Unpacking KDIGO Guidelines: Prioritizing and Applying Exposures and Susceptibilities for AKI in Clinical Practice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. AKI Definition
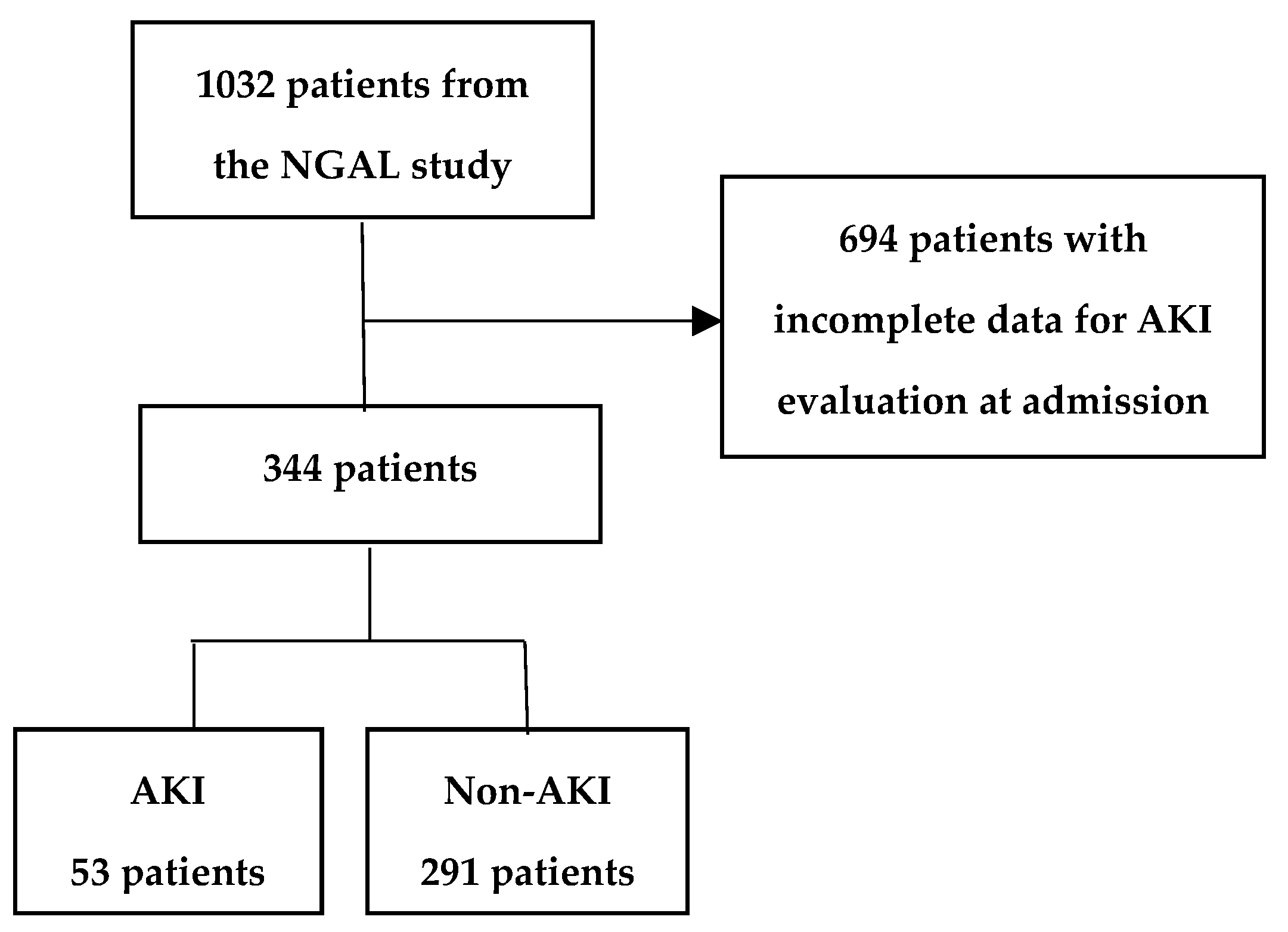
2.4. Participants and Evaluating AKI Risk Assessment
2.5. Statistical Method
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Medical Encounter, Diagnoses, and Conditions in AKI and Non-AKI Patients
3.2. Exposure and Susceptibility Distribution
3.3. Exposures and Susceptibilities for AKI Assessment
3.4. pNGAL and CRP for AKI Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKI | acute kidney injury |
| AUC | area under the curve |
| b-pCr | baseline plasma creatinine |
| CI- AKI | Contrast-induced AKI |
| CKD | chronic kidney disease |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| dm | diabetes mellitus |
| ED | emergency department |
| eGFR | estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| GFR | glomerular filtration rate |
| ICU | intensive care unit |
| IQR | interquartile range |
| KDIGO | Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes |
| mb-pCr | mean baseline plasma creatinine |
| ND | nephrotoxic drug |
| NGAL | neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin |
| NPV | negative predictive value |
| pCr | plasma creatinine |
| pNGAL | plasma NGAL |
| PPV | positive predictive value |
| ROC | receiver operating characteristic |
| sCr | serum creatinine |
| UNS | unspecified |
References
- Kellum, J.A.; Lameire, N.; Aspelin, P.; Barsoum, R.S.; Burdmann, E.A.; Goldstein, S.L.; Herzog, C.A.; Joannidis, M.; Kribben, A.; Levey, A.S.; et al. Kidney disease: Improving global outcomes (KDIGO) acute kidney injury work group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2012, 2, 1–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.L.; Cerdá, J.; Burdmann, E.A.; Tonelli, M.; García-García, G.; Jha, V.; Susantitaphong, P.; Rocco, M.; Vanholder, R.; Sever, M.S.; et al. International Society of Nephrology’s 0by25 initiative for acute kidney injury (zero preventable deaths by 2025): A human rights case for nephrology. Lancet 2015, 385, 2616–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellomo, R.; Ronco, C.; Kellum, J.A.; Mehta, R.L.; Palevsky, P.; Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative Workgroup. Acute renal failure—Definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: The Second International Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) Group. Crit. Care 2004, 8, R204–R212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.; Kellum, J.A.; Mehta, R.L. Acute kidney injury: Toward an integrated understanding through development of a research agenda. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 3, 862–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, R. Can we prevent acute kidney injury? Crit. Care Med. 2008, 36, S166–S171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, N.; Eldridge, J.; Prowle, J.R.; Forni, L.G. Postoperative Acute Kidney Injury. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 17, 1535–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartin-Ceba, R.; Kashiouris, M.; Plataki, M.; Kor, D.J.; Gajic, O.; Casey, E.T. Risk factors for development of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Crit. Care Res. Pract. 2012, 2012, 691013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, L.; Andrew, L. CME Renal medicine. Clin. Med. 2008, 9, 273. [Google Scholar]
