Nutritional Challenges in Patients with Advanced Liver Cirrhosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Comprehensive Assessment of Patients with Advanced Liver Cirrhosis
2.1. Malnutrition
2.2. Liver Function
2.3. Sarcopenia
2.4. Deficiencies of Vitamins and Micronutrients
2.4.1. Vitamin D
2.4.2. Vitamin A
2.4.3. Zinc
2.4.4. Selenium
2.5. Bone Disease
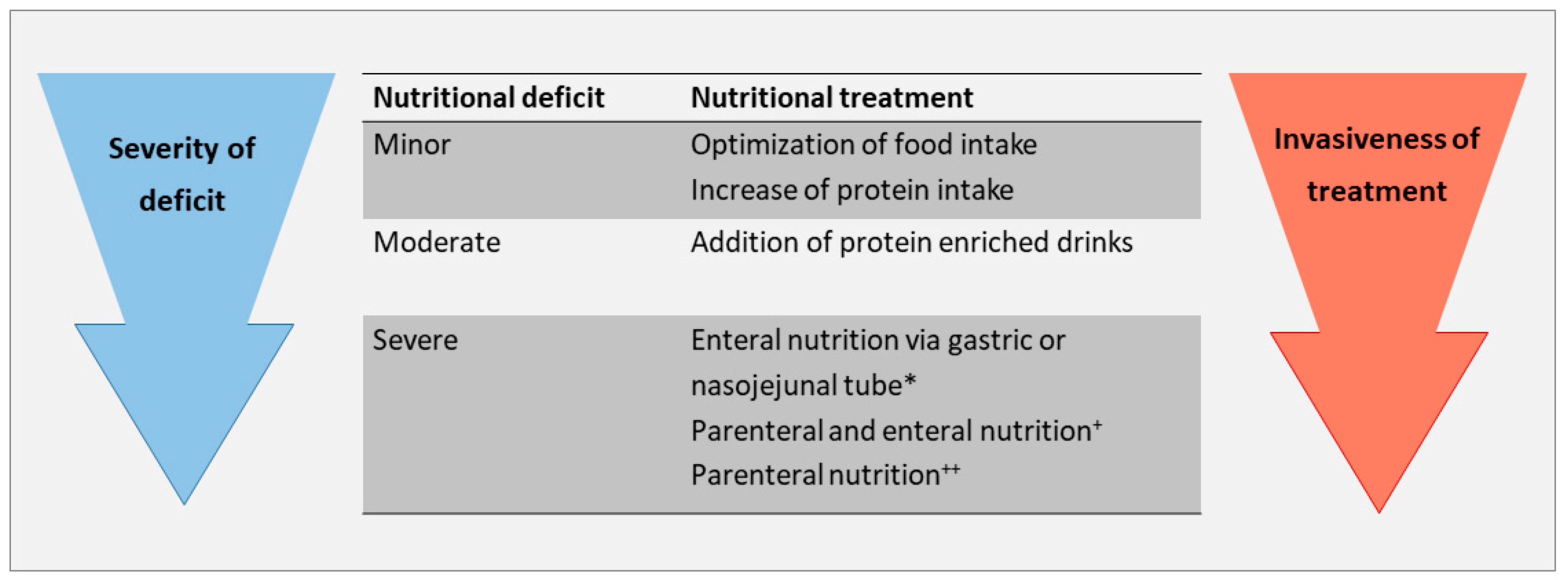
3. Therapeutic Approach to Treat Nutritional Deficits
3.1. Caloric, Protein and Lipid Supplementation
3.2. Albumin
3.3. Vitamins and Micronutrients
3.4. General Management
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ge, P.S.; Runyon, B.A. Treatment of Patients with Cirrhosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, K.; Lee, S.S.; Raman, M. Prevalence and mechanisms of malnutrition in patients with advanced liver disease, and nutrition management strategies. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ockenga, J.; Bischoff, S.C.; Tillmann, H.L.; Rifai, K.; Widjaja, A.; Boker, K.H.; Manns, M.P.; Brabant, G. Elevated bound leptin correlates with energy expenditure in cirrhotics. Gastroenterology 2000, 119, 1656–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ockenga, J.; Widjaja, A.; Holtmannspotter, M.; Schmidt, R.E.; Brabant, G. Bound leptin is regulated by tumour necrosis factor-alpha in HIV-infected patients: A potential mediator of wasting? AIDS 1998, 12, 2233–2235. [Google Scholar]
- Buechler, C.; Haberl, E.M.; Rein-Fischboeck, L.; Aslanidis, C. Adipokines in Liver Cirrhosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chander Roland, B.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Ciarleglio, M.M.; Deng, Y.; Sheth, A. Decompensated cirrhotics have slower intestinal transit times as compared with compensated cirrhotics and healthy controls. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2013, 47, 888–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergheim, I.; Parlesak, A.; Dierks, C.; Bode, J.C.; Bode, C. Nutritional deficiencies in German middle-class male alcohol consumers: Relation to dietary intake and severity of liver disease. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 57, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merli, M.; Giusto, M.; Gentili, F.; Novelli, G.; Ferretti, G.; Riggio, O.; Corradini, S.G.; Siciliano, M.; Farcomeni, A.; Attili, A.F.; et al. Nutritional status: Its influence on the outcome of patients undergoing liver transplantation. Liver Int. 2010, 30, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, G.R.; Moretti, E.W.; El-Moalem, H.; Clavien, P.A.; Tuttle-Newhall, J.E. Malnutrition in liver transplant patients: Preoperative subjective global assessment is predictive of outcome after liver transplantation. Transplantation 2001, 72, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moctezuma-Velazquez, C.; Ebadi, M.; Bhanji, R.A.; Stirnimann, G.; Tandon, P.; Montano-Loza, A.J. Limited performance of subjective global assessment compared to computed tomography-determined sarcopenia in predicting adverse clinical outcomes in patients with cirrhosis. Clin. Nutr. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Child, C.G.; Turcotte, J.G. Surgery and portal hypertension. Major Prob. Clin. Surg. 1964, 1, 1–85. [Google Scholar]
- Arroyo, V.; Garcia-Martinez, R.; Salvatella, X. Human serum albumin, systemic inflammation, and cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondana, M.; Milani, L.; Merkel, C.; Caregaro, L.; Gatta, A. Value of prealbumin plasma levels as liver test. Digestion 1987, 37, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Cai, L.Y.; Zhong, L.; Chen, C.; Xu, F.; Zhao, Z.X.; Chen, X.M. Model for end-stage liver disease combined with serum prealbumin to predict the prognosis of patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis. J. Dig. Dis. 2010, 11, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Li, J.; Yan, J.J.; Liu, C.F.; Wu, M.C.; Yan, Y.Q. Prealbumin is predictive for postoperative liver insufficiency in patients undergoing liver resection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 7021–7025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Yao, M.; Lu, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhou, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, W.; Qian, X.; Zhao, J.; et al. Integration of Prealbumin into Child-Pugh Classification Improves Prognosis Predicting Accuracy in HCC Patients Considering Curative Surgery. J. Clin. Trans. Hepatol. 