Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement Is Associated with Less Oxidative Stress and Faster Recovery of Antioxidant Capacity than Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Surgical Procedure (SAVR)
2.3. Percutaneous Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVR)
2.4. Serum Collection
2.5. Determination of Total Antioxidant Capacity
2.6. Determination of Lipid Peroxidation
2.7. Determination of the Cu/Zn Ratio
2.8. Determination of Total Activity of Lactate Dehydrogenase
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
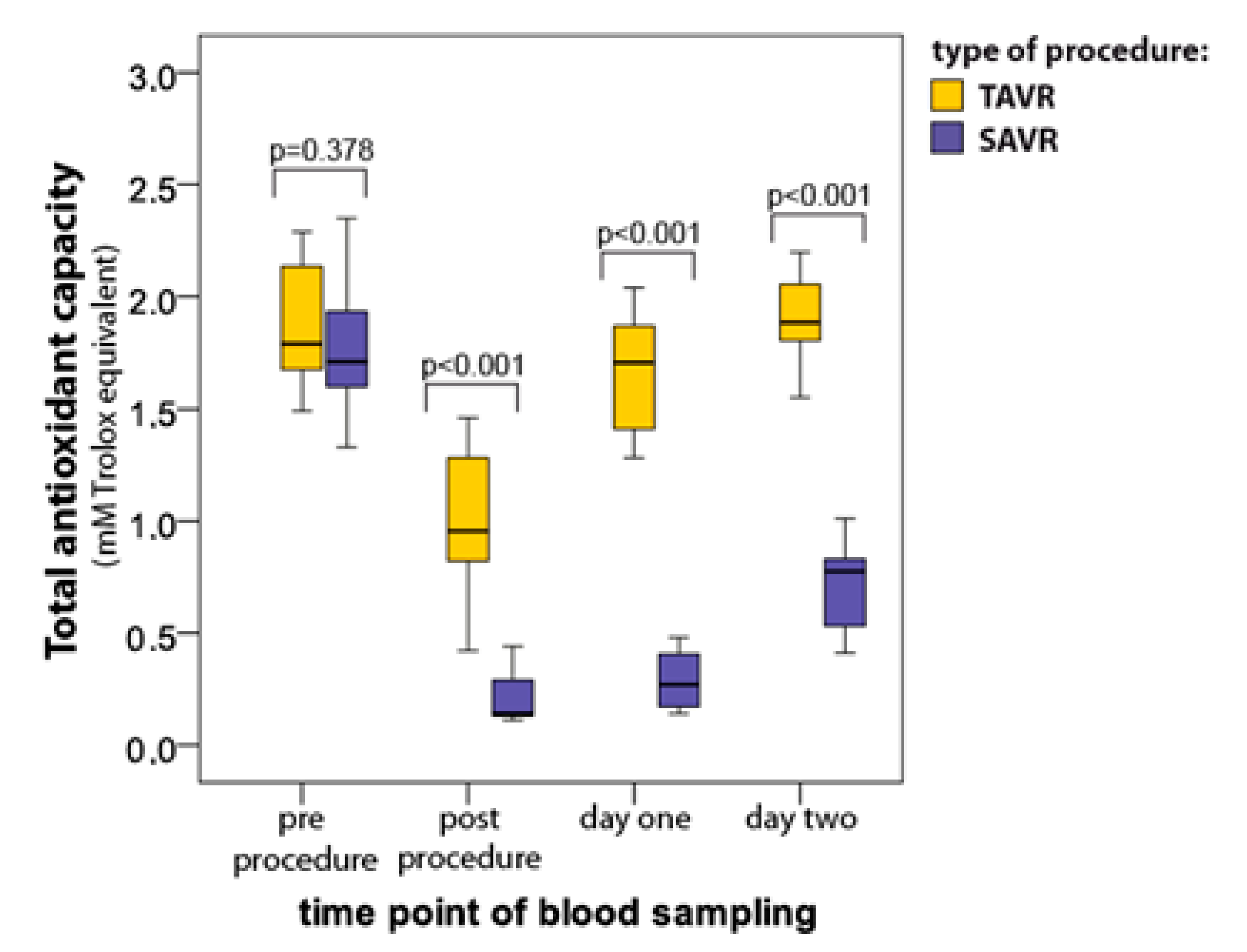
3.1. Total Antioxidant Capacity (TAC)
3.2. Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances (TBARS)
3.3. Copper/Zinc Ratio (Cu/Zn)
3.4. Total Lactate Dehydrogenase Activity (LDH)
3.5. Relationship Between Oxidative Stress Markers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andell, P.; Li, X.; Martinsson, A.; Andersson, C.; Stagmo, M.; Zöller, B.; Sundquist, K.; Smith, J.G. Epidemiology of valvular heart disease in a Swedish nationwide hospital-based register study. Heart 2017, 103, 1696–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iung, B.; Vahanian, A. Epidemiology of acquired valvular heart disease. Can. J. Cardiol. 2014, 30, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thourani, V.H.; Kodali, S.; Makkar, R.R.; Herrmann, H.C.; Williams, W.; Babaliaros, V.; Smalling, R.; Lim, S.; Malaisrie, C.; Kapadia, S.; et al. Transcatheter aortic valve replacement versus surgical valve replacement in intermediate-risk patients: A propensity score analysis. Lancet 2016, 387, 2218–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.R.; Leon, M.B.; Mack, M.J.; Miller, D.C.; Moses, J.W.; Svensson, L.G.; Tuzcu, E.M.; Webb, J.G.; Fontana, G.P.; Makkar, R.R.; et al. Transcatheter versus surgical aortic-valve replacement in high-risk patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2187–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corral-Velez, V.; Lopez-Delgado, J.C.; Betancur-Zambrano, N.L.; Lopez-Suñe, N.; Ojas-Lora, M.; Torrado, H.; Ballus, J. The inflammatory response in cardiac surgery: An overview of the pathophysiology and clinical implications. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets 2015, 13, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Yuan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, G.; Liu, T. Reactive oxygen species mediated oxidative stress links diabetes and atrial fibrillation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 4933–4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonopoulos, A.S.; Goliopoulou, A.; Oikonomou, E.; Tsalamandris, S.; Papamikroulis, G.-A.; Lazaros, G.; Tsiamis, E.; Latsios, G.; Brili, S.; Papaioannou, S.; et al. Redox State in Atrial Fibrillation Pathogenesis and Relevant Therapeutic Approaches. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 765–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melduni, R.M.; Schaff, H.V.; Bailey, K.R.; Cha, S.S.; Ammash, N.M.; Seward, G.B.; Gersh, B.J. Implications of new-onset atrial fibrillation after cardiac surgery on long-term prognosis: A community-based study. Am. Heart J. 2015, 170, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neal, J.B.; Shaw, A.D.; Billings, F.T. Acute kidney injury following cardiac surgery: Current understanding and future directions. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinness, S.P.; Parke, R.L.; Drummond, K.; Willcox, T.; Bailey, M. A Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled Phase IIb Trial of Avoidance of Hyperoxemia during Cardiopulmonary Bypass. Anesthesiology 2016, 125, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeldt, F.; Wilson, M.; Lee, G.; Kure, C.; Ou, R.; Braun, L.; de Haan, J. Oxidative stress in surgery in an ageing population: Pathophysiology and therapy. Exp. Gerontol. 2013, 48, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakkar, M.; Guida, G.; Suleiman, M.S.; Angelini, G.D. Cardiopulmonary bypass and oxidative stress. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezzetti, A.; Pierdomenico, S.D.; Costantini, F.; Romano, F.; de Cesare, D.; Cuccurullo, F.; Imbastaro, T.; Riario-Sforza, G.; di Giacomo, F.; Zuliani, G.; et al. Copper/zinc ratio and systemic oxidant load: Effect of aging and aging-related degenerative diseases. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1998, 25, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong-ekkabut, J.; Xu, Z.; Triampo, W.; Tang, I.-M.; Tieleman, D.P.; Monticelli, L. Effect of lipid peroxidation on the properties of lipid bilayers: A molecular dynamics study. Biophys. J. 2007, 93, 4225–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poniedziałek, B.; Rzymski, P.; Pięt, M.; Gąsecka, M.; Stroińska, A.; Niedzielski, P.; Mleczek, M.; Rzymski, P.; Wilczak, M. Relation between polyphenols, malondialdehyde, antioxidant capacity, lactate dehydrogenase and toxic elements in human colostrum milk. Chemosphere 2018, 191, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, F.K.; Moriwaki, K.; de Rosa, M.J. Detection of necrosis by release of lactate dehydrogenase activity. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 979, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Falk, V.; Baumgartner, H.; Bax, J.J.; de Bonis1, M.; Hamm, C.; Holm, P.; Iung, B.; Lancellotti, P.; Lansac, E.; Mu~noz, D.R.; et al. ESC/EACTS Guidelines for the management of valvular heart disease. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2017, 52, 616–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perek, B.; Casadei, V.; Puślecki, M.; Stefaniak, S.; Maison, D.; Gwizdała, A.; Perek, A.; Szarpak, Ł.; Jemielity, M. Clinical presentation, surgical management, and outcomes of patients treated for aortic stenosis and coronary artery disease. Does age matter? Kardiol. Pol. 2018, 76, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olasinska-Wisniewska, A.; Grygier, M.; Lesiak, M.; Trojnarska, O.; Araszkiewicz, A.; Komosa, A.; Misterski, M.; Jemielity, M.; Proch, M.; Grajek, S. Short-and mid-term outcome of transcatheter aortic valve implantation in patients with advanced age. Cardiol. J. 2017, 24, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olasinska-Wisniewska, A.; Grygier, M.; Lesiak, M.; Araszkiewicz, A.; Trojnarska, O.; Komosa, A.; Misterski, M.; Jemielity, M.; Proch, M.; Grajek, S. Femoral artery anatomy-tailored approach in transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Adv. Interv. Cardiol. 2017, 13, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice-Evans, C.; Miller, N.J. Total antioxidant status in plasma and body fluids. Method Enzymol. 1994, 234, 279–293. [Google Scholar]
