Cardiac Autonomic Modulation Is Different in Terms of Clinical Variant of Multiple Sclerosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Participants
2.2. Cardiac and Autonomic Measures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cardiac and Autonomic Assessment: Comparisons MS and Control Group
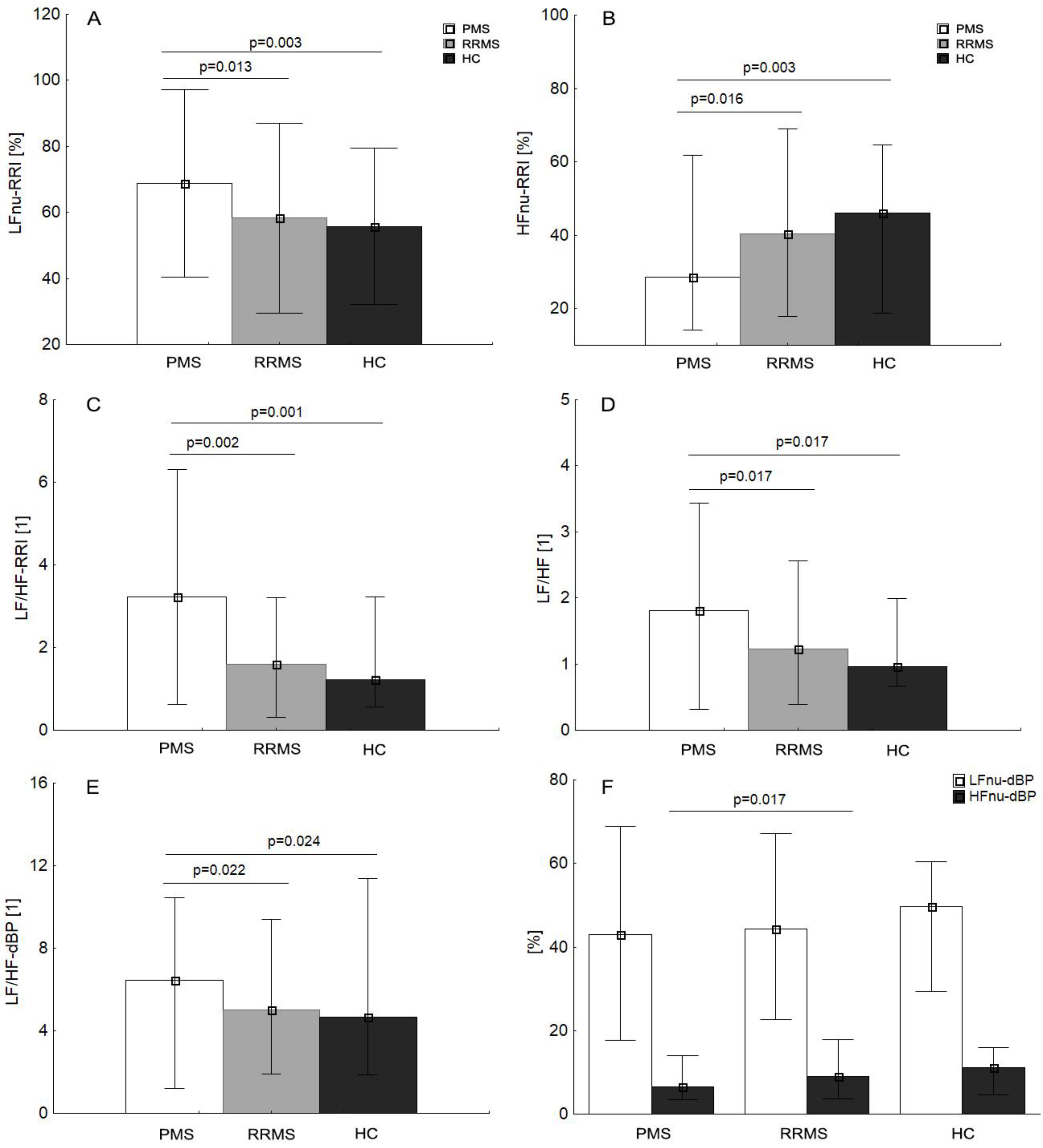
3.2. Cardiac and Autonomic Assessment: Comparison Clinical Variant of MS and Control Group
3.3. Relationship between Cardiovascular and Autonomic Parameters, Disease Duration and EDSS Score
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Age | EDSS | Disease Duration | HR | sBP | dBP | mBP | Delta HR | Delta sBP | Delta dBP | Delta mBP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 1.00 | 0.46 ** | 0.44 ** | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.29 * | 0.19 | −0.35 * | −0.04 | −0.26 | −0.13 |
| HR (1/min) | 0.00 | 0.37 ** | 0.04 | 1.00 | 0.12 | 0.21 | 0.17 | −0.04 | −0.18 | −0.20 | −0.23 |
| sBP (mmHg) | 0.04 | 0.23 | −0.18 | 0.12 | 1.00 | 0.83 ** | 0.93 *** | −0.15 | −0.13 | 0.02 | −0.12 |
| dBP (mmHg) | 0.29 * | 0.47 ** | 0.05 | 0.21 | 0.83 *** | 1.00 | 0.96 ** | −0.27 | −0.15 | −0.13 | −0.18 |
| mBP (mmHg) | 0.19 | 0.38 ** | −0.05 | 0.17 | 0.93 *** | 0.96 *** | 1.00 | −0.23 | −0.14 | −0.08 | −0.14 |
| LFnu-RRI (ms2) | 0.24 | 0.16 | 0.24 | 0.37 ** | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.17 | −0.15 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.12 |
| HFnu-RRI (ms2) | −0.23 | −0.16 | −0.24 | −0.36 * | −0.14 | −0.19 | −0.17 | 0.14 | −0.03 | −0.10 | −0.13 |
| LF-RRI (ms2) | −0.32 * | −0.25 | −0.07 | −0.54 *** | 0.01 | −0.17 | −0.11 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.32 * | 0.22 |
| HF-RRI (ms2) | −0.34 * | −0.25 | −0.18 | −0.58 *** | −0.04 | −0.22 | −0.16 | 0.19 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.03 |
| PSD-RRI (ms2) | −0.30 * | −0.22 | −0.08 | −0.59 *** | 0.02 | −0.15 | −0.08 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.22 | 0.16 |
| LF/HF-RRI [1] | 0.25 | 0.18 | 0.26 | 0.39 ** | 0.13 | 0.19 | 0.17 | −0.13 | −0.01 | 0.05 | 0.08 |
| LF/HF [1] | 0.02 | 0.16 | 0.20 | 0.40 ** | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.01 | −0.07 | 0.05 | 0.03 |
| LFnu-dBP (%) | −0.25 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.22 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.17 | −0.22 | −0.09 | −0.13 |
| HFnu-dBP (%) | −0.53 *** | −0.34 * | −0.18 | −0.14 | 0.13 | −0.04 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.12 | 0.01 |
| LF-dBP (%) | −0.13 | −0.12 | −0.14 | −0.21 | 0.17 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 0.11 | 0.25 | 0.21 |
| HF-dBP (%) | −0.36 * | −0.34 * | −0.24 | −0.31 * | 0.16 | −0.05 | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.26 | 0.40 ** | 0.30 * |
| PSD-dBP (mmHg2) | −0.05 | −0.17 | −0.15 | −0.30 * | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.35 * | 0.32 * |
| LF/HF-dBP | 0.31 * | 0.30 * | 0.21 | 0.19 | −0.10 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.02 | −0.14 | −0.16 | −0.06 |
| LF/HF | 0.02 | 0.16 | 0.20 | 0.40 ** | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.01 | −0.07 | 0.05 | 0.03 |
| LFnu-sBP (%) | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.23 | 0.13 | 0.23 | 0.22 | −0.01 | −0.22 | −0.18 | −0.12 |
| HFnu-sBP (%) | −0.17 | −0.30 * | −0.19 | −0.04 | −0.05 | −0.09 | −0.10 | 0.03 | −0.10 | −0.07 | −0.15 |
| LF-sBP (%) | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.01 | −0.12 | 0.17 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0.18 | 0.16 |
| HF-sBP (%) | −0.05 | −0.20 | −0.11 | −0.23 | 0.07 | −0.02 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.16 | 0.06 |