2018, 6, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberino, F.; Gatta, A.; Amodio, P.; Merkel, C.; Di Pascoli, L.; Boffo, G.; Caregaro, L. Nutrition and survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. Nutrition 2001, 17, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englesbe, M.J.; Patel, S.P.; He, K.; Lynch, R.J.; Schaubel, D.E.; Harbaugh, C.; Holcombe, S.A.; Wang, S.C.; Segev, D.L.; Sonnenday, C.J. Sarcopenia and mortality after liver transplantation. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2010, 211, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golse, N.; Bucur, P.O.; Ciacio, O.; Pittau, G.; Sa Cunha, A.; Adam, R.; Castaing, D.; Antonini, T.; Coilly, A.; Samuel, D.; et al. A new definition of sarcopenia in patients with cirrhosis undergoing liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2017, 23, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montano-Loza, A.J. Muscle wasting: A nutritional criterion to prioritize patients for liver transplantation. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2014, 17, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, F.; Buyse, S.; Francoz, C.; Laouenan, C.; Bruno, O.; Belghiti, J.; Moreau, R.; Vilgrain, V.; Valla, D. Prognostic value of muscle atrophy in cirrhosis using psoas muscle thickness on computed tomography. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebadi, M.; Wang, C.W.; Lai, J.C.; Dasarathy, S.; Kappus, M.R.; Dunn, M.A.; Carey, E.J.; Montano-Loza, A.J.; From the Fitness, Life Enhancement, and Exercise in Liver Transplantation (FLEXIT) Consortium. Poor performance of psoas muscle index for identification of patients with higher waitlist mortality risk in cirrhosis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2018, 9, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montano-Loza, A.J.; Angulo, P.; Meza-Junco, J.; Prado, C.M.M.; Sawyer, M.B.; Beaumont, C.; Esfandiari, N.; Ma, M.; Baracos, V.E. Sarcopenic obesity and myosteatosis are associated with higher mortality in patients with cirrhosis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2016, 7, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeiro, F.G.; Augusti, L. Nutritional assessment in cirrhotic patients with hepatic encephalopathy. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 2940–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, M.; Hoermann, R.; Peterson, A.; Testro, A.; Angus, P.W.; Hey, P.; Chapman, B.; Gow, P.J. Use of Dual X-ray Absorptiometry in men with advanced cirrhosis to predict sarcopenia-associated mortality risk. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusto, M.; Lattanzi, B.; Albanese, C.; Galtieri, A.; Farcomeni, A.; Giannelli, V.; Lucidi, C.; Di Martino, M.; Catalano, C.; Merli, M. Sarcopenia in liver cirrhosis: The role of computed tomography scan for the assessment of muscle mass compared with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and anthropometry. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 27, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamath, P.S.; Wiesner, R.H.; Malinchoc, M.; Kremers, W.; Therneau, T.M.; Kosberg, C.L.; D’Amico, G.; Dickson, E.R.; Kim, W.R. A model to predict survival in patients with end-stage liver disease. Hepatology 2001, 33, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montano-Loza, A.J.; Duarte-Rojo, A.; Meza-Junco, J.; Baracos, V.E.; Sawyer, M.B.; Pang, J.X.Q.; Beaumont, C.; Esfandiari, N.; Myers, R.P. Inclusion of Sarcopenia Within MELD (MELD-Sarcopenia) and the Prediction of Mortality in Patients with Cirrhosis. Clin. Trans. Gastroenterol. 2015, 6, e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuniga, S.; Firrincieli, D.; Housset, C.; Chignard, N. Vitamin D and the vitamin D receptor in liver pathophysiology. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2011, 35, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantakis, C.; Tselekouni, P.; Kalafateli, M.; Triantos, C. Vitamin D deficiency in patients with liver cirrhosis. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2016, 29, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putz-Bankuti, C.; Pilz, S.; Stojakovic, T.; Scharnagl, H.; Pieber, T.R.; Trauner, M.; Obermayer-Pietsch, B.; Stauber, R.E. Association of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels with liver dysfunction and mortality in chronic liver disease. Liver Int. 2012, 32, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, J.A. Serum levels of vitamin A and carotenoids as reflectors of nutritional status. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1984, 73, 1439–1444. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Newsome, P.N.; Beldon, I.; Moussa, Y.; Delahooke, T.E.; Poulopoulos, G.; Hayes, P.C.; Plevris, J.N. Low serum retinol levels are associated with hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic liver disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000, 14, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves, G.V.; Peres, W.A.; Goncalves, J.C.; Ramalho, A. Vitamin A and retinol-binding protein deficiency among chronic liver disease patients. Nutrition 2015, 31, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geubel, A.P.; De Galocsy, C.; Alves, N.; Rahier, J.; Dive, C. Liver damage caused by therapeutic vitamin A administration: Estimate of dose-related toxicity in 41 cases. Gastroenterology 1991, 100, 1701–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, M.; Keeling, P.W.; Feely, J. Tissue zinc status and drug elimination in patients with chronic liver disease. Clin. Sci. 1990, 78, 547–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grungreiff, K.; Reinhold, D.; Wedemeyer, H. The role of zinc in liver cirrhosis. Ann. Hepatol. 2016, 15, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takuma, Y.; Nouso, K.; Makino, Y.; Hayashi, M.; Takahashi, H. Clinical trial: Oral zinc in hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 32, 1080–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M.; Ikezawa, K.; Ono, A.; Okabayashi, S.; Hayashi, Y.; Shimizu, S.; Mizuno, T.; Maeda, K.; Akasaka, T.; Naito, M.; et al. Evaluation of the effects of combination therapy with branched-chain amino acid and zinc supplements on nitrogen metabolism in liver cirrhosis. Hepatol. Res. 2007, 37, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burk, R.F.; Early, D.S.; Hill, K.E.; Palmer, I.S.; Boeglin, M.E. Plasma selenium in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 1998, 27, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Munoz, S.J. Bone disease in cirrhosis. Clin. Liver Dis. 2015, 6, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakchbandi, I.A. Osteoporosis and fractures in liver disease: Relevance, pathogenesis and therapeutic implications. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 9427–9438. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Handzlik-Orlik, G.; Holecki, M.; Wilczynski, K.; Dulawa, J. Osteoporosis in liver disease: Pathogenesis and management. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 7, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plauth, M.; Bernal, W.; Dasarathy, S.; Merli, M.; Plank, L.D.; Schutz, T.; Bischoff, S.C. ESPEN guideline on clinical nutrition in liver disease. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 485–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EASL. Clinical Practice Guidelines on nutrition in chronic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 172–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amodio, P.; Bemeur, C.; Butterworth, R.; Cordoba, J.; Kato, A.; Montagnese, S.; Uribe, M.; Vilstrup, H.; Morgan, M.Y. The nutritional management of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis: International Society for Hepatic Encephalopathy and Nitrogen Metabolism Consensus. Hepatology 2013, 58, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druml, W.; Fischer, M.; Pidlich, J.; Lenz, K. Fat elimination in chronic hepatic failure: Long-chain vs medium-chain triglycerides. Am J Clin Nutr. 1995, 61, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, B.; Li, J. Effect of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids to reverse biopsy-proven parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease in adults. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsien, C.D.; McCullough, A.J.; Dasarathy, S. Late evening snack: Exploiting a period of anabolic opportunity in cirrhosis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 27, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordoba, J.; Lopez-Hellin, J.; Planas, M.; Sabin, P.; Sanpedro, F.; Castro, F.; Esteban, R.; Guardia, J. Normal protein diet for episodic hepatic encephalopathy: Results of a randomized study. J. Hepatol. 2004, 41, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ney, M.; Abraldes, J.G.; Ma, M.; Belland, D.; Harvey, A.; Robbins, S.; Den Heyer, V.; Tandon, P. Insufficient Protein Intake Is Associated with Increased Mortality in 630 Patients with Cirrhosis Awaiting Liver Transplantation. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2015, 30, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasarathy, S.; Merli, M. Sarcopenia from mechanism to diagnosis and treatment in liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 1232–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsien, C.; Davuluri, G.; Singh, D.; Allawy, A.; Ten Have, G.A.; Thapaliya, S.; Schulze, J.M.; Barnes, D.; McCullough, A.J.; Engelen, M.P.; et al. Metabolic and molecular responses to leucine-enriched branched chain amino acid supplementation in the skeletal muscle of alcoholic cirrhosis. Hepatology 2015, 61, 2018–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Les, I.; Doval, E.; Garcia-Martinez, R.; Planas, M.; Cardenas, G.; Gomez, P.; Flavià, M.; Jacas, C.; Mínguez, B.; Vergara, M.; et al. Effects of branched-chain amino acids supplementation in patients with cirrhosis and a previous episode of hepatic encephalopathy: A randomized study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EASL. Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with decompensated cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 406–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraceni, P.; Riggio, O.; Angeli, P.; Alessandria, C.; Neri, S.; Foschi, F.G.; Levantesi, F.; Airoldi, A.; Boccia, S.; Svegliati-Baroni, G.; et al. Long-term albumin administration in decompensated cirrhosis (ANSWER): An open-label randomised trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 2417–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sola, E.; Sole, C.; Simon-Talero, M.; Martin-Llahi, M.; Castellote, J.; Garcia-Martinez, R.; Moreira, R.; Torrens, M.; Márquez, F.; Fabrellas, N.; et al. Midodrine and albumin for prevention of complications in patients with cirrhosis awaiting liver transplantation. A randomized placebo-controlled trial. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 1250–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.F.; Binkley, N.C.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Gordon, C.M.; Hanley, D.A.; Heaney, R.P.; Murad, M.H.; Weaver, C.M.; Endocrine Society. Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: An Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 1911–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elangovan, H.; Chahal, S.; Gunton, J.E. Vitamin D in liver disease: Current evidence and potential directions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1863, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grungreiff, K. Branched Amino Acids and Zinc in the Nutrition of Liver Cirrhosis. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2018, 8, 480–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burk, R.F.; Hill, K.E.; Motley, A.K.; Byrne, D.W.; Norsworthy, B.K. Selenium deficiency occurs in some patients with moderate-to-severe cirrhosis and can be corrected by administration of selenate but not selenomethionine: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Cirrhosis with Malnutrition | Cirrhosis with Sarcopenic Obesity | |
|---|---|---|
| Caloric intake | 30–35 kcal/kg BW | 20–25 kcal/kg BW |
| Protein intake | 1.2 to 1.5 g/kg BW | >1.5 g, up to 2.5 g/kg BW |
| Lipid intake | No specific recommendation | No specific recommendation |
| Vitamins | ||
| Vitamin A * | Supplement if decreased | Supplement if decreased |
| Vitamin D | Supplement if decreased | Supplement if decreased |
| Micronutrients | ||
| Zinc | Supplement if decreased | Supplement if decreased |
| Selenium | Supplement if decreased | Supplement if decreased |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stirnimann, J.; Stirnimann, G. Nutritional Challenges in Patients with Advanced Liver Cirrhosis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1926. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8111926
Stirnimann J, Stirnimann G. Nutritional Challenges in Patients with Advanced Liver Cirrhosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(11):1926. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8111926
Chicago/Turabian StyleStirnimann, Jessica, and Guido Stirnimann. 2019. "Nutritional Challenges in Patients with Advanced Liver Cirrhosis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 11: 1926. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8111926
APA StyleStirnimann, J., & Stirnimann, G. (2019). Nutritional Challenges in Patients with Advanced Liver Cirrhosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(11), 1926. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8111926





