Diabetic Retinopathy Environment-Wide Association Study (EWAS) in NHANES 2005–2008
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
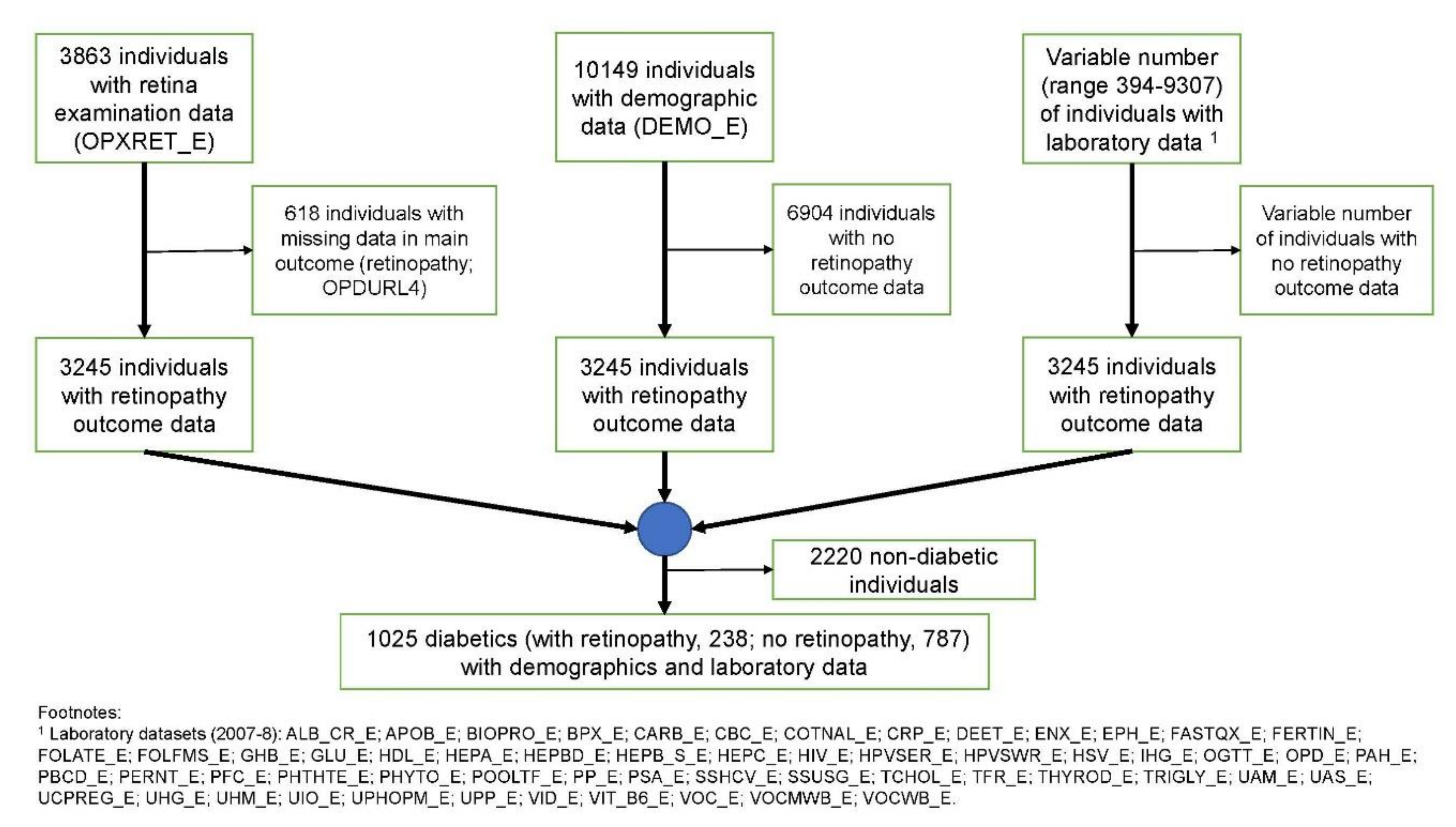
2.1. Study Data Collection
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Diabetes Status
2.4. Diabetic Retinopathy
2.5. Covariates
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Final Risk Models
3. Results
3.1. Study Cohort
3.2. Retinal Lesions of Diabetic Retinopathy
3.3. Univariate Logistic Regression Analysis
3.4. Principal Component Analysis
3.5. Penalised Regression Model
3.6. RandomForest™ Classification Model
3.7. Replication Cohort
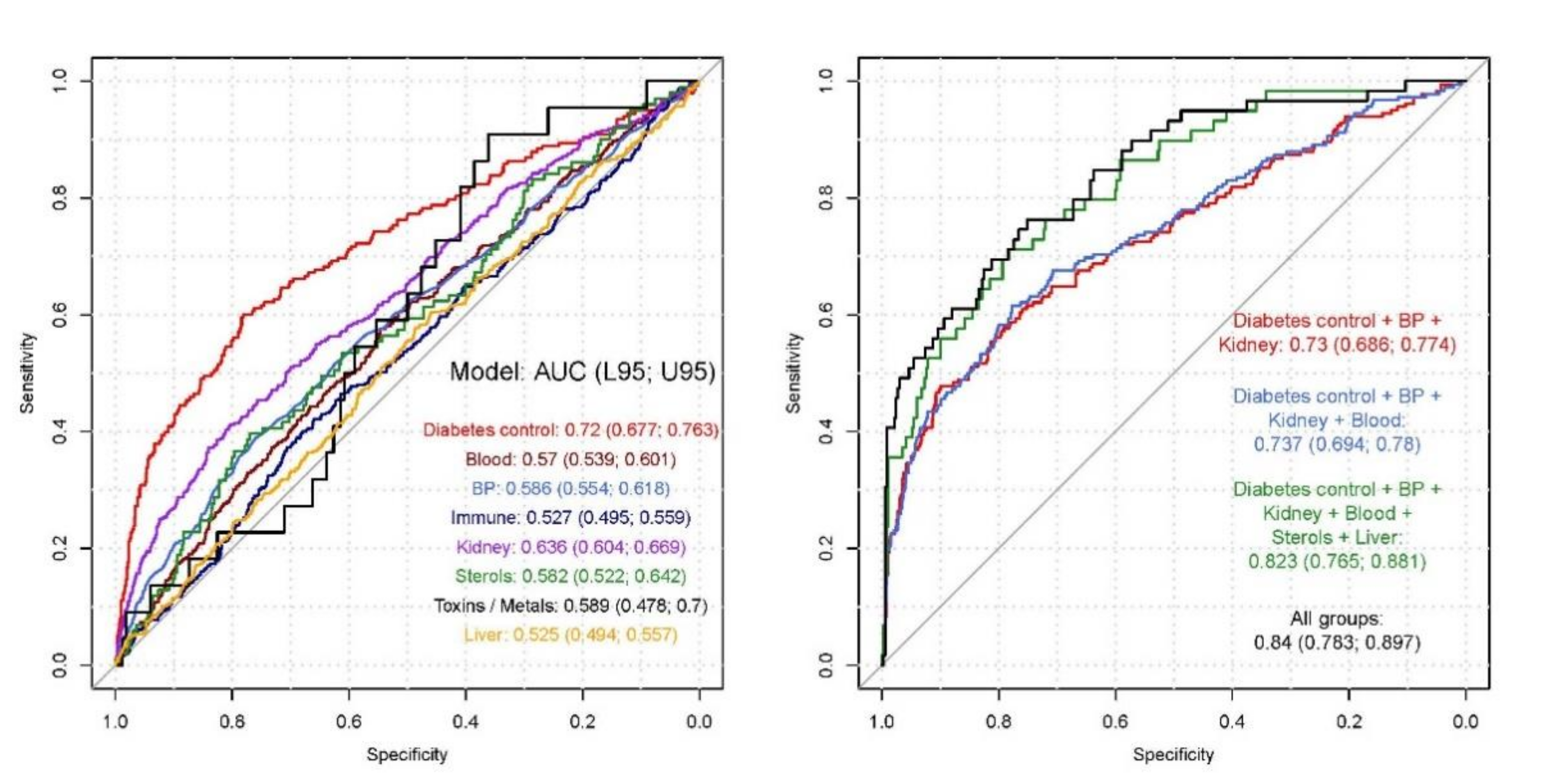
3.8. Final Clinical Risk Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feman, S.S. The natural history of the first clinically visible features of diabetic retinopathy. Trans. Am. Ophthalmol. Soc. 1994, 92, 745–773. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chao, J.R.; Lai, M.-Y.; Azen, S.P.; Klein, A.P.; Varma, R. Retinopathy in Persons without Diabetes: The Los Angeles Latino Eye Study. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 4019–4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatramani, J.; Mitchell, P. Ocular and systemic causes of retinopathy in patients without diabetes mellitus. BMJ 2004, 328, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gupta, A.; Singh, R.; Ramasamy, K.; Abraham, C.; Gupta, V. Diabetic retinopathy: An update. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2008, 56, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lo, A. Diabetic Retinopathy: Pathophysiology and Treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, J.W.; Rogers, S.L.; Kawasaki, R.; Lamoureux, E.L.; Kowalski, J.W.; Bek, T.; Chen, S.-J.; Dekker, J.M.; Fletcher, A.E.; Grauslund, J.; et al. Global Prevalence and Major Risk Factors of Diabetic Retinopathy. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heintz, E.; Wiréhn, A.B.; Peebo, B.B.; Rosenqvist, U.; Levin, L.A. Prevalence and healthcare costs of diabetic retinopathy: a population-based register study in Sweden. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 2147–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Group UPDSU. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 1998, 352, 837–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatziralli, I. The Role of Dyslipidemia Control in the Progression of Diabetic Retinopathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Ther. 2017, 8, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Quang, N.D.; Banu, R.; Kumar, H.; Tham, Y.-C.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Wong, T.Y.; Sabanayagam, C. Hypertension, blood pressure control and diabetic retinopathy in a large population-based study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Meng, Y.; Li, J.; She, H.