Blood-Flow Restriction Resistance Exercise for Older Adults with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Pilot Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Overview
2.2. Participants
2.3. Assessments
2.4. Interventions
2.5. Safety
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
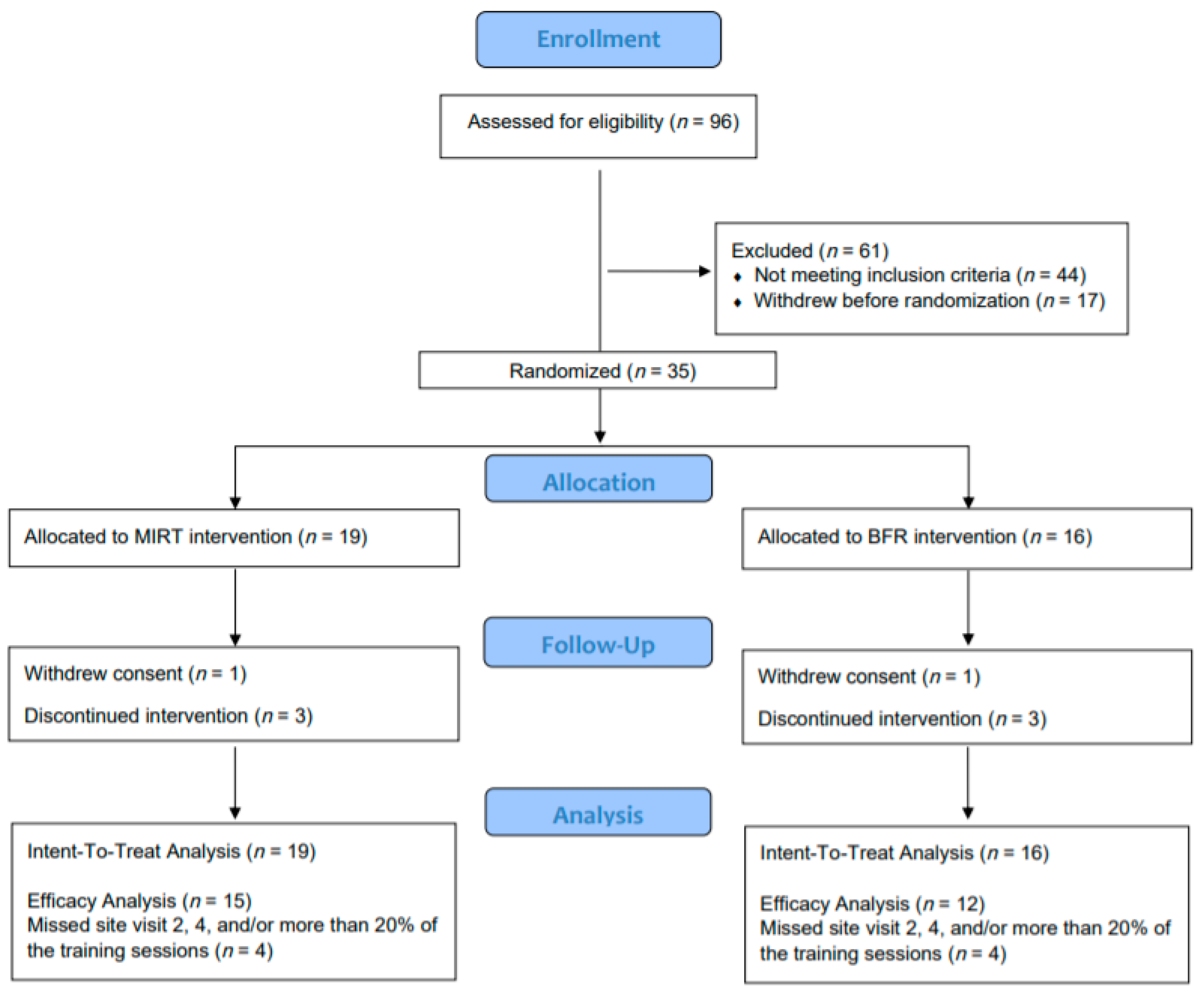
3.1. Participants
3.2. Retention, Adherence, and Safety
3.3. Exercise Training Volume and 1RM
3.4. Primary and Secondary Outcomes
3.5. Biomarkers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Lawrence, R.C.; Felson, D.T.; Helmick, C.G.; Arnold, L.M.; Choi, H.; Deyo, R.A.; Gabriel, S.; Hirsch, R.; Hochberg, M.C.; Hunder, G.G.; et al. Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and other rheumatic conditions in the United States. Part II. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, L.; Schwartz, T.A.; Helmick, C.G.; Renner, J.B.; Tudor, G.; Koch, G.; Dragomir, A.; Kalsbeek, W.D.; Luta, G.; Jordan, J.M.; et al. Lifetime risk of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 59, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hootman, J.M.; Helmick, C.G. Projections of US prevalence of arthritis and associated activity limitations. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 54, 226–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Jordan, J.M. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2010, 26, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochberg, M.C.; Kasper, J.; Williamson, J.; Skinner, A.; Fried, L.P. The contribution of osteoarthritis to disability: Preliminary data from the Women’s Health and Aging Study. J. Rheumatol. Suppl. 1995, 43, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ling, S.M.; Fried, L.P.; Garrett, E.S.; Fan, M.-Y.; Rantanen, T.; Bathon, J.M. Knee osteoarthritis compromises early mobility function: The Women’s Health and Aging Study II. J. Rheumatol. 2003, 30, 114–120. [Google Scholar]
- Loeser, R.F. Age-related changes in the musculoskeletal system and the development of osteoarthritis. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2010, 26, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.A.; Ettinger, W.H.; Neuhaus, J.M.; Mallon, K.P. Knee osteoarthritis and physical functioning: Evidence from the NHANES I Epidemiologic Followup Study. J. Rheumatol. 1991, 18, 591–598. [Google Scholar]
- Rejeski, W.J.; Shumaker, S. Knee osteoarthritis and health-related quality of life. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1994, 26, 1441–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semanik, P.A.; Chang, R.W.; Dunlop, D.D. Aerobic activity in prevention and symptom control of osteoarthritis. PM R 2012, 4 (Suppl. 5), S37–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gür, H.; Çakın, N. Muscle mass, isokinetic torque, and functional capacity in women with osteoarthritis of the knee. Arch. Phys Med. Rehabil. 2003, 84, 1534–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinks, C.; Jordan, K.; Croft, P. Osteoarthritis as a public health problem: The impact of developing knee pain on physical function in adults living in the community: (KNEST 3). Rheumatology 2007, 46, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, S.B.; Laroche, D.P.; Villa, M.R.; Barile, H.; Manini, T.M. Blood flow restricted resistance training in older adults at risk of mobility limitations. Exp. Geronto. 