Eosinophilia and Kidney Disease: More than Just an Incidental Finding?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Eosinophilia, Hypereosinophilia and the Hypereosinophilic Syndrome (HES)
2.1. Biology of Eosinophil Granulocytes
2.2. Definitions and Classification of Eosinophil Disorders
3. Eosinophilia in Kidney Disease
3.1. Kidney Involvement in the Hypereosinophilic Syndrome
3.2. Kidney Diseases Associated with Eosinophilia/Hypereosinophilia
3.2.1. Hypersensitivity Reactions
3.2.2. Autoimmune Reactions and Related Diseases
3.2.3. Vascular Diseases
3.2.4. Other Diseases Presenting with Eosinophilia
3.2.5. Chronic Kidney Disease, Dialysis, and Kidney Transplantation
3.2.6. Renal Cell Carcinoma
3.2.7. Eosinophilia on Nephrology Consultation Service
4. Proposed Approach for the Management of Unexplained Eosinophilia and Acute Kidney Injury
4.1. First Step Approach for the Patient with Unexplained Peripheral Blood Eosinophilia
4.2. Approach for the Patient with PBE and AKI
5. Conclusions
6. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of interest
References
- Radonjic-Hoesli, S.; Valent, P.; Klion, A.D.; Wechsler, M.E.; Simon, H.U. Novel targeted therapies for eosinophil-associated diseases and allergy. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2015, 55, 633–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valent, P.; Klion, A.D.; Horny, H.P.; Roufosse, F.; Gotlib, J.; Weller, P.F.; Hellmann, A.; Metzgeroth, G.; Leiferman, K.M.; Arock, M.; et al. Contemporary consensus proposal on criteria and classification of eosinophilic disorders and related syndromes. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 607–612.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gotlib, J. World Health Organization-defined eosinophilic disorders: 2017 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and management. Am. J. Hematol. 2017, 92, 1243–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hogan, S.P.; Rosenberg, H.F.; Moqbel, R.; Phipps, S.; Foster, P.S.; Lacy, P.; Kay, A.B.; Rothenberg, M.E. Eosinophils: Biological properties and role in health and disease. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2008, 38, 709–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleich, G.J. Mechanisms of eosinophil-associated inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 105, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, G.A.; Yacoub, M.R.; Ripa, M.; Mannina, D.; Cariddi, A.; Saporiti, N.; Ciceri, F.; Castagna, A.; Colombo, G.; Dagna, L. Eosinophils from Physiology to Disease: A Comprehensive Review. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 9095275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roufosse, F.; Weller, P.F. Practical approach to the patient with hypereosinophilia. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rothenberg, M.E. Eosinophilia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 1592–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, J.E.; Groh, M.; Lefevre, G. (A Critical Appraisal of) Classification of Hypereosinophilic Disorders. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, C.J. Interleukin-5, eosinophils, and disease. Blood 1992, 79, 3101–3109. [Google Scholar]
- Chusid, M.J.; Dale, D.C.; West, B.C.; Wolff, S.M. The hypereosinophilic syndrome: Analysis of fourteen cases with review of the literature. Medicine 1975, 54, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valent, P.; Horny, H.P.; Bochner, B.S.; Haferlach, T.; Reiter, A. Controversies and open questions in the definitions and classification of the hypereosinophilic syndromes and eosinophilic leukemias. Semin. Hematol. 2012, 49, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spry, C.J. The hypereosinophilic syndrome: Clinical features, laboratory findings and treatment. Allergy 1982, 37, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fauci, A.S.; Harley, J.B.; Roberts, W.C.; Ferrans, V.J.; Gralnick, H.R.; Bjornson, B.H. NIH conference. The idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. Clinical, pathophysiologic, and therapeutic considerations. Ann. Intern. Med. 1982, 97, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spry, C.J.; Davies, J.; Tai, P.C.; Olsen, E.G.; Oakley, C.M.; Goodwin, J.F. Clinical features of fifteen patients with the hypereosinophilic syndrome. Q. J. Med. 1983, 52, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ogbogu, P.U.; Bochner, B.S.; Butterfield, J.H.; Gleich, G.J.; Huss-Marp, J.; Kahn, J.E.; Leiferman, K.M.; Nutman, T.B.; Pfab, F.; Ring, J.; et al. Hypereosinophilic syndrome: A multicenter, retrospective analysis of clinical characteristics and response to therapy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 1319.e3–1325.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liapis, H.; Ho, A.K.; Brown, D.; Mindel, G.; Gleich, G. Thrombotic microangiopathy associated with the hypereosinophilic syndrome. Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 1806–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehwaro, N.; Langlois, A.L.; Gueutin, V.; Izzedine, H. Renal involvement in idiopathic hypereosinophic syndrome. Clin. Kidney J. 2013, 6, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muriithi, A.K.; Leung, N.; Valeri, A.M.; Cornell, L.D.; Sethi, S.; Fidler, M.E.; Nasr, S.H. Biopsy-proven acute interstitial nephritis, 1993–2011: A case series. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 64, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.J.; Pusey, C.D. The changing profile of acute tubulointerstitial nephritis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2004, 19, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kano, Y.; Ishida, T.; Hirahara, K.; Shiohara, T. Visceral involvements and long-term sequelae in drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 94, 743–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.H.; Chung-Yee Hui, R.; Chang, C.J.; Ho, H.C.; Yang, C.H.; Lin, Y.J.; Chung, W.H. Identifying prognostic factors for drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS). Eur. J. Dermatol. 2011, 21, 930–937. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, H. Recent Advances in Drug-Induced Hypersensitivity Syndrome/Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 5163129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinico, R.A.; Di Toma, L.; Maggiore, U.; Bottero, P.; Radice, A.; Tosoni, C.; Grasselli, C.; Pavone, L.; Gregorini, G.; Monti, S.; et al. Prevalence and clinical significance of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies in Churg-Strauss syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 2926–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Durel, C.A.; Berthiller, J.; Caboni, S.; Jayne, D.; Ninet, J.; Hot, A. Long-Term Followup of a Multicenter Cohort of 101 Patients with Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss). Arthritis Care Res. 2016, 68, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groh, M.; Pagnoux, C.; Baldini, C.; Bel, E.; Bottero, P.; Cottin, V.; Dalhoff, K.; Dunogue, B.; Gross, W.; Holle, J.; et al. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss) (EGPA) Consensus Task Force recommendations for evaluation and management. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 26, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertsias, G.K.; Tektonidou, M.; Amoura, Z.; Aringer, M.; Bajema, I.; Berden, J.H.; Boletis, J.; Cervera, R.; Dorner, T.; Doria, A.; et al. Joint European League Against Rheumatism and European Renal Association-European Dialysis and Transplant Association (EULAR/ERA-EDTA) recommendations for the management of adult and paediatric lupus nephritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 1771–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anzai, M.; Maezawai, R.; Ohara, T.; Kodama, K.; Fukuda, T.; Kurasawa, K. Systemic lupus erythematosus associated with facial edema, overproduction of interleukin-5, and eosinophilia. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2008, 14, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.; Yoo, S.H.; Oh, D.; Joo, K.W.; Kim, Y.S.; Yoon, S.S.; Kim, I.; Park, S.; Lee, H.; Koh, Y. Clinical dissection of thrombotic microangiopathy. Ann. Hematol. 2017, 96, 1715–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, A.; Ziccardi, M.R.; Witzke, C.; Palacios, I.; Rangaswami, J. Cholesterol embolization syndrome: An under-recognized entity in cardiovascular interventions. J. Interv. Cardiol. 2018, 31, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thadhani, R.I.; Camargo, C.A., Jr.; Xavier, R.J.; Fang, L.S.; Bazari, H. Atheroembolic renal failure after invasive procedures. Natural history based on 52 histologically proven cases. Medicine 1995, 74, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lye, W.C.; Cheah, J.S.; Sinniah, R. Renal cholesterol embolic disease. Case report and review of the literature. Am. J. Nephrol. 