Covid-19-Associated Coagulopathy: Biomarkers of Thrombin Generation and Fibrinolysis Leading the Outcome
Abstract
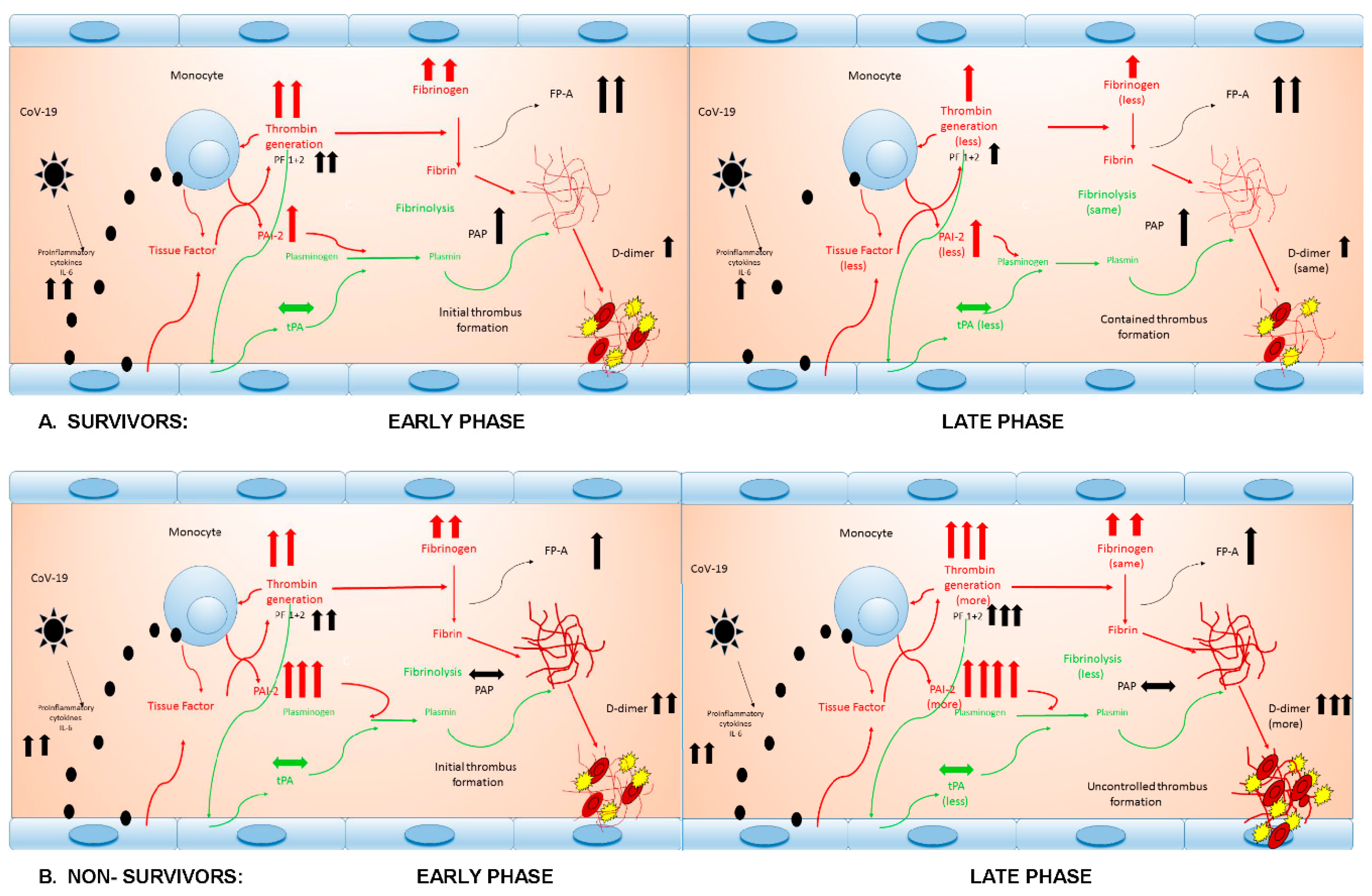
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patient Population and Treatments
2.2. Measurements
2.3. Outcome Assessment
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Thrombin Generation
4.2. Fibrinogen and Fibrin Generation
4.3. Fibrinolysis Activation
4.4. Fibrinolysis Inhibition
4.5. The Net Effect on Fibrinolysis
4.6. Thromboembolism, Mortality and Its Predictors and Therapeutic Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, N.; Zhou, M.; Dong, X.; Qu, J.; Gong, F.; Han, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Wei, Y.; et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. Lancet 2020, 395, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, N.; Li, D.; Wang, X.; Sun, Z. Abnormal coagulation parameters are associated with poor prognosis in patients with novel coronavirus pneumonia. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1233–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fogarty, H.; Townsend, L.; Cheallaigh, C.; Bergin, C.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Browne, P.; Bacon, C.L.; Gaule, R.; Gillett, A.; Byrne, M.; et al. COVID-19 Coagulopathy in Caucasian patients. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 189, 1044–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollias, A.; Kyriakoulis, K.G.; Dimakakos, E.; Poulakou, G.; Stergiou, G.S.; Syrigos, K. Thromboembolic risk and anticoagulant therapy in COVID-19 patients: Emerging evidence and call for action. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 189, 846–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranucci, M.; Ballotta, A.; Di Dedda, U.; Bayshnikova, E.; Poli, M.D.; Resta, M.; Falco, M.; Albano, G.; Menicanti, L. The procoagulant pattern of patients with COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1747–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xu, J.; Yu, Y.; Shang, Y. Thrombocytopenia and its association with mortality in patients with COVID-19. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1469–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, G.; Plebani, M.; Henry, B.M. Thrombocytopenia is associated with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infections: A meta-analysis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 506, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M.; Liang, X.; Wei, Y.D. Changes in blood coagulation in patients with severe Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Meta-Analysis. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 189, 1050–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Llitjos, J.F.; Leclerc, M.; Chochois, C.; Monsallier, J.; Ramakers, M.; Auvray, M.; Merouani, K. High incidence of venous thromboembolic events in anticoagulated severe COVID-19 patients. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1743–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magro, C.; Mulvey, J.J.; Berlin, D.; Nuovo, G.; Salvatore, S.; Harp, J.; Baxter-Stoltzfus, A.; Laurence, J. Complement associated microvascular injury and thrombosis in the pathogenesis of severe COVID-19 infection: A report of five cases. Transl. Res. 2020, 220, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, H.; Yang, M.; Wan, C.; Yi, L.-X.; Tang, F.; Zhu, H.; Yi, F.; Yang, H.; Fogo, A.B.; Nie, X.; et al. Renal histopathological analysis of 26 postmortem findings of patients with COVID-19 in China. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard-Lorant, I.; Delabranche, X.; Severac, F.; Helms, J.; Pauzet, C.; Collange, O.; Schneider, F.; Labani, A.; Bilbault, P.; Moliere, S.; et al. Acute pulmonary embolism in COVID-19 patients on CT angiography and relationship to D-Dimer levels. Radiology 2020, 286, E189–E191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Middeldorp, S.; Coppens, M.; van Haaps, T.F.; Foppen, M.; Vlaar, A.P.; Müller, M.C.A.; Bouman, C.C.S.; Beenen, L.F.M.; Kootte, R.S.; Heijmans, J.; et al. Incidence of venous thromboembolism in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1995–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigada, M.; Bottino, N.; Tagliabue, P.; Grasselli, G.; Novembrino, C.; Chantarangkul, V.; Pesenti, A.; Peyvandi, F.; Tripodi, A. Hypercoagulability of COVID-19 patients in Intensive Care Unit. A Report of thromboelastography findings and other parameters of hemostasis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1738–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiezia, L.; Boscolo, A.; Poletto, F.; Cerruti, L.; Tiberio, I.; Campello, E.; Navalesi, P.; Simioni, P. COVID-19-related severe hypercoagulability in patients admitted to Intensive Care Unit for acute respiratory failure. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 120, 998–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, F.L.; Vogler, T.O.; Moore, E.E.; Moore, H.B.; Wohlauer, M.V.; Urban, S.; Nydam, T.L.; Moore, P.K.; McIntyre, R.C. Fibrinolysis shutdown correlation with thromboembolic events in severe COVID-19 infection. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2020, 231, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S.; Verghese, S.; Roxby, D.; Dixon, D.; Bihari, S.; Bersten, A. Changes in fibrinolysis and severity of organ failure in sepsis: A prospective observational study using point-of-care test—ROTEM. J. Crit. Care 2015, 30, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gorp, E.C.M.; Minnema, M.C.; Suharti, C.; Mairuhu, A.T.A.; Brandjes, D.P.M.; Cate, H.T.; Hack, C.E.; Meijers, J.C.M. Activation of coagulation factor XI, without detectable contact activation in dengue haemorrhagic fever. Br. J. Haematol. 2001, 113, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskela, S.M.; Joutsi-Korhonen, L.; Makela, S.M.; Huhtala, H.; Vaheri, A.I.; Pörsti, I.; Mustonen, J.T.; Laine, O.K. Dimished coagulation capacity assessed by calibrated automated thrombography during acute Puumala hantavirus infection. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2018, 29, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russo, F.P.; Zanetto, A.; Campello, E.; Bulato, C.; Shalaby, S.; Spiezia, L.; Gavasso, S.; Franceschet, E.; Radu, C.; Senzolo, M.; et al. Reversal of hypercoagulability in patients with HCV-related cirrhosis after treatment with direct-acting antivirals. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 2210–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nossel, H.L.; Yudelman, I.; Canfield, R.E.; Butler, V.P., Jr.; Spanondis, K.; Wilner, G.D.; Qureshi, G.D. Measurement of fibrinopeptide A in human blood. J. Clin. Investig. 