Retinal Vascular Features in Ocular Blunt Trauma by Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography
2.3. Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography
2.4. Statistical Analysis
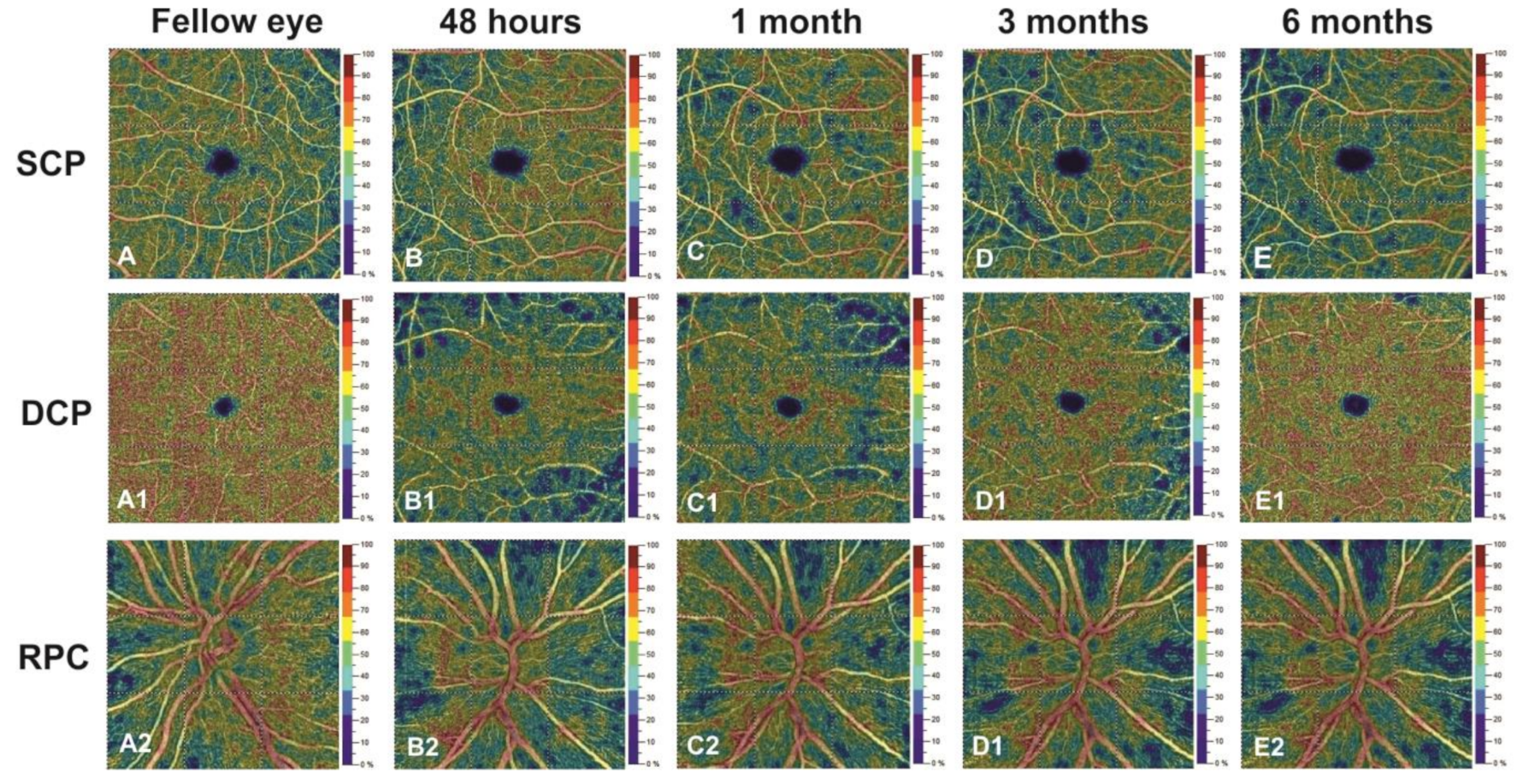
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Souza-Santos, F.; Lavinsky, D.; Moraes, N.S.; Castro, A.R.; Cardillo, J.A.; Farah, M.E. Spectral-domain optical coherence tomography in patients with commotio retinae. Retina 2012, 32, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, A.M.; Green, W.R.; Hogge, C. Histopathology of commotio retinae. Retina 1992, 12, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.; Jung, J.H.; Moon, S.W.; Song, S.J.; Yu, H.G.; Cho, H.Y. Commotio retinae with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Retina 2011, 31, 2044–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, S.; Campos, A.; Campos, J.; Neves, A.; Beselga, D.; Fernandes, C.; Castro Sousa, J.P. Cutting edge of traumatic maculopathy with spectral—Domain optical coherence tomography—A review. Med. Hypothesis Discov. Innov. Ophthalmol. 2015, 4, 56–63. [Google Scholar]
- Cennamo, G.; Forte, R.; Reibaldi, M.; Magli, A.; de Crecchio, G.; Cennamo, G. Evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer and ganglion cell complex thickness after ocular blunt trauma. Eye 2013, 27, 1382–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cunha, L.P.; Costa-Cunha, L.V.; Malta, R.F.; Monteiro, M.L. Comparison between retinal nerve fiber layer and macular thickness measured with OCT detecting progressive axonal loss following traumatic optic neuropathy. Arq. Bras. Oftalmol. 2009, 72, 622–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamori, A.; Nakamura, M.; Yamada, Y.; Negi, A. Longitudinal study of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and ganglion cell complex in traumatic optic neuropathy. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2012, 130, 1067–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Murphy, O.; Gonzalez Caldito, N.; Calabresi, P.A.; Saidha, S. Emerging Applications of Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography (OCTA) in neurological research. Eye Vis. 2018, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kniestedt, C.; Stamper, R.L. Visual acuity and its measurement. Ophthalmol. Clin. N. Am. 2003, 16, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cennamo, G.; Montorio, D.; Velotti, N.; Sparnelli, F.; Reibaldi, M.; Cennamo, G. Optical coherence tomography angiography in pre-perimetric open-angle glaucoma. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2017, 255, 1787–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Tan, O.; Tokayer, J.; Potsaid, B.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.J.; Kraus, M.F.; Subhash, H.; Fujimoto, J.G.; Hornegger, J.; et al. Split-spectrum amplitude-decorrelation angiography with optical coherence tomography. Opt. Express. 