How Effective Is Pulse Arrival Time for Evaluating Blood Pressure? Challenges and Recommendations from a Study Using the MIMIC Database
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Data Collection
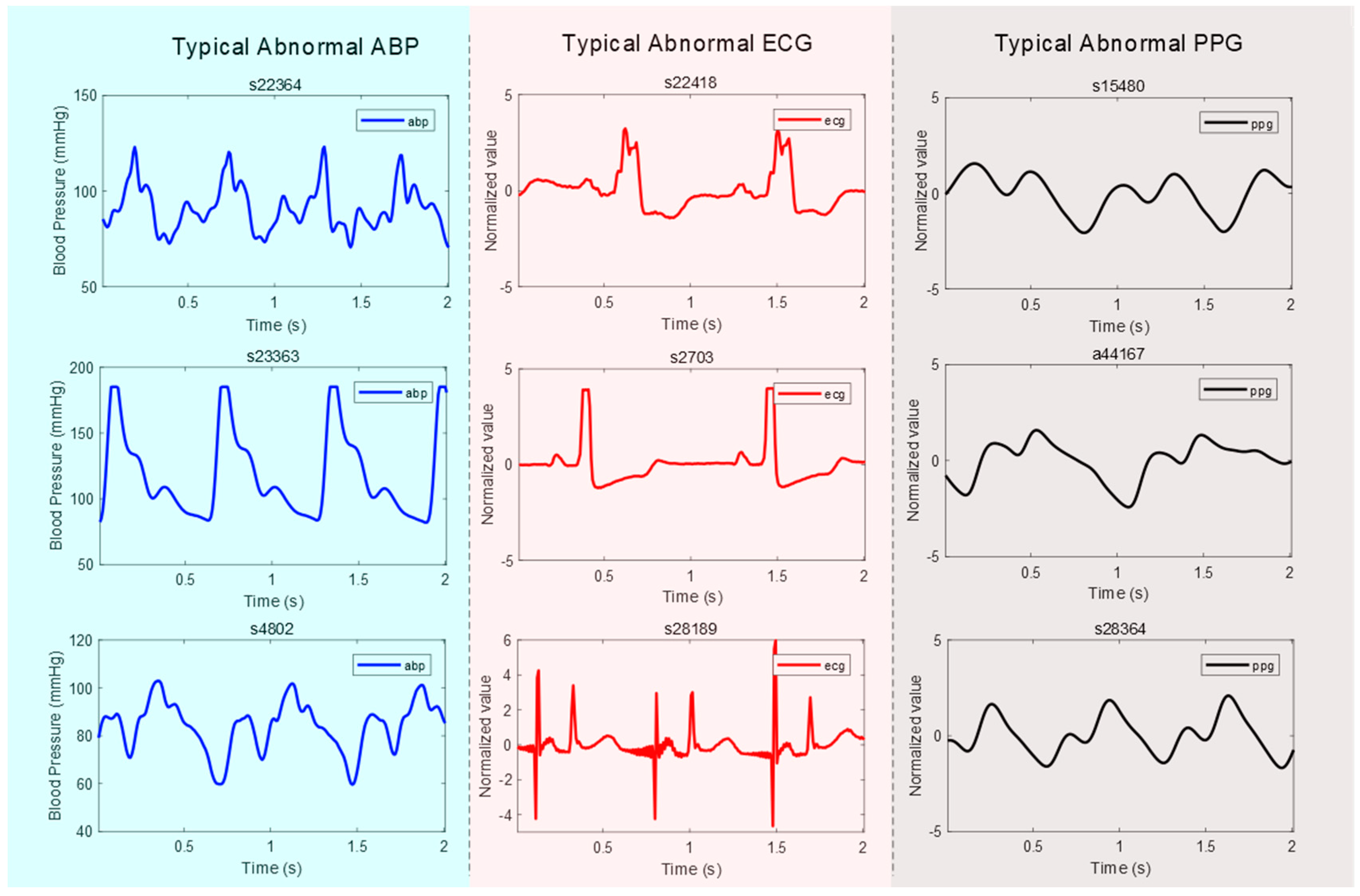
- Abnormal ABP signal: An “abnormal” ABP signal refers to an ABP signal where the systolic and diastolic waves cannot be distinguished, or their morphologies are highly distorted, as shown in Figure 1;
- Abnormal ECG signal: An “abnormal” ECG signal refers to an ECG signal where the morphology of the QRS waves is highly distorted, as shown in Figure 1;
- Abnormal PPG signal: An “abnormal” PPG signal refers to a PPG signal where the systolic and diastolic waves cannot be distinguished, their morphologies are highly distorted, and heart rate cannot be determined, as shown in Figure 1.
