Optimal Design of Patient-Specific Total Knee Arthroplasty for Improvement in Wear Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
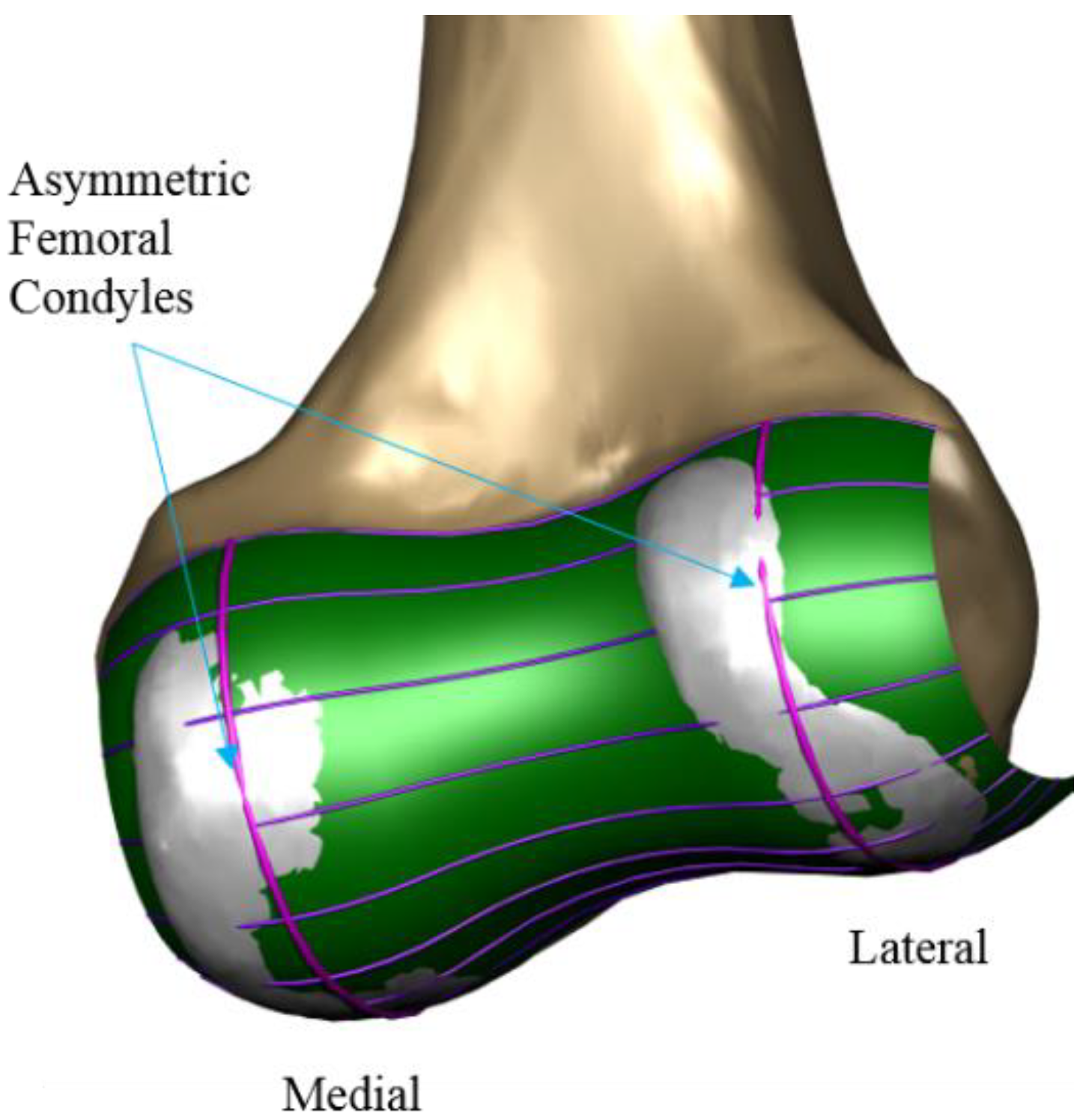
2.1. Design of Patient Specific TKA
2.2. Development of the Parametric FE Model for Patient-Specific TKA
2.3. Wear Prediction of Patient-Specific TKA
2.4. Design Optimization of Patient Specific TKA
2.5. Experimental Wear Simulation
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Noble, J.W., Jr.; Moore, C.A.; Liu, N. The value of patient-matched instrumentation in total knee arthroplasty. J. Arthroplasty 2012, 27, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockett, C.L.; Carbone, S.; Fisher, J.; Jennings, L.M. Influence of conformity on the wear of total knee replacement: An experimental study. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H 2018, 232, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, D.K.; Song, S.J.; Park, M.J.; Eoh, J.H.; Song, J.H.; Park, C.H. Twenty-year survival analysis in total knee arthroplasty by a single surgeon. J. Arthroplast. 2012, 27, 1297–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Keudell, A.; Sodha, S.; Collins, J.; Minas, T.; Fitz, W.; Gomoll, A.H. Patient satisfaction after primary total and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: An age-dependent analysis. Knee 2014, 21, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naudie, D.D.; Ammeen, D.J.; Engh, G.A.; Rorabeck, C.H. Wear and osteolysis around total knee arthroplasty. J. Am Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2007, 15, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharkey, P.F.; Hozack, W.J.; Rothman, R.H.; Shastri, S.; Jacoby, S.M. Insall Award paper. Why are total knee arthroplasties failing today? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2002, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, P.B.; Ranawat, A.S. Patient-Specific Total Knees Demonstrate a Higher Manipulation Rate Compared to “Off-the-Shelf Implants”. J. Arthroplasty 2016, 31, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauwens, K.; Matthes, G.; Wich, M.; Gebhard, F.; Hanson, B.; Ekkernkamp, A.; Stengel, D. Navigated total knee replacement. A meta-analysis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 2007, 89, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slover, J.D.; Tosteson, A.N.; Bozic, K.J.; Rubash, H.E.; Malchau, H. Impact of hospital volume on the economic value of computer navigation for total knee replacement. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 2008, 90, 1492–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.R.; Kang, K.T.; Son, J.; Suh, D.S.; Heo, D.B.; Koh, Y.G. Patient-specific instrumentation development in TKA: 1st and 2nd generation designs in comparison with conventional instrumentation. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2017, 137, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitz, W. Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with use of novel patient-specific resurfacing implants and personalized jigs. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 2009, 91, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steklov, N.; Slamin, J.; Srivastav, S.; D’Lima, D. Unicompartmental knee resurfacing: Enlarged tibio-femoral contact area and reduced contact stress using novel patient-derived geometries. Open Biomed. Eng. J. 2010, 4, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, G.; Swearingen, A.; Culler, S. Hospital outcomes and cost for patients undergoing a customized individually made TKA vs off-the-shelf TKA. JISRF Reconstr. Rev. 2014, 4, 103. [Google Scholar]