1993, 13, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajpoot, D.K.; Pahl, M.; Clark, J. Nephrotic syndrome associated with Kimura disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2000, 14, 486–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, T.; Tanaka, T.; Kinomura, M. Nephrotic syndrome during the tapering of oral steroids after pathological diagnosis of Kimura disease from a lacrimal gland mass: Case report and review of 10 Japanese patients. J. Clin. Exp. Hematop. 2017, 57, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandeville, J.T.; Levinson, R.D.; Holland, G.N. The tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis syndrome. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2001, 46, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito-Zeron, P.; Ramos-Casals, M.; Bosch, X.; Stone, J.H. The clinical spectrum of IgG4-related disease. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Torre, E.; Mattoo, H.; Mahajan, V.S.; Carruthers, M.; Pillai, S.; Stone, J.H. Prevalence of atopy, eosinophilia, and IgE elevation in IgG4-related disease. Allergy 2014, 69, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeki, T.; Kobayashi, D.; Ito, T.; Tamura, M.; Yoshikawa, S.; Yamazaki, H. Comparison of clinical and laboratory features of patients with and without allergic conditions in IgG4-related disease: A single-center experience in Japan. Mod. Rheumatol. 2018, 28, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, S.; Corbett, R.; Duncan, N.; Ashby, D. Increased prevalence of eosinophilia in a hemodialysis population: Longitudinal and case control studies. Hemodial. Int. 2016, 20, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, W.E.; Cestero, R.V. Eosinophilia in maintenance hemodialysis patients. J. Dial 1979, 3, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.I.; Song, J.O.; Park, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Shin, S.K. Idiopathic eosinophilic peritonitis in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis: Experience with percutaneous catheter placement. Nephrology 2007, 12, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandran, P.K.; Humayun, H.M.; Daugirdas, J.T.; Nawab, Z.M.; Gandhi, V.C.; Ing, T.S. Blood eosinophilia in patients undergoing maintenance peritoneal dialysis. Arch. Intern. Med. 1985, 145, 114–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongwei, W.; Nanra, R.S.; Stein, A.; Avis, L.; Price, A.; Hibberd, A.D. Eosinophils in acute renal allograft rejection. Transpl. Immunol. 1994, 2, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geri, G.; Rabbat, A.; Mayaux, J.; Zafrani, L.; Chalumeau-Lemoine, L.; Guidet, B.; Azoulay, E.; Pene, F. Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection syndrome: A case series and a review of the literature. Infection 2015, 43, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roxby, A.C.; Gottlieb, G.S.; Limaye, A.P. Strongyloidiasis in transplant patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 1411–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praga, M.; Sevillano, A.; Aunon, P.; Gonzalez, E. Changes in the aetiology, clinical presentation and management of acute interstitial nephritis, an increasingly common cause of acute kidney injury. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 1472–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muriithi, A.K.; Nasr, S.H.; Leung, N. Utility of urine eosinophils in the diagnosis of acute interstitial nephritis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 8, 1857–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praga, M.; Gonzalez, E. Acute interstitial nephritis. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 956–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, M.R.; Giblin, L.; O’Connell, F.P.; O’Kelly, P.; Walshe, J.J.; Conlon, P.; O’Meara, Y.; Dormon, A.; Campbell, E.; Donohoe, J. Acute interstitial nephritis: Clinical features and response to corticosteroid therapy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2004, 19, 2778–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, E.; Gutierrez, E.; Galeano, C.; Chevia, C.; de Sequera, P.; Bernis, C.; Parra, E.G.; Delgado, R.; Sanz, M.; Ortiz, M.; et al. Early steroid treatment improves the recovery of renal function in patients with drug-induced acute interstitial nephritis. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moledina, D.G.; Perazella, M.A. Treatment of Drug-Induced Acute Tubulointerstitial Nephritis: The Search for Better Evidence. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prendecki, M.; Tanna, A.; Salama, A.D.; Tam, F.W.; Cairns, T.; Taube, D.; Cook, H.T.; Ashby, D.; Duncan, N.D.; Pusey, C.D. Long-term outcome in biopsy-proven acute interstitial nephritis treated with steroids. Clin. Kidney J. 2017, 10, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Juarez, G.; Perez, J.V.; Caravaca-Fontan, F.; Quintana, L.; Shabaka, A.; Rodriguez, E.; Gadola, L.; de Lorenzo, A.; Cobo, M.A.; Oliet, A.; et al. Duration of Treatment with Corticosteroids and Recovery of Kidney Function in Acute Interstitial Nephritis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kano, Y.; Hiraharas, K.; Sakuma, K.; Shiohara, T. Several herpesviruses can reactivate in a severe drug-induced multiorgan reaction in the same sequential order as in graft-versus-host disease. Br. J. Dermatol. 2006, 155, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roujeau, J.C.; Dupin, N. Virus Reactivation in Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (Dress) Results from a Strong Drug-Specific Immune Response. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2017, 5, 811–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Descamps, V.; Ranger-Rogez, S. DRESS syndrome. Joint Bone Spine 2014, 81, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacoub, P.; Musette, P.; Descamps, V.; Meyer, O.; Speirs, C.; Finzi, L.; Roujeau, J.C. The DRESS syndrome: A literature review. Am. J. Med. 2011, 124, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roujeau, J.C.; Stern, R.S. Severe adverse cutaneous reactions to drugs. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 331, 1272–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, A.; Rajagopalan, M.; Sarda, A.; Das, S.; Biswas, P. Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms: An Update and Review of Recent Literature. Indian J. Dermatol. 2018, 63, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kito, Y.; Ito, T.; Tokura, Y.; Hashizume, H. High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin monotherapy for drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2012, 92, 100–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly, P.; Janela, B.; Tetart, F.; Rogez, S.; Picard, D.; D’Incan, M.; Descamps, V.; Collet, E.; Roujeau, J.C.; Musette, P. Poor benefit/risk balance of intravenous immunoglobulins in DRESS. Arch. Dermatol. 2012, 148, 543–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husain, Z.; Reddy, B.Y.; Schwartz, R.A. DRESS syndrome: Part II. Management and therapeutics. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 68, 709.e1-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumenthal, K.G.; Youngster, I.; Rabideau, D.J.; Parker, R.A.; Manning, K.S.; Walensky, R.P.; Nelson, S.B. Peripheral blood eosinophilia and hypersensitivity reactions among patients receiving outpatient parenteral antibiotics. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 1288.e1–1294.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masi, A.T.; Hunder, G.G.; Lie, J.T.; Michel, B.A.; Bloch, D.A.; Arend, W.P.; Calabrese, L.H.; Edworthy, S.M.; Fauci, A.S.; Leavitt, R.Y. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of Churg-Strauss syndrome (allergic granulomatosis and angiitis). Arthritis Rheum. 1990, 33, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comarmond, C.; Pagnoux, C.; Khellaf, M.; Cordier, J.F.; Hamidou, M.; Viallard, J.F.; Maurier, F.; Jouneau, S.; Bienvenu, B.; Puechal, X.; et al. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss): Clinical characteristics and long-term followup of the 383 patients enrolled in the French Vasculitis Study Group cohort. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sable-Fourtassou, R.; Cohen, P.; Mahr, A.; Pagnoux, C.; Mouthon, L.; Jayne, D.; Blockmans, D.; Cordier, J.F.; Delaval, P.; Puechal, X.; et al. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies and the Churg-Strauss syndrome. Ann. Intern. Med. 2005, 143, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healy, B.; Bibby, S.; Steele, R.; Weatherall, M.; Nelson, H.; Beasley, R. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies and myeloperoxidase autoantibodies in clinical expression of Churg-Strauss syndrome. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J.; Bacon, P.A.; Basu, N.; Cid, M.C.; Ferrario, F.; Flores-Suarez, L.F.; Gross, W.L.; Guillevin, L.; Hagen, E.C.; et al. 2012 revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaigne, B.; Terrier, B.; Thieblemont, N.; Witko-Sarsat, V.; Mouthon, L. Dividing the Janus vasculitis? Pathophysiology of eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangitis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2016, 15, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberici, F.; Martorana, D.; Vaglio, A. Genetic aspects of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30 (Suppl. 1), i37–i45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaglio, A.; Martorana, D.; Maggiore, U.; Grasselli, C.; Zanetti, A.; Pesci, A.; Garini, G.; Manganelli, P.; Bottero, P.; Tumiati, B.; et al. HLA-DRB4 as a genetic risk factor for Churg-Strauss syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 3159–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieczorek, S.; Hellmich, B.; Arning, L.; Moosig, F.; Lamprecht, P.; Gross, W.L.; Epplen, J.T. Functionally relevant variations of the interleukin-10 gene associated with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-negative Churg-Strauss syndrome, but not with Wegener’s granulomatosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 1839–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-Mendoza, E.P.; Tobon, G.J. Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis: Newer Therapies. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2018, 20, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, M.; Watts, R.; Bajema, I.; Cid, M.; Crestani, B.; Hauser, T.; Hellmich, B.; Holle, J.; Laudien, M.; Little, M.A.; et al. Validation of the EULAR/ERA-EDTA recommendations for the management of ANCA-associated vasculitis by disease content experts. RMD Open 2017, 3, e000449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, J.H.; Merkel, P.A.; Spiera, R.; Seo, P.; Langford, C.A.; Hoffman, G.S.; Kallenberg, C.G.; St Clair, E.W.; Turkiewicz, A.; Tchao, N.K.; et al. Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide for ANCA-associated vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.B.; Tervaert, J.W.; Hauser, T.; Luqmani, R.; Morgan, M.D.; Peh, C.A.; Savage, C.O.; Segelmark, M.; Tesar, V.; van Paassen, P.; et al. Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide in ANCA-associated renal vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, A.J.; Hot, A.; Arndt, F.; Moosig, F.; Guerry, M.J.; Amudala, N.; Smith, R.; Sivasothy, P.; Guillevin, L.; Merkel, P.A.; Jayne, D.R. Rituximab for the treatment of eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, M.E.; Akuthota, P.; Jayne, D.; Khoury, P.; Klion, A.; Langford, C.A.; Merkel, P.A.; Moosig, F.; Specks, U.; Cid, M.C.; et al. Mepolizumab or Placebo for Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1921–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raffray, L.; Guillevin, L. Treatment of Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis: A Review. Drugs 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Marigowda, G.; Oren, E.; Israel, E.; Wechsler, M.E. Mepolizumab as a steroid-sparing treatment option in patients with Churg-Strauss syndrome. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 1336–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosig, F.; Gross, W.L.; Herrmann, K.; Bremer, J.P.; Hellmich, B. Targeting interleukin-5 in refractory and relapsing Churg-Strauss syndrome. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 341–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartin-Ceba, R.; Keogh, K.A.; Specks, U.; Sethi, S.; Fervenza, F.C. Rituximab for the treatment of Churg-Strauss syndrome with renal involvement. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 2865–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuhn, D.; Hospowsky, C.; Both, M.; Hey, M.; Laudien, M. Manifestation of granulomatosis with polyangiitis in head and neck. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2018, 36 (Suppl. 111), 78–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Seccia, V.; Baldini, C.; Latorre, M.; Gelardi, M.; Dallan, I.; Cristofani-Mencacci, L.; Sellari-Franceschini, S.; Bartoli, M.L.; Bacci, E.; Paggiaro, P. Focus on the Involvement of the Nose and Paranasal Sinuses in Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss Syndrome): Nasal Cytology Reveals Infiltration of Eosinophils as a Very Common Feature. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 175, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, M.B.; Fincher, R.K.; Finger, D.R. Eosinophilia in Wegener’s granulomatosis. Chest 1999, 116, 1480–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoda, H.; Kanda, H.; Tanaka, R.; Komagata, Y.; Misaki, Y.; Yamamoto, K. Wegener’s granulomatosis with eosinophilia. Intern. Med. 2005, 44, 750–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uematsu, H.; Takata, S.; Sueishi, K.; Inoue, H. Polyangiitis overlap syndrome of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s granulomatosis) and eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss syndrome). BMJ Case Rep. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroegel, C.; Foerster, M.; Quickert, S.; Slevogt, H.; Neumann, T. Vasculitides and eosinophilic pulmonary diseases. Internist 2018, 59, 898–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, P.; Zagallo, P.; Talar-Williams, C.; Santos, C.S.; Dinerman, E.; Holland, N.C.; Klion, A.D. Serum biomarkers are similar in Churg-Strauss syndrome and hypereosinophilic syndrome. Allergy 2012, 67, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emmi, G.; Silvestri, E.; Marconi, R.; Carrai, V.; Fanelli, T.; Zucchini, P.; Marasca, R.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Emmi, L.; Prisco, D.; et al. First report of FIP1L1-PDGFRalpha-positive eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 1751–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beketova, T.V.; Volkov, M.Y.; Naryshkin, E.A.; Novoselova, T.M.; Nasonov, E.L. Imatinib mesylate use in refractory eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: A literature review and a case report. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 1729–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groh, M.; Kahn, J.E.; Puechal, X.; Guillevin, L. Comment on: First report of FIP1L1-PDGFRalpha-positive eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 384–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, A.M.; Shulman, L.E.; Tumulty, P.A.; Conley, C.L.; Schoenrich, E.H. Systemic lupus erythematosus: Review of the literature and clinical analysis of 138 cases. Medicine 1954, 33, 291–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomeer, M.; Moerman, P.; Westhovens, R.; Van den Eeckhout, A.; Dequeker, J.; Demedts, M. Systemic lupus erythematosus, eosinophilia and Loffler’s endocarditis. An unusual association. Eur. Respir. J. 1999, 13, 930–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydogdu, S.; Ucar, O.; Cetin, M. A case of systemic lupus erythematosus presenting with hypereosinophilia and Loeffler endocarditis. Acta Cardiol. 2010, 65, 571–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, G.; Xie, Q. Systemic lupus erythematosus associated with Wells’ syndrome. Rheumatol. Int. 2012, 32, 1087–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, T.; Umeno, M.; Takaki, K.; Tanaka, M.; Takeda, T.; Nagasawa, K. A case of SLE with the onset of pleuritis showing eosinophilia and elevation of serum IgE. Fukuoka Igaku Zasshi 1996, 87, 97–101. [Google Scholar]