2017, 99, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libardi, C.; Chacon-Mikahil, M.; Cavaglieri, C.; Tricoli, V.; Roschel, H.; Vechin, F.; Conceição, M.; Ugrinowitsch, C. Effect of Concurrent Training with Blood Flow Restriction in the Elderly. Int. J. Sports Med. 2015, 36, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segal, N.A.; Williams, G.N.; Davis, M.C.; Wallace, R.B.; Mikesky, A.E. Efficacy of blood flow-restricted, low-load resistance training in women with risk factors for symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. PM&R 2015, 7, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lees, F.D.; Clark, P.G.; Nigg, C.R.; Newman, P. Barriers to exercise behavior among older adults: A focus-group study. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2005, 13, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leveille, S.G.; Fried, L.P.; McMullen, W.; Guralnik, J.M. Advancing the taxonomy of disability in older adults. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2004, 59, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buford, T.W.; Fillingim, R.B.; Manini, T.M.; Sibille, K.T.; Vincent, K.R.; Wu, S.S. Kaatsu training to enhance physical function of older adults with knee osteoarthritis: Design of a randomized controlled trial. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2015, 43, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ettinger, W.H.; Burns, R.; Messier, S.P.; Applegate, W.; Rejeski, W.J.; Morgan, T.; Shumaker, S.; Berry, M.J.; O’Toole, M.; Monu, J.; et al. A randomized trial comparing aerobic exercise and resistance exercise with a health education program in older adults with knee osteoarthritis. The Fitness Arthritis and Seniors Trial (FAST). JAMA 1997, 277, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Focht, B.C. Effectiveness of exercise interventions in reducing pain symptoms among older adults with knee osteoarthritis: A review. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2006, 14, 212–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, N.E.; Dziedzic, K.S.; van der Windt, D.A.; Fritz, J.M.; Hay, E.M. Research priorities for non-pharmacological therapies for common musculoskeletal problems: Nationally and internationally agreed recommendations. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2009, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutron, I.; Moher, D.; Altman, D.G.; Schulz, K.F.; Ravaud, P.; CONSORT Group. Methods and processes of the CONSORT Group: Example of an extension for trials assessing nonpharmacologic treatments. Ann. Intern. Med. 2008, 148, W60–W66. [Google Scholar]
- Boutron, I.; Moher, D.; Altman, D.G.; Schulz, K.F.; Ravaud, P.; CONSORT Group. Extending the CONSORT statement to randomized trials of nonpharmacologic treatment: Explanation and elaboration. Ann. Intern. Med. 2008, 148, 295–309. [Google Scholar]
- Keefe, F.J.; Dworkin, S.F.; Von Korff, M.; Ormel, J. Grading the severity of chronic pain. Pain 1992, 50, 133–149. [Google Scholar]
- Kohn, M.D.; Sassoon, A.A.; Fernando, N.D. Classifications in Brief: Kellgren-Lawrence Classification of Osteoarthritis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2016, 474, 1886–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM). ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription, 9th ed.; American College of Sports Medicine: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Buford, T.W.; Cooke, M.B.; Manini, T.M.; Leeuwenburgh, C.; Willoughby, D.S. Effects of age and sedentary lifestyle on skeletal muscle NF-kappaB signaling in men. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2010, 65, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buford, T.W.; Cooke, M.B.; Redd, L.L.; Hudson, G.M.; Shelmadine, B.D.; Willoughby, D.S. Protease supplementation improves muscle function after eccentric exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 1908–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buford, T.W.; Manini, T.M.; Hsu, F.