- Dalury, D.F.; Pomeroy, D.L.; Gorab, R.S.; Adams, M.J. Why are total knee arthroplasties being revised? J. Arthroplast. 2013, 28, 120–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, W.B.; Slamin, J.E.; Doody, S.W. Bone Preservation in a Novel Patient Specific Total Knee Replacement. Reconstr. Rev. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.L.; Bicknell, V.L.; Wright, T.M. The effect of conformity, thickness, and material on stresses in ultra-high molecular weight components for total joint replacement. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 1986, 68, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, Y.G.; Son, J.; Kwon, O.R.; Kwon, S.K.; Kang, K.T. Tibiofemoral conformity variation offers changed kinematics and wear performance of customized posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2019, 27, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, Y.G.; Park, K.M.; Lee, J.A.; Nam, J.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Kang, K.T. Total knee arthroplasty application of polyetheretherketone and carbon-fiber-reinforced polyetheretherketone: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 100, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargahi, J.; Najarian, S.; Amiri, S. Optimization of the geometry of total knee implant in the sagittal plane using FEA. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 2003, 13, 439–449. [Google Scholar]
- Willing, R.; Kim, I.Y. Three dimensional shape optimization of total knee replacements for reduced wear. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2009, 38, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.T.; Koh, Y.G.; Nam, J.H.; Jung, M.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, S.H. Biomechanical evaluation of the influence of posterolateral corner structures on cruciate ligaments forces during simulated gait and squatting. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, Y.G.; Lee, J.A.; Lee, H.Y.; Chun, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, K.T. Anatomy-mimetic design preserves natural kinematics of knee joint in patient-specific mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, Y.G.; Lee, J.A.; Chung, P.K.; Kang, K.T. Computational analysis of customized cruciate retaining total knee arthroplasty restoration of native knee joint biomechanics. Artif. Organs 2019, 43, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.T.; Son, J.; Suh, D.S.; Kwon, S.K.; Kwon, O.R.; Koh, Y.G. Patient-specific medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty has a greater protective effect on articular cartilage in the lateral compartment: A Finite Element Analysis. Bone Joint Res. 2018, 7, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, Y.G.; Park, K.M.; Lee, H.Y.; Kang, K.T. Influence of tibiofemoral congruency design on the wear of patient-specific unicompartmental knee arthroplasty using finite element analysis. Bone Joint Res. 2019, 8, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kang, K.T.; Son, J.; Kwon, O.R.; Choi, Y.J.; Jo, S.B.; Choi, Y.W.; Koh, Y.G. Graft Extrusion Related to the Position of Allograft in Lateral Meniscal Allograft Transplantation: Biomechanical Comparison Between Parapatellar and Transpatellar Approaches Using Finite Element Analysis. Arthroscopy 2015, 31, 2380–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.T.; Son, J.; Kim, H.J.; Baek, C.; Kwon, O.R.; Koh, Y.G. Wear predictions for UHMWPE material with various surface properties used on the femoral component in total knee arthroplasty: A computational simulation study. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2017, 28, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godest, A.C.; Beaugonin, M.; Haug, E.; Taylor, M.; Gregson, P.J. Simulation of a knee joint replacement during a gait cycle using explicit finite element analysis. J. Biomech. 2002, 35, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, P.S.; Lowry, M.T.; Kumar, A. The effect of geometric variations in posterior-stabilized knee designs on motion characteristics measured in a knee loading machine. Clin. Orthop Relat. Res. 2014, 472, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ardestani, M.M.; Moazen, M.; Jin, Z. Contribution of geometric design parameters to knee implant performance: Conflicting impact of conformity on kinematics and contact mechanics. Knee 2015, 22, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archard, J.; Hirst, W. The wear of metals under unlubricated conditions. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1956, 236, 397–410. [Google Scholar]
- McGloughlin, T.M.; Murphy, D.M.; Kavanagh, A.G. A machine for the preliminary investigation of design features influencing the wear behaviour of knee prostheses. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H 2004, 218, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deb, K.; Pratap, A.; Agarwal, S.; Meyarivan, T. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2002, 6, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, H.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Wei, H. Multi-objective shape optimization of helico-axial multiphase pump impeller based on NSGA-II and ANN. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; Bunn, A.; Bugbee, W.D.; Colwell, C.W., Jr.; D’Lima, D.D. Patient-specific implants with custom cutting blocks better approximate natural knee kinematics than standard TKA without custom cutting blocks. Knee 2015, 22, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelgaied, A.; Brockett, C.L.; Liu, F.; Jennings, L.M.; Jin, Z.; Fisher, J. The effect of insert conformity and material on total knee replacement wear. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H 2014, 228, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luger, E.; Sathasivam, S.; Walker, P.S. Inherent differences in the laxity and stability between the intact knee and total knee replacements. Knee 1997, 4, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathasivam, S.; Walker, P.S. The conflicting requirements of laxity and conformity in total knee replacement. J. Biomech. 1999, 32, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, C.K.; Clary, C.W.; Laz, P.J.; Rullkoetter, P.J. Relative contributions of design, alignment, and loading variability in knee replacement mechanics. J. Orthop. Res. 2012, 30, 2015–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmer, M.A.; Laurent, M.P.; Haman, J.D.; Jacobs, J.J.; Galante, J.O. Surface damage versus tibial polyethylene insert conformity: A retrieval study. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2012, 470, 1814–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willing, R.; Kim, I.Y. Quantifying the competing relationship between durability and kinematics of total knee replacements using multiobjective design optimization and validated computational models. J. Biomech. 