- Candela-Toha, A.; Eli, E.; Abraira, V.; Parise, D.; Centella, T.; Lian, F. Predicting acute renal failure after cardiac surgery: External validation of two new clinical scores. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 3, 1260–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, A.O.; Foxwell, D.A.; Pradhan, S.; Zouwail, S.; Rainer, T.H. Derivation of a prediction model for emergency department acute kidney injury. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 40, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, A.Y.; Jun, M.; Pu, L.; Weisbord, S.D.; Bellomo, R.; Hong, D.; Gallagher, M. Characterization of Risk Prediction Models for Acute Kidney Injury A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2313359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.R.; Parikh, C.R. Biomarkers of Acute and Chronic Kidney Disease. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2019, 81, 309–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, J.; Lan, H.-Y.; Tang, Y. Role of C-Reactive Protein in Kidney Diseases. Kidney Dis. 2023, 9, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes-Ibrahim, M.S.; Younes-Ibrahim, M. Biomarkers and kidney diseases: A brief narrative review. J. Lab. Precis. Med. 2022, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetterstrand, V.J.R.; Schultz, M.; Kallemose, T.; Torre, A.; Larsen, J.J.; Friis-Hansen, L.; Brandi, L. Plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a single test rule out biomarker for acute kidney injury: A cross-sectional study in patients admitted to the emergency department. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0316897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicky, W.; Thomas, K.; Jesper, L.J.; Lennart, F.-H.; Lisbet, B. A longitudinal prospective study investigating serial measurements of plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalins (NGAL) for the prediction of acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease in patients admitted to the emergency department. BMJ Nephrol. 2025; to be submitted. [Google Scholar]
- North Zealand Hospital. 2024. Available online: http://www.nordsjaellandshospital.dk (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- Larsen, J.J.; Lauridsen, H.; Gundersen, L.W.; Riecke, B.F.; Schmidt, T.A. Abated crowding by fast-tracking the Throughput component of the ED for patients in no need of hospitalization with competency managed personnel. BMC Emerg. Med. 2024, 24, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish Society of Nephrology. Available online: http://www.nephrology.dk (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Zarbock, A.; Koyner, J.L.; Gomez, H.; Pickkers, P.; Forni, L. Sepsis-associated acute kidney injury—Treatment standard. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2024, 39, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kounatidis, D.; Vallianou, N.G.; Psallida, S.; Panagopoulos, F.; Margellou, E.; Tsilingiris, D.; Karampela, I.; Stratigou, T.; Dalamaga, M. Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury: Where Are We Now? Medicina 2024, 60, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Mo, Z.; Chu, H.; Hu, P.; Fan, W.; Wu, Y.; Song, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Liu, S.; et al. A model for predicting postoperative persistent acute kidney injury (AKI) in AKI after cardiac surgery patients with normal baseline renal function. Clin. Cardiol. 2023, 47, e24168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J. Contrast-induced acute kidney injury: A review of definition, pathogenesis, risk factors, prevention and treatment. BMC Nephrol. 2024, 25, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandiramani, R.; Cao, D.; Nicolas, J.; Mehran, R. Contrast-induced acute kidney injury. Cardiovasc. Interv. Ther. 2020, 35, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang-Panesso, M. Acute kidney injury and aging. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2021, 36, 2997–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, L.M. Sex and Gender Differences in AKI. Kidney360 2023, 5, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Exposures and Susceptibilities ^ and pNGAL and CRP | AKI (n = 53) | Non-AKI (n = 291) | Total (n = 344) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sepsis | 11 (20.8%) | 12 (4.1%) | 23 (6.7%) |
| Critical illness/ICU | 4 (7.5%) | 8 (2.8%) | 12 (3.5%) |
| Circulatory shock | 4 (7.5%) | 3 (1%) | 7 (2%) |
| Burns | 1 (1.9%) | 1 (0.3%) | 2 (0.6%) |
| Nephrotoxic drug | 38 (71.7%) | 127 (43.6%) | 165 (48%) |
| Radioactive contrast | 18 (34.6%) | 64 (22.5%) | 82 (24.3%) |
| Kidney transplant | 1 (1.9%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (0.3%) |
| Diabetics mellitus | 14 (26.9%) | 49 (17%) | 63 (18.5%) |
| Cancer | 10 (18.9%) | 34 (11.8%) | 44 (12.9%) |
| Anemia | 12 (22.6%) | 17 (5.9%) | 29 (8.5%) |
| Dehydration | 15 (28.3%) | 14 (4.8%) | 29 (8.5%) |
| Surgery | 10 (18.9%) | 13 (4.5%) | 23 (6.7%) |
| Chronic heart disease | 10 (18.9%) | 40 (13.7%) | 50 (14.5%) |
| Chronic lung disease | 16 (30.2%) | 56 (19.2%) | 72 (20.9%) |
| Chronic liver disease | 5 (9.4%) | 5 (1.7%) | 10 (2.9%) |
| Advanced age | 37 (69.8%) | 135 (46.4%) | 172 (50%) |
| CKD | 17 (32.1%) | 29 (10%) | 46 (13.5%) |
| Black race | 0 (0%) | 8 (2.9%) | 8 (2.4%) |
| Sex female | 26 (49.1%) | 166 (57%) | 192 (55.8%) |
| pNGAL (median (IQR)) | 173.5 ng/mL (115.5:369.5) | 59 ng/mL (50:83.5) | 65 ng/mL (50:103) |
| CRP (median (IQR)) | 49 mg/L (12:108) | 4 mg/L (3:13) | 5.5 mg/L (3:23.75) |
| Creatinine (median (IQR)) | 127 µmol/L (92:212) | 71 µmol/L (61:83.5) | 73 µmol/L (63:90.5) |
| Exposures and Susceptibilities and pNGAL and CRP | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | SENSPPV | Number of Patients ^ | Number of Patients with AKI # |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pNGAL | 0.78 | 0.87 | 0.52 | 0.96 | 1.30 | 321 | 50 |
| Black race * | 1.00 | 0.03 | 0.16 | 1.00 | 1.16 | 331 | 52 |
