Psoas Abscess Due to Mycobacterium avium in a Patient with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia—Case Report and Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
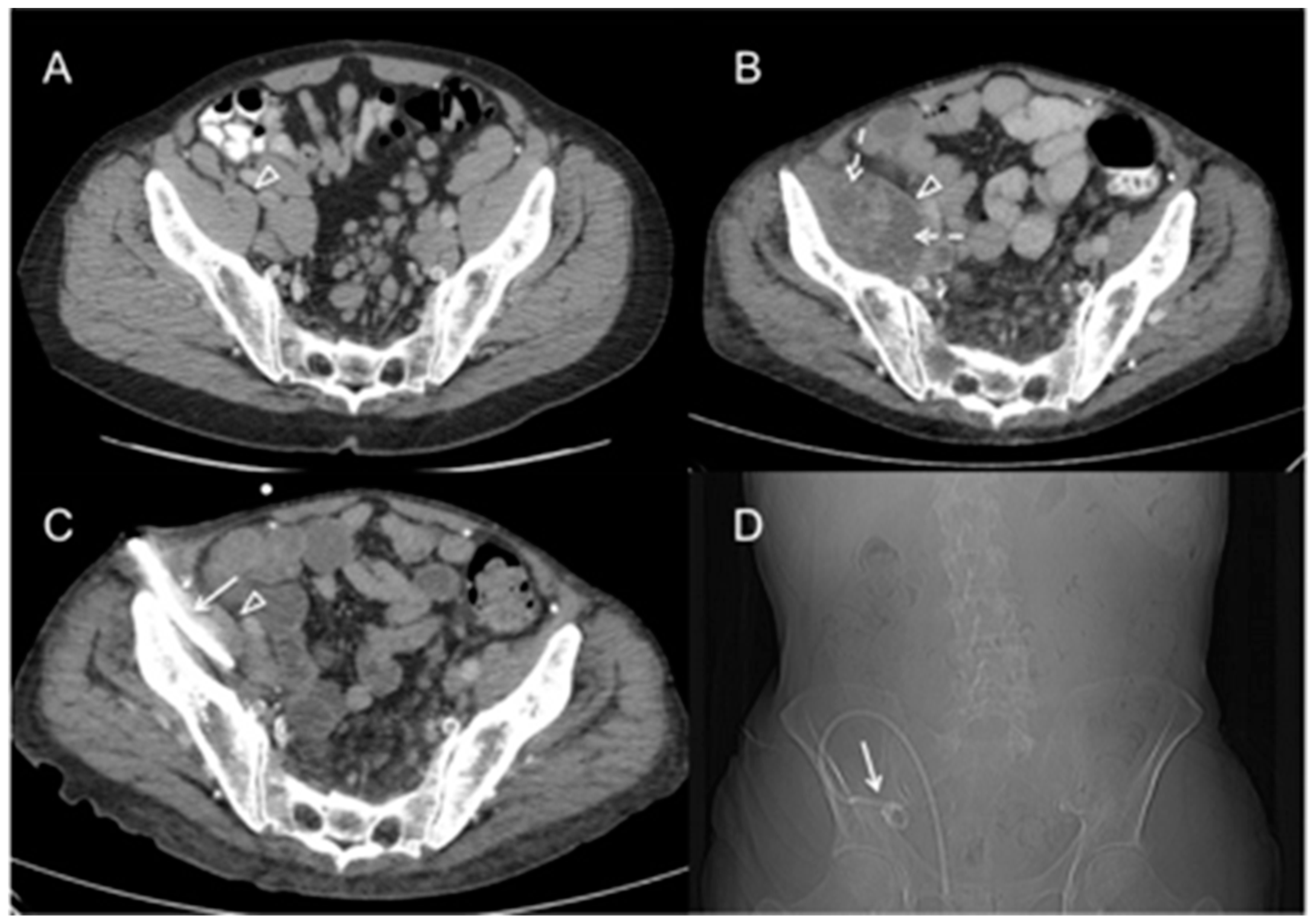
2. Case Report
3. Literature Review and Discussion
3.1. Infections with Non-Tuberculous Mycobacteria (NTM)
3.2. Infectious Complications in CLL
3.3. Obinutuzumab
3.4. Ibrutinib
4. Conclusions
- Our case and our literature review illustrate that physicians should be aware of opportunistic infections in patients with CLL.
- Infectious complications may be difficult to recognize clinically. Appropriate biopsy material from affected lymph nodes should be obtained. The key to diagnosis of opportunistic infection is microbiological confirmation and histological exclusion of secondary malignancies, Richter’s transformation, and progressive CLL.
- Diagnosis of NTM infection relies on mycobacterial PCR and culture done on biopsy material (or broncho-alveolar lavage fluid when there is respiratory involvement).
