The Furosemide Stress Test: A Dynamic Tool for Predicting Acute Kidney Injury Progression in Critical Care Medicine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Historical Background
3. Physiological Mechanisms
4. Clinical Considerations: Protocol, Timing, and Dosing
4.1. Protocol
4.2. Timing
4.3. Dosing
5. Possible Applications
6. Predictive Performance
7. Limitations and Practical Challenges
8. Future Research
- Integration with Artificial Intelligence
- Personalized Medicine Applications
- Novel Monitoring Technologies
- Protocol Standardization Efforts
- Biomarker Integration
- Pediatric Applications
- Point-of-Care Applications
- Recovery Prediction
- Protocol Refinements
- Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
- Quality Improvement Integration
- Multi-organ Assessment
- Studies Examining Special Populations
- Technical Validation Studies
- Integration with Modern Technologies
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FST | Furosemide Stress Test |
| AKI | Acute Kidney injury |
| NGAL | Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin |
| KIM-1 | Kidney Injury Molecule-1 |
| IL-18 | Interleukin-18 |
| NKCC2 | Na+/K+/2Cl− cotransporter |
| RRT | Renal replacement therapy |
References
- Hoste, E.A.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Bellomo, R.; Cely, C.M.; Colman, R.; Cruz, D.N.; Edipidis, K.; Forni, L.G.; Gomersall, C.D.; Govil, D.; et al. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: The multinational AKI-EPI study. Intensive Care Med. 2015, 41, 1411–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellum, J.A.; Romagnani, P.; Ashuntantang, G.; Ronco, C.; Zarbock, A.; Anderset, H.J. Acute kidney injury. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prowle, J.R.; Bellomo, R. Sepsis-associated acute kidney injury: Macrohemodynamic and microhemodynamic alterations in the renal circulation. Semin. Nephrol. 2015, 35, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KDIGO Group. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2012, 2, 1–138. [Google Scholar]
- Ostermann, M.; Joannidis, M. Acute kidney injury 2016: Diagnosis and diagnostic workup. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siew, E.D.; Matheny, M.E. Choice of Reference Serum Creatinine in Defining Acute Kidney Injury. Nephron 2015, 131, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.J.; Brandtner, A.K.; Lehner, G.F.; Ulmer, H.; M Bagshaw, S.M.; Wiedermann, C.J.; Joannidis, M. Biomarkers for prediction of renal replacement therapy in acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2018, 44, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashani, K.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Ronco, C. Biomarkers of acute kidney injury: The pathway from discovery to clinical adoption. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2017, 55, 1074–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, C.R.; Mansour, S.G. Perspective on Clinical Application of Biomarkers in AKI. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 1677–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, L.S.; Davison, D.L.; Brasha-Mitchell, E.; Koyner, J.L.; Arthur, J.M.; Shaw, A.D.; Tumlin, J.A.; Trevino, S.A.; Kimmel, P.L.; Seneff, M.G. Development and standardization of a furosemide stress test to predict the severity of acute kidney injury. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyner, J.L.; Davison, D.L.; Brasha-Mitchell, E.; Chalikonda, D.M.; Arthur, J.M.; Shaw, A.D.; Tumlin, J.A.; Trevino, S.A.; Bennett, M.R.; Kimmel, P.L.; et al. Furosemide Stress Test and Biomarkers for the Prediction of AKI Severity. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 2023–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rewa, O.G.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Wang, X.; Wald, R.; Smith, O.; Shapiro, J.; McMahon, B.; Liu, K.D.; Trevino, S.A.; Chawla, L.S.; et al. The furosemide stress test for prediction of worsening acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: A multicenter, prospective, observational study. J. Crit. Care 2019, 52, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuura, R.; Srisawat, N.; Claure-Del Granado, R. Use of the Furosemide Stress Test in the Early Management of Critical Care Patients with Acute Kidney Injury. Nephron 2018, 138, 98–106. [Google Scholar]