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Peng, Y.; Shang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, X.; et al. Serum uric acid concentration is associated with hypertensive retinopathy in hypertensive chinese adults. BMC Ophthalmol. 2017, 17, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, B.-A.; Gao, F.; Qin, L.-L. The Association between Vitamin D Deficiency and Diabetic Retinopathy in Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Nutrients 2017, 9, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Wang, J.; Gao, G.; Tan, M.; Ding, B.; Li, H.; Ma, J.-H. Association between Free Thyroxine Levels and Diabetic Retinopathy in Euthyroid Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Endocr. Res. 2020, 45, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merin, S.; Freund, M. Retinopathy in Severe Anemia. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1968, 66, 1102–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Rahmani, A.H.; Aldebasi, Y.H. Diabetic Retinopathy: Recent Updates on Different Biomarkers and Some Therapeutic Agents. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2018, 14, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriya, T.; Tanaka, S.; Kawasaki, R.; Ohashi, Y.; Akanuma, Y.; Yamada, N.; Sone, H.; Yamashita, H.; Katayama, S. Diabetic Retinopathy and Microalbuminuria Can Predict Macroalbuminuria and Renal Function Decline in Japanese Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 2803–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Chen, H.-S.; Tarng, D.-C. More Impact of Microalbuminuria on Retinopathy Than Moderately Reduced GFR Among Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.S.; Tai, E.S.; Mitchell, P.; Wang, J.J.; Tay, W.T.; Lamoureux, E.; Wong, T.Y. C-reactive Protein, Body Mass Index, and Diabetic Retinopathy. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 4458–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, N.T.; Varadhan, L.; Reynold, D.R.; Bush, K.; Sankaranarayanan, S.; Bellary, S.; Barnett, A.H.; Kumar, S.; O’Hare, J.P. Higher prevalence of retinopathy in diabetic patients of South Asian ethnicity compared with white Europeans in the community: A cross-sectional study. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanakis, E.K.; Golden, S.H. Race/Ethnic Difference in Diabetes and Diabetic Complications. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2013, 13, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.Y.; Klein, R.; Islam, F.M.A.; Cotch, M.F.; Folsom, A.R.; Klein, B.E.K.; Sharrett, A.R.; Shea, S. Diabetic Retinopathy in a Multi-ethnic Cohort in the United States. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2006, 141, 446–455.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGinnis, D.P.; Brownstein, J.S.; Patel, C.J. Environment-Wide Association Study of Blood Pressure in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (1999–2012). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, X.; Guo, Y.; Ni, A.; Yang, D.; Liao, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, H.; Sun, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; et al. Toward a panoramic perspective of the association between environmental factors and cardiovascular disease: An environment-wide association study from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999–2014. Environ. Int. 2018, 118, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, M.A.; Dudek, S.M.; Goodloe, R.; Crawford, D.C.; Pendergrass, S.A.; Peissig, P.; Brilliant, M.; McCarty, C.A.; Ritchie, M.D. Environment-wide association study (EWAS) for type 2 diabetes in the Marshfield Personalized Medicine Research Project Biobank. Pac. Symp. Biocomput. 2014, 2014, 200–211. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, C.J.; Rehkopf, D.H.; Leppert, J.T.; Bortz, W.M.; Cullen, M.R.; Chertow, G.M.; Ioannidis, J.P. Systematic evaluation of environmental and behavioural factors associated with all-cause mortality in the United States National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 42, 1795–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nembrini, S.; König, I.R.; Wright, M.N. The revival of the Gini importance? Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3711–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratton, I.M.; Kohner, E.M.; Aldington, S.J.; Turner, R.C.; Holman, R.R.; Manley, S.E.; Matthews, D.R. UKPDS 50: Risk factors for incidence and progression of retinopathy in Type II diabetes over 6 years from diagnosis. Diabetologia 2001, 44, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, R. (Ronald) Blood pressure control and diabetic retinopathy. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2002, 86, 365–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Lamoureux, E.L.; Lavanya, R.; Wu, R.; Ikram, M.K.; Wang, J.J.; Mitchell, P.; Cheung, N.; Aung, T.; Saw, S.-M.; et al. Prevalence and risk factors of diabetic retinopathy in migrant Indians in an urbanized society in Asia: The Singapore Indian eye study. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 2119–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics Mean (± SD) n (%) | Diabetes with Non-Diabetic Retinopathy (n = 787) | Diabetic Retinopathy (n = 238) | p-Value | β-Coefficient | OR (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | - | 62.39 (±11.02) | 63.53 (±10.54) | NS | 0.01 | 1.00 (1.00–1.02) |
| Sex | Male | 420 (53.37) | 126 (52.94) | - | - | - |
| Female | 367 (46.63) | 112 (47.06) | NS | 0.02 | 1.02 (0.76–1.36) | |
| Ethnicity | Non-Hispanic white | 369 (46.88) | 91 (38.23) | - | - | - |
| Non-Hispanic black | 166 (21.09) | 74 (31.09) | ** | 0.59 | 1.81 (1.27–2.58) | |
| Mexican-American | 138 (17.54) | 41 (17.23) | NS | 0.19 | 1.21 (0.79–1.83) | |
| Other Hispanic | 89 (11.31) | 28 (11.77) | NS | 0.24 | 1.28 (0.79–2.07) | |
