Risk Factors, Pathogenesis, and Strategies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Prevention: Emphasis on Secondary Prevention and Its Translational Challenges
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Risk Factors and Carcinogenesis
2.1. Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)
2.2. Hepatitis C Virus (HCV)
2.3. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)/Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)
2.4. Lifestyle Risk Factors
2.5. Environmental Carcinogens
2.6. Genetic Predisposition
2.7. Endocrine Risk Factors
3. Pathogenesis of HCC
4. Molecular Biomarkers of HCC—The Prognostic Liver Signature
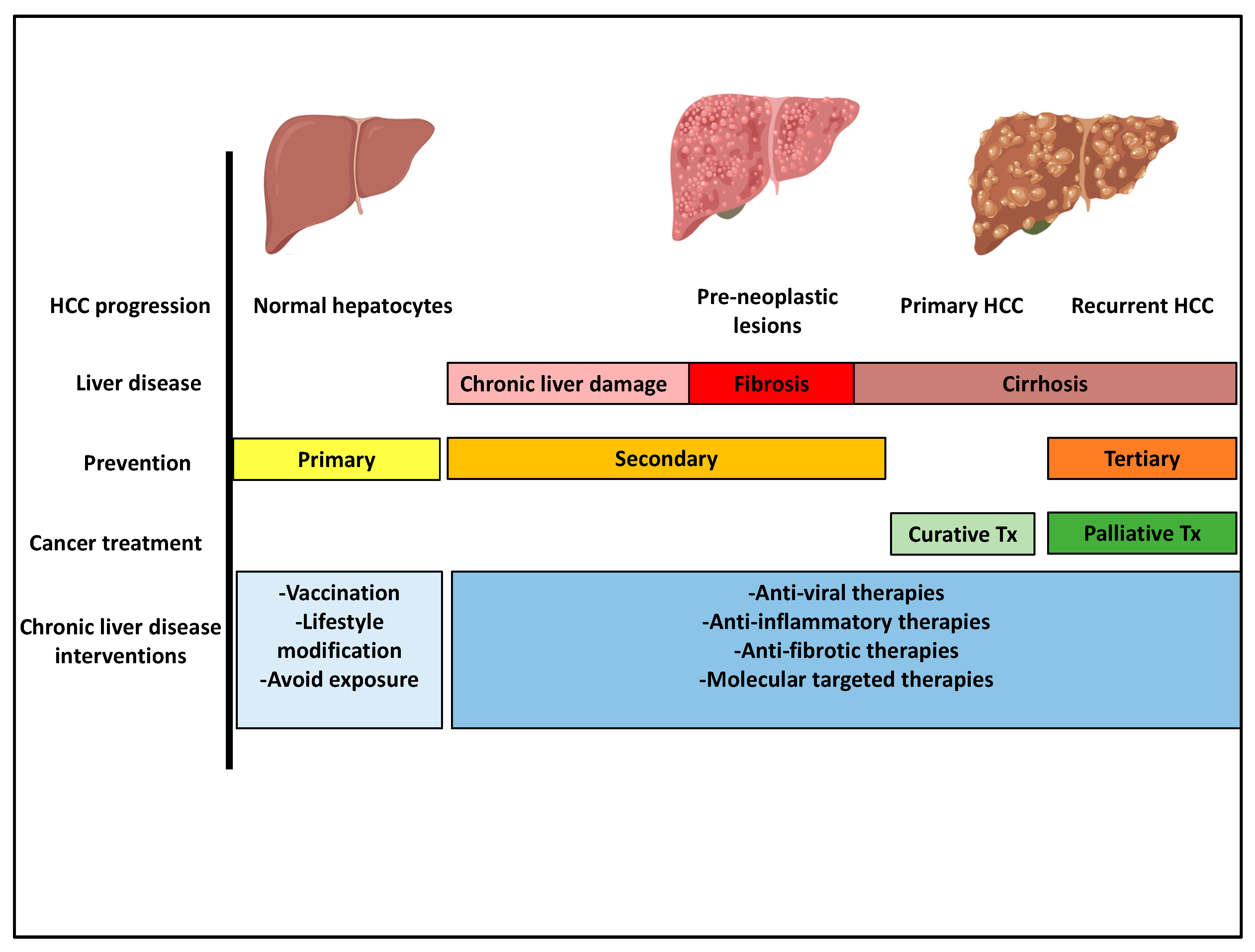
5. Prevention Strategies
6. Early Diagnosis and Surveillance
7. Etiology-Specific Secondary Chemoprevention
7.1. Hepatitis B
7.2. Hepatitis C
7.3. Alcohol
8. Etiology-Independent Secondary Chemoprevention Strategies
8.1. Statins
8.2. Aspirin, COX2 Inhibitors and Anti-Platelet Agents
8.3. Anti-Fibrosis Therapy
8.4. Nutritional Agents
9. Challenges and Obstacles in Prevention
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AR | Androgen receptor |
| ALD | Alcoholic liver disease |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| COX2 | Cyclooxygenease-2 |
| DAA | Direct-acting antivirals |
| DEN | N-diethylnitrosamine |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| EGF | Epidermal growth factor |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| GWAS | Genome wide associated studies |
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| IFN-α | Interferon alpha |
| LAR | Lysophosphatidic acid receptor |
| LPAR1 | Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 1 |
| mTOR | Mammalian target of rapamycin |
| NAFLD | Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor κB |
| NASH | Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis |
| NSAIDS | Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| PPAR | Peroxisome proliferator activated receptors |
| PLS | Prognostic liver signature |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SNP | Single nucleotide polymorphism |
| SVR | Sustained virologic response |
| TNF-a | Tumor-Necrosis-Factor alpha |
References
- Yang, J.D.; Hainaut, P.; Gores, G.J.; Amadou, A.; Plymoth, A.; Roberts, L.R. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: Trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Me, J.F.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asrani, S.K.; Devarbhavi, H.; Eaton, J.; Kamath, P.S. Burden of liver diseases in the world. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beste, L.A.; Leipertz, S.L.; Green, P.K.; Dominitz, J.A.; Ross, D.; Ioannou, G.N. Trends in Burden of Cirrhosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Underlying Liver Disease in US Veterans, 2001–2013. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1471–1482.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mokdad, A.H.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Daoud, F.; Mokdad, A.A.; El Bcheraoui, C.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; Kyu, H.H.; Barber, R.M.; Wagner, J.; Cercy, K.; et al. Global burden of diseases, injuries, and risk factors for young people’s health during 1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2016, 387, 2383–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, F.; Hoang, T.; Kramer, J.R.; Asch, S.M.; Goetz, M.B.; Zeringue, A.; Richardson, P.; El–Serag, H.B. Increasing Prevalence of HCC and Cirrhosis in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 1182–1188.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howlader, N.; Noone, A.M.; Krapcho, M.; Miller, D.; Brest, A.; Yu, M.; Ruhl, J.; Tatalovich, Z.; Mariotto, A.; Lewis, D.R.; et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2016; Based on November 2018 SEER Data Submission, Posted to the SEER Web Site; National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Altekruse, S.F.; McGlynn, K.A.; Reichman, M.E. Hepatocellular Carcinoma Incidence, Mortality, and Survival Trends in the United States From 1975 to 2005. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1485–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez, P.M.; Villanueva, A.; Llovet, J.M. Systematic review: Evidence-based management of hepatocellular carcinoma—An updated analysis of randomized controlled trials. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 23, 1535–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompili, M.; Saviano, A.; De Matthaeis, N.; Cucchetti, A.; Ardito, F.; Federico, B.; Brunello, F.; Pinna, A.D.; Giorgio, A.; Giulini, S.M.; et al. Long-term effectiveness of resection and radiofrequency ablation for single hepatocellular carcinoma ≤ 3 cm. Results of a multicenter Italian survey. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Ricci, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Hilgard, P.; Gane, E.; Blanc, J.-F.; De Oliveira, A.C.; Santoro, A.; Raoul, J.-L.; Forner, A.; et al. Sorafenib in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Meyer, T.; Cheng, A.-L.; El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Rimassa, L.; Ryoo, B.-Y.; Cicin, I.; Merle, P.; Chen, Y.; Park, J.-W.; et al. Cabozantinib in Patients with Advanced and Progressing Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, A.X.; Galle, P.R.; Kudo, M.; Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Xu, Y.; Abada, P.; Llovet, J. A study of ramucirumab (LY3009806) versus placebo in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and elevated baseline alpha-fetoprotein (REACH-2). J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, TPS538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Sangro, B.; Yau, T.; Crocenzi, T.S.; Kudo, M.; Hsu, C.; Kim, T.-Y.; Choo, S.-P.; Trojan, J.; Welling, T.H.; et al. Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): An open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 2492–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Ryoo, B.-Y.; Merle, P.; Kudo, M.; Bouattour, M.; Lim, H.-Y.; Breder, V.V.; Edeline, J.; Chao, Y.; Ogasawara, S.; et al. Results of KEYNOTE-240: Phase 3 study of pembrolizumab (Pembro) vs. best supportive care (BSC) for second line therapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinter, M.; Jain, R.K.; Duda, D.G. The Current Landscape of Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yang, Y.; Wen, F.; He, X.; Tang, R.; Du, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q. Cost-effectiveness of sorafenib as a first-line treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 27, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Serag, H.B.; Rudolph, K.L. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Epidemiology and Molecular Carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2557–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, E. Hepatitis B: Epidemiology and prevention in developing countries. World J. Hepatol. 2012, 4, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.-S.; Chien, R.-N.; Yeh, C.-T.; Sheen, I.-S.; Chiou, H.-Y.; Chu, C.-M.; Liaw, Y.-F. Long-term outcome after spontaneous HBeAg seroconversion in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2002, 35, 1522–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattovich, G.; Olivari, N.; Pasino, M.; D’Onofrio, M.; Martone, E.; Donato, F. Long-term outcome of chronic hepatitis B in Caucasian patients: Mortality after 25 years. Gut 2007, 57, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattovich, G. Natural History and Prognosis of Hepatitis B. Semin. Liver Dis. 2003, 23, 047–058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.D.; Kim, W.R.; Coelho, R.; Mettler, T.A.; Benson, J.T.; Sanderson, S.O.; Therneau, T.M.; Kim, B.; Roberts, L.R. Cirrhosis Is Present in Most Patients with Hepatitis B and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 9, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Osawa, M.; Akuta, N.; Suzuki, F.; Fujiyama, S.; Kawamura, Y.; Sezaki, H.; Hosaka, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Saitoh, S.; et al. Prognosis and predictors of hepatocellular carcinoma in elderly patients infected with hepatitis B virus. J. Med. Virol. 2017, 89, 2144–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of Viral Hepatitis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1264–1273.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soussan, P.; Garreau, F.; Zylberberg, H.; Ferray, C.; Brechot, C.; Kremsdorf, D. In vivo expression of a new hepatitis B virus protein encoded by a spliced RNA. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 105, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edmunds, W.J.; Medley, G.F.; Nokes, D.J.; Hall, A.J.; Whittle, H.C. The influence of age on the development of the hepatitis B carrier state. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 1993, 253, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, W.-K.; Zheng, H.; Li, S.; Chen, R.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Lee, N.P.; Lee, W.H.; Ariyaratne, P.N.; Tennakoon, C.; et al. Genome-wide survey of recurrent HBV integration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Tang, G.; Wang, Y.; Xue, G.; Zhou, W.; Sun, S. Characterization of the genotype and integration patterns of hepatitis B virus in early- and late-onset hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1821–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemin, I.; Zoulim, F. Hepatitis B virus induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2009, 286, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucifora, J.; Arzberger, S.; Durantel, D.; Belloni, L.; Strubin, M.; Levrero, M.; Zoulim, F.; Hantz, O.; Protzer, U. Hepatitis B virus X protein is essential to initiate and maintain virus replication after infection. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayliss, J.; Lim, L.; Thompson, A.J.; Desmond, P.; Angus, P.; Locarnini, S.; Revill, P.A. Hepatitis B virus splicing is enhanced prior to development of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, R.J.; Cheung, R.; Ahmed, A. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is the most rapidly growing indication for liver transplantation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in the U.S. Hepatology 2014, 59, 2188–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galbraith, J.W.; Franco, R.A.; Donnelly, J.P.; Rodgers, J.B.; Morgan, J.M.; Viles, A.F.; Overton, E.T.; Saag, M.S.; Wang, H.E. Unrecognized chronic hepatitis C virus infection among baby boomers in the emergency department. Hepatology 2015, 61, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, I.M.; Davis, G.L.; El–Serag, H.; Negro, F.; Trepo, C. Prevalence and Challenges of Liver Diseases in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 8, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.J.; Ward, J.W. Hepatitis C in Injection-Drug Users—A Hidden Danger of the Opioid Epidemic. New Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1169–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.D.; Magee, E.; Grant, G. National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention; CDC Health Disparities Inequalities Report—United States; CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2013; Volume 62, p. 149. [Google Scholar]