- Bellomo, R.; Kellum, J.A.; Ronco, C. Acute kidney injury. Lancet 2012, 380, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronco, C.; Bellomo, R.; Kellum, J.A. Acute kidney injury. Lancet 2019, 394, 1949–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobyan, D.C.; Levi, J.; Jacobs, C.; Kosek, J.; Weiner, M.W. Mechanism of cis-platinum nephrotoxicity, I.I. Morphologic observations. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1980, 213, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.L.; Pascual, M.T.; Soroko, S.; Savage, B.R.; Himmelfarb, J.; Ikizler, T.A.; Paganini, E.P.; Chertow, G.M.; Program to Improve Care in Acute Renal Disease. Spectrum of acute renal failure in the intensive care unit: The PICARD experience. Kidney Int. 2004, 66, 1613–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, B.A.; Koyner, J.L. Risk stratification for acute kidney injury: Are biomarkers enough? Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2016, 23, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumlertgul, N.; Peerapornratana, S.; Trakarnvanich, T.; Pongsittisak, W.; Surasit, K.; Chuasuwan, A.; Tankee, P.; Tiranathanagul, K.; Praditpornsilpa, K.; Tungsanga, K.; et al. Early versus standard initiation of renal replacement therapy in furosemide stress test non-responsive acute kidney injury patients (the FST trial). Crit. Care 2018, 22, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Chang, C.H.; Huang, Y.T.; Kuo, G. Furosemide stress test as a predictive marker of acute kidney injury progression or renal replacement therapy: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisawat, N.; Murugan, R.; Lee, M.; Kong, L.; Carter, M.; Angus, D.C.; Kellum, J.A.; Genetic and Inflammatory Markers of Sepsis (GenIMS) Study Investigators. Plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin predicted recovery from acute kidney injury following community-acquired pneumonia. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, L.; Ye, H. Impact of the furosemide stress test on prediction of acute kidney injury progression and clinical outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, R.K.; Kaddourah, A.; Goldstein, S.L.; AWARE Study Investigators. Assessment of a renal angina index for prediction of severe acute kidney injury in critically ill children: A multicentre, multinational, prospective observational study. Lancet Child. Adolesc. Health 2018, 2, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostermann, M.; Zarbock, A.; Goldstein, S.; Kashani, K.; Macedo, E.; Murugan, R.; Bell, M.; Forni, L.; Guzzi, L.; Joannidis, M.; et al. Recommendations on Acute Kidney Injury Biomarkers from the Acute Disease Quality Initiative Consensus Conference: A Consensus Statement. JAMA 2020, 324, 2451–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane-Gill, S.L.; Ostermann, M.; Shi, J. Pharmacologic Management of Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Disease in Critical Care. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 1677–1689. [Google Scholar]
- Ronco, C.; Bellomo, R.; Kellum, J.A. Understanding renal functional reserve. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 917–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, C.S. New insights into diuretic use in patients with chronic renal disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasannejad, H.; Takeda, M.; Taki, K.; Shin, H.J.; Babu, E.; Jutabha, P.; Khamdang, S.; Aleboyeh, M.; Onozato, M.L.; Tojo, A.; et al. Interactions of human organic anion transporters with diuretics. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 308, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.S.; Brater, D.C. Loop diuretics: From the Na-K-2Cl transporter to clinical use. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2003, 284, F11–F21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, D.H.; Felker, G.M. Diuretic Treatment in Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1964–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.M.; Power, B.M. Benefits and risks of furosemide in acute kidney injury. Anaesthesia 2010, 65, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brar, S.; Ye, F.; James, M.T. Association of Intra-operative Hypotension with Acute Kidney Injury after Elective Non-Cardiac Surgery. Anesthesiology 2021, 134, 227–238. [Google Scholar]
