Identifying Risk of Viral Failure in Treated HIV-Infected Patients Using Different Measures of Adherence: The Antiretroviral Therapy Cohort Collaboration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Cohorts and Patients
2.2. Deriving Measures of Adherence and Viral Suppression
2.3. Analysis
2.4. Sensitivity Analyses
3. Results
Sensitivity Analyses
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Results
4.2. Context
4.3. Strengths and Weaknesses
5. Implications
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wood, E.; Hogg, R.S.; Yip, B.; Harrigan, P.R.; O’Shaughnessy, M.V.; Montaner, J.S. Effect of medication adherence on survival of HIV-infected adults who start highly active antiretroviral therapy when the cd4+ cell count is 0.200 to 0.350 × 10(9) cells/L. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 139, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, V.D.; Geller, J.; Bangsberg, D.R.; Patterson, T.L.; Daniel, M.; Kerr, T.; Montaner, J.; Hogg, R.S. The effect of adherence on the association between depressive symptoms and mortality among HIV-infected individuals first initiating HAART. AIDS 2007, 21, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hogg, R.S.; Heath, K.; Bangsberg, D.; Yip, B.; Press, N.; O’Shaughnessy, M.V.; Montaner, J.S. Intermittent use of triple-combination therapy is predictive of mortality at baseline and after 1 year of follow-up. AIDS 2002, 16, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antinori, A.; Cozzi-Lepri, A.; Ammassari, A.; Trotta, M.P.; Nauwelaers, D.; Hoetelmans, R.; Murri, R.; Melzi, S.; Narciso, P.; Nasta, P.; et al. Relative prognostic value of self-reported adherence and plasma NNRTI/PI concentrations to predict virological rebound in patients initially responding to HAART. Antivir. Ther. 2004, 9, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garcia de Olalla, P.; Knobel, H.; Carmona, A.; Guelar, A.; Lopez-Colomes, J.L.; Cayla, J.A. Impact of adherence and highly active antiretroviral therapy on survival in HIV-infected patients. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2002, 30, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterson, D.L.; Swindells, S.; Mohr, J.; Brester, M.; Vergis, E.N.; Squier, C.; Wagener, M.M.; Singh, N. Adherence to protease inhibitor therapy and outcomes in patients with HIV infection. Ann. Intern. Med. 2000, 133, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.B.; Amico, K.R.; Bova, C.; Womack, J.A. A proposal for quality standards for measuring medication adherence in research. AIDS Behav. 2013, 17, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, K.M.; Arnsten, J.H. Practical and conceptual challenges in measuring antiretroviral adherence. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2006, 43, S79–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnsten, J.H.; Demas, P.A.; Farzadegan, H.; Grant, R.W.; Gourevitch, M.N.; Chang, C.J.; Buono, D.; Eckholdt, H.; Howard, A.A.; Schoenbaum, E.E. Antiretroviral therapy adherence and viral suppression in HIV-infected drug users: Comparison of self-report and electronic monitoring. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, J.H.; Jordan, M.R.; Kelley, K.; Bertagnolio, S.; Hong, S.Y.; Wanke, C.A.; Lewin, S.R.; Elliott, J.H. Pharmacy adherence measures to assess adherence to antiretroviral therapy: Review of the literature and implications for treatment monitoring. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimes, D.E.; Andrade, R.A.; Niemeyer, C.R.; Grimes, R.M. Measurement issues in using pharmacy records to calculate adherence to antiretroviral drugs. HIV Clin. Trials 2013, 14, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, J.F.; Prochazka, A.V. The assessment of refill compliance using pharmacy records: Methods, validity, and applications. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1997, 50, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, M.T.; Ingle, S.M.; Costagliola, D.; Justice, A.C.; de Wolf, F.; Cavassini, M.; D’Arminio Monforte, A.; Casabona, J.; Hogg, R.S.; Mocroft, A.; et al. Cohort profile: Antiretroviral therapy cohort collaboration (art-cc). Int. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 43, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammassari, A.; Murri, R.; Pezzotti, P.; Trotta, M.P.; Ravasio, L.; De Longis, P.; Lo Caputo, S.; Narciso, P.; Pauluzzi, S.; Carosi, G.; et al. Self-reported symptoms and medication side effects influence adherence to highly active antiretroviral therapy in persons with HIV infection. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2001, 28, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, T.R.; Battegay, M.; Cavassini, M.; De Geest, S.; Furrer, H.; Vernazza, P.L.; Hirschel, B.; Bernasconi, E.; Rickenbach, M.; Gunthard, H.F.; et al. Longitudinal analysis of patterns and predictors of changes in self-reported adherence to antiretroviral therapy: Swiss HIV cohort study. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2010, 54, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, S.; Cescon, A.; Samji, H.; Cui, Z.; Yip, B.; Lepik, K.J.; Moore, D.; Lima, V.D.; Nosyk, B.; Harrigan, P.R.; et al. Cohort profile: Haart observational medical evaluation and research (homer) cohort. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- StataCorp LP. Stata Statistical Software: Release 13; StataCorp LP: College Station, TX, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, N.; Agostini, J.; Justice, A. Measuring persistence to oral hypoglycemic agents in type 2 diabetic veterans. J. Pharm. Technol. 2009, 25, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.; Agostini, J.V.; Justice, A.C. Refill adherence to oral hypoglycemic agents and glycemic control in veterans. Ann. Pharmacother. 2010, 44, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Golin, C.E.; Miller, L.G.; Hays, R.D.; Beck, C.K.; Sanandaji, S.; Christian, J.; Maldonado, T.; Duran, D.; Kaplan, A.H.; et al. A comparison study of multiple measures of adherence to HIV protease inhibitors. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001, 134, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitahata, M.M.; Reed, S.D.; Dillingham, P.W.; Van Rompaey, S.E.; Young, A.A.; Harrington, R.D.; Holmes, K.K. Pharmacy-based assessment of adherence to haart predicts virologic and immunologic treatment response and clinical progression to aids and death. Int. J. STD AIDS 2004, 15, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, M.L.; Jackson, G.L.; Smith, R.; Wilson, K.H. Association between pharmacy medication refill-based adherence rates and cd4 count and viral-load responses: A retrospective analysis in treatment-experienced adults with HIV. Clin. Ther. 2007, 29, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cambiano, V.; Lampe, F.C.; Rodger, A.J.; Smith, C.J.; Geretti, A.M.; Lodwick, R.K.; Holloway, J.; Johnson, M.; Phillips, A.N. Use of a prescription-based measure of antiretroviral therapy adherence to predict viral rebound in HIV-infected individuals with viral suppression. HIV Med. 2010, 11, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simoni, J.M.; Kurth, A.E.; Pearson, C.R.; Pantalone, D.W.; Merrill, J.O.; Frick, P.A. Self-report measures of antiretroviral therapy adherence: A review with recommendations for HIV research and clinical management. AIDS Behav. 2006, 10, 227–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieuwkerk, P.T.; Oort, F.J. Self-reported adherence to antiretroviral therapy for HIV-1 infection and virologic treatment response: A meta-analysis. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2005, 38, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tommelein, E.; Mehuys, E.; Van Tongelen, I.; Brusselle, G.; Boussery, K. Accuracy of the medication adherence report scale (mars-5) as a quantitative measure of adherence to inhalation medication in patients with copd. Ann. Pharmacother. 2014, 48, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Steenis, M.N.A.; Driesenaar, J.A.; Bensing, J.M.; Van Hulten, R.; Souverein, P.C.; Van Dijk, L.; De Smet, P.A.G.M.; Van Dulmen, A.M. Relationship between medication beliefs, self-reported and refill adherence, and symptoms in patients with asthma using inhaled corticosteroids. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2014, 8, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilson, I.B.; Carter, A.E.; Berg, K.M. Improving the self-report of HIV antiretroviral medication adherence: Is the glass half full or half empty? Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2009, 6, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



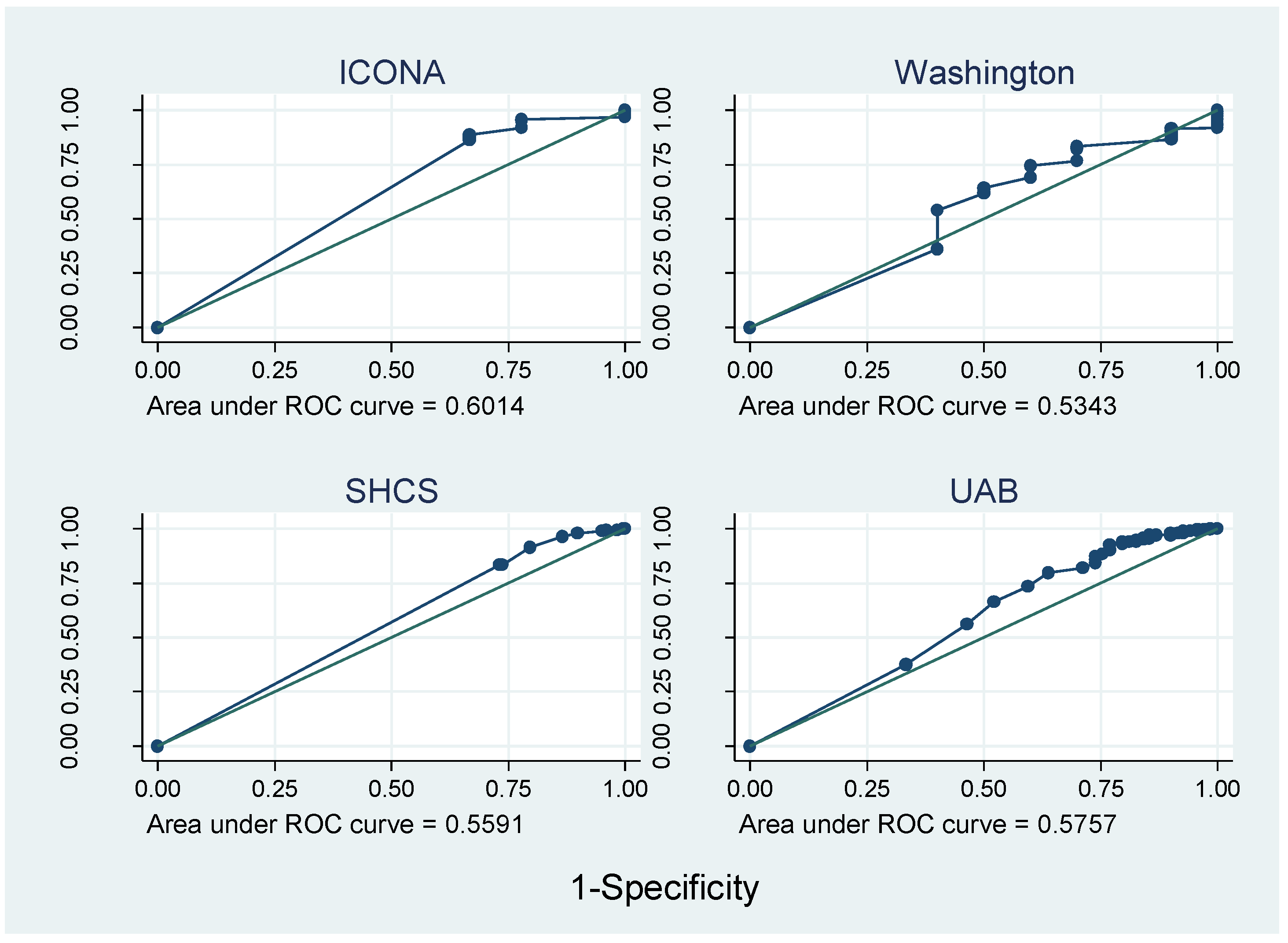
| Pharmacy refills | Self-Report | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | N (%) | Alberta | HOMER | VACS | HAVACS | ICONA | Washington | SHCS | UAB |
| Total, N (%) | 1,1689 | 485 (4.2) | 2241 (19.2) | 4404 (37.8) | 26 (0.2) | 203 (1.7) | 198 (1.7) | 3607 (30.9) | 525 (4.5) |
| Female, N (%) | 1883 (16.1) | 97 (20.0) | 386 (17.2) | 111 (2.5) | 0 (0) | 42 (20.7) | 29 (14.7) | 1114 (30.9) | 104 (19.8) |