2012, 20, 4710–4725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, D.; Jia, Y.; Gao, S.S.; Lumbroso, B.; Rispoli, M. Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography Using the Optovue Device. Dev. Ophthalmol. 2016, 56, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, H.L.; Pradhan, Z.S.; Weinreb, R.N.; Reddy, H.B.; Riyazuddin, M.; Dasari, S.; Palakurthy, M.; Puttaiah, N.K.; Rao, D.A.; Webers, C.A. Regional Comparisons of Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography Vessel Density in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 171, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moein, H.R.; Novais, E.A.; Rebhun, C.B.; Cole, E.D.; Louzada, R.N.; Witkin, A.J.; Baumal, C.R.; Duker, J.S.; Waheed, N.K. Optical coherence tomography angiography to detect macular capillary ischemia in patients with inner retinal changes after resolved diabetic. Retina 2018, 38, 2277–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.P.; Zhang, M.; Hwang, T.S.; Bailey, S.T.; Wilson, D.J.; Jia, Y.; Huang, D. Detailed Vascular Anatomy of the Human Retina by Projection-Resolved Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cioffi, G.A. Ischemic model of optic nerve injury. Trans. Am. Ophthalmol. Soc. 2005, 103, 592–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichi, F.; Sarraf, D.; Morara, M.; Mazumdar, S.; Neri, P.; Gupta, V. Pearls and pitfalls of optical coherence tomography angiography in the multimodal evaluation of uveitis. J. Ophthalmic Inflamm. Infect. 2017, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, A.M.; Shields, C.L. Microvascular capillary plexus findings of commotion retinae on optical coherence tomography angiography. Case Rep. Ophthalmol. 2018, 9, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangsathaporn, K.; Tsui, I. Commotio retinae resulting from rubber band injury in two girls. Ophthalmic Surg. Lasers Imaging Retin. 2019, 50, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, E.; Voutsas, N.; Kotoula, M.; Dastiridou, A.; Tsironi, E.E.; Androudi, S. Optical coherence tomography angiography reveals vascular alterations in pediatric commotio retinae. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blight, R.; Hart, J.C. Structural changes in the outer retinal layers following blunt mechanical non-perforating trauma to the globe: An experimental study. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1977, 61, 573–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sipperley, J.O.; Quigley, H.A.; Gass, D.M. Traumatic retinopathy in primates. The explanation of commotio retinae. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1978, 96, 2267–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Control Group | 48 Hours | 1 Month | 3 Months | 6 Months | ANOVA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | ||||||
