Longitudinal Imaging Using PET/CT with Collagen-I PET-Tracer and MRI for Assessment of Fibrotic and Inflammatory Lesions in a Rat Lung Injury Model
Abstract
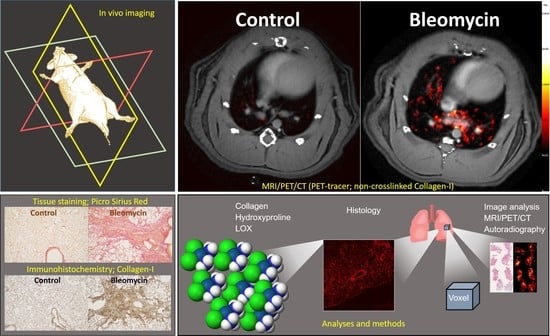
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Animals and Ethical Permit
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.3. Bleomycin Challenge
2.4. In Vivo Imaging
2.4.1. MRI
2.4.2. PET/CT
2.5. Imaging Data Analysis
2.6. Termination of Experiment and Sample Collection
2.7. Hydroxyproline Analysis
2.8. Lysyl Oxidase (LOX) Activity Assay
2.9. Autoradiography
2.10. Histology Staining and Analysis
2.11. Gene Expression Analysis from Lung Tissue Homogenates
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Model Characterization and Health Check Parameters
3.2. Lesion Assessment by CT and MRI
3.3. Using the PET-tracer CBP-Cu64 to Assess Non-Cross-linked Collagen-I
3.4. Molecular Assessment of Collagen Production and Cross-Linking
3.5. Observed Gene Expression Levels in Bleomycin Challenged Rats from Inflammation to Fibrosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| CT | computed tomography |
| DAB | 3,3′-diaminobenzidine |
| DIILD | drug-induced interstitial lung disease |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| FDG | fludeoxyglucose |
| FOV | field of view |
| HRCT | high resolution computed tomography |
| H&E | hematoxylin and Eosin |
| IBs | imaging biomarkers |
| IL | interleukin |
| ILD | interstitial lung disease |
| IPF | idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| i.t. | intratracheal |
| LBIC | Lund university BioImaging Centre |
| LOX | Lysyl Oxidase |
| MMPs | Matrix metallopeptidases |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| PET | positron emission tomography |
| ROI | region of interest |
| TGF-β | tissue growth factor β |
| TIMP1 | tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 |
| TRISTAN-IMI | Translational Imaging in Drug Safety Assessment—Innovative Medicines Initiative |
| UTE | ultra short echo time |
References
- Schwaiblmair, M.; Behr, W.; Haeckel, T.; Markl, B.; Foerg, W.; Berghaus, T. Drug induced interstitial lung disease. Open Respir. Med. J. 2012, 6, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsuno, O. Drug-induced interstitial lung disease: Mechanisms and best diagnostic approaches. Respir. Res. 2012, 13, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antoniou, K.M.; Margaritopoulos, G.A.; Tomassetti, S.; Bonella, F.; Costabel, U.; Poletti, V. Interstitial lung disease. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2014, 23, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hashisako, M.; Fukuoka, J. Pathology of Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. Clin. Med. Insights Circ. Respir. Pulm. Med. 2015, 9, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poletti, V.; Egan, J. Classification, natural history and staging of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2013, 30 (Suppl. S1), 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Skeoch, S.; Weatherley, N.; Swift, A.J.; Oldroyd, A.; Johns, C.; Hayton, C.; Giollo, A.; Wild, J.M.; Waterton, J.C.; Buch, M.; et al. Drug-Induced Interstitial Lung Disease: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ripley, B.A.; Kelil, T.; Gill, R.R. Deciphering drug-induced interstitial lung disease: A mechanistic approach. Appl. Radiol. 2016, 45, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Thannickal, V.J.; Toews, G.B.; White, E.S.; Lynch, J.P., 3rd; Martinez, F.J. Mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. Annu. Rev. Med. 2004, 55, 395–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, T.A.; Ramalingam, T.R. Mechanisms of fibrosis: Therapeutic translation for fibrotic disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1028–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wynn, T.A. Integrating mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 1339–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munger, J.S.; Sheppard, D. Cross talk among TGF-beta signaling pathways, integrins, and the extracellular matrix. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a005017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karsdal, M.A.; Nielsen, S.H.; Leeming, D.J.; Langholm, L.L.; Nielsen, M.J.; Manon-Jensen, T.; Siebuhr, A.; Gudmann, N.S.; Ronnow, S.; Sand, J.M.; et al. The good and the bad collagens of fibrosis—Their role in signaling and organ function. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 121, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjin, G.; White, E.S.; Faiz, A.; Sicard, D.; Tschumperlin, D.J.; Mahar, A.; Kable, E.P.W.; Burgess, J.K. Lysyl oxidases regulate fibrillar collagen remodelling in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Dis. Model. Mech. 2017, 10, 1301–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Young, H.M.; Eddy, R.L.; Parraga, G. MRI and CT lung biomarkers: Towards an in vivo understanding of lung biomechanics. Clin. Biomech. 2019, 66, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baues, M.; Dasgupta, A.; Ehling, J.; Prakash, J.; Boor, P.; Tacke, F.; Kiessling, F.; Lammers, T. Fibrosis imaging: Current concepts and future directions. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 121, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmutovic Persson, I.; Falk Hakansson, H.; Orbom, A.; Liu, J.; von Wachenfeldt, K.; Olsson, L.E. Imaging Biomarkers and Pathobiological Profiling in a Rat Model of Drug-Induced Interstitial Lung Disease Induced by Bleomycin. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desogere, P.; Tapias, L.F.; Hariri, L.P.; Rotile, N.J.; Rietz, T.A.; Probst, C.K.; Blasi, F.; Day, H.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Weinreb, P.; et al. Type I collagen-targeted PET probe for pulmonary fibrosis detection and staging in preclinical models. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desogere, P.; Tapias, L.F.; Rietz, T.A.; Rotile, N.; Blasi, F.; Day, H.; Elliott, J.; Fuchs, B.C.; Lanuti, M.; Caravan, P. Optimization of a Collagen-Targeted PET Probe for Molecular Imaging of Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 1991–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montesi, S.B.; Izquierdo-Garcia, D.; Desogere, P.; Abston, E.; Liang, L.L.; Digumarthy, S.; Seethamraju, R.; Lanuti, M.; Caravan, P.; Catana, C. Type I Collagen-targeted Positron Emission Tomography Imaging in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: First-in-Human Studies. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, D.M.; Kleeberger, S.R. Mouse models of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Curr. Protoc. Pharmacol. 2008, 40, 5–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, B.B.; Lawson, W.E.; Oury, T.D.; Sisson, T.H.; Raghavendran, K.; Hogaboam, C.M. Animal models of fibrotic lung disease. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 49, 167–179. [Google Scholar]
- Babin, A.L.; Cannet, C.; Gérard, C.; Wyss, D.; Page, C.P.; Beckmann, N. Noninvasive assessment of bleomycin-induced lung injury and the effects of short-term glucocorticosteroid treatment in rats using MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2011, 33, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babin, A.L.; Cannet, C.; Gerard, C.; Saint-Mezard, P.; Page, C.P.; Sparrer, H.; Matsuguchi, T.; Beckmann, N. Bleomycin-induced lung injury in mice investigated by MRI: Model assessment for target analysis. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012, 67, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caravan, P.; Yang, Y.; Zachariah, R.; Schmitt, A.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Chen, H.H.; Sosnovik, D.E.; Dai, G.; Fuchs, B.C.; Lanuti, M. Molecular magnetic resonance imaging of pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 49, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egger, C.; Cannet, C.; Gérard, C.; Jarman, E.; Jarai, G.; Feige, A.; Suply, T.; Micard, A.; Dunbar, A.; Tigani, B.; et al. Administration of Bleomycin via the Oropharyngeal Aspiration Route Leads to Sustained Lung Fibrosis in Mice and Rats as Quantified by UTE-MRI and Histology. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egger, C.; Gerard, C.; Vidotto, N.; Accart, N.; Cannet, C.; Dunbar, A.; Tigani, B.; Piaia, A.; Jarai, G.; Jarman, E.; et al. Lung volume quantified by MRI reflects extracellular-matrix deposition and altered pulmonary function in bleomycin models of fibrosis: Effects of SOM230. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2014, 306, L1064–L1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Egger, C.; Cannet, C.; Gérard, C.; Dunbar, A.; Tigani, B.; Beckmann, N. Hyaluronidase modulates bleomycin-induced lung injury detected noninvasively in small rodents by radial proton MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2015, 41, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmouty-Quintana, H.; Cannet, C.; Zurbruegg, S.; Ble, F.X.; Fozard, J.R.; Page, C.P.; Beckmann, N. Bleomycin-induced lung injury assessed noninvasively and in spontaneously breathing rats by proton MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2007, 26, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velde, G.V.; De Langhe, E.; Poelmans, J.; Dresselaers, T.; Lories, R.J.; Himmelreich, U. Magnetic resonance imaging for noninvasive assessment of lung fibrosis onset and progression: Cross-validation and comparison of different magnetic resonance imaging protocols with micro-computed tomography and histology in the bleomycin-induced mouse model. Investig. Radiol. 2014, 49, 691–698. [Google Scholar]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G.; Group NCRRGW. Animal research: Reporting in vivo experiments: The ARRIVE guidelines. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 1577–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbom, A.; Ahlstedt, J.; Seren, T.; Auterinen, I.; Kotiluoto, P.; Hauge, H.; Ostlund, K.; Olafsen, T.; Wu, A.M.; Dahlbom, M.; et al. Characterization of a double-sided silicon strip detector autoradiography system. Med. Phys. 2015, 42, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hubner, R.H.; Gitter, W.; El Mokhtari, N.E.; Mathiak, M.; Both, M.; Bolte, H.; Freitag-Wolf, S.; Bewig, B. Standardized quantification of pulmonary fibrosis in histological samples. Biotechniques 2008, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Langhe, E.; Vande Velde, G.; Hostens, J.; Himmelreich, U.; Nemery, B.; Luyten, F.P.; Vanoirbeek, J.; Lories, R.J. Quantification of lung fibrosis and emphysema in mice using automated micro-computed tomography. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Velde, G.V.; Poelmans, J.; De Langhe, E.; Hillen, A.; Vanoirbeek, J.; Himmelreich, U.; Lories, R.J. Longitudinal micro-CT provides biomarkers of lung disease that can be used to assess the effect of therapy in preclinical mouse models, and reveal compensatory changes in lung volume. Dis. Model. Mech. 2016, 9, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leith, D.E.; Brown, R. Human lung volumes and the mechanisms that set them. Eur. Respir. J. 1999, 13, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bianchi, A.; Tibiletti, M.; Kjorstad, A.; Birk, G.; Schad, L.R.; Stierstorfer, B.; Rasche, V.; Stiller, D. Three-dimensional accurate detection of lung emphysema in rats using ultra-short and zero echo time MRI. NMR Biomed. 2015, 28, 1471–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tielemans, B.; Dekoster, K.; Verleden, S.E.; Sawall, S.; Leszczynski, B.; Laperre, K.; Vanstapel, A.; Verschakelen, J.; Kachelriess, M.; Verbeken, E.; et al. From Mouse to Man and Back: Closing the Correlation Gap between Imaging and Histopathology for Lung Diseases. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izbicki, G.; Segel, M.J.; Christensen, T.G.; Conner, M.W.; Breuer, R. Time course of bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2002, 83, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinert, T.; Baldotto, C.S.D.R.; Nunes, F.A.P.; Scheliga, A.A.D.S. Bleomycin-Induced Lung Injury. J. Cancer Res. 2013, 2013, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Potente, G.; Bellelli, A.; Nardis, P. Specific diagnosis by CT and HRCT in six chronic lung diseases. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 1992, 16, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legmann, P. Imaging and lung disease: Uses and interpretation. Tuber. Lung Dis. 1993, 74, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, L.; Thickett, D.R.; Mansell, J.P.; Ionescu, M.; Hoyle, E.; Billinghurst, R.C.; Poole, A.R.; Millar, A.B. Changes in collagen turnover in early acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 160, 1910–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, D.H.; Ingvarsen, S.; Jurgensen, H.J.; Melander, M.C.; Kjoller, L.; Moyer, A.; Honore, C.; Madsen, C.A.; Garred, P.; Burgdorf, S.; et al. The non-phagocytic route of collagen uptake: A distinct degradation pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 26996–27010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manka, S.W.; Carafoli, F.; Visse, R.; Bihan, D.; Raynal, N.; Farndale, R.W.; Murphy, G.; Enghild, J.J.; Hohenester, E.; Nagase, H. Structural insights into triple-helical collagen cleavage by matrix metalloproteinase 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12461–12466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, K.G.; Stultz, C.M. Insight into the degradation of type-I collagen fibrils by MMP-8. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 1815–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, P.K.; Bozyk, P.D.; Bentley, J.K.; Popova, A.P.; Birch, C.M.; Wilke, C.A.; Fry, C.D.; White, E.S.; Sisson, T.H.; Tayob, N.; et al. Periostin promotes fibrosis and predicts progression in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2012, 303, L1046–L1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Satoh, H.; Kurishima, K.; Ishikawa, H.; Ohtsuka, M. Increased levels of KL-6 and subsequent mortality in patients with interstitial lung diseases. J. Intern. Med. 2006, 260, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koli, K.; Myllarniemi, M.; Vuorinen, K.; Salmenkivi, K.; Ryynanen, M.J.; Kinnula, V.L.; Keski-Oja, J. Bone morphogenetic protein-4 inhibitor gremlin is overexpressed in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 169, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flevaris, P.; Vaughan, D. The Role of Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor Type-1 in Fibrosis. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2017, 43, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoury, B.; Caulet-Maugendre, S.; Guenon, I.; Lagente, V.; Boichot, E. TIMP-1 is a key factor of fibrogenic response to bleomycin in mouse lung. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2006, 19, 471–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Headley, L.; Bi, W.; Wilson, C.; Collum, S.D.; Chavez, M.; Darwiche, T.; Mertens, T.C.J.; Hernandez, A.M.; Siddiqui, S.R.; Rosenbaum, S.; et al. Low-dose administration of bleomycin leads to early alterations in lung mechanics. Exp. Physiol. 2018, 103, 1692–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Latta, V.; Cecchettini, A.; Del Ry, S.; Morales, M.A. Bleomycin in the setting of lung fibrosis induction: From biological mechanisms to counteractions. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 97, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justet, A.; Laurent-Bellue, A.; Thabut, G.; Dieudonne, A.; Debray, M.P.; Borie, R.; Aubier, M.; Lebtahi, R.; Crestani, B. [(18)F]FDG PET/CT predicts progression-free survival in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, M.; Li, L.; Chen, L. Involvement of the Warburg effect in non-tumor diseases processes. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 2839–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahmutovic Persson, I.; Fransén Pettersson, N.; Liu, J.; Falk Håkansson, H.; Örbom, A.; In ’t Zandt, R.; Gidlöf, R.; Sydoff, M.; von Wachenfeldt, K.; Olsson, L.E., on behalf of the TRISTAN Consortium. Longitudinal Imaging Using PET/CT with Collagen-I PET-Tracer and MRI for Assessment of Fibrotic and Inflammatory Lesions in a Rat Lung Injury Model. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3706. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113706
Mahmutovic Persson I, Fransén Pettersson N, Liu J, Falk Håkansson H, Örbom A, In ’t Zandt R, Gidlöf R, Sydoff M, von Wachenfeldt K, Olsson LE on behalf of the TRISTAN Consortium. Longitudinal Imaging Using PET/CT with Collagen-I PET-Tracer and MRI for Assessment of Fibrotic and Inflammatory Lesions in a Rat Lung Injury Model. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(11):3706. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113706
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahmutovic Persson, Irma, Nina Fransén Pettersson, Jian Liu, Hanna Falk Håkansson, Anders Örbom, René In ’t Zandt, Ritha Gidlöf, Marie Sydoff, Karin von Wachenfeldt, and Lars E. Olsson on behalf of the TRISTAN Consortium. 2020. "Longitudinal Imaging Using PET/CT with Collagen-I PET-Tracer and MRI for Assessment of Fibrotic and Inflammatory Lesions in a Rat Lung Injury Model" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 11: 3706. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113706
APA StyleMahmutovic Persson, I., Fransén Pettersson, N., Liu, J., Falk Håkansson, H., Örbom, A., In ’t Zandt, R., Gidlöf, R., Sydoff, M., von Wachenfeldt, K., & Olsson, L. E., on behalf of the TRISTAN Consortium. (2020). Longitudinal Imaging Using PET/CT with Collagen-I PET-Tracer and MRI for Assessment of Fibrotic and Inflammatory Lesions in a Rat Lung Injury Model. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(11), 3706. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113706