Present and Future of Autologous Breast Reconstruction: Advancing Techniques to Minimize Morbidity and Complications, Enhancing Quality of Life and Patient Satisfaction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Innovations to Minimize Morbidity and Complications in Autologous Breast Reconstruction
2.1. Expanding the Use of Perforator Flaps: Superficial Circumflex Iliac Artery Perforator (SCIP) Flap for Breast Reconstruction
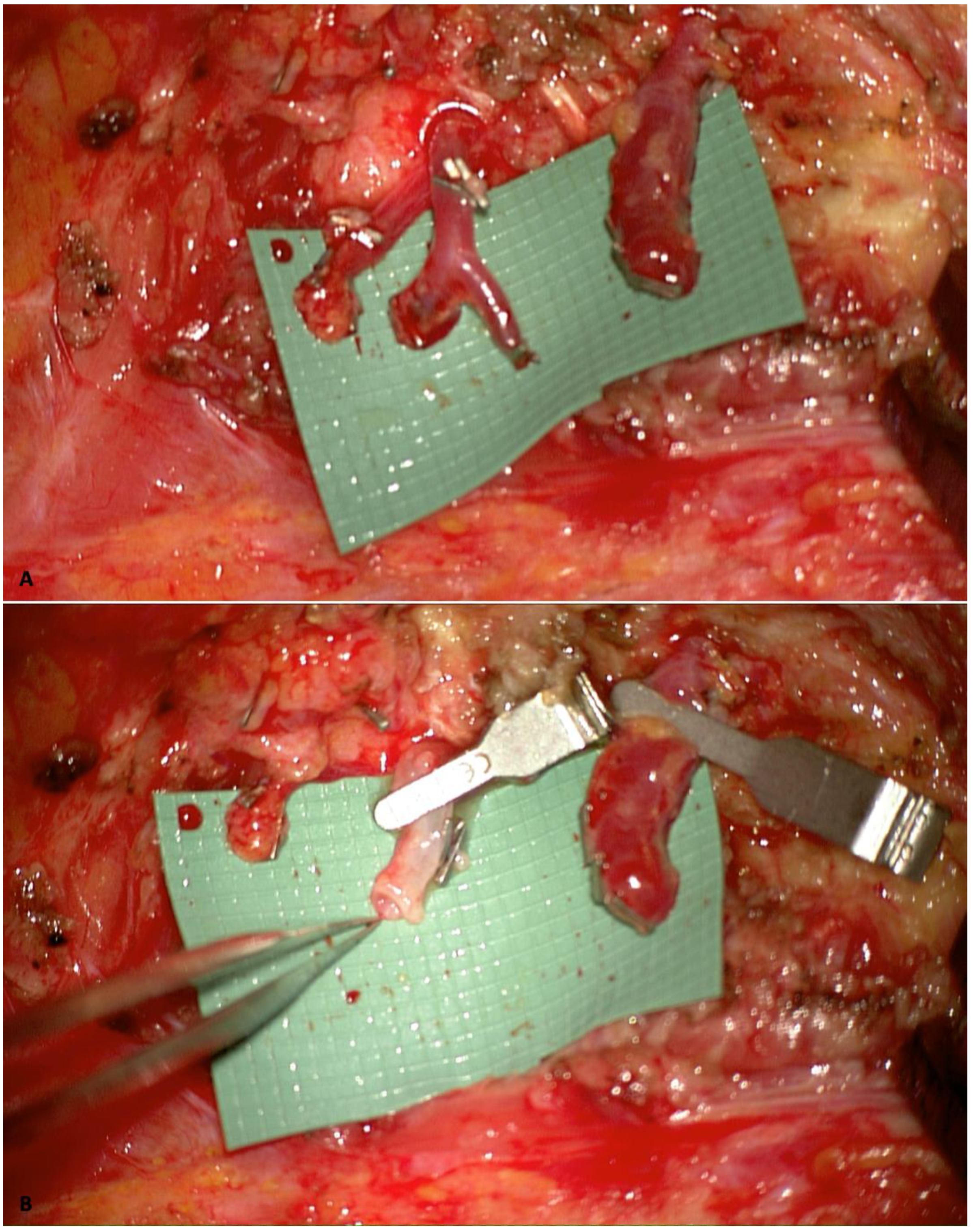
2.2. Internal Mammary Artery Perforator-to-Perforator Anastomosis and Rib-Sparing Approach
2.3. Indocyanine Green Fluorescence Angiography (ICG)
2.4. Preoperative Imaging Evaluation
2.5. Robotic-Assisted Surgery
2.6. Buried Flaps: Innovation in Flap Monitoring
2.7. Lymphatic Complications Prevention
2.8. Enhanced Recovery Protocols
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, W.; Lv, X.; Xu, X.; Gao, X.; Wang, B. Meta-analysis for psychological impact of breast reconstruction in patients with breast cancer. Breast Cancer 2018, 25, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santosa, K.B.; Qi, J.; Kim, H.M.; Hamill, J.B.; Wilkins, E.G.; Pusic, A.L. Long-term Patient-Reported Outcomes in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction. JAMA Surg. 2018, 153, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartrampf, C.R.; Scheflan, M.; Black, P.W. Breast reconstruction with a transverse abdominal island flap. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1982, 69, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.Y.B.; El Eter, L.B.; Yesantharao, P.; Hung, B.B.; Owens, H.; Persing, S.; Sacks, J.M.M. Complications and Patient-reported Outcomes after TRAM and DIEP Flaps: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Plast. Reconstr. Surg.-Glob. Open 2020, 8, e3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.J.; Treece, P. Deep inferior epigastric perforator flap for breast reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1994, 32, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.E.; Shenaq, D.S.; Silva, A.K.; Mhlaba, J.M.; Song, D.H. Breast Reconstruction with SIEA Flaps: A Single-Institution Experience with 145 Free Flaps. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 137, 1682–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coroneos, C.J.; Heller, A.M.; Voineskos, S.H.; Avram, R. SIEA versus DIEP Arterial Complications: A Cohort Study. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2015, 135, 802e–807e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.J.; Haddock, N.T.; Ahn, C.Y.; Sadeghi, A. Breast Reconstruction with the Profunda Artery Perforator Flap. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2012, 129, 16e–23e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitgasser, L.; Mahrhofer, M.; Schwaiger, K.; Bachleitner, K.; Russe, E.; Wechselberger, G.; Schoeller, T. Lessons Learned from 30 Years of Transverse Myocutaneous Gracilis Flap Breast Reconstruction: Historical Appraisal and Review of the Present Literature and 300 Cases. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martineau, J.; Kalbermatten, D.F.; Oranges, C.M. Safety and Efficacy of the Superior Gluteal Artery Perforator (SGAP) Flap in Autologous Breast Reconstruction: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2022, 14, 4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, S.M.; Greenspun, D.T. Lumbar Artery Perforator Flaps in Autologous Breast Reconstruction. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2023, 50, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LoTempio, M.M.; Allen, R.J. Breast Reconstruction with SGAP and IGAP Flaps. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2010, 126, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourani, S.S. Breast cancer related lymphoedema: A review of contemporary preventive strategies. ANZ J. Surg. 2024, 94, 2105–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geddes, C.R.; Morris, S.F.; Neligan, P.C. Perforator Flaps: Evolution, Classification, and Applications. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2003, 50, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hivelin, M.; Soprani, A.; Schaffer, N.; Hans, S.; Lantieri, L. Minimally Invasive Laparoscopically Dissected Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap: An Anatomical Feasibility Study and a First Clinical Case. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 141, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, K.T.; Mun, G.H. Short Fasciotomy-Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap Harvest for Breast Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2023, 152, 972e–984e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddock, N.T.; Culver, A.J.; Teotia, S.S. Abdominal weakness, bulge, or hernia after DIEP flaps: An algorithm of management, prevention, and surgical repair with classification. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2021, 74, 2194–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaiger, K.; Scharfetter, S.; Russe, E.; Köninger, F.; Pumberger, P.; Wechselberger, G. Breast reconstruction using the superficial circumflex iliac artery superficial branch perforator (SCISP) flap. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franchi, A.; Patanè, L.; Hummel, C.E.; Walber, J.; Zadeh, S.N.; Jandali, A.R.; Jung, F. The Preferential Use of Subcutaneous Arteries (SCIA-SB and SIEA) in Abdominal-based Autologous Breast Reconstruction with a Modified Flap Design. Plast. Reconstr. Surg.-Glob. Open 2024, 12, e6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, H.S.P.; Jeong, H.H.; Choi, D.H.; Hong, J.P.J.P. Study of the Medial Superficial Perforator of the Superficial Circumflex Iliac Artery Perforator Flap Using Computed Tomographic Angiography and Surgical Anatomy in 142 Patients. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 139, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, M.; Blondeel, P.; Van Landuyt, K.; Monstrey, S. Algorithm in choosing recipient vessels for perforator free flap in breast reconstruction: The role of the internal mammary perforators. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 2004, 57, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacks, J.M.; Chang, D.W. Rib-Sparing Internal Mammary Vessel Harvest for Microvascular Breast Reconstruction in 100 Consecutive Cases. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 123, 1403–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vourvachis, M.; Goodarzi, M.R.; Scaglioni, M.F.; Tartanus, J.; Jones, A.; Cheng, H.; Abdelrahman, M. Utilization of the internal mammary perforators as the recipient vessels for microsurgical breast reconstruction: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. Microsurgery 2023, 44, 31105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocini, R.; Pinto, V.; Contu, L.; De Santis, G.; Pignatti, M. “Solving vessel caliber mismatch in microvascular anasto-mosis: A comprehensive review, novel techniques, and a surgical guide for optimal outcomes”. J. Hand Micro-Surg. 2024, 17, 100179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alander, J.T.; Kaartinen, I.; Laakso, A.; Pätilä, T.; Spillmann, T.; Tuchin, V.V.; Venermo, M.; Välisuo, P. A Review of Indocyanine Green Fluorescent Imaging in Surgery. Int. J. Biomed. Imaging 2012, 