-C.; Cesari, M.; Anton, S.D.; Nayfield, S.; Stafford, R.S.; Church, T.S.; Pahor, M.; Carter, C.S.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor use by older adults is associated with greater functional responses to exercise. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2012, 60, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buford, T.W.; Miller, M.E.; Church, T.S.; Gill, T.M.; Henderson, R.; Hsu, F.-C.; McDermott, M.M.; Nadkarni, N.; Pahor, M.; Stafford, R.S.; et al. Antihypertensive Use and the Effect of a Physical Activity Intervention in the Prevention of Major Mobility Disability among Older Adults: The LIFE Study. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2016, 71, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buford, T.W.; Lott, D.J.; Marzetti, E.; Wohlgemuth, S.E.; Vandenborne, K.; Pahor, M.; Leeuwenburgh, C.; Manini, T.M. Age-related Differences in Lower Extremity Tissue Compartments and Associations with Physical Function in Older Adults. Exp. Gerontol. 2012, 47, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layne, A.S.; Hsu, F.-C.; Blair, S.N.; Chen, S.-H.; Dungan, J.; Fielding, R.A.; Glynn, N.W.; Hajduk, A.M.; King, A.C.; Manini, T.M.; et al. Predictors of Change in Physical Function in Older Adults in Response to Long-Term, Structured Physical Activity: The LIFE Study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 98, 11–24.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haley, S.M.; Jette, A.M.; Coster, W.J.; Kooyoomjian, J.T.; Levenson, S.; Heeren, T.; Ashba, J. Late Life Function and Disability Instrument: II. Development and evaluation of the function component. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2002, 57, M217–M222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jette, A.M.; Haley, S.M.; Coster, W.J.; Kooyoomjian, J.T.; Levenson, S.; Heeren, T.; Ashba, J. Late life function and disability instrument: I. Development and evaluation of the disability component. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2002, 57, M209–M216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellamy, N.; Buchanan, W.W.; Goldsmith, C.H.; Campbell, J.; Stitt, L.W. Validation study of WOMAC: A health status instrument for measuring clinically important patient relevant outcomes to antirheumatic drug therapy in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee. J. Rheumatol. 1988, 15, 1833–1840. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- American College of Sports Medicine; Chodzko-Zajko, W.J.; Proctor, D.N.; Fiatarone Singh, M.A.; Minson, C.T.; Nigg, C.R.; Salem, G.J.; Skinner, J.S. American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Exercise and physical activity for older adults. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 1510–1530. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, M.E.; Rejeski, W.J.; Blair, S.N.; Duncan, P.W.; Judge, J.O.; King, A.C.; Macera, C.A.; Castaneda-Sceppa, C. Physical activity and public health in older adults: Recommendation from the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Heart Association. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 1435–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.E.; Rejeski, W.J.; Blair, S.N.; Duncan, P.W.; Judge, J.O.; King, A.C.; Macera, C.A.; Castaneda-Sceppa, C.; American College of Sports Medicine; American Heart Association. Physical activity and public health in older adults: Recommendation from the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Heart Association. Circulation 2007, 116, 1094–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Larkin, K.A.; MacNeil, R.G.; Dirain, M.; Sandesara, B.; Manini, T.M.; Buford, T.W. Blood flow restriction enhances post-resistance exercise angiogenic gene expression. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2012, 44, 2077–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manini, T.M.; Vincent, K.R.; Leeuwenburgh, C.L.; Lees, H.A.; Kavazis, A.N.; Borst, S.E.; Clark, B.C. Myogenic and proteolytic mRNA expression following blood flow restricted exercise. Acta Physiol. 2011, 201, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loenneke, J.P.; Fahs, C.A.; Rossow, L.M.; Sherk, V.D.; Thiebaud, R.S.; Abe, T.; Bemben, D.A.; Bemben, M.G. Effects of cuff width on arterial occlusion: Implications for blood flow restricted exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 112, 2903–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, J.A.; Murray, D.G. The relationship between tourniquet pressure and underlying soft-tissue pressure in the thigh. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1982, 64, 1148–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Roekel, H.E.; Thurston, A.J. Tourniquet pressure: The effect of limb circumference and systolic blood pressure. J. Hand Surg. Br. 1985, 10, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzmaurice, G.M.; Laird, N.M.; Ware, J.H. Applied Longitudinal Analysis; Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; Volume 998. [Google Scholar]
- Searle, S.R.; Speed, F.M.; Milliken, G.A. Population Marginal Means in the Linear Model: An Alternative to Least Squares Means. Am. Stat. 1980, 34, 216–221. [Google Scholar]
- Eldridge, S.M.; Chan, C.L.; Campbell, M.J.; Bond, C.M.; Hopewell, S.; Thabane, L.; Lancaster, G.A.; PAFS Consensus Group. CONSORT 2010 statement: Extension to randomised pilot and feasibility trials. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2016, 2, 64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Horne, E.; Lancaster, G.A.; Matson, R.; Cooper, A.; Ness, A.; Leary, S. Pilot trials in physical activity journals: A review of reporting and editorial policy. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2018, 4, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borg, G. Borg’s Perceived Exertion and Pain Scales; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Thabane, L.; Ma, J.; Chu, R.; Cheng, J.; Ismaila, A.; Rios, L.P.; Robson, R.; Thabane, M.; Giangregorio, L.; Goldsmith, C.H.; et al. A tutorial on pilot studies: The what, why and how. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2010, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, B.C.; Manini, T.M. Can KAATSU Exercise Cause Rhabdomyolysis? Clin. J. Sport Med. 2017, 27, e1–e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- In, J. Introduction of a pilot study. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2017, 70, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajadhyaksha, V. Conducting Feasibilities in Clinical Trials: An Investment to Ensure a Good Study. Perspect. Clin. Res. 2010, 1, 106–109. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, S.D.; Ramachandran, V.S.; Cawthon, P.M.; Gona, P.; McLean, R.R.; Cupples, L.A.; Kiel, D.P. Procollagen type III N-terminal peptide (P3NP) and lean mass: A cross-sectional study. J. Frailty Aging 2013, 2, 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Hamarneh, S.R.; Murphy, C.A.; Shih, C.W.; Frontera, W.; Torriani, M.; Irazoqui, J.E.; Makimura, H. Relationship between serum IGF-1 and skeletal muscle IGF-1 mRNA expression to phosphocreatine recovery after exercise in obese men with reduced GH. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Bhatnagar, S.; Kumar, A.; Lach-Trifilieff, E.; Wauters, S.; Li, H.; Makonchuk, D.Y.; Glass, D.J. The TWEAK-Fn14 system is a critical regulator of denervation-induced skeletal muscle atrophy in mice. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 188, 833–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





