Predictors of Response to a Medial Branch Block: MRI Analysis of the Lumbar Spine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Interventions
2.3. Outcome Measures and Follow-Up
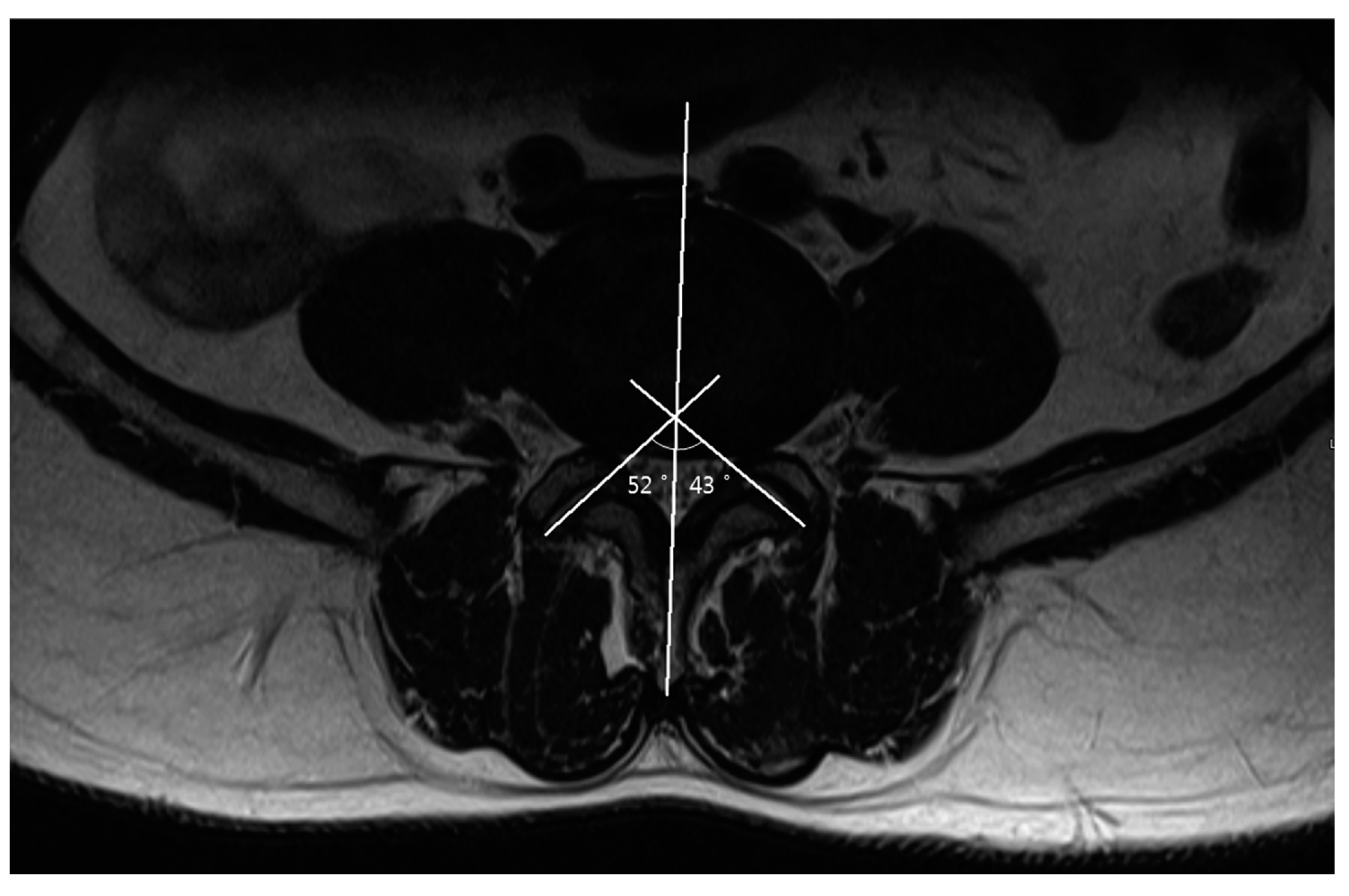
2.4. Measurements
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eubanks, J.D.; Lee, M.J.; Cassinelli, E.; Ahn, N.U. Prevalence of lumbar facet arthrosis and its relationship to age, sex, and race: An anatomic study of cadaveric specimens. Spine 2007, 32, 2058–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balagué, F.; Mannion, A.F.; Pellisé, F.; Cedraschi, C. Non-specific low back pain. Lancet 2012, 379, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, E.J.; Moon, J.Y.; Park, K.S.; Yoo da, H.; Kim, Y.C.; Sim, W.S.; Lee, C.J.; Shin, H.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.D.; et al. Epidural steroid injection in korean pain physicians: A national survey. Korean J. Pain 2014, 27, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, G.B. Epidemiological features of chronic low-back pain. Lancet 1999, 354, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldthwait, J.E. The lumbo-sacral articulation; An explanation of many cases of “lumbago,” “sciatica” and paraplegia. Boston Med. Surg. J. 1911, 164, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kleef, M.; Barendse, G.A.; Kessels, A.; Voets, H.M.; Weber, W.E.; de Lange, S. Randomized trial of radiofrequency lumbar facet denervation for chronic low back pain. Spine 1999, 24, 1937–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.P.; Jacobs, R.R.; Montesano, P.X. 1988 Volvo award in clinical sciences. Facet joint injection in low-back pain. A prospective statistical study. Spine 1988, 13, 966–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.P.; Raja, S.N. Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of lumbar zygapophysial (facet) joint pain. Anesthesiology 2007, 106, 591–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beresford, Z.M.; Kendall, R.W.; Willick, S.E. Lumbar facet syndromes. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2010, 9, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grogan, J.; Nowicki, B.H.; Schmidt, T.A.; Haughton, V.M. Lumbar facet joint tropism does not accelerate degeneration of the facet joints. Ajnr. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1997, 18, 1325–1329. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Berlemann, U.; Jeszenszky, D.J.; Buhler, D.W.; Harms, J. Facet joint remodeling in degenerative spondylolisthesis: An investigation of joint orientation and tropism. Eur. Spine J. 1998, 7, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasan, A.D.; Jamison, R.N.; Pham, L.; Tipirneni, N.; Nedeljkovic, S.S.; Katz, J.N. Psychopathology predicts the outcome of medial branch blocks with corticosteroid for chronic axial low back or cervical pain: A prospective cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2009, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jentzsch, T.; Geiger, J.; Zimmermann, S.M.; Slankamenac, K.; Nguyen-Kim, T.D.; Werner, C.M. Lumbar facet joint arthritis is associated with more coronal orientation of the facet joints at the upper lumbar spine. Radiol. Res. Pract. 