- Galbraith, J.W.; Donnelly, J.P.; Franco, R.A.; Overton, E.T.; Rodgers, J.B.; Wang, H.E. National Estimates of Healthcare Utilization by Individuals with Hepatitis C Virus Infection in the United States. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 59, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, H.; Shiratori, Y.; Moriyama, M.; Arakawa, Y.; Ide, T.; Sata, M.; Inoue, O.; Yano, M.; Tanaka, M.; Fujiyama, S.; et al. Interferon Therapy Reduces the Risk for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: National Surveillance Program of Cirrhotic and Noncirrhotic Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C in Japan. Ann. Intern. Med. 1999, 131, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, F.; Kramer, J.R.; Ilyas, J.; Duan, Z.; El-Serag, H.B. HCV genotype 3 is associated with an increased risk of cirrhosis and hepatocellular cancer in a national sample of U.S. Veterans with HCV. Hepatology 2014, 60, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoshida, Y.; Fuchs, B.C.; Bardeesy, N.; Baumert, T.F.; Chung, R.T. Pathogenesis and prevention of hepatitis C virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, S79–S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vescovo, T.; Refolo, G.; Vitagliano, G.; Fimia, G.; Piacentini, M. Molecular mechanisms of hepatitis C virus–induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Street, A.; Macdonald, A.; McCormick, C.J.; Harris, M. Hepatitis C Virus NS5A-Mediated Activation of Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Results in Stabilization of Cellular β-Catenin and Stimulation of β-Catenin-Responsive Transcription. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 5006–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salloum, S.; Wang, H.; Ferguson, C.; Parton, R.G.; Tai, A.W. Rab18 Binds to Hepatitis C Virus NS5A and Promotes Interaction between Sites of Viral Replication and Lipid Droplets. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.D.; Roberts, L.R. Hepatocellular carcinoma: A global view. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.; Li, A.A.; Gadiparthi, C.; Khan, M.A.; Cholankeril, G.; Glenn, J.S.; Ahmed, A. Changing Trends in Etiology-Based Annual Mortality From Chronic Liver Disease, From 2007 through 2016. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1154–1163.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piscaglia, F.; Svegliati-Baroni, G.; Barchetti, A.; Pecorelli, A.; Marinelli, S.; Tiribelli, C.; Bellentani, S.; HCC-NAFLD Italian Study Group. Clinical patterns of hepatocellular carcinoma in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A multicenter prospective study. Hepatology 2016, 63, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.L.; Kanwal, F.; El–Serag, H.B. Association Between Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Risk for Hepatocellular Cancer, Based on Systematic Review. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 1342–1359.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKeating, J.A.; Pfister, D.; O’Connor, T.; Pikarsky, E.; Heikenwalder, M. The immunology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.; Anstee, Q.M.; Marietti, M.; Hardy, T.; Henry, L.; Eslam, M.; George, J.; Bugianesi, E. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: Trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Mao, H.; Li, J.; Mills, G.B.; Shu, Y.; Li, L.; et al. Comprehensive Characterization of Molecular Differences in Cancer between Male and Female Patients. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, R.; Kaushik, S.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Novak, I.; Komatsu, M.; Tanaka, K.; Cuervo, A.M.; Czaja, M.J. Autophagy regulates lipid metabolism. Nature 2009, 458, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, S.; Hikita, H.; Tatsumi, T.; Sakamori, R.; Nozaki, Y.; Sakane, S.; Shiode, Y.; Nakabori, T.; Saito, Y.; Hiramatsu, N.; et al. Rubicon inhibits autophagy and accelerates hepatocyte apoptosis and lipid accumulation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Hepatology 2016, 64, 1994–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gäbele, E.; Dostert, K.; Hofmann, C.; Wiest, R.; Schölmerich, J.; Hellerbrand, C.; Obermeier, F. DSS induced colitis increases portal LPS levels and enhances hepatic inflammation and fibrogenesis in experimental NASH. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL). Liver Int. 2001, 21, 71. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ganne-Carrié, N.; Nahon, P. Hepatocellular carcinoma in the setting of alcohol-related liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meadows, G.G.; Zhang, H. Effects of Alcohol on Tumor Growth, Metastasis, Immune Response, and Host Survival. Alcohol Res. Curr. Rev. 2015, 37, 311–322. [Google Scholar]
- Persson, E.C.; Schwartz, L.M.; Park, Y.; Trabert, B.; Hollenbeck, A.R.; Graubard, B.I.; Freedman, N.D.; McGlynn, K.A. Alcohol consumption, folate intake, hepatocellular carcinoma, and liver disease mortality. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2013, 22, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donato, F.; Tagger, A.; Gelatti, U.; Parrinello, G.; Boffetta, P.; Albertini, A.; DeCarli, A.; Trevisi, P.; Ribero, M.L.; Martelli, C.; et al. Alcohol and hepatocellular carcinoma: The effect of lifetime intake and hepatitis virus infections in men and women. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2002, 155, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loomba, R.; Yang, H.-I.; Su, J.; Brenner, D.A.; Iloeje, U.; Chen, C.-J. Obesity and Alcohol Synergize to Increase the Risk of Incident Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Men. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 8, 891–898.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Tanaka, N.; Fujimori, N.; Sugiura, A.; Yamazaki, T.; Joshita, S.; Komatsu, M.; Umemura, T.; Matsumoto, A.; Tanaka, E. Mild drinking habit is a risk factor for hepatocarcinogenesis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with advanced fibrosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 1440–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochiai, Y.; Kawamura, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Shindoh, J.; Kobayashi, Y.; Okubo, S.; Muraishi, N.; Kajiwara, A.; Iritani, S.; Fujiyama, S.; et al. Effects of alcohol consumption on multiple hepatocarcinogenesis in patients with fatty liver disease. Hepatol. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setshedi, M.; Wands, J.R.; De La Monte, S.M. Acetaldehyde Adducts in Alcoholic Liver Disease. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2010, 3, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fischer, M.; You, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Crabb, D.W. Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor α (PPARα) Agonist Treatment Reverses PPARα Dysfunction and Abnormalities in Hepatic Lipid Metabolism in Ethanol-fed Mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 27997–28004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Yang, W.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, X.; Yao, Y.; Tu, K.; Liu, Q. SREBP-1 Has a Prognostic Role and Contributes to Invasion and Metastasis in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 7124–7138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Wang, F.; Li, X.; Rogers, C.Q.; Liang, X.; Finck, B.N.; Mitra, M.S.; Zhang, R.; Mitchell, D.A.; You, M. Regulation of hepatic lipin-1 by ethanol: Role of AMP-activated protein kinase/sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 signaling in mice. Hepatology 2011, 55, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, S.; McPhaul, C.; Li, J.Z.; Garuti, R.; Kinch, L.; Grishin, N.V.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. A Sequence Variation (I148M) in PNPLA3 Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Disrupts Triglyceride Hydrolysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 6706–6715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bucher, S.S.; Stickel, F.; Trépo, E.; Way, M.M.; Herrmann, A.; Nischalke, H.D.; Brosch, M.M.; Rosendahl, J.J.; Berg, T.; Ridinger, M.M.; et al. A genome-wide association study confirms PNPLA3 and identifies TM6SF2 and MBOAT7 as risk loci for alcohol-related cirrhosis. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baecker, A.; Liu, X.; La Vecchia, C.; Zhang, Z.-F. Worldwide incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma cases attributable to major risk factors. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 27, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrick, J.L.; Campbell, P.T.; Koshiol, J.; Thistle, J.E.; Andreotti, G.; Freeman, L.E.B.; Buring, J.E.; Chan, A.T.; Chong, D.Q.; Doody, M.M.; et al. Tobacco, alcohol use and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: The Liver Cancer Pooling Project. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolly, P.; Knöpfli, M.; Dufour, J.-F.F. Effect of smoking on survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 1682–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staretz, M.E.; Murphy, S.E.; Patten, C.J.; Nunes, M.G.; Koehl, W.; Amin, S.; Koenig, L.A.; Guengerich, F.P.; Hecht, S.S. Comparative metabolism of the tobacco-related carcinogens benzo[a]pyrene, 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone, 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanol, and N’- nitrosonornicotine in human hepatic microsomes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1997, 25, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, S.S.; Zacchi, E.; Amadio, P.; Gianellini, S.; Mussoni, L.; Weksler, B.B.; Tremoli, E. Cytokines present in smokers’ serum interact with smoke components to enhance endothelial dysfunction. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 90, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- JM, D.P.; MJ, F.A.; MJ, L.A.; Álvarez, A. Tumor necrosis factor as an early marker of inflammation in healthy smokers. Med. Clin. 2012, 139, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Dooley, K.; Von Tungeln, L.; Bucci, T.; Fu, P.; Kadlubar, F. Comparative carcinogenicity of 4-aminobiphenyl and the food pyrolysates, Glu-P-1, IQ, PhIP, and MeIQx in the neonatal B6C3F1 male mouse. Cancer Lett. 1992, 62, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzalini, L.; Ferrer, E.; Ramalho, L.N.; Moreno, M.; Domínguez, M.; Colmenero, J.; Peinado, V.I.; Barberà, J.A.; Arroyo, V.; Ginès, P.; et al. Cigarette smoking exacerbates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in obese rats. Hepatology 2009, 51, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kew, M. Aflatoxins as a cause of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2013, 22, 305–310. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.-C.; Santella, R. The Role of Aflatoxins in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Zahedan J. Res. Med Sci. 2012, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woo, L.L.; Egner, P.A.; Belanger, C.L.; Wattanawaraporn, R.; Trudel, L.J.; Croy, R.G.; Groopman, J.D.; Essigmann, J.M.; Wogan, G.N.; Bouhenguel, J.T. Aflatoxin B1-DNA Adduct Formation and Mutagenicity in Livers of Neonatal Male and Female B6C3F1 Mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 122, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.-W.; Lien, J.-P.; Chiu, Y.-H.; Santella, R.M.; Liaw, Y.-F.; Chen, C.-J. Effect of aflatoxin metabolism and DNA adduct formation on hepatocellular carcinoma among chronic hepatitis B carriers in Taiwan. J. Hepatol. 1997, 27, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.D.; A Mohamed, E.; Aziz, A.O.A.; I Shousha, H.; Hashem, M.B.; Nabeel, M.M.; Abdelmaksoud, A.H.; Elbaz, T.M.; Afihene, M.Y.; Duduyemi, B.M.; et al. Characteristics, management, and outcomes of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in Africa: A multicountry observational study from the Africa Liver Cancer Consortium. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eriksson, S.G. Liver Disease in α 1 -Antitrypsin Deficiency: Aspects of Incidence and Prognosis. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1985, 20, 907–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janecke, A.R.; Mayatepek, E.; Utermann, G. Molecular Genetics of Type 1 Glycogen Storage Disease. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2001, 73, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, L. Glycogen storage disease I and hepatocellular tumours. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 1993, 152, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmberg, M.; Hultcrantz, R.; Ekbom, A.; Brandt, L.; Olsson, S.; Olsson, R.; Lindgren, S.; Lööf, L.; Stål, P.; Wallerstedt, S.; et al. Cancer risk in patients with hereditary hemochromatosis and in their first-degree relatives. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, C.R. The genetic tyrosinemias. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part C Semin. Med. Genet. 2006, 142, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, A.G.; Mize, C.E.; Worthen, H.G. The occurrence of hepatoma in the chronic form of hereditary tyrosinemia. J. Pediatr. 1976, 88, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, K.K.; Lemoine, A.; Finkelstein, D.M.; Kawasaki, H.; Fujii, T.; Chung, R.T.; Lauwers, G.Y.; Kulu, Y.; Muzikansky, A.; Kuruppu, D.; et al. Epidermal Growth Factor Gene Functional Polymorphism and the Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Cirrhosis. JAMA 2008, 299, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhai, Y.; Hu, Z.; Wu, C.; Qian, J.; Jia, W.; Ma, F.; Huang, W.; Yu, L.; Yue, W.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies 1p36.22 as a new susceptibility locus for hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B virus carriers. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Kato, N.; Urabe, Y.; Takahashi, A.; Muroyama, R.; Hosono, N.; Otsuka, M.; Tateishi, R.; Omata, M.; Nakagawa, H.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies a susceptibility locus for HCV-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, D.; Ochi, H.; Hayes, C.N.; Abe, H.; Yoshima, T.; Aikata, H.; Ikeda, K.; Kumada, H.; Toyota, J.; Morizono, T.; et al. Variation in the DEPDC5 locus is associated with progression to hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis C virus carriers. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 797–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonardo, A.; Mantovani, A.; Lugari, S.; Targher, G. NAFLD in Some Common Endocrine Diseases: Prevalence, Pathophysiology, and Principles of Diagnosis and Management. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antonelli, A.; Ferri, C.; Pampana, A.; Fallahi, P.; Nesti, C.; Pasquini, M.; Marchi, S.; Ferrannini, E. Thyroid disorders in chronic hepatitis C. Am. J. Med. 2004, 117, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.M.; Kaseb, A.; Li, D.; Patt, Y.Z.; Vauthey, J.-N.; Thomas, M.B.; Curley, S.A.; Spitz, M.R.; Sherman, S.I.; Abdalla, E.K.; et al. Association between hypothyroidism and hepatocellular carcinoma: A case-control study in the United States. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1563–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lonardo, A.; Ballestri, S.; Mantovani, A.; Nascimbeni, F.; Lugari, S.; Targher, G. Pathogenesis of hypothyroidism-induced NAFLD: Evidence for a distinct disease entity? Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinter, M.; Haupt, L.; Hucke, F.; Bota, S.; Bucsics, T.; Trauner, M.; Peck-Radosavljevic, M.; Sieghart, W. The impact of thyroid hormones on patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, P.-S.; Lin, Y.-H.; Chi, H.-C.; Hsiang-Cheng, C.; Huang, Y.-H.; Yeh, C.-T.; Kwang-Huei, L.; Lin, K.-H. Thyroid hormone inhibits growth of hepatoma cells through induction of miR-214. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent–Puig, P.; Legoix, P.; Bluteau, O.; Belghiti, J.; Franco, D.; Binot, F.; Monges, G.; Thomas, G.; Bioulac–Sage, P.; Zucman-Rossi, J. Genetic alterations associated with hepatocellular carcinomas define distinct pathways of hepatocarcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 2001, 120, 1763–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeh, S.-H.; Chen, P.-J. Gender Disparity of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Roles of Sex Hormones. Oncology 2010, 78, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-H.; Ma, W.-L.; Hsu, C.-L.; Chen, Y.-L.; Ou, J.-H.J.; Ryan, C.K.; Hung, Y.-C.; Yeh, S.; Chang, C. Androgen Receptor Promotes Hepatitis B Virus-Induced Hepatocarcinogenesis Through Modulation of Hepatitis B Virus RNA Transcription. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 32ra35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, C.-L.; Hsu, C.; Wu, M.; Wu, C.; Wu, C.; Lai, J.; Jou, Y.; Cheng-Lung, H.; Yeh, S.; Chang, C. Androgen Receptor Is a New Potential Therapeutic Target for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 947–955.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kanda, T.; Yokosuka, O. The androgen receptor as an emerging target in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2015, 2, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shimizu, I. Impact of oestrogens on the progression of liver disease. Liver Int. 2003, 23, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGlynn, K.A.; Sahasrabuddhe, V.V.; Campbell, P.T.; Graubard, B.I.; Chen, J.; Schwartz, L.M.; Petrick, J.L.; Alavanja, M.C.; Andreotti, G.; Boggs, D.A.; et al. Reproductive factors, exogenous hormone use and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma among US women: Results from the Liver Cancer Pooling Project. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1266–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsia, C.-Y.; Huo, T.-I.; Chiang, S.-Y.; Lu, M.-F.; Sun, C.-L.; Wu, J.-C.; Lee, P.