| Age (median, IQR) | 41 (34–49) | 38 (32–44) | 40 (33–47) | 46 (39–52) | 43 (39–50) | 37 (32–43) | 37 (31–44) | 37 (31–44) | 37 (29–45) |
| Transmission risk group | |||||||||
| MSM | 2667 (22.8) | 235 (48.5) | 494 (22.0) | 66 (1.5) | 11 (42.3) | 67 (33.0) | 100 (50.5) | 1384 (38.4) | 310 (59.1) |
| IDU | 1824 (15.6) | 73 (15.1) | 796 (35.5) | 574 (13.0) | 6 (23.1) | 41 (20.2) | 52 (26.3) | 263 (7.3) | 19 (3.6) |
| Heterosexual | 2291 (19.6) | 167 (34.4) | 164 (7.3) | 7 (0.2) | 2 (7.7) | 85 (41.9) | 0 (0) | 1671 (46.3) | 195 (37.1) |
| Blood | 107 (0.9) | 7 (1.4) | 0 (0) | 24 (0.5) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 46 (23.2) | 30 (0.8) | 0 (0) |
| Other/unknown | 4800 (41.1) | 3 (0.6) | 787 (35.1) | 3733 (84.8) | 7 (26.9) | 10 (4.9) | 0 (0) | 259 (7.2) | 1 (0.2) |
| Median (IQR) CD4 count (cells/mm3) | 200 (80–320) | 178 (69–281) | 180 (80–300) | 192 (61–333) | 140 (54–280) | 285 (178–375) | 213 (72–271) | 207 (104–315) | 239 (62–358) |
| Median (IQR) viral load (log10 copies/mL) | 4.9 (4.4–5.3) | 4.8 (4.2–5.3) | 5.0 (4.7–5.2) | 4.9 (4.4–5.3) | 4.8 (4.5–5.3) | 4.8 (4.4–5.3) | 5.1 (4.6–5.6) | 4.9 (4.4–5.4) | 4.9 (4.3-5.4) |
| AIDS at baseline | 2711 (23.2) | 121 (25.0) | 405 (18.1) | 1244 (28.3) | 10 (38.5) | 13 (6.4) | 42 (21.2) | 701 (19.4) | 175 (33.3) |
| Mean (SD) % adherence, | 88.7 (20.1) | 89.5 (20.5) | 85.2 (24.8) | 80.8 (22.0) | 80.3 (20.9) | 97.4 (11.2) | 94.9 (11.4) | 99.0 (5.1) | 94.1 (15.2) |
| Median (IQR) year of adherence measurement | 2003 (2000–2006 | 2006 (2005–2007) | 2001 (1998–2004) | 2000 (1998–2002) | 2002 (2001–2005) | 2010 (2009–2011) | 2009 (2008–2010) | 2004 (2003–2007) | 2009 (2008–2011) |
| Number of sites in cohorts * | 1 | 500 | 125 | 1 | 32 | 1 | 7 | 1 | |
| Location (regional or national cohort?) | Regional | Regional | National | Regional | National | Regional | National | Regional | |
| Is prescription filled at once or with refills? | Refills | Refills | Refills | Refills | Refills | Refills | Refills | Refills | |
| Is refill drug supplied automatically without patient requesting it? | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes if mail order drug | |
| Pharmacy Refill Data | Self-Report Data | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohort | Alberta (Canada) | HOMER (Canada) | VACS (USA) | HAVACS (USA) | ICONA (Italy) | Washington (USA) | SHCS (Switzerland) | UAB (USA) |
| N | 485 | 2241 | 4404 | 26 | 203 | 198 | 3607 | 525 |
| % suppressed | 89.3 | 73.7 | 63.0 | 61.5 | 95.6 | 95.0 | 91.7 | 86.9 |
| Median (IQR) % adherence | 100 (90–100) | 100 (80–100) | 89 (68–100) | 85 (70–100) | 100 (100–100) | 99 (94–100) | 100 (100–100) | 99 (96–100) |
| Among those suppressed | 100 (95–100) | 100 (100–100) | 94 (80–100) | 85 (71–96) | 100 (100–100) | 99 (94–100) | 100 (100–100) | 99 (96–100) |
| Among those not suppressed | 49 (27–89) | 61 (33–88) | 73 (52–92) | 87 (70–100) | 100 (95–100) | 97 (90–100) | 100 (98–100) | 98 (91–100) |
| Proportion with ≥95% adherence | 67% | 62% | 39% | 38% | 91% | 74% | 96% | 81% |
