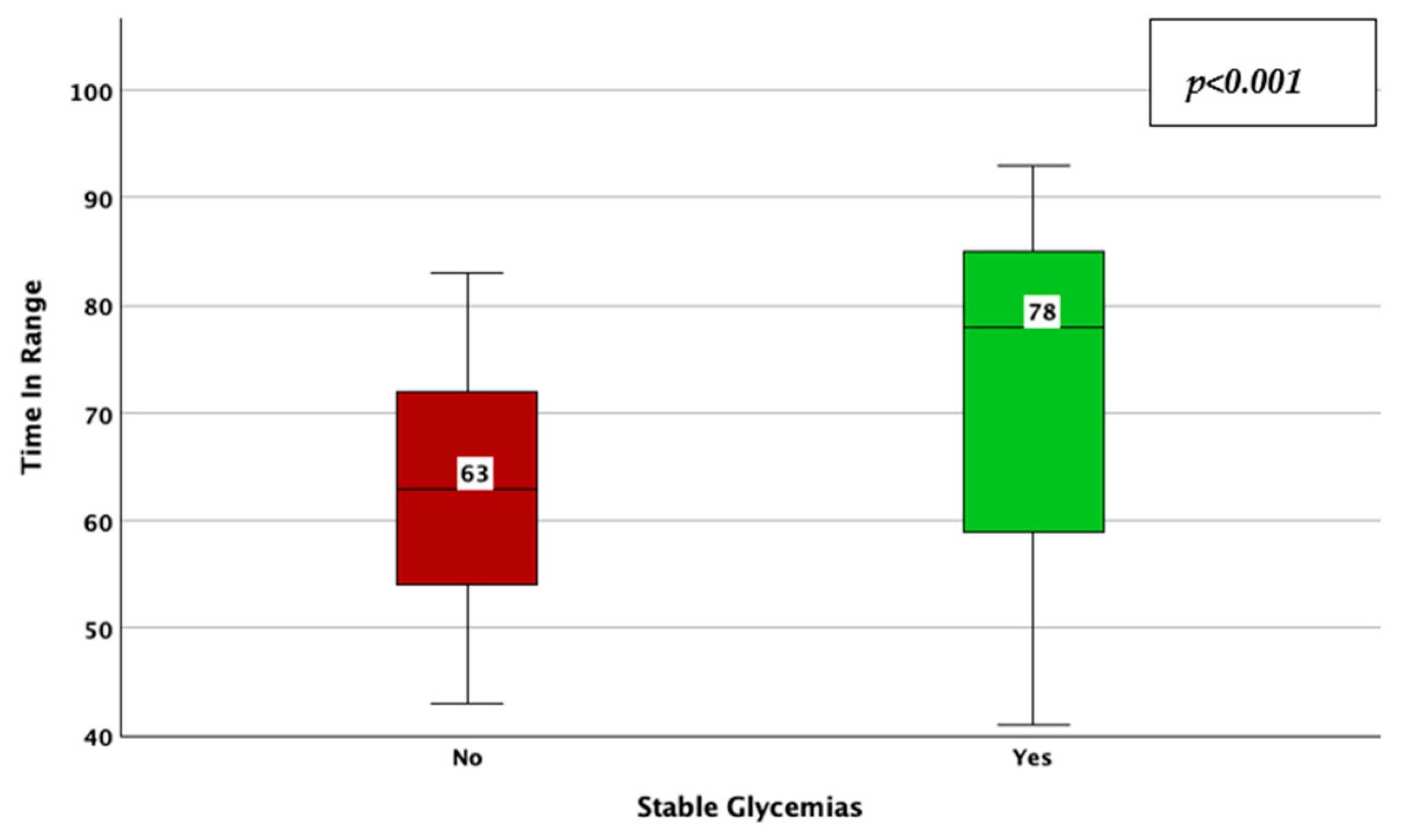


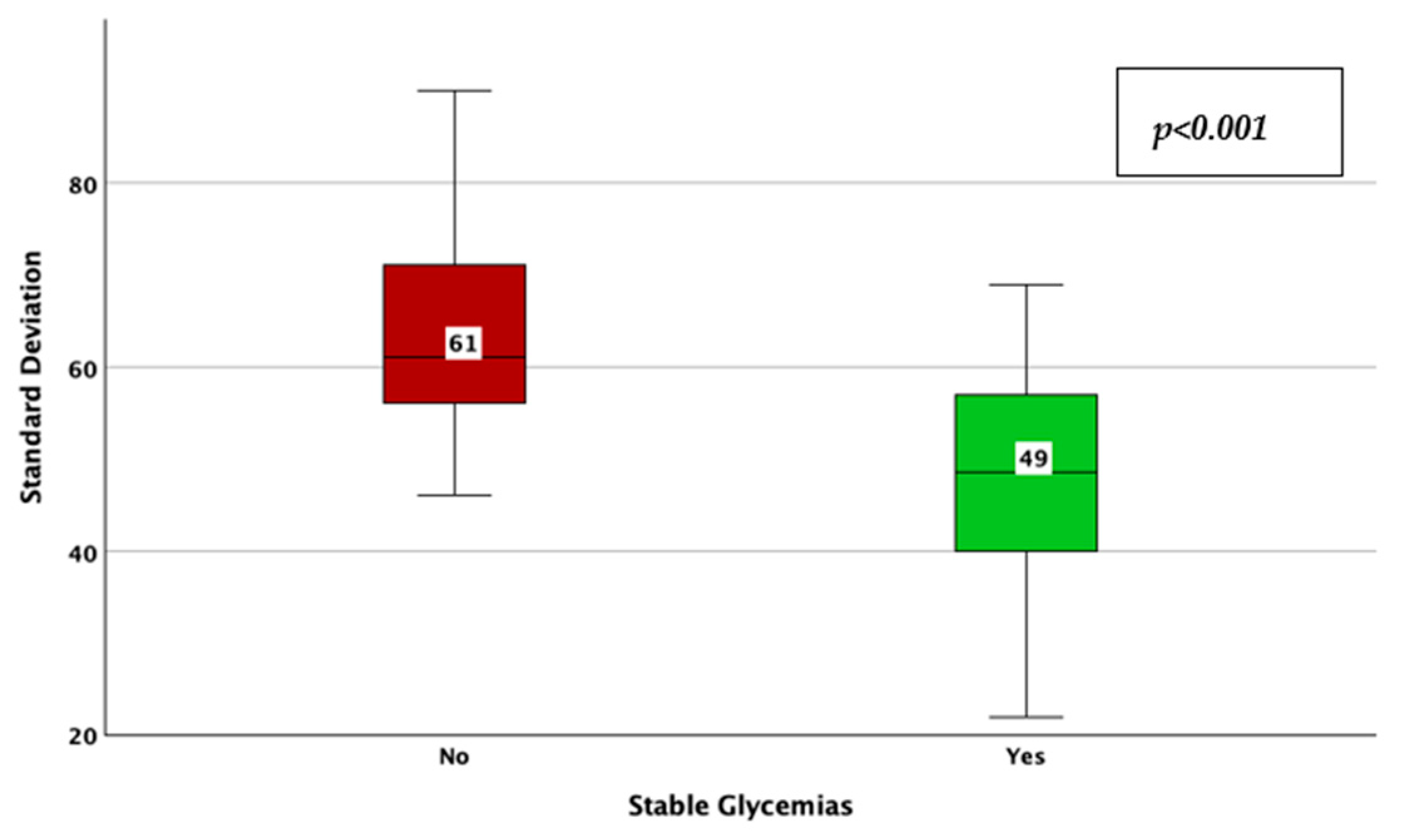

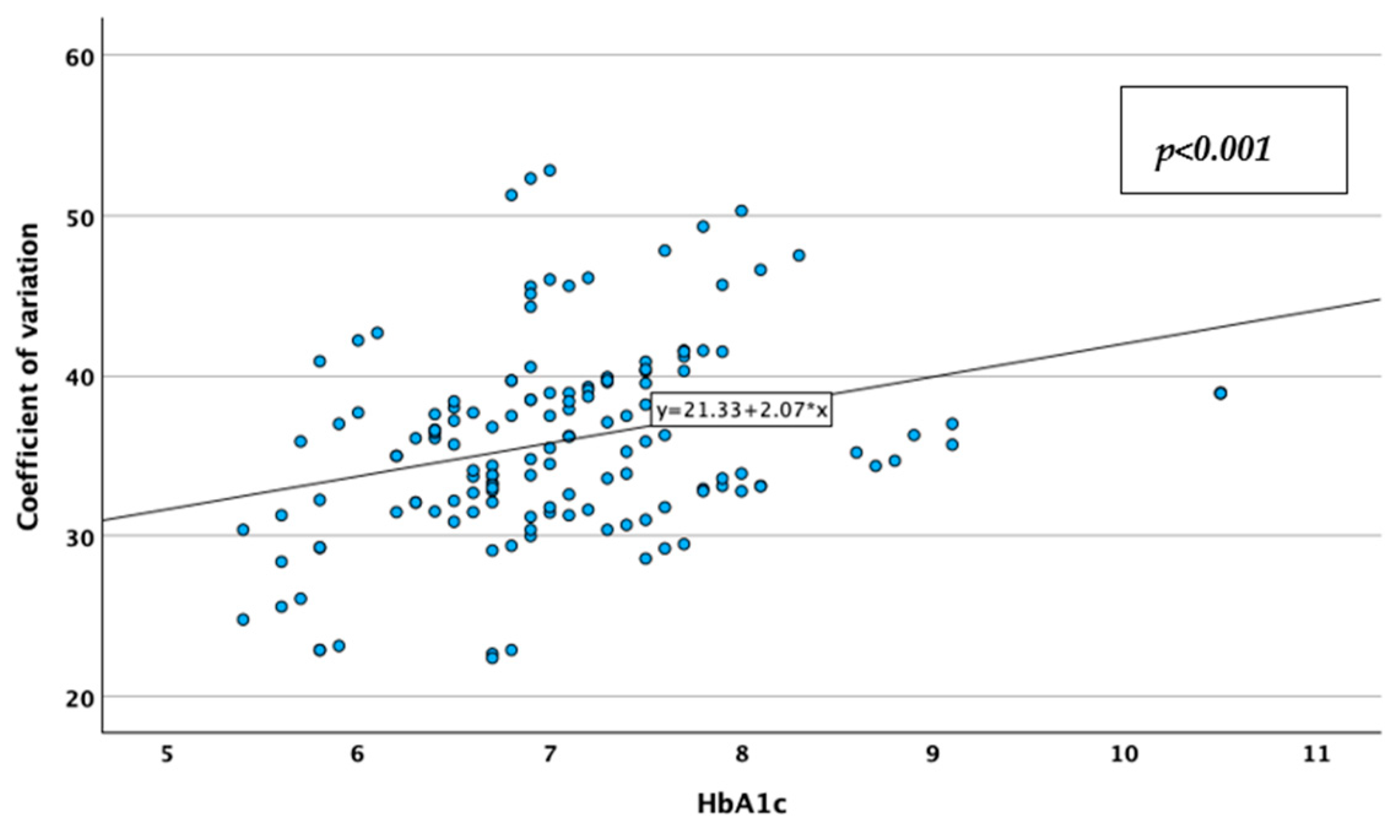


| Parameter | Result | |
|---|---|---|
| Gender a | Men | 60 (40.8%) |
| Women | 87 (59.2%) | |
| Age b | 32 years [15] | |
| Diabetes Duration b | 7 years [10] | |
| HbA1c b | 7.0% [0.9] | |
| Therapy type a | Basal bolus (multiple injections) | 84 (57.1%) |
| Insulin pump | 63 (42.9%) | |
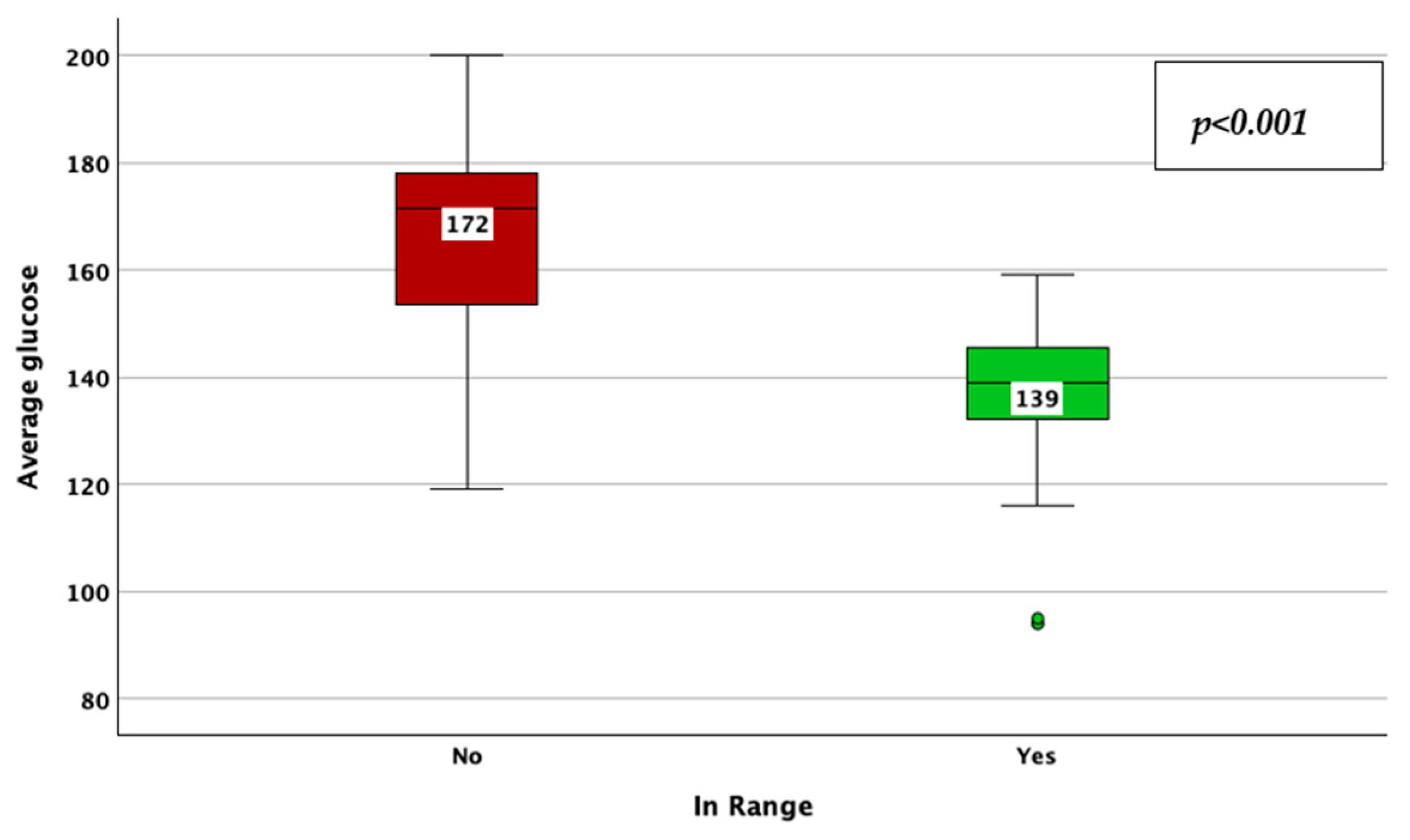