-C.; Chi, C.-W.; Lui, W.-Y.; Lee, S.-D. Evaluation of interleukin-6, interleukin-10 and human hepatocyte growth factor as tumor markers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2007, 33, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naugler, W.E.; Sakurai, T.; Kim, S.; Maeda, S.; Kim, K.; Elsharkawy, A.M.; Karin, M. Gender Disparity in Liver Cancer Due to Sex Differences in MyD88-Dependent IL-6 Production. Science 2007, 317, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, G.; Yu, G.-Y.; Temkin, V.; Ogata, H.; Kuntzen, C.; Sakurai, T.; Sieghart, W.; Peck-Radosavljevic, M.; Leffert, H.L.; Karin, M. Hepatocyte IKKβ/NF-κB Inhibits Tumor Promotion and Progression by Preventing Oxidative Stress-Driven STAT3 Activation. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calvisi, D.F. Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde: A paradoxical oncogenic and tumor suppressive role of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in liver cancer. Hepatology 2011, 54, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edamoto, Y.; Hara, A.; Biernat, W.; Terracciano, L.; Cathomas, G.; Riehle, H.-M.; Matsuda, M.; Fujii, H.; Scoazec, J.-Y.; Ohgaki, H. Alterations of RB1, p53 and Wnt pathways in hepatocellular carcinomas associated with hepatitis C, hepatitis B and alcoholic liver cirrhosis. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 106, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Hirohashi, S.; Sekiya, T. Aberrations of the tumor suppressor p53 and retinoblastoma genes in human hepatocellular carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 5520–5525. [Google Scholar]
- Liew, C.T.; Li, H.-M.; Lo, K.-W.; Leow, C.K.; Chan, J.Y.; Hin, L.Y.; Lau, W.Y.; Lai, P.B.S.; Lim, B.K.; Huang, J.; et al. High frequency of p16INK4A gene alterations in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 1999, 18, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, A.T.; Hankins, G.R.; Washington, M.K.; Orton, T.C.; Jirtle, R.L. M6P/IGF2R gene is mutated in human hepatocellular carcinomas with loss of heterozygosity. Nat. Genet. 1995, 11, 447–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, S.; Hua, F.; Hu, Z.-W. The regulation of β-catenin activity and function in cancer: Therapeutic opportunities. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 33972–33989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, C.M.; Fan, S.T.; Ng, I.O.L. β-catenin mutation and overexpression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 2001, 92, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.W.; Forrester, K.; Yeh, H.; Feitelson, M.A.; Gu, J.R.; Harris, C.C. Hepatitis B virus X protein inhibits p53 sequence-specific DNA binding, transcriptional activity, and association with transcription factor ERCC3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 2230–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, J.; Wang, X.W. New kids on the block: Diagnostic and prognostic microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2009, 8, 1683–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, J.; Yamashita, T.; Budhu, A.; Forgues, M.; Jia, H.-L.; Li, C.; Deng, C.; Wauthier, E.; Reid, L.M.; Ye, Q.-H.; et al. Identification of microRNA-181 by genome-wide screening as a critical player in EpCAM-positive hepatic cancer stem cells. Hepatology 2009, 50, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gong, J.; He, X.-X.; Tian, D.-A. Emerging role of microRNA in hepatocellular carcinoma (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2015, 9, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kojima, K.; Takata, A.; Vadnais, C.; Otsuka, M.; Yoshikawa, T.; Akanuma, M.; Kondo, Y.; Kang, Y.J.; Kishikawa, T.; Kato, N.; et al. MicroRNA122 is a key regulator of α-fetoprotein expression and influences the aggressiveness of hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.-S.; Chu, I.-S.; Heo, J.; Calvisi, D.F.; Sun, Z.; Roskams, T.; Durnez, A.; Demetris, A.J.; Thorgeirsson, S.S. Classification and prediction of survival in hepatocellular carcinoma by gene expression profiling. Hepatology 2004, 40, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulouarn, C.; Factor, V.M.; Thorgeirsson, S.S. Transforming growth factor-β gene expression signature in mouse hepatocytes predicts clinical outcome in human cancer. Hepatology 2008, 47, 2059–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaposi-Novak, P.; Lee, J.-S.; Gòmez-Quiroz, L.; Coulouarn, C.; Factor, V.M.; Thorgeirsson, S.S. Met-regulated expression signature defines a subset of human hepatocellular carcinomas with poor prognosis and aggressive phenotype. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1582–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goossens, N.; Sun, X.; Hoshida, Y. Molecular classification of hepatocellular carcinoma: Potential therapeutic implications. Hepatic Oncol. 2015, 2, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Jiang, L.; Guan, X.-Y. The genetic and epigenetic alterations in human hepatocellular carcinoma: A recent update. Protein Cell 2014, 5, 673–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoshida, Y.; Nijman, S.M.; Kobayashi, M.; Chan, J.A.; Brunet, J.-P.; Chiang, D.Y.; Villanueva, A.; Newell, P.; Ikeda, K.; Hashimoto, M.; et al. Integrative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Common Molecular Subclasses of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 7385–7392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lachenmayer, A.; Alsinet, C.; Savic, R.; Cabellos, L.; Toffanin, S.; Hoshida, Y.; Villanueva, A.; Minguez, B.; Newell, P.; Tsai, H.W.; et al. Wnt-pathway activation in two molecular classes of hepatocellular carcinoma and experimental modulation by sorafenib. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4997–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zucman-Rossi, J.; Villanueva, A.; Nault, J.