| Proportion with 100% adherence | 52% | 60% | 28% | 27% | 85% | 36% | 82% | 37% |
| Adherence | ||||||||
| Lower | 6.4 | 10.6 | 9.0 | 7.7 | 12.3 | 31.3 | 4.3 | 22.3 |
| Medium | 36.9 | 29.1 | 60.7 | 65.4 | 2.5 | 32.3 | 13.3 | 40.7 |
| Higher | 56.7 | 60.3 | 30.3 | 26.9 | 85.2 | 36.4 | 82.4 | 37.0 |
| OR (95% CI) lower † vs. higher | 80.4 (27.8,233) | 85.2 (55.6,131) | 12.3 (9.42,16.1) | 0.75 (0.03,17.5) | 3.8 (0.9,16.3) | 1.2 (0.3,4.9) | 4.4 (3.0,6.4) | 2.0 (1.1,3.8) |
| OR (95% CI) medium † vs. higher | 5.9 (2.5,14.1) | 10.5 (8.1,13.6) | 2.6 (2.2,3.0) | 0.3 (0.1,1.9) | * | 0.5 (0.1,3.1) | 1.2 (0.8,1.7) | 0.8 (0.4,1.5) |
| OR (95% CI) lower vs. medium | 13.6 (5.7,32.3) | 8.1 (5.4,12.1) | 4.8 (3.7,6.1) | 2.4 (0.1,46.4) | * | 2.1 (0.4,12.1) | 3.7 (2.3,6.0) | 2.5 (1.3,4.7) |
| Overall ORs | ||||||||
| OR (95% CI) lower † vs. higher | 26.13 (21.05, 32.42) | 3.14 (2.36, 4.19) | ||||||
| OR (95% CI) medium † vs. higher | 4.41 (3.88, 5.01) | 1.15 (0.86, 1.53) | ||||||
| OR (95% CI) lower † vs. medium | 5.92 (4.86, 7.23) | 2.74 (1.91, 3.95) | ||||||
| Adjusted ORs | ||||||||
| OR (95% CI) lower † vs. higher | 23.04 (18.44, 28.78) | 3.19 (2.31, 4.40) | ||||||
| OR (95% CI) medium † vs. higher | 3.84 (3.36, 4.39) | 1.08 (0.80, 1.46) | ||||||
| OR (95% CI) lower † vs. medium | 5.73 (4.67, 7.04) | 3.13 (2.13, 4.59) | ||||||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ingle, S.M.; Crane, H.M.; Glass, T.R.; Yip, B.; Lima, V.D.; Gill, M.J.; Hanhoff, N.; Ammassari, A.; Mugavero, M.J.; Tate, J.P.; et al. Identifying Risk of Viral Failure in Treated HIV-Infected Patients Using Different Measures of Adherence: The Antiretroviral Therapy Cohort Collaboration. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7100328
Ingle SM, Crane HM, Glass TR, Yip B, Lima VD, Gill MJ, Hanhoff N, Ammassari A, Mugavero MJ, Tate JP, et al. Identifying Risk of Viral Failure in Treated HIV-Infected Patients Using Different Measures of Adherence: The Antiretroviral Therapy Cohort Collaboration. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2018; 7(10):328. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7100328
Chicago/Turabian StyleIngle, Suzanne M., Heidi M. Crane, Tracy R. Glass, Benita Yip, Viviane D. Lima, M John Gill, Nikola Hanhoff, Adriana Ammassari, Michael J. Mugavero, Jan P. Tate, and et al. 2018. "Identifying Risk of Viral Failure in Treated HIV-Infected Patients Using Different Measures of Adherence: The Antiretroviral Therapy Cohort Collaboration" Journal of Clinical Medicine 7, no. 10: 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7100328
APA StyleIngle, S. M., Crane, H. M., Glass, T. R., Yip, B., Lima, V. D., Gill, M. J., Hanhoff, N., Ammassari, A., Mugavero, M. J., Tate, J. P., Guest, J., Turner, N. L., May, M. T., & Sterne, J. A. C. (2018). Identifying Risk of Viral Failure in Treated HIV-Infected Patients Using Different Measures of Adherence: The Antiretroviral Therapy Cohort Collaboration. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 7(10), 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7100328





