Transition to Adult Care for Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. What is Pediatric to Adult Health Care Transition?
3. Obstructive Sleep Apnea
4. OSA and Treatments
5. Why is a Transition Process Necessary for Adolescents with OSA?
6. Transition Programs for Youth with OSA
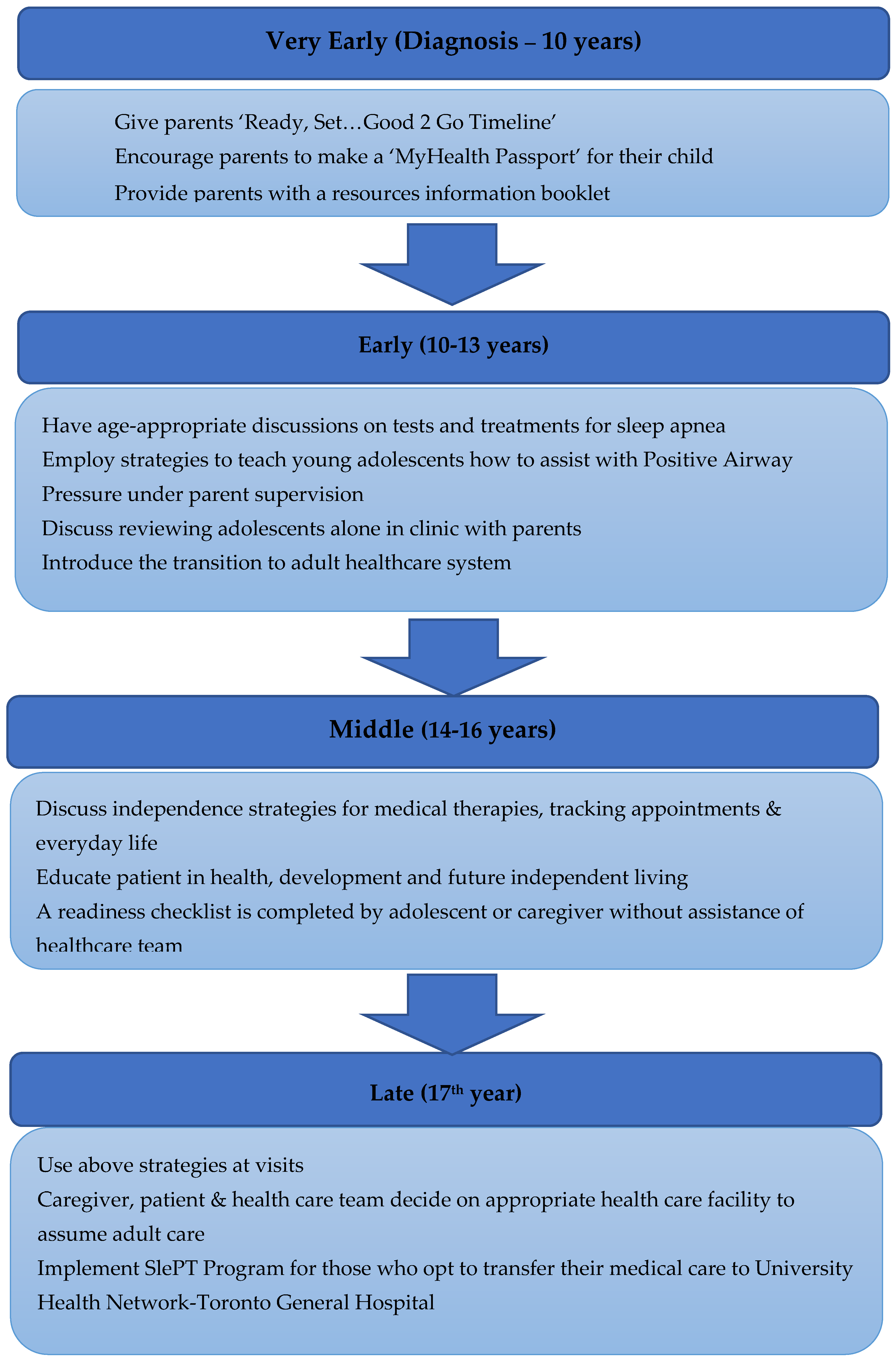
7. Establishing a Transition Program for Youth with OSA
8. Clinical Transition Program—General Principles
9. Sleep Disorders Pediatric Transition (SlePT) Program
10. Evaluation of a Sleep Disorders Program
11. Limitations
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Academy of Pediatrics. A Consensus statement on health care transitions for young adults with special health care needs. Pediatrics 2002, 110, 1304–1306. [Google Scholar]
- Colver, A.; Longwell, S. New understanding of adolescent brain development: Relevance to transitional healthcare for young people with long term conditions. Arch. Dis. Child. 2013, 98, 902–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breakey, V.R.; Blanchette, V.S.; Bolton-Maggs, P.H. Towards comprehensive care in transition for young people with haemophilia. Haemophilia 2010, 16, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalkut, M.K.; Allen, P.J. Transition from pediatric to adult healthcare for adolescents with congenital heart disease_a review of the literature and clinical implications. Pediatr. Nurs. 2009, 35, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nagra, A.; McGinnity, P.M.; Davis, N.; Salmon, A.P. Implementing transition: Ready Steady Go. Arch. Dis. Child. Educ. Pract. Ed. 2015, 100, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, E.; Carter, B.; Gillibrand, W. The transition of adolescents with diabetes from the children’s health care service into the adult health care service_a review of the literature. J. Clin. Nurs. 2002, 11, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, L. When should young people with chronic rheumatic disease move from paediatric to adult-centred care? Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2006, 20, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.H.; Cooley, C. Supporting the Health Care Transition From Adolescence to Adulthood in the Medical Home. Pediatrics 2018, 142, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, J.E.; Kelly, D.A. Transitioning care of the pediatric recipient to adult caregivers. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2003, 50, 1561–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scal, P.; Davern, M.; Ireland, M.; Park, K. Transition to adulthood: Delays and unmet needs among adolescents and young adults with asthma. J. Pediatr. 2008, 152, 471–475.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, W.C.; Sagerman, P.J. Supporting the health care transition from adolescence to adulthood in the medical home. Pediatrics 2011, 128, 182–200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gabriel, P.; McManus, M.; Rogers, K.; White, P. Outcome Evidence for Structured Pediatric to Adult Health Care Transition Interventions: A Systematic Review. J. Pediatr. 2017, 188, 263–269.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prior, M.; McManus, M.; White, P.; Davidson, L. Measuring the “triple aim” in transition care: A systematic review. Pediatrics 2014, 134, e1648–e1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canadian Association of Pediatric Health Centres (CAPHC), National Transitions Community of Practice. A Guideline for Transition from Paediatric to Adult Health Care for Youth with Special Health Care Needs: A National Approach. 2016. Available online: https://ken.childrenshealthcarecanada.ca/xwiki/bin/view/Transitioning+from+Paediatric+to+Adult+Care/A+Guideline+for+Transition+from+Paediatric+to+Adult+Care (accessed on 1 November 2019).