| Median | 95.0% Lower CL for Median | 95.0% Upper CL for Median | Percentile 25 | Percentile 75 | Minimum | Maximum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Deviation (mg/dL) | 57 | 56 | 59 | 46 | 63 | 22 | 90 |
| Coefficient of variation | 35.9 | 34.5 | 37.0 | 32.1 | 39.1 | 22.4 | 52.8 |
| Time In Range (%) | 69 | 66 | 72 | 56 | 79 | 41 | 93 |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.0 | 6.9 | 7.2 | 6.6 | 7.5 | 5.4 | 10.5 |
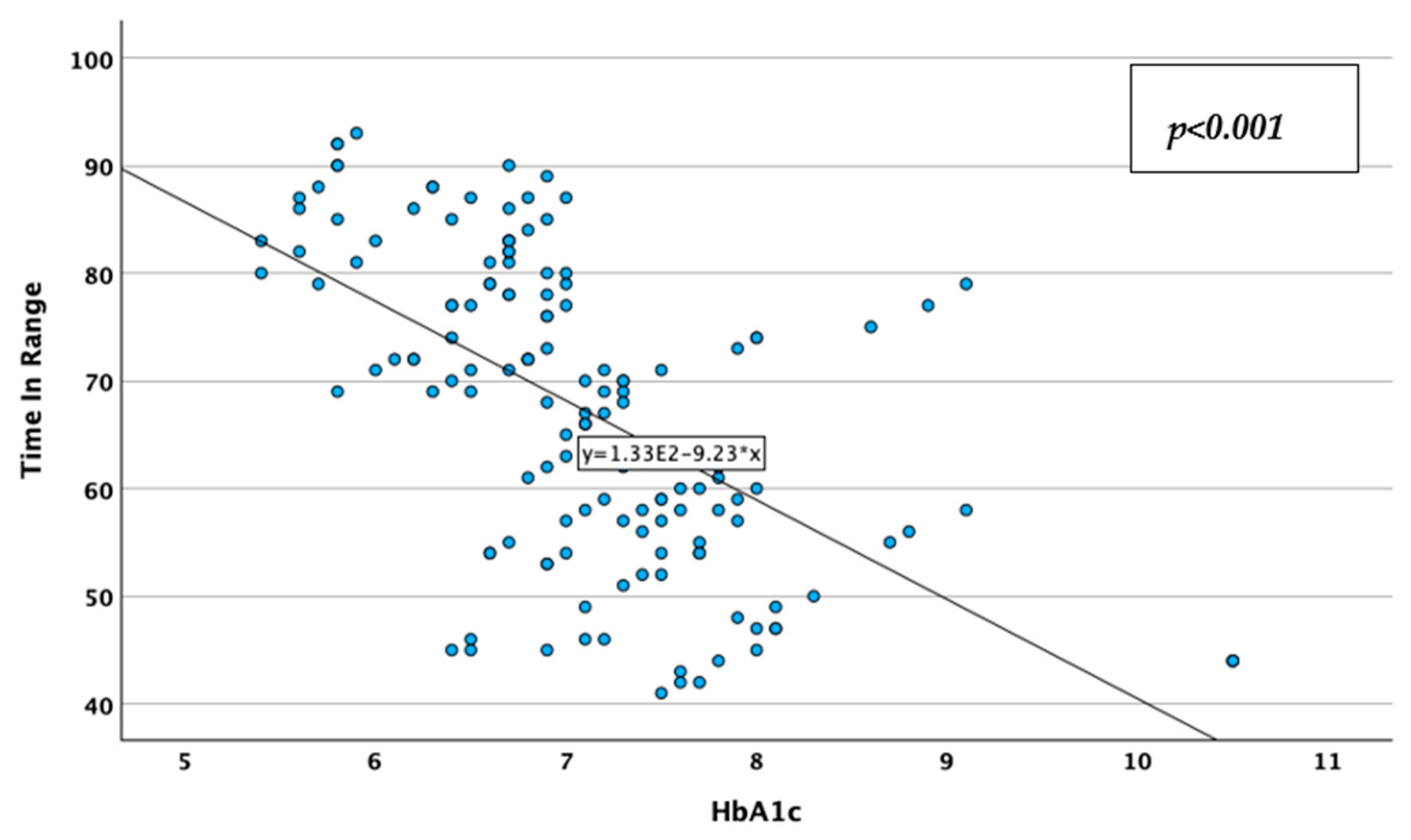
