Predictive Value of Cortical Thickness Measured by Ultrasonography for Renal Impairment: A Longitudinal Study in Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
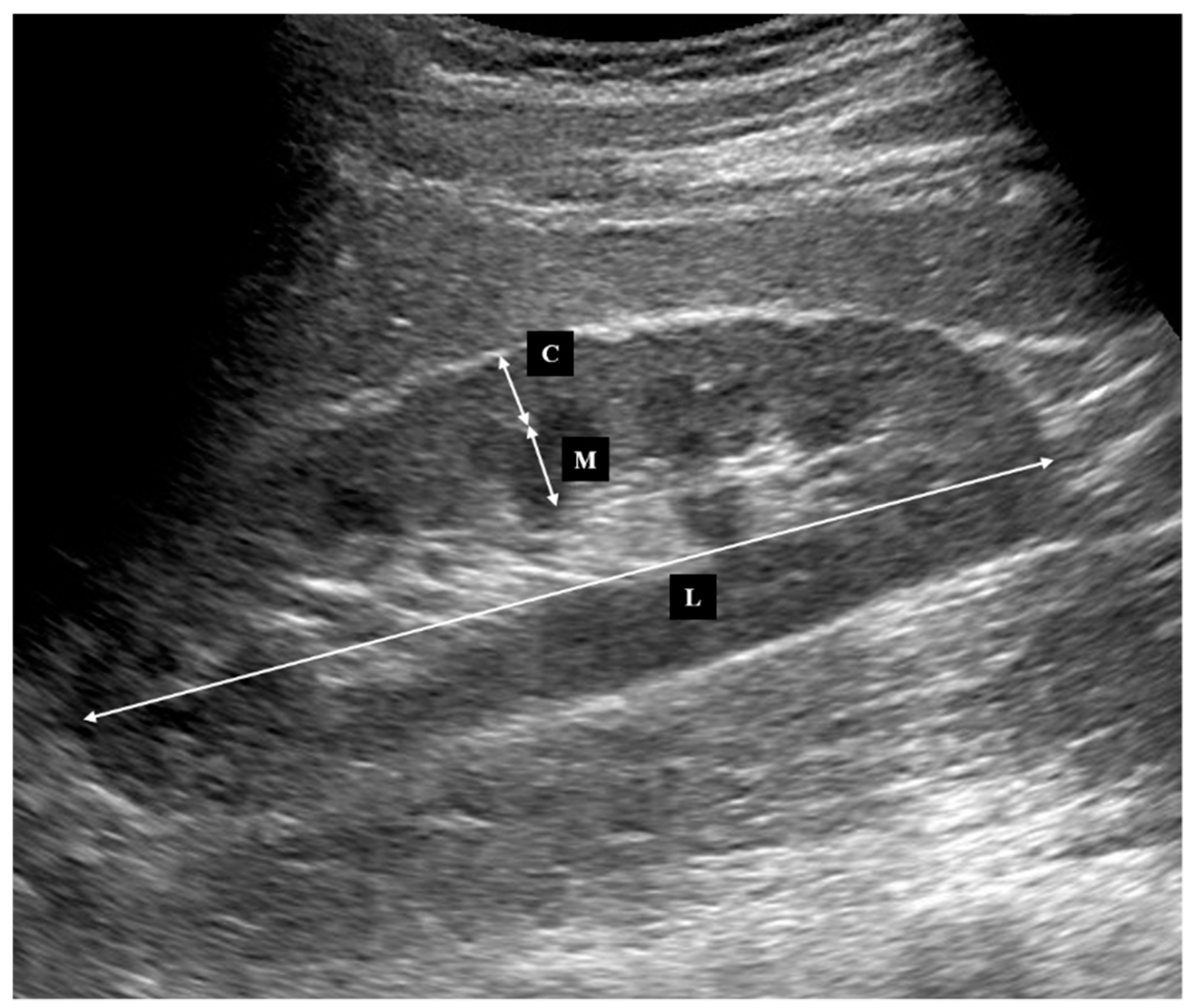
2.2. Ultrasonography
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient’s Characteristics and Baseline Evaluation
3.2. Association between Decline in Kidney Function and Kidney Morphology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Go, A.S.; Chertow, G.M.; Fan, D.; McCulloch, C.E.; Hsu, C.Y. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keith, D.S.; Nichols, G.A.; Gullion, C.M.; Brown, J.B.; Smith, D.H. Longitudinal follow-up and outcomes among a population with chronic kidney disease in a large managed care organization. Arch. Int. Med. 2004, 164, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anavekar, N.S.; McMurray, J.J.; Velazquez, E.J.; Solomon, S.D.; Kober, L.; Rouleau, J.L.; White, H.D.; Nordlander, R.; Maggioni, A.; Dickstein, K.; et al. Relation between renal dysfunction and cardiovascular outcomes after myocardial infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roger, S.D.; Beale, A.M.; Cattell, W.R.; Webb, J.A. What is the value of measuring renal parenchymal thickness before renal biopsy? Clin. Radiol. 1994, 49, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beland, M.D.; Walle, N.L.; Machan, J.T.; Cronan, J.J. Renal cortical thickness measured at ultrasound: Is it better than renal length as an indicator of renal function in chronic kidney disease? Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 195, W146–W149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, S.; Kwon, T.H.; Fenton, R.A.; Praetroius, J. Anatomy of the kidney. In Brenner and Rector’s the Kidney E-Book, 9th ed.; Taal, M.W., Chertow, G.M., Marsden, P.A., Skorecki, K., Yu, A.S., Brenner, B.M., Eds.; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012; pp. 31–93. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Vrtiska, T.J.; Avula, R.T.; Walters, L.R.; Chakkera, H.A.; Kremers, W.K.; Lerman, L.O.; Rule, A.D. Age, kidney function, and risk factors associate differently with cortical and medullary volumes of the kidney. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bellomo, R.; Ronco, C.; Kellum, J.A.; Mehta, R.L.; Palevsky, P. Acute renal failure-definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: The Second International Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) Group. Crit. Care 2004, 8, R204–R212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iyama, T.; Takata, T.; Koda, M.; Fukuda, S.; Hoi, S.; Mae, Y.; Fukui, T.; Munemura, C.; Isomoto, H. Renal shear wave elastography for the assessment of nephron hypertrophy: A cross-sectional in chronic kidney disease. J. Med. Ultrason. 2018, 45, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanriover, B.; Fernandez, S.; Campenot, E.S.; Newhouse, J.H.; Oyfe, I.; Mohan, P.; Sandikci, B.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Wexler, J.J.; Carroll, M.A.; et al. Live donor renal anatomic asymmetry and posttransplant renal function. Transplantation 2015, 99, e66–e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Bois, D.; Du Bois, E.F. A formula to estimate the approximate surface area if height and weight be known. Nutrition 1989, 5, 303–311. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo, S.; Imai, E.; Horio, M.; Yasuda, Y.; Tomita, K.; Nitta, K.; Yamagata, K.; Tomino, Y.; Yokoyama, H.; Hishida, A. Collaborators developing the Japanese equation for estimated GFR. Revised equations for estimated GFR from serum creatinine in Japan. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 53, 982–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coresh, J.; Turin, T.C.; Matsushita, K.; Sang, Y.; Ballew, S.H.; Appel, L.J.; Arima, H.; Chadban, S.J.; Cirillo, M.; Djurdjev, O.; et al. Decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate and subsequent risk of end-stage renal disease and mortality. JAMA 2014, 311, 2518–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushita, K.; Chen, J.; Sang, Y.; Ballew, S.H.; Shimazaki, R.; Fukagawa, M.; Imai, E.; Coresh, J.; Hishida, A. Risk of end-stage renal disease in Japanese patients with chronic kidney disease increases proportionately to decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate. Kidney Int. 2016, 90, 1109–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takata, T.; Koda, M.; Sugihara, T.; Sugihara, S.; Okamoto, T.; Miyoshi, K.; Hodotsuka, M.; Fujise, Y.; Matono, T.; Okano, J.; et al. Left renal cortical thickness measured by ultrasound can predict early progression of chronic kidney disease. Nephron 2016, 132, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Neill, W.C.; Robbin, M.L.; Bae, K.T.; Grantham, J.J.; Chapman, A.B.; Guay-Woodford, L.M.; Torres, V.E.; King, B.F.; Wetzel, L.H.; Thompson, P.A.; et al. Sonographic assessment of the severity and progression of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: The Consortium of Renal Imaging Studies in Polycystic Kidney Disease (CRISP). Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2005, 46, 1058–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bostom, A.G.; Kronenberg, F.; Ritz, E. Predictive performance of renal function equations for patients with chronic kidney disease and normal serum creatinine levels. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 2140–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsherbiny, H.E.; Alexander, M.P.; Kremers, W.K.; Park, W.D.; Poggio, E.D.; Prieto, M.; Lieske, J.C.; Rule, A.D. Nephron hypertrophy and glomerulosclerosis and their association with kidney function and risk factors among living kidney donors. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 1892–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, W. How does early chronic kidney disease progress? A background paper prepared for the UK Consensus Conference on early chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2007, 22, ix26–ix30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, E.; Horio, M.; Yamagata, K.; Iseki, K.; Hara, S.; Ura, N.; Kiyohara, Y.; Makino, H.; Hishida, A.; Matsuo, S. Slower decline of glomerular filtration rate in the Japanese general population: A longitudinal 10-year follow-up study. Hypertens. Res. 2008, 31, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, W.C. Structure, not just function. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 503–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, W.C. Sonographic evaluation of renal failure. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2000, 35, 1021–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Päivänsalo, M.; Huttunen, K.; Suramo, I. Ultrasonographic findings in renal parenchymal diseases. Scand. J. Urol. Nephrol. 1985, 19, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noda, Y.; Ito, K.; Kanki, A.; Tamada, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Kazuya, Y.; Higaki, A. Measurement of renal cortical thickness using noncontrast-enhanced steady-state free precession MRI with spatially selective inversion recovery pulse: Association with renal function. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2015, 41, 1615–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Number | 87 |