2012, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimatsu, H.; Karakawa, R.; Scaglioni, M.F.; Fuse, Y.; Tanakura, K.; Yano, T. Application of intraoperative indocyanine green angiography for detecting flap congestion in the use of free deep inferior epigastric perforator flaps for breast reconstruction. Microsurgery 2021, 41, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panettella, T.; Meroni, M.; Scaglioni, M.F. How to increase success rate in microsurgical free and pedicled flap reconstructions with intra-operative multiple-step ICG imaging: A case series with 400 consecutive cases. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2024, 97, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Jiao, L.; Chen, S.; Li, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Du, F.; Huang, J.; Long, X. Flap perfusion assessment with indocyanine green angiography in deep inferior epigastric perforator flap breast reconstruction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Microsurgery 2023, 43, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, R.; Morimoto, Y.; Masumoto, K.; Nambu, M.; Takikawa, M.; Yanagibayashi, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Kikuchi, M.; Kiyosawa, T. Detection of Skin Perforators by Indocyanine Green Fluorescence Nearly Infrared Angiography. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2008, 122, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmeshwar, N.; Sultan, S.M.; Kim, E.A.; Piper, M.L. A Systematic Review of the Utility of Indocyanine Angiography in Autologous Breast Reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2020, 86, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliara, D.; Schiavone, L.; Garganese, G.; Bove, S.; Montella, R.A.; Costantini, M.; Rinaldi, P.M.; Bottosso, S.; Grieco, F.; Rubino, C.; et al. Predicting Mastectomy Skin Flap Necrosis: A Systematic Review of Preoperative and Intraoperative Assessment Techniques. Clin. Breast Cancer 2023, 23, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddock, N.T.; Dumestre, D.O.; Teotia, S.S. Efficiency in DIEP Flap Breast Reconstruction: The Real Benefit of Computed Tomographic Angiography Imaging. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2020, 146, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neil-Dwyer, J.; Ludman, C.; Schaverien, M.; McCulley, S.; Perks, A. Magnetic resonance angiography in preoperative planning of deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flaps. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2008, 62, 1661–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevik, J.; Seth, I.; Hunter-Smith, D.J.; Rozen, W.M. A History of Innovation: Tracing the Evolution of Imaging Modalities for the Preoperative Planning of Microsurgical Breast Reconstruction. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, B.; Cevik, J.; Seth, I.; Sofiadellis, F.; Ross, R.J.; Rozen, W.M.; Cuomo, R. Evaluating Artificial Intelligence’s Role in Teaching the Reporting and Interpretation of Computed Tomographic Angiography for Preoperative Planning of the Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap. JPRAS Open 2024, 40, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, N.; Alessandro, C.J.; Ibelli, T.J.; Akhavan, A.A.; Sharaf, J.M.; Rabinovitch, D.; Henderson, P.W.; Yao, A. The Expanding Utility of Robotic-Assisted Flap Harvest in Autologous Breast Reconstruction: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elameen, A.M.; Dahy, A.A. Surgical outcomes of robotic versus conventional autologous breast reconstruction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Robot. Surg. 2024, 18, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, H.R.; McLennan, A.; Xue, E.Y.; Yu, J.Z.; Selber, J.C. Robotics in Microsurgery and Supermicrosurgery. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2023, 37, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, M.; Jiao, Y.; Xu, L.; Lin, R.; Zhong, X.; Lv, Q. Long-term outcomes of skin-sparing mastectomy and nipple-sparing mastectomy versus traditional mastectomy in breast cancer: A case-control study based on preoperative ultrasound and clinical indicators. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2025, 23, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, J.D.; Stranix, J.T.; Chiodo, M.V.; Alperovich, M.; Ahn, C.Y.; Allen, R.J.; Choi, M.; Karp, N.S.; Levine, J.P. Evolution in Monitoring of Free Flap Autologous Breast Reconstruction after Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy: Is There a Best Way? Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 141, 1086–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lignieres, A.; Andejani, D.F.; Chu, C.K.; Largo, R.D.; Mericli, A.F. No Skin Paddle, No Problem: Burying Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps in the Immediate Setting is Safe in Select Patient Populations. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2024, 40, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halani, S.H.M.; Jones, K.B.; Liu, Y.; Teotia, S.S.; Haddock, N.T. Reconstructive Burnout after Mastectomy: Implications for Patient Selection. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2022, 151, 13e–19e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creasy, H.; Citron, I.; Davis, T.P.; Cooper, L.; Din, A.H.; Rose, V. Buried Autologous Breast Reconstruction: Outcomes and Technical Considerations. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowe, C.; Twigg, J.; Salker, A.; Doumas, S.; Ho, M. Outcomes of anastomotic venous flow couplers in head and neck free flap reconstruction–five-year experience in a single centre. Br. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 60, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadwick, S.; Khaw, R.; Duncan, J.; Wilson, S.; Highton, L.; O’Ceallaigh, S. The use of venous anastomotic flow couplers to monitor buried free DIEP flap reconstructions following nipple-sparing mastectomy. JPRAS Open 2019, 23, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, A.Y.; Lonie, S.; Lim, K.; Farthing, H.; Hunter-Smith, D.J.; Rozen, W.M. Free Flap Monitoring, Salvage, and Failure Timing: A Systematic Review. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2021, 37, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.-Y.; Lee, Y.-C.; Lin, Y.-C.; Wong, S.T.-S.; Hsueh, Y.-Y.; Kuo, Y.-L.; Shieh, S.-J.; Lee, J.-W. Implantable Doppler Probes for Postoperatively Monitoring Free Flaps: Efficacy. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Plast. Reconstr. Surg.-Glob. Open 2016, 4, e1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.S.; Akoh, J.A.; Houlberg, K. The Use of the Implantable Doppler Probe as a Blood Flow Monitoring Device in Clinical Settings: A Narrative Review of the Evidence. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2023, 21, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shen, Z.; Shao, Z.; Yu, P.; Wu, J. Free Flap Monitoring Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy: A Systemic Review. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2016, 76, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festa, B.M.; Costantino, A.; Pace, G.M.; Spriano, G.; De Virgilio, A. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy for Continuous Noninvasive Monitoring of Free Flap in Head and Neck Reconstruction: Systematic Review of the Literature and Personal Experience. Surg. Innov. 