- Infection prophylaxis including vaccinations or intravenous immune globulin replacement should be considered in all CLL patients when appropriate.
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saadeh, C.E.; Srkalovic, G. Mycobacterium avium complex infection after alemtuzumab therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Pharmacotherapy 2008, 28, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, A.; Kantner, J.; Tzankov, A. Granulomatous reactions cause symptoms or clinically imitate treatment resistance in small lymphocytic lymphoma/chronic lymphocytic leukaemia more frequently than in other non-Hodgkin lymphomas. J. Clin. Pathol. 2005, 58, 815–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nannini, E.C.; Keating, M.; Binstock, P.; Samonis, G.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Successful treatment of refractory disseminated Mycobacterium avium complex infection with the addition of linezolid and mefloquine. J. Infect. 2002, 44, 201–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, D.A.; Rabe, K.G.; Schwager, S.M.; Slager, S.L.; Call, T.G.; Viswanatha, D.S.; Zent, C.S. Infectious lymphadenitis in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma: A rare, but important, complication. Leuk. Lymphoma 2015, 56, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, D.E.; Aksamit, T.; Brown-Elliott, B.A.; Catanzaro, A.; Daley, C.; Gordin, F.; Holland, S.M.; Horsburgh, R.; Huitt, G.; Iademarco, M.F.; et al. An official ATS/IDSA statement: Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care. Med. 2007, 175, 367–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.M.; Odell, J.A. Nontuberculous mycobacterial pulmonary infections. J. Thorac. Dis. 2014, 6, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haworth, C.S.; Banks, J.; Capstick, T.; Fisher, A.J.; Gorsuch, T.; Laurenson, I.F.; Leitch, A.; Loebinger, M.R.; Milburn, H.J.; Nightingale, M.; et al. British Thoracic Society guidelines for the management of non-tuberculous mycobacterial pulmonary disease (NTM-PD). Thorax 2017, 72 (Suppl. 2), ii1–ii64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winthrop, K.L.; McNelley, E.; Kendall, B.; Marsahll-Olson, A.; Morris, C.; Cassidy, M.; Saulson, A.; Hedberg, K.; et al. Pulmonary nontuberculous mycobacterial disease prevalence and clinical features: An emerging public health disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care. Med. 2010, 182, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winthrop, K.L.; Chang, E.; Yamashita, S.; Iademarco, M.F.; LoBue, P.A. Nontuberculous mycobacteria infections and anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha therapy. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1556–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, A.J.; Mahdi, E.J.; Salamat, A.; Al-Bouri, K. Invasive Mycobacterium chelonea infection. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 164, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dousa, K.M.; Babiker, A.; Van Aarten, D.; Shah, N.; Bonomo, R.A.; Johnson, J.L.; Skalweit, M.J. Ibrutinib Therapy and Mycobacterium chelonae Skin and Tissue Infection. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2018, 5, ofy168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dungarwalla, M.; Field-Smith, A.; Jameson, C.; Riley, U.; Chapman, A.; Bunker, C.B.; Dearden, C.E.; Matutes, E. Cutaneous Mycobacteria chelonea infection in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Haematologica 2007, 92, e5–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sillito, F.; Cervi, P.; Skibinska, M. Something fishy in the immunocompromised. Br. J. Haematol. 2011, 153, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awais, A.; Tam, C.S.; Kontoyiannis, D.; Ferrajoli, A.; Duvic, M.; Cortes, J.; Keating, M.J. Rapid resolution of Mycobacteria marinum chronic skin infection during lenalidomide therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, e69–e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, J.J.; Gelman, S.S. Multifocal osteomyelitis due to Mycobacterium szulgai in patient with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J. Infect. 2008, 56, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, H.; Smith, S. Mycobacterium fortuitum infection in a patient with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2004, 127, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, T.; Zimmerli, S.; Bodmer, T.; Lämmle, B. Mycobacterium genavense infection in a patient with long-standing chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. J. Intern. Med. 2000, 248, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilal, T.; Gea-Banacloche, J.C.; Leis, J.F. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia and infection risk in the era of targeted therapies: Linking mechanisms with infections. Blood Rev. 2018, 32, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensel, M.; Kornacker, M.; Yammeni, S.; Egerer, G.; Ho, A.D. Disease activity and pretreatment, rather than hypogammaglobulinaemia, are major risk factors for infectious complications in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2003, 122, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, S.; Karanth, M.; Pratt, G.; Starczynski, J.; Hopper, L.; Fegan, C.; Pepper, C.; Valcarcel, D.; Milligan, D.W.; Delgado, J. The effect of immunoglobulin VH gene mutation status and other prognostic factors on the incidence of major infections in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer 2006, 107, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallek, M.