Preclinical Evidence of STAT3 Inhibitor Pacritinib Overcoming Temozolomide Resistance via Downregulating miR-21-Enriched Exosomes from M2 Glioblastoma-Associated Macrophages
Abstract
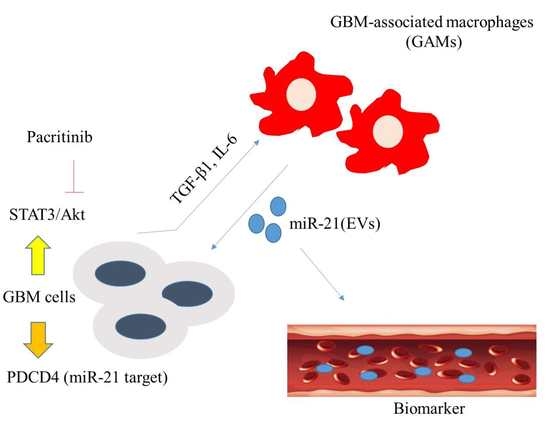
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Cell Culture
2.2. Transfection
2.3. Exosome Isolation
2.4. miRNA PCR Array Analysis
2.5. Real-Time PCR
2.6. SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
2.7. In Vivo Xenograft Model
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. M2 Polarization of GAMs Promotes GBM Tumorigenesis
3.2. Exosome Enriched with miR-21 from GAMs Promotes Tumorigenic Properties
3.3. MiR-21 Is Associated with GBM Tumorigenic Properties
3.4. STAT3 and PDCD4 are Targets of miR-21-5p
3.5. Pacritinib Suppresses GBM Tumorigenesis and M2 Polarization of GAMs
3.6. In Vivo Evaluation of Pacritinib
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| M2 GAMs | M2 polarization of glioblastoma associated macrophages |
| NC | negative controls |
| GBM | glioblastoma multiforme |
| TMZ | temozolomide |
| GSCs | glioma stem cells |
| lncRNAs | long noncoding RNAs |
| IRB | Institutional Review Board |
| TME | tumor microenvironment |
References
- Khosla, D. Concurrent therapy to enhance radiotherapeutic outcomes in glioblastoma. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Hambardzumyan, D.; Gutmann, D.H.; Kettenmann, H. The role of microglia and macrophages in glioma maintenance and progression. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, R.L.; A Joyce, J. Therapeutic targeting of tumor-associated macrophages and microglia in glioblastoma. Immunother. 2014, 6, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skog, J.; Würdinger, T.; Van Rijn, S.; Meijer, D.H.; Gainche, L.; Curry, W.T.; Carter, B.S.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Breakefield, X.O.; Sena-Esteves, M.; et al. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1470–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graner, M.W.; Cumming, R.I.; Bigner, D.D. The Heat Shock Response and Chaperones/Heat Shock Proteins in Brain Tumors: Surface Expression, Release, and Possible Immune Consequences. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 11214–11227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murgoci, A.-N.; Cízková, D.; Majerova, P.; Petrovová, E.; Medvecký, Ľ.; Fournier, I.; Salzet, M. Brain-Cortex Microglia-Derived Exosomes: Nanoparticles for Glioma Therapy. ChemPhysChem 2018, 19, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caccese, M.; Indraccolo, S.; Zagonel, V.; Lombardi, G.; Mario, C.; Giuseppe, L.; Stefano, I.; Vittorina, Z. PD-1/PD-L1 immune-checkpoint inhibitors in glioblastoma: A concise review. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2019, 135, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stechishin, O.D.; Luchman, H.A.; Ruan, Y.; Blough, M.D.; Nguyen, S.A.; Kelly, J.J.; Cairncross, J.G.; Weiss, S. On-target JAK2/STAT3 inhibition slows disease progression in orthotopic xenografts of human glioblastoma brain tumor stem cells. Neuro-Oncology 2013, 15, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.J.P.; Stechishin, O.; Chojnacki, A.; Lun, X.; Sun, B.; Senger, D.L.; Forsyth, P.; Auer, R.N.; Dunn, J.F.; Cairncross, J.G.; et al. Proliferation of Human Glioblastoma Stem Cells Occurs Independently of Exogenous Mitogens. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 1722–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortensi, B.; Osti, D.; Pellegatta, S.; Pisati, F.; Brescia, P.; Fornasari, L.; Levi, D.; Gaetani, P.; Colombo, P.; Ferri, A.; et al. Rai is a New Regulator of Neural Progenitor Migration and Glioblastoma Invasion. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 817–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliano; Costa, F.; Cossetti, C.; Pettinari, L.; Bassi, R.; Chiriva-Internati, M.; Cobos, E.; Gioia, M.; Pluchino, S. Glioma-astrocyte interaction modifies the astrocyte phenotype in a co-culture experimental model. Oncol. Rep. 2009, 22, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thery, C.; Amigorena, S.; Raposo, G.; Clayton, A. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2006, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beznoussenko, G.V.; Dolgikh, V.V.; Seliverstova, E.V.; Semenov, P.B.; Tokarev, Y.S.; Trucco, A.; Micaroni, M.; Di Giandomenico, D.; Auinger, P.; Senderskiy, I.V.; et al. Analogs of the Golgi complex in microsporidia: structure and avesicular mechanisms of function. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 1288–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahmood, T.; Yang, P.-C. Western Blot: Technique, Theory, and Trouble Shooting. North Am. J. Med Sci. 2012, 4, 429–434. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, B.L.; Pokorny, J.L.; Schroeder, M.A.; Sarkaria, J.N. Establishment, Maintenance and in vitro and in vivo Applications of Primary Human Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM) Xenograft Models for Translational Biology Studies and Drug Discovery. Curr. Protocols Pharmacol. 2011, 52, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Ganguly, D.; Fan, M.; Yang, C.H.; Zbytek, B.; Finkelstein, D.; Roussel, M.F.; Pfeffer, L.M. The critical role that STAT3 plays in glioma-initiating cells: STAT3 addiction in glioma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 22095–22112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, N.; Feng, L.; Qu, H.; Lu, K.; Li, P.; Lv, X.; Wang, X. Overexpression of IL-9 induced by STAT3 phosphorylation is mediated by miR-155 and miR-21 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Oncology reports 2018, 39, 3064–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, X.; Wu, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, K.; Lin, Y.; Wang, X. Exosomes Released from Tumor-Associated Macrophages Transfer miRNAs That Induce a Treg/Th17 Cell Imbalance in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018, 6, 1578–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harris, M.A.; Yang, H.; Low, B.E.; Mukherje, J.; Guha, A.; Bronson, R.T.; Shultz, L.D.; Israel, M.A.; Yun, K. Cancer stem cells are enriched in the side-population cells in a mouse model of glioma. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 10051–10059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Ye, H.; Qi, Z.; Mo, L.; Yue, Q.; Baral, A.; Hoon, D.S.; Vera, J.C.; Heiss, J.D.; Chen, C.C.; et al. B7-H4(B7x)-mediated cross-talk between glioma initiating cells and macrophages via the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 pathway lead to poor prognosis in glioma patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2778–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Ke, S.Q.; Huang, Z.; Flavahan, W.; Fang, X.; Paul, J.; Wu, L.; Sloan, A.E.; McLendon, R.E.; Li, X.; et al. Periostin secreted by glioblastoma stem cells recruits M2 tumour-associated macrophages and promotes malignant growth. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oushy, S.; Hellwinkel, J.E.; Wang, M.; Nguyen, G.J.; Gunaydin, D.; Harland, T.A.; Anchordoquy, T.J.; Graner, M.W. Glioblastoma multiforme-derived extracellular vesicles drive normal astrocytes towards a tumour-enhancing phenotype. Philosophical transactions of the Royal Society of London. Biologic. Sci. 2018, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoudi, M.S.; Mehrabian, E.; Mirzaei, H. MiR-21: A key player in glioblastoma pathogenesis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 1285–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruivo, C.F.; Adem, B.; Silva, M.; Melo, S.A. The Biology of Cancer Exosomes: Insights and New Perspectives. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 6480–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, F.; Wang, X.; Zhu, F.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Guo, C.; Zhou, C.; Ma, C.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Y.; et al. PDCD4 gene silencing in gliomas is associated with 5’CpG island methylation and unfavourable prognosis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 4257–4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, C.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, F.; Ma, C.; Sun, W.; Zhang, L. Frequent loss of PDCD4 expression in human glioma: Possible role in the tumorigenesis of glioma. Oncol. Rep. 2007, 17, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Wang, J.J.; Tang, H.M.; To, S.S.T. Targeting strategies on miRNA-21 and PDCD4 for glioblastoma. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 580, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forloni, M.; Dogra, S.K.; Dong, Y.; Conte, D.; Ou, J.; Zhu, L.J.; Deng, A.; Mahalingam, M.; Green, M.R.; Wajapeyee, N. miR-146a promotes the initiation and progression of melanoma by activating Notch signaling. eLife 2014, 3, e01460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, I.-D.; Codrici, E.; Enciu, A.-M.; Mihai, S.; Tanase, C. Glioma Stem Cells and Their Microenvironments: Providers of Challenging Therapeutic Targets. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 5728438. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, J.; Torre-Healy, L.; Lathia, J.D.; Nakano, I.; Guo, Y.; Thompson, R.C.; Freeman, M.L.; Wang, J. Inhibition of Farnesyltransferase Potentiates NOTCH-Targeted Therapy against Glioblastoma Stem Cells. Stem Cell Rep. 2017, 9, 1948–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutsaeva, D.R.; Thounaojam, M.; Rajpurohit, S.; Powell, F.L.; Martin, P.M.; Goei, S.; Duncan, M.; Bartoli, M. STAT3-mediated activation of miR-21 is involved in down-regulation of TIMP3 and neovascularization in the ischemic retina. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 103568–103580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ning, S.-L.; Zhu, H.; Shao, J.; Liu, Y.-C.; Lan, J.; Miao, J. MiR-21 inhibitor improves locomotor function recovery by inhibiting IL-6R/JAK-STAT pathway-mediated inflammation after spinal cord injury in model of rat. Eur. Rev. Med Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 433–440. [Google Scholar]
- Betts, B.C.; Bastian, D.; Iamsawat, S.; Nguyen, H.; Heinrichs, J.L.; Wu, Y.; Daenthanasanmak, A.; Veerapathran, A.; O’Mahony, A.; Walton, K.; et al. Targeting JAK2 reduces GVHD and xenograft rejection through regulation of T cell differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 1582–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mascarenhas, J.; Hoffman, R.; Talpaz, M.; Gerds, A.T.; Stein, B.; Gupta, V.; Szoke, A.; Drummond, M.; Pristupa, A.; Granston, T.; et al. Pacritinib vs Best Available Therapy, Including Ruxolitinib, in Patients With Myelofibrosis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couto, M.; Coelho-Santos, V.; Santos, L.; Fontes-Ribeiro, C.; Silva, A.P.; Gomes, C.M.F. The Interplay between Glioblastoma and Microglia Cells Leads to Endothelial Cell Monolayer Dysfunction via the Interleukin-6-Induced JAK2/STAT3 Pathway. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/jcp.28575 (accessed on 26 May 2019).
