A Tale of Two Diseases: Decoding Aortic Stenosis and Cardiac Amyloidosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pathophysiology of the High Prevalence of Cardiac Amyloidosis in Patients with Aortic Stenosis
2.1. Common Epidemiology
2.2. Transthyretin Deposition to Aortic Valve
2.3. Common Etiology for Both Pathologies
2.4. Aortic Stenosis Is the Etiology of Cardiac Amyloidosis
3. Clinical Findings Associated with AS and CA
4. Electrocardiographic Findings in Cardiac Amyloidosis and Aortic Stenosis
- A lower Sokolow–Lyon index;
- A longer QRS duration;
- A higher prevalence of right bundle branch block (RBBB) [39].
5. Biomarkers in ATTR-CA and Aortic Stenosis
6. Scoring Systems for Identifying Cardiac Amyloidosis in Aortic Stenosis
6.1. The RAISE Score
- Cardiac remodeling (LVH and diastolic dysfunction);
- Age;
- Cardiac injury (hsTnT);
- Systemic disease (CTS);
- Electrical disturbances (RBBB and low voltage electrocardiogram).
- One point for age ≥ 85 years, Sokolow/Lyon index < 1.9 mV, hsTnT > 20 ng/mL, and E/A ratio > 1.4;
- Two points for the presence of RBBB;
- Three points for a history of CTS.
6.2. Electronic Medical Record-Based Scoring System
- Four points for AF (prevalence 15–40%), atrioventricular block, peripheral neuropathy, RVHF, or pulmonary hypertension;
- Three points for bundle branch block (odds ratio 3);
- Two points for less specific findings, such as hip and knee arthroplasty.
7. The Role of Imaging in the Diagnosis of Aortic Stenosis and Cardiac Amyloidosis
7.1. The Role of Echocardiography
7.1.1. Key Echocardiographic Finding in Cardiac Amyloidosis
7.1.2. Pericardial and Valve Involvement
7.1.3. Tissue Doppler and Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography
7.1.4. Echocardiographic Indicators of Cardiac Amyloidosis in Coexisting Aortic Stenosis
7.2. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging
7.3. Cardiac Computed Tomography
7.4. Scintigraphy
8. The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Diagnosis and Early Identification
9. Therapeutic Approaches in Patients with Coexisting Cardiac Amyloidosis and Aortic Stenosis
9.1. Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement in Cardiac Amyloidosis and Aortic Stenosis
9.2. Comparing TAVR and SAVR in Patients with Aortic Stenosis and Cardiac Amyloidosis
9.2.1. Transthyretin Stabilizers
9.2.2. Transthyretin Knockdown/Silencing Therapies
9.2.3. Emerging Agents for Degradation/Extraction
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| AL-CA | Light-Chain Cardiac Amyloidosis |
| AS | Aortic Stenosis |
| AF | Atrial Fibrillation |
| AS-CA | Aortic Stenosis and Cardiac Amyloidosis |
| ASGPR | Asialoglycoprotein Receptor |
| ASO | Antisense Oligonucleotide |
| ATTR | Transthyretin Amyloidosis |
| ATTR-CA | Transthyretin Amyloidosis Cardiac Amyloidosis |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| AVCS | Aortic Valve Calcium Scores |
| CA | Cardiac Amyloidosis |
| CMR | Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance |
| CCT | Cardiac Computed Tomography |
| CTS | Carpal Tunnel Syndrome |
| DECT | Dual-Energy Computed Tomography |
| DPD | Technetium−99m 3,3-Diphosphono−1,2-Propanodicarboxylic Acid Bone Scintigraphy |
| ECG | Electrocardiogram |
| ECV | Extracellular Volume |
| EF | Ejection Fraction |
| EMR | Electronic Medical Record |
| GalNAc | N-acetyl Galactosamine |
| GLS | Global Longitudinal Strain |
| HCM | Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathies |
| HF | Heart Failure |
| HFpEF | Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction |
| HMDP | Hydroxymethylene Diphosphonate |
| hATTR | Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis |
| hsTnT | High Sensitive Troponin T |
| KCCQ-OS | Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire-Overall Summary |
| LA | Left Atrium |
| LFLG-AS | Low-Flow, Low-Gradient Aortic Stenosis |
| LGE | Late Gadolinium Enhancement |
| LIE | Late Iodine Enhancement |
| LV | Left Ventricular |
| LVH | Left Ventricular Hypertrophy |
| MCF | Myocardial Contraction Fraction |
| NIS | National Inpatient Sample |
| NSAID | Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drug |
| NT-proBNP | B-type Natriuretic Peptide |
| PSM | Propensity-Score Matching |
| PYP | Pyrophosphate |
| RV | Right Ventricle |
| RVHF | Right Ventricular Heart Failure |
| SAVR | Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement |
| siRNA | Small Interfering RNA |
| STE | Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography |
| TAPSE | Tricuspid Annular Plane Systolic Excursion |
| TAVR | Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement |
| TAVI | Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation |
| TDI | Tissue Doppler Imaging |
| TTE | Transthoracic Echocardiography |
| TTR | Transthyretin |
| VMR | Voltage/Mass Ratio |
| wtATTR | Wild-Type Transthyretin Amyloidosis |
References