- Mar, D.J.; Gharaie, S.; Pai, A.B. Molecular Mechanisms of Diuretic Resistance in Cardiorenal Syndrome. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 704–716. [Google Scholar]
- Cowland, J.B.; Borregaard, N. Molecular characterization and pattern of tissue expression of the gene for neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin from humans. Genomics 1997, 45, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagshaw, S.M.; Gibney, R.T.N.; McAlister, F.A.; Bellomo, R. The SPARK Study: A phase II randomized blinded controlled trial of the effect of furosemide in critically ill patients with early acute kidney injury. Trials 2010, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testani, J.M.; Coca, S.G.; McCauley, B.D.; Shannon, R.P.; Kimmel, S.E. Impact of changes in blood pressure during the treatment of acute decompensated heart failure on renal and clinical outcomes. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2011, 13, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarbock, A.; Kellum, J.A.; Schmidt, C.; Van Aken, H.; Wempe, C.; Pavenstädt, H.; Boanta, A.; Gerß, J.; Meersch, M. Effect of Early vs Delayed Initiation of Renal Replacement Therapy on Mortality in Critically Ill Patients with Acute Kidney Injury: The ELAIN Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2016, 315, 2190–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prowle, J.R.; Kirwan, C.J.; Bellomo, R. Fluid management for the prevention and attenuation of acute kidney injury. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2014, 10, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coca, S.G.; Garg, A.X.; Thiessen-Philbrook, H.; Koyner, J.L.; Patel, U.D.; Krumholz, H.M.; Shlipak, M.G.; Parikh, C.R.; TRIBE-AKI Consortium. Urinary biomarkers of AKI and mortality 3 years after cardiac surgery. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, K.; Rabb, H. Impact of acute kidney injury on distant organ function: Recent findings and potential therapeutic targets. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyner, J.L.; Coca, S.G.; Thiessen-Philbrook, H.; Patel, U.D.; Shlipak, M.G.; Garg, A.X.; Parikh, C.R.; Translational Research Investigating Biomarker Endpoints for Acute Kidney Injury (TRIBE-AKI) Consortium; Translational Research Investigating Biomarker Endpoints for Acute Kidney Injury TRIBE-AKI Consortium. Urine biomarkers perioperative acute kidney injury: The impact of preoperative estimated, G.F.R. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 66, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, D.J.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.H. Standardization of furosemide stress test and its clinical implications in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 39, 425–435. [Google Scholar]
- Kane-Gill, S.L.; Bihorac, A.; Kellum, J.A. Clinical utility of furosemide stress test in the prediction of acute kidney injury progression. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 47, e449–e450. [Google Scholar]
- Ostermann, M.; Joannidis, M.; Pani, A. Patient care and clinical outcomes for patients with COVID-19 infection admitted to African high-care or intensive care units (ACCCOS): A multicentre, prospective, observational cohort study. Lancet 2021, 397, 1885–1894. [Google Scholar]
- Ostermann, M.; Liu, K.; Kashani, K. Fluid Management in Acute Kidney Injury. Chest 2019, 156, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shen, Y. Association between body mass index and acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery: A dose-response meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228974. [Google Scholar]
