Beyond Pulmonary Vein Reconnection: Exploring the Dynamic Pathophysiology of Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence After Catheter Ablation
Abstract
1. Introduction
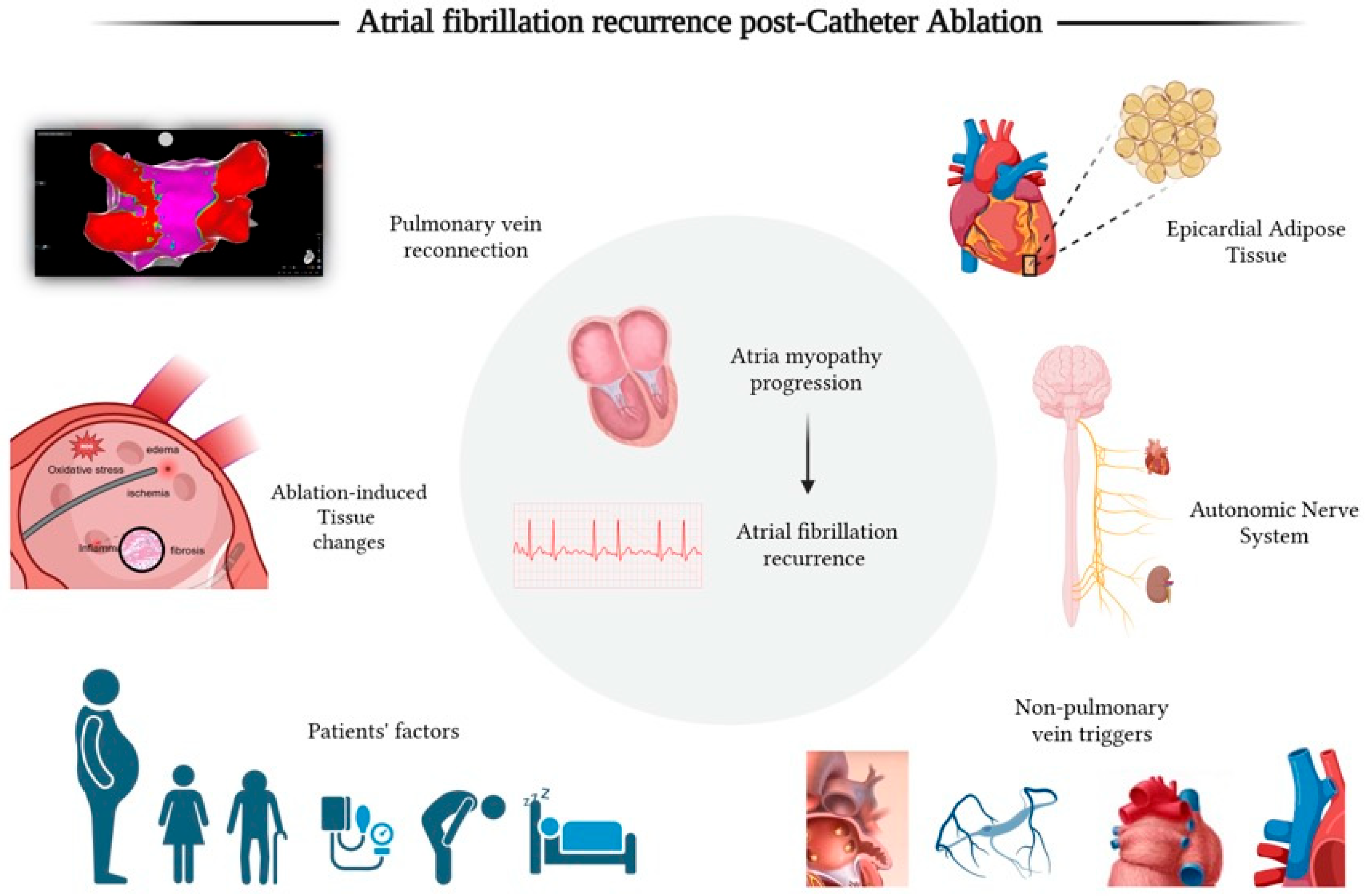
2. Pathophysiology of Afib Recurrence After Catheter Ablation
2.1. Pre-Ablation Atrial Substrate and Patients’ Factors
2.2. Ablation-Induced Myocardial Injury, Inflammation, and Atrial Fibrosis
2.3. Pulmonary Vein Reconnection
2.4. Non-Pulmonary Vein Triggers
2.5. Autonomic Nervous System Modulation
2.6. Epicardial Adipose Tissue (EAT)
3. Current State and Future Directions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lip, G.Y.; Beevers, D.G. ABC of atrial fibrillation. History, epidemiology, and importance of atrial fibrillation. BMJ 1995, 311, 1361–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chugh, S.S.; Havmoeller, R.; Narayanan, K.; Singh, D.; Rienstra, M.; Benjamin, E.J.; Gillum, R.F.; Kim, Y.H.; McAnulty, J.H., Jr.; Zheng, Z.J.; et al. Worldwide epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: A Global Burden of Disease 2010 Study. Circulation 2014, 129, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Wolf, P.A.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Silbershatz, H.; Kannel, W.B.; Levy, D. Impact of atrial fibrillation on the risk of death: The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 1998, 98, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachakis, P.K.; Tsiachris, D.; Doundoulakis, I.; Tsioufis, P.; Kordalis, A.; Botis, M.; Leontsinis, I.; Antoniou, C.K.; Papachrysostomou, C.; Dimitroula, V.; et al. Therapeutic inertia in rhythm control strategies in hospitalized patients with fibrillation: Insights from Hellenic Cardiorenal Morbidity Snapshot (HECMOS) study. J. Cardiol. 2024, 83, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haissaguerre, M.; Jais, P.; Shah, D.C.; Takahashi, A.; Hocini, M.; Quiniou, G.; Garrigue, S.; Le Mouroux, A.; Le Metayer, P.; Clementy, J. Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, D.L.; Mark, D.B.; Robb, R.A.; Monahan, K.H.; Bahnson, T.D.; Poole, J.E.; Noseworthy, P.A.; Rosenberg, Y.D.; Jeffries, N.; Mitchell, L.B.; et al. Effect of Catheter Ablation vs Antiarrhythmic Drug Therapy on Mortality, Stroke, Bleeding, and Cardiac Arrest Among Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: The CABANA Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2019, 321, 1261–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, D.L.; Kowal, R.C.; Wheelan, K.R.; Irwin, J.M.; Champagne, J.; Guerra, P.G.; Dubuc, M.; Reddy, V.; Nelson, L.; Holcomb, R.G.; et al. Cryoballoon ablation of pulmonary veins for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: First results of the North American Arctic Front (STOP AF) pivotal trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 61, 1713–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulai, R.; Sulke, N.; Freemantle, N.; Lambiase, P.D.; Farwell, D.; Srinivasan, N.T.; Tan, S.; Patel, N.; Graham, A.; Veasey, R.A. Pulmonary Vein Isolation vs Sham Intervention in Symptomatic Atrial Fibrillation: The SHAM-PVI Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2024, 332, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calkins, H.; Kuck, K.H.; Cappato, R.; Brugada, J.; Camm, A.J.; Chen, S.A.; Crijns, H.J.; Damiano, R.J., Jr.; Davies, D.W.; DiMarco, J.; et al. 2012 HRS/EHRA/ECAS Expert Consensus Statement on Catheter and Surgical Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation: Recommendations for patient selection, procedural techniques, patient management and follow-up, definitions, endpoints, and research trial design. Europace 2012, 14, 528–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzeis, S.; Gerstenfeld, E.P.; Kalman, J.; Saad, E.B.; Sepehri Shamloo, A.; Andrade, J.G.; Barbhaiya, C.R.; Baykaner, T.; Boveda, S.; Calkins, H.; et al. 2024 European Heart Rhythm Association/Heart Rhythm Society/Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society/Latin American Heart Rhythm Society expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation. Europace 2024, 26, euae043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leventopoulos, G.; Koros, R.; Travlos, C.; Perperis, A.; Chronopoulos, P.; Tsoni, E.; Koufou, E.E.; Papageorgiou, A.; Apostolos, A.; Kaouris, P.; et al. Mechanisms of Atrial Fibrillation: How Our Knowledge Affects Clinical Practice. Life 2023, 13, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudis, C.A.; Kallergis, E.M.; Vardas, P.E. Extracellular matrix alterations in the atria: Insights into the mechanisms and perpetuation of atrial fibrillation. Europace 2012, 14, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.T.; Kim, I.S.; Kim, T.H.; Uhm, J.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Joung, B.; Lee, M.H.; Pak, H.N. Persistent atrial fibrillation over 3 years is associated with higher recurrence after catheter ablation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2020, 31, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, D.S.; Black-Maier, E.; Loring, Z.; Noseworthy, P.A.; Packer, D.L.; Exner, D.V.; Mark, D.B.; Piccini, J.P. Diagnosis-to-Ablation Time and Recurrence of Atrial Fibrillation Following Catheter Ablation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2020, 13, e008128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehmer, A.A.; Rothe, M.; Wiedenmann, L.; Nussbaum, E.; Schneider, K.Y.; Spork, P.; Keim, C.; Dobre, B.C.; Kaess, B.M.; Ehrlich, J.R. Impact of age on atrial arrhythmia recurrence following cryoballoon pulmonary-vein isolation. EP Eur. 2024, 26, euae102.139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehmer, A.A.; Rothe, M.; Ruckes, C.; Eckardt, L.; Kaess, B.M.; Ehrlich, J.R. Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation in Elderly Patients: An Updated Meta-analysis of Comparative Studies. Can. J. Cardiol. 2024, 40, 2441–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar-Neves, I.; Sa Carvalho, A.; Diaz, S.O.; Ribeiro Silva, M.; Santos Silva, G.; Teixeira, R.; Lopes Fernandes, S.; Cruz, I.; Almeida, J.G.; Fonseca, P.; et al. Sex-based differences and risk of recurrence in patients with atrial fibrillation undergoing pulmonary vein isolation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2024, 409, 132161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifci, G.; Wen, S.; Pislaru, S.V.; Pellikka, P.A.; Kane, G.C.; Asirvatham, S.J.; Pislaru, C. Left atrial stiffness and sex differences in atrial fibrillation recurrence after catheter ablation. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, ehad655.019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, H.N.; Park, J.W.; Yang, S.Y.; Kim, M.; Yu, H.T.; Kim, T.H.; Uhm, J.S.; Joung, B.; Lee, M.H. Sex differences in mapping and rhythm outcomes of a repeat atrial fibrillation ablation. Heart 2021, 107, 1862–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takigawa, M.; Kuwahara, T.; Takahashi, A.; Watari, Y.; Okubo, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Takagi, K.; Kuroda, S.; Osaka, Y.; Kawaguchi, N.; et al. Differences in catheter ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation between males and females. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 1984–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koniari, I.; Bozika, M.; Nastouli, K.M.; Tzegka, D.; Apostolos, A.; Velissaris, D.; Leventopoulos, G.; Perperis, A.; Kounis, N.G.; Tsigkas, G.; et al. The Role of Early Risk Factor Modification and Ablation in Atrial Fibrillation Substrate Remodeling Prevention. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medi, C.; Kalman, J.M.; Spence, S.J.; Teh, A.W.; Lee, G.; Bader, I.; Kaye, D.M.; Kistler, P.M. Atrial electrical and structural changes associated with longstanding hypertension in humans: Implications for the substrate for atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2011, 22, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrid, A.H.; Peng, J.; Zamora, J.; Marin, I.; Bernal, E.; Escobar, C.; Munos-Tinoco, C.; Rebollo, J.M.; Moro, C. The role of angiotensin receptor blockers and/or angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors in the prevention of atrial fibrillation in patients with cardiovascular diseases: Meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 2004, 27, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Xia, Y.L.; Zhang, S.L.; Gao, L.J.; Xie, Z.Z.; Yang, Y.Z.; Zhao, J. The impact of hypertension on the electromechanical properties and outcome of catheter ablation in atrial fibrillation patients. J. Thorac. Dis. 2014, 6, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdecchia, P.; Reboldi, G.; Gattobigio, R.; Bentivoglio, M.; Borgioni, C.; Angeli, F.; Carluccio, E.; Sardone, M.G.; Porcellati, C. Atrial fibrillation in hypertension: Predictors and outcome. Hypertension 2003, 41, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakasis, P.; Patoulias, D.; Popovic, D.S.; Pamporis, K.; Theofilis, P.; Nasoufidou, A.; Stachteas, P.; Samaras, A.; Tzikas, A.; Giannakoulas, G.; et al. Effects of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists on new-onset or recurrent atrial fibrillation: A Bayesian and frequentist network meta-analysis of randomized trials. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2024, 49, 102742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, R.K.; Conen, D.; Tedrow, U.B.; Fitzgerald, K.C.; Pradhan, A.D.; Ridker, P.M.; Glynn, R.J.; Albert, C.M. Predisposing factors associated with development of persistent compared with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, e000916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkle, R.A.; Mead, R.H.; Engel, G.; Kong, M.H.; Fleming, W.; Salcedo, J.; Patrawala, R.A. Impact of obesity on atrial fibrillation ablation: Patient characteristics, long-term outcomes, and complications. Heart Rhythm 2017, 14, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, R.; Lau, D.H.; Brooks, A.G.; Shipp, N.J.; Wood, J.P.M.; Manavis, J.; Samuel, C.S.; Patel, K.P.; Finnie, J.W.; Alasady, M.; et al. Atrial Fibrillation and Obesity: Reverse Remodeling of Atrial Substrate With Weight Reduction. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2021, 7, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, R.K.; Middeldorp, M.E.; Meredith, M.; Mehta, A.B.; Mahajan, R.; Wong, C.X.; Twomey, D.; Elliott, A.D.; Kalman, J.M.; Abhayaratna, W.P.; et al. Long-Term Effect of Goal-Directed Weight Management in an Atrial Fibrillation Cohort: A Long-Term Follow-Up Study (LEGACY). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 2159–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, R.K.; Middeldorp, M.E.; Lau, D.H.; Mehta, A.B.; Mahajan, R.; Twomey, D.; Alasady, M.; Hanley, L.; Antic, N.A.; McEvoy, R.D.; et al. Aggressive risk factor reduction study for atrial fibrillation and implications for the outcome of ablation: The ARREST-AF cohort study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 64, 2222–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McManus, D.D.; Yin, X.; Gladstone, R.; Vittinghoff, E.; Vasan, R.S.; Larson, M.G.; Benjamin, E.J.; Marcus, G.M. Alcohol Consumption, Left Atrial Diameter, and Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e004060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Shi, R.; Hou, B.; Wu, L.; Zheng, L.; Ding, L.; Chen, G.; Zhang, S.; Yao, Y. Impact of Alcohol Consumption on Substrate Remodeling and Ablation Outcome of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4, e002349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottlieb, L.A.; Dekker, L.R.C.; Coronel, R. The Blinding Period Following Ablation Therapy for Atrial Fibrillation: Proarrhythmic and Antiarrhythmic Pathophysiological Mechanisms. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2021, 7, 416–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, J.G.; Macle, L.; Khairy, P.; Khaykin, Y.; Mantovan, R.; De Martino, G.; Chen, J.; Morillo, C.A.; Novak, P.; Guerra, P.G.; et al. Incidence and significance of early recurrences associated with different ablation strategies for AF: A STAR-AF substudy. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2012, 23, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.I.; Pak, H.N.; Park, J.S.; Kwak, J.J.; Nagamoto, Y.; Lim, H.E.; Park, S.W.; Hwang, C.; Kim, Y.H. Clinical significance of early recurrences of atrial tachycardia after atrial fibrillation ablation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2010, 21, 1331–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calkins, H.; Hindricks, G.; Cappato, R.; Kim, Y.H.; Saad, E.B.; Aguinaga, L.; Akar, J.G.; Badhwar, V.; Brugada, J.; Camm, J.; et al. 2017 HRS/EHRA/ECAS/APHRS/SOLAECE expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 2017, 14, e275–e444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.S.; Schultz, C.; Dang, J.; Alasady, M.; Lau, D.H.; Brooks, A.G.; Wong, C.X.; Roberts-Thomson, K.C.; Young, G.D.; Worthley, M.I.; et al. Time course of inflammation, myocardial injury, and prothrombotic response after radiofrequency catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2014, 7, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizilirmak, F.; Gokdeniz, T.; Gunes, H.M.; Demir, G.G.; Cakal, B.; Guler, G.B.; Guler, E.; Olgun, F.E.; Kilicaslan, F. Myocardial injury biomarkers after radiofrequency catheter and cryoballoon ablation for atrial fibrillation and their impact on recurrence. Kardiol. Pol. 2017, 75, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Yui, Y.; Kimata, A.; Koda, N.; Kato, J.; Baba, M.; Misaki, M.; Abe, D.; Tokunaga, C.; Akishima, S.; et al. Troponin elevation after radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: Relevance to AF substrate, procedural outcomes, and reverse structural remodeling. Heart Rhythm 2014, 11, 1336–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castano, A.; Crawford, T.; Yamazaki, M.; Avula, U.M.; Kalifa, J. Coronary artery pathophysiology after radiofrequency catheter ablation: Review and perspectives. Heart Rhythm 2011, 8, 1975–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.L.; De Venecia, T.; Patnaik, S.; Figueredo, V.M. Atrial myocardial infarction: A tale of the forgotten chamber. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 202, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinno, H.; Derakhchan, K.; Libersan, D.; Merhi, Y.; Leung, T.K.; Nattel, S. Atrial ischemia promotes atrial fibrillation in dogs. Circulation 2003, 107, 1930–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, K.; Qi, X.Y.; Wakili, R.; Comtois, P.; Chartier, D.; Harada, M.; Iwasaki, Y.K.; Romeo, P.; Maguy, A.; Dobrev, D.; et al. Mechanisms of atrial tachyarrhythmias associated with coronary artery occlusion in a chronic canine model. Circulation 2011, 123, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleber, A.G. ST-segment elevation in the electrocardiogram: A sign of myocardial ischemia. Cardiovasc. Res. 2000, 45, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, J.R.; Coronel, R. Acute ischemia-induced gap junctional uncoupling and arrhythmogenesis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004, 62, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorisch, W.; Boergen, K.P. Heat-induced contraction of blood vessels. Lasers Surg. Med. 1982, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasady, M.; Abhayaratna, W.P.; Leong, D.P.; Lim, H.S.; Abed, H.S.; Brooks, A.G.; Mattchoss, S.; Roberts-Thomson, K.C.; Worthley, M.I.; Chew, D.P.; et al. Coronary artery disease affecting the atrial branches is an independent determinant of atrial fibrillation after myocardial infarction. Heart Rhythm 2011, 8, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bakker, J.M.; van Capelle, F.J.; Janse, M.J.; Tasseron, S.; Vermeulen, J.T.; de Jonge, N.; Lahpor, J.R. Slow conduction in the infarcted human heart. ‘Zigzag’ course of activation. Circulation 1993, 88, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, K.J.; Miklavcic, D.; Vlachos, K.; Bordignon, S.; Scherr, D.; Jais, P.; Schmidt, B. State-of-the-art pulsed field ablation for cardiac arrhythmias: Ongoing evolution and future perspective. Europace 2024, 26, euae134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohm, A.; Tothova, L.; Urban, L.; Slezak, P.; Bacharova, L.; Musil, P.; Hatala, R. The relation between oxidative stress biomarkers and atrial fibrillation after pulmonary veins isolation. J. Electrocardiol. 2016, 49, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, B.; Gwechenberger, M.; Socas, A.; Zorn, G.; Albinni, S.; Marx, M.; Bergler-Klein, J.; Binder, T.; Wojta, J.; Gossinger, H.D. Markers of oxidative stress after ablation of atrial fibrillation are associated with inflammation, delivered radiofrequency energy and early recurrence of atrial fibrillation. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2012, 101, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerasooriya, R.; Jais, P.; Sanders, P.; Scavee, C.; Hsu, L.F.; Hocini, M.; Clementy, J.; Haissaguerre, M. Images in cardiovascular medicine. Early appearance of an edematous tissue reaction during left atrial linear ablation using intracardiac echo imaging. Circulation 2003, 108, e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, M.A.; Pozzoli, A.; Maat, G.; Alfieri, O.R.; Benussi, S. What Does The Blanking Period Blank? J. Atr. Fibrillation 2015, 8, 1268. [Google Scholar]
- Veeraraghavan, R.; Lin, J.; Hoeker, G.S.; Keener, J.P.; Gourdie, R.G.; Poelzing, S. Sodium channels in the Cx43 gap junction perinexus may constitute a cardiac ephapse: An experimental and modeling study. Pflug. Arch. 2015, 467, 2093–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.Y.; Sorota, S. Cardiac swelling-induced chloride current depolarizes canine atrial myocytes. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 272, H1904–H1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, J.M.; Smith, L.M.; Tseng, Z.H.; Badhwar, N.; Lee, B.K.; Lee, R.J.; Scheinman, M.M.; Olgin, J.E.; Marcus, G.M. Protracted CRP elevation after atrial fibrillation ablation. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 2008, 31, 1146–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.R.; Nam, G.B.; Han, S.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Choi, K.J.; Kim, Y.H. Effect of Short-Term Steroid Therapy on Early Recurrence During the Blanking Period After Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2015, 8, 1366–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heijman, J.; Muna, A.P.; Veleva, T.; Molina, C.E.; Sutanto, H.; Tekook, M.; Wang, Q.; Abu-Taha, I.H.; Gorka, M.; Kunzel, S.; et al. Atrial Myocyte NLRP3/CaMKII Nexus Forms a Substrate for Postoperative Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 1036–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Veleva, T.; Scott, L., Jr.; Cao, S.; Li, L.; Chen, G.; Jeyabal, P.; Pan, X.; Alsina, K.M.; Abu-Taha, I.D.; et al. Enhanced Cardiomyocyte NLRP3 Inflammasome Signaling Promotes Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2018, 138, 2227–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachakis, P.K.; Theofilis, P.; Kachrimanidis, I.; Giannakopoulos, K.; Drakopoulou, M.; Apostolos, A.; Kordalis, A.; Leontsinis, I.; Tsioufis, K.; Tousoulis, D. The Role of Inflammasomes in Heart Failure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachakis, P.K.; Theofilis, P.; Kordalis, A.; Tousoulis, D. Systemic immune inflammation index as a predictor for atrial fibrillation recurrence after catheter ablation. World J. Cardiol. 