2012, 45, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DesJardins, J.D.; Walker, P.S.; Haider, H.; Perry, J. The use of a force-controlled dynamic knee simulator to quantify the mechanical performance of total knee replacement designs during functional activity. J. Biomech. 2000, 33, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Sakoda, H.; Sawyer, W.G.; Banks, S.A.; Fregly, B.J. Predicting knee replacement damage in a simulator machine using a computational model with a consistent wear factor. J. Biomech. Eng. 2008, 130, 011004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fregly, B.J.; Marquez-Barrientos, C.; Banks, S.A.; DesJardins, J.D. Increased conformity offers diminishing returns for reducing total knee replacement wear. J. Biomech. Eng. 2010, 132, 021007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathasivam, S.; Walker, P.S. Optimization of the bearing surface geometry of total knees. J. Biomech. 1994, 27, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei, Y.; Fregly, B.J.; Sawyer, W.G.; Banks, S.A.; Kim, N.H. The relationship between contact pressure, insert thickness, and mild wear in total knee replacements. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2004, 6, 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Essner, A.; Klein, R.; Bushelow, M.; Wang, A.; Kvitnitsky, M.; Mahoney, O. The effect of sagittal conformity on knee wear. Wear 2003, 255, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaha, J.D. The rationale for a total knee implant that confers anteroposterior stability throughout range of motion. J. Arthroplasty 2004, 19, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netter, J.; Hermida, J.; Flores-Hernandez, C.; Steklov, N.; Kester, M.; D’Lima, D.D. Prediction of wear in crosslinked polyethylene unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Lubricants 2015, 3, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Design Variables (mm) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCA | MCB | MSA | MSB | LCA | LCB | LSA | LSB | |
| Initial | 17.00 | 30.00 | 38.00 | 24.00 | 17.00 | 32.00 | 50.00 | 23.00 |
| Optimal | 18.03 | 33.87 | 39.15 | 25.11 | 18.31 | 34.32 | 52.02 | 24.31 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koh, Y.-G.; Jung, K.-H.; Hong, H.-T.; Kim, K.-M.; Kang, K.-T. Optimal Design of Patient-Specific Total Knee Arthroplasty for Improvement in Wear Performance. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8112023
Koh Y-G, Jung K-H, Hong H-T, Kim K-M, Kang K-T. Optimal Design of Patient-Specific Total Knee Arthroplasty for Improvement in Wear Performance. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(11):2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8112023
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoh, Yong-Gon, Kyung-Hwan Jung, Hyoung-Taek Hong, Kang-Min Kim, and Kyoung-Tak Kang. 2019. "Optimal Design of Patient-Specific Total Knee Arthroplasty for Improvement in Wear Performance" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 11: 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8112023
APA StyleKoh, Y.-G., Jung, K.-H., Hong, H.-T., Kim, K.-M., & Kang, K.-T. (2019). Optimal Design of Patient-Specific Total Knee Arthroplasty for Improvement in Wear Performance. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(11), 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8112023