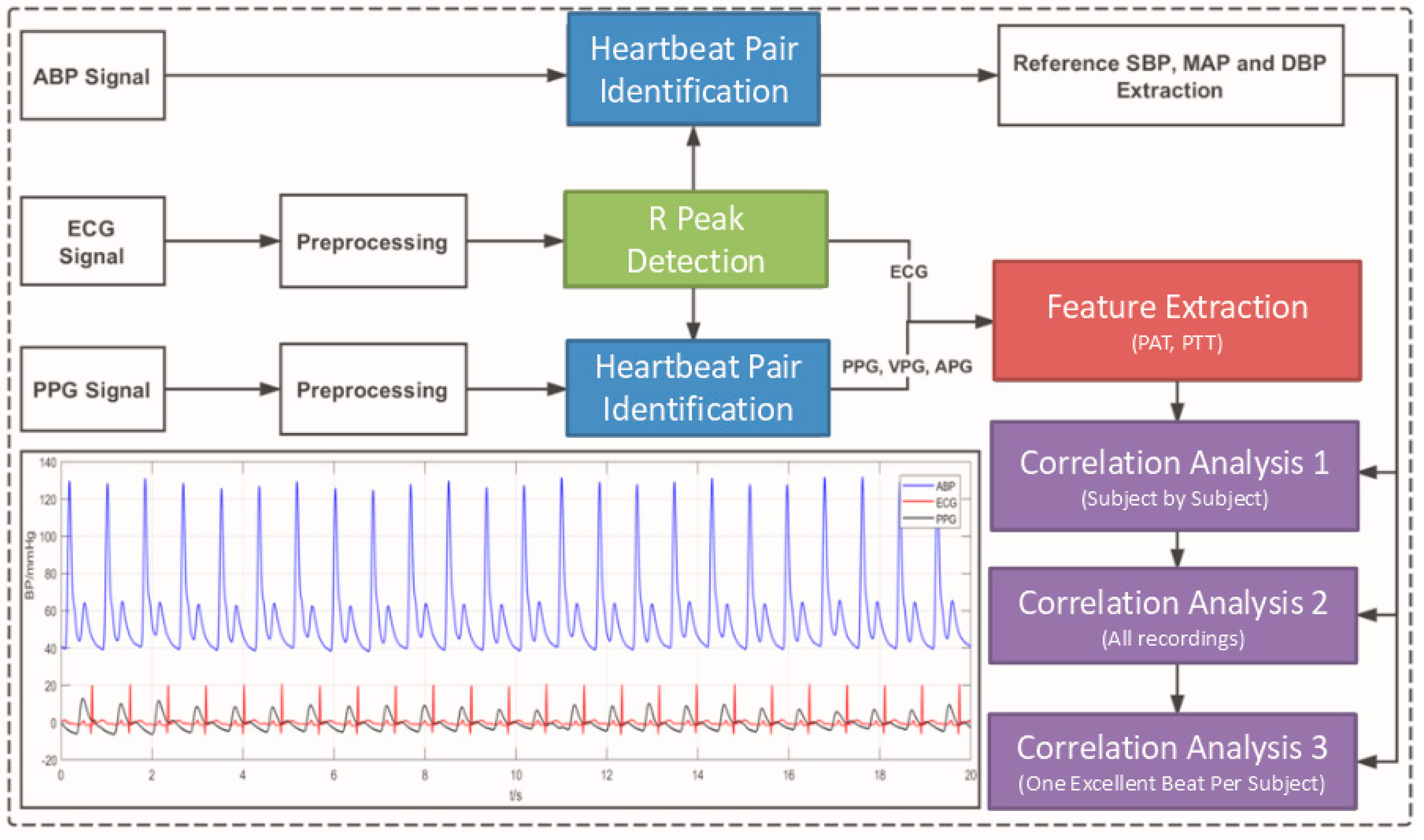
2.2. Signal Preprocessing and Feature Definition
2.3. Correlation
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mukkamala, R.; Hahn, J.O.; Inan, O.T.; Mestha, L.K.; Kim, C.S.; Töreyin, H.; Kyal, S. Toward Ubiquitous Blood Pressure Monitoring via Pulse Transit Time: Theory and Practice. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 1879–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcante, J.L.; Lima, J.A.; Redheuil, A.; Al-Mallah, M.H. Aortic stiffness: Current understanding and future directions. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 1511–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.L.O.; Carek, A.M.; Kim, C.S.; Ashouri, H.; Inan, O.T.; Hahn, J.O.; Mukkamala, R. Weighing Scale-Based Pulse Transit Time is a Superior Marker of Blood Pressure than Conventional Pulse Arrival Time. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foo, J.Y.; Wilson, S.J.; Wang, P. Factors that affect pulse wave time transmission in the monitoring of cardiovascular system. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2008, 22, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.E.; Pollard, T.J.; Shen, L.; Li-wei, H.L.; Feng, M.; Ghassemi, M.; Moody, B.; Szolovits, P.; Celi, L.A.; Mark, R.G. MIMIC-III, a freely accessible critical care database. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forouzanfar, M.; Ahmad, S.; Batkin, I.; Dajani, H.R.; Groza, V.Z.; Bolic, M. Coefficient-free blood pressure estimation based on pulse transit time–cuff pressure dependence. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 60, 1814–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Jia, W.; Mao, Z.-H.; Sclabassi, R.J.; Sun, M. Cuff-Free Blood Pressure Estimation Using Pulse Transit Time and Heart Rate. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Signal Processing, Hangzhou, China, 19–23 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Fang, Z.; Xue, Y.; Zhan, Q.; Yang, T.; Xia, S. Cuff-less blood pressure measurement using pulse arrival time and a Kalman filter. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2017, 27, 024002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflugradt, M.; Geissdoerfer, K.; Goernig, M.; Orglmeister, R. A fast multimodal ectopic beat detection method applied for blood pressure estimation based on pulse wave velocity measurements in wearable sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, C.; Ye, X. Study of continuous blood pressure estimation based on pulse transit time, heart rate and photoplethysmography-derived hemodynamic covariates. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2018, 41, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ward, R.; Elgendi, M. Hypertension Assessment via ECG and PPG Signals: An Evaluation Using MIMIC Database. Diagnostics 2018, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifford, G.D.; Scott, D.J.; Villarroel, M. User Guide and Documentation for the MIMIC II Database; MIMIC-II Database Version; Physionet.org: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberger, A.L.; Amaral, L.A.; Glass, L.