- Linder, B.; Weirauch, U.; Ewe, A.; Uhmann, A.; Seifert, V.; Mittelbronn, M.; Harter, P.N.; Aigner, A.; Kögel, D. Therapeutic Targeting of Stat3 Using Lipopolyplex Nanoparticle-Formulated siRNA in a Syngeneic Orthotopic Mouse Glioma Model. Cancers 2019, 11, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Li, A.; Xu, Y.; Xin, Y. Momelotinib sensitizes glioblastoma cells to temozolomide by enhancement of autophagy via JAK2/STAT3 inhibition. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 41, 1883–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ashizawa, T.; Akiyama, Y.; Miyata, H.; Iizuka, A.; Komiyama, M.; Kume, A.; Omiya, M.; Sugino, T.; Asai, A.; Hayashi, N.; et al. Effect of the STAT3 inhibitor STX-0119 on the proliferation of a temozolomide-resistant glioblastoma cell line. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, H.; Ashizawa, T.; Iizuka, A.; Kondou, R.; Nonomura, C.; Sugino, T.; Urakami, K.; Asai, A.; Hayashi, N.; Mitsuya, K.; et al. Combination of a STAT3 Inhibitor and an mTOR Inhibitor Against a Temozolomide-resistant Glioblastoma Cell Line. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2017, 14, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, Y.; Nonomura, C.; Ashizawa, T.; Iizuka, A.; Kondou, R.; Miyata, H.; Sugino, T.; Mitsuya, K.; Hayashi, N.; Nakasu, Y.; et al. The anti-tumor activity of the STAT3 inhibitor STX-0119 occurs via promotion of tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte accumulation in temozolomide-resistant glioblastoma cell line. Immunol. Lett. 2017, 190, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Long, L.; Pu, P.; Ren, Y.; Shi, Z.; Sheng, J.; Yuan, X.; Kang, C. Sequence-Dependent Synergistic Inhibition of Human Glioma Cell Lines by Combined Temozolomide and miR-21 Inhibitor Gene Therapy. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 2636–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.V.; Cseh, O.; Aman, A.; Weiss, S.; Luchman, H.A. The JAK2/STAT3 inhibitor pacritinib effectively inhibits patient-derived GBM brain tumor initiating cells in vitro and when used in combination with temozolomide increases survival in an orthotopic xenograft model. PLos ONE 2017, 12, e0189670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chuang, H.-Y.; Su, Y.-k.; Liu, H.-W.; Chen, C.-H.; Chiu, S.-C.; Cho, D.-Y.; Lin, S.-Z.; Chen, Y.-S.; Lin, C.-M. Preclinical Evidence of STAT3 Inhibitor Pacritinib Overcoming Temozolomide Resistance via Downregulating miR-21-Enriched Exosomes from M2 Glioblastoma-Associated Macrophages. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8070959
Chuang H-Y, Su Y-k, Liu H-W, Chen C-H, Chiu S-C, Cho D-Y, Lin S-Z, Chen Y-S, Lin C-M. Preclinical Evidence of STAT3 Inhibitor Pacritinib Overcoming Temozolomide Resistance via Downregulating miR-21-Enriched Exosomes from M2 Glioblastoma-Associated Macrophages. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(7):959. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8070959
Chicago/Turabian StyleChuang, Hao-Yu, Yu-kai Su, Heng-Wei Liu, Chao-Hsuan Chen, Shao-Chih Chiu, Der-Yang Cho, Shinn-Zong Lin, Yueh-Sheng Chen, and Chien-Min Lin. 2019. "Preclinical Evidence of STAT3 Inhibitor Pacritinib Overcoming Temozolomide Resistance via Downregulating miR-21-Enriched Exosomes from M2 Glioblastoma-Associated Macrophages" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 7: 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8070959
APA StyleChuang, H.-Y., Su, Y.-k., Liu, H.-W., Chen, C.-H., Chiu, S.-C., Cho, D.-Y., Lin, S.-Z., Chen, Y.-S., & Lin, C.-M. (2019). Preclinical Evidence of STAT3 Inhibitor Pacritinib Overcoming Temozolomide Resistance via Downregulating miR-21-Enriched Exosomes from M2 Glioblastoma-Associated Macrophages. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(7), 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8070959