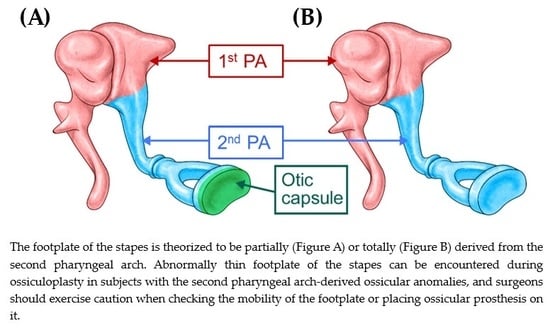
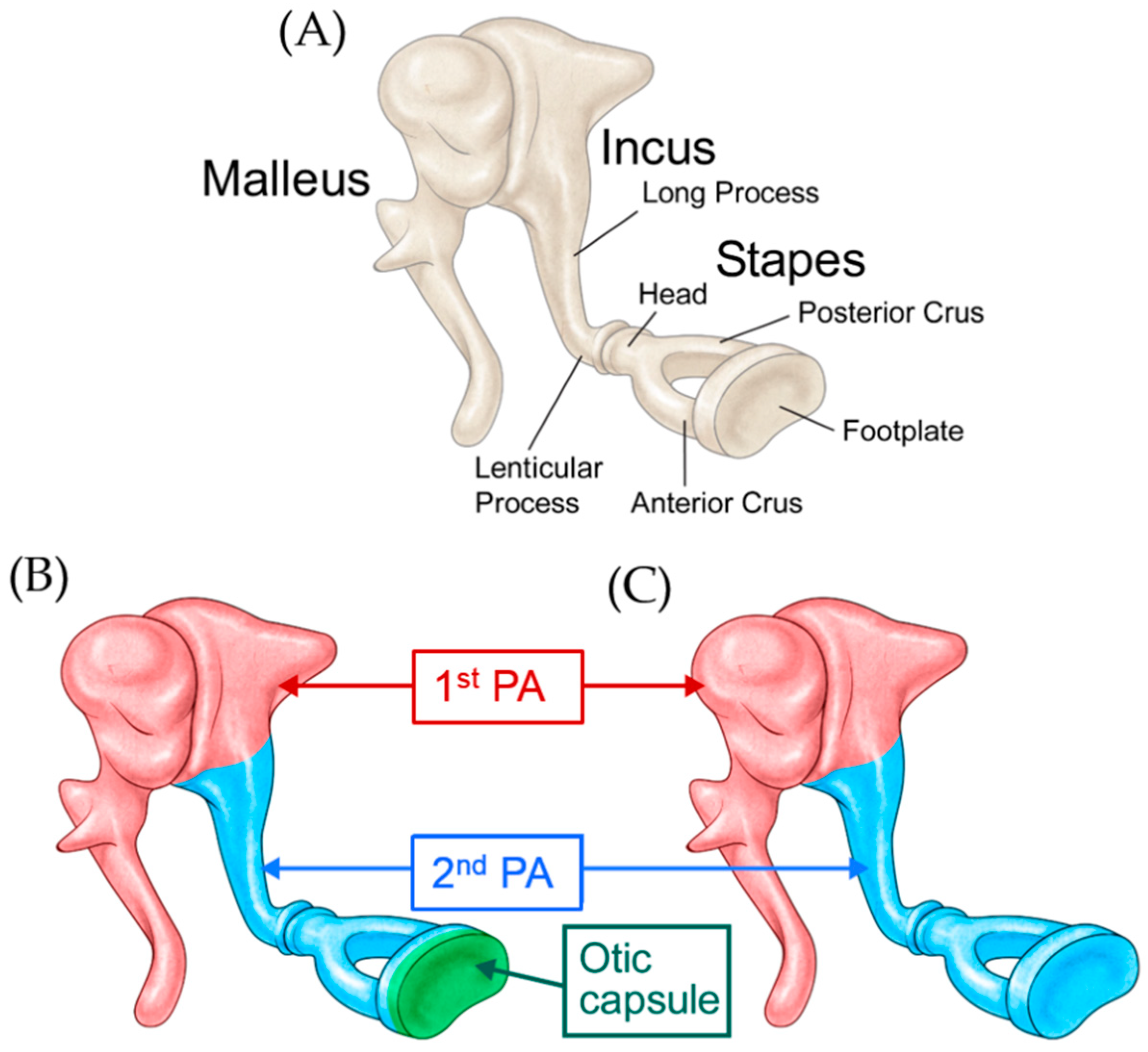
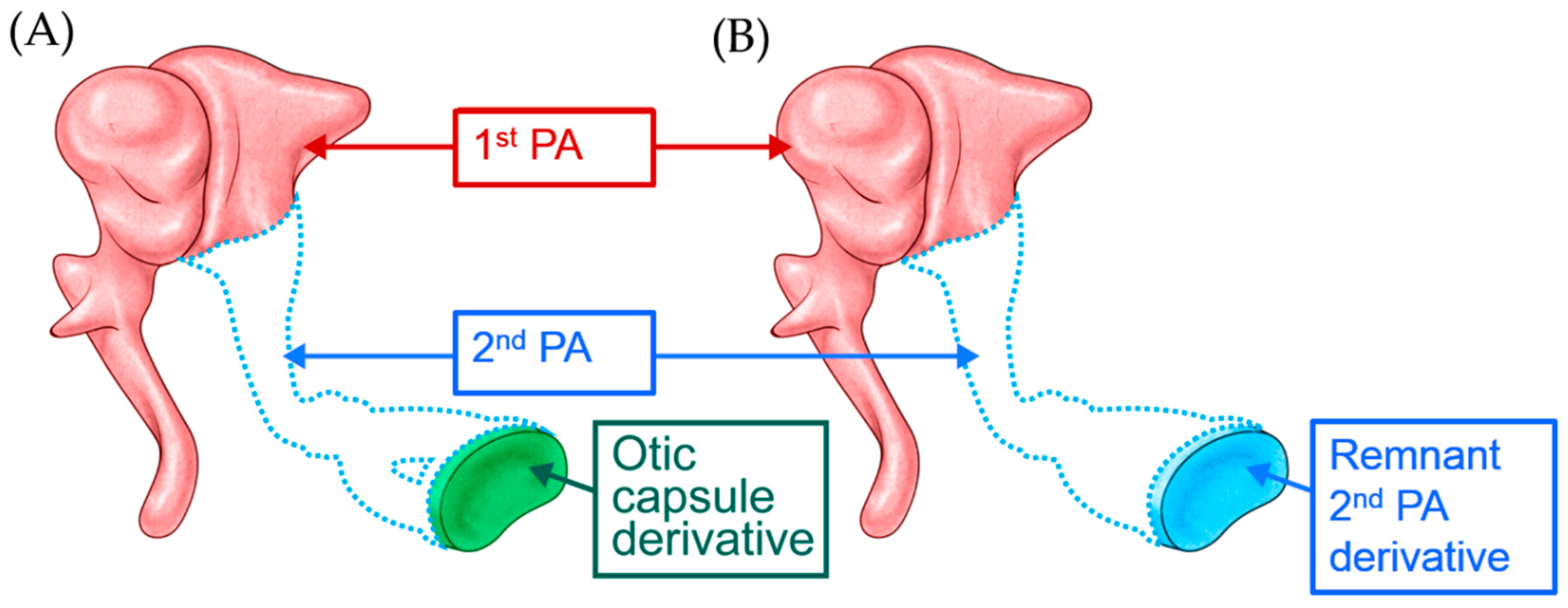
Beware of a Fragile Footplate: Lessons from Ossiculoplasty in Patients with Ossicular Anomalies Related to Second Pharyngeal Arch Defects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Clinical Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics and TBCT Findings
3.2. Postoperative Hearing Outcomes
3.3. Intraoperative Complications
4. Discussion
4.1. Postoperative Audiometric Outcomes in Subjects with Second Pharyngeal Arch Related Ossicular Anomalies
4.2. Risk Factors Associated with Ossiculoplasty in Subjects with Second Pharyngeal Arch Related Ossicular Anomalies
4.3. Study Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Altmann, F. Problem of so-called congenital atresia of the ear; histologic report of a new case. Arch. Otolaryngol. 1949, 50, 759–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anson, B.J.; Cauldwell, E.W. Stapes, fistula ante fenestram and associated structures in man; from the fetus of 160 mm. (5 months) to newborn infant. Arch. Otolaryngol. 1948, 48, 263–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anson, B.J.; Hanson, J.S.; Richany, S.F. Early embryology of the auditory ossicles and associated structures in relation to certain anomalies observed clinically. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1960, 69, 427–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richany, S.F.; Bast, T.H.; Anson, B.J. The development and adult structure of the malleus, incus and stapes. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1954, 63, 394–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Vazquez, J.F. Development of the stapes and associated structures in human embryos. J. Anat. 2005, 207, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louryan, S.; Vanmuylder, N.; Resimont, S. Ectopic stapes: A case report with embryologic correlations. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2003, 25, 342–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funasaka, S. Congenital ossicular anomalies without malformations of the external ear. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 1979, 224, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, J.R.; Anson, B.J.; Strickland, E.M. Branchial sources of the auditory ossicles in man. II. Observations of embryonic stages from 7 mm. to 28 mm. (CR length). Arch. Otolaryngol. 1962, 76, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henner, R.; Buckingham, R.A. The recognition and surgical treatment of congenital ossicular defects. Laryngoscope 1956, 66, 526–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Choung, Y.H. Isolated congenital ossicular anomalies. Acta Otolaryngol. 