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Ivanov, P.C.; Mark, R.G.; Mietus, J.E.; Moody, G.B.; Peng, C.-K.; Stanley, H.E. PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: Components of a New Research Resource for Complex Physiologic Signals. Circulation 2000, 101, e215–e220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgendi, M. Optimal Signal Quality Index for Photoplethysmogram Signals. Bioengineering 2016, 3, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Sohn, J.; Park, J.; Yang, S.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.C. Novel blood pressure and pulse pressure estimation based on pulse transit time and stroke volume approximation. Biomed. Eng. Online 2018, 17, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgendi, M. On the Analysis of Fingertip Photoplethysmogram Signals. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2012, 8, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgendi, M.; Liang, Y.; Ward, R. Toward Generating More Diagnostic Features from Photoplethysmogram Waveforms. Diseases 2018, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgendi, M. Standard Terminologies for Photoplethysmogram Signals. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2012, 8, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ko, S. Noninvasive cuffless blood pressure estimation using pulse transit time and Hilbert-Huang transform. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2013, 39, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattivelli, F.S.; Garudadri, H. Noninvasive Cuffless Estimation of Blood Pressure from Pulse Arrival Time and Heart Rate with Adaptive Calibration. In Proceedings of the 2009 Sixth International Workshop on Wearable and Implantable Body Sensor Networks, Berkeley, CA, USA, 3–5 June 2009; pp. 114–119. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Liu, M.; Zhang, X.; Hu, X.; Pang, B.; Yao, Z.; Chen, H. Novel wavelet neural network algorithm for continuous and noninvasive dynamic estimation of blood pressure from photoplethysmography. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2016, 59, 042405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iokibe, T. Chaos and Complexity. Nihon Chinou Joho Fuzzy J. 2003, 15, 606. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Elgendi, M.; Chen, Z.; Ward, R. An optimal filter for short photoplethysmogram signals. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgendi, M.; Mohamed, A.; Ward, R. Efficient ECG Compression and QRS Detection for E-Health Applications. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgendi, M.; Norton, I.; Brearley, M.; Abbott, D.; Schuurmans, D. Systolic peak detection in acceleration photoplethysmograms measured from emergency responders in tropical conditions. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgendi, M. Detection of c, d, and e waves in the acceleration photoplethysmogram. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2014, 117, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgendi, M.; Norton, I.; Brearley, M.; Abbott, D.; Schuurmans, D. Detection of a and b waves in the acceleration photoplethysmogram. Biomed. Eng. Online 2014, 13, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ward, R.; Elgendi, M. Photoplethysmography and Deep Learning: Enhancing Hypertension Risk Stratification. Biosensors 2018, 8, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, G.; Elgendi, M. A new, short-recorded photoplethysmogram dataset for blood pressure monitoring in China. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.E.W.; Pollard, T.J.; Shen, L.; Lehman, L.; Feng, M.; Ghassemi, M.; Moody, B.; Szolovits, P.; Celi, L.A.; Mark, R.G. Scientific Data; Nature Research: London, UK, 2016; Available online: http://www.nature.com/articles/sdata201635 (accessed on 12 January 2018). [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ward, R.; Elgendi, M. Hypertension Assessment Using Photoplethysmography: A Risk Stratification Approach. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeberg, T.M.; Orr, J.G.; Opsahl, H.; Austad, H.O.; Røed, M.H.; Dalgard, S.H.; Houghton, D.; Jones, D.E.J.; Strisland, F. A novel method for continuous, non-invasive, cuff-less measurement of blood pressure: Evaluation in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 64, 1469–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Song, J. Characters available in photoplethysmogram for blood pressure estimation: Beyond the pulse transit time. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2014, 37, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Tavassolian, N. Pulse Transit Time Measurement Using Seismocardiogram, Photoplethysmogram, and Acoustic Recordings: Evaluation and Comparison. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2018, 22, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kachuee, M.; Kiani, M.M.; Mohammadzade, H.; Shabany, M. Cuffless Blood Pressure Estimation Algorithms for Continuous Health-Care Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 64, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, Y.Z.; Kang, J.M.; Kwon, Y.; Park, S.; Noh, S.; Kim, Y.; Park, J.; Hwang, S.W. Cuff-less Blood Pressure Estimation using Pulse Waveform Analysis and Pulse Arrival Time. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2018, 22, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Goubran, R.A.; Liu, X.P. Secondary Peak Detection of PPG Signal for Continuous Cuffless Arterial Blood Pressure Measurement. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2014, 63, 1431–1439. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, G.; Howard, N.; Abbott, D.; Lim, K.; Ward, R.; Elgendi, M. Can Photoplethysmography Replace Arterial Blood Pressure in the Assessment of Blood Pressure? J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Type | Record Description |
