Containment, Contact Tracing and Asymptomatic Transmission of Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): A Modelling Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
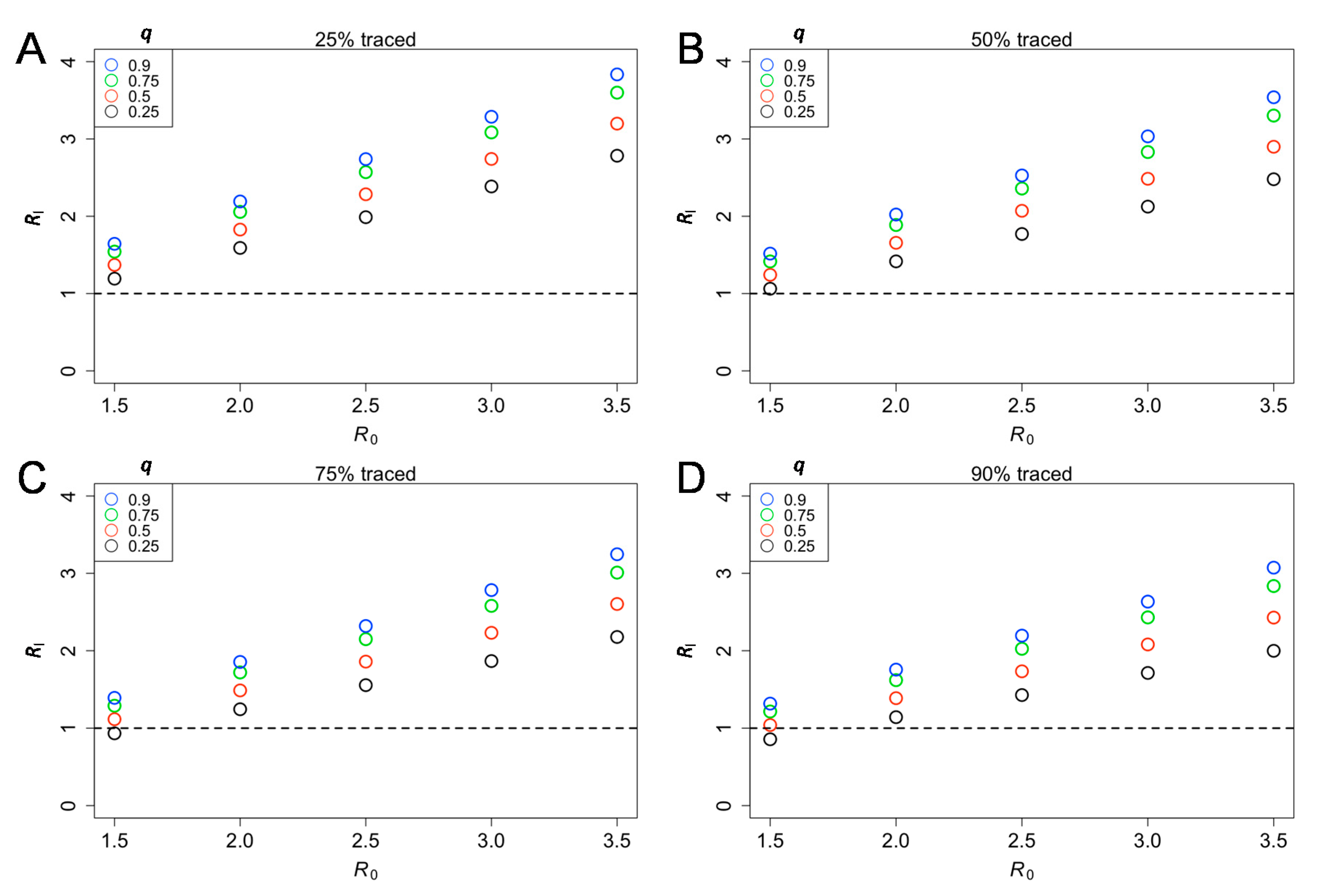
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anzai, A.; Kobayashi, T.; Linton, N.M.; Kinoshita, R.; Hayashi, K.; Suzuki, A.; Yang, Y.; Jung, S.-M.; Miyama, T.; Akhmetzhanov, A.R. Assessing the impact of reduced travel on exportation dynamics of novel coronavirus infection (COVID-19). J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiura, H.; Linton, N.M.; Akhmetzhanov, A.R. Serial interval of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) infections. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 93, 284–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Cheng, W.; Luo, L.; Ma, Y.; Xu, C.; Qin, P.; Zhang, Z. Secondary Transmission of Coronavirus Disease from Presymptomatic Persons, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1924–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiura, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Miyama, T.; Suzuki, A.; Jung, S.-M.; Hayashi, K.; Kinoshita, R.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, B.; Akhmetzhanov, A.R.; et al. Estimation of the asymptomatic ratio of novel coronavirus infections (COVID-19). Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 94, 154–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizumoto, K.; Kagaya, K.; Zarebski, A.; Chowell, G. Estimating the asymptomatic proportion of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) cases on board the Diamond Princess cruise ship, Yokohama, Japan, 2020. Euro. Surveill. 2020, 25, 2000180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oran, D.P.; Topol, E.J. Prevalence of Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Narrative Review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, M20–M3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, G.; Lim, W.; Ho, L.-M.; Lam, T.-H.; Ghani, A.; Donnelly, C.; Fraser, C.; Riley, S.; Ferguson, N.; Anderson, R. Seroprevalence of IgG antibodies to SARS-coronavirus in asymptomatic or subclinical population groups. Epidemiol. Infect. 2006, 134, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Peiris, J.S.M.; Chu, C.-M.; Cheng, V.C.-C.; Chan, K.; Hung, I.; Poon, L.L.; Law, K.-I.; Tang, B.; Hon, T.; Chan, C. Clinical progression and viral load in a community outbreak of coronavirus-associated SARS pneumonia: A prospective study. Lancet 2003, 361, 1767–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiris, J.S.; Yuen, K.Y.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Stöhr, K. The severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 2431–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, C.; Riley, S.; Anderson, R.M.; Ferguson, N.M. Factors that make an infectious disease outbreak controllable. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6146–6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadas, S.M.; Fitzpatrick, M.C.; Sah, P.; Pandey, A.; Shoukat, A.; Singer, B.H.; Galvani, A.P. The implications of silent transmission for the control of COVID-19 outbreaks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 17513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, G.; Yang, N.; Ma, A.H.Y.; Wang, L.; Li, G.; Chen, X.; Chen, X. COVID-19 Transmission Within a Family Cluster by Presymptomatic Carriers in China. Clin. Infect. Dis 2020. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, L.; Ruan, F.; Huang, M.; Liang, L.; Huang, H.; Hong, Z.; Yu, J.; Kang, M.; Song, Y.; Xia, J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load in Upper Respiratory Specimens of Infected Patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, A.; Abbott, S.; Kucharski, A.J.; Funk, S. Estimating the overdispersion in COVID-19 transmission using outbreak sizes outside China. Wellcome Open Res. 2020, 5, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellewell, J.; Abbott, S.; Gimma, A.; Bosse, N.I.; Jarvis, C.I.; Russell, T.W.; Munday, J.D.; Kucharski, A.J.; Edmunds, W.J.; Sun, F. Feasibility of controlling COVID-19 outbreaks by isolation of cases and contacts. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e488–e496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peak, C.M.; Kahn, R.; Grad, Y.H.; Childs, L.M.; Li, R.; Lipsitch, M.; Buckee, C.O. Individual quarantine versus active monitoring of contacts for the mitigation of COVID-19: A modelling study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 209, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharski, A.J.; Klepac, P.; Conlan, A.; Kissler, S.M.; Tang, M.; Fry, H.; Gog, J.; Edmunds, J.; Group, C.C.-W. Effectiveness of isolation, testing, contact tracing and physical distancing on reducing transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in different settings. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeling, M.J.; Hollingsworth, T.D.; Read, J.M. The Efficacy of Contact Tracing for the Containment of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19). J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2020, 74, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, L.; Wymant, C.; Kendall, M.; Zhao, L.; Nurtay, A.; Abeler-Dörner, L.; Parker, M.; Bonsall, D.; Fraser, C. Quantifying SARS-CoV-2 transmission suggests epidemic control with digital contact tracing. Science 2020, 368, eabb6938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, M.S.; Mandl, K.D. Early in the epidemic: Impact of preprints on global discourse about COVID-19 transmissibility. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e627–e630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Lau, E.H.; Wu, P.; Deng, X.; Wang, J.; Hao, X.; Lau, Y.C.; Wong, J.Y.; Guan, Y.; Tan, X. Temporal dynamics in viral shedding and transmissibility of COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 672–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.N.; Gilligan, C.A.; Cunniffe, N.J. Detecting Presymptomatic Infection Is Necessary to Forecast Major Epidemics in the Earliest Stages of Infectious Disease Outbreaks. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1004836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucharski, A.J.; Edmunds, W.J. Characterizing the transmission potential of zoonotic infections from minor outbreaks. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiura, H.; Cook, A.J.; Cowling, B.J. Assortativity and the Probability of Epidemic Extinction: A Case Study of Pandemic Influenza A (H1N1-2009). Interdiscip. Perspect. Infect. Dis. 2011, 2011, 194507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Smith, J.O.; Schreiber, S.J.; Kopp, P.E.; Getz, W.M. Superspreading and the effect of individual variation on disease emergence. Nature 2005, 438, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, D.C.; Wu, P.; Wong, J.Y.; Lau, E.H.Y.; Tsang, T.K.; Cauchemez, S.; Leung, G.M.; Cowling, B.J. Clustering and superspreading potential of SARS-CoV-2 infections in Hong Kong. Nat. Med. 2020, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riou, J.; Althaus, C.L. Pattern of early human-to-human transmission of Wuhan 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), December 2019 to January 2020. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, N.G. Analysis of Infectious Disease Data; CRC Press: Cleaveland, OH, USA, 1989; Volume 33. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, R.M.; Heesterbeek, H.; Klinkenberg, D.; Hollingsworth, T.D. How will country-based mitigation measures influence the course of the COVID-19 epidemic? Lancet 2020, 395, 931–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiura, H.; Schwehm, M.; Kakehashi, M.; Eichner, M. Transmission potential of primary pneumonic plague: Time inhomogeneous evaluation based on historical documents of the transmission network. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2006, 60, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiura, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Yang, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Miyama, T.; Kinoshita, R.; Linton, N.M.; Jung, S.M.; Yuan, B.; Suzuki, A.; et al. The Rate of Underascertainment of Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Infection: Estimation Using Japanese Passengers Data on Evacuation Flights. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kinoshita, R.; Anzai, A.; Jung, S.-m.; Linton, N.M.; Miyama, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Hayashi, K.; Suzuki, A.; Yang, Y.; Akhmetzhanov, A.R.; et al. Containment, Contact Tracing and Asymptomatic Transmission of Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): A Modelling Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3125. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103125
Kinoshita R, Anzai A, Jung S-m, Linton NM, Miyama T, Kobayashi T, Hayashi K, Suzuki A, Yang Y, Akhmetzhanov AR, et al. Containment, Contact Tracing and Asymptomatic Transmission of Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): A Modelling Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(10):3125. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103125
Chicago/Turabian StyleKinoshita, Ryo, Asami Anzai, Sung-mok Jung, Natalie M. Linton, Takeshi Miyama, Tetsuro Kobayashi, Katsuma Hayashi, Ayako Suzuki, Yichi Yang, Andrei R. Akhmetzhanov, and et al. 2020. "Containment, Contact Tracing and Asymptomatic Transmission of Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): A Modelling Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 10: 3125. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103125
APA StyleKinoshita, R., Anzai, A., Jung, S.-m., Linton, N. M., Miyama, T., Kobayashi, T., Hayashi, K., Suzuki, A., Yang, Y., Akhmetzhanov, A. R., & Nishiura, H. (2020). Containment, Contact Tracing and Asymptomatic Transmission of Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): A Modelling Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(10), 3125. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103125