| Other race—including multiracial | 25 (3.18) | 4 (1.68) | NS | −0.43 | 0.65 (0.22–1.91) | |
| Education | Less than 9th grade | 148 (18.8) | 54 (22.69) | - | - | - |
| 9–11th grade ± | 148 (18.8) | 51 (21.43) | NS | −0.06 | 0.94 (0.61–1.47) | |
| High school graduate/GED or equivalent | 199 (25.29) | 56 (23.53) | NS | −0.26 | 0.77 (0.5–1.19) | |
| Some college or AA degree | 172 (21.86) | 55 (23.11) | NS | −0.13 | 0.88 (0.57–1.35) | |
| College graduate or above | 120 (15.25) | 22 (9.24) | * | −0.69 | 0.5 0.29–0.87) | |
| Marital status | Married | 464 (58.96) | 133 (55.88) | - | - | - |
| Widowed | 119 (15.12) | 36 (15.13) | NS | 0.05 | 1.06 (0.69–1.61) | |
| Divorced | 90 (11.44) | 37 (15.55) | NS | 0.36 | 1.43 (0.94–2.2) | |
| Separated | 32 (4.07) | 7 (2.94) | NS | −0.27 | 0.76 (0.33–1.77) | |
| Never married | 53 (6.73) | 18 (7.56) | NS | 0.17 | 1.19 (0.67–2.09) | |
| Living with partner | 29 (3.68) | 7 (2.94) | NS | −0.17 | 0.84 (0.36–1.97) | |
| Family income | $0–$4999 | 11 (1.4) | 3 (1.26) | - | - | - |
| $5000–$9999 | 47 (5.97) | 12 (5.04) | NS | −0.07 | 0.94 (0.23–3.89) | |
| $10,000–$14,999 | 82 (10.42) | 22 (9.25) | NS | −0.02 | 0.98 (0.25–3.84) | |
| $15,000–$19,999 | 68 (8.64) | 22 (9.25) | NS | 0.17 | 1.19 (0.30–4.64) | |
| $20,000–$24,999 | 69 (8.77) | 25 (10.5) | NS | 0.28 | 1.33 (0.34–5.16) | |
| $25,000–$34,999 | 103 (13.09) | 42 (17.65) | NS | 0.40 | 1.50 (0.40–5.63) | |
| $35,000–$44,999 | 68 (8.64) | 23 (9.66) | NS | 0.22 | 1.24 (0.32–4.84) | |
| $45,000–$54,999 | 55 (6.99) | 12 (5.04) | NS | −0.22 | 0.80 (0.19–3.31) | |
| $55,000–$64,999 | 41 (5.21) | 15 (6.3) | NS | 0.29 | 1.34 (0.33–5.48) | |
| $65,000–$74,999 | 36 (4.57) | 6 (2.52) | NS | −0.49 | 0.61 (0.13–2.86) | |
| $75,000–$99,999 | 44 (5.59) | 12 (5.04) | NS | 0.00 | 1.00 (0.24–4.17) | |
| ≥$100,000 | 88 (11.18) | 17 (7.14) | NS | −0.35 | 0.71 (0.18–2.81) | |
| Over $20,000 | 31 (3.94) | 9 (3.78) | NS | 0.06 | 1.06 (0.24–4.66) | |
| Under $20,000 | 17 (2.16) | 2 (0.84) | NS | −0.84 | 0.43 (0.06–3.01) | |
| Missing | 27 (3.43) | 16 (6.73) | - | - | - | |
| Diabetes duration | - | 9.05 (±11.05) | 16.33 (±12.57) | *** | 0.05 | 1.05 (1.04–1.07) |
| Clinical Signs of DR | n (%) | β-Coefficient | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | FDR-Adjusted p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retinal microaneurysms only, worse eye | 129 (12.59) | 5.67 | 288.87 (127.66–653.68) | *** | *** |
| Retinal hard exudate, worse eye | 86 (8.39) | 3.72 | 41.34 (20.31–84.17) | *** | *** |
| Retinal blot haemorrhages, worse eye | 47 (4.59) | 3.36 | 28.71 (14.11–58.42) | *** | *** |
| Retinal soft exudate, worse eye | 76 (7.41) | 4.2 | 66.49 (26.44–167.21) | *** | *** |
| IRMA, worse eye | 62 (6.05) | 2.85 | 17.36 (9.06–33.26) | *** | *** |
| Macular oedema, worse eye | 51 (4.98) | 3.88 | 48.24 (17.18–135.44) | *** | *** |
| Retinal fibrous proliferation, worse eye | 19 (1.85) | 3.41 | 30.19 (6.92–131.67) | *** | *** |