- Ichibori, Y.; Mizote, I.; Tsuda, M.; Mukai, T.; Maeda, K.; Onishi, T.; Kuratani, T.; Sawa, Y.; Sakata, Y. Long-Term Outcomes of High-Risk or Inoperable Patients Who Underwnet Tanscatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indolfi, C.; Bartorelli, A.L.; Berti, S.; Golino, P.; Esposito, G.; Musumeci, G.; Petronio, S.; Tamburino, C.; Tarantini, G.; Ussia, G.; et al. Updated clinical indications for transcatheter aortic valve implantation in patients with severe aortic stenosis: Expert opinion of the Italian Society of Cardiology and GISE. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 19, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.; Carson, K.; Rashid, M.K.; Jayasinghe, R.; AlQahtani, A.; Dick, A.; Glover, G.; Labinaz, M. Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation in Intermediate Surgical Risk Patients With Severe Aortic Stenosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Heart Lung Cir. 2018, 27, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusari, M.; Bona, V.; Muratori, M.; Salvi, L.; Salis, S.; Tamborini, G.; Biglioli, P. Transcatheter vs. surgical aortic valve replacement: A retrospective analysis assessing clinical effectiveness and safety. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2012, 13, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohr, R.; Dohmen, G.; Herpertz, R.; Brehmer, K.; Aktug, Ö.; Koos, R.; Altiok, E.; Stegemann, E.; Autschbach, R.; Marx, N.; et al. Thirty-day outcome after transcatheter aortic valve implantation compared with surgical valve replacement in patients with high-risk aortic stenosis: A matched comparison. Coron. Artery. Dis. 2011, 22, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heldmaier, K.; Stoppe, C.; Goetzenich, A.; Foldenauer, A.-C.; Zayat, R.; Breuer, T.; Schaelte, G. Oxidation-Reduction Potential in Patients Undergoing Transcathether or Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement. BioMed. Res. Intern. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maluenda, G.; Gormaz, J.G.; Mahmoudi, M.; Curzen, N.; Baeza, C.; Howard, M.W.; Sepulveda, E.; Erazo, M.; Valls, N.; Gajardo, A.; et al. TCT-696 Oxidative Stress Response in Patients with Severe Aortic Stenosis Undergoing Transcatheter And Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 68, B281–B282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaharalambus, C.A.; Griendling, K.K. Basic mechanisms of oxidative stress and reactive oxygen species in cardiovascular injury. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2007, 17, 48–54. [Google Scholar]
- Sena, L.A.; Chandel, N.S. Physiological roles of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. Mol. Cell. 2012, 48, 158–167. [Google Scholar]
- Komosa, A.; Rzymski, P.; Perek, B.; Ropacka-Lesiak, M.; Lesiak, M.; Siller-Matula, J.M.; Poniedziałek, B. Platelets redox balance assessment: Current evidence and methodological Considerations. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2017, 93, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungvári, Z.; Gupte, S.A.; Recchia, F.A.; Bátkai, S.; Pacher, P. Role of oxidative-nitrosative stress and downstream pathways in various forms of cardiomyopathy and heart failure. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2005, 3, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacher, P.; Schulz, R.; Liaudet, L.; Szabó, C. Nitrosative stress and pharmacological modulation of heart failure. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2005, 26, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, R.; Guardigli, G.; Mele, D.; Percoco, G.F.; Ceconi, C.; Curello, S. Oxidative stress during myocardial ischaemia and heart failure. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2004, 10, 1699–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suciu, A.; Chirulescu, Z.; Zeana, C.; Pîrvulescu, R. Study of serum ceruloplasmin and of the copper/zinc ratio in cardiovascular diseases. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 1992, 30, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]