- O’Donnell, A.R.; Bjornson, C.L.; Bohn, S.G.; Kirk, V.G. Compliance Rates in Children Using Noninvasice Continuous Positive Airway Pressure. Sleep 2006, 29, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Lee, D.; Guo, G.; Harris, K.M. Trends in body mass index in adolescence and young adulthood in the United States: 1959–2002. J. Adolesc. Health 2011, 49, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spilsbury, J.C.; Storfer-Isser, A.; Rosen, C.L.; Redline, S. Remission and incidence of obstructive sleep apnea from middle childhood to late adolescence. Sleep 2015, 38, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, J.L.; Vasquez, M.M.; Silva, G.E.; Quan, S.F. Incidence and remission of sleep-disordered breathing and related symptoms in 6- to 17-year old children--the Tucson Children’s Assessment of Sleep Apnea Study. J. Pediatr. 2010, 157, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peppard, P.E.; Young, T.; Palta, M.; Skatrud, J. Prospective Study of the Association Between Sleep Disordered Breathing and Hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1378–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendzerska, T.; Gershon, A.S.; Hawker, G.; Leung, R.S.; Tomlinson, G. Obstructive sleep apnea and risk of cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality: A decade-long historical cohort study. PLoS Med. 2014, 11, e1001599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon-Larsen, P.; Adair, L.S.; Nelson, M.C.; Popkin, B.M. Five-year obesity incidence in the transition period between adolescence and adulthood: The National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent Health. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 569–575. [Google Scholar]
- Marcus, C.L.; Moore, R.H.; Rosen, C.L.; Giordani, B.; Garetz, S.L.; Taylor, H.G.; Mitchell, R.B.; Amin, R.; Katz, E.S.; Arens, R.; et al. A randomized trial of adenotonsillectomy for childhood sleep apnea. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2366–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDougall, C.M.; Adderley, R.J.; Wensley, D.F.; Seear, M.D. Long-term ventilation in children: Longitudinal trends and outcomes. Arch. Dis. Child. 2013, 98, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alebraheem, Z.; Toulany, A.; Baker, A.; Christian, J.; Narang, I. Facilitators and Barriers to Positive Airway Pressure Adherence for Adolescents. A Qualitative Study. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2018, 15, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesman, G.R.; Kuo, D.Z.; Carroll, J.L.; Ward, W.L. The impact of technology dependence on children and their families. J. Pediatr. Health Care 2013, 27, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaton, J.; Noyes, J.; Sloper, P.; Shah, R. Families’ experiences of caring for technology-dependent children_a temporal perspective. Health Soc. Care Community 2005, 13, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppard, P.E.; Young, T.; Barnet, J.H.; Palta, M.; Hagen, E.W.; Hla, K.M. Increased prevalence of sleep-disordered breathing in adults. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 177, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, V.; Clarke, V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual. Res. Psychol. 2006, 3, 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, C.M.; King, J.; Amin, R.; Katz, S.; McKim, D.; Road, J.; Rose, L. Health transition experiences of Canadian ventilator-assisted adolescents and their family caregivers: A qualitative interview study. Paediatr. Child Health 2017, 22, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semelka, M.; Wilson, J.; Floyd, R. Diagnosis and Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Adults. Am. Fam. Phys. 2016, 94, 355–360. [Google Scholar]