- Coffey, S.; Cox, B.; Williams, M.J. The prevalence, incidence, progression, and risks of aortic valve sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 2852–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlini, G.; Bellotti, V. Molecular mechanisms of amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertz, M.A.; Dispenzieri, A.; Sher, T. Pathophysiology and treatment of cardiac amyloidosis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2015, 12, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornwell, G.G., 3rd; Murdoch, W.L.; Kyle, R.A.; Westermark, P.; Pitkanen, P. Frequency and distribution of senile cardiovascular amyloid. A clinicopathologic correlation. Am. J. Med. 1983, 75, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsche, C.; Scully, P.R.; Patel, K.P.; Kammerlander, A.A.; Koschutnik, M.; Dona, C.; Wollenweber, T.; Ahmed, N.; Thornton, G.D.; Kelion, A.D.; et al. Prevalence and Outcomes of Concomitant Aortic Stenosis and Cardiac Amyloidosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittleson, M.M.; Maurer, M.S.; Ambardekar, A.V.; Bullock-Palmer, R.P.; Chang, P.P.; Eisen, H.J.; Nair, A.P.; Nativi-Nicolau, J.; Ruberg, F.L.; American Heart Association Heart Failure; et al. Cardiac Amyloidosis: Evolving Diagnosis and Management: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2020, 142, e7–e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balciunaite, G.; Rimkus, A.; Zurauskas, E.; Zaremba, T.; Palionis, D.; Valeviciene, N.; Aidietis, A.; Serpytis, P.; Rucinskas, K.; Sogaard, P.; et al. Transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis in aortic stenosis: Prevalence, diagnostic challenges, and clinical implications. Hell. J. Cardiol. 2020, 61, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witteles, R.M.; Bokhari, S.; Damy, T.; Elliott, P.M.; Falk, R.H.; Fine, N.M.; Gospodinova, M.; Obici, L.; Rapezzi, C.; Garcia-Pavia, P. Screening for Transthyretin Amyloid Cardiomyopathy in Everyday Practice. JACC Heart Fail. 2019, 7, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lousada, I.; Comenzo, R.L.; Landau, H.; Guthrie, S.; Merlini, G. Light Chain Amyloidosis: Patient Experience Survey from the Amyloidosis Research Consortium. Adv. Ther. 2015, 32, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, M.D.; Buxbaum, J.N.; Eisenberg, D.S.; Merlini, G.; Saraiva, M.J.M.; Sekijima, Y.; Sipe, J.D.; Westermark, P. Amyloid nomenclature 2018: Recommendations by the International Society of Amyloidosis (ISA) nomenclature committee. Amyloid 2018, 25, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galat, A.; Guellich, A.; Bodez, D.; Slama, M.; Dijos, M.; Zeitoun, D.M.; Milleron, O.; Attias, D.; Dubois-Randé, J.-L.; Mohty, D.; et al. Aortic stenosis and transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis: The chicken or the egg? Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 3525–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaño, A.; Narotsky, D.L.; Hamid, N.; Khalique, O.K.; Morgenstern, R.; DeLuca, A.; Rubin, J.; Chiuzan, C.; Nazif, T.; Vahl, T.; et al. Unveiling transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis and its predictors among elderly patients with severe aortic stenosis undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 2879–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhi, S.; Guidalotti, P.L.; Quarta, C.C.; Gagliardi, C.; Milandri, A.; Lorenzini, M.; Potena, L.; Leone, O.; Bartolomei, I.; Pastorelli, F.; et al. Identification of TTR-Related Subclinical Amyloidosis With 99mTc-DPD Scintigraphy. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 7, 531–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tini, G.; Sessarego, E.; Benenati, S.; Vianello, P.F.; Musumeci, B.; Autore, C.; Canepa, M. Yield of bone scintigraphy screening for transthyretin-related cardiac amyloidosis in different conditions: Methodological issues and clinical implications. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 51, e13665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanskanen, M.; Peuralinna, T.; Polvikoski, T.; Notkola, I.L.; Sulkava, R.; Hardy, J.; Singleton, A.; Kiuru-Enari, S.; Paetau, A.; Tienari, P.J.; et al. Senile systemic amyloidosis affects 25% of the very aged and associates with genetic variation in alpha2-macroglobulin and tau: A population-based autopsy study. Ann. Med. 2008, 40, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, M.; Horibata, Y.; Shono, M.; Misumi, Y.; Oshima, T.; Su, Y.; Tasaki, M.; Shinriki, S.; Kawahara, S.; Jono, H.; et al. Clinicopathological features of senile systemic amyloidosis: An ante- and post-mortem study. Mod. Pathol. 2011, 24, 1533–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed-Salem, L.; Santos-Mateo, J.J.; Sanchez-Serna, J.; Hernández-Vicente, Á.; Reyes-Marle, R.; Sánchez, M.I.C.; Claver-Valderas, M.A.; Gonzalez-Vioque, E.; Haro-del Moral, F.J.; García-Pavía, P.; et al. Prevalence of wild type ATTR assessed as myocardial uptake in bone scan in the elderly population. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 270, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristen, A.V.; Schnabel, P.A.; Winter, B.; Helmke, B.M.; Longerich, T.; Hardt, S.; Koch, A.; Sack, F.-U.; Katus, H.A.; Linke, R.P.; et al. High prevalence of amyloid in 150 surgically removed heart valves—A comparison of histological and clinical data reveals a correlation to atheroinflammatory conditions. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2010, 19, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audet, A.; Côté, N.; Couture, C.; Bossé, Y.; Després, J.-P.; Pibarot, P.; Mathieu, P. Amyloid substance within stenotic aortic valves promotes mineralization. Histopathology 2012, 61, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, A.K.; Bansal, R.; Singh, A.; Dorbala, S.; Sharma, G.; Gupta, K.; Saxena, A.; Bhargava, B.; Karthikeyan, G.; Ramakrishnan, S.; et al. Concomitant Transthyretin Amyloidosis and Severe Aortic Stenosis in Elderly Indian Population. JACC CardioOncol. 2021, 3, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffin, Y. Microscopic amyloid deposits in the heart valves: A common local complication of chronic damage and scarring. J. Clin. Pathol. 1980, 33, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, T.; Nakamura, H.; Nagasawa, T.; Kamel, T.; Fujihara, S.; Yokota, T.; Uchino, F. Amyloid deposits in heart valves. Acta Pathol. Jpn. 1982, 32, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.H. Localized dystrophic amyloidosis of heart valves. Hum. Pathol. 1983, 14, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.Q.; Binger, K.J.; Howlett, G.J.; Griffin, M.D.W. Methionine oxidation induces amyloid fibril formation by full-length apolipoprotein A-I. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1977–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Buxbaum, J.N.; Reixach, N. Age-related oxidative modifications of transthyretin modulate its amyloidogenicity. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 1913–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewkowicz, E.; Jayaraman, S.; Gursky, O. Protein Amyloid Cofactors: Charged Side-Chain Arrays Meet Their Match? Trends Biochem. Sci. 2021, 46, 626–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcoux, J.; Mangione, P.P.; Porcari, R.; Degiacomi, M.T.; Verona, G.; Taylor, G.W.; Giorgetti, S.; Raimondi, S.; Sanglier-Cianférani, S.; Benesch, J.L.P.; et al. A novel mechano-enzymatic cleavage mechanism underlies transthyretin amyloidogenesis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2015, 7, 1337–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangione, P.P.; Verona, G.; Corazza, A.; Marcoux, J.; Canetti, D.; Giorgetti, S.; Raimondi, S.; Stoppini, M.; Esposito, M.; Relini, A.; et al. Plasminogen activation triggers transthyretin amyloidogenesis in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 14192–14199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratchi, S.; Zaldivia, M.T.K.; Wallert, M.; Loseff-Silver, J.; Al-Aryahi, S.; Zamani, J.; Thurgood, P.; Salim, A.; Htun, N.M.; Stub, D.; et al. Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Represents an Anti-Inflammatory Therapy Via Reduction of Shear Stress–Induced, Piezo-1–Mediated Monocyte Activation. Circulation 2020, 142, 1092–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantarutti, C.; Mimmi, M.C.; Verona, G.; Mandaliti, W.; Taylor, G.W.; Mangione, P.P.; Giorgetti, S.; Bellotti, V.; Corazza, A. Calcium Binds to Transthyretin with Low Affinity. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimo, A.; Camerini, L.; Fabiani, I.; Morfino, P.; Panichella, G.; Barison, A.; Pucci, A.; Castiglione, V.; Vergaro, G.; Sinagra, G.; et al. Valvular heart disease in patients with cardiac amyloidosis. Heart Fail. Rev. 2024, 29, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bequignon, E.; Guellich, A.; Bartier, S.; Raynal, M.; Pruliere-Escabasse, V.; Canoui-Poitrine, F.; Coste, A.; Damy, T. How your ears can tell what is hidden in your heart: Wild-type transthyretin amyloidosis as potential cause of sensorineural hearing loss inelderly-AmyloDEAFNESS pilot study. Amyloid 2017, 24, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caponetti, A.G.; Accietto, A.; Saturi, G.; Ponziani, A.; Sguazzotti, M.; Massa, P.; Giovannetti, A.; Ditaranto, R.; Parisi, V.; Leone, O.; et al. Screening approaches to cardiac amyloidosis in different clinical settings: Current practice and future perspectives. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1146725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delbarre, M.A.; Chadha, G.D.; Annabi, M.S.; Nouri, R.; Zaroui, A.; Blanc-Durand, P.; Rasolonirina, D.; Kharoubi, M.; Bejan, A.; Galat, A.; et al. Wild-type transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis and aortic stenosis: Can carpal tunnel syndrome help distinguish the chicken from the egg? J. Intern. Med. 2025, 297, 186–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penalver, J.; Ambrosino, M.; Jeon, H.D.; Agrawal, A.; Kanjanahattakij, N.; Pitteloud, M.; Stempel, J.; Amanullah, A. Transthyretin Cardiac Amyloidosis and Aortic Stenosis: Connection and Therapeutic Implications. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2020, 16, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelli, F.; Perfetto, F.; Martone, R.; Di Mario, C. Cardiac Amyloidosis in Patients Undergoing TAVR: Why We Need to Think About It. Cardiovasc. Revasc. Med. 2021, 22, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonelli, A.; Paris, S.; Nardi, M.; Henein, M.Y.; Agricola, E.; Troise, G.; Faggiano, P. Aortic Valve Stenosis and Cardiac Amyloidosis: A Misleading Association. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.; El-Ali, A.; Morland, D.; Dejust, S.; Papathanassiou, D.; Nazeyrollas, P.; Metz, D. Cardiac amyloidosis prevalence and 1-year outcome in patients with aortic stenosis undergoing transaortic valve implantation: Findings from the CAMPOS-TAVI study. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2024, 117, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myasoedova, V.A.; Conte, M.; Valerio, V.; Moschetta, D.; Massaiu, I.; Petraglia, L.; Leosco, D.; Poggio, P.; Parisi, V. Red Flags, Prognostic Impact, and Management of Patients with Cardiac Amyloidosis and Aortic Valve Stenosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 858281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruberg, F.L.; Grogan, M.; Hanna, M.; Kelly, J.W.; Maurer, M.S. Transthyretin Amyloid Cardiomyopathy: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 2872–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, P.R.; Patel, K.P.; Treibel, T.A.; Thornton, G.D.; Hughes, R.K.; Chadalavada, S.; Katsoulis, M.; Hartman, N.; Fontana, M.; Pugliese, F.; et al. Prevalence and outcome of dual aortic stenosis and cardiac amyloid pathology in patients referred for transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 2759–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitsche, C.; Aschauer, S.; Kammerlander, A.A.; Schneider, M.; Poschner, T.; Duca, F.; Binder, C.; Koschutnik, M.; Stiftinger, J.; Goliasch, G.; et al. Light-chain and transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis in severe aortic stenosis: Prevalence, screening possibilities, and outcome. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 1852–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergaro, G.; Castiglione, V.; Aimo, A.; Prontera, C.; Masotti, S.; Musetti, V.; Nicol, M.; Cohen Solal, A.; Logeart, D.; Georgiopoulos, G.; et al. N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide and high-sensitivity troponin T hold diagnostic value in cardiac amyloidosis. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2023, 25, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.S.; Kor, Q.; Kong, W.K.; Lim, Y.C.; Chan, M.Y.; Syn, N.L.; Ngiam, J.N.; Chew, N.W.; Yeo, T.C.; Chai, P.; et al. Prevalence and outcomes of concomitant cardiac amyloidosis and aortic stenosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hell. J. Cardiol. 2022, 64, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.P.; Scully, P.R.; Nitsche, C.; Kammerlander, A.A.; Joy, G.; Thornton, G.; Hughes, R.; Williams, S.; Tillin, T.; Captur, G.; et al. Impact of afterload and infiltration on coexisting aortic stenosis and transthyretin amyloidosis. Heart 2022, 108, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsche, C.; Mascherbauer, J. Double trouble: Severe aortic stenosis and cardiac amyloidosis. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2020, 132, 705–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pibarot, P.; Lancellotti, P.; Narula, J. Concomitant Cardiac Amyloidosis in Severe Aortic Stenosis: The Trojan Horse? J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascoe, M.A.; Kolodziej, A.; Birks, E.J.; Vaidya, G. Using electronic medical records to identify patients at risk for underlying cardiac amyloidosis. J. Cardiol. 2025, 85, 43–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luke, P.; Alkhalil, M.; Eggett, C. Current and novel echocardiographic assessment of left ventricular systolic function in aortic stenosis—A comprehensive review. Echocardiography 2022, 39, 1470–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, W.E.; Turvey-Haigh, L.; Knight, D.; Coats, C.J.; Cooper, R.M.; Schofield, R.; Robinson, S.; Harkness, A.; Oxborough, D.L.; Gillmore, J.D.; et al. British Society of Echocardiography guideline for the transthoracic echocardiographic assessment of cardiac amyloidosis. Echo Res. Pract. 2023, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESC/EACTS Scientific Document Group. Corrigendum to: 2021 ESC/EACTS Guidelines for the management of valvular heart disease: Developed by the Task Force for the management of valvular heart disease of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Writing, C.; Kittleson, M.M.; Ruberg, F.L.; Ambardekar, A.V.; Brannagan, T.H.; Cheng, R.K.; Clarke, J.O.; Dember, L.M.; Frantz, J.G.; Hershberger, R.E.; et al. 2023 ACC Expert Consensus Decision Pathway on Comprehensive Multidisciplinary Care for the Patient With Cardiac Amyloidosis: A Report of the American College of Cardiology Solution Set Oversight Committee. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 81, 1076–1126. [Google Scholar]