|---|---|
| Missing signal (Excluded records) | Without ABP waveform (no abp signal or just a straight line in whole record, 284 records): a44002, a44005, a44007, a44011, a44026, a44027, a44032, a44044, a44053, a44059, a44060, a44061, a44073, a44080, a44083, a44084, a44094, a44096, a44101, a44107, a44109, a44110, a44116, a44127, a44129, a44132, a44134, a44136, a44141, a44145, a44159, a44170, a44178, a44180, a44182, a44188, a44192, a44197, a44200, a44204, a44209, a44213, a44220, a44222, a44226, a44241, a44256, a44291, a44294, a44304, a44306, a44307, a44314, a44322, a44337, a44358, a44382, a44383, a44391, a44402, a44405, a44406, a44428, a44459, a44463, a44466, a44491, a44507, a44512, a44518, a44537, a44539, a44559, a44561, a44570, a44571, a44578, a44582, a44602, a44610, a44611, a44612, a44617, a44625, a44639, a44648, a44651, a44659, a44674, a44710, a44712, a44718, a44727, a44740, a44745, a44755, a44757, a44762, a44772, a44791, a44807, a44813, a44830, a44838, a44863, a44868, a44895, a44907, a44911, a44921, a44941, a44946, a44947, a44979, a45014, a45050, a45062, a45065, a45071, a45072, a45077, a45091, a45095, a45097, a45105, a45121, a45133, a45158, a45161, a45177, a45184, a45228, a45229, a45260, a45262, a45264, a45265, a45275, a45276, a45298, a45301, a45303, a45346, a45355, a45369, a45375, a45379, a45427, a45464, a45515, a45516, a45524, a45532, a45538, a45541, a45546, a45554, a45562, a45582, a45583, a45601, a45617, a45619, a45629, a45639, a45663, a45665, a45676, a46002, a46008, a46009, a46013, a46017, a46074, a46104, a46147, a46154, a46165, a46200, a46208, a46236, a46280, a46292, a46302, a46313, a46329, a46339, a46365, a46383, a46387, a46391, a46430, a46433, n10036, n10309, s00618, s00631, s01049, s01158, s01621, s01791, s01978, s02586, s02906, s02981, s03345, s03386, s03695, s03920, s04641, s04833, s04904, s04906, s05030, s05345, s05742, s06116, s06381, s08061, s08122, s08396, s08915, s09473, s09798, s09870, s09920, s09993, s10152, s10475, s10667, s10799, s11004, s11342, s11388, s12508, s12589, s12632, s13599, s14058, s14325, s14579, s14714, s14936, s15298, s15852, s16112, s16139, s16391, s17112, s17394, s17497, s17875, s18082, s18123, s18225, s18393, s18727, s18975, s19093, s19726, s19827, s20612, s23038, s23762, s23824, s25954, s26039, s26211, s26330, s26712, s27060, s27194, s27212, s27338, s27551, s27638, s27689, s28083, s28611, s28808, s28863, s28927, s29057, s29093. Without ECG waveform (no ecg signal or just a straight line in whole record, 9 records): a44243, a44264, a44558, a44903, a45005, a45046, a45468, a46377, n10139. Without PPG waveform (no ppg signal or just a straight line in whole record, 22 records): a44087, a44162, a44166, a44190, a44238, a44385, a44469, a44588, a44716, a45159, a46269, s00652, s04324, s06158, s06539, s07445, s09058, s10842, s14266, s20196, s23238, s28625. |
