Identification of a Shared Microbiomic and Metabolomic Profile in Systemic Autoimmune Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patients and Controls
2.2. Collection and Storage of Samples
2.3. 16S rRNA Gene-Sequencing
2.4. Metabolomic Analysis in Plasma
2.5. HPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.6.1. Canonical Analysis of Microbiota
2.6.2. Data Mining Classification and Non-Linear Interactions Analysis
2.6.3. Post-Hoc Statistical Analysis on Classification Data
2.6.4. Cross-Correlation Analysis
3. Results
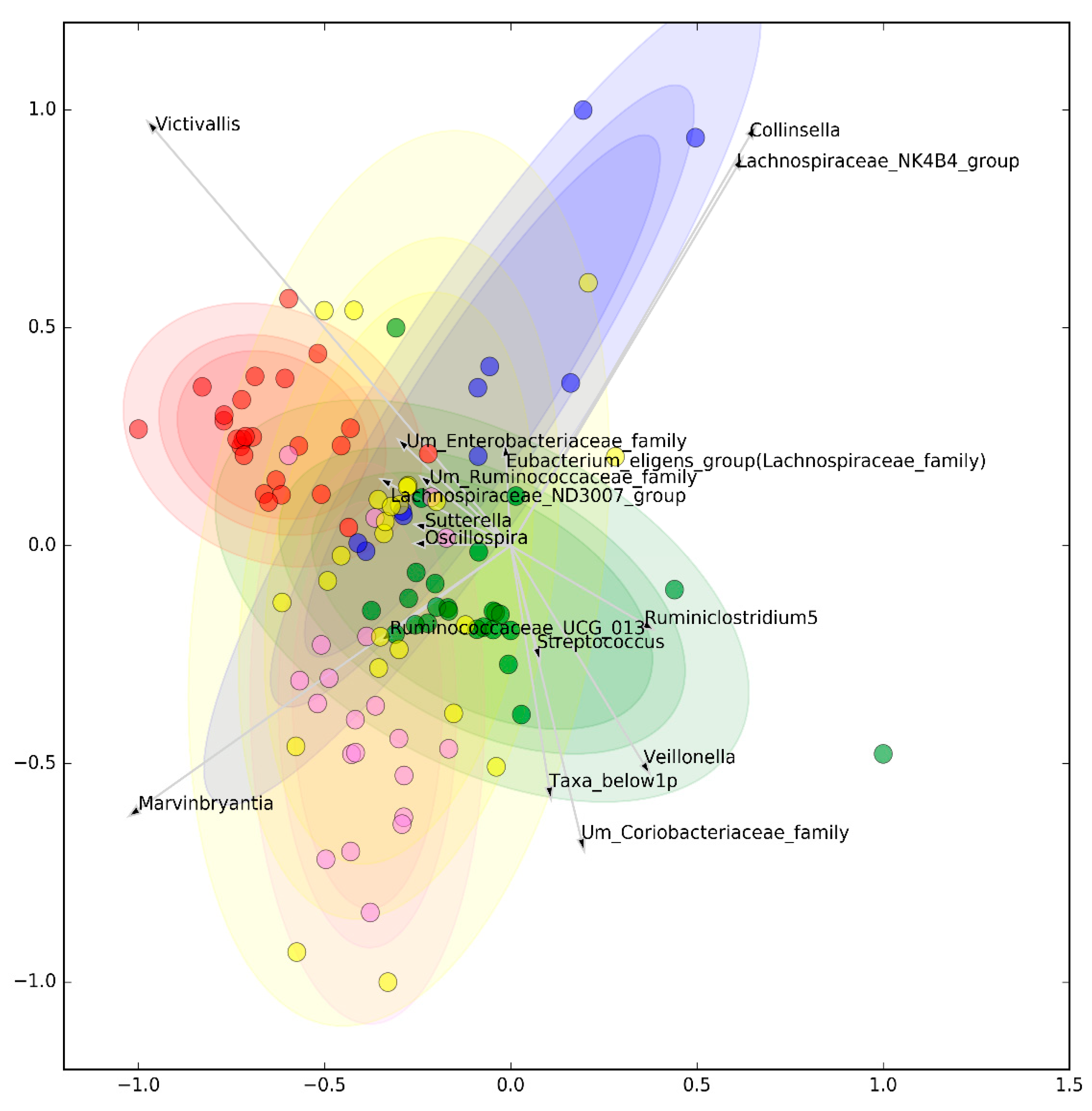
3.1. Microbiomic Analysis
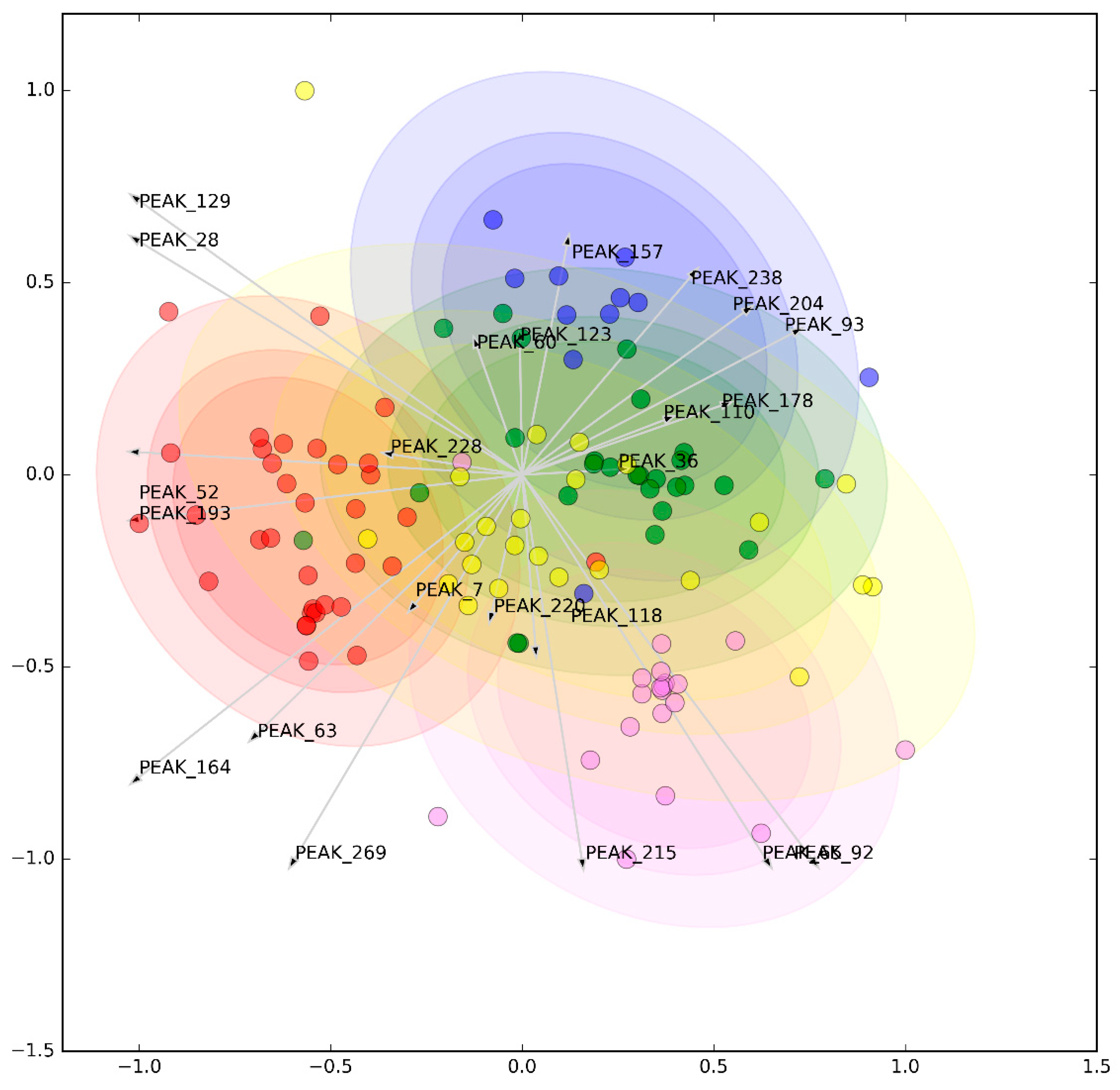
3.2. Metabolomic Analysis
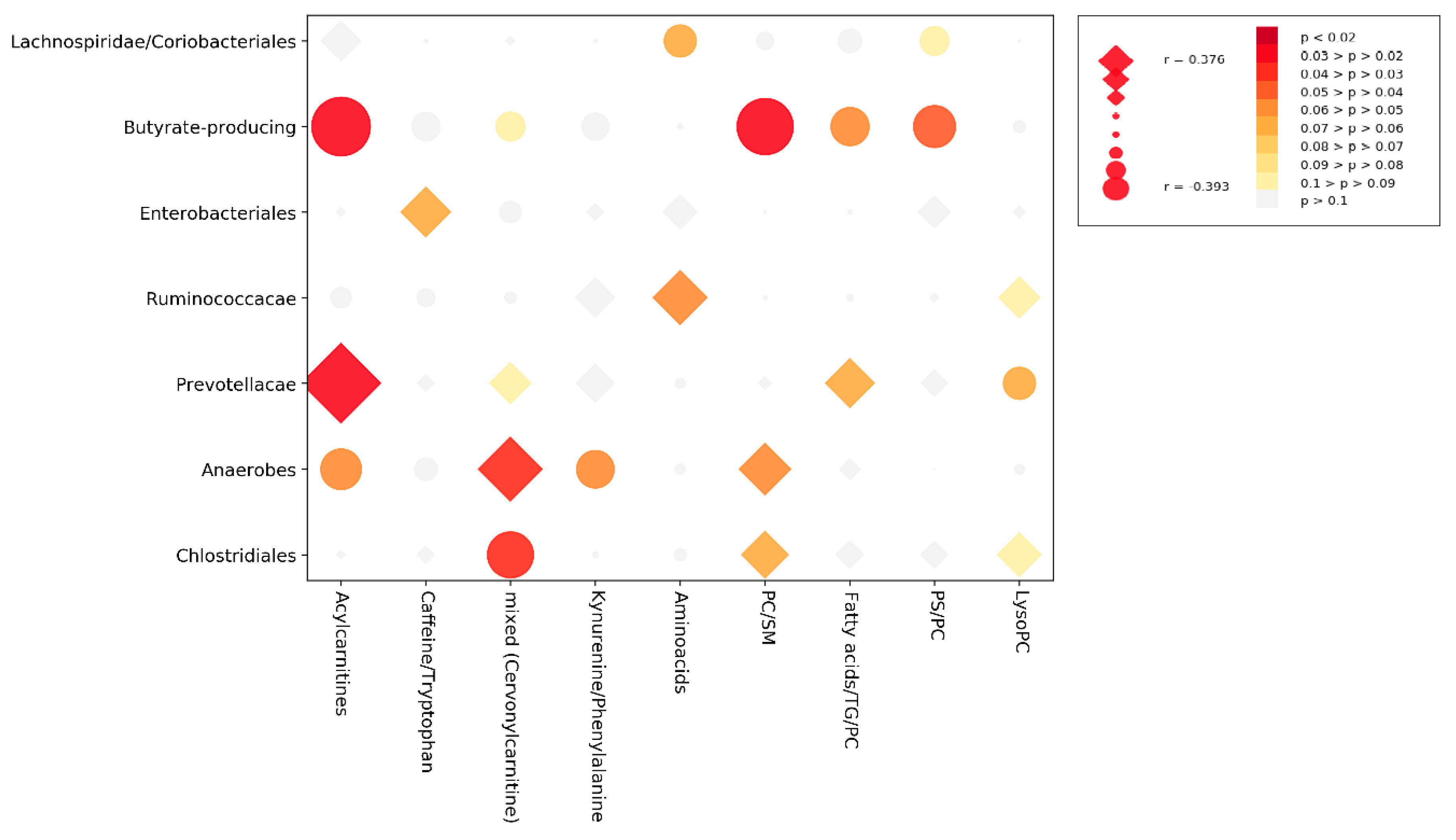
3.3. Cross-Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suzuki, K.; Maruya, M.; Kawamoto, S.; Sitnik, K.; Kitamura, H.; Agace, W.W.; Fagarasan, S. The sensing of environmental stimuli by follicular dendritic cells promotes immunoglobulin A generation in the gut. Immunity 2010, 33, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Costello, E.K.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Delivery mode shapes the acquisition and structure of the initial microbiota across multiple body habitats in newborns. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11971–11975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umesaki, Y.; Setoyama, H.; Matsumoto, S.; Okada, Y. Expansion of axf T-cell receptor-bearing intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes after microbial colonization in germ-free mice and its independence from thymus. Immunology 1993, 79, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lundin, A.; Bok, C.M.; Aronsson, L.; Björkholm, B.; Gustafsson, J.Å.; Pott, S.; Arulampalam, V.; Hibberd, M.; Rafter, J.; Pettersson, S. Gut flora, Toll-like receptors and nuclear receptors: A tripartite communication that tunes innate immunity in large intestine. Cell Microbiol. 