- Jaiswal, V.; Ang, S.P.; Chia, J.E.; Abdelazem, E.M.; Jaiswal, A.; Biswas, M.; Gimelli, A.; Parwani, P.; Siller-Matula, J.M.; Mamas, M.A. Echocardiographic predictors of presence of cardiac amyloidosis in aortic stenosis. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 23, 1290–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, J.S.; Magne, J.; Pellikka, P.A.; Donal, E.; Marwick, T.H. Assessment of Subclinical Left Ventricular Dysfunction in Aortic Stenosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblum, H.; Masri, A.; Narotsky, D.L.; Goldsmith, J.; Hamid, N.; Hahn, R.T.; Kodali, S.; Vahl, T.; Nazif, T.; Khalique, O.K.; et al. Unveiling outcomes in coexisting severe aortic stenosis and transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2021, 23, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ternacle, J.; Krapf, L.; Mohty, D.; Magne, J.; Nguyen, A.; Galat, A.; Gallet, R.; Teiger, E.; Côté, N.; Clavel, M.-A.; et al. Aortic Stenosis and Cardiac Amyloidosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 2638–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelan, D.; Collier, P.; Thavendiranathan, P.; Popovic, Z.B.; Hanna, M.; Plana, J.C.; Marwick, T.H.; Thomas, J.D. Relative apical sparing of longitudinal strain using two-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography is both sensitive and specific for the diagnosis of cardiac amyloidosis. Heart 2012, 98, 1442–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, J.L.; Rijal, S.; Abdelkarim, I.; Althouse, A.D.; Sharbaugh, M.S.; Fridman, Y.; Soman, P.; Forman, D.E.; Schindler, J.T.; Gleason, T.G.; et al. Cardiac amyloidosis is prevalent in older patients with aortic stenosis and carries worse prognosis. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2017, 19, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhi, S.; Lorenzini, M.; Gagliardi, C.; Milandri, A.; Marzocchi, A.; Marrozzini, C.; Saia, F.; Ortolani, P.; Biagini, E.; Guidalotti, P.L.; et al. Coexistence of Degenerative Aortic Stenosis and Wild-Type Transthyretin-Related Cardiac Amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 9, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergaro, G.; Aimo, A.; Rapezzi, C.; Castiglione, V.; Fabiani, I.; Pucci, A.; Buda, G.; Passino, C.; Lupon, J.; Bayes-Genis, A.; et al. Atrial amyloidosis: Mechanisms and clinical manifestations. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2022, 24, 2019–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, D.J.; Han, Y.; Silvestry, F.E.; Ferrari, V.A. Atypical presentation of lipomatous hypertrophy of the interatrial septum: A case report. Eur. Heart J. Case Rep. 2019, 3, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rausch, K.; Scalia, G.M.; Sato, K.; Edwards, N.; Lam, A.K.; Platts, D.G.; Chan, J. Left atrial strain imaging differentiates cardiac amyloidosis and hypertensive heart disease. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2021, 37, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozbay, B.; Satyavolu, B.S.; Rearick, C.; Soman, P.; Katz, W.E.; Sezer, A.; Sade, L.E. Right Ventricular Strain Improves the Echocardiographic Diagnosis and Risk Stratification of Transthyretin Cardiac Amyloidosis Among Other Phenotypes of Left Ventricular Hypertrophy. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2024, 37, 947–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boldrini, M.; Cappelli, F.; Chacko, L.; Restrepo-Cordoba, M.A.; Lopez-Sainz, A.; Giannoni, A.; Aimo, A.; Baggiano, A.; Martinez-Naharro, A.; Whelan, C.; et al. Multiparametric Echocardiography Scores for the Diagnosis of Cardiac Amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, V.; Kong, W.K.F.; Bax, J.J. Myocardial fibrosis in severe aortic stenosis: How and when should we measure it? EuroIntervention 2020, 15, 1390–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, R.H.; Quarta, C.C.; Dorbala, S. How to image cardiac amyloidosis. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 7, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, S.; Lensing, S.Y.; Nairooz, R.S.; Pothineni, N.V.; Hakeem, A.; Bhatti, S.; Pandey, T. Prognostic Value of Late Gadolinium Enhancement CMR in Systemic Amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 9, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, T.; Jambhekar, K.; Shaikh, R.; Lensing, S.; Viswamitra, S. Utility of the inversion scout sequence (TI scout) in diagnosing myocardial amyloid infiltration. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 29, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.A.; Kerwin, M.J.; Salerno, M. Native T1 Mapping, Extracellular Volume Mapping, and Late Gadolinium Enhancement in Cardiac Amyloidosis: A Meta-Analysis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, 1299–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamitsos, T.D.; Piechnik, S.K.; Banypersad, S.M.; Fontana, M.; Ntusi, N.B.; Ferreira, V.M.; Whelan, C.J.; Myerson, S.G.; Robson, M.D.; Hawkins, P.N.; et al. Noncontrast T1 mapping for the diagnosis of cardiac amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 6, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawade, T.; Sheth, T.; Guzzetti, E.; Dweck, M.R.; Clavel, M.A. Why and How to Measure Aortic Valve Calcification in Patients With Aortic Stenosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, 1835–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ternacle, J.; Pibarot, P.; Clavel, M.A. Aortic Stenosis and Cardiac Amyloidosis: Watch Out for Traps! JACC Case Rep. 2020, 2, 2210–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, S.; Nakaura, T.; Utsunomiya, D.; Hirakawa, K.; Takashio, S.; Izumiya, Y.; Tsujita, K.; Hata, H.; Ando, Y.; Yamashita, Y. Late