2009, 129, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, E.B.; Cremers, W.R. Classification of congenital middle ear anomalies. Report on 144 ears. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1993, 102, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Ffoundation, Inc. Committee on Hearing and Equilibrium guidelines for the evaluation of results of treatment of conductive hearing loss. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 1995, 113, 186–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, Y.J.; Bae, Y.J.; An, G.S.; Lee, K.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Choi, B.Y.; Choi, B.S.; Kim, J.H.; Koo, J.W.; et al. Involvement of the Internal Auditory Canal in Subjects With Cochlear Otosclerosis: A Less Acknowledged Third Window That Affects Surgical Outcome. Otol. Neurotol. 2019, 40, e186–e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Song, S.K.; Park, S.J.; Park, H.G.; Choi, B.Y.; Koo, J.W.; Song, J.J. Jugular Bulb Resurfacing With Bone Cement for Patients With High Dehiscent Jugular Bulb and Ipsilateral Pulsatile Tinnitus. Otol. Neurotol. 2019, 40, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, Y.J.; Shim, Y.J.; Choi, B.S.; Kim, J.H.; Koo, J.W.; Song, J.J. “Third Window” and “Single Window” Effects Impede Surgical Success: Analysis of Retrofenestral Otosclerosis Involving the Internal Auditory Canal or Round Window. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, J.J.; Hong, S.K.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, S.J.; Kang, S.I.; An, Y.H.; Jang, J.H.; Kim, J.S.; Koo, J.W. Vestibular Manifestations in Subjects With Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct. Otol. Neurotol. 2018, 39, e461–e467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, Y.J.; Song, J.J.; Choi, B.S.; Kang, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Koo, J.W. Differentiation Between Intralabyrinthine Schwannoma and Contrast-enhancing Labyrinthitis on MRI: Quantitative Analysis of Signal Intensity Characteristics. Otol. Neurotol. 2018, 39, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunwoo, W.; Jeon, Y.J.; Bae, Y.J.; Jang, J.H.; Koo, J.W.; Song, J.J. Typewriter tinnitus revisited: The typical symptoms and the initial response to carbamazepine are the most reliable diagnostic clues. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quesnel, S.; Benchaa, T.; Bernard, S.; Martine, F.; Viala, P.; Van Den Abbeele, T.; Teissier, N. Congenital middle ear anomalies: Anatomical and functional results of surgery. Audiol. Neurootol. 