- Kellum, J.A.; Lameire, N.; KDIGO AKI Guideline Work Group. Diagnosis, evaluation, and management of acute kidney injury: A KDIGO summary (Part 1). Crit. Care 2013, 17, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forni, L.G.; Darmon, M.; Ostermann, M.; Oudemans-van Straaten, H.M.; Pettilä, V.; Prowle, J.R.; Schetz, M.; Joannidis, M. Renal recovery after acute kidney injury. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagshaw, S.M.; Wald, R.; Adhikari, N.K.J. Timing of initiation of renal-replacement therapy in acute kidney injury. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 240–251. [Google Scholar]
- Zarbock, A.; Kullmar, M.; Kindgen-Milles, D.; Wempe, C.; Gerss, J.; Brandenburger, T.; Dimski, T.; Tyczynski, B.; Michael Jahn, M.; Mülling, N.; et al. Effect of Regional Citrate Anticoagulation vs Systemic Heparin Anticoagulation During Continuous Kidney Replacement Therapy on Dialysis Filter Life Span and Mortality Among Critically Ill Patients with Acute Kidney Injury: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 324, 1629–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göcze, I.; Jauch, D.; Götz, M.; Kennedy, P.; Jung, B.; Zeman, F.; Gnewuch, C.; Graf, B.M.; Gnann, W.; Banas, B.; et al. Biomarker-guided intervention to prevent acute kidney injury after major surgery: The prospective randomized BigpAK study. Ann. Surg. 2018, 267, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickkers, P.; Ostermann, M.; Joannidis, M.; Zarbock, A.; Hoste, E.; Bellomo, R.; Prowle, J.; Darmon, M.; Joseph V Bonventre, J.V.; Forni, L.; et al. The intensive care medicine agenda on acute kidney injury. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 1198–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, L.S.; Bellomo, R.; Bihorac, A.; Goldstein, S.L.; Siew, E.D.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Bittleman, D.; Cruz, D.; Endre, Z.; Fitzgerald, R.L.; et al. Acute kidney disease and renal recovery: Consensus report of the Acute Disease Quality Initiative (ADQI) 16 Workgroup. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meersch, M.; Schmidt, C.; Hoffmeier, A.; Van Aken, H.; Wempe, C.; Gerss, J.; Zarbock, A. Prevention of cardiac surgery-associated AKI by implementing the KDIGO guidelines in high risk patients identified by biomarkers: The PrevAKI randomized controlled trial. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 1551–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarbock, A.; Kellum, J.A.; Van Aken, H.; Schmidt, C.; Küllmar, M.; Rosenberger, P.; Martens, S.; Görlich, D.; Meersch, M. Long-term Effects of Remote Ischemic Preconditioning on Kidney Function in High-risk Cardiac Surgery Patients: Follow-up Results from the RenalRIP Trial. Anesthesiology 2017, 126, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, H.; Ince, C.; De Backer, D.; Pickkers, P.; Payen, D.; Hotchkiss, J.; Kellum, J.A. A unified theory of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury: Inflammation, microcirculatory dysfunction, bioenergetics, and the tubular cell adaptation to injury. Shock 2014, 41, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honore, P.M.; Spapen, H.D.; Marik, P. Dosing loop diuretics in acute kidney injury: A critical review. Ann. Intensive Care 2019, 9, 52. [Google Scholar]
- Mullens, W.; Damman, K.; Harjola, V.P.; Mebazaa, A.; Brunner-la Rocca, H.P.; Martens, P.; Testani, J.M.; Tang, W.H.; Orso, F.; Rossignol, P.; et al. The use of diuretics in heart failure with congestion—A position statement from the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2019, 21, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangaswami, J.; Bhalla, V.; Blair, J.E.A.; Chang, T.I.; Costa, S.; Lentine, K.L.; Lerma, E.V.; Mezue, K.; Molitch, M.; Mullens, W.; et al. Cardiorenal Syndrome: Classification, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Strategies: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 139, e840–e878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josephson, M.A. Monitoring and Managing Graft Health in the Kidney Transplant Recipient. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 1774–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Acker, K.; Devuyst, O.; Venkatachalam, M.A. Urinary biomarkers in the early diagnosis of acute kidney injury: Discoveries and classification. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3914. [Google Scholar]