- Cielo, C.M.; Gungor, A. Treatment Options for Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Curr. Probl. Pediatr. Adolesc. Health Care 2016, 46, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, F.R.; Lentini-Oliveira, D.A.; Prado, L.B.; Prado, G.F.; Carvalho, L.B. Oral appliances and functional orthopaedic appliances for obstructive sleep apnoea in children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 10, CD005520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diercks, G.R.; Wentland, C.; Keamy, D.; Kinane, T.B.; Skotko, B.; de Guzman, V.; Grealish, E.; Dobrowski, J.; Soose, R.; Hartnick, C.J. Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation in Adolescents With Down Syndrome and Obstructive Sleep Apnea. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2017, 144, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.C.; Au, C.T.; Hui, L.L.; Ng, S.K.; Wing, Y.K.; Li, A.M. How OSA Evolves From Childhood to Young Adulthood: Natural History From a 10-Year Follow-up Study. Chest 2019, 156, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, C.F. Sleep apnea, alertness, and motor vehicle crashes. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 176, 954–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strohl, K.; Brown, D.B.; Collop, N.; George, C.; Grunstein, R.; Han, F.; Kline, L.; Malhotra, A.; Pack, A.; Phillips, B.; et al. Sleep apnea, sleepiness, and driving risk. American Thoracic Society. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 150 Pt 1, 1463–1473. [Google Scholar]
- McEvoy, R.D.; Antic, N.A.; Heeley, E.; Luo, Y.; Ou, Q.; Zhang, X.; Mediano, O.; Chen, R.; Drager, L.F.; Liu, Z.; et al. CPAP for Prevention of Cardiovascular Events in Obstructive Sleep Apnea. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drager, L.F.; Lee, C.H. Treatment of obstructive sleep apnoea as primary or secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease: Where do we stand now? Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2018, 24, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, S.L.; MacLean, J.E.; Hoey, L.; Horwood, L.; Barrowman, N.; Foster, B.; Hadjiyannakis, S.; Legault, L.; Bendiak, G.N.; Kirk, V.G.; et al. Insulin Resistance and Hypertension in Obese Youth With Sleep-Disordered Breathing Treated With Positive Airway Pressure: A Prospective Multicenter Study. J. Clin. Sleep Med. JCSM off. Publ. Am. Acad. Sleep Med. 2017, 13, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garbarino, S.; Bardwell, W.A.; Guglielmi, O.; Chiorri, C.; Bonanni, E.; Magnavita, N. Association of Anxiety and Depression in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Behav. Sleep Med. 2018, 18, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, R.; Kivity, S.; Peker, M.; Reinhorn, D.; Keinan-Boker, L.; Silverman, B.; Liphsitz, I.; Kolitz, T.; Levy, C.; Shlomi, D.; et al. Increased Risk for Cancer in Young Patients with Severe Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Respiration 2019, 97, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narang, I.; McCrindle, B.W.; Manlhiot, C.; Lu, Z.; Al-Saleh, S.; Birken, C.S.; Hamilton, J. Intermittent nocturnal hypoxia and metabolic risk in obese adolescents with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath. Schlaf Atm. 2018, 22, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patinkin, Z.W.; Feinn, R.; Santos, M. Metabolic Consequences of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Adolescents with Obesity: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis. Child. Obes. 2017, 13, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galland, B.; Spruyt, K.; Dawes, P.; McDowall, P.S.; Elder, D.; Schaughency, E. Sleep Disordered Breathing and Academic Performance: A Meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2015, 