2008, 10, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Round, J.L.; Mazmanian, S.K. Inducible Foxp3+ regulatory T-cell development by\na commensal bacterium of the intestinal microbiota. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12204–12209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macfarlane, S.; Macfarlane, G.T. Regulation of short-chain fatty acid production. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2003, 62, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.M.; Howitt, M.R.; Panikov, N.; Michaud, M.; Gallini, C.A.; Bohlooly-Y, M.; Glickman, J.N.; Garrett, W.S. The microbial metabolites, short-chain fatty acids, regulate colonic Treg cell homeostasis. Science 2013, 341, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, P.; De Paz, B.; Rodríguez-Carrio, J.; Hevia, A.; Sánchez, B.; Margolles, A.; Suárez, A. Th17 responses and natural IgM antibodies are related to gut microbiota composition in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Carrio, J.; López, P.; Sánchez, B.; González, S.; Gueimonde, M.; Margolles, A.; de los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G.; Suárez, A. Intestinal Dysbiosis Is Associated with Altered Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Serum-Free Fatty Acids in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opazo, M.C.; Ortega-Rocha, E.M.; Coronado-Arrázola, I.; Bonifaz, L.C.; Boudin, H.; Neunlist, M.; Bueno, S.M.; Kalergis, A.M.; Riedel, C.A. Intestinal Microbiota Influences Non-intestinal Related Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellocchi, C.; Fernandez-Ochoa, A.; Montanelli, G.; Vigone, B.; Santaniello, A.; Milani, C.; Quirantes-Piné, R.; Borrás-Linares, I.; Ventura, M.; Segura-Carrettero, A.; et al. Microbial and metabolic multi-omic correlations in systemic sclerosis patients. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Meulen, T.A.