- Fukui, S.; Iwamoto, N.; Tsuji, S.; Umeda, M.; Nishino, A.; Nakashima, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Horai, Y.; Koga, T.; Kawashiri, S.Y.; et al. Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis With Thrombotic Microangiopathy: Is Simultaneous Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Associated with Clinical Manifestations? A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Medicine 2015, 94, e1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargili, A.; Bavbek, N.; Kaya, A.; Kosar, A.; Karaaslan, Y. Eosinophilia in rheumatologic diseases: A prospective study of 1000 cases. Rheumatol. Int. 2004, 24, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, F.; Ren, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhong, R.; Liang, Y. Comparisons of neutrophil-, monocyte-, eosinophil-, and basophil-lymphocyte ratios among various systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases. APMIS 2017, 125, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brocklebank, V.; Wood, K.M.; Kavanagh, D. Thrombotic Microangiopathy and the Kidney. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 13, 300–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohguchi, H.; Sugawara, T.; Harigae, H. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura complicated with hypereosinophilic syndrome. Intern. Med. 2009, 48, 1687–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuste, C.; Quiroga, B.; Verde, E.; Barraca, D.; Reque, J.E.; Perez de Jose, A.; Luno, J. The non-casual relation between eosinophilia and thrombotic microangiopathy. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2012, 47, 365–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langlois, A.L.; Shehwaro, N.; Rondet, C.; Benbrik, Y.; Maloum, K.; Gueutin, V.; Rouvier, P.; Izzedine, H. Renal thrombotic microangiopathy and FIP1L1/PDGFRalpha-associated myeloproliferative variant of hypereosinophilic syndrome. Clin. Kidney J. 2013, 6, 418–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, L.N.; Bailey, N.G.; Vos, J.A.; Stotler, C.J. Unique association of myeloid neoplasm with eosinophilia and abnormalities of PDGFRA with TTP. W. V. Med. J. 2013, 109, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mulvey, J.J.; Magro, C.; Chadburn, A. Resolution of a steroid-resistant, hypereosinophilic immune diathesis with mepolizumab and concomitant amelioration of a mixed thrombotic microangiopathy. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2018, 69, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basak, R.; Wang, X.; Keane, C.; Woroniecki, R. Atypical presentation of atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome. BMJ Case Rep. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, M.; Ferreiro, T.; Leite, B.N.; Pita, F.; Bolanos, L.; Valdes, F.; Alonso, A.; Vazquez, E.; Mosquera, J.; Trigas, M.; et al. Two cases of atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS) and eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA): A possible relationship. CEN Case Rep. 2017, 6, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maino, A.; Rossio, R.; Cugno, M.; Marzano, A.V.; Tedeschi, A. Hypereosinophilic syndrome, Churg-Strauss syndrome and parasitic diseases: Possible links between eosinophilia and thrombosis. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2012, 10, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roufosse, F. L4. Eosinophils: How they contribute to endothelial damage and dysfunction. Presse Med. 2013, 42, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bayliss, G.; Zhuang, S. Cholesterol Crystal Embolism and Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scolari, F.; Ravani, P.; Gaggi, R.; Santostefano, M.; Rollino, C.; Stabellini, N.; Colla, L.; Viola, B.F.; Maiorca, P.; Venturelli, C.; et al. The challenge of diagnosing atheroembolic renal disease: Clinical features and prognostic factors. Circulation 2007, 116, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusco, M.A.; Najafian, B.; Alpers, C.E.; Fogo, A.B. AJKD Atlas of Renal Pathology: Cholesterol Emboli. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 67, e23–e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, Y.; Tsutsui, H.; Tsuchihashi, M.; Masumoto, A.; Takeshita, A.; Cholesterol Embolism Study (CHEST). Investigators The incidence and risk factors of cholesterol embolization syndrome, a complication of cardiac catheterization: A prospective study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 42, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, G.; O’Neill, W.M., Jr.; Lambert, R.; Bloomer, H. Cholesterol embolization: A complication of angiography. Arch. Intern. Med. 1978, 138, 1430–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo, R.R.; Swartz, R.D. Redefining the incidence of clinically detectable atheroembolism. Am. J. Med. 1996, 100, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, R.; Fujita, S.; Kizawa, S.; Sakane, K.; Morita, H.; Ozeki, M.; Sohmiya, K.; Hoshiga, M.; Ishizaka, N. Association between absolute blood eosinophil count and CKD stages among cardiac patients. Heart Vessels 2016, 31, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igarashi, Y.; Akimoto, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Iwazu, Y.; Miki, T.; Otani-Takei, N.; Imai, T.; Sugase, T.; Masuda, T.; Takeda, S.I.; et al. Performing Anticoagulation: A Puzzling Case of Cholesterol Embolization Syndrome. Clin. Med. Insights Case Rep. 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiyama, K.; Sato, T.; Taguma, Y. Low-Density Lipoprotein Apheresis Ameliorates Renal Prognosis of Cholesterol Crystal Embolism. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2015, 19, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scolari, F.; Ravani, P.; Pola, A.; Guerini, S.; Zubani, R.; Movilli, E.; Savoldi, S.; Malberti, F.; Maiorca, R. Predictors of renal and patient outcomes in atheroembolic renal disease: A prospective study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 1584–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.Y.; Ye, S.B.; Luo, R.Z.; Yan, S.M.; Gao, Y.F.; Yang, Y.Z.; Guo, Z.M.; Chen, Y.F. Notch-1 and Ki-67 receptor as predictors for the recurrence and prognosis of Kimura’s disease. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 2402–2410. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Glibbery, N.; Muscat, K.; Cascarini, L. Kimura’s disease of the parotid gland with cutaneous features in a Caucasian female patient. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2018, 2018, rjy067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drouillard, M.; Steve, M.; Ranoarivony, T.; Souraud, J.B. Kimura’s disease in a 50-year-old Tunisian man. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2017, 134, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osuch-Wojcikiewicz, E.; Bruzgielewicz, A.; Lachowska, M.; Wasilewska, A.; Niemczyk, K. Kimura’s Disease in a Caucasian Female: A Very Rare Cause of Lymphadenopathy. Case Rep. Otolaryngol. 2014, 2014, 415865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKelvie, P.A.; Lyons, B.; Barnett, G.; Allen, P.W. Kimura’s disease in two Caucasians, one with multiple recurrences associated with prominent IgG4 production. Pathology 2012, 44, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noel, N.; Meignin, V.; Rosenstingl, S.; Ronco, P.; Boffa, J.J. Nephrotic syndrome associated with immune thrombocytopenia revealing Kimura’s disease in a non-Asian male. NDT Plus 2009, 2, 452–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller-Richter, U.D.; Moralis, A.; Reuther, T.; Kochel, M.; Reichert, T.E.; Driemel, O. Kimura’s disease in a white man. Head Neck 2011, 33, 138–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bastos, J.T.; da Rocha, C.R.M.; Silva, P.M.C.; de Freitas, B.M.P.; Cassia, F.F.; Avelleira, J.C.R. Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia versus Kimura’s disease: A case report and a clinical and histopathological comparison. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2017, 92, 392–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, S.S.; Arora, P.; Usha; Prakash, J. Mesangioproliferative glomerulonephritis in a patient with Kimura’s disease presenting as Nephrotic syndrome. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 2015, 26, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Y.; Mao, J.H.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, W.Z.; Zhao, S.A.; Chen, Y.F.; Liu, A.M. Kimura disease: A case report and review of the Chinese literature. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2009, 111, c55–c61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okura, T.; Miyoshi, K.; Irita, J.; Enomoto, D.; Nagao, T.; Kukida, M.; Tanino, A.; Kudo, K.; Higaki, J. Kimura’s disease associated with membranous nephropathy with IgG4 and phospholipase A2 receptor-positive staining of the glomerular basement membrane. Intern. Med. 2014, 53, 1435–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obata, Y.; Furusu, A.; Nishino, T.; Ichinose, H.; Ohnita, A.; Iwasaki, K.; Taguchi, T.; Kohno, S. Membranous nephropathy and Kimura’s disease manifesting a hip mass. A case report with literature review. Intern. Med. 2010, 49, 1405–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kar, I.B.; Sethi, A.K. Kimura’s Disease: Report of a Case & Review of Literature. J. Maxillofac. Oral. Surg. 2013, 12, 109–112. [Google Scholar]