136, e934–e946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yilmaz, E.; Sedky, K.; Bennett, D.S. The relationship between depressive symptoms and obstructive sleep apnea in pediatric populations: A meta-analysis. J. Clin. Sleep Med. JCSM off. Publ. Am. Acad. Sleep Med. 2013, 9, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lynch, M.K.; Elliott, L.C.; Avis, K.T.; Schwebel, D.C.; Goodin, B.R. Quality of Life in Youth With Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome (OSAS) Treated With Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Therapy. Behav. Sleep Med. 2019, 17, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Hedner, J.; Habel, H.; Nerman, O.; Grote, L. Sleep apnea-related risk of motor vehicle accidents is reduced by continuous positive airway pressure: Swedish Traffic Accident Registry data. Sleep 2015, 38, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, A.H.; Webb, G.D. Preparing Pediatric Patients for Adult Care: Are We Ready? J. Pediatr. 2015, 167, 1194–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, M.; Westover, M.B.; Kelly, J.; Bianchi, M.T. Decision Modeling in Sleep Apnea: The Critical Roles of Pretest Probability, Cost of Untreated Obstructive Sleep Apnea, and Time Horizon. J. Clin. Sleep Med. JCSM off. Publ. Am. Acad. Sleep Med. 2016, 12, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pietzsch, J.B.; Garner, A.; Cipriano, L.E.; Linehan, J.H. An integrated health-economic analysis of diagnostic and therapeutic strategies in the treatment of moderate-to-severe obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep 2011, 34, 695–709. [Google Scholar]
- Streatfeild, J.; Hillman, D.; Adams, R.; Mitchell, S.; Pezzullo, L. Cost-effectiveness of continuous positive airway pressure therapy for obstructive sleep apnea: Health care system and societal perspectives. Sleep 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, E.A.; Corrigan, J.; Shurpin, K. Building the bridge from pediatric to adult diabetes care: Making the connection. Diabetes Educ. 2015, 41, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, S.R.; Keaton, M.; Nasr, S.Z. Evaluation of a cystic fibrosis transition program from pediatric to adult care. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2013, 48, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hilderson, D.; Moons, P.; Van der Elst, K.; Luyckx, K.; Wouters, C.; Westhovens, R. The clinical impact of a brief transition programme for young people with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Results of the DON’T RETARD project. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sawyer, A.M.; Gooneratne, N.S.; Marcus, C.L.; Ofer, D.; Richards, K.C.; Weaver, T.E. A systematic review of CPAP adherence across age groups: Clinical and empiric insights for developing CPAP adherence interventions. Sleep Med. Rev. 2011, 15, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taranto-Montemurro, L.; Messineo, L.; Sands, S.A.; Azarbarzin, A.; Marques, M.; Edwards, B.A.; Eckert, D.J.; White, D.P.; Wellman, A. The Combination of Atomoxetine and Oxybutynin Greatly Reduces Obstructive Sleep Apnea Severity. A Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Double-Blind Crossover Trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narang, I.; Mathew, J.L. Childhood obesity and obstructive sleep apnea. J. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 2012, 134202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Health PCfMaC: Transition to Adult Healthcare Services Work Group Recommendations that Have Clinical Applicability. Available online: https://www.pcmch.on.ca/health-care-providers/paediatric-care/pcmch-strategies-and-initiatives/transition-to-adult-healthcare-services/ (accessed on 1 November 2019).