| Variable | TAVR (n = 12) | SAVR (n = 12) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (Male) | 6 (50%) | 7 (58%) | 0.70 |
| Age (years) | 80 (± 3) | 63(± 10) | 0.0006 |
| Weight (kg) | 1.64 (± 0.06) | 1.67 (± 0.11) | 0.43 |
| Height (m) | 74.2 (± 12.3) | 78.8 (± 13.2) | 0.39 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.5 (± 4.7) | 28.2 (± 3.9) | 0.73 |
| Obesity (BMI > 30 kg/m2) | 5 (42%) | 4 (33%) | 0.69 |
| Systemic hypertension | 5 (42%) | 8 (67%) | 0.24 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 6 (50%) | 3 (34%) | 0.43 |
| Prior PCI | 5 (42%) | 3 (25%) | 0.41 |
| Prior MI | 3 (25%) | 0 | 0.08 |
| Prior stroke/TIA | 2 (17%) | 0 | 0.17 |
| Prior CABG | 2 (17%) | 1 (8%) | 0.56 |
| COPD | 2 (17%) | 1 (8%) | 0.56 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 3 (25%) | 2 (17%) | 0.63 |
| Variable | TAVR (n = 12) | SAVR (n = 12) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| WBC (10 × 9/L) | 7.5 (± 2.0) | 7.7(± 1.9) | 0.20 |
| HGB (mmol/L) | 8.2 (± 0.9) | 8.6 (± 0.9) | 0.30 |
| RBC (10 × 12/L) | 4.2 (± 0.4) | 4,5 (± 0.5) | 0.14 |
| HCT (L/L) | 0.40 (± 0.04) | 0.41 (± 0.04) | 0.56 |
| PLT (10 × 9/L) | 215 (± 115) | 207 (± 86) | 0.81 |
| CREA (µmol/L) | 98 (± 23) | 82 (± 22) | 0.08 |
| eGFR | 64.4 (± 15.5) | 80.7 (± 21.3) | 0.02 |
| ESR | 18.3 (± 15.3) | 11.8 (± 13.8) | 0.27 |
| TAC | LDH | Cu/Zn Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TAVR | |||
| TAC | −0.80 | −0.73 | |
| LDH | −0.80 | 0.57 | |
| Cu/Zn ratio | −0.73 | 0.57 | |
| SAVR | |||
| TAC | −0.88 | −0.61 | |
| LDH | −0.87 | 0.66 | |
| Cu/Zn ratio | −0.61 | 0.66 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Komosa, A.; Perek, B.; Rzymski, P.; Lesiak, M.; Siller-Matula, J.M.; Grygier, M.; Puślecki, M.; Misterski, M.; Olasińska-Wiśniewska, A.; Ropacka-Lesiak, M.; et al. Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement Is Associated with Less Oxidative Stress and Faster Recovery of Antioxidant Capacity than Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8091364
Komosa A, Perek B, Rzymski P, Lesiak M, Siller-Matula JM, Grygier M, Puślecki M, Misterski M, Olasińska-Wiśniewska A, Ropacka-Lesiak M, et al. Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement Is Associated with Less Oxidative Stress and Faster Recovery of Antioxidant Capacity than Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(9):1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8091364
Chicago/Turabian StyleKomosa, Anna, Bartłomiej Perek, Piotr Rzymski, Maciej Lesiak, Jolanta M. Siller-Matula, Marek Grygier, Mateusz Puślecki, Marcin Misterski, Anna Olasińska-Wiśniewska, Mariola Ropacka-Lesiak, and et al. 2019. "Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement Is Associated with Less Oxidative Stress and Faster Recovery of Antioxidant Capacity than Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 9: 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8091364
APA StyleKomosa, A., Perek, B., Rzymski, P., Lesiak, M., Siller-Matula, J. M., Grygier, M., Puślecki, M., Misterski, M., Olasińska-Wiśniewska, A., Ropacka-Lesiak, M., Krasiński, Z., Niedzielski, P., Mularek-Kubzdela, T., & Poniedziałek, B. (2019). Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement Is Associated with Less Oxidative Stress and Faster Recovery of Antioxidant Capacity than Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(9), 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8091364








