Application of A Convolutional Neural Network in The Diagnosis of Gastric Mesenchymal Tumors on Endoscopic Ultrasonography Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Training and Test Image Datasets
2.2. Histopathology
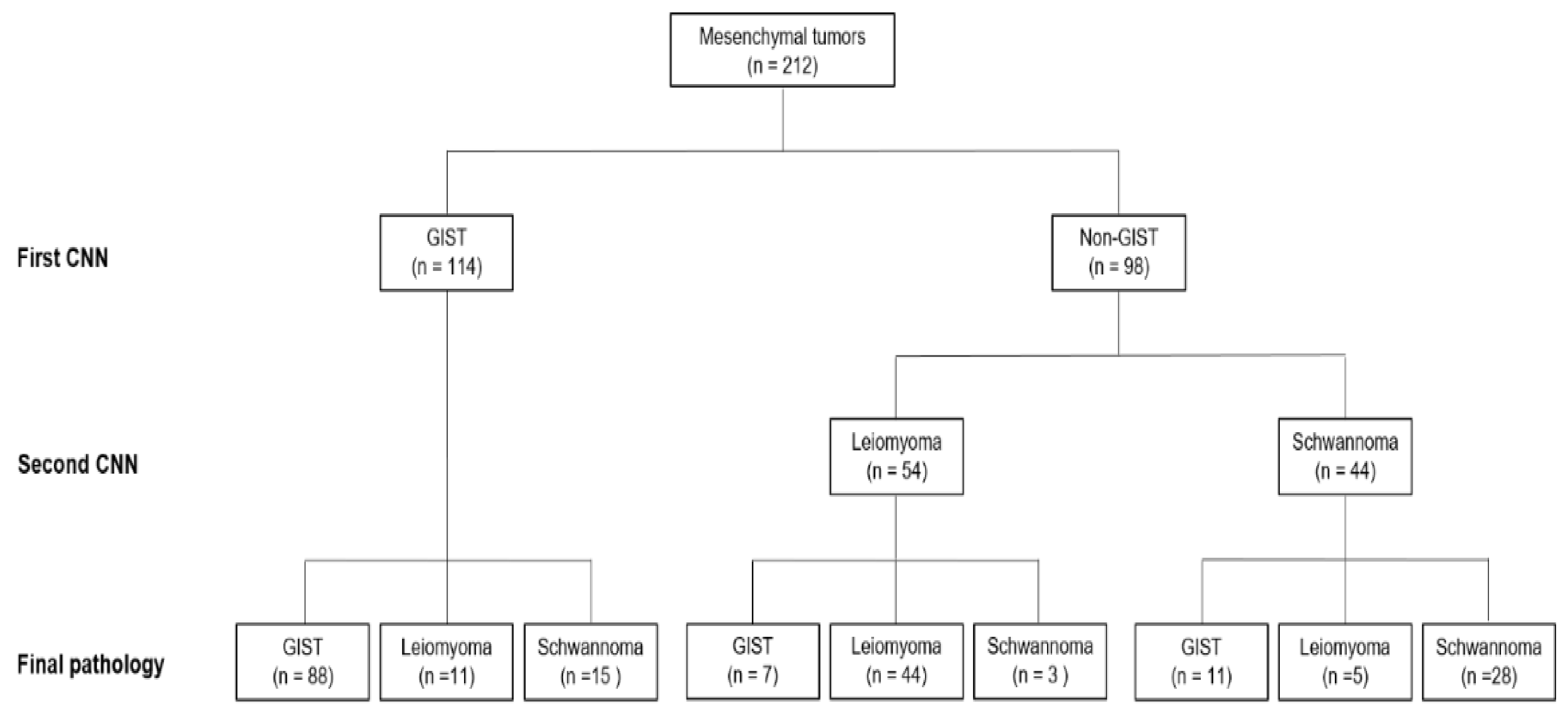
2.3. Mesenchymal Tumor Classification Algorithm
2.3.1. Tumor Dataset Generation
2.3.2. Dataset Configuration
2.3.3. CNN Algorithm Construction to Develop a Tumor Classification Model
2.4. Outcome Measures
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
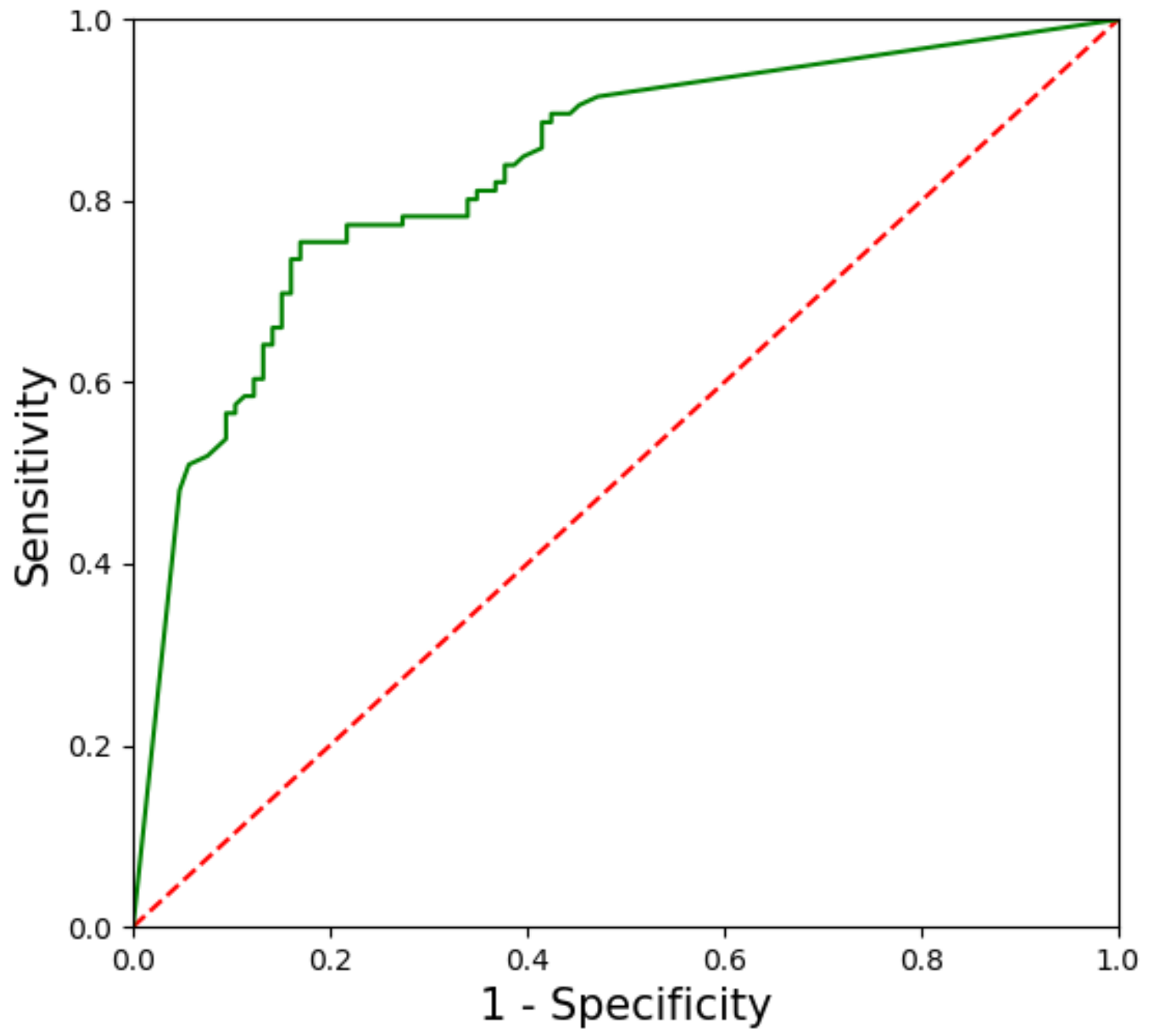
3.1. Performance of the CNN-CAD System in the Training Dataset
3.2. Performance of the CNN-CAD System in the Test Dataset
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, M.W.; Kim, G.H.; Kim, K.B.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, D.Y.; Choi, C.I.; Kim, D.H.; Jeon, T.Y. Digital image analysis-based scoring system for endoscopic ultrasonography is useful in predicting gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Gastric Cancer 2019, 22, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.L.; Ahn, Y.W.; Lee, K.N.; Jun, D.W.; Lee, O.Y.; Han, D.S.; Yoon, B.C.; Choi, H.S. Prevalence of gastric subepithelial tumors in Korea: A single center experience. Korean J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 66, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarlomo-Rikala, M.; Kovatich, A.J.; Barusevicius, A.; Miettinen, M. CD117: A sensitive marker for gastrointestinal stromal tumors that is more specific than CD34. Mod. Pathol. 1998, 11, 728–734. [Google Scholar]
- Pidhorecky, I.; Cheney, R.T.; Kraybill, W.G.; Gibbs, J.F. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: Current diagnosis, biologic behavior, and management. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2000, 7, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miettinen, M.; Sobin, L.H.; Sarlomo-Rikala, M. Immunohistochemical spectrum of GISTs at different sites and their differential diagnosis with a reference to CD117 (KIT). Mod. Pathol. 2000, 13, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blay, J.Y.; Bonvalot, S.; Casali, P.; Choi, H.; Debiec-Richter, M.; Dei Tos, A.P.; Emile, J.F.; Gronchi, A.; Hogendoorn, P.C.; Joensuu, H.; et al. Consensus meeting for the management of gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Report of the GIST Consensus Conference of 20–21 March 2004, under the auspices of ESMO. Ann. Oncol. 2005, 16, 566–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, M.; Sobin, L.H.; Lasota, J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors of the stomach: A clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic study of 1765 cases with long-term follow-up. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2005, 29, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, C.D.; Berman, J.J.; Corless, C.; Gorstein, F.; Lasota, J.; Longley, B.J.; Miettinen, M.; O’Leary, T.J.; Remotti, H.; Rubin, B.P.; et al. Diagnosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: A consensus approach. Hum. Pathol. 2002, 33, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demetri, G.D.; von Mehren, M.; Antonescu, C.R.; DeMatteo, R.P.; Ganjoo, K.N.; Maki, R.G.; Pisters, P.W.; Raut, C.P.; Riedel, R.F.; Schuetze, S.; et al. NCCN Task Force report: Update on the management of patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors. J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw. 2010, 8 (Suppl. 2), S1–S41, quiz S42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Soft Tissue Sarcoma. Version 2.2020. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/sarcoma.pdf (accessed on 16 September 2010).