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; Bootsma, H.; Spijkervet, F.K.L.; Kroese, F.G.M.; Vissink, A. The microbiome-systemic diseases connection. Oral Dis. 2016, 22, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzosa, E.A.; Hsu, T.; Sirota-Madi, A.; Shafquat, A.; Abu-Ali, G.; Morgan, X.C.; Huttenhower, C. Sequencing and beyond: Integrating molecular “omics” for microbial community profiling. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Q.; Tavella, V.J.; Kirby, J.L.; Cecere, T.E.; Chung, M.; Lee, J.; Li, S.; Ahmed, S.A.; Eden, K.; Allen, I.C.; et al. Antibiotics ameliorate lupus-like symptoms in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, S.M.; Hiltensperger, M.; Kumar, V.; Zegarra-Ruiz, D.; Dehner, C.; Khan, N.; Costa, F.R.C.; Tiniakou, E.; Greiling, T.; Ruff, W.; et al. Translocation of a gut pathobiont drives autoimmunity in mice and humans. Science 2018, 359, 1156–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Xie, C.; Han, J.; Ye, Y.; Weiel, J.; Li, Q.; Blanco, I.; Ahn, C.; Olsen, N.; Putterman, C.; et al. Metabolic disturbances associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengtsson, A.A.; Trygg, J.; Wuttge, D.M.; Sturfelt, G.; Theander, E.; Donten, M.; Moritz, T.; Sennbro, C.J.; Torell, F.; Lood, C.; et al. Metabolic profiling of systemic lupus erythematosus and comparison with primary Sjögren’s syndrome and systemic sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paiva, C.S.; Jones, D.B.; Stern, M.E.; Bian, F.; Moore, Q.L.; Corbiere, S.; Streckfus, C.F.; Hutchinson, D.S.; Ajami, N.J.; Petrosino, J.F.; et al. Altered Mucosal Microbiome Diversity and Disease Severity in Sjögren Syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, G.; Saegusa, J.; Irino, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Tsuda, K.; Takahashi, S.; Sendo, S.; Morinobu, A. Metabolomics analysis of saliva from patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 182, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandl, T.; Marsal, J.; Olsson, P.; Ohlsson, B.; Andréasson, K. Severe intestinal dysbiosis is prevalent in primary Sjögren’s syndrome and is associated with systemic disease activity. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Che, N.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Tan, W.; Zhang, M. LC-MS-based serum metabolomics reveals a distinctive signature in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 1493–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruff, W.E.; Vieira, S.M.; Kriegel, M.A. The role of the gut microbiota in the pathogenesis of antiphospholipid syndrome. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2015, 17, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguiar, C.L.; Ruff, W.; Goodman, A.; Erkan, D.; Kriegel, M. Cardiolipin-Producing Candidate Commensals in the Gut Microbiome of Antiphospholipid Syndrome Patients. In ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY; WILEY: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Palisi, A.; Grimaldi, M.; Sabatini, P.; Montoro, P.; Scrima, M.; Rodriquez, M.; D’Ursi, A.M. A serum nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomic signature of antiphospholipid syndrome. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 133, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, M.; Scirè, C.A.; Talarico, R.; Alexander, T.; Avcin, T.; Belocchi, C.; Doria, A.; Franceschini, F.; Galetti, I.; Govoni, M.; et al. Undifferentiated connective tissue disease: State of the art on clinical practice guidelines. RMD open 2018, 4, e000786. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hochberg, M.C. Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitali, C.B.S.J.; Bombardieri, S.; Jonsson, R.; Moutsopoulos, H.M.; Alexander, E.L.; Carsons, S.E.; Daniels, T.E.; Fox, P.C.; Fox, R.I.; Kassan, S.; et al. Classification criteria for Sjögren’s syndrome: A revised version of the European criteria proposed by the American-European Consensus Group. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2002, 61, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyakis, S.; Lockshin, M.D.; Atsumi, T.; Branch, D.W.; Brey, R.L.; Cervera, R.H.W.M.; Derksen, R.H.; de Groot, P.G.; Koike, T.; Meroni, P.L.; et al. International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, C.; Hevia, A.; Foroni, E.; Duranti, S.; Turroni, F.; Lugli, G.A.; Sanchez, B.; Martin, R.; Gueimonde, M.; Van Sinderen, D.; et al. Assessing the fecal microbiota: An optimized ion torrent 16S rRNA gene-based analysis protocol. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genprobio. Available online: www.genprobio.com (accessed on 14 July 2019).
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, S.J.; Tavazzi, I.; Parisod, V.; Rezzi, S.; Kochhar, S.; Guy, P.A. Investigation of human blood plasma sample preparation for performing metabolomics using ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 3285–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Livera, A.M.; Olshansky, M.; Speed, T.P. Statistical Analysis of Metabolomics Data. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.; Knight, R. UniFrac: A new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8228–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demšar, J.; Leban, G.; Zupan, B. FreeViz—An intelligent multivariate visualization approach to explorative analysis of biomedical data. J. Biomed. Inform. 2007, 40, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousseeuw, P.J. Silhouettes: A graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 1987, 20, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westfall, P.H.; Young, S.S. Resampling-Based Multiple Testing: Examples and Methods for p-Value Adjustment; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.J.; Robinson, J. Permutation tests for linear models. Aust. N. Z. J. Stat. 2001, 43, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scikit-Learn Modules. Available online: https://scikit-learn.org (accessed on 14 July 2019).