| Abnormal signal (Excluded records) | Abnormal ABP waveform (114 records): a44046, a44227, a44331, a44486, a44591, a44599, a44694, a44859, a44891, a44900, a45013, a45357, a45401, a45461, a45467, a45493, a45519, a45535, a46108, a46133, a46192, a46379, a46423, s01840, s01855, s01949, s06946, s07251, s07614, s07654, s08142, s10049, s12351, s14533, s14947, s15545, s21247, s22585, s24942, s25411, s26709, s26978, s27084, s27193, s27232, s27890, s28075, s28702, s28897, s29199 s1004, s2063, s2614, s2858, s3617, s3744, s4331, s4802, s6875, s9258, s10629, s11431, s12878, s15488, s17421, s17582, s18274, s21002, s21202, s22364, s22462, s23363, s23876, s25284, s25724, s27192, s27425, s27585, s27687, s27696, s28044, s28048, s28364, s28774, s29215, a44033, a44047, a44089, a44106, a44113, a44117, a44139, a44164, a44215, a44318, a44332, a44348, a44349, a44368, a44378, a44442, a44452, a44505, a44585, a44644, a44992, a45045, a45222, a45495, a45511, a45648, a46098, a46176, a46289 Abnormal ECG waveform (21 records): s2703, s7415, s8281, s17795, s22418, s27542, s27636, s28079, s28189, s28354, s28507, s28698, s28707, s28762, s28901, s28905, a44082, a44398, a44474, a44715, a45060 abnormal PPG waveform (7 records): s15480, s27374, a44041, a44167, a44228, a44426, a44508 |
| Good quality signals (Included records) | s10464, s11187, s11727, s12174, s12531, s13600, s01501, s15218, s15716, s15902, s01606, s16129, s17848, s18642, s18970, s19578, s19700, s20726, s02104, s21730, s22335, s23201, s02458, s02513, s26897, s27241, s27337, s27434, s27436, s27446, s27648, s27833, s27845, s27887, s28077, s28187, s28499, s28510, s28758, s28775, s28813, s28882, s28910, s29102, s29120, s29127, s29167, s03039, a44088, a44104, a44118, a44165, a44171, a44173, a44201, a44223, a44233, a44347, a44409, a44422, a44432, a44458, 44496, a44526, a44572, a44590, a44598, a44601, a44615, a44616, a44623, a44626, a44629, a44640, a44647, a44671, a44704, a44758, a44763, a44810, a44839, a44902, a44981, a45049, a45098, a45140, a45181, a45186, a45212, a45227, a45311, a45343, a45353, a45384, a45426, a45456, a45487, a45533, a45550, a45572, a45627, a45636, a45641, a45645, a46122, a46138, a46216, a46230, a46297, a46303, a46416, a46424, s04679, s06581, s06692, s07614, s00801, s08141, s08318, s09124, s00946 |
| Name | Start Point | End Point | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| SBP | - | - | Systolic blood pressure |
| MAP | - | - | Mean arterial pressure |
| DBP | - | - | Diastolic blood pressure |
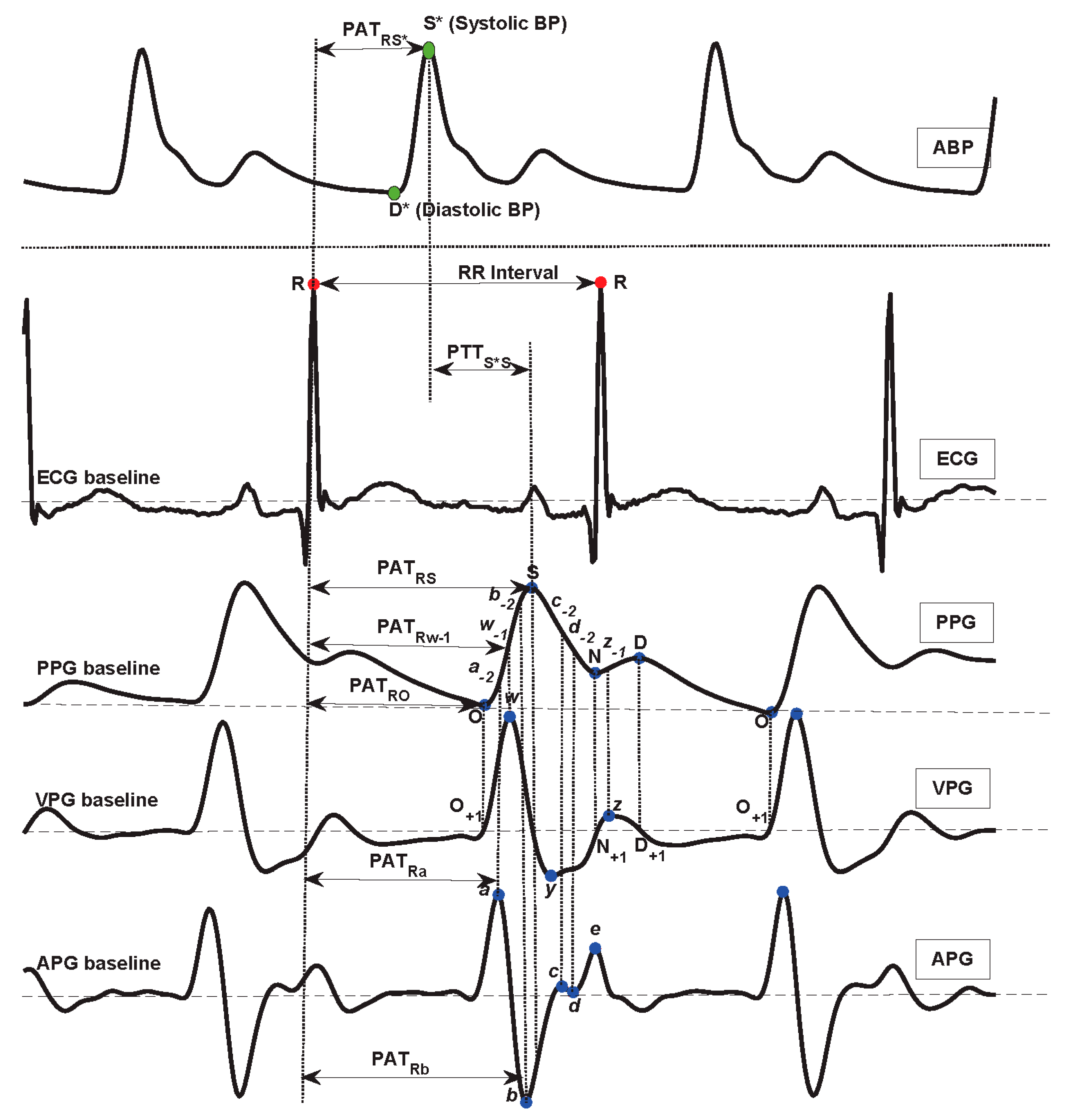
| PATRO | ECG R | PPG O | Pulse transit time from R wave to O wave |
| PATRa | ECG R | APG a | Pulse transit time from R wave to a wave |
| PATRw-1 | ECG R | PPG w-1 | Pulse transit time from R wave to w-1 wave |