iodine enhancement and myocardial extracellular volume quantification in cardiac amyloidosis by using dual-energy cardiac computed tomography performed on a dual-layer spectral detector scanner. Amyloid 2018, 25, 137–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gama, F.; Rosmini, S.; Bandula, S.; Patel, K.P.; Massa, P.; Tobon-Gomez, C.; Ecke, K.; Stroud, T.; Condron, M.; Thornton, G.D.; et al. Extracellular Volume Fraction by Computed Tomography Predicts Long-Term Prognosis Among Patients with Cardiac Amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 15, 2082–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, P.R.; Patel, K.P.; Saberwal, B.; Klotz, E.; Augusto, J.B.; Thornton, G.D.; Hughes, R.K.; Manisty, C.; Lloyd, G.; Newton, J.D.; et al. Identifying Cardiac Amyloid in Aortic Stenosis: ECV Quantification by CT in TAVR Patients. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, 2177–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Bai, P.; Xu, H.-Y.; Li, Z.-L.; Xia, C.-C.; Zhou, X.; Gong, L.-G.; Guo, Y.-K. Distinguishing Cardiac Amyloidosis and Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy by Thickness and Myocardial Deformation of the Right Ventricle. Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2022, 2022, 4364279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillmore, J.D.; Maurer, M.S.; Falk, R.H.; Merlini, G.; Damy, T.; Dispenzieri, A.; Wechalekar, A.D.; Berk, J.L.; Quarta, C.C.; Grogan, M.; et al. Nonbiopsy Diagnosis of Cardiac Transthyretin Amyloidosis. Circulation 2016, 133, 2404–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapezzi, C.; Giannini, F.; Campo, G. Aortic stenosis, transcatheter aortic valve replacement and transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis: Are we progressively unraveling the tangle? Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2021, 23, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, S.; Mahara, K.; Beussink-Nelson, L.; Ikura, H.; Katsumata, Y.; Endo, J.; Gaggin, H.K.; Shah, S.J.; Itabashi, Y.; MacRae, C.A.; et al. Artificial intelligence-enabled fully automated detection of cardiac amyloidosis using electrocardiograms and echocardiograms. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiri, I.; Balzer, S.; Baj, G.; Bernhard, B.; Hundertmark, M.; Bakula, A.; Nakase, M.; Tomii, D.; Barbati, G.; Dobner, S.; et al. Multi-modality artificial intelligence-based transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy detection in patients with severe aortic stenosis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2025, 52, 485–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereyra Pietri, M.; Farina, J.M.; Mahmoud, A.K.; Scalia, I.G.; Galasso, F.; Killian, M.E.; Suppah, M.; Kenyon, C.R.; Koepke, L.M.; Padang, R.; et al. The prognostic value of artificial intelligence to predict cardiac amyloidosis in patients with severe aortic stenosis undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement. Eur. Heart J. Digit. Health 2024, 5, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, J.M.; Nuis, R.J.; de Jaegere, P.P.T. Artificial intelligence-empowered treatment decision-making in patients with aortic stenosis via early detection of cardiac amyloidosis. Eur. Heart J. Digit. Health 2024, 5, 505–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porcari, A.; Cappelli, F.; Nitsche, C.; Tomasoni, D.; Sinigiani, G.; Longhi, S.; Bordignon, L.; Masri, A.; Serenelli, M.; Urey, M.; et al. SGLT2 Inhibitor Therapy in Patients With Transthyretin Amyloid Cardiomyopathy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2024, 83, 2411–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolisso, P.; Belmonte, M.; Gallinoro, E.; Scarsini, R.; Bergamaschi, L.; Portolan, L.; Armillotta, M.; Esposito, G.; Moscarella, E.; Benfari, G.; et al. SGLT2-inhibitors in diabetic patients with severe aortic stenosis and cardiac damage undergoing transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI). Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperry, B.W. Coprevalence of Amyloidosis and Aortic Stenosis: When to Screen and Who to Treat? J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2025, 14, e038279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannata, F.; Chiarito, M.; Pinto, G.; Villaschi, A.; Sanz-Sanchez, J.; Fazzari, F.; Regazzoli, D.; Mangieri, A.; Bragato, R.M.; Colombo, A.; et al. Transcatheter aortic valve replacement in aortic stenosis and cardiac amyloidosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. ESC Heart Fail. 2022, 9, 3188–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, J.M.; Junarta, J.; Ullah, W.; Siddiqui, M.U.; Anzelmi, A.; Ruge, M.; Vishnevsky, A.; Alvarez, R.J.; Ruggiero, N.J.; Rajapreyar, I.N.; et al. Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation in Cardiac Amyloidosis and Aortic Stenosis. Am. J. Cardiol. 