| Age, years | 67.0 (28–95) |
| Male | 44 (50.6) |
| Height, cm | 159.0 (140–182) |
| Body weight, kg | 55.7 (36.8–92.0) |
| Body surface area, m2 | 1.43 (1.21–2.12) |
| Serum creatinine, mg/dL | 0.76 (0.35–4.72) |
| Estimated GFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 67.0 (10.2–137.7) |
| Kidney parameters | |
| Length, mm/cm | 60.9 (49.9–73.7) |
| Volume, ×1000 mm3/cm | 69.7 (39.6–129.3) |
| Cortical thickness, mm/cm | 4.4 (3.0–6.9) |
| Medullary thickness, mm/cm | 5.4 (3.5–8.8) |
| Parameters | Reference | Average Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | M/F Ratio | ||
| Length, mm | None | 100.4 | 94.4 | 1.063 |
| Height, cm | 60.1 | 62.1 | 0.968 | |
| BSA, m2 | 58.2 | 62.1 | 0.937 | |
| Volume, ×1000 mm3 | None | 138.0 | 97.6 | 1.414 |
| Height, cm | 82.7 | 63.9 | 1.295 | |
| BSA, m2 | 79.5 | 67.1 | 1.185 | |
| Cortical thickness, mm | None | 7.7 | 6.9 | 1.123 |
| Height, cm | 4.6 | 4.5 | 1.028 | |
| BSA, m2 | 4.4 | 4.8 | 0.936 | |
| Medullary thickness, mm | None | 9.1 | 8.4 | 1.072 |
| Height, cm | 5.4 | 5.5 | 0.982 | |
| BSA, m2 | 5.3 | 5.8 | 0.899 | |
| Variables | r | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| Length | 0.439 | <0.001 |
| Volume | 0.236 | 0.034 |
| Cortical thickness | 0.253 | 0.019 |
| Medullary thickness | 0.166 | 0.128 |
| Variable | Std β | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| Cortical thickness | 0.458 | <0.001 |
| Length | −0.208 | 0.058 |
| eGFR | 0.001 | 0.990 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoi, S.; Takata, T.; Sugihara, T.; Ida, A.; Ogawa, M.; Mae, Y.; Fukuda, S.; Munemura, C.; Isomoto, H. Predictive Value of Cortical Thickness Measured by Ultrasonography for Renal Impairment: A Longitudinal Study in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7120527
Hoi S, Takata T, Sugihara T, Ida A, Ogawa M, Mae Y, Fukuda S, Munemura C, Isomoto H. Predictive Value of Cortical Thickness Measured by Ultrasonography for Renal Impairment: A Longitudinal Study in Chronic Kidney Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2018; 7(12):527. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7120527
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoi, Shotaro, Tomoaki Takata, Takaaki Sugihara, Ayami Ida, Masaya Ogawa, Yukari Mae, Satoko Fukuda, Chishio Munemura, and Hajime Isomoto. 2018. "Predictive Value of Cortical Thickness Measured by Ultrasonography for Renal Impairment: A Longitudinal Study in Chronic Kidney Disease" Journal of Clinical Medicine 7, no. 12: 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7120527
APA StyleHoi, S., Takata, T., Sugihara, T., Ida, A., Ogawa, M., Mae, Y., Fukuda, S., Munemura, C., & Isomoto, H. (2018). Predictive Value of Cortical Thickness Measured by Ultrasonography for Renal Impairment: A Longitudinal Study in Chronic Kidney Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 7(12), 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7120527