2013, 2013, 693971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, W.E., 3rd; Ahmad, M. Pain relief with intraarticular or medial branch nerve blocks in patients with positive lumbar facet joint SPECT imaging: A 12-week outcome study. South. Med. J. 2008, 101, 931–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derby, R.; Melnik, I.; Lee, J.E.; Lee, S.H. Correlation of lumbar medial branch neurotomy results with diagnostic medial branch block cutoff values to optimize therapeutic outcome. Pain Med. 2012, 13, 1533–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, S.; Aprill, C.; Laslett, M. Correlation of clinical examination characteristics with three sources of chronic low back pain. Spine J. 2003, 3, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laslett, M.; McDonald, B.; Aprill, C.N.; Tropp, H.; Oberg, B. Clinical predictors of screening lumbar zygapophyseal joint blocks: Development of clinical prediction rules. Spin J. 2006, 6, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorbach, C.; Schmid, M.R.; Elfering, A.; Hodler, J.; Boos, N. Therapeutic efficacy of facet joint blocks. Ajr Am. J. Roentgenol. 2006, 186, 1228–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spine, A.; Middleton, W.; is Chief, H.; Datta, S.; Healthcare, T.V. Systematic assessment of diagnostic accuracy and therapeutic utility of lumbar facet joint interventions. Pain Physician 2009, 12, 437–460. [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss, P.H.; Dreyer, S.J.; Herring, S.A. Lumbar zygapophysial (facet) joint injections. Spine 1995, 20, 2040–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovic, M.P.; Sethee, J.; Mohiuddin, M.; Cheng, J.; Barker, A.; Wang, J.; Palmer, W.; Huang, A.; Cohen, S.P. MRI analysis of the lumbar spine: Can it predict response to diagnostic and therapeutic facet procedures? Clin. J. Pain 2010, 26, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahezi, S.E.; Alexeev, E.; Georgy, J.S.; Haramati, N.; Erosa, S.A.; Shah, J.M.; Downie, S. Lumbar Medial Branch Block Volume-Dependent Dispersion Patterns as a Predictor for Ablation Success: A Cadaveric Study. PM R 2018, 10, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derby, R.; Melnik, I.; Choi, J.; Lee, J.E. Indications for repeat diagnostic medial branch nerve blocks following a failed first medial branch nerve block. Pain Physician 2013, 16, 479–488. [Google Scholar]
- Bogduk, N. Evidence-informed management of chronic low back pain with facet injections and radiofrequency neurotomy. Spin J. 2008, 8, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dworkin, R.H.; Turk, D.C.; Farrar, J.T.; Haythornthwaite, J.A.; Jensen, M.P.; Katz, N.P.; Kerns, R.D.; Stucki, G.; Allen, R.R.; Bellamy, N.; et al. Core outcome measures for chronic pain clinical trials: IMMPACT recommendations. Pain 2005, 113, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farrar, J.T.; Young, J.P., Jr.; LaMoreaux, L.; Werth, J.L.; Poole, R.M. Clinical importance of changes in chronic pain intensity measured on an 11-point numerical pain rating scale. Pain 2001, 94, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadha, M.; Sharma, G.; Arora, S.S.; Kochar, V. Association of facet tropism with lumbar disc herniation. Eur. Spine J. 2013, 22, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Duan, Y.; Rong, X.; Wang, B.; Chen, H.; Liu, H. Variation of facet joint orientation and tropism in lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis and disc herniation at L4-L5: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2017, 161, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weishaupt, D.; Zanetti, M.; Boos, N.; Hodler, J. MR imaging and CT in osteoarthritis of the lumbar facet joints. Skelet. Radiol. 