2025, 17, 103993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, L., Jr.; Fender, A.C.; Saljic, A.; Li, L.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Linz, D.; Lang, J.; Hohl, M.; Twomey, D.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasome is a key driver of obesity-induced atrial arrhythmias. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117, 1746–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.S.; Chen, L.S.; Fishbein, M.C.; Lin, S.F.; Nattel, S. Role of the autonomic nervous system in atrial fibrillation: Pathophysiology and therapy. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 1500–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyama, Y.; Pak, H.N.; Miyauchi, Y.; Liu, Y.B.; Chou, C.C.; Hayashi, H.; Fu, K.J.; Kerwin, W.F.; Kar, S.; Hata, C.; et al. Nerve sprouting induced by radiofrequency catheter ablation in dogs. Heart Rhythm 2004, 1, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, W.J.; Clarke, S.A.; Quinn, T.A.; Holmes, J.W. Physiological Implications of Myocardial Scar Structure. Compr. Physiol. 2015, 5, 1877–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakasis, P.; Theofilis, P.; Vlachakis, P.K.; Korantzopoulos, P.; Patoulias, D.; Antoniadis, A.P.; Fragakis, N. Atrial Fibrosis in Atrial Fibrillation: Mechanistic Insights, Diagnostic Challenges, and Emerging Therapeutic Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 26, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, B.R.; Jarrett, T.R.; Kholmovski, E.G.; Hu, N.; Parker, D.; MacLeod, R.S.; Marrouche, N.F.; Ranjan, R. Poor scar formation after ablation is associated with atrial fibrillation recurrence. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2015, 44, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaitani, K.; Inoue, K.; Kobori, A.; Nakazawa, Y.; Ozawa, T.; Kurotobi, T.; Morishima, I.; Miura, F.; Watanabe, T.; Masuda, M.; et al. Efficacy of Antiarrhythmic Drugs Short-Term Use After Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation (EAST-AF) trial. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong-Sit, P.; Roux, J.F.; Zado, E.; Callans, D.J.; Garcia, F.; Lin, D.; Marchlinski, F.E.; Bala, R.; Dixit, S.; Riley, M.; et al. Antiarrhythmics after ablation of atrial fibrillation (5A Study): Six-month follow-up study. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2011, 4, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohnloser, S.H.; Singh, B.N. Proarrhythmia with class III antiarrhythmic drugs: Definition, electrophysiologic mechanisms, incidence, predisposing factors, and clinical implications. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 1995, 6, 920–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jais, P.; Cauchemez, B.; Macle, L.; Daoud, E.; Khairy, P.; Subbiah, R.; Hocini, M.; Extramiana, F.; Sacher, F.; Bordachar, P.; et al. Catheter ablation versus antiarrhythmic drugs for atrial fibrillation: The A4 study. Circulation 2008, 118, 2498–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbelt, A.H.; Spronk, H.M.; Crijns, H.; Ten Cate, H.; Rienstra, M.; Van Gelder, I.C. Prethrombotic State in Young Very Low-Risk Patients With Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 1990–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, M.; Samiei, S.; Ambale Venkatesh, B.; Opdahl, A.; Helle-Valle, T.M.; Zareian, M.; Almeida, A.L.; Choi, E.Y.; Wu, C.; Alonso, A.; et al. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance-Measured Left Atrial Volume and Function and Incident Atrial Fibrillation: Results From MESA (Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis). Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 9, e004299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karanikola, A.E.; Tzortzi, M.; Kordalis, A.; Doundoulakis, I.; Antoniou, C.K.; Laina, A.; Tsioufis, P.; Argyriou, N.; Sakalidis, A.; Pamporis, K.; et al. Clinical, Electrocardiographic and Echocardiographic Predictors of Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence After Pulmonary Vein Isolation. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A.A.; Saliba, W.I.; Martin, D.O.; Bhargava, M.; Sherman, M.; Magnelli-Reyes, C.; Chamsi-Pasha, M.; John, S.; Williams-Adrews, M.; Baranowski, B.; et al. Natural history and long-term outcomes of ablated atrial fibrillation. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2011, 4, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Santangeli, P.; Zado, E.S.; Bala, R.; Hutchinson, M.D.; Riley, M.P.; Frankel, D.S.; Garcia, F.; Dixit, S.; Callans, D.J.; et al. Electrophysiologic findings and long-term outcomes in patients undergoing third or more catheter ablation procedures for atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2015, 26, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mujovic, N.M.; Marinkovic, M.M.; Potpara, T.S.; Geller, L. Catheter ablation of lone atrial fibrillation. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 591–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla-Cueto, D.; Ferro, E.; Garre, P.; Prat, S.; Guichard, J.B.; Perea, R.J.; Tolosana, J.M.; Guasch, E.; Arbelo, E.; Porta-Sanchez, A.; et al. Non-invasive assessment of pulmonary vein isolation durability using late gadolinium enhancement magnetic resonance imaging. Europace 2023, 25, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althoff, T.F.; Garre, P.; Caixal, G.; Perea, R.; Prat, S.; Tolosana, J.M.; Guasch, E.; Roca-Luque, I.; Arbelo, E.; Sitges, M.; et al. Late gadolinium enhancement-MRI determines definite lesion formation most accurately at 3 months post ablation compared to later time points. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 2022, 45, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinto, L.; Cozzari, J.; Benito, E.; Alarcon, F.; Bisbal, F.; Trotta, O.; Caixal, G.; San Antonio, R.; Garre, P.; Prat-Gonzalez, S.; et al. Magnetic resonance-guided re-ablation for atrial fibrillation is associated with a lower recurrence rate: A case-control study. Europace 2020, 22, 1805–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Garg, L.; Kanjwal, M.Y.; Bliden, K.; Tantry, U.S.; Gurbel, P.A.; Alraies, M.C.; Damluji, A.A. Catheter Ablation in Atrial Fibrillation: Recent Advances. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 7700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutalas, E.; Kallergis, E.; Nedios, S.; Kochiadakis, G.; Kanoupakis, E. P-wave duration as a marker of atrial remodeling in patients referred to ablation for atrial fibrillation: A new stratification tool emerging? Hell. J. Cardiol. 2023, 73, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Rocca, D.G.; Tarantino, N.; Trivedi, C.; Mohanty, S.; Anannab, A.; Salwan, A.S.; Gianni, C.; Bassiouny, M.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Romero, J.; et al. Non-pulmonary vein triggers in nonparoxysmal atrial fibrillation: Implications of pathophysiology for catheter ablation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2020, 31, 2154–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.S.; Tai, C.T.; Hsieh, M.H.; Tsai, C.F.; Lin, Y.K.; Tsao, H.M.; Huang, J.L.; Yu, W.C.; Yang, S.P.; Ding, Y.A.; et al. Catheter ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation initiated by non-pulmonary vein ectopy. Circulation 2003, 107, 3176–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nademanee, K.; McKenzie, J.; Kosar, E.; Schwab, M.; Sunsaneewitayakul, B.; Vasavakul, T.; Khunnawat, C.; Ngarmukos, T. A new approach for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: Mapping of the electrophysiologic substrate. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 43, 2044–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Rocca, D.G.; Di Biase, L.; Mohanty, S.; Trivedi, C.; Gianni, C.; Romero, J.; Tarantino, N.; Magnocavallo, M.; Bassiouny, M.; Natale, V.N.; et al. Targeting non-pulmonary vein triggers in persistent atrial fibrillation: Results from a prospective, multicentre, observational registry. Europace 2021, 23, 1939–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jais, P.; Hocini, M.; Macle, L.; Choi, K.J.; Deisenhofer, I.; Weerasooriya, R.; Shah, D.C.; Garrigue, S.; Raybaud, F.; Scavee, C.; et al. Distinctive electrophysiological properties of pulmonary veins in patients with atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2002, 106, 2479–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrev, D.; Friedrich, A.; Voigt, N.; Jost, N.; Wettwer, E.; Christ, T.; Knaut, M.; Ravens, U. The G protein-gated potassium current I(K,ACh) is constitutively active in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2005, 112, 3697–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulla, R.; Blew, G.A.; Holterman, M.J. Cardiovascular embryology. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2004, 25, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashakhanloo, F.; Herzka, D.A.; Ashikaga, H.; Mori, S.; Gai, N.; Bluemke, D.A.; Trayanova, N.A.; McVeigh, E.R. Myofiber Architecture of the Human Atria as Revealed by Submillimeter Diffusion Tensor Imaging. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2016, 9, e004133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianni, C.; Sanchez, J.E.; Mohanty, S.; Trivedi, C.; Della Rocca, D.G.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Burkhardt, J.D.; Gallinghouse, G.J.; Hranitzky, P.M.; Horton, R.P.; et al. Isolation of the superior vena cava from the right atrial posterior wall: A novel ablation approach. Europace 2018, 20, e124–e132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, S.; Takigawa, M.; Kusa, S.; Kuwahara, T.; Taniguchi, H.; Okubo, K.; Nakamura, H.; Hachiya, H.; Hirao, K.; Takahashi, A.; et al. Role of arrhythmogenic superior vena cava on atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2014, 25, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X. The role of superior vena cava in catheter ablation of long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation. Europace 2017, 19, 1670–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haissaguerre, M.; Hocini, M.; Takahashi, Y.; O’Neill, M.D.; Pernat, A.; Sanders, P.; Jonsson, A.; Rotter, M.; Sacher, F.; Rostock, T.; et al. Impact of catheter ablation of the coronary sinus on paroxysmal or persistent atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2007, 18, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaita, F.; Scaglione, M.; Ferraris, F. Left persistent superior vena cava as a source of focal atrial fibrillation. Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hsu, L.F.; Jais, P.; Keane, D.; Wharton, J.M.; Deisenhofer, I.; Hocini, M.; Shah, D.C.; Sanders, P.; Scavee, C.; Weerasooriya, R.; et al. Atrial fibrillation originating from persistent left superior vena cava. Circulation 2004, 109, 828–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselmino, M.; Ferraris, F.; Cerrato, N.; Barbero, U.; Scaglione, M.; Gaita, F. Left persistent superior vena cava and paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: The role of selective radio-frequency transcatheter ablation. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2014, 15, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachos, K.; Denis, A.; Takigawa, M.; Kitamura, T.; Martin, C.A.; Frontera, A.; Martin, R.; Bazoukis, G.; Bourier, F.; Cheniti, G.; et al. The role of Marshall bundle epicardial connections in atrial tachycardias after atrial fibrillation ablation. Heart Rhythm 2019, 16, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derejko, P.; Szumowski, L.J.; Sanders, P.; Krupa, W.; Bodalski, R.; Orczykowski, M.; Urbanek, P.; Zakrzewska, J.; Lim, H.S.; Lau, D.H.; et al. Atrial fibrillation in patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: Role of pulmonary veins. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2012, 23, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anter, E.; Di Biase, L.; Contreras-Valdes, F.M.; Gianni, C.; Mohanty, S.; Tschabrunn, C.M.; Viles-Gonzalez, J.F.; Leshem, E.; Buxton, A.E.; Kulbak, G.; et al. Atrial Substrate and Triggers of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation in Patients With Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2017, 10, e005407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.; Michaud, G.F.; Avendano, R.; Briceno, D.F.; Kumar, S.; Carlos Diaz, J.; Mohanty, S.; Trivedi, C.; Gianni, C.; Della Rocca, D.; et al. Benefit of left atrial appendage electrical isolation for persistent and long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Europace 2018, 20, 1268–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akoum, N.; Fernandez, G.; Wilson, B.; McGann, C.; Kholmovski, E.; Marrouche, N. Association of atrial fibrosis quantified using LGE-MRI with atrial appendage thrombus and spontaneous contrast on transesophageal echocardiography in patients with atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2013, 24, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, M.; Mandapati, R.; Berenfeld, O.; Chen, J.; Samie, F.H.; Jalife, J. Left-to-right gradient of atrial frequencies during acute atrial fibrillation in the isolated sheep heart. Circulation 2001, 103, 2631–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.Y.; Tai, C.T.; Huang, B.H.; Higa, S.; Lin, Y.J.; Huang, J.L.; Yuniadi, Y.; Lee, P.C.; Ding, Y.A.; Chen, S.A. Functional characterization of the crista terminalis in patients with atrial flutter: Implications for radiofrequency ablation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 43, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fynn, S.P.; Morton, J.B.; Deen, V.R.; Kistler, P.M.; Vohra, J.K.; Sparks, P.B.; Kalman, J.M. Conduction characteristics at the crista terminalis during onset of pulmonary vein atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2004, 15, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proietti, R.; Santangeli, P.; Di Biase, L.; Joza, J.; Bernier, M.L.; Wang, Y.; Sagone, A.; Viecca, M.; Essebag, V.; Natale, A. Comparative effectiveness of wide antral versus ostial pulmonary vein isolation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2014, 7, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilz, R.R.; Heeger, C.H.; Vogler, J.; Eitel, C.; Feher, M.; Phan, H.L.; Mushfiq, I.; Popescu, S.S.; Zetzsch, L.; Traub, A.; et al. Wide antral circumferential vs. ostial pulmonary vein isolation using pulsed field ablation-the butterfly effect. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1217745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kistler, P.M.; Chieng, D.; Sugumar, H.; Ling, L.H.; Segan, L.; Azzopardi, S.; Al-Kaisey, A.; Parameswaran, R.; Anderson, R.D.; Hawson, J.; et al. Effect of Catheter Ablation Using Pulmonary Vein Isolation With vs Without Posterior Left Atrial Wall Isolation on Atrial Arrhythmia Recurrence in Patients With Persistent Atrial Fibrillation: The CAPLA Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2023, 329, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanitsoraphan, C.; Rattanawong, P.; Techorueangwiwat, C.; Kewcharoen, J.; Mekritthikrai, R.; Prasitlumkum, N.; Shah, P.; El Masry, H. The efficacy of posterior wall isolation in atrial fibrillation ablation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Arrhythmia 2022, 38, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.; Trivedi, C.; Gianni, C.; Della Rocca, D.G.; Morris, E.H.; Burkhardt, J.D.; Sanchez, J.E.; Horton, R.; Gallinghouse, G.J.; Hongo, R.; et al. Procedural findings and ablation outcome in patients with atrial fibrillation referred after two or more failed catheter ablations. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2017, 28, 1379–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Biase, L.; Burkhardt, J.D.; Mohanty, P.; Mohanty, S.; Sanchez, J.E.; Trivedi, C.; Gunes, M.; Gokoglan, Y.; Gianni, C.; Horton, R.P.; et al. Left Atrial Appendage Isolation in Patients With Longstanding Persistent AF Undergoing Catheter Ablation: BELIEF Trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 1929–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derval, N.; Duchateau, J.; Denis, A.; Ramirez, F.D.; Mahida, S.; Andre, C.; Krisai, P.; Nakatani, Y.; Kitamura, T.; Takigawa, M.; et al. Marshall bundle elimination, Pulmonary vein isolation, and Line completion for ANatomical ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation (Marshall-PLAN): Prospective, single-center study. Heart Rhythm 2021, 18, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrabano, M.; Peterson, L.E.; Swarup, V.; Schurmann, P.A.; Makkar, A.; Doshi, R.N.; DeLurgio, D.; Athill, C.A.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Natale, A.; et al. Effect of Catheter Ablation With Vein of Marshall Ethanol Infusion vs Catheter Ablation Alone on Persistent Atrial Fibrillation: The VENUS Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 324, 1620–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avazzadeh, S.; McBride, S.; O’Brien, B.; Coffey, K.; Elahi, A.; O’Halloran, M.; Soo, A.; Quinlan, L.R. Ganglionated Plexi Ablation for the Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.K.; Zhao, Y.; Everett, T.H.t.; Chen, P.S. Ganglionated plexi as neuromodulation targets for atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2017, 28, 1485–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, J.; Yin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, Q.; Dong, J.; Ma, C.; Liu, X. Ablation of epicardial ganglionated plexi increases atrial vulnerability to arrhythmias in dogs. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2014, 7, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaei, N.; Montazerghaem, H.; Azarfarin, R.; Alizadehasl, A.; Alikhah, H. Radiofrequency ablation for treatment of atrial fibrillation. BioImpacts BI 2011, 1, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrakis, S.; Nakagawa, H.; Po, S.S.; Scherlag, B.J.; Lazzara, R.; Jackman, W.M. The role of the autonomic ganglia in atrial fibrillation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2015, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driessen, A.H.G.; Berger, W.R.; Krul, S.P.J.; van den Berg, N.W.E.; Neefs, J.; Piersma, F.R.; Chan Pin Yin, D.; de Jong, J.; van Boven, W.P.; de Groot, J.R. Ganglion Plexus Ablation in Advanced Atrial Fibrillation: The AFACT Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 1155–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katritsis, D.G.; Pokushalov, E.; Romanov, A.; Giazitzoglou, E.; Siontis, G.C.; Po, S.S.; Camm, A.J.; Ioannidis, J.P. Autonomic denervation added to pulmonary vein isolation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: A randomized clinical trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 2318–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goff, Z.D.; Laczay, B.; Yenokyan, G.; Sivasambu, B.; Sinha, S.K.; Marine, J.E.; Ashikaga, H.; Berger, R.D.; Akhtar, T.; Spragg, D.D.; et al. Heart rate increase after pulmonary vein isolation predicts freedom from atrial fibrillation at 1 year. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2019, 30, 2818–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, J.S.; Shabanov, V.; Ponomarev, D.; Losik, D.; Ivanickiy, E.; Kropotkin, E.; Polyakov, K.; Ptaszynski, P.; Keweloh, B.; Yao, C.J.; et al. Effect of Renal Denervation and Catheter Ablation vs Catheter Ablation Alone on Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence Among Patients With Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation and Hypertension: The ERADICATE-AF Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 323, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobellis, G. Epicardial adipose tissue in contemporary cardiology. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2022, 19, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocyigit, D.; Gurses, K.M.; Yalcin, M.U.; Turk, G.; Evranos, B.; Yorgun, H.; Sahiner, M.L.; Kaya, E.B.; Hazirolan, T.; Tokgozoglu, L.; et al. Periatrial epicardial adipose tissue thickness is an independent predictor of atrial fibrillation recurrence after cryoballoon-based pulmonary vein isolation. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2015, 9, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaborit, B.; Venteclef, N.; Ancel, P.; Pelloux, V.; Gariboldi, V.; Leprince, P.; Amour, J.; Hatem, S.N.; Jouve, E.; Dutour, A.; et al. Human epicardial adipose tissue has a specific transcriptomic signature depending on its anatomical peri-atrial, peri-ventricular, or peri-coronary location. Cardiovasc. Res. 2015, 108, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venteclef, N.; Guglielmi, V.; Balse, E.; Gaborit, B.; Cotillard, A.; Atassi, F.; Amour, J.; Leprince, P.; Dutour, A.; Clement, K.; et al. Human epicardial adipose tissue induces fibrosis of the atrial myocardium through the secretion of adipo-fibrokines. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 795–805a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xi, W.; Yin, L.; Wang, J.; Shen, H.; Gao, Y.; Min, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. Human Epicardial Adipose Tissue cTGF Expression is an Independent Risk Factor for Atrial Fibrillation and Highly Associated with Atrial Fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaihov-Teper, O.; Ram, E.; Ballan, N.; Brzezinski, R.Y.; Naftali-Shani, N.; Masoud, R.; Ziv, T.; Lewis, N.; Schary, Y.; Levin-Kotler, L.P.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles From Epicardial Fat Facilitate Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2021, 143, 2475–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalliah, C.J.; Bell, J.R.; Raaijmakers, A.J.A.; Waddell, H.M.; Wells, S.P.; Bernasochi, G.B.; Montgomery, M.K.; Binny, S.; Watts, T.; Joshi, S.B.; et al. Epicardial Adipose Tissue Accumulation Confers Atrial Conduction Abnormality. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 1197–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munger, T.M.; Dong, Y.X.; Masaki, M.; Oh, J.K.; Mankad, S.V.; Borlaug, B.A.; Asirvatham, S.J.; Shen, W.K.; Lee, H.C.; Bielinski, S.J.; et al. Electrophysiological and hemodynamic characteristics associated with obesity in patients with atrial fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.K.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, J.H.; Chen, S.A.; Chen, Y.J. Adipocytes modulate the electrophysiology of atrial myocytes: Implications in obesity-induced atrial fibrillation. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2012, 107, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, M.; Macle, L.; Deyell, M.W.; Yao, R.; Hawkins, N.M.; Khairy, P.; Andrade, J.G. Influence of Monitoring Strategy on Assessment of Ablation Success and Postablation Atrial Fibrillation Burden Assessment: Implications for Practice and Clinical Trial Design. Circulation 2022, 145, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avram, R.; Ramsis, M.; Cristal, A.D.; Nathan, V.; Zhu, L.; Kim, J.; Kuang, J.; Gao, A.; Vittinghoff, E.; Rohdin-Bibby, L.; et al. Validation of an algorithm for continuous monitoring of atrial fibrillation using a consumer smartwatch. Heart Rhythm 2021, 18, 1482–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gelder, I.C.; Rienstra, M.; Bunting, K.V.; Casado-Arroyo, R.; Caso, V.; Crijns, H.; De Potter, T.J.R.; Dwight, J.; Guasti, L.; Hanke, T.; et al. 2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 3314–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joglar, J.A.; Chung, M.K.; Armbruster, A.L.; Benjamin, E.J.; Chyou, J.Y.; Cronin, E.M.; Deswal, A.; Eckhardt, L.L.; Goldberger, Z.D.; Gopinathannair, R.; et al. 2023 ACC/AHA/ACCP/HRS Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2024, 83, 109–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, E.W.; Antman, E.M.; Javaheri, S. Breathless nights and heart flutters: Understanding the relationship between obstructive sleep apnea and atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 2023, 20, 1267–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonnesen, J.; Pallisgaard, J.; Ruwald, M.H.; Rasmussen, P.V.; Johannessen, A.; Hansen, J.; Worck, R.H.; Zorner, C.R.; Riis-Vestergaard, L.; Middelfart, C.; et al. Short- and long-term risk of atrial fibrillation recurrence after first time ablation according to body mass index: A nationwide Danish cohort study. Europace 2023, 25, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Lai, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Peng, X.; Li, M.; et al. Impact of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor on recurrence and cardiovascular outcomes after catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation in patients with heart failure. Heart Rhythm 2024, 22, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, M.T.B.; Kuklik, P.; Briosa, E.G.A.; Leo, M.; Mahmoudi, M.; Paisey, J.; Betts, T.R. Impact of Adenosine on Wavefront Propagation in Persistent Atrial Fibrillation: Insights From Global Noncontact Charge Density Mapping of the Left Atrium. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022, 11, e021166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, P.M.; Zghaib, T.; Zahid, S.; Ali, R.L.; Deng, D.; Franceschi, W.H.; Hakim, J.B.; Murphy, M.J.; Prakosa, A.; Zimmerman, S.L.; et al. Computationally guided personalized targeted ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 870–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakasis, P.; Theofilis, P.; Sagris, M.; Pamporis, K.; Stachteas, P.; Sidiropoulos, G.; Vlachakis, P.K.; Patoulias, D.; Antoniadis, A.P.; Fragakis, N. Artificial Intelligence in Atrial Fibrillation: From Early Detection to Precision Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouselimis, D.; Tsarouchas, A.S.; Pagourelias, E.D.; Bakogiannis, C.; Theofilogiannakos, E.K.; Loutradis, C.; Fragakis, N.; Vassilikos, V.P.; Papadopoulos, C.E. Left atrial strain, intervendor variability, and atrial fibrillation recurrence after catheter ablation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hell. J. Cardiol. 2020, 61, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntalianis, E.; Sabovcik, F.; Cauwenberghs, N.; Kouznetsov, D.; Daels, Y.; Claus, P.; Kuznetsova, T. Unsupervised Time-Series Clustering of Left Atrial Strain for Cardiovascular Risk Assessment. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2023, 36, 778–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razeghi, O.; Kapoor, R.; Alhusseini, M.I.; Fazal, M.; Tang, S.; Roney, C.H.; Rogers, A.J.; Lee, A.; Wang, P.J.; Clopton, P.; et al. Atrial fibrillation ablation outcome prediction with a machine learning fusion framework incorporating cardiac computed tomography. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2023, 34, 1164–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baessler, B.; Engelhardt, S.; Hekalo, A.; Hennemuth, A.; Hullebrand, M.; Laube, A.; Scherer, C.; Tolle, M.; Wech, T. Perfect Match: Radiomics and Artificial Intelligence in Cardiac Imaging. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2024, 17, e015490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewin, S.; Chetty, R.; Ihdayhid, A.R.; Dwivedi, G. Ethical Challenges and Opportunities in Applying Artificial Intelligence to Cardiovascular Medicine. Can. J. Cardiol. 2024, 40, 1897–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, T.; Lim, B.; Kwon, O.S.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, D.; Park, J.W.; Yu, H.T.; Kim, T.H.; Uhm, J.S.; Joung, B.; et al. Clinical usefulness of digital twin guided virtual amiodarone test in patients with atrial fibrillation ablation. NPJ Digit. Med. 2024, 7, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Strategy | Mechanism | Potential Benefit | Current Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Mapping Technologies | AI-driven electrogram analysis, charge density mapping, digital twins | Improves identification of arrhythmogenic regions and ablation precision | Standardization and validation in large-scale clinical trials needed. Temporal resolution with multidiscipline catheters is a current limitation. It may also be worth splitting this into contact and non-contact mapping approaches |
| Pulsed Field Ablation (PFA) | Non-thermal ablation minimizing collateral damage | Reduced risk of esophageal, phrenic nerve, and pulmonary vein injury | Long-term efficacy and optimal lesion durability require further study |
| Targeting Non-PV Triggers | Ablation of LAA, CS, SVC, and posterior wall | Addresses drivers beyond PV reconnection to reduce recurrence | Complex mapping and risk of atrial tachycardia post-isolation. Heterogeneity in response to empirical approaches indicates these are not triggers in all patients. There is a need to develop individualized pathophysiology-based treatment approaches |
| Hybrid Ablation Approaches | Combination of endocardial and epicardial ablation | Enhances lesion durability, especially in persistent AF | Higher procedural risk and need for standardized protocols |
| Autonomic Modulation (GP Ablation, RDN) | Alters vagal and sympathetic tone to reduce Afib triggers | Potential adjunct to PVI in selected patients | Variable success rates and risk of autonomic reinnervation |
| Risk Factor Optimization | Weight loss, OSA treatment, blood pressure control | Modifies atrial substrate to improve long-term outcomes | Patient adherence and long-term sustainability of interventions |
| AI & Computational Modeling | Machine learning prediction models and digital twins | Enables personalized ablation strategies and risk assessment | Requires integration into clinical workflows and validation across diverse populations |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vlachakis, P.K.; Theofilis, P.; Apostolos, A.; Karakasis, P.; Ktenopoulos, N.; Boulmpou, A.; Drakopoulou, M.; Leontsinis, I.; Xydis, P.; Kordalis, A.; et al. Beyond Pulmonary Vein Reconnection: Exploring the Dynamic Pathophysiology of Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence After Catheter Ablation. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2919. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092919
Vlachakis PK, Theofilis P, Apostolos A, Karakasis P, Ktenopoulos N, Boulmpou A, Drakopoulou M, Leontsinis I, Xydis P, Kordalis A, et al. Beyond Pulmonary Vein Reconnection: Exploring the Dynamic Pathophysiology of Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence After Catheter Ablation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(9):2919. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092919
Chicago/Turabian StyleVlachakis, Panayotis K., Panagiotis Theofilis, Anastasios Apostolos, Paschalis Karakasis, Nikolaos Ktenopoulos, Aristi Boulmpou, Maria Drakopoulou, Ioannis Leontsinis, Panagiotis Xydis, Athanasios Kordalis, and et al. 2025. "Beyond Pulmonary Vein Reconnection: Exploring the Dynamic Pathophysiology of Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence After Catheter Ablation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 9: 2919. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092919
APA StyleVlachakis, P. K., Theofilis, P., Apostolos, A., Karakasis, P., Ktenopoulos, N., Boulmpou, A., Drakopoulou, M., Leontsinis, I., Xydis, P., Kordalis, A., Koniari, I., Gatzoulis, K. A., Sideris, S., & Tsioufis, C. (2025). Beyond Pulmonary Vein Reconnection: Exploring the Dynamic Pathophysiology of Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence After Catheter Ablation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(9), 2919. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092919