| PATRb | ECG R | APG b | Pulse transit time from R wave to b wave |
| PATRS | ECG R | PPG S | Pulse transit time from R wave to S wave |
| PATRS* | ECG R | ABP S* | Pulse transit time from R wave to S* wave |
| PTTS*S | ABP S* | PPG S | Pulse transit time from S* wave to S wave |
| RRI | ECG R | ECG R | R-R interval |
| Index | Subject ID | # PATs | r (SBP, PATRO) | r (SBP, PATRa) | r (SBP, PATRw-1) | r (SBP, PATRb) | r (SBP, PATRS) | r (SBP, PATRS*) | r (SBP, PTTS*S) | r (SBP, RRI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 801 | 149 | 0.01 | −0.02 | −0.05 | −0.05 | −0.18 | −0.37 | −0.10 | −0.36 |
| 2 | 946 | 77 | −0.39 | −0.57 | −0.42 | −0.12 | −0.14 | −0.46 | 0.16 | 0.04 |
| 3 | 1501 | 120 | −0.35 | −0.31 | −0.46 | −0.25 | 0.13 | −0.72 | 0.36 | −0.03 |
| 4 | 1606 | 55 | −0.22 | −0.45 | −0.37 | −0.38 | −0.16 | −0.36 | 0.03 | −0.05 |
| 5 | 2104 | 95 | 0.03 | −0.07 | −0.09 | −0.18 | −0.11 | −0.28 | 0.04 | 0.05 |
| 6 | 2458 | 84 | −0.04 | −0.25 | −0.07 | 0.00 | 0.37 | 0.08 | 0.30 | 0.50 |
| 7 | 2513 | 79 | −0.20 | −0.57 | −0.52 | −0.52 | −0.54 | −0.70 | −0.21 | −0.14 |
| 8 | 3039 | 53 | −0.45 | −0.55 | −0.50 | −0.43 | −0.37 | −0.75 | 0.40 | −0.13 |
| 9 | 4679 | 140 | −0.43 | −0.53 | −0.62 | −0.46 | −0.63 | −0.66 | −0.45 | −0.54 |
| 10 | 6581 | 52 | 0.03 | −0.10 | −0.15 | −0.10 | −0.09 | 0.08 | −0.11 | 0.64 |
| 11 | 6692 | 154 | −0.75 | −0.73 | −0.74 | −0.68 | −0.68 | −0.53 | −0.53 | 0.16 |
| 12 | 7614 | 62 | −0.02 | −0.24 | 0.02 | −0.07 | 0.10 | −0.33 | 0.29 | −0.01 |
| … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
| … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
| 110 | 45627 | 77 | −0.27 | −0.05 | 0.00 | −0.09 | 0.30 | 0.36 | 0.19 | −0.10 |
| 111 | 45636 | 53 | −0.35 | −0.41 | −0.29 | −0.29 | −0.29 | −0.09 | −0.28 | −0.09 |
| 112 | 45641 | 117 | −0.45 | −0.40 | −0.43 | −0.22 | −0.44 | −0.21 | −0.32 | −0.02 |
| 113 | 45645 | 118 | −0.27 | −0.36 | −0.43 | −0.51 | −0.49 | 0.08 | −0.63 | −0.06 |
| 114 | 46122 | 94 | 0.01 | −0.62 | −0.60 | −0.44 | −0.27 | −0.42 | −0.11 | 0.50 |
| 115 | 46138 | 119 | −0.30 | −0.44 | −0.48 | −0.52 | 0.31 | −0.07 | 0.41 | 0.13 |
| 116 | 46216 | 35 | 0.02 | 0.28 | 0.31 | 0.28 | 0.32 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 0.28 |
| 117 | 46230 | 73 | −0.60 | −0.72 | −0.76 | −0.78 | −0.75 | −0.92 | 0.27 | 0.35 |
| 118 | 46297 | 170 | −0.50 | −0.47 | −0.43 | −0.44 | −0.40 | −0.85 | 0.05 | −0.17 |
| 119 | 46303 | 83 | −0.37 | −0.34 | −0.30 | −0.33 | 0.05 | −0.27 | 0.17 | −0.08 |
| 120 | 46416 | 88 | −0.44 | −0.27 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.05 | −0.40 | 0.15 | 0.53 |
| 121 | 46424 | 122 | −0.16 | −0.16 | −0.30 | −0.19 | −0.21 | −0.54 | 0.15 | −0.04 |
| Mean ± STD | 110 ± 45 | −0.20 ± 0.25 | −0.30 ± 0.25 | −0.30 ± 0.27 | −0.26 ± 0.25 | −0.12 ± 0.31 | −0.30 ± 0.36 | 0.04 ± 0.27 | −0.03 ± 0.31 |
| Strength of Correlation | Range of Absolute Correlation Coefficient (r) | Count of Subjects |