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Eichhorst, B. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Lancet 2018, 391, 1524–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teh, B.W.; Tam, C.S.; Handunnetti, S.; Worth, L.J.; Slavin, M.A. Infections in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: Mitigating risk in the era of targeted therapy. Blood Rev. 2018, 32, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goede, V.; Fischer, K.; Busch, R.; Engelke, A.; Eichhorst, B.; Wendtner, C.M.; Chagorova, T.; de la Serna, J.; Dilhuydy, M.-S.; Illmer, T.; et al. Obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil in patients with CLL and coexisting conditions. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, J.A.; Tedeschia, A.; Barr, P.M.; Robak, T.; Owen, C.; Ghia, P.; Bairey, O.; Hillmen, P.; Bartlett, N.L.; Li, J.; et al. Ibrutinib as Initial Therapy for Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2425–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woyach, J.A.; Ruppert, A.S.; Heerema, N.A.; Zhao, W.; Booth, A.M.; Ding, W.; Bartlett, N.L.; Brander, D.M.; Barr, P.M.; Rogers, K.A.; et al. Ibrutinib Regimens versus Chemoimmunotherapy in Older Patients with Untreated CLL. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Age at CLL (year) | Age at MAC (year) | Sex | Clinical Manifestations of MAC Infection | Site of MAC Detection | CLL Treatment before MAC Diagnosis | Outcome | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60 | 74 | Male | retroperitoneal and inguinal lymphadenitis, psoas abscess | Inguinal lymph node biopsy | chlorambucil, prednisone, fludarabine, rituximab, cyclophosphamide, bendamustin, ofatumumab, lenalidomide; intravenous immune globulin; obinutuzumab | MAC successfully treated, patient dies several months later | present case |
| 38 | 46 | Male | lymphadenitis | lymph node biopsy | alemtuzumab | alive | [1] |
| 41 | 55 | Male | lymphadenitis, small bowel infection | n/a | cyclophosphamide/oncovine/prednisone chemotherapy | alive | [2] |
| 49 | 59 | Male | disseminated cutaneous disease | skin biopsy | fludarabine, prednisone, cyclophosphamide, rituximab, alemtuzumab | died | [3] |
| n/a | n/a | Male | lymphadenitis | lymph node biopsy | none | alive | [4] |
| Age at CLL (year) | Age at NTM (year) | Sex | NTM Species | Clinical Manifestations of NTM Infection | Site of NTM Detection | CLL Treatment before NTM Diagnosis | Outcome | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 48 | 58 | F | M. chelonae | disseminated cutaneous disease | skin biopsy | methylprednisolone and other 5 non specified agents | alive | [10] |
| 74 | 85 | M | M. chelonae | skin lesions on arms and legs | skin biopsy | bendamustin, rituximab, fludarabine | alive | [11] |
| 67 | 74 | M | M. chelonae | skin lesions | skin biopsy | chlorambucil, fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, alemtuzumab | alive | [12] |
| 62 | n/a | M | M. marinum | erythematous cutaneous nodules, pulmonary nodule | skin biopsy | prednisolone, ciclosporin | died | [13] |
| 57 | 64 | M | M. marinum | skin lesions | skin biopsy | fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, rituximab | alive | [14] |
| 61 | 62 | M | M. fortuitum | pulmonary nodules | sputum | chlorambucile, fludarabine | died | [16] |
| 62 | 79 and 83 | F | M. genavense | lymphadenitis | blood culture and bone marrow biopsy | chlorambucil, prednisone | died | [17] |
| 59 | 66 | F | M. szulgai | multifocal osteomyelitis, cutaneous lesions | bone biopsy | fludarabine, chlorambucil | died | [15] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diaco, N.D.; Strohdach, B.; Falkowski, A.L.; Hainc, N.; Brunner, P.; Rutishauser, J.; Jost, L.; Tarr, P.E. Psoas Abscess Due to Mycobacterium avium in a Patient with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia—Case Report and Review. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8020216
Diaco ND, Strohdach B, Falkowski AL, Hainc N, Brunner P, Rutishauser J, Jost L, Tarr PE. Psoas Abscess Due to Mycobacterium avium in a Patient with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia—Case Report and Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(2):216. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8020216
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiaco, Natascha D., Bettina Strohdach, Anna L. Falkowski, Nicolin Hainc, Philippe Brunner, Jonas Rutishauser, Lorenz Jost, and Philip E. Tarr. 2019. "Psoas Abscess Due to Mycobacterium avium in a Patient with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia—Case Report and Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 2: 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8020216
APA StyleDiaco, N. D., Strohdach, B., Falkowski, A. L., Hainc, N., Brunner, P., Rutishauser, J., Jost, L., & Tarr, P. E. (2019). Psoas Abscess Due to Mycobacterium avium in a Patient with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia—Case Report and Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(2), 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8020216