1999, 28, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyerding, H.W. Spondylolisthesis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1931, 13, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Hoy, D.; March, L.; Brooks, P.; Blyth, F.; Woolf, A.; Bain, C.; Williams, G.; Smith, E.; Vos, T.; Barendregt, J.; et al. The global burden of low back pain: Estimates from the Global Burden of Disease 2010 study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, J.S.; Khalsa, P.S. Human lumbar spine creep during cyclic and static flexion: Creep rate, biomechanics, and facet joint capsule strain. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 33, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzer, A.C.; Wang, S.C.; Bogduk, N.; McNaught, P.J.; Laurent, R. Prevalence and clinical features of lumbar zygapophysial joint pain: A study in an Australian population with chronic low back pain. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1995, 54, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, M.H.; He, W.; Tsai, Y.D.; Chen, N.F.; Keorochana, G.; Do, D.H.; Wang, J.C. Relationship of facet tropism with degeneration and stability of functional spinal unit. Yonsei Med. J. 2009, 50, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karavelioglu, E.; Kacar, E.; Gonul, Y.; Eroglu, M.; Boyaci, M.G.; Eroglu, S.; Unlu, E.; Ulasli, A.M. Ligamentum flavum thickening at lumbar spine is associated with facet joint degeneration: An MRI study. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2016, 29, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoddy, M.C.; Sielatycki, J.A.; Sivaganesan, A.; Engstrom, S.M.; McGirt, M.J.; Devin, C.J. Can facet joint fluid on MRI and dynamic instability be a predictor of improvement in back pain following lumbar fusion for degenerative spondylolisthesis? Eur. Spine J. 2016, 25, 2408–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, W.U.; Kim, S.H.; Hwang, B.Y.; Choi, W.J.; Song, J.G.; Suh, J.H.; Leem, J.G.; Shin, J.W. Value of Bone Scintigraphy and Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) in Lumbar Facet Disease and Prediction of Short-term Outcome of Ultrasound Guided Medial Branch Block with Bone SPECT. Korean J. Pain 2011, 24, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horwitz, T.; Smith, R.M. An anatomical, pathological and roentgenological study of the intervertebral joints of the lumbar spine and of the sacroiliac joints. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1940, 43, 86. [Google Scholar]