| PSD-sBP (mmHg2) | 0.07 | −0.09 | −0.03 | −0.24 | 0.08 | −0.03 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.26 | 0.29 | 0.24 |
| LF/HF-sBP [1] | 0.19 | 0.31 * | 0.20 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.19 | 0.19 | −0.02 | −0.05 | −0.02 | 0.05 |
| LF/HF [1] | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.41 ** | 0.16 | 0.27 | 0.24 | −0.09 | −0.08 | −0.01 | 0.03 |
| BRS (ms/mmHg) | −0.33 * | −0.21 | −0.08 | −0.28 | −0.35 * | −040 ** | −0.39 ** | 0.13 | −0.04 | −0.01 | −0.02 |
| Total BEI (%) | −0.07 | 0.05 | −0.16 | −0.16 | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.01 | −0.11 | −005 | −0.10 |
| Age | EDSS | Disease Duration | HR | sBP | dBP | mBP | Delta HR | Delta sBP | Delta dBP | Delta mBP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Delta HR (1/min) | −0.35 * | −0.15 | −0.26 | −0.04 | −0.15 | −0.27 | −0.23 | 1.00 | 0.08 | 0.19 | 0.07 |
| Delta sBP (mmHg) | −0.04 | −0.07 | −0.03 | −0.18 | −0.13 | −0.15 | −0.14 | 0.08 | 1.00 | 0.84 *** | 0.90 *** |
| Delta dBP (mmHg) | −0.26 | −0.20 | −0.13 | −0.20 | 0.02 | −0.13 | −0.08 | 0.19 | 0.84 *** | 1.00 | 0.89 *** |
| Delta mBP (mmHg) | −0.13 | −0.13 | 0.01 | −0.23 | −0.12 | −0.18 | −0.14 | 0.07 | 0.90 *** | 0.89 *** | 1.00 |
| Delta LFnu-RRI (ms2) | −0.45 *** | −0.22 | −0.17 | −0.14 | 0.08 | −0.08 | −0.01 | 0.41 ** | −0.04 | 0.04 | −0.09 |
| Delta HFnu-RRI (ms2) | 0.45 ** | 0.22 | 0.17 | 0.14 | −0.08 | 0.08 | 0.01 | −0.41 ** | 0.04 | −0.04 | 0.09 |
| Delta LF-RRI (ms2) | 0.07 | 0.12 | −0.04 | 0.46 *** | −0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | −0.08 | 0.11 | −0.08 | −0.05 |
| Delta HF-RRI (ms2) | 0.38 * | 0.26 | 0.20 | 0.45 *** | −0.08 | 0.10 | 0.04 | −0.31 * | 0.10 | −0.07 | 0.06 |
| Delta PSD-RRI (ms2) | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.52 *** | −0.07 | 0.04 | 0.00 | −0.19 | 0.07 | −0.07 | −0.05 |
| Delta LF/HF-RRI [1] | −0.32 * | −0.12 | −0.03 | 0.11 | 0.16 | −0.02 | 0.05 | 0.34 * | −0.07 | 0.08 | −0.06 |
| Delta LF/HF [1] | −0.31 * | −0.13 | −0.08 | 0.18 | 0.16 | −0.04 | 0.05 | 0.39 ** | −0.07 | 0.13 | −0.04 |
| Delta LFnu-dBP (%) | −0.23 | −0.11 | −0.08 | 0.11 | −0.09 | −0.20 | −0.13 | 0.30 * | 0.11 | 0.18 | 0.16 |
| Delta HFnu-dBP (%) | 0.31 * | 0.23 | 0.10 | 0.26 | −0.21 | −0.11 | −0.15 | 0.07 | −0.09 | −0.20 | −0.16 |
| Delta LF-dBP (%) | −0.10 | −0.03 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.21 | 0.04 | 0.12 | −0.14 | 0.12 | 0.18 | 0.22 |
| Delta HF-dBP (%) | 0.25 | 0.34 * | 0.10 | 0.35 * | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.11 | −0.18 | −0.10 | −0.17 | −0.10 |
| PSD-dBP (mmHg2) | 0.03 | 0.22 | 0.17 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.21 | −0.35 * | −0.09 | −0.07 | −0.05 |
| Delta LF/HF-dBP | −0.23 | −0.22 | 0.01 | −0.19 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.07 | −0.04 | 0.13 | 0.29 ** | 0.26 |
| Delta LF/HF | −0.31 * | −0.13 | −0.08 | 0.18 | 0.16 | −0.04 | 0.05 | 0.39 ** | −0.07 | 0.13 | −0.04 |
| Delta LFnu-sBP (%) | −0.32 * | −0.14 | −0.17 | 0.07 | 0.13 | −0.07 | 0.04 | 0.27 | 0.26 | 0.41 ** | 0.30 * |
| Delta HFnu-sBP (%) | 0.12 | 0.17 | −0.06 | 0.26 | −0.15 | −0.10 | −0.15 | 0.31 * | −0.03 | −0.04 | −0.09 |
| Delta LF-sBP (%) | −0.15 | −0.12 | −0.10 | 0.00 | 0.16 | −0.04 | 0.06 | −0.03 | 0.21 | 0.26 | 0.25 |
| Delta HF-sBP (%) | 0.18 | 0.23 | 0.04 | 0.25 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | −0.07 | −0.10 | −0.06 |
| Delta PSD-sBP (mmHg2) | −0.05 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.18 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.13 | −0.25 | −0.13 | −0.12 | −0.05 |
| Delta LF/HF-sBP [1] | −0.25 | −0.30 * | −0.08 | −0.20 | 0.09 | −0.05 | 0.03 | −0.09 | 0.13 | 0.21 | 0.20 |
| Delta LF/HF [1] | −0.27 | −0.12 | −0.06 | 0.15 | 0.20 | −0.01 | 0.09 | 0.33 * | −0.02 | 0.16 | −0.01 |
References