- Chim, C.S.; Liang, R.; Fung, A.; Kwong, Y.L.; Shek, T.W. Further analysis of clonality in Kimura’s disease. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2003, 27, 703–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Park, S.J.; Han, K.H.; Kronbichler, A.; Saleem, M.A.; Oh, J.; Lim, B.J.; Shin, J.I. Pathogenesis of minimal change nephrotic syndrome: An immunological concept. Korean J. Pediatr. 2016, 59, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.L.; Wei, P.F.; Chen, J.H.; Zhao, Z.F.; Xu, Q.N.; Ye, L. Diagnosis and treatment of a patient with Kimura’s disease associated with nephrotic syndrome and lymphadenopathy of the epitrochlear nodes. BMC Nephrol. 2015, 16, 10-015-0007-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrin, R.S.; Vernier, R.L.; Fish, A.L. Acute eosinophilic interstitial nephritis and renal failure with bone marrow-lymph node granulomas and anterior uveitis. A new syndrome. Am. J. Med. 1975, 59, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clive, D.M.; Vanguri, V.K. The Syndrome of Tubulointerstitial Nephritis with Uveitis (TINU). Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 72, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azar, R.; Verove, C.; Boldron, A. Delayed onset of uveitis in TINU syndrome. J. Nephrol. 2000, 13, 381–383. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, A.K.; Hwang, Y.S.; Mandelcorn, E.D.; Davis, J.L. HLA-DR, DQ class II DNA typing in pediatric panuveitis and tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 157, 678.e1-2–686.e1-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peräsaari, J.; Saarela, V.; Nikkilä, J.; Ala-Houhala, M.; Arikoski, P.; Kataja, J.; Rönnholm, K.; Merenmies, J.; Nuutinen, M.; Jahnukainen, T. HLA associations with tubulointerstitial nephritis with or without uveitis in Finnish pediatric population: A nation-wide study. Tissue Antigens 2013, 81, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levinson, R.D.; Park, M.S.; Rikkers, S.M.; Reed, E.F.; Smith, J.R.; Martin, T.M.; Rosenbaum, J.T.; Foster, C.S.; Sherman, M.D.; Holland, G.N. Strong associations between specific HLA-DQ and HLA-DR alleles and the tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis syndrome. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackensen, F.; David, F.; Schwenger, V.; Smith, L.K.; Rajalingam, R.; Levinson, R.D.; Austin, C.R.; Houghton, D.; Martin, T.M.; Rosenbaum, J.T. HLA-DRB1*0102 is associated with TINU syndrome and bilateral, sudden-onset anterior uveitis but not with interstitial nephritis alone. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 95, 971–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Yu, F.; Qu, Z.; Su, T.; Xing, G.Q.; Wu, L.H.; Wang, F.M.; Liu, G.; Yang, L.; Zhao, M.H. Modified C-reactive protein might be a target autoantigen of TINU syndrome. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyekpe, I.; Shenoy, M.; Denley, H.; Riad, H.; Webb, N.J. Recurrent tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis syndrome in a renal transplant recipient. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 3060–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stone, J.H.; Zen, Y.; Deshpande, V. IgG4-related disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamano, H.; Kawa, S.; Horiuchi, A.; Unno, H.; Furuya, N.; Akamatsu, T.; Fukushima, M.; Nikaido, T.; Nakayama, K.; Usuda, N.; et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamisawa, T.; Funata, N.; Hayashi, Y.; Eishi, Y.; Koike, M.; Tsuruta, K.; Okamoto, A.; Egawa, N.; Nakajima, H. A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 38, 982–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Buy Wenniger, L.J.; Culver, E.L.; Beuers, U. Exposure to occupational antigens might predispose to IgG4-related disease. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1453–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Culver, E.L.; Vermeulen, E.; Makuch, M.; van Leeuwen, A.; Sadler, R.; Cargill, T.; Klenerman, P.; Aalberse, R.C.; van Ham, S.M.; Barnes, E.; et al. Increased IgG4 responses to multiple food and animal antigens indicate a polyclonal expansion and differentiation of pre-existing B cells in IgG4-related disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 944–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akiyama, M.; Takeuchi, T. IgG4-Related Disease: Beyond Glucocorticoids. Drugs Aging 2018, 35, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubers, L.M.; Vos, H.; Schuurman, A.R.; Erken, R.; Oude Elferink, R.P.; Burgering, B.; van de Graaf, S.F.J.; Beuers, U. Annexin A11 is targeted by IgG4 and IgG1 autoantibodies in IgG4-related disease. Gut 2018, 67, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawa, S.; Ota, M.; Yoshizawa, K.; Horiuchi, A.; Hamano, H.; Ochi, Y.; Nakayama, K.; Tokutake, Y.; Katsuyama, Y.; Saito, S.; et al. HLA DRB10405-DQB10401 haplotype is associated with autoimmune pancreatitis in the Japanese population. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 1264–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aalberse, R.C.; Stapel, S.O.; Schuurman, J.; Rispens, T. Immunoglobulin G4: An odd antibody. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2009, 39, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiokawa, M.; Kodama, Y.; Kuriyama, K.; Yoshimura, K.; Tomono, T.; Morita, T.; Kakiuchi, N.; Matsumori, T.; Mima, A.; Nishikawa, Y.; et al. Pathogenicity of IgG in patients with IgG4-related disease. Gut 2016, 65, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, J.H.; Brito-Zeron, P.; Bosch, X.; Ramos-Casals, M. Diagnostic Approach to the Complexity of IgG4-Related Disease. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2015, 90, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Cornell, L.D. IgG4-Related Tubulointerstitial Nephritis. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2017, 24, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeki, T.; Nishi, S.; Imai, N.; Ito, T.; Yamazaki, H.; Kawano, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Takahashi, H.; Matsui, S.; Nakada, S.; et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of patients with IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. Kidney Int. 2010, 78, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raissian, Y.; Nasr, S.H.; Larsen, C.P.; Colvin, R.B.; Smyrk, T.C.; Takahashi, N.; Bhalodia, A.; Sohani, A.R.; Zhang, L.; Chari, S.; et al. Diagnosis of IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1343–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, M.; Saeki, T.; Nakashima, H.; Nishi, S.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Hisano, S.; Yamanaka, N.; Inoue, D.; Yamamoto, M.; Takahashi, H.; et al. Proposal for diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related kidney disease. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2011, 15, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Kim, J.H.; Byun, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, M.G. IgG4-related kidney disease: MRI findings with emphasis on the usefulness of diffusion-weighted imaging. Eur. J. Radiol. 2014, 83, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.I.; Li, H.Z.; Zhang, Y.S. IgG4-related inflammatory pseudotumor of the kidney mimicking renal cell carcinoma: A case report. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 3438–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Danlos, F.X.; Rossi, G.M.; Blockmans, D.; Emmi, G.; Kronbichler, A.; Durupt, S.; Maynard, C.; Luca, L.; Garrouste, C.; Lioger, B.; et al. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitides and IgG4-related disease: A new overlap syndrome. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, S.Y.; Keogh, K.A.; Lewis, J.E.; Ryu, J.H.; Cornell, L.D.; Garrity, J.A.; Yi, E.S. IgG4-positive plasma cells in granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s): A clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study on 43 granulomatosis with polyangiitis and 20 control cases. Hum. Pathol. 2013, 44, 2432–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della-Torre, E.; Lanzillotta, M.; Campochiaro, C.; Bozzalla, E.; Bozzolo, E.; Bandiera, A.; Bazzigaluppi, E.; Canevari, C.; Modorati, G.; Stone, J.H.; et al. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody positivity in IgG4-related disease: A case report and review of the literature. Medicine 2016, 95, e4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruthers, M.N.; Park, S.; Slack, G.W.; Dalal, B.I.; Skinnider, B.F.; Schaeffer, D.F.; Dutz, J.P.; Law, J.K.; Donnellan, F.; Marquez, V.; et al. IgG4-related disease and lymphocyte-variant hypereosinophilic syndrome: A comparative case series. Eur. J. Haematol. 2017, 98, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khosroshahi, A.; Wallace, Z.S.; Crowe, J.L.; Akamizu, T.; Azumi, A.; Carruthers, M.N.; Chari, S.T.; Della-Torre, E.; Frulloni, L.; Goto, H.; et al. International Consensus Guidance Statement on the Management and Treatment of IgG4-Related Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 1688–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Najafian, B.; Fogo, A.B.; Lusco, M.A.; Alpers, C.E. AJKD Atlas of Renal Pathology: IgG4-Related Tubulointerstitial Nephritis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 69, e19–e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.P.; Larsen, C.P.; Gibson, I.W.; Nasr, S.H.; Sethi, S.; Fidler, M.E.; Raissian, Y.; Takahashi, N.; Chari, S.; Smyrk, T.C.; et al. Membranous glomerulonephritis is a manifestation of IgG4-related disease. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Takahashi, H.; Shinomura, Y. Mechanisms and assessment of IgG4-related disease: Lessons for the rheumatologist. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2014, 10, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattrocchio, G.; Barreca, A.; Demarchi, A.; Solfietti, L.; Beltrame, G.; Fenoglio, R.; Ferro, M.; Mesiano, P.; Murgia, S.; Del Vecchio, G.; et al. IgG4-related kidney disease: The effects of a Rituximab-based immunosuppressive therapy. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 21337–21347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, Z.S.; Deshpande, V.; Mattoo, H.; Mahajan, V.S.; Kulikova, M.; Pillai, S.; Stone, J.H. IgG4-Related Disease: Clinical and Laboratory Features in One Hundred Twenty-Five Patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 2466–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carruthers, M.N.; Topazian, M.D.; Khosroshahi, A.; Witzig, T.E.; Wallace, Z.S.; Hart, P.A.; Deshpande, V.; Smyrk, T.C.; Chari, S.; Stone, J.H. Rituximab for IgG4-related disease: A prospective, open-label trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvadori, M.; Tsalouchos, A. Immunoglobulin G4-related kidney diseases: An updated review. World J. Nephrol. 2018, 7, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, Z.S.; Mattoo, H.; Mahajan, V.S.; Kulikova, M.; Lu, L.; Deshpande, V.; Choi, H.K.; Pillai, S.; Stone, J.H. Predictors of disease relapse in IgG4-related disease following rituximab. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shilpa, R.; Sreekrishnan, T.P.; Kumar, K.P.G.; Neethu, C.M. A Case Report on Pregabalin-Induced Eosinophilia. Consult. Pharm. 2018, 33, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, M.; Jhinger, R.K.; Wuerz, T.; Walkty, A. Marked peripheral eosinophilia due to prolonged administration of posaconazole. JMM Case Rep. 2017, 4, e005100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogo, A.B. Quiz page. Diabetic nephropathy with superimposed acute interstitial nephritis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2003, 41, A47, E1–E3. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, D.F.; Sasaki, K.; Lin, M.Y.; Smith, K.D.; Nicosia, R.F.; Alpers, C.E.; Najafian, B. Interstitial eosinophilic aggregates in diabetic nephropathy: Allergy or not? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 1370–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, R.; Thompson, F.; Esterman, A.; McDermott, R. Strongyloides stercoralis, Eosinophilia, and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The Predictive Value of Eosinophilia in the Diagnosis of S stercoralis Infection in an Endemic Community. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2016, 3, ofw029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.D.; Kopp, J.B.; Kimmel, P.L. Kidney Diseases Associated with Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2363–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Mohajer, M.; Villarreal-Williams, E.; Andrade, R.A.; Giordano, T.P.; Serpa, J.A. Eosinophilia and associated factors in a large cohort of patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. South Med. J. 2014, 107, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivaram, M.; White, A.; Radcliffe, K.W. Eosinophilia: Clinical significance in HIV-infected individuals. Int. J. STD AIDS 2012, 23, 635–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, A.; Serpa, J.A. Eosinophilia in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2015, 12, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudtson, E.; Para, M.; Boswell, H.; Fan-Havard, P. Drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms syndrome and renal toxicity with a nevirapine-containing regimen in a pregnant patient with human immunodeficiency virus. Obstet. Gynecol. 2003, 101, 1094–1097. [Google Scholar]
- Angel-Moreno-Maroto, A.; Suarez-Castellano, L.; Hernandez-Cabrera, M.; Perez-Arellano, J.L. Severe efavirenz-induced hypersensitivity syndrome (not-DRESS) with acute renal failure. J. Infect. 2006, 52, e39–e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandariz, D.; Smithson, A.; Anton-Vazquez, V. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms related to antiretroviral treatment in human immunodeficiency virus patients. Indian J. Sex. Transm. Dis. AIDS 2017, 38, 163–170. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, M.; Hopkins, C.; Duffy, E.; Lee, D.; Loulergue, P.; Ripamonti, D.; Ostrov, D.A.; Phillips, E. Association of the HLA-B*53:01 Allele with Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) Syndrome During Treatment of HIV Infection with Raltegravir. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 1198–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akosa, A.B.; Sherif, A.; Maidment, C.G. Kimura’s disease and membranous nephropathy. Nephron 1991, 58, 472–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigui, M.; Hmida, M.B.; Jallouli, M.; Kechaou, M.; Frikha, F.; Bahloul, Z. Membranous glomerulopathy associated with idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 2010, 21, 320–322. [Google Scholar]
- Yim, H.E.; Yoo, K.H.; Won, N.H.; Hong, Y.S.; Lee, J.W. Churg-Strauss syndrome in a child with IgA nephropathy. Clin. Nephrol. 2009, 71, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natov, S.N.; Strom, J.A.; Ucci, A. Relapsing nephrotic syndrome in a patient with Kimura’s disease and IgA glomerulonephritis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1998, 13, 2358–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitazawa, A.; Koda, R.; Yoshino, A.; Ueda, Y.; Takeda, T. An IgA1-lambda-type monoclonal immunoglobulin deposition disease associated with membranous features in a patient with IgG4-related kidney disease: A case report. BMC Nephrol. 2018, 19, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, S.; Takazakura, E.; Fukui, Y. Tubulointerstitial nephritis in a patient with eosinophilic fasciitis and IgA nephropathy. Nephron 1995, 69, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S.B.; Vanikar, A.V.; Gumber, M.R.; Kute, V.B.; Shah, P.R.; Patel, H.V.; Trivedi, H.L. Churg-Strauss syndrome presenting with acute kidney injury in a case of primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2014, 46, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romao, J.E.; Saldanha, L.B.; Ianez, L.E.; Sabbaga, E. Recurrence of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis associated with Kimura’s disease after kidney transplantation. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1998, 31, E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dede, F.; Ayli, D.; Atilgan, K.G.; Yuksel, C.; Duranay, M.; Sener, D.; Turker, F. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis associating Kimura disease. Ren. Fail. 2005, 27, 353–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, R.; Light, R.P. Patterns and prognostic value of total and differential leukocyte count in chronic kidney disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 1393–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, M.; Tanaka, M.; Hamaguchi, M.; Senmaru, T.; Sakabe, K.; Shiraishi, E.; Harusato, I.; Yamazaki, M.; Hasegawa, G.; Nakamura, N. Eosinophil count is positively correlated with albumin excretion rate in men with type 2 diabetes. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 1761–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solak, B.; Acikgoz, S.B.; Sipahi, S.; Erdem, T. Epidemiology and determinants of pruritus in pre-dialysis chronic kidney disease patients. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2016, 48, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabizon, D.; Kaufman, S.; Shaked, U.; Evans, S.Y.; Modai, D. Eosinophilia in uremia. Nephron 1981, 29, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallgren, R.; Grefberg, N.; Venge, P. Elevated circulating levels of eosinophil cationic protein in uremia as signs of abnormal eosinophil homeostasis. Nephron 1984, 36, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockel, A.; Klinke, B.; Hertel, J.; Baur, X.; Thiel, C.; Abdelhamid, S.; Fiegel, P.; Walb, D. Allergy to dialysis materials. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1989, 4, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rumpf, K.W.; Seubert, S.; Seubert, A.; Lowitz, H.D.; Valentin, R.; Rippe, H.; Ippen, H.; Scheler, F. Association of ethylene-oxide-induced IgE antibodies with symptoms in dialysis patients. Lancet 1985, 2, 1385–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommer, J.; Ritz, E. Ethylene oxide (ETO) as a major cause of anaphylactoid reactions in dialysis (a review). Artif. Organs 1987, 11, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vienken, J.; Diamantoglou, M.; Henne, W.; Nederlof, B. Artificial dialysis membranes: From concept to large scale production. Am. J. Nephrol. 