2023, 198, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismayl, M.; Abbasi, M.; Al-Abcha, A.; El-Am, E.; Alkhouli, M.; Guerrero, M.; Dispenzieri, A.; Nkomo, V.T.; Abou Ezzeddine, O.F.; Grogan, M.; et al. Outcomes of transcatheter aortic valve replacement in patients with and without amyloidosis: A nationwide analysis from the United States. Cardiovasc. Revasc. Med. 2024, 58, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsche, C.; Koschutnik, M.; Dona, C.; Radun, R.; Mascherbauer, K.; Kammerlander, A.; Heitzinger, G.; Dannenberg, V.; Spinka, G.; Halavina, K.; et al. Reverse Remodeling Following Valve Replacement in Coexisting Aortic Stenosis and Transthyretin Cardiac Amyloidosis. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 15, e014115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argiro, A.; Cappelli, F.; Di Mario, C. Aortic Stenosis and Cardiac Amyloidosis: PARTNERs in Crime? Cardiovasc. Revasc. Med. 2022, 43, 26–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.; Brailovsky, Y.; Vishnevsky, O.A.; Baqi, A.; Patel, K.; Alvarez, R.J. Clinical Outcome of TAVR vs. SAVR in Patients With Cardiac Amyloidosis. Cardiovasc. Revasc. Med. 2022, 43, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masri, A.; Chen, Y.; Colavecchia, A.C.; Benjumea, D.; Crowley, A.; Jhingran, P.; Kent, M.; Wogen, J.; Pankratova, C.; Jimenez Alvir, J.M.; et al. Coexisting Calcific Aortic Stenosis and Transthyretin Cardiac Amyloidosis: Real-World Evaluation of Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2025, 14, e033251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, T.; Uddin, M.; Ulbeh, T.M.; Perveiz, E.; Lohia, P.; Sattar, Y.; Abohashem, S.; Ullah, W.; Maganti, K.; Qureshi, W.T.; et al. Clinical Outcomes of Aortic Stenosis in Amyloidosis: A United States National Cohort Study. Heart Lung Circ. 2024, 33, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.; Ahsan, M.J.; Newlun, M.; Sand, M.; Rmilah, A.A.; Yousaf, A.; Shabbir, M.A.; Malik, S.A.; Goldsweig, A.M. Outcomes of aortic stenosis in patients with cardiac amyloidosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiovasc. Revasc. Med. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, J.M.; Rosenthal, J.L.; Grodin, J.L.; Maurer, M.S.; Grogan, M.; Cheng, R.K. ATTR Amyloidosis: Current and Emerging Management Strategies: JACC: CardioOncology State-of-the-Art Review. JACC CardioOncol. 2021, 3, 488–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, M.S.; Schwartz, J.H.; Gundapaneni, B.; Elliott, P.M.; Merlini, G.; Waddington-Cruz, M.; Kristen, A.V.; Grogan, M.; Witteles, R.; Damy, T.; et al. Tafamidis Treatment for Patients with Transthyretin Amyloid Cardiomyopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judge, D.P.; Heitner, S.B.; Falk, R.H.; Maurer, M.S.; Shah, S.J.; Witteles, R.M.; Grogan, M.; Selby, V.N.; Jacoby, D.; Hanna, M.; et al. Transthyretin Stabilization by AG10 in Symptomatic Transthyretin Amyloid Cardiomyopathy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillmore, J.D.; Judge, D.P.; Cappelli, F.; Fontana, M.; Garcia-Pavia, P.; Gibbs, S.; Grogan, M.; Hanna, M.; Hoffman, J.; Masri, A.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Acoramidis in Transthyretin Amyloid Cardiomyopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razvi, Y.; Judge, D.P.; Martinez-Naharro, A.; Ioannou, A.; Venneri, L.; Patel, R.; Gillmore, J.D.; Kellman, P.; Edwards, L.; Taubel, J.; et al. Effect of Acoramidis on Myocardial Structure and Function in Transthyretin Amyloid Cardiomyopathy: Insights From the ATTRibute-CM Cardiac Magnetic Resonance (CMR) Substudy. Circ. Heart Fail. 2024, 17, e012135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judge, D.P.; Gillmore, J.D.; Alexander, K.M.; Ambardekar, A.V.; Cappelli, F.; Fontana, M.; Garcia-Pavia, P.; Grodin, J.L.; Grogan, M.; Hanna, M.; et al. Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of Acoramidis in ATTR-CM: Initial Report From the Open-Label Extension of the ATTRibute-CM Trial. Circulation 2024, 151, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.; Gonzalez-Duarte, A.; O’Riordan, W.D.; Yang, C.C.; Ueda, M.; Kristen, A.V.; Tournev, I.; Schmidt, H.H.; Coelho, T.; Berk, J.L.; et al. Patisiran, an RNAi Therapeutic, for Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, M.S.; Kale, P.; Fontana, M.; Berk, J.L.; Grogan, M.; Gustafsson, F.; Hung, R.R.; Gottlieb, R.L.; Damy, T.; Gonzalez-Duarte, A.; et al. Patisiran Treatment in Patients with Transthyretin Cardiac Amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1553–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, M.; Maurer, M.S.; Gillmore, J.D.; Bender, S.; Jay, P.Y.; Solomon, S.D. Worsening of Heart Failure in Outpatients with Transthyretin Amyloidosis and Cardiomyopathy in the APOLLO-B Trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2024, 85, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, M.D.; Waddington-Cruz, M.; Berk, J.L.; Polydefkis, M.; Dyck, P.J.; Wang, A.K.; Plante-Bordeneuve, V.; Barroso, F.A.; Merlini, G.; Obici, L.; et al. Inotersen Treatment for Patients with Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, M.; Berk, J.L.; Gillmore, J.D.; Witteles, R.M.; Grogan, M.; Drachman, B.; Damy, T.; Garcia-Pavia, P.; Taubel, J.; Solomon, S.D.; et al. Vutrisiran in Patients with Transthyretin Amyloidosis with Cardiomyopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masri, A.; Maurer, M.S.; Claggett, B.L.; Kulac, I.; Waddington Cruz, M.; Conceicao, I.; Weiler, M.; Berk, J.L.; Gertz, M.; Gillmore, J.D.; et al. Effect of Eplontersen on Cardiac Structure and Function in Patients With Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis. J. Card. Fail. 2024, 30, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Pavia, P.; Aus dem Siepen, F.; Donal, E.; Lairez, O.; van der Meer, P.; Kristen, A.V.; Mercuri, M.F.; Michalon, A.; Frost, R.J.A.; Grimm, J.; et al. Phase 1 Trial of Antibody NI006 for Depletion of Cardiac Transthyretin Amyloid. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechalekar, A.; Antoni, G.; Al Azzam, W.; Bergstrom, M.; Biswas, S.; Chen, C.; Cheriyan, J.; Cleveland, M.; Cookson, L.; Galette, P.; et al. Pharmacodynamic evaluation and safety assessment of treatment with antibodies to serum amyloid P component in patients with cardiac amyloidosis: An open-label Phase 2 study and an adjunctive immuno-PET imaging study. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2022, 22, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

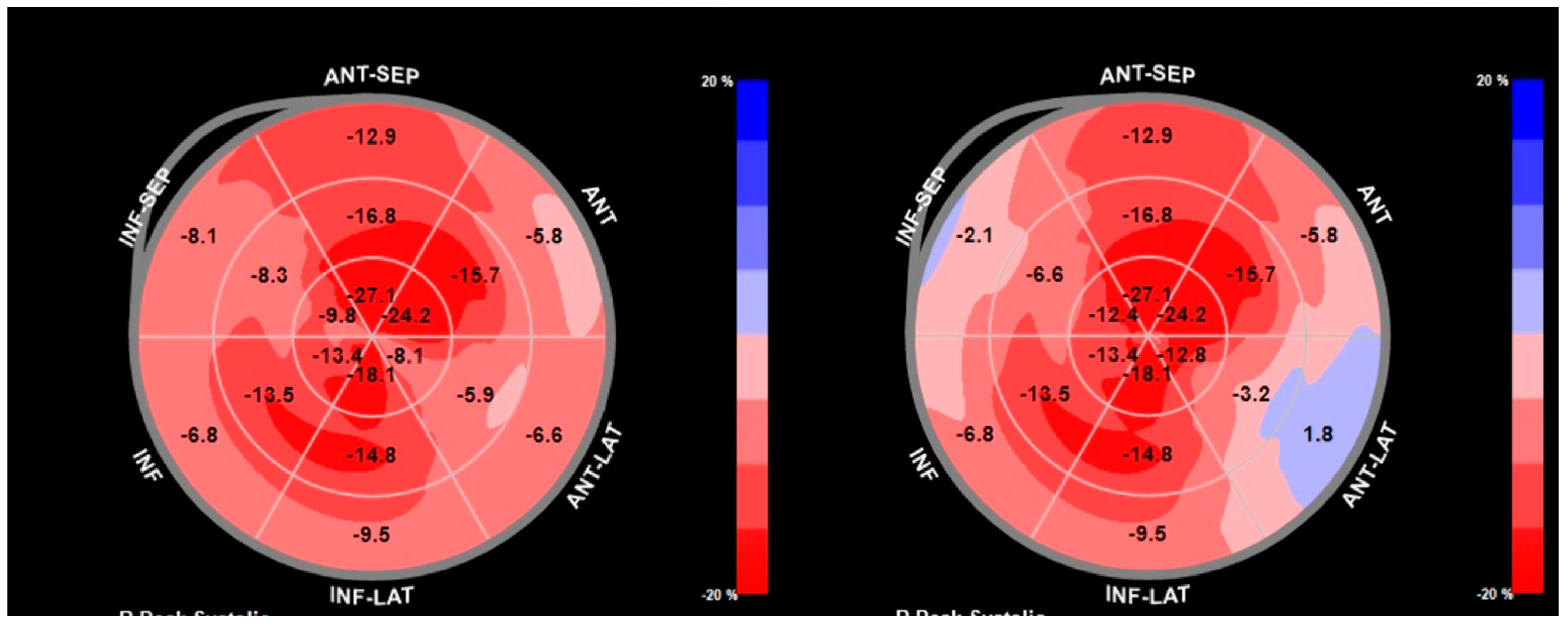
| Characteristics | AS | AS-CA |
|---|---|---|
| LGE pattern | Patchy/mid-wall and localized fibrosis | Global subendocardial/transmural |
| T1 mapping | Mildly elevated | Markedly elevated |
| ECV fraction | Mildly elevated | Highly elevated (>40–50%) |
| Nulling pattern | Normal nulling | Abnormal nulling (blood nulls before myocardium) |
| Atrial size | Left atrial enlargement | Bi-atrial enlargement |
| Right ventricular involvement | Uncommon | Frequent |
| Study | Design and Population | Sample Size | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Myasoedova et al. (2022) [39] | Systematic review and meta-analysis | 10 studies (330 AS-CA patients) | SAVR and TAVR had a similar overall mortality risk but were lower than medication-treated only patients |
| Khan et al. (2022) [91] | Retrospective cohort | 208,540 patients—TAVR (18,745, 8.9%) and SAVR (189,795, 91.01%) | SAVR was associated with higher rates of acute kidney injury, acute myocardial infarction, and major bleeding compared to TAVR. The TAVR group had a higher incidence of stroke, vascular complications, and permanent pacemaker implantation. In the SAVR group, mortality was higher in 2011 and 2014 but was not statistically different in 2010, 2012, and 2013. The length of stay was longer, and the cost was higher in the SAVR group annually compared to the TAVR group |
| Mir et al. (2024) [93] | Retrospective study—national cohort study | 4820 patients AS-CA (464 intervention: 251 TAVR, 213 SAVR) | AS patients with amyloidosis and in-hospital mortality were significantly lower for patients undergoing TAVR (4.4%) compared to SAVR (11.9%). Complications such as acute kidney injury, sepsis, and cardiogenic shock were more frequent in the SAVR group Acute heart failure was higher among patients who had TAVR All conduction blocks and cases of ischemic stroke were similar between the two groups (p = 0.09 and p = 0.1) |
| Masri et al. (2025) [92] | Retrospective analysis | 1239 patients | Patients with AS-CA who underwent TAVR showed no significant difference in mortality or major cardiovascular events compared to those who underwent SAVRTAVR patients were older and had more comorbidities, including HF and chronic kidney disease, yet outcomes were similar between the two procedures |
| Ahmad et al. (2025) [94] | Systematic review and meta-analysis | 15 studies (6704 patients) | TAVR was associated with lower all-cause mortality compared to both medical therapy (RR = 0.50, 95% CI 0.29–0.89, p = 0.02) and SAVR (RR = 0.41, 95% CI 0.22–0.78, p = 0.007) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gialamas, I.; Zakynthinos, G.E.; Dimeas, G.; Pantelidis, P.; Gialafos, E.; Brili, S.; Goliopoulou, A.; Katsarou, O.; Tryfou, E.; Kalogeras, K.; et al. A Tale of Two Diseases: Decoding Aortic Stenosis and Cardiac Amyloidosis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2652. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082652
Gialamas I, Zakynthinos GE, Dimeas G, Pantelidis P, Gialafos E, Brili S, Goliopoulou A, Katsarou O, Tryfou E, Kalogeras K, et al. A Tale of Two Diseases: Decoding Aortic Stenosis and Cardiac Amyloidosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(8):2652. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082652
Chicago/Turabian StyleGialamas, Ioannis, George E. Zakynthinos, George Dimeas, Panteleimon Pantelidis, Elias Gialafos, Styliani Brili, Athina Goliopoulou, Ourania Katsarou, Elsi Tryfou, Konstantinos Kalogeras, and et al. 2025. "A Tale of Two Diseases: Decoding Aortic Stenosis and Cardiac Amyloidosis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 8: 2652. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082652
APA StyleGialamas, I., Zakynthinos, G. E., Dimeas, G., Pantelidis, P., Gialafos, E., Brili, S., Goliopoulou, A., Katsarou, O., Tryfou, E., Kalogeras, K., Siasos, G., & Oikonomou, E. (2025). A Tale of Two Diseases: Decoding Aortic Stenosis and Cardiac Amyloidosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(8), 2652. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082652