- Leray, E.; Yaouanq, J.; Le Page, E.; Coustans, M.; Laplaud, D.; Oger, J.; Edan, G. Evidence for a two-stage disability progression in multiple sclerosis. Brain 2010, 133, 1900–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Confavreux, C.; Vukusic, S. Natural history of multiple sclerosis: A unifying concept. Brain 2006, 129, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremenchutzky, M.; Wingerchuk, D.M.; Rice, G.P.A.; Baskerville, J.; Ebers, G. The natural history of multiple sclerosis: A geographically based study 9: Observations on the progressive phase of the disease. Brain 2006, 129, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkish Multiple Sclerosis Study Group (TUMSSG). Survival and predictors of disability in Turkish MS patients. Neurology 1998, 51, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutuncu, M.; Tang, J.; Zeid, N.A.; Kale, N.; Crusan, D.J.; Atkinson, E.J.; Siva, A.; Pittock, S.J.; Pirko, I.; Keegan, B.M.; et al. Onset of progressive phase is an age-dependent clinical milestone in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2012, 19, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racosta, J.M.; Kimpinski, K. Autonomic dysfunction, immune regulation, and multiple sclerosis. Clin. Auton. Res. 2015, 26, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Videira, G.; Castro, P.; Vieira, B.; Filipe, J.P.; Santos, R.; Azevedo, E.; Paula-Barbosa, M.; Abreu, P. Autonomic dysfunction in multiple sclerosis is better detected by heart rate variability and is not correlated with central autonomic network damage. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 367, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habek, M. Immune and autonomic nervous system interactions in multiple sclerosis: Clinical implications. Clin. Auton. Res. 2019, 29, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamec, I.; Crnošija, L.; Junaković, A.; Skorić, M.K.; Habek, M. Progressive multiple sclerosis patients have a higher burden of autonomic dysfunction compared to relapsing remitting phenotype. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2018, 129, 1588–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studer, V.; Rocchi, C.; Motta, C.; Lauretti, B.; Perugini, J.; Brambilla, L.; Centonze, D. Heart rate variability is diferentially altered in multiple sclerosis: Implications for acute. worsening and progressive disability. Mult. Scler. J. Exp. Transl. Clin. 2017, 3, 2055217317701317. [Google Scholar]
- Flachenecker, P.; Reiners, K.; Krauser, M.; Wolf, A.; Toyka, K.V. Autonomic dysfunction in multiple sclerosis is related to disease activity and progression of disability. Mult. Scler. J. 2001, 7, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.P.; Young, C.N.; Fadel, P.J. Central sympathetic overactivity: Maladies and mechanisms. Auton. Neurosci. 2009, 148, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suorsa, E.; Korpelainen, J.T.; Ansakorpi, H.; Huikuri, H.V.; Suorsa, V.; Myllylä, V.V.; Isojärvi, J.I. Heart rate dynamics in temporal lobe epilepsy—A long-term follow-up study. Epilepsy Res. 2011, 93, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Seze, J.; Stojkovic, T.; Gauvrit, J.-Y.; Devos, D.P.; Ayachi, M.; Cassim, F.; Michel, T.S.; Pruvo, J.-P.; Guieu, J.-D.; Vermersch, P. Autonomic dysfunction in multiple sclerosis: Cervical spinal cord atrophy correlates. J. Neurol. 2001, 248, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilz, M.J. Cardiac stunning as first manifestation of multiple sclerosis: A case report reminding us not to overlook cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2016, 22, 847–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cygankiewicz, I.; Zareba, W. Chapter 31—Heart rate variability. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology Autonomic Nervous System; Buijs, R.M., Swaab, D.F., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 117, pp. 379–393. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, W.I.; Compston, A.; Edan, G.; Goodkin, N.; Hartung, H.-P.; Lublin, F.D.; McFarland, H.F.; Paty, N.W.; Polman, C.H.; Reingold, S.C.; et al. Recommended diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: Guidelines from the International Panel on the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2001, 50, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polman, C.H.; Reingold, S.C.; Banwell, B.; Clanet, M.; Cohen, J.A.; Filippi, M.; Fujihara, K.; Havrdova, E.K.; Hutchinson, M.; Kappos, L.; et al. Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2010 Revisions to the McDonald criteria. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 69, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lublin, F.D.; Reingold, S.C. Defining the clinical course of multiple sclerosis: Results of an international survey. Neurology 1996, 46, 907–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtzke, J.F. Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: An expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 1983, 33, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neurostatus Scoring. Available online: https://www.neurostatus.net/media/specimen/Definitions_0410-2_s.pdf (accessed on 21 August 2020).
- Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Assessment clinical autonomic testing report of the therapeutics and technology subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 1996, 46, 873–880. [Google Scholar]
- Schwalm, T. Modern Tilt Table Testing and Non-Invasive Monitoring. Traditional and Innovative Applications in Theory and Practice; ABW Wissenschaftsverlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Fortin, J.; Klinger, T.; Wagner, C.; Sterner, H.; Madritsch, C.; Grüllenberger, R.; Hacker, A.; Habenbacher, W.; Skrabal, F. The task force monitor—A non-invasive beat-to beat monitor for hemodynamic and autonomic function of the human body. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Hong Kong, China, 1 November 1998; Volume 66, pp. 63–151. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, A.M.; Mainardi, L.; Meloni, C.; Chierchiu, S.; Cerutti, S. Continuous monitoring of the sympatho-vagal balance through spectral analysis. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 1997, 16, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlögl, A.; Flotzinger, D.; Pfurtscheller, G. Adaptive Autoregressive Modeling used for Single-trial EEG Classification—Verwendung eines Adaptiven Autoregressiven Modells für die Klassifikation von Einzeltrial-EEG-Daten. Biomed. Tech. 1997, 42, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parati, G.; Di Rienzo, M.; Mancia, G. How to measure baroreflex sensitivity: From the cardiovascular laboratory to daily life. J. Hypertens. 2000, 18, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lees, T.; Shad-Kaneez, F.; Simpson, A.M.; Nassif, N.T.; Lin, Y.; Lal, S. Heart Rate Variability as a Biomarker for Predicting Stroke, Post-stroke Complications and Functionality. Biomark. Insights 2018, 13, 1177271918786931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taskforce of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Heart rate variability: Standards of measurement. physiological interpretation. and clinical use. Eur. Heart J. 1996, 17, 354–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Rüdiger, H.; Ziemssen, T. Spectral Analysis of Heart Rate Variability: Time Window Matters. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/.2012/01/20 (accessed on 21 August 2020).