1974, 54, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mavrommatis, A.C.; Theodoridis, T.; Orfanidou, A.; Roussos, C.; Christopoulou-Kokkinou, V.; Zakynthinos, S. Coagulation system and platelets are fully activated in uncomplicated sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 28, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leipnitz, G.; Miyashita, C.; Heiden, M.; Blohn, G.v.; Köhler, M.; Wenzel, E. Reference values and variability of plasminogen in healthy blood donors and its relation to parameters of the fibrinolytic system. Haemostasis 1988, 18, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiman, B.; Andersson, T.; Hallqvist, J.; Reuterwall, C.; Ahlbom, A.; deFaire, U. Plasma levels of tissue plasminogen activator/plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 complex and von Willebrand factor are significant risk markers for recurrent myocardial infarction in the Stockholm Heart Epidemiology Program (SHEEP) study. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 2019–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Premkumar, M.; Saxena, P.; Rangegowda, D.; Baweja, S.; Mirza, R.; Jain, P.; Bhatia, P.; Kumar, G.; Bihari, C.; Kalal, C.; et al. Coagulation failure is associated with bleeding events and clinical outcome during systemic inflammatory response and sepsis in acute-on-chronic liver failure: An observational cohort study. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbie, L.A.; Dummer, S.; Booth, N.A.; Adey, G.D.; Bennett, B. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 2 and urokinase-type plasminogen activator in plasma and leucocytes in patients with severe sepsis. Br. J. Haematol. 2000, 109, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semeraro, F.; Colucci, M.; Caironi, P.; Masson, S.; Ammollo, C.T.; Teli, R.; Semeraro, N.; Magnoli, M.; Salati, G.; Isetta, M.; et al. Platelet drop and fibrinolytic shutdown in patients with sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 46, e221–e228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachil, J. All those D-dimers in COVID-19. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 2075–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, M.; Thachil, J. Coronavirus disease 2019 coagulopathy: Disseminated intravascular coagulation and thrombotic microangiopathy-either, neither, or both. Semin. Thromb. Haemost. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RECOVERY Collaborative Group. Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19—Preliminary report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, L.; Palumbo, F.P.; Ardita, G.; Antignani, P.L.; Arosio, E.; Failla, G.; Italian Society for Vascular Investigation and the Italian Society of Vascular Medicine. Coagulopathy, thromboembolic complications, and the use of heparin in COVID-19 pneumonia. J. Vasc. Surg. Venous Lymphat. Disord. 2020, 8, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thachil, J.; Juffermans, N.P.; Ranucci, M.; Connors, J.M.; Warkentin, T.E.; Ortel, T.L.; Levi, M.; Iba, T.; Levy, J.H. ISTH DIC subcommittee communication on anticoagulation in COVID-19. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 2138–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Variable | Overall (n = 20) | Survivors (n = 8) | Nonsurvivors (n = 12) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 63.9 (56.3–71) | 59.6 (53.8–63.4 | 69.4 (63.6–72.3) | 0.037 |
| Gender male | 16 (80) | 7 (87.5) | 9 (75) | 0.619 |
| Weight (kg) | 90.5 (71.2–90) | 87.5 (81.2–102.5) | 77.5 (66.2–84) | 0.075 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 26.5 (24.6–31.2) | 27.7 (26.3–33.5) | 25.4 (23.4-30) | 0.077 |
| Hypertension | 6 (30) | 2 (25) | 4 (33.3) | 0.690 |
| Diabetes | 5 (25) | 3 (37.5) | 2 (16.7) | 0.296 |
| Smoking history | 3 (15) | 2 (25) | 1 (8.3) | 0.537 |
| Heart disease | 3 (15) | 0 (0) | 3 (25) | 0.242 |
| Chronic lung disease | 2 (10) | 1 (12.5) | 1 (8.3) | 0.796 |