-C.; Llovet, J.M. Genetic Landscape and Biomarkers of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1226–1239.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castven, D.; Fischer, M.; Becker, D.; Heinrich, S.; Andersen, J.B.; Strand, D.; Sprinzl, M.F.; Strand, S.; Czauderna, C.; Heilmann-Heimbach, S.; et al. Adverse genomic alterations and stemness features are induced by field cancerization in the microenvironment of hepatocellular carcinomas. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 48688–48700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elsharkawy, A.M.; Mann, D.A. Nuclear factor-κB and the hepatic inflammation-fibrosis-cancer axis. Hepatology 2007, 46, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoda, M.; Mellody, K.T.; Orimo, A. Carcinoma-associated fibroblasts are a rate-limiting determinant for tumour progression. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2010, 21, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, E.Y.T.; Lo, J.; Cheng, B.Y.L.; Ma, M.K.F.; Lee, J.M.F.; Ng, J.K.Y.; Chai, S.; Lin, C.H.; Tsang, S.Y.; Ma, S.; et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts regulate tumor-initiating cell plasticity in hepatocellular carcinoma through c-Met/FRA1/HEY1 signaling. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 1175–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faouzi, S.; Lepreux, S.; Bedin, C.; Dubuisson, L.; Balabaud, C.; Bioulac-Sage, P.; Desmoulière, A.; Rosenbaum, J. Activation of cultured rat hepatic stellate cells by tumoral hepatocytes. Lab. Investig. 1999, 79, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Noy, R.; Pollard, J.W. Tumor-associated macrophages: From mechanisms to therapy. Immunity 2014, 41, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mantovani, A.; Bottazzi, B.; Colotta, F.; Sozzani, S.; Ruco, L.P. The origin and function of tumor-associated macrophages. Immunol. Today 1992, 13, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Schwartz, M.; Mazzaferro, V. Resection and Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Semin. Liver Dis. 2005, 25, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshida, Y.; Villanueva, A.; Kobayashi, M.; Peix, J.; Chiang, D.Y.; Camargo, A.; Gupta, S.; Moore, J.; Wrobel, M.J.; Lerner, J.; et al. Gene Expression in Fixed Tissues and Outcome in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1995–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoshida, Y.; Villanueva, A.; SanGiovanni, A.; Sole, M.; Hur, C.; Andersson, K.L.; Chung, R.T.; Gould, J.; Kojima, K.; Gupta, S.; et al. Prognostic Gene Expression Signature for Patients with Hepatitis C–Related Early-Stage Cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakagawa, S.; Wei, L.; Song, W.M.; Higashi, T.; Ghoshal, S.; Kim, R.S.; Bian, C.B.; Yamada, S.; Sun, X.; Venkatesh, A.; et al. Molecular Liver Cancer Prevention in Cirrhosis by Organ Transcriptome Analysis and Lysophosphatidic Acid Pathway Inhibition. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, B.C.; Hoshida, Y.; Fujii, T.; Wei, L.; Yamada, S.; Lauwers, G.Y.; McGinn, C.M.; Deperalta, D.K.; Chen, X.; Kuroda, T.; et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition attenuates liver fibrosis and development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1577–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burra, P.; Rodriguez-Castro, K.I. Neoplastic disease after liver transplantation: Focus onde novoneoplasms. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihara, Y.; Mizuno, H.; Chun, J. Lysophospholipid receptors in drug discovery. Exp. Cell Res. 2015, 333, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakai, N.; Chun, J.; Duffield, J.S.; Wada, T.; Luster, A.D.; Tager, A.M. LPA 1 -induced cytoskeleton reorganization drives fibrosis through CTGF-dependent fibroblast proliferation. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 1830–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoshida, Y.; Toffanin, S.; Lachenmayer, A.; Villanueva, A.; Minguez, B.; Llovet, J.M. Molecular Classification and Novel Targets in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Recent Advancements. Semin. Liver Dis. 2010, 30, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jühling, F.; Hamdane, N.; Crouchet, E.; Li, S.; El Saghire, H.; Mukherji, A.; Fujiwara, N.; Oudot, M.A.; Thumann, C.; Saviano, A.; et al. Targeting clinical epigenetic reprogramming for chemoprevention of metabolic and viral hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, E.; Critelli, R.; Lei, B.; Marzocchi, G.; Cammà, C.; Giannelli, G.; Pontisso, P.; Cabibbo, G.; Enea, M.; Colopi, S.; et al. Neoangiogenesis-related genes are hallmarks of fast-growing hepatocellular carcinomas and worst survival. Results from a prospective study. Gut 2015, 65, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanetti, A.R.; Van Damme, P.; Shouval, D. The global impact of vaccination against hepatitis B: A historical overview. Vaccine 2008, 26, 6266–6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.-H.; Chang, M.-H.; Huang, L.-M.; Chen, H.-L.; Hsu, H.-Y.; Chiu, T.-Y.; Tsai, K.-S.; Chen, D.-S. Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Children and Adolescents in a Hyperendemic Area: 15 Years after Mass Hepatitis B Vaccination. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001, 135, 796–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-H.; Yang, P.-M.; Huang, G.-T.; Lee, H.-S.; Sung, J.-L.; Sheu, J.-C. Estimation of Seroprevalence of Hepatitis B Virus and Hepatitis C Virus in Taiwan from a Large-scale Survey of Free Hepatitis Screening Participants. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2007, 106, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aitken, C.; Lewis, J.; Hocking, J.; Bowden, D.; Hellard, M. Does information about IDUs’ injecting networks predict exposure to the hepatitis C virus? Hepat Monthly. 