- Pinson, J.; Harvey, J. Care of Adolescents with Chronic Conditions. Paediatr. Child Health 2006, 11, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tools and Resources. Available online: https://www.healthypeople.gov/2020/tools-resources (accessed on 26 August 2019).
- Patient and Family Resources: Transitioning to Adult Care. Available online: http://www.sickkids.ca/patient-family-resources/resource-navigation-service/transitioning-to-adult-care/index.html (accessed on 29 October 2019).
- Costanzo, M.R.; Dipchand, A.; Starling, R.; Anderson, A.; Chan, M.; Desai, S.; Fedson, S.; Fisher, P.; Gonzales-Stawinski, G.; Martinelli, L.; et al. The International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation Guidelines for the care of heart transplant recipients. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2010, 29, 914–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmanova, E.; Kirvan, C.; Verma, J.; Mukerji, G.; Akunov, N.; Phillips, K.; Samis, S. Triple Aim in Canada: Developing capacity to lead to better health, care and cost. Int. J. Qual. Health Care 2016, 28, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferris, M.; Cohen, S.; Haberman, C.; Javalkar, K.; Massengill, S.; Mahan, J.D.; Kim, S.; Bickford, K.; Cantu, G.; Medeiros, M.; et al. Self-Management and Transition Readiness Assessment: Development, Reliability, and Factor Structure of the STARx Questionnaire. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2015, 30, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varni, J.W.; Burwinkle, T.M.; Seid, M.; Skarr, D. The PedsQL 4.0 as a pediatric population health measure: Feasibility, reliability, and validity. Ambul. Pediatr. Off. J. Ambul. Pediatr. Assoc. 2003, 3, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, A.; Lamping, D.L.; Ploubidis, G.B. When to use broader internalising and externalising subscales instead of the hypothesised five subscales on the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ): Data from British parents, teachers and children. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 2010, 38, 1179–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, H.R.; Shaffer, D.; Fisher, P.; Gould, M.S. The Columbia Impairment Scale (CIS): Pilot findings on a measure of global impairment for children and adolescents. Int. J. Methods Psychiat. Res. 1993, 3, 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, R.L.; Rounds, L.A. Conjoint screening questionnaires for alcohol and other drug abuse: Criterion validity in a primary care practice. Wis. Med. J. 1995, 94, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chasens, E.R.; Ratcliffe, S.J.; Weaver, T.E. Development of the FOSQ-10: A short version of the Functional Outcomes of Sleep Questionnaire. Sleep 2009, 32, 915–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, S.L.; Duncan, C.L.; Janicke, D.M.; Wagner, M.H. Barriers to treatment of paediatric obstructive sleep apnoea: Development of the adherence barriers to continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) questionnaire. Sleep Med. 2012, 13, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Got transition: Center for Health Care Transition Improvement: National Alliance to Advance Adolescent Health. Available online: https://www.GOtTransition.org (accessed on 30 October 2019).



| Guiding Principles | Details |
|---|---|
| 1. Begin Transition Planning Early | Begin at diagnosis or 10 years Provides sufficient time for transition preparation |
| 2. Uninterrupted Healthcare Delivery | Ensure a continuous source of care for adolescent population |
| 3. Comprehensive Involvement | Patient, caregiver(s), family, and interdisciplinary team of healthcare Professionals should be involved in transition process |
| 4. Recognize Differences in Needs | Patients and their caregivers and family may have differing needs Needs must be assessed and addressed regularly Applicable resource: readiness checklists |
| Element of Triple Aim | Measure |
|---|---|
| Health of a Population | |
| Disease Management and Self-Efficacy |
|
| Psychosocial Functioning, Mental Health and Health-Related Quality of Life | |
| OSA-Specific Outcomes | |
| Individual Experiences of Care | |
| Expectations and satisfaction with healthcare Barriers to Care |
|
| Cost Measures | |
| Gaps in Care |
|
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heffernan, A.; Malik, U.; Cheng, R.; Yo, S.; Narang, I.; Ryan, C.M. Transition to Adult Care for Obstructive Sleep Apnea. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122120
Heffernan A, Malik U, Cheng R, Yo S, Narang I, Ryan CM. Transition to Adult Care for Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(12):2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122120
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeffernan, Austin, Uzair Malik, Russell Cheng, Shaun Yo, Indra Narang, and Clodagh M. Ryan. 2019. "Transition to Adult Care for Obstructive Sleep Apnea" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 12: 2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122120