| MIRT (n = 19) | BFR (n = 16) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 69.1 ± 7.1 | 67.2 ± 5.2 |
| Sex, Female | 15 (78.9%) | 10 (62.5%) |
| Race, White | 73.7% | 81.2% |
| Ethnicity, Hispanic | 6.2% | 6.2% |
| Body Mass Index, kg/m2 | 29.8 ± 5.3 | 31.7 ± 5.9 |
| Systolic blood pressure, mm Hg | 132 ± 19 | 126 ± 15 |
| Diastolic blood pressure, mm Hg | 80 ± 10 | 73 ± 6 |
| Kellgren and Lawrence score, grade | 2.9 ± 0.8 | 2.8 ± 0.8 |
| Visual analog pain scale, mm | 28.1 ± 19.9 | 11.1 ± 11.1 |
| 400 m walk gait speed, m/s | 1.01 ±0.11 | 1.04 ± 0.12 |
| WOMAC pain subscale, points | 7.23 ± 4.87 | 6.19 ± 3.04 |
| 60 deg/s peak torque extension, Nm | 45.3 ± 19.3 | 52.3 ± 12.1 |
| 90 deg/s peak torque extension, Nm | 41.5 ± 17.1 | 49.7 ± 12.4 |
| 120 deg/s peak torque extension, Nm | 35.1 ± 14.7 | 46.2 ± 13.3 |
| Total SPPB, points | 10.2 ± 1.9 | 10.4 ± 1.9 |
| Leg Press 1RM, lbs | 130.1 ± 63.4 | 139.7 ± 38.0 |
| Leg Extension 1RM, lbs | 90.6 ± 41.6 | 92.5 ± 20.3 |
| Leg Curl 1RM, lbs | 94.8 ± 23.1 | 101.3 ± 21.1 |
| Calf Flexion 1RM, lbs | 147.1 ± 56.3 | 160.3 ± 68.4 |
| BFR | MIRT | |
|---|---|---|
| Leg press total volume, lbs. | 793 ± 495 | 1709 ± 908 |
| Leg press repetitions | 452.04 ± 369.82 | 376.94 ± 166.04 |
| Leg press weight, lbs. | 885.05 ± 666.26 | 2436.22 ± 1712.89 |
| Leg extension total volume, lbs. | 357 ± 165 | 639 ± 363 |
| Leg extension repetitions | 213.13 ± 163.63 | 180.75 ± 154.44 |
| Leg extension weight, lbs. | 511.33 ± 345.41 | 1051.31 ± 1099.43 |
| Leg curl total volume, lbs. | 900 ± 377 | 931 ±303 |
| Leg curl repetitions | 367.88 ± 283.26 | 310.67 ± 160.05 |
| Leg curl weight, lbs. | 1014.70 ± 616.26 | 1595.05 ± 955.81 |
| Calf flexion total volume, lbs. | 1314 ± 921 | 1779 ± 858 |
| Calf flexion repetitions | 570.07 ± 473.99 | 383.57 ± 224.55 |
| Calf flexion weight, lbs. | 1025.27 ± 886.93 | 2485.47 ± 1507.80 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harper, S.A.; Roberts, L.M.; Layne, A.S.; Jaeger, B.C.; Gardner, A.K.; Sibille, K.T.; Wu, S.S.; Vincent, K.R.; Fillingim, R.B.; Manini, T.M.; et al. Blood-Flow Restriction Resistance Exercise for Older Adults with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Pilot Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8020265
Harper SA, Roberts LM, Layne AS, Jaeger BC, Gardner AK, Sibille KT, Wu SS, Vincent KR, Fillingim RB, Manini TM, et al. Blood-Flow Restriction Resistance Exercise for Older Adults with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Pilot Randomized Clinical Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(2):265. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8020265
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarper, Sara A., Lisa M. Roberts, Andrew S. Layne, Byron C. Jaeger, Anna K. Gardner, Kimberly T. Sibille, Samuel S. Wu, Kevin R. Vincent, Roger B. Fillingim, Todd M. Manini, and et al. 2019. "Blood-Flow Restriction Resistance Exercise for Older Adults with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Pilot Randomized Clinical Trial" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 2: 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8020265
APA StyleHarper, S. A., Roberts, L. M., Layne, A. S., Jaeger, B. C., Gardner, A. K., Sibille, K. T., Wu, S. S., Vincent, K. R., Fillingim, R. B., Manini, T. M., & Buford, T. W. (2019). Blood-Flow Restriction Resistance Exercise for Older Adults with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Pilot Randomized Clinical Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(2), 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8020265