| Macular oedema in centre, worse eye | 26 (2.54) | 4.53 | 92.33 (12.45–684.9) | *** | *** |
| Retinal new vessels elsewhere, worse eye | 15 (1.46) | 3.12 | 22.68 (5.08–101.23) | *** | *** |
| Unadjusted/Non-Covariate Adjusted | Age-Adjusted | Ethnicity-Adjusted | Diabetes Duration-Adjusted | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Description | β-Coefficient | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | FDR-Adjusted p-Value | β-Coefficient | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | FDR-Adjusted p-Value | β-Coefficient | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | FDR-Adjusted p-Value | β-Coefficient | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | FDR-Adjusted p-Value |
| Glycohemoglobin (HbA1c) (%) | 0.82 | 2.27 (1.84–2.8) | *** | *** | 0.85 | 2.34 (1.87–2.92) | *** | ** | 0.83 | 2.28 (1.82–2.87) | *** | ** | 0.72 | 2.05 (1.55–2.73) | *** | * |
| Random Glucose, serum (RBS) (mmol/L) | 0.54 | 1.72 (1.42–2.08) | *** | ** | 0.57 | 1.77 (1.45–2.15) | *** | * | 0.54 | 1.71 (1.41–2.09) | *** | * | 0.36 | 1.43 (1.1–1.86) | * | NS |
| Osmolality (mmol/Kg) | 0.49 | 1.63 (1.34–1.99) | *** | * | 0.45 | 1.57 (1.3–1.9) | *** | * | 0.49 | 1.63 (1.34–1.99) | *** | NS | 0.39 | 1.48 (1.12–1.94) | * | * |
| Albumin, urine (mg/L) | 0.45 | 1.57 (1.28–1.93) | *** | * | 0.43 | 1.53 (1.24–1.88) | ** | * | 0.42 | 1.53 (1.25–1.87) | ** | NS | 0.25 | 1.28 (0.98–1.68) | NS | NS |
| Haemoglobin (g/dL) | −0.33 | 0.72 (0.61–0.85) | ** | * | −0.30 | 0.74 (0.63–0.88) | ** | * | −0.29 | 0.75 (0.62–0.9) | ** | NS | 0.00 | 1 (0.73–1.37) | NS | NS |
| Fasting Glucose(FBS) (mmol/L) | 0.49 | 1.63 (1.28–2.07) | ** | * | 0.51 | 1.66 (1.3–2.13) | ** | * | 0.46 | 1.59 (1.25–2.02) | ** | NS | 0.22 | 1.24 (0.93–1.66) | NS | NS |
| 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanol (NNAL), urine (ng/mL) | −0.26 | 0.77 (0.67–0.88) | ** | NS | −0.20 | 0.82 (0.71–0.94) | * | NS | −0.28 | 0.75 (0.65–0.87) | ** | NS | −0.25 | 0.78 (0.52–1.19) | NS | NS |
| Iodine, urine (ug/L) | −0.17 | 0.84 (0.76–0.93) | ** | NS | −0.21 | 0.81 (0.73–0.9) | ** | * | −0.15 | 0.86 (0.77–0.96) | * | NS | −0.29 | 0.75 (0.63–0.89) | ** | * |
| Cobalt, urine (ug/L) | −0.51 | 0.6 (0.44–0.82) | ** | NS | −0.50 | 0.6 (0.45–0.82) | ** | * | −0.51 | 0.6 (0.44–0.81) | ** | NS | −0.52 | 0.59 (0.45–0.78) | ** | * |
| Haematocrit (%) | −0.31 | 0.73 (0.6–0.89) | ** | NS | −0.28 | 0.76 (0.62–0.92) | * | NS | −0.28 | 0.75 (0.62–0.92) | * | NS | −0.03 | 0.97 (0.7–1.35) | NS | NS |
| Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) (mmol/L) | 0.33 | 1.4 (1.13–1.73) | ** | NS | 0.27 | 1.31 (1.01–1.71) | NS | NS | 0.35 | 1.43 (1.16–1.75) | ** | NS | 0.15 | 1.17 (0.87–1.57) | NS | NS |
| Albumin (g/L) | −0.22 | 0.8 (0.69–0.93) | * | NS | −0.21 | 0.81 (0.69–0.94) | * | NS | −0.19 | 0.83 (0.7–0.99) | NS | NS | −0.09 | 0.92 (0.74–1.14) | NS | NS |