- Masharawi, Y.; Rothschild, B.; Dar, G.; Peleg, S.; Robinson, D.; Been, E.; Hershkovitz, I. Facet orientation in the thoracolumbar spine: Three-dimensional anatomic and biomechanical analysis. Spine 2004, 29, 1755–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linov, L.; Klindukhov, A.; Li, L.; Kalichman, L. Lumbar facet joint orientation and osteoarthritis: A cross-sectional study. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2013, 26, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.Y. Orientation and tropism of lumbar facet joints in degenerative spondylolisthesis. Int. Orthop. 2001, 25, 40–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, W.M.; Kim, K.; Kim, Y.H. Effects of degenerated intervertebral discs on intersegmental rotations, intradiscal pressures, and facet joint forces of the whole lumbar spine. Comput. Biol. Med. 2013, 43, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainka, T.; Lemburg, S.P.; Heyer, C.M.; Altenscheidt, J.; Nicolas, V.; Maier, C. Association between clinical signs assessed by manual segmental examination and findings of the lumbar facet joints on magnetic resonance scans in subjects with and without current low back pain: A prospective, single-blind study. Pain 2013, 154, 1886–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchikanti, L.; Singh, V.; Falco, F.J.; Cash, K.A.; Pampati, V. Evaluation of lumbar facet joint nerve blocks in managing chronic low back pain: A randomized, double-blind, controlled trial with a 2-year follow-up. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2010, 7, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dworkin, R.H.; Turk, D.C.; Wyrwich, K.W.; Beaton, D.; Cleeland, C.S.; Farrar, J.T.; Haythornthwaite, J.A.; Jensen, M.P.; Kerns, R.D.; Ader, D.N.; et al. Interpreting the clinical importance of treatment outcomes in chronic pain clinical trials: IMMPACT recommendations. J. Pain 2008, 9, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganau, M.; Ennas, F.; Bellisano, G.; Ganau, L.; Ambu, R.; Faa, G.; Maleci, A. Synovial cysts of the lumbar spine--pathological considerations and surgical strategy. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2013, 53, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganau, M.; Ennas, F.; Ambu, R.; Faa, G.; Maleci, A. Excision of synovial cysts: Pathology matters. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2013, 19, 266–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senteler, M.; Weisse, B.; Rothenfluh, D.A.; Farshad, M.T.; Snedeker, J.G. Fusion angle affects intervertebral adjacent spinal segment joint forces-Model-based analysis of patient specific alignment. J. Orthop. Res. 2017, 35, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Negative Response to MBB (n = 66) | Positive Response to MBB (n = 99) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) (median, IQR) | 63.0 (53.0–72.0) | 64.0 (57.0–71.0) | 0.454 |
| Gender (male/female) (number, %) | 17/49 (25.8/74.2%) | 34/65 (34.3/65.7%) | 0.303 |
| Weight (kg) (median, IQR) | 60.7 (53.4–68.8) | 61.3 (55.0–68.0) | 0.680 |
| Height (cm) (median, IQR) | 158.2 (152.4–165.0) | 157.0 (152.0–164.4) | 0.854 |
| BMI (kg/m2) (median, IQR) | 24.63 (18.38–30.27) | 25.10 (19.51–30.42) | 0.927 |
| MQS (points) (median, IQR) | 8.00 (4.80–9.60) | 8.00 (4.15 –9.00) | 0.216 |
| Pain intensity (NRS) (mean ± SD) | 6.37 ± 1.85 | 6.64 ± 1.69 | 0.366 |
| Negative Response to MBB (n = 66) | Positive Response to MBB (n = 99) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Facet angle (°) (mean ± SD) | |||