2023, 30, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, A.; Orihashi, K.; Yoshida, Y.; Kuriyama, M. Near-infrared spectroscopy for monitoring free jejunal flap. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2021, 74, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Umemoto, Y.; Ohashi, W.; Watanabe, H.; Nagata, A.; Furukawa, H. NIRO200NX: Reliable Monitoring System for Buried Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap. Plast. Reconstr. Surg.-Glob. Open 2024, 12, e6096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaglioni, M.F.; Suami, H. Anatomy of the Lymphatic System and the Lymphosome Concept with Reference to Lymphedema. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2018, 32, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaglioni, M.F.; Fontein, D.B.Y.; Arvanitakis, M.; Giovanoli, P. Systematic review of lymphovenous anastomosis (LVA) for the treatment of lymphedema. Microsurgery 2017, 37, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccardo, F.; Casabona, F.; DeCian, F.; Friedman, D.; Murelli, F.; Puglisi, M.; Campisi, C.C.; Molinari, L.; Spinaci, S.; Dessalvi, S. Lymphatic Microsurgical Preventing Healing Approach (LYMPHA) for primary surgical prevention of breast cancer-related lymphedema: Over 4 years follow-up. Microsurgery 2014, 34, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciudad, P.; Escandón, J.M.; Bustos, V.P.; Manrique, O.J.; Kaciulyte, J. Primary Prevention of Cancer-Related Lymphedema Using Preventive Lymphatic Surgery: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Indian J. Plast. Surg. 2022, 55, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Offodile, A.C., 2nd; Gu, C.; Boukovalas, S.; Coroneos, C.J.; Chatterjee, A.; Largo, R.D.; Butler, C. Enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) pathways in breast reconstruction: Systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 173, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, S.; Walle, L.; Loucas, M.; Loucas, R.; Frerichs, O.; Fansa, H. Enhanced Recovery after Surgery (ERAS) in DIEP-Flap Breast Reconstructions—A Comparison of Two Reconstructive Centers with and without ERAS-Protocol. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scaglioni, M.F.; Martini, F.; Meroni, M. Present and Future of Autologous Breast Reconstruction: Advancing Techniques to Minimize Morbidity and Complications, Enhancing Quality of Life and Patient Satisfaction. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2599. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082599
Scaglioni MF, Martini F, Meroni M. Present and Future of Autologous Breast Reconstruction: Advancing Techniques to Minimize Morbidity and Complications, Enhancing Quality of Life and Patient Satisfaction. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(8):2599. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082599
Chicago/Turabian StyleScaglioni, Mario F., Federica Martini, and Matteo Meroni. 2025. "Present and Future of Autologous Breast Reconstruction: Advancing Techniques to Minimize Morbidity and Complications, Enhancing Quality of Life and Patient Satisfaction" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 8: 2599. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082599
APA StyleScaglioni, M. F., Martini, F., & Meroni, M. (2025). Present and Future of Autologous Breast Reconstruction: Advancing Techniques to Minimize Morbidity and Complications, Enhancing Quality of Life and Patient Satisfaction. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(8), 2599. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082599