- Prowle, J.R.; Liu, Y.L.; Licari, E.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Egi, M.; Haase, M.; Haase-Fielitz, A.; Kellum, J.A.; Cruz, D.; Ronco, C.; et al. Oliguria as predictive biomarker of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients. Crit. Care 2011, 15, R172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane-Gill, S.L.; Meersch, M.; Bell, M. Biomarker-guided management of acute kidney injury. CurrOpin Crit. Care 2020, 26, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husain-Syed, F.; Ferrari, F.; Sharma, A.; Danesi, T.H.; Bezerra, P.; Lopez-Giacoman, S.; Samoni, S.; de Cal, M.; Corradi, V.; Virzì, G.M.; et al. Preoperative Renal Functional Reserve Predicts Risk of Acute Kidney Injury After Cardiac Operation. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2018, 105, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellum, J.A.; Sileanu, F.E.; Bihorac, A.; Hoste, E.A.J.; Chawla, L.S. Recovery after Acute Kidney Injury. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoste, E.A.; Kellum, J.A.; Selby, N.M.; Zarbock, A.; Palevsky, P.M.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Goldstein, S.L.; Cerdá, J.; Chawla, L.S. Global epidemiology and outcomes of acute kidney injury. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 607–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silver, S.A.; Chertow, G.M. The Economic Consequences of Acute Kidney Injury. Nephron 2017, 137, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, M.; Bedford, M.; Matthews, B.; O’Donoghue, D. The economic impact of acute kidney injury in England. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29, 1362–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatraju, P.K.; Zelnick, L.R.; Katz, R. A Comparison of Novel and Clinical Measures of Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Patients. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 47, e607–e614. [Google Scholar]
- Parikh, C.R.; Moledina, D.G.; Coca, S.G.; Heather R Thiessen-Philbrook, H.R.; Garg, A.X. Application of new acute kidney injury biomarkers in human randomized controlled trials. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashani, K.; Al-Khafaji, A.; Ardiles, T.; Artigas, A.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Bell, M.; Bihorac, A.; Birkhahn, R.; Cely, C.M.; Chawla, L.S.; et al. Discovery and validation of cell cycle arrest biomarkers in human acute kidney injury. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meersch, M.; Schmidt, C.; Zarbock, A. Patient with chronic renal failure undergoing cardiac surgery. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2017, 31, 205–215. [Google Scholar]
- Honore, P.M.; Jacobs, R.; Joannes-Boyau, O.; Verfaillie, L.; De Regt, J.; Van Gorp, V.; De Waele, E.; Boer, W.; Collin, V.; Spapen, H.D. Biomarkers for early diagnosis of AKI in the ICU: Ready for prime time use at the bedside? Ann. Intensive Care 2012, 2, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Ni, H.; Deng, H. Predictive value of ionized calcium in critically ill patients: An analysis of a large clinical database MIMIC II. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoste, E.A.; McCullough, P.A.; Kashani, K.; Chawla, L.S.; Joannidis, M.; Shaw, A.D.; Feldkamp, T.; Uettwiller-Geiger, D.L.; McCarthy, P.; Shi, J.; et al. Derivation and validation of cutoffs for clinical use of cell cycle arrest biomarkers. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29, 2054–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyner, J.L.; Parikh, C.R. Clinical utility of biomarkers of AKI in cardiac surgery and critical illness. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 8, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshaer, M.H.; Kilbride, H.S.; Stevens, P.E. External validation of the kidney failure risk equation and re-calibration with addition of community-based cohort. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 371. [Google Scholar]