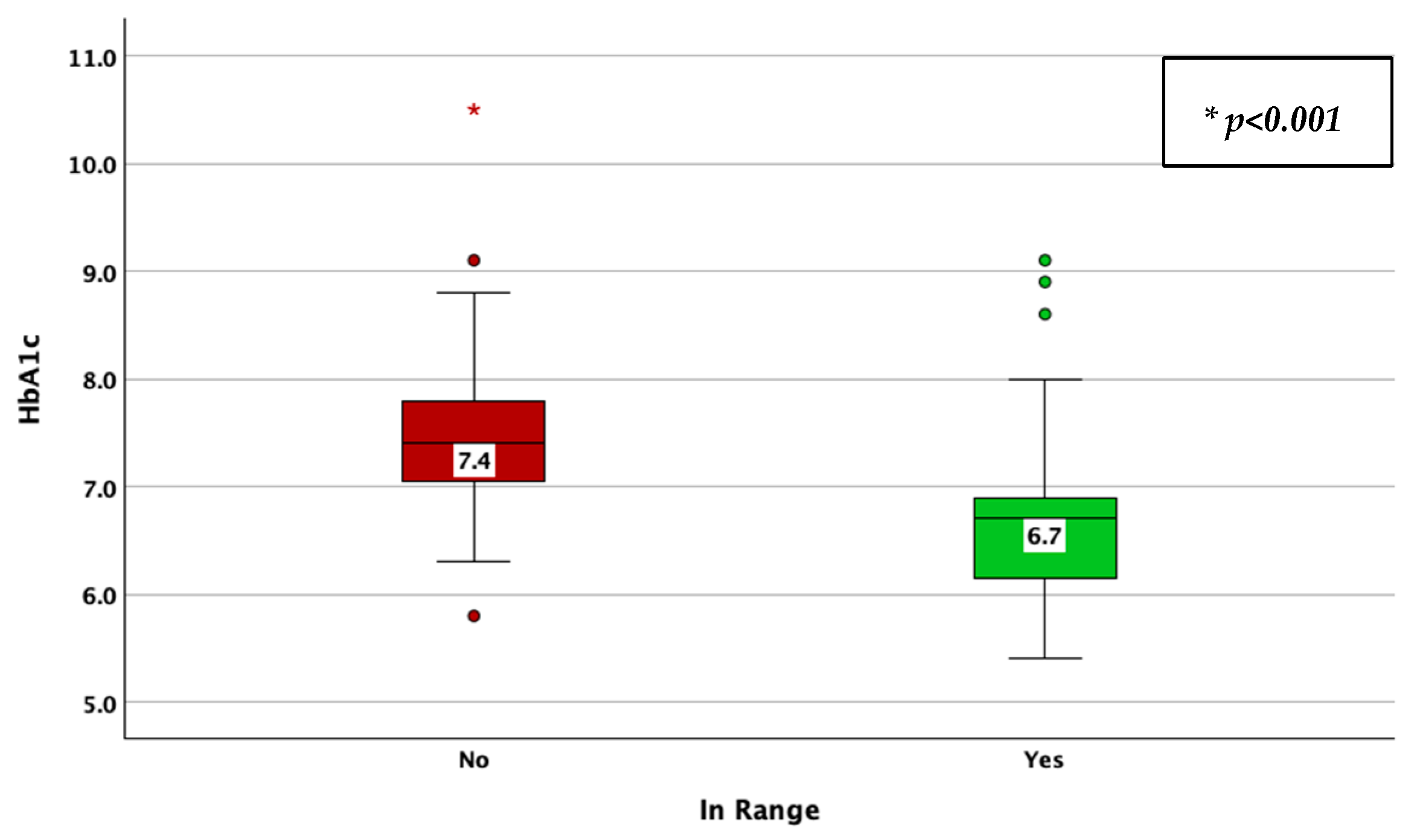
| Correlations | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient of Variation | Time in Range | ||
| Time in Range | Spearman’s r | −0.513 ** | -- |
| p-value | <0.001 | . | |
| n | 147 | 147 | |
| HbA1c | Spearman’s r | 0.349 ** | −0.637 ** |
| p-value | <0.001 | 0.000 | |
| n | 147 | 147 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lazar, S.; Reurean-Pintilei, D.-V.; Ionita, I.; Avram, V.-F.; Herascu, A.; Timar, B. Glycemic Variability and Its Association with Traditional Glycemic Control Biomarkers in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional, Multicenter Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2434. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072434
Lazar S, Reurean-Pintilei D-V, Ionita I, Avram V-F, Herascu A, Timar B. Glycemic Variability and Its Association with Traditional Glycemic Control Biomarkers in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional, Multicenter Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(7):2434. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072434
Chicago/Turabian StyleLazar, Sandra, Delia-Viola Reurean-Pintilei, Ioana Ionita, Vlad-Florian Avram, Andreea Herascu, and Bogdan Timar. 2025. "Glycemic Variability and Its Association with Traditional Glycemic Control Biomarkers in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional, Multicenter Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 7: 2434. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072434
APA StyleLazar, S., Reurean-Pintilei, D.-V., Ionita, I., Avram, V.-F., Herascu, A., & Timar, B. (2025). Glycemic Variability and Its Association with Traditional Glycemic Control Biomarkers in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional, Multicenter Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(7), 2434. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14072434