| CRP | 0.74 | 0.77 | 0.37 | 0.94 | 1.10 | 342 | 53 |
| Kidney transplant | 0.02 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.85 | 1.02 | 344 | 53 |
| Nephrotoxic drug | 0.72 | 0.56 | 0.23 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 344 | 53 |
| Advanced age | 0.70 | 0.54 | 0.22 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 344 | 53 |
| Dehydration | 0.28 | 0.95 | 0.52 | 0.88 | 0.80 | 342 | 53 |
| CKD | 0.32 | 0.90 | 0.37 | 0.88 | 0.69 | 342 | 53 |
| Sex male | 0.51 | 0.57 | 0.18 | 0.86 | 0.69 | 344 | 53 |
| Sepsis | 0.21 | 0.96 | 0.48 | 0.87 | 0.69 | 343 | 53 |
| Circulatory shock | 0.08 | 0.99 | 0.57 | 0.85 | 0.65 | 343 | 53 |
| Anemia | 0.23 | 0.94 | 0.41 | 0.87 | 0.64 | 343 | 53 |
| Surgery | 0.19 | 0.96 | 0.43 | 0.87 | 0.62 | 342 | 53 |
| Chronic liver disease | 0.09 | 0.98 | 0.50 | 0.86 | 0.59 | 344 | 53 |
| Radioactive contrast | 0.35 | 0.78 | 0.22 | 0.87 | 0.57 | 337 | 52 |
| Chronic lung disease | 0.30 | 0.81 | 0.22 | 0.86 | 0.52 | 344 | 53 |
| Burns | 0.02 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 0.85 | 0.52 | 343 | 53 |
| Diabetics mellitus | 0.27 | 0.83 | 0.22 | 0.86 | 0.49 | 341 | 52 |
| Cancer | 0.19 | 0.88 | 0.23 | 0.86 | 0.42 | 341 | 53 |
| Critical illness/ICU | 0.08 | 0.97 | 0.33 | 0.85 | 0.41 | 343 | 53 |
| Chronic heart disease | 0.19 | 0.86 | 0.20 | 0.85 | 0.39 | 344 | 53 |
| The Most Effective Predictive Analysis | Exposures and Susceptibilities |
|---|---|
| High-PPV cluster | kidney transplant, dehydration, surgery |
| High-sensitivity cluster | sepsis, critical illness/ICU, circulatory shock, nephrotoxic drugs, anemia, sex |
| AKI risk assessment | radioactive contrast, advanced age, CKD |
| Included Exposures and Susceptibilities with pNGAL or CRP | Number of Variables Included | Sens. | Spec. | PPV | NPV | Sens-PPV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pNGAL | 1 | 0.780 | 0.870 | 0.520 | 0.960 | 1.300 |
| seps shock burn ND kdntrans dm canc anem surg chd lung liver black sex NGAL_first | 15 | 0.792 | 0.930 | 0.679 | 0.960 | 1.470 |
| seps shock burn ND kdntrans dm canc anem surg chd ckd black NGAL_first | 13 | 0.854 | 0.898 | 0.612 | 0.970 | 1.466 |
| icu shock burn ND kdntrans dm canc anem chd ckd black NGAL_first | 12 | 0.833 | 0.907 | 0.625 | 0.967 | 1.458 |
| seps icu shock burn ND kdntrans dm canc anem chd ckd black NGAL_first | 13 | 0.833 | 0.907 | 0.625 | 0.967 | 1.458 |
| seps shock burn ND kdntrans dm anem surg chd lung liver black sex NGAL_first | 14 | 0.792 | 0.927 | 0.667 | 0.960 | 1.458 |
| shock burn ND kdntrans dm canc anem surg chd lung liver black sex NGAL_first | 14 | 0.792 | 0.926 | 0.667 | 0.960 | 1.458 |
| seps shock burn ND kdntrans dm anem surg chd lung liver ckd black sex NGAL_first | 15 | 0.792 | 0.926 | 0.667 | 0.960 | 1.458 |
| seps shock burn ND kdntrans dm surg chd lung liver ckd black sex NGAL_first | 14 | 0.771 | 0.934 | 0.685 | 0.956 | 1.456 |
| seps shock burn ND kdntrans dm canc surg chd lung liver ckd black sex NGAL_first | 15 | 0.771 | 0.934 | 0.685 | 0.956 | 1.456 |
| seps shock burn ND kdntrans dm canc anem surg chd lung liver ckd black sex NGAL_first | 16 | 0.771 | 0.934 | 0.685 | 0.956 | 1.456 |