2015, 20, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrior, J.B. Surgical management of congenital conductive deafness. South. Med. J. 1987, 80, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousins, V.C.; Milton, C.M. Congenital ossicular abnormalities: A review of 68 cases. Am. J. Otol. 1988, 9, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, T.; Kakigi, A.; Kashio, A.; Kanaya, K.; Suzuki, M.; Yamasoba, T. Evaluation of the Carhart effect in congenital middle ear malformation with both an intact external ear canal and a mobile stapes footplate. ORL J. Otorhinolaryngol. Relat Spec. 2011, 73, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomeer, H.G.; Kunst, H.P.; Cremers, C.W. Congenital ossicular chain anomalies associated with a mobile stapes footplate: Surgical results for 23 ears. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2012, 121, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Lane, J.I.; Carlson, M.L.; Bruesewitz, M.R.; Witte, R.J.; Koeller, K.K.; Eckel, L.J.; Carter, R.E.; McCollough, C.H.; Leng, S. Comparison of a Photon-Counting-Detector CT with an Energy-Integrating-Detector CT for Temporal Bone Imaging: A Cadaveric Study. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 1733–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, S.A.; Choe, G.; Kim, Y.; Koo, J.-W.; Choi, B.Y.; Song, J.-J. Beware of a Fragile Footplate: Lessons from Ossiculoplasty in Patients with Ossicular Anomalies Related to Second Pharyngeal Arch Defects. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122130
Han SA, Choe G, Kim Y, Koo J-W, Choi BY, Song J-J. Beware of a Fragile Footplate: Lessons from Ossiculoplasty in Patients with Ossicular Anomalies Related to Second Pharyngeal Arch Defects. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(12):2130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122130
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Sun A, Goun Choe, Yoonjoong Kim, Ja-Won Koo, Byung Yoon Choi, and Jae-Jin Song. 2019. "Beware of a Fragile Footplate: Lessons from Ossiculoplasty in Patients with Ossicular Anomalies Related to Second Pharyngeal Arch Defects" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 12: 2130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122130
APA StyleHan, S. A., Choe, G., Kim, Y., Koo, J. -W., Choi, B. Y., & Song, J. -J. (2019). Beware of a Fragile Footplate: Lessons from Ossiculoplasty in Patients with Ossicular Anomalies Related to Second Pharyngeal Arch Defects. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(12), 2130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122130