- Chak, A.; Canto, M.I.; Rosch, T.; Dittler, H.J.; Hawes, R.H.; Tio, T.L.; Lightdale, C.J.; Boyce, H.W.; Scheiman, J.; Carpenter, S.L.; et al. Endosonographic differentiation of benign and malignant stromal cell tumors. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1997, 45, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzo, L.; Landi, B.; Cellier, C.; Cuillerier, E.; Roseau, G.; Barbier, J.P. Endosonographic features predictive of benign and malignant gastrointestinal stromal cell tumours. Gut 2000, 46, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.H.; Park do, Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, D.H.; Choi, C.W.; Heo, J.; Song, G.A. Is it possible to differentiate gastric GISTs from gastric leiomyomas by EUS? World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 3376–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okai, T.; Minamoto, T.; Ohtsubo, K.; Minato, H.; Kurumaya, H.; Oda, Y.; Mai, M.; Sawabu, N. Endosonographic evaluation of c-kit-positive gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Abdom. Imaging 2003, 28, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Catalano, M.F.; Sivak, M.V., Jr.; Bedford, R.A.; Falk, G.W.; van Stolk, R.; Presa, F.; Van Dam, J. Observer variation and reproducibility of endoscopic ultrasonography. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1995, 41, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gress, F.; Schmitt, C.; Savides, T.; Faigel, D.O.; Catalano, M.; Wassef, W.; Roubein, L.; Nickl, N.; Ciaccia, D.; Bhutani, M.; et al. Interobserver agreement for EUS in the evaluation and diagnosis of submucosal masses. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2001, 53, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.H.; Kim, K.B.; Lee, S.H.; Jeon, H.K.; Park, D.Y.; Jeon, T.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Song, G.A. Digital image analysis of endoscopic ultrasonography is helpful in diagnosing gastric mesenchymal tumors. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mori, Y.; Kudo, S.E.; Mohmed, H.E.N.; Misawa, M.; Ogata, N.; Itoh, H.; Oda, M.; Mori, K. Artificial intelligence and upper gastrointestinal endoscopy: Current status and future perspective. Dig. Endosc. 2019, 31, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruffle, J.K.; Farmer, A.D.; Aziz, Q. Artificial intelligence-assisted gastroenterology-promises and pitfalls. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In NIPS’12 Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2012; Volume 1, pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C.H.; Kim, G.H.; Lee, B.E.; Song, G.A.; Park, D.Y.; Choi, K.U.; Kim, D.H.; Jeon, T.Y. Two staging systems for gastrointestinal stromal tumors in the stomach: Which is better? BMC Gastroenterol. 2017, 17, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, S.C.; Gatt, A.; Stamatescu, V.; McDonnell, M.D. Understanding data augmentation for classification: When to warp? In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA), Gold Coast, QLD, Australia, 30 November–2 December 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, E.; Uhl, A.; Wimmer, G.; Hafner, M. Exploring deep learning and transfer learning for colonic polyp classification. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2016, 2016, 6584725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, Q.C.; Xu, M.D.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, J.; Zhong, Y.S.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Chen, W.F.; Yao, L.Q.; Zhou, P.H.; et al. Application of convolutional neural network in the diagnosis of the invasion depth of gastric cancer based on conventional endoscopy. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2019, 89, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.M.; Kim, G.H.; Park, D.Y.; Shin, N.R.; Ahn, S.; Park, C.H.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, K.J.; Lee, B.E.; Song, G.A. Endosonographic features of gastric schwannoma: A single center experience. Clin. Endosc. 2016, 49, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.H.; Rulyak, S.D.; Kimmey, M.B.; American Gastroenterological Association Institute. American Gastroenterological Association Institute technical review on the management of gastric subepithelial masses. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 2217–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, T.; Blay, J.Y.; Hirota, S.; Kitagawa, Y.; Kang, Y.K. The standard diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of gastrointestinal stromal tumors based on guidelines. Gastric Cancer 2016, 19, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirasawa, T.; Aoyama, K.; Tanimoto, T.; Ishihara, S.; Shichijo, S.; Ozawa, T.; Ohnishi, T.; Fujishiro, M.; Matsuo, K.; Fujisaki, J.; et al. Application of artificial intelligence using a convolutional neural network for detecting gastric cancer in endoscopic images. Gastric Cancer 2018, 21, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Characteristics | Training Dataset (n = 179) | Test Dataset (n = 69) |
|---|---|---|
| Age, Years (mean ± SD) | 57.7 ± 11.9 | 56.9 ± 13.7 |
| Sex | ||
| Male | 80 (44.7) | 31 (44.9) |
| Female | 99 (55.3) | 38 (55.1) |
| Tumor Location | ||
| Upper | 105 (58.7) | 43 (62.3) |
| Middle | 57 (31.8) | 21 (30.4) |
| Lower | 17 (9.5) | 5 (7.2) |
| Tumor Size, cm (mean ± SD) | 3.6 ± 2.1 | 3.2 ± 1.6 |
| Final Histopathology | ||
| Leiomyoma | 33 (18.4) | 23 (33.3) |
| Schwannoma | 21 (11.7) | 14 (20.3) |
| Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor | 125 (69.8) | 32 (46.4) |
| Very Low Risk | 27 | 7 |
| Low Risk | 50 | 14 |
| Intermediate Risk | 29 | 7 |
| High Risk | 19 | 4 |
| CNN-CAD System | Endoscopists | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experienced 1 | Experienced 2 | Experienced 3 | Junior 1 | Junior 2 | Junior 3 | ||
| Sensitivity, % | 83.0 (77.4–87.5) | 83.0 (77.4–87.5) | 74.5 (68.3–79.9) | 71.7 (65.3–77.3) | 84.0 (78.4–88.3) | 73.6 (67.3–79.1) | 84.9 (79.5–89.1) |
| Specificity, % | 75.5 (69.3–80.8) | 68.9 (62.3–74.7) | 61.3 * (54.6–67.6) | 56.6 * (49.9–63.1) | 63.2 (56.5–69.4) | 77.4 (71.3–82.5) | 53.8 * (47.1–60.4) |
| Positive predictive value, % | 77.2 (71.1–82.3) | 72.7 (66.4–78.3) | 65.8 (59.2–71.9) | 62.3 * (55.6–68.5) | 69.5 (63.0–75.3) | 76.5 (70.3–81.7) | 64.7 * (58.1–70.9) |
| Negative predictive value, % | 81.6 (75.9–86.3) | 80.2 (74.3–85.0) | 70.7 (64.2–76.4) | 66.7 * (60.1–72.7) | 79.8 (73.8–84.6) | 74.5 (68.3–79.9) | 78.1 (72.0–83.1) |
| Accuracy, % | 79.2 (73.3–84.2) | 75.9 (69.8–81.2) | 67.9 * (61.4–73.8) | 64.2 * (57.5–70.3) | 73.6 (67.3–79.1) | 75.5 (69.3–80.8) | 69.3 * (62.8–75.2) |
| CNN-CAD System | Endoscopists | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experienced 1 | Experienced 2 | Experienced 3 | Junior 1 | Junior 2 | Junior 3 | ||
| Accuracy, % | 75.5 (69.3–80.8) | 72.6 (66.3–78.2) | 61.8 * (55.1–68.1) | 59.0 * (52.2–65.4) | 67.0 (60.4–73.0) | 68.4 (61.9–74.3) | 66.0 * (59.4–72.1) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.H.; Kim, G.H.; Kim, K.B.; Lee, M.W.; Lee, B.E.; Baek, D.H.; Kim, D.H.; Park, J.C. Application of A Convolutional Neural Network in The Diagnosis of Gastric Mesenchymal Tumors on Endoscopic Ultrasonography Images. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3162. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103162
Kim YH, Kim GH, Kim KB, Lee MW, Lee BE, Baek DH, Kim DH, Park JC. Application of A Convolutional Neural Network in The Diagnosis of Gastric Mesenchymal Tumors on Endoscopic Ultrasonography Images. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(10):3162. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103162
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Yoon Ho, Gwang Ha Kim, Kwang Baek Kim, Moon Won Lee, Bong Eun Lee, Dong Hoon Baek, Do Hoon Kim, and Jun Chul Park. 2020. "Application of A Convolutional Neural Network in The Diagnosis of Gastric Mesenchymal Tumors on Endoscopic Ultrasonography Images" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 10: 3162. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103162
APA StyleKim, Y. H., Kim, G. H., Kim, K. B., Lee, M. W., Lee, B. E., Baek, D. H., Kim, D. H., & Park, J. C. (2020). Application of A Convolutional Neural Network in The Diagnosis of Gastric Mesenchymal Tumors on Endoscopic Ultrasonography Images. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(10), 3162. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103162