| Urinary Triclosan (ng/mL) | −0.42 | 0.65 (0.49–0.88) | * | NS | −0.40 | 0.67 (0.5–0.89) | * | NS | −0.42 | 0.66 (0.49–0.89) | * | NS | −0.60 | 0.55 (0.36–0.83) | * | * |
| Mean cell haemoglobin (pg) | −0.24 | 0.79 (0.66–0.93) | * | NS | −0.27 | 0.77 (0.65–0.91) | ** | * | −0.17 | 0.84 (0.7–1.02) | NS | NS | −0.01 | 0.99 (0.76–1.28) | NS | NS |
| Lead, urine (µg/L) | −0.40 | 0.67 (0.49–0.91) | * | NS | −0.40 | 0.67 (0.49–0.91) | * | NS | −0.41 | 0.66 (0.49–0.9) | * | NS | −0.43 | 0.65 (0.43–0.99) | NS | NS |
| Creatinine, urine (µmol/L) | −0.22 | 0.8 (0.67–0.97) | * | NS | −0.19 | 0.83 (0.68–1) | NS | NS | −0.27 | 0.77 (0.64–0.92) | * | NS | −0.28 | 0.76 (0.64–0.9) | ** | * |
| Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) (U/L) | −0.25 | 0.78 (0.62–0.97) | * | NS | −0.20 | 0.82 (0.66–1.02) | NS | NS | −0.22 | 0.81 (0.64–1.01) | NS | NS | −0.09 | 0.92 (0.68–1.23) | NS | NS |
| Creatinine (µmol/L) | 0.24 | 1.27 (1.04–1.54) | * | NS | 0.18 | 1.19 (0.96–1.48) | NS | NS | 0.20 | 1.23 (0.99–1.53) | NS | NS | 0.13 | 1.14 (0.89–1.45) | NS | NS |
| Red blood cell count (million cells/µL) | −0.19 | 0.82 (0.7–0.97) | * | NS | −0.13 | 0.88 (0.74–1.04) | NS | NS | −0.19 | 0.83 (0.7–0.98) | NS | NS | 0.01 | 1.01 (0.74–1.37) | NS | NS |
| Mean cell volume (fL) | −0.21 | 0.81 (0.68–0.98) | * | NS | −0.25 | 0.78 (0.65–0.93) | * | NS | −0.15 | 0.86 (0.71–1.06) | NS | NS | −0.05 | 0.95 (0.72–1.26) | NS | NS |
| Platelet count (1000 cells/µL) | −0.21 | 0.81 (0.68–0.98) | * | NS | −0.18 | 0.83 (0.68–1.02) | NS | NS | −0.23 | 0.79 (0.67–0.94) | * | NS | −0.29 | 0.75 (0.57–0.99) | NS | NS |
| Mean platelet volume (fL) | 0.24 | 1.27 (1.04–1.55) | * | NS | 0.26 | 1.3 (1.06–1.59) | * | NS | 0.22 | 1.25 (1.02–1.53) | NS | NS | 0.09 | 1.09 (0.83–1.43) | NS | NS |
| Cotinine (ng/mL) | −0.15 | 0.86 (0.76–0.99) | * | NS | −0.09 | 0.91 (0.79–1.04) | NS | NS | −0.18 | 0.84 (0.74–0.95) | * | NS | −0.06 | 0.94 (0.66–1.34) | NS | NS |
| Insulin (pmol/L) | −0.32 | 0.73 (0.55–0.97) | * | NS | −0.30 | 0.74 (0.55–1) | NS | NS | −0.29 | 0.75 (0.56–1) | NS | NS | −0.22 | 0.8 (0.51–1.26) | NS | NS |
| Blood cadmium (nmol/L) | −0.23 | 0.8 (0.65–0.97) | * | NS | −0.25 | 0.78 (0.64–0.95) | * | NS | −0.23 | 0.79 (0.64–0.98) | NS | NS | −0.28 | 0.76 (0.5–1.16) | NS | NS |
| Urinary perchlorate (ng/mL) | −0.25 | 0.78 (0.63–0.95) | * | NS | −0.24 | 0.78 (0.63–0.98) | * | NS | −0.24 | 0.78 (0.64–0.96) | * | NS | −0.31 | 0.73 (0.53–1.01) | NS | NS |
| Urinary nitrate (ng/mL) | −0.28 | 0.75 (0.6–0.94) | * | NS | −0.23 | 0.79 (0.63–1) | NS | NS | −0.27 | 0.76 (0.6–0.96) | * | NS | −0.34 | 0.71 (0.55–0.91) | * | NS |
| Cesium, urine (µg/L) | −0.33 | 0.72 (0.54–0.95) | * | NS | −0.32 | 0.72 (0.55–0.96) | * | NS | −0.33 | 0.72 (0.54–0.95) | * | NS | −0.34 | 0.71 (0.47–1.06) | NS | NS |
| Thallium, urine (µg/L) | −0.40 | 0.67 (0.48–0.95) | * | NS | −0.39 | 0.68 (0.48–0.96) | * | NS | −0.42 | 0.66 (0.47–0.92) | * | NS | −0.48 | 0.62 (0.4–0.94) | * | NS |