| CRP | 1 | 0.740 | 0.770 | 0.370 | 0.940 | 1.100 |
| seps icu shock ND canc anem liver age_65 black NGAL_first CRP_first | 11 | 0.816 | 0.907 | 0.625 | 0.963 | 1.441 |
| seps icu shock ND canc anem lung liver age_65 black NGAL_first CRP_first | 12 | 0.816 | 0.907 | 0.625 | 0.963 | 1.441 |
| seps icu shock ND canc anem liver age_65 ckd black NGAL_first CRP_first | 12 | 0.816 | 0.907 | 0.625 | 0.963 | 1.441 |
| seps icu shock ND canc anem lung liver age_65 ckd black NGAL_first CRP_first | 13 | 0.816 | 0.907 | 0.625 | 0.963 | 1.441 |
| seps icu shock ND canc anem lung liver age_65 black sex NGAL_first CRP_first | 13 | 0.816 | 0.907 | 0.625 | 0.963 | 1.441 |
| seps shock ND canc anem chd lung liver age_65 black NGAL_first CRP_first | 12 | 0.796 | 0.915 | 0.639 | 0.959 | 1.435 |
| seps shock ND anem chd lung liver age_65 black sex NGAL_first CRP_first | 12 | 0.796 | 0.915 | 0.639 | 0.960 | 1.435 |
| seps shock ND canc anem chd lung liver age_65 black sex NGAL_first CRP_first | 13 | 0.796 | 0.915 | 0.639 | 0.959 | 1.435 |
| seps icu shock burn ND canc anem liver age_65 black NGAL_first CRP_first | 12 | 0.816 | 0.903 | 0.615 | 0.963 | 1.432 |
| seps icu shock ND canc anem liver age_65 black sex NGAL_first CRP_first | 12 | 0.816 | 0.903 | 0.615 | 0.963 | 1.432 |
| Variables | Sens. | Spec. | PPV | NPV | SENSPPV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| seps shock burn ND kdntrans dm canc anem surg chd lung liver black sex NGAL_first | 0.792 | 0.930 | 0.679 | 0.960 | 1.470 |
| pNGAL | 0.780 | 0.870 | 0.520 | 0.960 | 1.300 |
| burn contrast kdntrans canc dehy surg chd lung liver age_65 ckd black | 0.255 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.878 | 1.255 |
| CRP | 0.740 | 0.770 | 0.370 | 0.940 | 1.100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wetterstrand, V.J.R.; Kallemose, T.; Larsen, J.J.; Friis-Hansen, L.J.; Brandi, L. Unpacking KDIGO Guidelines: Prioritizing and Applying Exposures and Susceptibilities for AKI in Clinical Practice. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2572. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082572
Wetterstrand VJR, Kallemose T, Larsen JJ, Friis-Hansen LJ, Brandi L. Unpacking KDIGO Guidelines: Prioritizing and Applying Exposures and Susceptibilities for AKI in Clinical Practice. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(8):2572. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082572
Chicago/Turabian StyleWetterstrand, Vicky Jenny Rebecka, Thomas Kallemose, Jesper Juul Larsen, Lennart Jan Friis-Hansen, and Lisbet Brandi. 2025. "Unpacking KDIGO Guidelines: Prioritizing and Applying Exposures and Susceptibilities for AKI in Clinical Practice" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 8: 2572. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082572
APA StyleWetterstrand, V. J. R., Kallemose, T., Larsen, J. J., Friis-Hansen, L. J., & Brandi, L. (2025). Unpacking KDIGO Guidelines: Prioritizing and Applying Exposures and Susceptibilities for AKI in Clinical Practice. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(8), 2572. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082572