- The Consensus Committee of the American Autonomic Society and the American Academy of Neurology. Consensus statement on the definition of orthostatic hypotension, pure autonomic failure, and multiple system atrophy. Neurology 1996, 46, 1470. [Google Scholar]
- Monge-Argilés, J.A.; Palacios-Ortega, F.; Vila-Sobrino, J.A.; Matías-Guiu, J. Heart rate variability in multiple sclerosis during a stable phase. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1998, 97, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezinova, M.; Goldenberg, Z.; Kucera, P. Autonomic nervous system dysfunction in multiple sclerosis patients. Bratisl Lek List. 2004, 105, 404–407. [Google Scholar]
- Damla, O.; Altug, C.; Pinar, K.K.; Alper, K.; Dilek, I.G.; Kadriye, A. Heart rate variability analysis in patients with multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2018, 24, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahovic, D.; Lakušić, N. Progressive Impairment of Autonomic Control of Heart Rate in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Arch. Med. Res. 2007, 38, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tombul, T.; Anlar, O.; Tuncer, M.; Huseyinoglu, N.; Eryonucu, B. Impaired heart rate variability as a marker of cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction in multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2011, 111, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sternberg, Z. Impaired Neurovisceral Integration of Cardiovascular Modulation Contributes to Multiple Sclerosis Morbidities. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanya, E.O.; Tutaj, M.; Brown, C.M.; Goel, N.; Neundörfer, B.; Hilz, M.J.; Sanya, E.O. Abnormal heart rate and blood pressure responses to baroreflex stimulation in multiple sclerosis patients. Clin. Auton. Res. 2005, 15, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habek, M.; Crnošija, L.; Lovrić, M.; Junaković, A.; Skorić, M.K.; Adamec, I. Sympathetic cardiovascular and sudomotor functions are frequently affected in early multiple sclerosis. Clin. Auton. Res. 2016, 26, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbardella, E.; Petsas, N.; Tona, F.; Prosperini, L.; Raz, E.; Pace, G.; Pozzilli, C.; Pantano, P. Assessing the correlationbetween grey and white matter damage with motor and cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis patients. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63250. [Google Scholar]
- Hilz, M.J.; Devinsky, O.; Szczepanska, H.; Borod, J.C.; Marthol, H.; Tutaj, M. Right ventromedial prefrontal lesions result in paradoxical cardiovascular activation with emotional stimuli. Brain 2006, 129, 3343–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winder, K.; Linker, R.A.; Seifert, F.; Wang, R.; Lee, D.; Engelhorn, T.; Dörfler, A.; Fröhlich, K.; Hilz, M. Cerebral lesion correlates of sympathetic cardiovascular activation in multiple sclerosis. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2019, 40, 5083–5093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, M.J.; Ganta, C.K. Autonomic Nervous System and Immune System Interactions. Compr. Physiol. 2014, 4, 1177–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woiciechowsky, C.; Asadullah, K.; Nestler, D.; Eberhardt, B.; Platzer, C.; Schöning, B.; Glöckner, F.; Lanksch, W.R.; Volk, H.-D.; Döcke, W.-D. Sympathetic activation triggers systemic interleukin-10 release in immunodepression induced by brain injury. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 808–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabi, S.; Hassan, Z.M.; Jazani, N.H.; Ebtekar, M. Sympathetic nervous system plays an important role in the relationship between immune mediated diseases. Med. Hypotheses 2006, 67, 900–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellinger, D.L.; Lorton, D. Sympathetic Nerve Hyperactivity in the Spleen: Causal for Nonpathogenic-Driven Chronic Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases (IMIDs)? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynders, T.; Gidron, Y.; De Ville, J.; Bjerke, M.; Weets, I.; Van Remoortel, A.; Devolder, L.; D’Haeseleer, M.; De Keyser, J.; Nagels, G.; et al. Relation between Heart Rate Variability and Disease Course in Multiple Sclerosis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, D.L.; Bristow, M.R. Mechanisms and models in heart failure: The biomechanical model and beyond. Circulation 2005, 111, 2837–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floras, J.S. Sympathetic nervous system activation in human heart failure: Clinical implications of an updated model. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olindo, S.; Guillon, B.; Helias, J.; Phillibert, B.; Magne, C.; Feve, J.R. Decrease in heart ventricular ejection fraction during multiple sclerosis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2002, 9, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, D.S. Statistical considerations for reporting and planning heart rate variability case-control studies. Psychophysiology 2017, 54, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, S.; Pecchia, L. Heart Rate Variability (HRV) Analysis: A Methodology for Organizational Neuroscience. Organ. Res. Methods 2019, 22, 354–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findling, O.; Hauer, L.; Pezawas, T.; Rommer, P.S.; Struhal, W.; Sellner, J. Cardiac Autonomic Dysfunction in Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Review of Current Knowledge and Impact of Immunotherapies. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porumb, M.; Iadanza, E.; Massaro, S.; Pecchia, L. A convolutional neural network approach to detect congestive heart failure. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2020, 55, 101597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| MS Patients | HC | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of subjects | 49 | 25 | |
| Age (years) | 46.0 ± 11.0 | 42.3 ± 12.4 | 0.164 |
| Sex (male/female) | 10/39 | 5/20 | 0.967 |
| MS variant, n (%) | |||
| RRMS | 28 (57.1%) | ||
| SPMS | 17 (34.7%) | ||
| PPMS | 4 (6.1%) | ||
| Disease duration (years), mean (range) | 10.1 ± 7.2 (0.5–28) | ||
| EDSS score | 3.5 ± 1.0 (0.5–7) | ||
| Mild | 26 (53.6%) | ||
| Moderate | 14 (28.6%) | ||
| Severe | 9 (18.4%) | ||
| Localization of the First Demyelinating Lesions, n (%) | |||
| Supratentorial and optic nerves | 32 (65.3%) | ||
| Spinal cord | 12 (24.5%) | ||
| Cerebellum | 4 (8.2%) | ||
| Brain stem | 1 (2.0%) | ||
| Autonomic symptoms, n (%) | |||
| Orthostatic disorders | 32 (65.3%) | 3 (12.0%) | <0.001 |
| Vertigo | 30 (61.2%) | 1 (4.0%) | <0.001 |
| Arrhythmia | 13 (26.5%) | 3 (12.0%) | 0.150 |
| Vasomotor disorders | 8 (17.0%) | 4 (16%) | 0.911 |
| Secretory disorders | 10 (20.4%) | 1 (4.0%) | 0.060 |
| Thermoregulatory disorders | 17 (34.7%) | 1 (4.0%) | 0.036 |
| Stomach ache | 17 (34.6%) | 1 (4.0%) | 0.047 |
| Constipation | 8 (16.3%) | 4 (16.0%) | 0.971 |
| Diarrhea | 21 (42.9%) | 1 (4%) | <0.001 |
| Postmeal symptoms | 7 (14.3%) | 1 (4%) | 0.047 |
| Urinary bladder dysfunctions | 21 (42.9%) | 1 (4%) | <0.001 |
| Sexual dysfunction | 15 (30.6%) | 0 (0%) | 0.008 |
| Sleep disorders | 23 (46.9%) | 5 (20.0%) | 0.023 |
| Pupillary disorders | 26 (53.1%) | 1 (4%) | <0.001 |
| Group | MS | HC |
|---|---|---|
| Cardiac autonomic tests | n (%) | n (%) |
| Blood pressure response to standing (fall in BP in mmHg) | ||
| Normal | 47 (96%) | 25 (100%) |
| Abnormal (OH) | 2 (4%) | 0 (0%) |
| Heart rate response to standing (increase in HR in bpm/min) | ||
| Normal | 47 (96%) | 25 (100%) |
| Abnormal (POTS) | 2 (4%) | 0 (0%) |
| Group | MS | HC | MS | HC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Delta (change baseline-tilt) | |||
| Cardiac data | ||||
| HR (1/min) | 66.5 ± 7.3 | 66.3 ± 9.2 | 12.7 ± 7.7 | 14.2 ± 8.1 |
| sBP (mmHg) | 1134.0 ± 12.0 | 115.0 ± 11.4 | 12.1 ± 14.2 | 11.7 ± 9.9 |
| dBP (mmHg) | 73.4 ± 8.9 | 75.3 ± 8.5 | 16.1 ± 11.5 | 14.6 ± 8.0 |