- Hjortrup, P.B.; Haase, N.; Bundgaard, H.; Thomsen, S.L.; Winding, R.; Pettilä, V.; Aaen, A.; Lodahl, D.; Berthelsen, R.E.; Christensen, H.; et al. Restricting volumes of resuscitation fluid in adults with septic shock after initial management: The CLASSIC randomised, parallel-group, multicentre feasibility trial. Intensive Care Med. 2016, 42, 1695–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.L.; Cerdá, J.; Burdmann, E.A.; Tonelli, M.; García-García, G.; Jha, V.; Susantitaphong, P.; Rocco, M.; Vanholder, R.; Sever, M.S.; et al. International Society of Nephrology’s 0by25 initiative for acute kidney injury (zero preventable deaths by 2025): A human rights case for nephrology. Lancet 2015, 385, 2616–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickkers, P.; Darmon, M.; Hoste, E.; Joannidis, M.; Legrand, M.; Ostermann, M.; Prowle, J.R.; Schneider, A.; Schetz, M. Acute kidney injury in the critically ill: An updated review on pathophysiology and management. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 835–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, R.; Iwagami, M.; Moriya, H. The clinical importance of novel biomarkers for acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14879. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.D.; Vijayan, A.; Rosner, M.H.; Shi, J.; Chawla, L.S.; Kellum, J.A. Clinical Adjudication in Acute Kidney Injury Studies: Findings from the FDA Acute Kidney Injury Biomarkers Workshop. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 1337–1339. [Google Scholar]
- Moledina, D.G.; Parikh, C.R. Phenotyping of Acute Kidney Injury: Beyond Serum Creatinine. Semin. Nephrol. 2018, 38, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumlertgul, N.; Peerapornratana, S.; Trakarnvanich, T. Implementation challenges of the furosemide stress test in clinical practice. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar]
- Forni, L.G.; Joannidis, M. Blood pressure deficits in acute kidney injury: Not all about the mean arterial pressure? Crit. Care 2017, 21, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anceschi, U.; Brassetti, A.; Tuderti, G.; Ferriero, M.C.; Andrea Minervin, A.; Mari, A.; Grosso, A.A.; Carini, M.; Capitanio, U.; Larcher, A.; et al. Risk factors for progression of chronic kidney disease after robotic partial nephrectomy in elderly patients: Results from a multi-institutional collaborative series. Minerva Urol. Nephrol. 2022, 74, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meersch, M.; Küllmar, M.; Schmidt, C.; Gerss, J.; Weinhage, T.; Margraf, A.; Ermert, T.; Kellum, J.A.; Zarbock, A. Long-term Clinical Outcomes After Early Initiation of RRT in Critically Ill Patients with, AKI. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane-Gill, S.L.; Goldstein, S.L. Drug-Induced Acute Kidney Injury: A Focus on Risk Assessment for Prevention. Crit. Care Clin. 2015, 31, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.D.; Himmelfarb, J.; Paganini, E.; Ikizler, T.A.; Soroko, S.H.; Mehta, R.L.; Chertow, G.M. Timing of initiation of dialysis in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 1, 915–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudry, S.; Hajage, D.; Schortgen, F.; Martin-Lefevre, L.; Verney, C.; Pons, B.; Boulet, E.; Boyer, A.; Chevrel, G.; Lerolle, M.; et al. Timing of Renal Support and Outcome of Septic Shock and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatraju, P.K.; Mukherjee, P.; Robinson-Cohen, C.; O’Keefe, G.E.; Frank, A.J.; Christie, J.D.; Meyer, N.J.; Liu, K.D.; Matthay, M.A.; Calfee, C.S.; et al. Acute kidney injury subphenotypes based on creatinine trajectory identifies patients at increased risk of death. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joannidis, M.; Druml, W.; Forni, L.G.; Groeneveld, A.B.J.; Honore, P.M.; Hoste, E.; Ostermann, M.; Oudemans-van Straaten, H.M.; Schetz, M. Prevention of acute kidney injury and protection of renal function in the intensive care unit: Update 2017. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 730–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostermann, M.; Bellomo, R.; Burdmann, E.A.; Doi, K.; Endre, Z.H.; Goldstein, S.L.; Kane-Gill, S.L.; Liu, K.D.; Prowle, J.R.; Andrew D Shaw, A.D.; et al. Controversies in acute kidney injury: Conclusions from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Conference. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, H.; Kellum, J.A. Sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Curr. Opin Crit. Care 2016, 22, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavalle, S.; Caruso, S.; Foti, R.; Gagliano, C.; Cocuzza, S.; La Via, L.; Parisi, F.M.; Calvo-Henriquez, C.; Maniaci, A. Behçet’s Disease, Pathogenesis, Clinical Features, and Treatment Approaches: A Comprehensive Review. Medicina 2024, 60, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyner, J.L.; Shaw, A.D.; Chawla, L.S.; Hoste, E.A.J.; Bihorac, A.; Kashani, K.; Haase, M.; Shi, J.; Kellum, J.A. Sapphire Investigators Tissue Inhibitor Metalloproteinase-2 (TIMP-2)·IGF-Binding Protein-7 (IGFBP7) Levels Are Associated with Adverse Long-Term Outcomes in Patients with, AKI. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 1747–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashani, K.; Rosner, M.H.; Haase, M.; Lewington, A.J.P.; O’Donoghue, D.J.; Wilson, F.P.; Nadim, M.K.; Silver, S.A.; Zarbock, A.; Ostermann, M.; et al. Quality Improvement Goals for Acute Kidney Injury. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 14, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selby, N.M.; Casula, A.; Lamming, L.; Stoves, J.; Samarasinghe, Y.; Lewington, A.J.; Roberts, R.; Shah, N.; Johnson, M.; Jackson, N.; et al. An Organizational-Level Program of Intervention for AKI: A Pragmatic Stepped Wedge Cluster Randomized Trial. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 30, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomašev, N.; Glorot, X.; Rae, J.W.; Zielinski, M.; Askham, H.; Saraiva, A.; Mottram, A.; Meyer, C.; Ravuri, S.; Protsyuk, I.; et al. A clinically applicable approach to continuous prediction of future acute kidney injury. Nature 2019, 572, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churpek, M.M.; Carey, K.A.; Edelson, D.P.; Singh, T.; Astor, B.C.; Gilbert, E.R.; Winslow, C.; Shah, N.; Afshar, M.; Koyner, J.L. Internal and External Validation of a Machine Learning Risk Score for Acute Kidney Injury. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2012892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treacy, O.; Brown, F.G.; McCaffrey, J. Precision Medicine in Acute Kidney Injury: A Promising Future? Am. J. Nephrol. 2022, 53, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Koyner, J.L.; Adhikari, L.; Edelson, D.P.; Churpek, M.M. Development of a Multicenter Ward-Based AKI Prediction Model. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 17, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, R.L.; Burdmann, E.A.; Cerda, J.; Feehally, J.; Finkelstein, F.; García-García, G.; Godin, M.; Jha, V.; Lameire, N.H.; Levin, N.W.; et al. Recognition and management of acute kidney injury in the International Society of Nephrology 0by25 Global Snapshot: A multinational cross-sectional study. Lancet 2023, 387, 2017–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.D.; Yang, J.; Tan, T.C. Risk Prediction Models for Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Adults: A Systematic Review. Kidney Int. Rep. 2023, 5, 1462–1473. [Google Scholar]
- Hoste, E.; Bihorac, A.; Al-Khafaji, A.; Ortega, L.M.; Ostermann, M.; Haase, M.; Zacharowski, K.; Wunderink, R.; Heung, M.; Lissauer, M.; et al. Identification and validation of biomarkers of persistent acute kidney injury: The RUBY study. Intensive Care Med. 2023, 46, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellum, J.A.; Wen, X.; de Caestecker, M.P.; Neil A Hukriede, N.A. Affiliations Expand. Sepsis-associated acute kidney injury: A problem deserving of new solutions. Nephron 2022, 143, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deep, A.; Saha, A.; Wilson, B. Acute kidney injury in children: Looking beyond serum creatinine. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2022, 37, 1697–1708. [Google Scholar]