- Gil de la Fuente, A.; Grace Armitage, E.; Otero, A.; Barbas, C.; Godzien, J. Differentiating signals to make biological sense—A guide through databases for MS-based non-targeted metabolomics. Electrophoresis 2017, 38, 2242–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, M.; Shang, Z.; Teng, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, M.; Lv, H.; Zhang, R. The shared and specific mechanism of four autoimmune diseases. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 108355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosca, M.; Tani, C.; Talarico, R.; Bombardieri, S. Undifferentiated connective tissue diseases (UCTD): Simplified systemic autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2011, 10, 256–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, L.; Zhou, R.; Wang, X.; Song, L.; Huang, S.; Wang, G.; Xia, B. Increased proportions of Bifidobacterium and the Lactobacillus group and loss of butyrate-producing bacteria in inflammatory bowel disease. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gevers, D.; Kugathasan, S.; Denson, L.A.; Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; Van Treuren, W.; Ren, B.; Schwager, E.; Knights, D.; Song, S.J.; Yassour, M.; et al. The treatment-naive microbiome in new-onset Crohn’s disease. Cell Host Microbe. 2014, 15, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, A.; Luckey, D.; Taneja, V. The gut microbiome in autoimmunity: Sex matters. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 159, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosorich, I.; Dalla-Costa, G.; Sorini, C.; Ferrarese, R.; Messina, M.J.; Dolpady, J.; Radice, E.; Mariani, A.; Testoni, P.A.; Canducci, F.; et al. High frequency of intestinal TH17 cells correlates with microbiota alterations and disease activity in multiple sclerosis. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wright, K.; Davis, J.M.; Jeraldo, P.; Marietta, E.V.; Murray, J.; Nelson, H.; Matteson, E.L.; Taneja, V. An expansion of rare lineage intestinal microbes characterizes rheumatoid arthritis. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meehan, C.J.; Beiko, R.G. A phylogenomic view of ecological specialization in the Lachnospiraceae, a family of digestive tract-associated bacteria. Genome Biol. Evol. 2014, 6, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surowiec, I.; Ärlestig, L.; Rantapää-Dahlqvist, S.; Trygg, J. Metabolite and Lipid Profiling of Biobank Plasma Samples Collected Prior to Onset of Rheumatoid Arthritis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krähenbühl, S.; Willer, B.; Brühlmann, P.; Hoppeler, H.; Stucki, G. Carnitine homeostasis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Chim. Acta. 1999, 279, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiziltunc, A.; Coğalgil, S.; Cerrahoğlu, L. Carnitine and antioxidants levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 1998, 27, 441–445. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Ochoa, Á.; Quirantes-Piné, R.; Borrás-Linares, I.; Gemperline, D.; Riquelme, M.E.A.; Beretta, L.; Segura-Carretero, A. PRECISESADS Clinical Consortium. Urinary and plasma metabolite differences detected by HPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS in systemic sclerosis patients. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 162, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Jameson, E.; Crosatti, M.; Schäfer, H.; Rajakumar, K.; Bugg, T.D.; Chen, Y. Carnitine metabolism to trimethylamine by an unusual Rieske-type oxygenase from human microbiota. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4268–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeth, R.A.; Wang, Z.; Levison, B.S.; Buffa, J.A.; Org, E.; Sheehy, B.T.; Britt, E.B.; Fu, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, L.; et al. Intestinal microbiota metabolism of L-carnitine, a nutrient in red meat, promotes atherosclerosis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vital, M.; Karch, A.; Pieper, D.H. Colonic Butyrate-Producing Communities in Humans: An Overview Using Omics Data. Msystems 2017, 2, e00130-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amir, I.; Bouvet, P.; Legeay, C.; Gophna, U.; Weinberger, A. Eisenbergiella tayi gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from human blood. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandri, M.; Dal Monego, S.; Conte, G.; Sgorlon, S.; Stefanon, B. Raw meat based diet influences faecal microbiome and end products of fermentation in healthy dogs. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, A.; Chaussonnerie, S.; Tarrade, A.; Dauga, C.; Bouchez, T.; Pelletier, E.; Le Paslier, D.; Sghir, A. Cloacibacillus evryensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel asaccharolytic, mesophilic, amino-acid-degrading bacterium within the phylum “Synergistetes”, isolated from an anaerobic sludge digester. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 2003–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohira, H.; Tsutsui, W.; Mamoto, R.; Yamaguchi, S.; Nishida, M.; Ito, M.; Fujioka, Y. Butyrate attenuates lipolysis in adipocytes co-cultured with macrophages through non-prostaglandin E2-mediated and prostaglandin E2-mediated pathways. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treede, I.; Braun, A.; Sparla, R.; Kühnel, M.; Giese, T.; Turner, J.R.; Anes, E.; Kulaksiz, H.; Füllekrug, J.; Stremmel, W.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of phosphatidylcholine. J. Biol Chem. 2007, 282, 27155–27164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, R.; Zechner, R. Lipolysis meets inflammation: Arachidonic acid mobilization from fat. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 2447–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, A.; Hentzien, M.; Toquet, S.; Didier, K.; Servettaz, A.; PHAM, B.N.; Giusti, D. Diagnostic Utility of Separate Anti-Ro60 and Anti-Ro52/TRIM21 Antibody Detection in Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temmoku, J.; Sato, S.; Fujita, Y.; Asano, T.; Suzuki, E.; Kanno, T.; Furuya, M.Y.; Matsuoka, N.; Kobayashi, H.; Watanabe, H.; et al. Clinical significance of myositis-specific autoantibody profiles in Japanese patients with polymyositis/dermatomyositis. Medicine 2019, 98, e15578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, D.L.; Fernando, M.M.A.; Taylor, K.E.; Chung, S.A.; Nititham, J.; Alarcon-Riquelme, M.E.; Barcellos, L.F.; Behrens, T.W.; Cotsapas, C.; Gaffney, P.M.; et al. MHC associations with clinical and autoantibody manifestations in European SLE. Genes Immun. 2014, 15, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, R.; Chauhan, S.K.; Singh, V.V.; Rai, M.; Rai, G. RNA-seq Analysis Reveals Unique Transcriptome Signatures in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients with Distinct Autoantibody Specificities. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| SLE (n = 27) | SjS (n = 23) | PAPS (n = 11) | UCTD (n = 26) | HC (n = 27) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean (SD) | 47.70 (16.55) | 65.91 (12.72) | 40.36 (6.17) | 52.23 (12.01) | 52.47 (9.96) |
| Females, n (%) | 24 (88.9) | 22 (95.65) | 8 (72.72) | 23 (88.46) | 20 (74.07) |
| Disease duration years, mean (SD) | 15.16 (10.92) | 9.95 (9.38) | 11.17 (5.92) | 9.43 (5.09) | - |
| AutoAb profile, n (%) | |||||
| ANA | 27 (100) | 20 (86.97) | 2 (16.67) | 26 (100) | |
| Anti-Ro 60/SSA | 4 (14.81) | 15 (65.22) | 0 (0) | 3 (11.53) | |
| Anti-La/SSB | 1 (3.70) | 10 (43.48) | 0 | 0 | |
| Anti dsDNA | 13 (48.14) | 0 (0) | 2 (18.18) | 5 (19.23) | |
| Anti Sm | 2 (7.4) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| ACL | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 6 (54.54) | 1 (3.85) | |
| Anti B2GP | 1 (3.70) | 0 (0) | 8 (72.72) | 1 (3.85) | |
| RF | 1 (3.70) | 11 (47.83) | 0 (0) | 3 (11.54) | |
| C3c mg/dL, mean ± SD | 82.7 ± 21.6 | 101.8 ± 25.3 | 100.1 ± 21.2 | 101.3 ± 28.9 | |
| C4 mg/dL, mean ± SD | 14.6 ± 7.2 | 19.1 ± 8.8 | 16.9 ± 9.1 | 16.6 ± 6.2 | |
| Abnormal Liver function, n (%) | 4 (14.81) | 1 (4.35) | 0 (0) | 2 (7.69) | - |
| GERD, n (%) | 5 (18.51) | 11 (47.83) | 1 (9.09) | 10 (38.46) | - |
| Pericarditis, n (%) | 4 (14.81) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | - |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 6 (22.22) | 2 (8.69) | 2 (18.18) | 5 (19.23) | - |