| e-GFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 101 (58–148) | 101 (45–137) | 105 (58–159) | 0.624 |
| Interleukin-6 (pg/mL) | 181 (40–338) | 126 (4–126) | 182 (43–467) | 0.398 |
| aPTT (s) | 35.6 (30.3–45.5) | 33.5 (28.8–59.8) | 38.3 (30.3-45.5) | 0.680 |
| Prothrombin activity (%) | 86 (78–92) | 87 (79–97) | 83 (64–91) | 0.432 |
| Antithrombin activity (%) | 91 (80–98) | 91 (81–100) | 91 (68-95) | 0.276 |
| Platelets (×1000 cells/μL) | 254 (148–295) | 237 (156–356) | 254 (128–295) | 0.939 |
| ICU length of stay (days) | 13.5 (8–32) | 25 (3.5–35) | 11.5 (8–17.2) | 0.699 |
| Pulmonary TE | 7 (35) | 0 (0) | 7 (58.3) | 0.015 |
| (documented at CT scan) | ||||
| Variable | Time | Overall (n = 20) | Survivors (n = 8) | Nonsurvivors (n = 12) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fibrinogen (mg/dL) | Baseline | 592 (378–745) | 485 (288–720) | 664 (466–753) | 0.215 |
| Follow-up | 476 (297–706) | 319 (255–475) | 576 (362–737) | 0.086 | |
| D-dimers (μg/mL) | Baseline | 2.02 (0.82–3.6) | 0.98 (0.64–2.6) | 2.26(1.67–4.90) | 0.123 |
| Follow-up | 2.74 (1.55–3.6) | 1.61 (1.09–2.4) | 3.50(2.66–6.45) | 0.003 | |
| tPA (pg/mL) | Baseline | 4660 (3620–7663) | 6323 (4160–7967) | 4438 (3482–6387) | 0.335 |
| Follow-up | 3622 (1964–10,012) | 2233 (1865–7506) | 3822 (2751–12,243) | 0.123 | |
| PAI-2 (pg/mL) | Baseline | 400 (50–842) | 191 (50–514) | 567 (50–2132) | 0.184 |
| Follow-up | 423 (50–1238) | 161 (50–334) | 1088(177–1565) | 0.026 | |
| PF 1+2 (pg/mL) | Baseline | 442 (302–649) | 396 (185–585) | 442 (302–973) | 0.671 |
| Follow-up | 371 (119–763) | 237 (120–393) * | 557 (106–767) | 0.247 | |
| PAP (ng/mL) | Baseline | 23.9 (3.02–44.2) | 33.9 (13.9–61.8) | 17.4 (0.97–41.2) | 0.164 |
| Follow-up | 23.4 (6.3–55) | 27.1 (13.3–95.7) | 14.8 (4.2–52) | 0.247 | |
| FPA (ng/mL) | Baseline | 19.3 (5.5–33.8) | 23.4 (11–36.4) | 12.3 (4.4–29.3) | 0.165 |
| Follow-up | 14.1 (5.8–60.2) | 20.5 (11.3–63.6) | 10.7 (4.4–56.4) | 0.247 | |
| PAI-2/PAP ratio | Baseline | 19.4 (5–125) | 8.7 (2.9–12.6) | 109 (18.1–216) | 0.014 |
| Follow-up | 17.4 (1.8–149) | 3.5 (1.8–18.7) | 74 (4.2–255) | 0.064 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ranucci, M.; Sitzia, C.; Baryshnikova, E.; Di Dedda, U.; Cardani, R.; Martelli, F.; Corsi Romanelli, M. Covid-19-Associated Coagulopathy: Biomarkers of Thrombin Generation and Fibrinolysis Leading the Outcome. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3487. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113487
Ranucci M, Sitzia C, Baryshnikova E, Di Dedda U, Cardani R, Martelli F, Corsi Romanelli M. Covid-19-Associated Coagulopathy: Biomarkers of Thrombin Generation and Fibrinolysis Leading the Outcome. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(11):3487. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113487
Chicago/Turabian StyleRanucci, Marco, Clementina Sitzia, Ekaterina Baryshnikova, Umberto Di Dedda, Rosanna Cardani, Fabio Martelli, and Massimiliano Corsi Romanelli. 2020. "Covid-19-Associated Coagulopathy: Biomarkers of Thrombin Generation and Fibrinolysis Leading the Outcome" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 11: 3487. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113487
APA StyleRanucci, M., Sitzia, C., Baryshnikova, E., Di Dedda, U., Cardani, R., Martelli, F., & Corsi Romanelli, M. (2020). Covid-19-Associated Coagulopathy: Biomarkers of Thrombin Generation and Fibrinolysis Leading the Outcome. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(11), 3487. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113487