|---|---|---|
| Very strong | 0.8–1.0 | 11 |
| Strong | 0.6–0.79 | 17 |
| Moderate | 0.4–0.59 | 27 |
| Weak | 0.2–0.39 | 33 |
| Very weak | 0–0.19 | 33 |
| Trial | BP | # PATs | r (SBP, PATRO) | r (SBP, PATRa) | r (SBP, PATRw-1) | r (SBP, PATRb) | r (SBP, PATRS) | r (SBP, PATRS*) | r (SBP, PTTS*S) | r (SBP, RRI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collective beats all subjects | SBP | 13311 | −0.41 | −0.47 | −0.49 | −0.50 | −0.43 | −0.41 | −0.22 | −0.08 |
| MAP | 13311 | −0.30 | −0.38 | −0.40 | −0.42 | −0.35 | −0.29 | −0.23 | −0.02 | |
| DBP | 13311 | −0.20 | −0.27 | −0.29 | −0.31 | −0.26 | −0.17 | −0.20 | 0.03 | |
| One excellent beat per subject | SBP | 121 | −0.50 | −0.51 | −0.52 | −0.54 | −0.46 | −0.39 | −0.28 | 0.01 |
| MAP | 121 | −0.37 | −0.38 | −0.41 | −0.42 | −0.37 | −0.28 | −0.26 | 0.01 | |
| DBP | 121 | −0.23 | −0.23 | −0.27 | −0.28 | −0.25 | −0.16 | −0.20 | 0.01 |
| Author (s) | Number of Subjects | Analysis | Relationship | Pearson Correlation Coefficient (r) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| This study, 2019 | 121 | Collective | (SBP, PATRb) (MAP, PATRb) (DBP, PATRb) | −0.54 −0.42 −0.28 |
| Kachuee et al. [35], 2017 | 942 | Collective | (BP, PAT) | N/R |
| Yoon et al. [36], 2017 | 23 | Subject by subject | (SBP, PATRw-1) (MAP, PATRw-1) (DBP, PATRw-1) | −0.53 ± 0.32 −0.49 ± 0.34 −0.40 ± 0.35 |
| He et al. [37], 2014 | 100 | Collective | (SBP, PATRO) (MAP, PATRO) (DBP, PATRO) | −0.7 N/R N/R |
| Choi et al. [19], 2013 | 25 | Collective | (SBP, PATRS) (DBP, PATRS) | −0.71 −0.69 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, Y.; Abbott, D.; Howard, N.; Lim, K.; Ward, R.; Elgendi, M. How Effective Is Pulse Arrival Time for Evaluating Blood Pressure? Challenges and Recommendations from a Study Using the MIMIC Database. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8030337
Liang Y, Abbott D, Howard N, Lim K, Ward R, Elgendi M. How Effective Is Pulse Arrival Time for Evaluating Blood Pressure? Challenges and Recommendations from a Study Using the MIMIC Database. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(3):337. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8030337
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Yongbo, Derek Abbott, Newton Howard, Kenneth Lim, Rabab Ward, and Mohamed Elgendi. 2019. "How Effective Is Pulse Arrival Time for Evaluating Blood Pressure? Challenges and Recommendations from a Study Using the MIMIC Database" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 3: 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8030337
APA StyleLiang, Y., Abbott, D., Howard, N., Lim, K., Ward, R., & Elgendi, M. (2019). How Effective Is Pulse Arrival Time for Evaluating Blood Pressure? Challenges and Recommendations from a Study Using the MIMIC Database. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(3), 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8030337