1999, 19, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.L.; Liu, J.; Cui, W.Y.; Ji, D.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.H. Differences in bio-incompatibility among four biocompatible dialyzer membranes using in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Ren. Fail. 2011, 33, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tielemans, C.; Madhoun, P.; Lenaers, M.; Schandene, L.; Goldman, M.; Vanherweghem, J.L. Anaphylactoid reactions during hemodialysis on AN69 membranes in patients receiving ACE inhibitors. Kidney Int. 1990, 38, 982–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebo, D.G.; Bosmans, J.L.; Couttenye, M.M.; Stevens, W.J. Haemodialysis-associated anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions. Allergy 2006, 61, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simon, P.; Potier, J.; Thebaud, H.E. Risk factors for acute hypersensitivity reactions in hemodialysis. Nephrologie 1996, 17, 163–170. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Ma, L.; Zhao, S. Effect of polyflux membranes on the improvement of hemodialysis-associated eosinophilia: A case series. Ren. Fail. 2016, 38, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Schoen, I. Eosinophilia of peritoneal fluid and peripheral blood associated with chronic peritoneal dialysis. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1967, 47, 638–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.Y.; Kim, H.; Kang, J.M.; Lim, S.H.; Park, H.D.; Jung, S.S.; Lee, K.B. Eosinophilic peritonitis in a patient with continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD). Korean J. Intern. Med. 2004, 19, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, M.K.; Chow, L.; Lam, S.S.; Jones, B. Peritoneal eosinophilia in patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis: A prospective study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1988, 11, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzvi-Behr, S.; Frishberg, Y.; Ben-Shalom, E.; Rinat, C.; Becker-Cohen, R. Eosinophilia in a peritoneal dialysis patient: Answers. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2018, 33, 1507–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacGinley, R.; Cooney, K.; Alexander, G.; Cohen, S.; Goldsmith, D.J. Relapsing culture-negative peritonitis in peritoneal dialysis patients exposed to icodextrin solution. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2002, 40, 1030–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, Y.; Okada, H.; Yasui, A.; Koh, T.; Yamane, T. Sclerosing encapsulating peritonitis associated with recurrent eosinophilic peritonitis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1999, 14, 768–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, R.; Woodrow, G.; Turney, J.H. A case of eosinophilic peritonitis treated with oral corticosteroids. Perit. Dial. Int. 2000, 20, 579–580. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, S.S.; Unikowsky, B.; Prichard, S. Eosinophilic peritonitis in CAPD: Treatment with prednisone and diphenhydramine. Perit. Dial. Int. 1997, 17, 402–403. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, A.C.; Orange, G.; Henderson, I.S. Intraperitoneal hydrocortisone in eosinophilic peritonitis associated with continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Br. Med. J. 1983, 286, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, T.A.; Lunn, A.J. Montelukast: A novel therapeutic option in eosinophilic peritonitis. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2014, 29, 1279–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalev, O.; Rubinger, D.; Barlatzky, Y.; Kopolovic, J.; Drukker, A. Eosinophilia associated with acute allograft kidney rejection. Nephron 1982, 31, 182–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kormendi, F.; Amend, W.J., Jr. The importance of eosinophil cells in kidney allograft rejection. Transplantation 1988, 45, 537–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almirall, J.; Campistol, J.M.; Sole, M.; Andreu, J.; Revert, L. Blood and graft eosinophilia as a rejection index in kidney transplant. Nephron 1993, 65, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meleg-Smith, S.; Gauthier, P.M. Abundance of interstitial eosinophils in renal allografts is associated with vascular rejection. Transplantation 2005, 79, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanikar, A.V.; Kanodia, K.V.; Patel, R.D.; Suthar, K.S.; Nigam, L.A.; Thakkar, U.G.; Patel, H.V.; Kute, V.B.; Trivedi, H.L. Repercussions of eosinophils in a renal allograft—Predictor of early graft loss! Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 2017, 28, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, M.R.; Hall-Craggs, M.; Shen, S.Y.; Posner, J.N.; Alongi, S.V.; Dagher, F.J.; Sadler, J.H. The prognostic value of the eosinophil in acute renal allograft rejection. Transplantation 1986, 41, 709–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuna, M.; Ramos, A.; Santonja, C.; Barat, A.; Egido, J.; Ortiz, A. Delayed graft function and cotrimoxazole. Transplant. Proc. 2011, 43, 2502–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josephson, M.A.; Chiu, M.Y.; Woodle, E.S.; Thistlethwaite, J.R.; Haas, M. Drug-induced acute interstitial nephritis in renal allografts: Histopathologic features and clinical course in six patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1999, 34, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genta, R.M. Global prevalence of strongyloidiasis: Critical review with epidemiologic insights into the prevention of disseminated disease. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1989, 11, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, A.; van Lieshout, L.; Marti, H.; Polderman, T.; Polman, K.; Steinmann, P.; Stothard, R.; Thybo, S.; Verweij, J.J.; Magnussen, P. Strongyloidiasis—The most neglected of the neglected tropical diseases? Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 103, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisoffi, Z.; Buonfrate, D.; Montresor, A.; Requena-Mendez, A.; Munoz, J.; Krolewiecki, A.J.; Gotuzzo, E.; Mena, M.A.; Chiodini, P.L.; Anselmi, M.; et al. Strongyloides stercoralis: A plea for action. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiser, P.B.; Nutman, T.B. Strongyloides stercoralis in the Immunocompromised Population. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 17, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamilton, K.W.; Abt, P.L.; Rosenbach, M.A.; Bleicher, M.B.; Levine, M.S.; Mehta, J.; Montgomery, S.P.; Hasz, R.D.; Bono, B.R.; Tetzlaff, M.T.; et al. Donor-derived Strongyloides stercoralis infections in renal transplant recipients. Transplantation 2011, 91, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roseman, D.A.; Kabbani, D.; Kwah, J.; Bird, D.; Ingalls, R.; Gautam, A.; Nuhn, M.; Francis, J.M. Strongyloides stercoralis transmission by kidney transplantation in two recipients from a common donor. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13, 2483–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, M.; Ravin, K.; Hasan, A.; Clauss, H.; Muchant, D.G.; Pasko, J.K.; Cipollina, G.; Abanyie, F.; Montgomery, S.P.; Loy, M.; et al. Single donor-derived strongyloidiasis in three solid organ transplant recipients: Case series and review of the literature. Am. J. Transplant. 2014, 14, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdalhamid, B.A.; Al Abadi, A.N.; Al Saghier, M.I.; Joudeh, A.A.; Shorman, M.A.; Amr, S.S. Strongyloides stercoralis infection in kidney transplant recipients. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 2015, 26, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abanyie, F.A.; Gray, E.B.; Delli Carpini, K.W.; Yanofsky, A.; McAuliffe, I.; Rana, M.; Chin-Hong, P.V.; Barone, C.N.; Davis, J.L.; Montgomery, S.P.; et al. Donor-derived Strongyloides stercoralis infection in solid organ transplant recipients in the United States, 2009–2013. Am. J. Transplant. 2015, 15, 1369–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiano, A.; Trelis, M.; Moya-Herraiz, A.; Sanchez-Plumed, J.; Merino, J.F. Donor-derived Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection syndrome after simultaneous kidney/pancreas transplantation. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 51, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, D.S.; Yoon, Y.K.; Sohn, J.W.; Kim, M.J. Donor-Derived Strongyloidiasis Infection in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients: A Review and Pooled Analysis. Transplant. Proc. 2016, 48, 2442–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.A.; Avery, R.K.; AST Infectious Disease Community of Practice. Screening of donor and recipient prior to solid organ transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2009, 9 (Suppl. 