2009, 9, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Razali, K.; Thein, H.-H.; Bell, J.; Cooper-Stanbury, M.; Dolan, K.; Dore, G.; George, J.; Kaldor, J.; Karvelas, M.; Li, J.; et al. Modelling the hepatitis C virus epidemic in Australia. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2007, 91, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azziz-Baumgartner, E.; Lindblade, K.; Gieseker, K.; Rogers, H.S.; Kieszak, S.; Njapau, H.; Schleicher, R.; McCoy, L.F.; Misore, A.; Decock, K.; et al. Case–Control Study of an Acute Aflatoxicosis Outbreak, Kenya, 2004. Environ. Heal. Perspect. 2005, 113, 1779–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luedde, T.; Schwabe, R.F. NF-κB in the liver—Linking injury, fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 8, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ikeda, K.; Arase, Y.; Saitoh, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Suzuki, F.; Tsubota, A.; Chayama, K.; Murashima, N.; Kumada, H. Interferon beta prevents recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after complete resection or ablation of the primary tumor—A prospective randomized study of hepatitis C virus–related liver cancer. Hepatology 2000, 32, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzaferro, V.; Romito, R.; Schiavo, M.; Mariani, L.; Camerini, T.; Bhoori, S.; Capussotti, L.; Calise, F.; Pellicci, R.; Belli, G.; et al. Prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence with alpha-interferon after liver resection in HCV cirrhosis. Hepatology 2006, 44, 1543–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinnakotla, S.; Davis, G.L.; Vasani, S.; Kim, P.; Tomiyama, K.; Sanchez, E.; Onaca, N.; Goldstein, R.; Levy, M.; Klintmalm, G.B. Impact of sirolimus on the recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation. Liver Transplant. 2009, 15, 1834–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toso, C.; Merani, S.; Bigam, D.L.; Shapiro, A.J.; Kneteman, N.M. Sirolimus-based immunosuppression is associated with increased survival after liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costentin, C.; Layese, R.; Bourcier, V.; Cagnot, C.; Marcellin, P.; Guyader, D.; Pol, S.; Larrey, D.; De Lédinghen, V.; Ouzan, D.; et al. Compliance with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Surveillance Guidelines Associated With Increased Lead-Time Adjusted Survival of Patients With Compensated Viral Cirrhosis: A Multi-Center Cohort Study. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 431–442.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galle, P.R.; Forner, A.; Llovet, J.M.; Mazzaferro, V.; Piscaglia, F.; Raoul, J.-L.; Schirmacher, P.; Vilgrain, V. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heimbach, J.K.; Kulik, L.M.; Finn, R.S.; Sirlin, C.B.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Zhu, A.X.; Murad, M.H.; Marrero, J.A. AASLD guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2018, 67, 358–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ganne-Carrié, N.; Layese, R.; Bourcier, V.; Cagnot, C.; Marcellin, P.; Guyader, D.; Pol, S.; Larrey, D.; De Lédinghen, V.; Ouzan, D.; et al. Nomogram for individualized prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma occurrence in hepatitis C virus cirrhosis (ANRS CO12 CirVir). Hepatology 2016, 64, 1136–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, A.S.; Seeff, L.B.; Morgan, T.R.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Sterling, R.K.; Curto, T.M.; Everson, G.T.; Lindsay, K.L.; Lee, W.M.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; et al. Incidence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Associated Risk Factors in Hepatitis C-Related Advanced Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flemming, J.A.; Yang, J.D.; Vittinghoff, E.; Kim, W.R.; Terrault, N.A. Risk prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: The ADRESS-HCC risk model. Cancer 2014, 120, 3485–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Dayyeh, B.K.; Yang, M.; Fuchs, B.C.; Karl, D.L.; Yamada, S.; Sninsky, J.J.; O’Brien, T.R.; Dienstag, J.L.; Tanabe, K.K.; Chung, R.T. A Functional Polymorphism in the Epidermal Growth Factor Gene Is Associated with Risk for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ioannou, G.N.; Green, P.; Kerr, K.F.; Berry, K. Models estimating risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with alcohol or NAFLD-related cirrhosis for risk stratification. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancebo, A.; González-Diéguez, M.L.; Navascués, C.A.; Cadahía, V.; Varela, M.; Pérez, R.; Rodrigo, L.; Rodríguez, M. Adherence to a Semiannual Surveillance Program for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients With Liver Cirrhosis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 51, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davila, J.A.; Henderson, L.; Kramer, J.R.; Kanwal, F.; Richardson, P.A.; Duan, Z.; El-Serag, H.B. Utilization of Surveillance for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Among Hepatitis C Virus–Infected Veterans in the United States. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 154, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.S.; Hansen, R.M.; Gray, M.E.; Massoud, O.I.; McGuire, B.M.; Shoreibah, M.G. Hepatocellular carcinoma surveillance: An evidence-based approach. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 1550–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Sang, L.Y.; Lim, Y.-S.; Han, S.; Lee, J.-Y.; Byun, J.H.; Won, H.J.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, H.C.; Lee, Y.S. MRI With Liver-Specific Contrast for Surveillance of Patients with Cirrhosis at High Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.-M.; