Anti-Stress and Anti-Depressive Effects of Spinach Extracts on a Chronic Stress-Induced Depression Mouse Model through Lowering Blood Corticosterone and Increasing Brain Glutamate and Glutamine Levels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Spinach Extracts
2.3. Free Amino Acids Analysis of Spinach Extracts
2.4. Free Glu and Gln Analysis in the PFC
2.5. CIS Regimen
2.6. Behavioral Tests
2.7. Measurement of Plasma CORT
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Free Amino Acid Contents of Spinach Extracts Differ by the Extraction Method
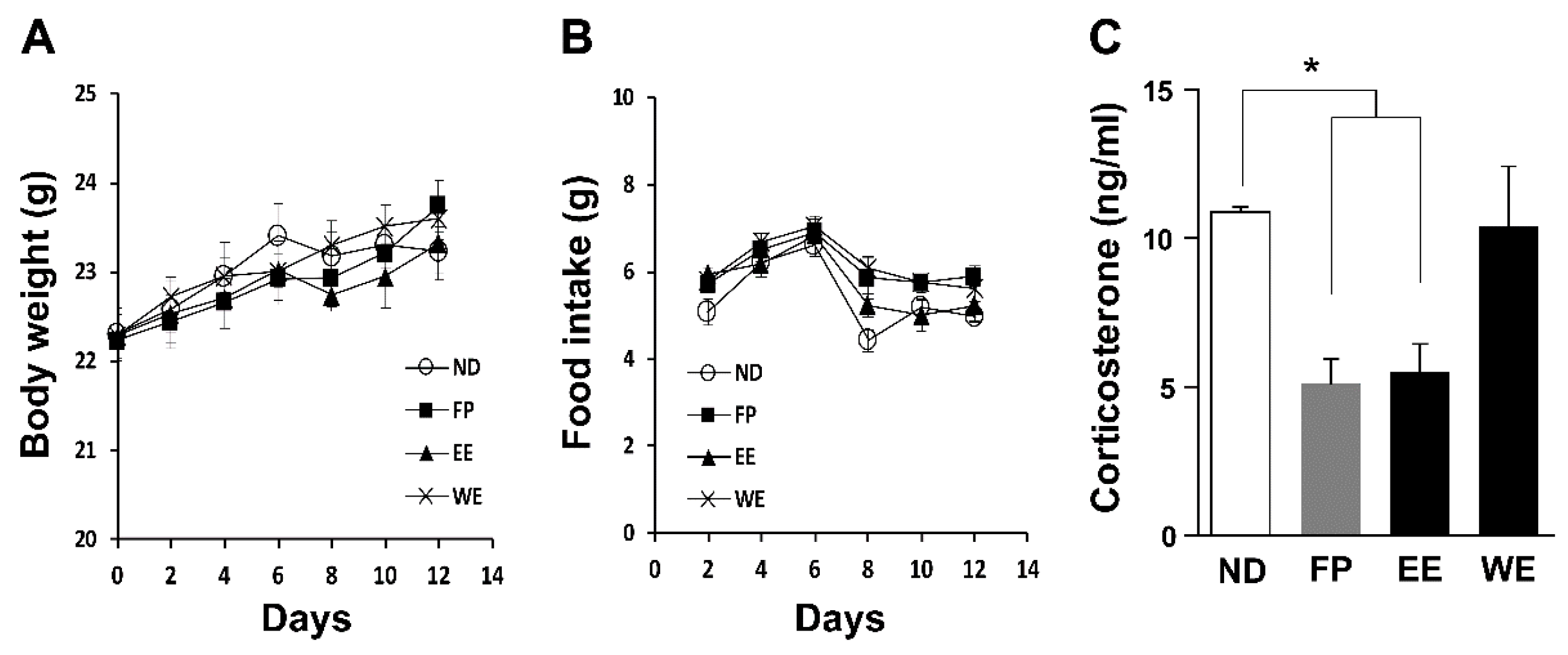
3.2. FP and EE-Supplemented Diets Decrease Blood CORT Levels in Mice
3.3. FP and EE-Supplemented Diet Attenuates Depressive-Like Behaviors Induced by CIS
3.4. FP and EE-Supplemented Diet Increases Brain Glu and Gln Levels
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lupien, S.J.; McEwen, B.S.; Gunnar, M.R.; Heim, C. Effects of stress throughout the lifespan on the brain, behaviour and cognition. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, A.J.; Charlson, F.J.; Norman, R.E.; Patten, S.B.; Freedman, G.; Murray, C.J.L.; Vos, T.; Whiteford, H.A. Burden of depressive disorders by country, sex, age, and year: Findings from the global burden of disease study 2010. PLoS Med. 2013, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, M.H.; Rush, A.J.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Nierenberg, A.A.; Warden, D.; Ritz, L.; Norquist, G.; Howland, R.H.; Lebowitz, B.; McGrath, P.J.; et al. Evaluation of outcomes with citalopram for depression using measurement-based care in STAR*D: Implications for clinical practice. Am. J. Psychiatry 2006, 163, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gartlehner, G.; Hansen, R.A.; Morgan, L.C.; Thaler, K.; Lux, L.J.; Van Noord, M.; Mager, U.; Gaynes, B.N.; Thieda, P.; Strobelberger, M.; et al. Second-Generation Antidepressants in the Pharmacologic Treatment of Adult Depression: An Update of the 2007 Comparative Effectiveness Review. Available online: http://www.diva-portal.org/smash/record.jsf?pid=diva2%3A810275&dswid=-7243 (accessed on 30 October 2018).