| mBP (mmHg) | 90.4 ± 9.8 | 92.5 ± 9.2 | 16.1 ± 16.8 | 13.1 ± 8.5 |
| Heart rate variability (HRV) | ||||
| LFnu-RRI (ms2) | 62.8 ± 15.1 | 55.7 ± 11.8 * | 12.1 ± 15.0 | 13.7 ± 17.0 |
| HFnu-RRI (ms2) | 37.3 ± 15.0 | 44.3. ± 11.8 * | −12.2 ± 14.9 | −13.7 ± 17.0 |
| LF-RRI (ms2) | 746.6 ± 896.0 | 619.7 ± 514.9 | −281.4 ± 895.2 | −44.7 ± 498.0 |
| HF-RRI (ms2) | 507.9 ± 703.0 | 575.3 ± 668.5 | −381.5 ± 659.5 | −342.4 ± 550.4 |
| PSD-RRI (ms2) | 1713.8 ± 1700.8 | 1538.3 ± 1262.5 | −955.8 ± 1573.8 | −432.3 ± 1024.6 |
| LF/HF-RRI [1] | 2.4 ± 1.5 | 1.6 ± 0.9 * | 2.4 ± 3.0 | 1.8 ± 2.5 |
| LF/HF [1] | 1.5 ± 0.9 | 1.3 ± 0.7 | 1.6 ± 2.0 | 1.5 ± 1.5 |
| Systolic and diastolic pressure variability (BPV) | ||||
| LFnu-dBP (%) | 43.7 ± 12.2 | 48.5 ± 11.9 | 6.9 ± 8.8 | 3.5 ± 11.8 |
| HFnu-dBP (%) | 9.1 ± 3.9 | 11.1 ± 4.7 * | 0.8 ± 2.3 | 0.4 ± 3.4 |
| LF-dBP (%) | 3.9 ± 2.6 | 4.1 ± 3.5 | −0.4 ± 1.0 | −0.9 ± 1.7 |
| HF-dBP (%) | 0.8 ± 0.7 | 0.9 ± 0.8 | −0.2 ± 0.3 | −0.2 ± 0.3 |
| PSD-dBP (mmHg2) | 8.8 ± 5.2 | 8.2 ± 5.9 | −2.0 ± 1.8 | −1.6 ± 2.7 |
| LF/HF-dBP | 5.7 ± 2.6 | 5.2 ± 2.5 | 0.4 ± 2.0 | 0.6 ± 2.6 |
| LF/HF | 1.5 ± 0.9 | 1.3 ± 0.7 * | 1.6 ± 2.0 | 1.2 ± 1.5 |
| LFnu-sBP (%) | 43.2 ± 12.1 | 42.2 ± 12.0 | 9.0 ± 11.6 | 5.9 ± 11.0 |
| HFnu-sBP (%) | 11.5 ± 6.8 | 12.6 ± 6.8 | 3.2 ± 4.9 | 2.2 ± 4.4 |
| LF-sBP (%) | 6.0 ± 5.6 | 6.3 ± 6.2 | −0.4 ± 2.1 | −1.5 ± 2.7 * |
| HF-sBP (%) | 1.4 ± 1.0 | 1.8 ± 1.9 | −0.1 ± 0.5 | −0.4 ± 0.7 * |
| PSD-sBP (mmHg2) | 135 ± 9.5 | 14.0 ± 11.2 | −3.3 ± 3.5 | −4.1 ± 4.9 |
| LF/HF-sBP [1] | 4.8 ± 2.6 | 4.1 ± 1.7 | −0.1 ± 1.7 | 0.1 ± 1.5 |
| LF/HF [1] | 1.5 ± 0.9 | 1.1 ± 0.7 | 1.7 ± 2.1 | 1.2 ± 1.5 |
| BRS (ms/mmHg) | 60.0 ± 21.5 | 69.3 ± 19.3 | - | - |
| Total BEI (%) | 15.8 ± 11.4 | 18.7 ± 10.2 | - | - |
| Group | RRMS | PMS | HC | RRMS | PMS | HC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Delta (change baseline-tilt) | |||||
| Cardiac data | ||||||
| HR (1/min) | 64.3 ± 7.4 | 69.4 ± 6.2 | 66.3 ± 9.2 | 13.8 ± 8.1 | 11.2 ± 6.2 | 14.2 ± 8.1 |
| sBP (mmHg) | 110.6 ± 11.1 | 117.2 ± 12.5 | 115.0 ± 11.4 | 141 ± 9.9 | 9.5 ± 12.5 | 11.7 ± 9.9 |
| dBP (mmHg) | 70.0 ± 8.1 | 77.9 ± 8.0 * | 75.3 ± 8.5 | 19.0 ± 8.0 | 12.4 ± 8.0 | 14.6 ± 8.0 |
| mBP (mmHg) | 87.3 ± 8.9 | 94.5 ± 9.7 * | 92.5 ± 9.2 | 16.8 ± 8.5 | 15.2 ± 9.7 | 13.1 ± 8.5 |
| Heart rate variability (HRV) | ||||||
| LFnu-RRI (ms2) | 58.3 ± 14.3 | 68.9 ± 14.2 * | 55.7 ± 11.8 | 15.8 ± 17.0 | 7.1 ± 14.2 | 13.7 ± 17.0 |
| HFnu-RRI (ms2) | 41.7 ± 14.3 | 31.4 ± 14.1 * | 44.3 ± 11.8 | −15.8 ± 17.0 | −7.4 ± 14.1 | −13.7 ± 17.0 |
| LF-RRI (ms2) | 790.1 ± 645.3 | 688.5 ± 1165.5 | 619.7 ± 514.9 | −363.1 ± 498.0 | −172.4 ± 1165.5 | −44.7 ± 498.0 |
| HF-RRI (ms2) | 675.1 ± 851.3 | 285.1 ± 341.3 * | 575.3 ± 668.5 | −544.7 ± 550.4 | −163.9 ± 341.3 * | −342.4 ± 550.4 |
| PSD-RRI (ms2) | 2044.4 ± 1749.0 | 1273.0 ± 1566.9 | 1538.3 ± 1262.5 | −1304.6 ± 1024.6 | −490.8 ± 1566.9 | −432.3 ± 1024.6 |
| LF/HF-RRI [1] | 1.8 ± 1.1 | 3.1 ± 1.7 * | 1.6 ± 0.9 | 2.4 ± 2.5 | 2.5 ± 1.7 | 1.8 ± 2.5 |
| LF/HF [1] | 1.3 ± 0.7 | 1.8 ± 1.0 * | 1.3 ± 0.7 | 1.5 ± 1.5 | 1.7 ± 1.0 | 1.5 ± 1.5 |
| Systolic and diastolic pressure variability (BPV) | ||||||
| LFnu-dBP (%) | 44.3 ± 11.1 | 42.9 ± 13.8 | 48.5 ± 11.9 | 8.0 ± 11.8 | 5.5 ± 13.8 | 3.5 ± 11.8 |
| HFnu-dBP (%) | 10.2 ± 3.9 | 7.6 ± 3.5 * | 11.1 ± 4.7 | 0.3 ± 3.4 | 1.4 ± 3.5 | 0.4 ± 3.4 |
| LF-dBP (%) | 3.8 ± 1.9 | 3.9 ± 3.4 | 4.1 ± 3.5 | −0.4 ± 1.7 | −0.4 ± 3.4 | −0.9 ± 1.7 |
| HF-dBP (%) | 0.9 ± 0.8 | 0.6 ± 0.5 | 0.9 ± 0.8 | −0.2 ± 0.3 | −0.1 ± 0.5 | −0.2 ± 0.3 |
| PSD-dBP (mmHg2) | 8.9 ± 4.8 | 8.6 ± 5.8 | 8.2 ± 5.9 | −2.0 ± 2.7 | −2.0 ± 5.8 | −1.6 ± 2.7 |
| LF/HF-dBP | 5.1 ± 2.4 | 6.6 ± 2.7 * | 5.2 ± 2.5 | 0.7 ± 2.6 | −0.0 ± 2.7 | 0.6 ± 2.6 |
| LF/HF | 1.3 ± 0.7 | 1.8 ± 1.0 * | 1.3 ± 0.7 | 1.5 ± 1.5 | 1.7 ± 1.0 | 1.2 ± 1.5 |
| LFnu-sBP (%) | 40.7 ± 10.3 | 46.5 ± 13.7 * | 42.2 ± 12.0 | 11.5 ± 11.0 | 5.7 ± 13.7 | 5.9 ± 11.0 |
| HFnu-sBP (%) | 11.5 ± 5.4 | 11.5 ± 8.5 | 12.6 ± 6.8 | 2.8 ± 4.4 | 3.7 ± 8.5 | 2.2 ± 4.4 |