| Vitamin D2 or D3 25OHD2 + 25OHD3 (nmol/L) | −0.24 | 0.79 (0.65–0.95) | * | NS | −0.25 | 0.78 (0.65–0.94) | * | NS | −0.18 | 0.83 (0.66–1.04) | NS | NS | −0.20 | 0.82 (0.61–1.1) | NS | NS |
| Blood Toluene (ng/mL) | −0.21 | 0.81 (0.68–0.96) | * | NS | −0.20 | 0.82 (0.69–0.97) | * | NS | −0.22 | 0.8 (0.65–0.98) | NS | NS | −0.30 | 0.74 (0.45–1.21) | NS | NS |
| C-reactive protein (mg/dL) | −0.19 | 0.82 (0.69–0.99) | NS | NS | −0.18 | 0.83 (0.69–1.01) | NS | NS | −0.25 | 0.78 (0.66–0.92) | * | NS | −0.27 | 0.77 (0.6–0.98) | * | NS |
| Barium, urine (µg/L) | −0.39 | 0.68 (0.47–0.99) | NS | NS | −0.38 | 0.69 (0.48–0.99) | NS | NS | −0.38 | 0.68 (0.47–1) | NS | NS | −0.44 | 0.64 (0.47–0.87) | * | * |
| Urinary 4-tert-octylphenol (ng/mL) | −0.34 | 0.71 (0.45–1.12) | NS | NS | −0.33 | 0.72 (0.46–1.12) | NS | NS | −0.42 | 0.66 (0.43–1.01) | NS | NS | −0.82 | 0.44 (0.23–0.87) | * | NS |
| Dimethyl dithiophosphate (µg/L) | −0.31 | 0.74 (0.51–1.06) | NS | NS | −0.35 | 0.71 (0.49–1.01) | NS | NS | −0.21 | 0.81 (0.59–1.12) | NS | NS | −0.67 | 0.51 (0.29–0.91) | * | NS |
| Marker | Group | Mean Decrease Accuracy | Mean Decrease Gini |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glycohemoglobin (%) | Diabetes status | 31.93719324 | 21.75225602 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/dL) | Immune markers | 11.51047187 | 10.1975135 |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | Renal function | 11.44142126 | 8.198116194 |
| Albumin, urine (mg/L) | Renal function | 8.220187056 | 10.21346621 |
| Monocyte number (1000 cells/uL) | Immune markers | 7.663589246 | 3.957711466 |
| Osmolality (mmol/Kg) | Renal function | 7.510989556 | 5.33445026 |
| White blood cell count (1000 cells/uL) | Immune markers | 7.440157644 | 4.405168072 |
| Blood urea nitrogen (mmol/L) | Renal function | 7.224789174 | 5.073947519 |
| Segmented neutrophils num (1000 cell/uL) | Immune markers | 7.020397225 | 4.067402271 |
| Fasting Glucose (mmol/L) | Diabetes status | 6.563694988 | 2.826827797 |
| Red cell distribution width (%) | Haematocrit | 6.138538515 | 4.947185792 |
| Urinary nitrate (ng/mL) | Renal function | 5.899174386 | 5.844258103 |
| Glucose, serum (mmol/L) | Diabetes status | 5.85339684 | 4.77357191 |
| 2-hydroxyphenanthrene (ng/L) | Toxins/Metals | 4.028082549 | 2.307374348 |
| MCHC (g/dL) | Haematocrit | 3.936015913 | 3.896804592 |
| Creatinine (µmol/L) | Renal function | 3.530916132 | 3.747500758 |
| Mono-2-ethyl-5-carboxypentyl phthalate | Toxins/Metals | 2.996581682 | 2.212151134 |
| Blood Nitromethane (pg/mL) | Toxins/Metals | 2.936160917 | 3.31634662 |
| Phosphorus (mmol/L) | Toxins/Metals | 2.819084205 | 3.768671211 |
| Total Cholesterol (mmol/L) | Sterols | 2.448578413 | 3.833301666 |
| Enterodiol (ng/mL) | Sterols | 2.401651721 | 2.722762228 |
| Haematocrit (%) | Haematocrit | 2.364741874 | 4.841281382 |
| Mono-n-octyl phthalate (ng/mL) | Toxins/Metals | 2.215508752 | 0.231647322 |
| Mean cell haemoglobin (pg) | Haematocrit | 2.183482824 | 4.292282119 |
| Gamma glutamyl transferase (U/L) | Liver Function | 1.989695745 | 4.015070221 |
| Systolic blood pressure | Blood pressure | 1.892815461 | 8.85430752 |
| Blood o-Xylene (ng/mL) | Toxins/Metals | 1.670964308 | 3.708248225 |
| Lactate dehydrogenase LDH (U/L) | Liver Function | 1.593869272 | 4.231659273 |
| 9-hydroxyfluorene (ng/L) | Toxins/Metals | 1.430814333 | 2.206778568 |
| Cholesterol (mmol/L) | Sterols | 1.201366974 | 4.025207689 |
| 3-hydroxyphenanthrene (ng/L) | Toxins/Metals | 1.00569817 | 1.63630888 |
| Model | Wald Test p-Value | McFadden R2 | Nagelkerke R2 | AUC (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetes Status | *** | 0.102 | 0.142 | 0.72 (0.677–0.763) |
| Haematocrit | ** | 0.007 | 0.009 | 0.57 (0.539–0.601) |
| Blood Pressure (BP) | *** | 0.017 | 0.024 | 0.586 (0.554–0.618) |
| Immune Markers | NS | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.527 (0.495–0.559) |
| Renal function tests (renal) | *** | 0.039 | 0.054 | 0.636 (0.604–0.669) |
| Sterols (include cholesterol) | NS | 0.012 | 0.017 | 0.582 (0.522–0.642) |
| Toxins/Metals | NS | 0.029 | 0.041 | 0.589 (0.478–0.7) |
| Liver function tests | NS | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.525 (0.494–0.557) |
| Diabetes control + BP + Renal function | *** | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.73 (0.686–0.774) |
| Diabetes control + BP + renal function + Haematocrit | *** | 0.135 | 0.184 | 0.737 (0.694–0.78) |
| Diabetes control + BP + renal function + Haematocrit + Sterols + Liver function | *** | 0.238 | 0.315 | 0.823 (0.765–0.881) |
| All groups ± | *** | 0.272 | 0.355 | 0.84 (0.783–0.897) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blighe, K.; Gurudas, S.; Lee, Y.; Sivaprasad, S. Diabetic Retinopathy Environment-Wide Association Study (EWAS) in NHANES 2005–2008. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3643. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113643
Blighe K, Gurudas S, Lee Y, Sivaprasad S. Diabetic Retinopathy Environment-Wide Association Study (EWAS) in NHANES 2005–2008. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(11):3643. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113643
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlighe, Kevin, Sarega Gurudas, Ying Lee, and Sobha Sivaprasad. 2020. "Diabetic Retinopathy Environment-Wide Association Study (EWAS) in NHANES 2005–2008" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 11: 3643. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113643
APA StyleBlighe, K., Gurudas, S., Lee, Y., & Sivaprasad, S. (2020). Diabetic Retinopathy Environment-Wide Association Study (EWAS) in NHANES 2005–2008. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(11), 3643. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113643