4), S7–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulware, D.R.; Stauffer, W.M.; Hendel-Paterson, B.R.; Rocha, J.L.; Seet, R.C.; Summer, A.P.; Nield, L.S.; Supparatpinyo, K.; Chaiwarith, R.; Walker, P.F. Maltreatment of Strongyloides infection: Case series and worldwide physicians-in-training survey. Am. J. Med. 2007, 120, 545.e1–545.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abanyie, F.A.; Valice, E.; Delli Carpini, K.W.; Gray, E.B.; McAuliffe, I.; Chin-Hong, P.V.; Handali, S.; Montgomery, S.P.; Huprikar, S. Organ donor screening practices for Strongyloides stercoralis infection among US organ procurement organizations. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2018, 20, e12865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascarello, M.; Gobbi, F.; Angheben, A.; Gobbo, M.; Gaiera, G.; Pegoraro, M.; Lanzafame, M.; Buonfrate, D.; Concia, E.; Bisoffi, Z. Prevalence of Strongyloides stercoralis infection among HIV-positive immigrants attending two Italian hospitals, from 2000 to 2009. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2011, 105, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramirez-Olivencia, G.; Espinosa, M.A.; Martin, A.B.; Nunez, N.I.; de Las Parras, E.R.; Nunez, M.L.; Puente, S.P. Imported strongyloidiasis in Spain. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 18, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Perez, A.; Roure Diez, S.; Belhassen-Garcia, M.; Torrus-Tendero, D.; Perez-Arellano, J.L.; Cabezas, T.; Soler, C.; Diaz-Menendez, M.; Navarro, M.; Trevino, B.; et al. Management of severe strongyloidiasis attended at reference centers in Spain. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVault, G.A., Jr.; King, J.W.; Rohr, M.S.; Landreneau, M.D.; Brown, S.T., 3rd; McDonald, J.C. Opportunistic infections with Strongyloides stercoralis in renal transplantation. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1990, 12, 653–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, J.S.; Schaffner, W.; Stone, W.J. Opportunistic strongyloidiasis in renal transplant recipients. Transplantation 1986, 42, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedke, J.; Buse, S.; Kurosch, M.; Haferkamp, A.; Jager, D.; Hohenfellner, M. Paraneoplastic syndrome in renal cell carcinoma. Urologe A 2007, 46, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, J.L.; Lacombe, C.; Bruneval, P.; Casadevall, N.; Leporrier, M.; Camilleri, J.P.; Bariety, J.; Tambourin, P.; Varet, B. Tumor cells are the site of erythropoietin synthesis in human renal cancers associated with polycythemia. Blood 1990, 75, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hegemann, M.; Kroeger, N.; Stenzl, A.; Bedke, J. Rare and changeable as a chameleon: Paraneoplastic syndromes in renal cell carcinoma. World J. Urol. 2018, 36, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.W.; Guan, Y.Y.; Liu, X.M. Paraneoplastic Eosinophilia in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Chin. Med. J. 2015, 128, 2271–2272. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.B.; Yan, B.; Yin, Z.; Yang, J.R. Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma associated with eosinophilia: A report of three cases. Exp. Ther. Med. 2014, 8, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rajpara, A.; Liolios, A.; Fraga, G.; Blackmon, J. Recurrent paraneoplastic wells syndrome in a patient with metastatic renal cell cancer. Dermatol. Online J. 2014, 20, 13030/qt35w8r1g3. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lowe, D.; Jorizzo, J.; Hutt, M.S. Tumour-associated eosinophilia: A review. J. Clin. Pathol. 1981, 34, 1343–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todenhofer, T.; Wirths, S.; von Weyhern, C.H.; Heckl, S.; Horger, M.; Hennenlotter, J.; Stenzl, A.; Kanz, L.; Schwentner, C. Severe paraneoplastic hypereosinophilia in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. BMC Urol. 2012, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, G.J.; Castro, D.M.; Vigo-Guevara, G.L.; Ferrua, M.; Barriga-Maldonado, V.; Rotta-Escalante, R. Hypereosinophilic encephalopathy with multiple cerebral infarctions in neighbouring vascular territories associated with prostate cancer. Rev. Neurol. 2006, 43, 762–764. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, R.P.; Carvalho, S.D.; Ferreira, O.; Brito, C. Wells syndrome associated with lung cancer. BMJ Case Rep. 2017, 2017, bcr-2017-220323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balian, A.; Bonte, E.; Naveau, S.; Foussat, A.; Bouchet-Delbos, L.; Berrebi, D.; Vons, C.; Capron, F.; Chaput, J.C.; Emilie, D. Intratumoral production of interleukin-5 leading to paraneoplastic peripheral eosinophilia in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2001, 34, 355–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostopoulos, G.K.; Sakorafas, G.H.; Kostopoulos, P.; Margantinis, G.; Tsiakos, S.; Terpos, E.; Pavlakis, G.; Fortun, P.; Arvanitidis, D. Disseminated colon cancer with severe peripheral blood eosinophilia and elevated serum levels of interleukine-2, interleukine-3, interleukine-5, and GM-CSF. J. Surg. Oncol. 2005, 89, 273–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diskin, C.J.; Stokes, T.J.; Dansby, L.M.; Radcliff, L.; Carter, T.B. The prevalence and meaning of eosinophilia in renal diseases on a nephrology consultation service. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 2549–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dejaco, C.; Oppl, B.; Monach, P.; Cuthbertson, D.; Carette, S.; Hoffman, G.; Khalidi, N.; Koening, C.; Langford, C.; McKinnon-Maksimowicz, K.; et al. Serum biomarkers in patients with relapsing eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
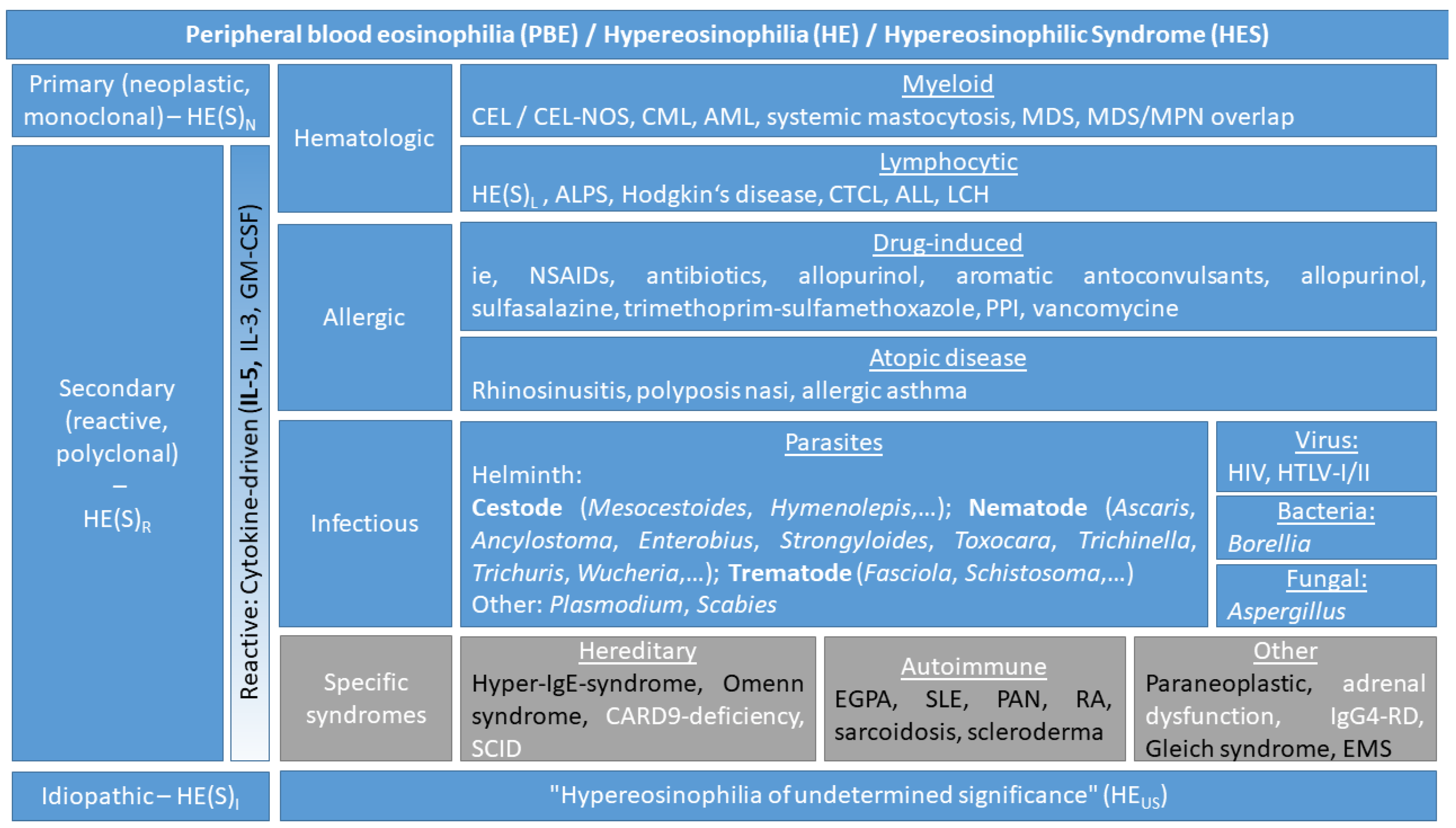



| Term | Definition and Criteria |
|---|---|
| Peripheral blood eosinophilia (PBE) | >0.5 × 109/L blood |
| HE | >1.5 × 109/L blood on two examinations (interval ≥4 weeks *) and/or tissue HE defined by the following:
|
| HES |
|
| Eosinophil-associated single-organ diseases |
|
| Category | Kidney Disease | % with Renal Involvement | % with PBE | Exclude |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a. Hypersensitivity reactions | AIN | 100% | App. 22% [19,20] | ATN |
| DRESS | 11–57% [21,22] | 52–95% [23] | ||
| b. Autoimmune disease | EGPA | App. 26%; Higher prevalence (up to 51.4%) with ANCA-positivity [24,25] | 100%; Typically, >1500/µL abs. and >10% rel.; Eosinophilic activity may occasionally be organ-limited without blood eosinophilia [26] | MPA, GPA, HESI, aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease, eosinophilic pneumonia, allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, parasitic diseases, allergic conditions, Gleich syndrome, IgG4-RD, diffuse fasciitis with eosinophilia, eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome, eosinophilic myositis, cryoglobulinemic vasculitis, IgA vasculitis |
| SLE | app. 50% [27] | <5% [28] | ||
| c. Vascular disease | TMA | App. 77% overall (depending on subtype) [29] | Very rare (number not known) | |
| CES | app. 92% [30] | 14–71% [31,32] | ||
| d. Other | Kimura’s disease | 12–18% [33] | 100% [34] | ALHE |
| TINU syndrome | 100% | app. 17% [35] | Sarcoidosis, Sjögren syndrome, SLE, TB | |
| IgG4-RD | 10–15% [36] | app. 30% [36,37,38] | HES, AAV, malignancies, autoimmune disorders, DI-AIN, MN | |
| e. CKD & RRT | CKD | number not known | ||
| Dialysis | HD-associated eosinophilia | app. 5% (2012) [39], up to 39% in the 1970s [40] | ||
| PD-associated eosinophilia | <10% (2007) [41], up to 60% in the 1980s [42] | |||
| Kidney transplant | Acute allograft rejection | 20–36% (≥4% eosinophils) [43] | (DI-)AIN, Strongyloides hyperinfection | |
| Strongyloides superinfection | app. 34% [44]; 67% of pretransplant patients with chronic Strongyloides infection [45] | |||
| f. Renal cell carcinoma | Very rare (number not known) | IgG4-RKD |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gauckler, P.; Shin, J.I.; Mayer, G.; Kronbichler, A. Eosinophilia and Kidney Disease: More than Just an Incidental Finding? J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7120529
Gauckler P, Shin JI, Mayer G, Kronbichler A. Eosinophilia and Kidney Disease: More than Just an Incidental Finding? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2018; 7(12):529. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7120529
Chicago/Turabian StyleGauckler, Philipp, Jae Il Shin, Gert Mayer, and Andreas Kronbichler. 2018. "Eosinophilia and Kidney Disease: More than Just an Incidental Finding?" Journal of Clinical Medicine 7, no. 12: 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7120529
APA StyleGauckler, P., Shin, J. I., Mayer, G., & Kronbichler, A. (2018). Eosinophilia and Kidney Disease: More than Just an Incidental Finding? Journal of Clinical Medicine, 7(12), 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7120529