| Valve lesions, n (%) | 1 (3.70) | 1 (4.35) | 1 (9.09) | 1 (3.85) | - |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 5 (18.51) | 2 (8.69) | 3 (27.27) | 3 (11.54) | - |
| Abnormal creatinine, n (%) | 7 (25.92) | 1 (4.35) | 2 (18.18) | 3 (11.54) | - |
| Abnormal urine, n (%) | 10 (37.03) | 1 (4.35) | 3 (27.27) | 2 (7.69) | - |
| Proteinuria, n (%) | 7 (25.92) | 1 (4.35) | 3 (27.27) | 0 (0) | - |
| Anemia past, n (%) | 3 (11.1) | 1 (4.35) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | - |
| Low platelet count, n (%) | 8 (29.62) | 2 (8.69) | 2 (18.18) | 1 (3.85) | - |
| Low WBC, n (%) | 18 (66.67) | 6 (26.09) | 2 (18.18) | 7 (26.92) | - |
| Pleuritis, n (%) | 1 (3.70) | 1 (4.35) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | - |
| Arthritis, n (%) | 17 (62.96) | 3 (13.04) | 1 (9.09) | 6 (23.08) | - |
| Myopathy, n (%) | 2 (7.4) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | - |
| CNS involvement, n (%) | 3 (11.1) | 1 (4.35) | 4 (36.36) | 0 (0) | - |
| PNS involvement, n (%) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (18.18) | 1 (3.85) | - |
| Mucositis, n (%) | 10 (37.03) | 0 (0) | 2 (18.18) | 4 (15.38) | - |
| Cutaneous active lupus, n (%) | 19 (70.37) | 1 (4.35) | 1 (9.09) | 2 (7.69) | - |
| Cutaneous chronic lupus, n (%) | 5 (18.51) | 0 (0) | 1 (9.09) | 4 (15.38) | - |
| Photosensitivity, n (%) | 22 (81.48) | 2 (8.69) | 1 (9.09) | 13 (50) | - |
| Puffy fingers, n (%) | 2 (7.4) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | - |
| Sicca, n (%) | 12 (44.44) | 21 (91.30) | 1 (9.09) | 9 (34.62) | - |
| Inflammation, n (%) | 17 (62.96) | 10 (43.48) | 1 (9.09) | 13 (50) | - |
| PGA, mean (SD) | 28.52 (21.61) | 30.78 (18.97) | 47.27 (29.44) | 30.28 (18.2) | - |
| Fever, n (%) | 0 (0) | 2 (8.69) | 1 (9.09) | 2 (7.69) | - |
| Hypergammaglobulinemia, n (%) | 12 (44.44) | 12 (52.17) | 0 (0) | 9 (34.62) | - |
| Venous thrombosis, n (%) | 2 (7.4) | 0 (0) | 6 (54.54) | 1 (3.85) | - |
| Raynaud’s phenomenon, n (%) | 8 (29.62) | 2 (8.69) | 1 (9.09) | 11 (42.3) | - |
| Miscarriage, n (%) | 2 (7.4) | 1 (4.35) | 7 (63.63) | 0 (0) | - |
| Statin use, n (%) | 2 (7.4) | 2 (8.69) | 1 (9.09) | 2 (7.69) | - |
| Prednisone (>5 mg/day), n (%) | 7 (25.92) | 3 (13.04) | 1 (9.09) | 9 (34.62) | - |
| Prednisone dose, mean mg/day | 7.55 | 8.62 | 7 | 5.67 | - |
| HCQ use, n (%) | 19 (70.37) | 9 (39.13) | 8 (72.72) | 13 (50) | - |
| Immunosuppressant use, n (%) | 10 (37.04) | 2 (8.69) | 0 (0) | 3 (11.54) | - |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bellocchi, C.; Fernández-Ochoa, Á.; Montanelli, G.; Vigone, B.; Santaniello, A.; Quirantes-Piné, R.; Borrás-Linares, I.; Gerosa, M.; Artusi, C.; Gualtierotti, R.; et al. Identification of a Shared Microbiomic and Metabolomic Profile in Systemic Autoimmune Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8091291
Bellocchi C, Fernández-Ochoa Á, Montanelli G, Vigone B, Santaniello A, Quirantes-Piné R, Borrás-Linares I, Gerosa M, Artusi C, Gualtierotti R, et al. Identification of a Shared Microbiomic and Metabolomic Profile in Systemic Autoimmune Diseases. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(9):1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8091291
Chicago/Turabian StyleBellocchi, Chiara, Álvaro Fernández-Ochoa, Gaia Montanelli, Barbara Vigone, Alessandro Santaniello, Rosa Quirantes-Piné, Isabel Borrás-Linares, Maria Gerosa, Carolina Artusi, Roberta Gualtierotti, and et al. 2019. "Identification of a Shared Microbiomic and Metabolomic Profile in Systemic Autoimmune Diseases" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 9: 1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8091291
APA StyleBellocchi, C., Fernández-Ochoa, Á., Montanelli, G., Vigone, B., Santaniello, A., Quirantes-Piné, R., Borrás-Linares, I., Gerosa, M., Artusi, C., Gualtierotti, R., Segura-Carrettero, A., Alarcón-Riquelme, M. E., & Beretta, L. (2019). Identification of a Shared Microbiomic and Metabolomic Profile in Systemic Autoimmune Diseases. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(9), 1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8091291