| L3–4 | 38.82 ± 10.74 | 37.07 ± 10.69 | 0.304 |
| L4–5 | 45.15 ± 9.81 | 45.08 ± 9.68 | 0.661 |
| L5–S1 | 47.88 ± 9.04 | 49.44 ± 11.97 | 0.345 |
| Facet angle difference (°) (mean ± SD) | |||
| L3–4 | 7.42 (2.09–14.70) | 6.02 (2.54–9.26) | 0.087 |
| L4–5 | 7.38 (3.00–12.76) | 6.54 (3.27–11.10) | 0.313 |
| L5–S1 | 9.20 (5.00–16.57) | 7.78 (4.33–11.18) | 0.102 |
| Facet degeneration grading (number, %) | |||
| L3–4 (Gr 0/1/2/3) | 15 (22.7%)/31 (47.0%)/12 (18.2%)/8 (12.1%) | 21 (21.2%)/51 (51.5%)/21 (21.2%)/6 (6.1%) | 0.551 |
| L4–5 (Gr 0/1/2/3) | 14 (21.2%)/25 (37.9%)/22 (33.3%)/5 (7.6%) | 14 (12.1%)/42 (42.4%)/39 (39.4%)/6 (6.1%) | 0.432 |
| L5–S1(Gr 0/1/2/3) | 15 (22.7%)/26 (39.4%)/18 (27.3%)/7 (10.6%) | 21 (21.4%)/41 (41.8%)/31 (31.6%)/5 (5.1%) | 0.578 |
| Facet fluid (mm) (median, IQR) | |||
| L3–4 | 1.11 (0.77–2.22) | 0.98 (0.80–1.44) | 0.443 |
| L4–5 | 1.13 (0.79–2.46) | 1.10 (0.65–1.77) | 0.353 |
| L5–S1 | 0.98 (0.65–2.10) | 0.98 (0.54–1.29) | 0.189 |
| Spondylolisthesis (number, %) | |||
| L3–4 | 9 (13.6%) | 14 (14.1%) | 0.927 |
| L4–5 | 14 (21.2%) | 15 (15.2%) | 0.405 |
| L5–S1 | 6 (9.1%) | 14 (14.2%) | 0.531 |
| Disc height (mm) | |||
| L3–4 | 7.85 (6.65–9.06) | 7.55 (6.09–8.90) | 0.198 |
| L4–5 | 8.21 (6.56–9.72) | 8.20 (6.62–9.87) | 0.713 |
| L5–S1 | 9.94 (7.51–11.26) | 8.73 (6.70–10.31) | 0.022 |
| Variables | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | Coefficient | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Facet angle difference (°) | ||||||||
| L3–4 | −0.06 | 0.94 | 0.90–0.99 | 0.020 | −0.05 | 0.95 | 0.90–0.10 | 0.038 |
| L5–S1 | −0.04 | 0.96 | 0.93–1.00 | 0.080 | ||||
| Disc height (mm) | ||||||||
| L3–4 | −0.12 | 0.89 | 0.75–1.05 | 0.164 | ||||
| L5–S1 | −0.15 | 0.86 | 0.75–0.98 | 0.022 | −0.15 | 0.86 | 0.75–0.99 | 0.038 |
| Facet fluid (mm) | ||||||||
| L5–S1 | −0.22 | 0.81 | 0.63–1.02 | 0.078 | −0.24 | 0.79 | 0.61–1.01 | 0.056 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.-Y.; Kim, D.-H.; Seo, D.-K.; Yoon, S.-H.; Lee, G.; Lee, S.; Park, C.-H.; Sim, S.E.; Suh, J.-H. Predictors of Response to a Medial Branch Block: MRI Analysis of the Lumbar Spine. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8040538
Park J-Y, Kim D-H, Seo D-K, Yoon S-H, Lee G, Lee S, Park C-H, Sim SE, Suh J-H. Predictors of Response to a Medial Branch Block: MRI Analysis of the Lumbar Spine. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(4):538. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8040538
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Jun-Young, Doo-Hwan Kim, Dong-Kyun Seo, Syn-Hae Yoon, Gunn Lee, Sukyung Lee, Chan-Hye Park, Sung Eun Sim, and Jeong-Hun Suh. 2019. "Predictors of Response to a Medial Branch Block: MRI Analysis of the Lumbar Spine" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 4: 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8040538
APA StylePark, J.-Y., Kim, D.-H., Seo, D.-K., Yoon, S.-H., Lee, G., Lee, S., Park, C.-H., Sim, S. E., & Suh, J.-H. (2019). Predictors of Response to a Medial Branch Block: MRI Analysis of the Lumbar Spine. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(4), 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8040538