- Menon, S.; Goldstein, S.L.; Mottes, T.; Fei, L.; Kaddourah, A.; Terrell, T.; Arnold, P.; Bennett, M.; Basu, R.K. Urinary biomarker incorporation into the renal angina index early in intensive care unit admission optimizes acute kidney injury prediction in critically ill children. Kidney Int. 2023, 89, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, S.A.; Goldstein, S.L.; Harel, Z.; Harvey, A.; Rompies, E.; Adhikari, N.K.; Acedillo, R.; Jain, A.K.; Richardson, R.; Chan, C.T.; et al. Ambulatory care after acute kidney injury: An opportunity to improve patient outcomes. Can. J. Kidney Health Dis. 2022, 2, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffl, H.; Lang, S.M. Update on biomarkers of acute kidney injury: Moving closer to clinical impact? Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2023, 16, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarbock, A.; Kellum, J.A.; Schmidt, C. Effect of timing of renal replacement therapy initiation on recovery from acute kidney injury. Intensive Care Med. 2022, 46, 943–953. [Google Scholar]
- Coca, S.G.; Zabetian, A.; Ferket, B.S.; Zhou, J.; Testani, J.M.; Garg, A.X.; Parikh, C.R. Evaluation of Short-Term Changes in Serum Creatinine Level as a Meaningful End Point in Randomized Clinical Trials. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2023, 27, 2529–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCullough, P.A.; Ostermann, M.; Forni, L.G.; Bihorac, A.; Koyner, J.L.; Chawla, L.S.; Shi, J.; Kampf, J.P.; Paul McPherson, P.; Kellum, J.A.; et al. Serial urinary tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7 and the prognosis for acute kidney injury in critically ill adults. Kidney Int. Rep. 2023, 4, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadim, M.K.; Forni, L.G.; Bihorac, A.; Hobson, C.; Koyner, J.L.; Shaw, A.; Arnaoutakis, G.J.; Ding, X.; Engelman, D.T.; Gasparovic, H.; et al. Cardiac and Vascular Surgery-Associated Acute Kidney Injury: The 20th International Consensus Conference of the ADQI (Acute Disease Quality Initiative) Group. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 7, e008834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniaci, A.; Lavalle, S.; Gagliano, C.; Lentini, M.; Masiello, E.; Parisi, F.; Iannella, G.; Cilia, N.D.; Salerno, V.; Cusumano, G.; et al. The Integration of Radiomics and Artificial Intelligence in Modern Medicine. Life 2024, 14, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
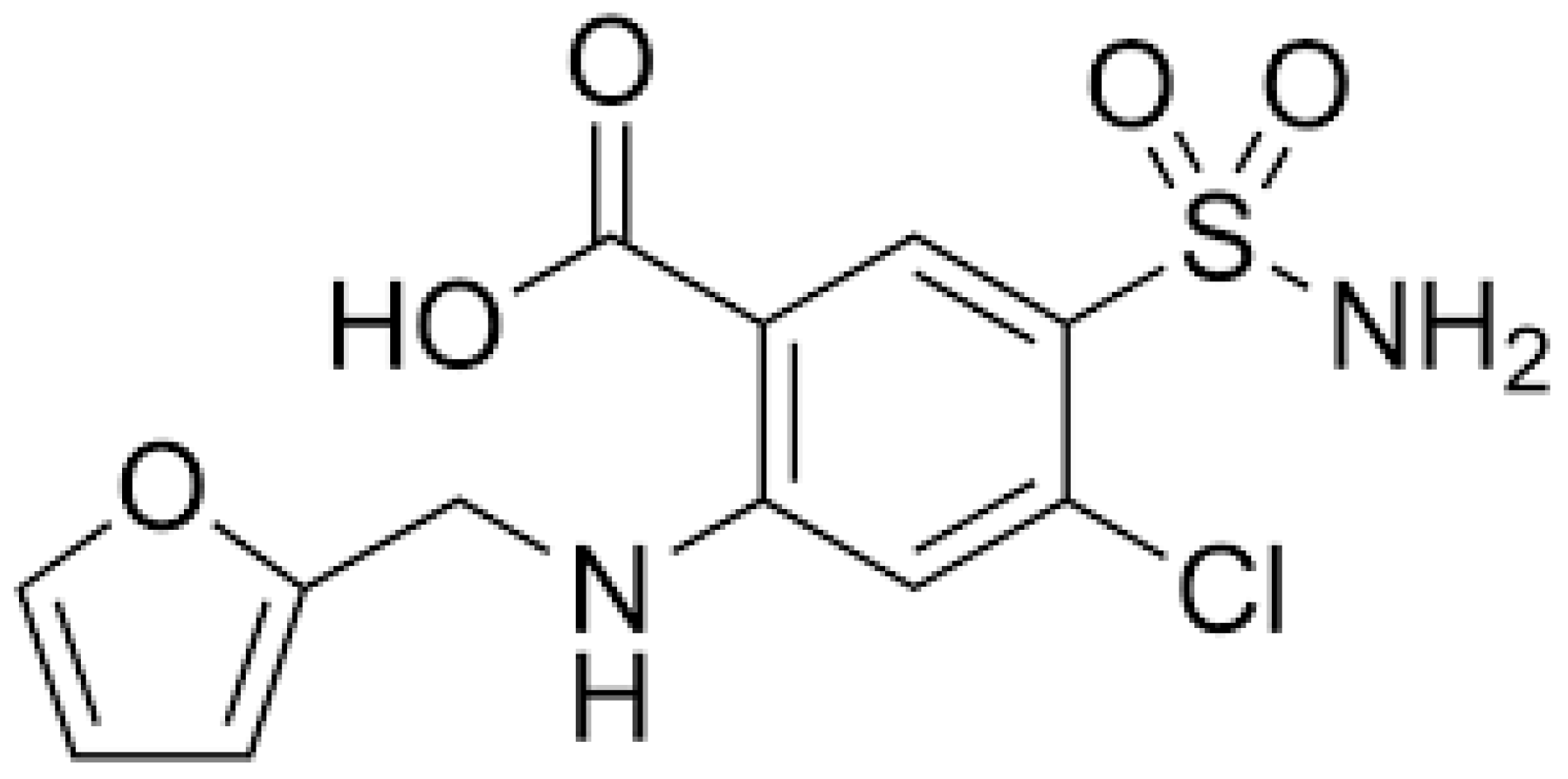
| CRITICAL CARE SETTING | |
| CARDIAC SURGERY |
|
| SEPSIS-ASSOCIATED AKI |
|
| HEART FAILURE |
|
| TRANSPLANT RECIPIENS | |
| EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT APPLICATIONS |
|
| SPECIAL POPULATIONS |
|
| INTEGRATION WITH BIOMARKERS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
La Via, L.; Cuttone, G.; Sinatra, N.; Abrignani, M.G.; Geraci, G.; Ippati, G.; Rubulotta, F.M. The Furosemide Stress Test: A Dynamic Tool for Predicting Acute Kidney Injury Progression in Critical Care Medicine. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2595. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082595
La Via L, Cuttone G, Sinatra N, Abrignani MG, Geraci G, Ippati G, Rubulotta FM. The Furosemide Stress Test: A Dynamic Tool for Predicting Acute Kidney Injury Progression in Critical Care Medicine. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(8):2595. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082595
Chicago/Turabian StyleLa Via, Luigi, Giuseppe Cuttone, Nicola Sinatra, Maurizio Giuseppe Abrignani, Giulio Geraci, Giovanni Ippati, and Francesca Maria Rubulotta. 2025. "The Furosemide Stress Test: A Dynamic Tool for Predicting Acute Kidney Injury Progression in Critical Care Medicine" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 8: 2595. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082595
APA StyleLa Via, L., Cuttone, G., Sinatra, N., Abrignani, M. G., Geraci, G., Ippati, G., & Rubulotta, F. M. (2025). The Furosemide Stress Test: A Dynamic Tool for Predicting Acute Kidney Injury Progression in Critical Care Medicine. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(8), 2595. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082595