| LF-sBP (%) | 5.2 ± 2.6 | 7.2 ± 8.1 | 6.3 ± 6.2 | −0.1 ± 2.7 | −0.7 ± 8.1 | −1.5 ± 2.7 |
| HF-sBP (%) | 1.4 ± 0.8 | 1.5 ± 1.3 | 1.8 ± 1.9 | −0.1 ± 0.7 | 0.1 ± 1.3 | −0.4 ± 0.7 |
| PSD-sBP (mmHg2) | 13.3 ± 7.40 | 13.9 ± 12.0 | 14.0 ± 11.2 | −3.5 ± 4.9 | −2.9 ± 12.0 | −4.1 ± 4.9 |
| LF/HF-sBP [1] | 4.3 ± 2.0 | 5.5 ± 3.1 | 4.1 ± 1.7 | 0.4 ± 1.5 | −0.7 ± 3.1 | 0.1 ± 1.5 |
| LF/HF [1] | 1.2 ± 0.6 | 2.0 ± 1.1 | 1.1 ± 0.7 | 1.7 ± 1.5 | 1.8 ± 1.1 | 1.2 ± 1.5 |
| BRS (ms/mmHg) | 58.9 ± 20.4 | 61.4 ± 23.5 | 69.3 ± 19.3 | - | - | - |
| Total BEI (%) | 18.5 ± 12.8 | 12.2 ± 7.9 | 18.7 ± 10.2 | - | - | - |
| Dependent Variables | Independent Variables | β | SE | t | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR R = 0.45; R2 = 0.20 F(4.42) = 2.7; p < 0.042 | Sex | 0.02 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.880 |
| Variant | 0.33 | 0.22 | 1.48 | 0.147 | |
| Age | −0.28 | 0.16 | −1.72 | 0.093 | |
| EDSS | 0.22 | 0.20 | 1.11 | 0.272 | |
| dBP R = 0.6; R2 = 0.36 F(4.42) = 16.67; p < 0.001 | Sex * | 0.44 | 0.15 | 3.04 | 0.004 |
| Variant | −0.05 | 0.20 | −0.25 | 0.804 | |
| Age | 0.04 | 0.14 | 0.28 | 0.782 | |
| EDSS | 0.30 | 0.18 | 1.67 | 0.103 | |
| mBP R = 0.49; R2 = 0.24 F(4.42) = 3.33; p < 0.018 | Sex * | 0.37 | 0.16 | 2.35 | 0.023 |
| Variant | −0.02 | 0.22 | −0.07 | 0.944 | |
| Age | −0.05 | 0.16 | −0.34 | 0.736 | |
| EDSS | 0.25 | 0.19 | 1.27 | 0.210 | |
| LFnu-RRI R = 0.48; R2 = 0.23 F(4.42) = 3.18; p < 0.022 | Sex | 0.14 | 0.16 | 0.88 | 0.384 |
| Variant | 0.43 | 0.22 | 1.93 | 0.061 | |
| Age | 0.22 | 0.16 | 1.37 | 0.179 | |
| EDSS | −0.30 | 0.19 | −1.57 | 0.125 | |
| HFnu-RRI R = 0.47; R2 = 0.22 F(4.42) = 2.97; p < 0.029 | Gender | −0.13 | 0.16 | −0.79 | 0.432 |
| Variant | −0.42 | 0.22 | −1.91 | 0.063 | |
| Age | −0.21 | 0.16 | −1.30 | 0.202 | |
| EDSS | 0.30 | 0.20 | 1.51 | 0.138 | |
| LF/HF-RRI R = 0.49; R2 = 0.24 F(4.42) = 3.36; p < 0.017 | Sex | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.93 | 0.356 |
| Variant * | 0.48 | 0.22 | 2.20 | 0.033 | |
| Age | 0.08 | 0.16 | 0.52 | 0.607 | |
| EDSS | −0.21 | 0.19 | −1.08 | 0.286 | |
| LF/HF R = 0.38; R2 = 0.15 F(4.42) = 6.1096; p < 0.143 | Gender | 0.11 | 0.17 | 0.65 | 0.519 |
| Variant | 0.38 | 0.23 | 1.63 | 0.110 | |
| Age | −0.05 | 0.17 | −0.27 | 0.786 | |
| EDSS | −0.07 | 0.21 | −0.34 | 0.738 | |
| LF/HF-dBP R = 0.40; R2 = 0.16 F(1.53) = 10.23; p < 0.01 | Sex | −0.26 | 0.15 | −1.70 | 0.097 |
| Variant | 0.25 | 0.21 | 1.18 | 0.245 | |
| Age | 0.25 | 0.15 | 1.62 | 0.113 | |
| EDSS | 0.20 | 0.19 | 1.06 | 0.296 | |
| HF-RRI R = 0.43; R2 = 0.19 F(1.53) = 2.4; p < 0.064 | Sex | 0.08 | 0.16 | 0.50 | 0.623 |
| Variant | −0.33 | 0.23 | −1.46 | 0.152 | |
| Age * | −0.34 | 0.16 | −2.10 | 0.041 | |
| EDSS | 0.28 | 0.20 | 1.38 | 0.174 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zawadka-Kunikowska, M.; Rzepiński, Ł.; Newton, J.L.; Zalewski, P.; Słomko, J. Cardiac Autonomic Modulation Is Different in Terms of Clinical Variant of Multiple Sclerosis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3176. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103176
Zawadka-Kunikowska M, Rzepiński Ł, Newton JL, Zalewski P, Słomko J. Cardiac Autonomic Modulation Is Different in Terms of Clinical Variant of Multiple Sclerosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(10):3176. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103176
Chicago/Turabian StyleZawadka-Kunikowska, Monika, Łukasz Rzepiński, Julia L. Newton, Paweł Zalewski, and Joanna Słomko. 2020. "Cardiac Autonomic Modulation Is Different in Terms of Clinical Variant of Multiple Sclerosis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 10: 3176. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103176
APA StyleZawadka-Kunikowska, M., Rzepiński, Ł., Newton, J. L., Zalewski, P., & Słomko, J. (2020). Cardiac Autonomic Modulation Is Different in Terms of Clinical Variant of Multiple Sclerosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(10), 3176. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103176