- Checkley, S. The neuroendocrinology of depression and chronic stress. Br. Med. Bull. 1996, 52, 597–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gregus, A.; Wintink, A.J.; Davis, A.C.; Kalynchuk, L.E. Effect of repeated corticosterone injections and restraint stress on anxiety and depression-like behavior in male rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2005, 156, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolley, C.S.; Gould, E.; McEwen, B.S. Exposure to excess glucocorticoids alters dendritic morphology of adult hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Brain Res. 1990, 531, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapolsky, R.M. Glucocorticoids and hippocampal atrophy in neuropsychiatric disorders. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2000, 57, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, K.J.; Schatzberg, A.F.; Lyons, D.M. Neuroendocrine aspects of hypercortisolism in major depression. Horm. Behav. 2003, 43, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Son, H.; Kim, G.; Kim, S.; Lee, D.H.; Roh, G.S.; Kang, S.S.; Cho, G.J.; Choi, W.S.; Kim, H.J. Glutamine deficiency in the prefrontal cortex increases depressive-like behaviours in male mice. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2013, 38, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.; Jung, S.; Son, H.; Joon, H. Glutamine-supplement diet maintains growth performance and reduces blood corticosterone level in cage-reared growing chicks. J. Agric. Life Sci. 2018, 52, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.; Baek, J.H.; Go, B.S.; Jung, D.; Sontakke, S.B.; Chung, H.J.; Lee, D.H.; Roh, G.S.; Kang, S.S.; Cho, G.J.; et al. Glutamine has antidepressive effects through increments of glutamate and glutamine levels and glutamatergic activity in the medial prefrontal cortex. Neuropharmacology 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergman, M.; Varshavsky, L.; Gottlieb, H.E.; Grossman, S. The antioxidant activity of aqueous spinach extract: chemical identification of active fractions. Phytochemistry 2001, 58, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, A.; Ng, A.; Kwan, T.; Cusmano-Ozog, K.; Cowan, T.M. A rapid, sensitive method for quantitative analysis of underivatized amino acids by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2014, 944, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Angelis, M.; Montemurno, E.; Piccolo, M.; Vannini, L.; Lauriero, G.; Maranzano, V.; Gozzi, G.; Serrazanetti, D.; Dalfino, G.; Gobbetti, M.; et al. Microbiota and metabolome associated with Immunoglobulin A Nephropathy (IgAN). PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, H.; Jung, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Goo, Y.M.; Cho, K.M.; Lee, D.H.; Roh, G.S.; Kang, S.S.; Cho, G.J.; Choi, W.S.; et al. Type 1 diabetes alters astrocytic properties related with neurotransmitter supply, causing abnormal neuronal activities. Brain Res. 2015, 1602, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiechter, G.; Mayer, H.K. UPLC analysis of free amino acids in wines: Profiling of on-lees aged wines. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2011, 879, 1361–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.; Chen, W.; Luo, G.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, S.; Ling, Z.; Chen, G. Rapid determination of underivatized pyroglutamic acid, glutamic acid, glutamine and other relevant amino acids in fermentation media by LC-MS-MS. Analyst 2002, 127, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, Y.; Choi, K.M.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, G.; Lee, D.H.; Roh, G.S.; Kang, S.S.; Cho, G.J.; Choi, W.S.; Kim, H.J. Chronic immobilization stress induces anxiety- and depression-like behaviors and decreases transthyretin in the mouse cortex. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 461, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.; Lee, Y.; Kim, G.; Son, H.; Lee, D.H.; Roh, G.S.; Kang, S.S.; Cho, G.J.; Choi, W.S.; Kim, H.J. Decreased expression of extracellular matrix proteins and trophic factors in the amygdala complex of depressed mice after chronic immobilization stress. BMC Neurosci. 2012, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryan, J.F.; Mombereau, C.; Vassout, A. The tail suspension test as a model for assessing antidepressant activity: review of pharmacological and genetic studies in mice. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2005, 29, 571–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.; Jung, S.; Son, H.; Kim, S.; Choi, J.; Lee, D.H.; Roh, G.S.; Kang, S.S.; Cho, G.J.; Choi, W.S.; et al. The GABAB receptor associates with regulators of G-protein signaling 4 protein in the mouse prefrontal cortex and hypothalamus. BMB Rep. 2014, 47, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs from 1981 to 2014. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, Q.X.; Venkatanarayanan, N.; Ho, C.Y. Clinical use of Hypericum perforatum (St John’s wort) in depression: A meta-analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2017, 210, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.F.; Gao, W.C.; Cheng, W.M.; Lu, W.L.; Tang, J.; Peng, L.; Li, N.; Chen, F.H. Orcinol glucoside produces antidepressant effects by blocking the behavioural and neuronal deficits caused by chronic stress. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 24, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.-F.; Yang, J.; Ma, S.-P.; Qu, R. Magnolol treatment reversed the glial pathology in an unpredictable chronic mild stress-induced rat model of depression. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 711, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, H.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, R.; Shi, H.; Bi, K.; Chen, X. Antidepressant-like effect of the water extract of the fixed combination of Gardenia jasminoides, Citrus aurantium and Magnolia officinalis in a rat model of chronic unpredictable mild stress. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiraungkoorskul, W. Review of Neuro-nutrition Used as Anti-Alzheimer Plant, Spinach, Spinacia oleracea. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2016, 10, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brocardo, P.S.; Budni, J.; Kaster, M.P.; Santos, A.R.; Rodrigues, A.L. Folic acid administration produces an antidepressant-like effect in mice: evidence for the involvement of the serotonergic and noradrenergic systems. Neuropharmacology 2008, 54, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowda, U.; Mutowo, M.P.; Smith, B.J.; Wluka, A.E.; Renzaho, A.M. Vitamin D supplementation to reduce depression in adults: Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutrition 2015, 31, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, L.P.; Liu, B.Y. Antidepressant-like effects and mechanisms of flavonoids and related analogues. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 121, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikkelsen, K.; Stojanovska, L.; Apostolopoulos, V. The Effects of Vitamin B in Depression. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 4317–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Min, S.G.; Jo, Y.J.; Chun, J.Y. Effects of ethanol addition on the efficiency of subcritical water extraction of proteins and amino acids from porcine placenta. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2015, 35, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dashdorj, D.; Hwang, I. Effect of extraction methods on the types and levels of free amino acid of beef longissimus muscle. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2012, 32, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houpert, Y.; Tarallo, P.; Siest, G. Comparison of procedures for extracting free amino acids from polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Clin. Chem. 1976, 22, 1618–1622. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jongkees, B.J.; Hommel, B.; Kühn, S.; Colzato, L.S. Effect of tyrosine supplementation on clinical and healthy populations under stress or cognitive demands—A review. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2015, 70, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabuki, Y.; Mizobe, Y.; Yamada, S.; Furuse, M. Dietary l-tyrosine alleviates the behavioral alterations induced by social isolation stress in mice. Brain Res. Bull. 2009, 80, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, S.N. Behavioral effects of dietary neurotransmitter precursors: basic and clinical aspects. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1996, 20, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajami, V.R.Y.; Ajami, A.M. Glutamine: The emperor or his clothes? J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 2505–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmore, D.W. The effect of glutamine supplementation in patients following elective surgery and accidental injury. J. Nutr. 2001, 2543–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnone, D.; Mumuni, A.N.; Jauhar, S.; Condon, B.; Cavanagh, J. Indirect evidence of selective glial involvement in glutamate-based mechanisms of mood regulation in depression: Meta-analysis of absolute prefrontal neuro-metabolic concentrations. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luykx, J.J.; Laban, K.G.; van den Heuvel, M.P.; Boks, M.P.M.; Mandl, R.C.W.; Kahn, R.S.; Bakker, S.C. Region and state specific glutamate downregulation in major depressive disorder: A meta-analysis of (1)H-MRS findings. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2011, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.J. Could glutamate spectroscopy differentiate bipolar depression from unipolar? J. Affect. Disord. 2014, 167, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Amino Acids | Ethanol Extract | Water Extract | Frozen Powder |
|---|---|---|---|
| L-Phenylalanine | ND | 44.13 ± 0.21 | 1.48 ± 0.15 |
| L-Aspartic Acid | 26.11 ± 1.31 | ND | ND |
| L-Threonine | 32.28 ± 1.54 | 68.44 ± 1.36 | 11.18 ± 0.45 |
| L-Serine | 32.11 ± 1.36 | 98.80 ± 6.32 | 23.78 ± 0.36 |
| L-Asparagine | 23.68 ± 0.25 | 3.43 ± 0.24 | 30.55 ± 0.33 |
| L-Glutamate | 23.65 ± 0.84 | 1171.38 ± 15.27 | 146.69 ± 2.58 |
| L-Glutamine | 29.13 ± 0.25 | ND | 62.88 ± 3.36 |
| L-Proline | 549.98 ± 5.64 | 564.45 ± 4.25 | 145.72 ± 4.68 |
| Glycine | 9.24 ± 0.24 | 66.79 ± 0.65 | 5.45 ± 0.65 |
| L-Alanine | 62.88 ± 2.65 | 233.74 ± 3.54 | 20.23 ± 0.36 |
| L-Citrulline | 13.98 ± 0.25 | 44.80 ± 3.54 | 2.54 ± 0.04 |
| α-Aminobutyric acid | 8.74 ± 0.21 | 17.03 ± 0.25 | 0.65 ± 0.15 |
| L-Valine | 80.82 ± 0.14 | 105.14 ± 4.62 | 24.23 ± 1.23 |
| L-Cystine | 2.36 ± 0.73 | 0.35 ± 0.03 | 2.46 ± 0.54 |
| L-Methionine | 11.19 ± 0.21 | 58.20 ± 1.75 | 16.39 ± 0.36 |
| L-Isoleucine | 104.12 ± 0.41 | 168.15 ± 4.56 | 40.07 ± 0.45 |
| L-Leucine | 43.77 ± 0.36 | 94.14 ± 2.36 | 17.09 ± 0.50 |
| L-Tyrosine | 162.88 ± 10.94 | ND | 38.75 ± 0.61 |
| β-Alanine | 29.41 ± 0.21 | 79.61 ± 1.25 | 14.30 ± 0.45 |
| L-Homocystine | 189.05 ± 8.50 | 668.55 ± 4.66 | 83.38 ± 0.86 |
| γ-Amino-n-butyric acid | 158.99 ± 7.64 | 231.14 ± 1.35 | 42.32 ± 0.64 |
| Ethanolamine | 108.29 ± 3.50 | 448.94 ± 4.25 | 20.58 ± 0.03 |
| δ-Hydroxylysine | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 89.18 ± 0.58 | 2.43 ± 0.05 |
| Ornithine | 5.48 ± 0.14 | 75.49 ± 0.25 | 1.73 ± 0.04 |
| 1-Methylhistidine | 8.96 ± 0.65 | 43.87 ± 0.36 | 13.21 ± 0.10 |
| L-Histidine | 9.47 ± 1.58 | 26.47 ± 1.27 | 2.77 ± 0.05 |
| L-Arginine | 16.84 ± 0.24 | 0.28 ± 0.04 | 19.97 ± 1.25 |
| Total | 1743.51 ± 49.81 | 4402.50 ± 62.96 | 790.83 ± 20.27 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Son, H.; Jung, S.; Shin, J.H.; Kang, M.J.; Kim, H.J. Anti-Stress and Anti-Depressive Effects of Spinach Extracts on a Chronic Stress-Induced Depression Mouse Model through Lowering Blood Corticosterone and Increasing Brain Glutamate and Glutamine Levels. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7110406
Son H, Jung S, Shin JH, Kang MJ, Kim HJ. Anti-Stress and Anti-Depressive Effects of Spinach Extracts on a Chronic Stress-Induced Depression Mouse Model through Lowering Blood Corticosterone and Increasing Brain Glutamate and Glutamine Levels. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2018; 7(11):406. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7110406
Chicago/Turabian StyleSon, Hyeonwi, Soonwoong Jung, Jung Hye Shin, Min Jung Kang, and Hyun Joon Kim. 2018. "Anti-Stress and Anti-Depressive Effects of Spinach Extracts on a Chronic Stress-Induced Depression Mouse Model through Lowering Blood Corticosterone and Increasing Brain Glutamate and Glutamine Levels" Journal of Clinical Medicine 7, no. 11: 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7110406
APA StyleSon, H., Jung, S., Shin, J. H., Kang, M. J., & Kim, H. J. (2018). Anti-Stress and Anti-Depressive Effects of Spinach Extracts on a Chronic Stress-Induced Depression Mouse Model through Lowering Blood Corticosterone and Increasing Brain Glutamate and Glutamine Levels. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 7(11), 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7110406