| GCC (µm) | ||||||
| Average | 105.55 ± 7.45 | 105.38 ± 7.56 | 94.55 ± 6.38 | 88.05 ± 5.76 | 88.11 ± 5.76 | <0.001 |
| Superior | 106.66 ± 7.95 | 106.38 ± 7.94 | 94.66 ± 5.43 | 90.61 ± 3.03 | 90.72 ± 3.04 | <0.001 |
| Inferior | 104.16 ± 7.83 | 104.05 ± 7.99 | 94.22 ± 6.69 | 86.38 ± 4.27 | 86.50 ± 4.28 | <0.001 |
| RNFL (µm) | ||||||
| Average | 110.44 ± 4.74 | 110.55 ± 5.54 | 109.50 ± 5.61 | 98.33 ± 3.80 | 98.61 ± 5.58 | <0.001 |
| Superior | 112.45 ± 6.59 | 111.46 ± 5.78 | 110.88 ± 6.07 | 100.27 ± 5.73 | 99.05 ± 3.42 | <0.001 |
| Inferior | 108.50 ± 4.66 | 106.27 ± 4.86 | 105.77 ± 5.09 | 96.38 ± 6.16 | 99.72 ± 5.73 | <0.001 |
| Control Group | 48 Hours | 1 Month | 3 Months | 6 Months | ANOVA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | ||||||
| SCP (%) | ||||||
| Whole Image | 51.38 ± 4.47 | 51.45 ± 4.28 | 46.12 ± 5.95 | 44.45 ± 4.65 | 44.23 ± 4.09 | <0.001 |
| Parafovea | 53.77 ± 4.58 | 52.61 ± 4.59 | 47.50 ± 6.01 | 46.55 ± 4.67 | 46.11 ± 5.36 | <0.001 |
| Fovea | 27.94 ± 4.33 | 26.55 ± 4.35 | 23.35 ± 4.29 | 22.53 ± 4.53 | 22.12 ± 5.12 | <0.001 |
| DCP (%) | ||||||
| Whole Image | 55.72 ± 5.22 | 48.33 ± 5.17 | 54.38 ± 4.23 | 55.16 ± 4.55 | 55.50 ± 4.41 | <0.001 |
| Parafovea | 58.55 ± 3.46 | 53.23 ± 4.53 | 57.95 ± 5.90 | 58.06 ± 4.15 | 58.23 ± 5.32 | 0.005 |
| Fovea | 43.16 ± 2.97 | 35.21 ± 3.32 | 41.26 ± 6.54 | 41.16 ± 5.99 | 42.82 ± 3.67 | <0.001 |
| FAZ (mm2) | 0.310 ± 0.14 | 0.308 ± 0.15 | 0.311 ± 0.18 | 0.309 ± 0.12 | 0.307 ± 0.10 | 0.998 |
| RPC (%) | ||||||
| Whole Image | 55.55 ± 4.09 | 55.21 ± 6.09 | 54.08 ± 3.98 | 46.31 ± 3.72 | 46.13 ± 5.01 | <0.001 |
| Inside Disc | 51.88 ± 3.49 | 50.19 ± 4.68 | 50.20 ± 4.21 | 44.86 ± 3.90 | 43.88 ± 3.18 | <0.001 |
| Peripapillary Region | 54.44 ± 3.11 | 54.31 ± 3.71 | 53.52 ± 3.77 | 45.75 ± 3.85 | 45.75 ± 4.16 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montorio, D.; D’Andrea, L.; Cennamo, G. Retinal Vascular Features in Ocular Blunt Trauma by Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3329. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103329
Montorio D, D’Andrea L, Cennamo G. Retinal Vascular Features in Ocular Blunt Trauma by Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(10):3329. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103329
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontorio, Daniela, Luca D’Andrea, and Gilda Cennamo. 2020. "Retinal Vascular Features in Ocular Blunt Trauma by Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 10: 3329. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103329
APA StyleMontorio, D., D’Andrea, L., & Cennamo, G. (2020). Retinal Vascular Features in Ocular Blunt Trauma by Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(10), 3329. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103329






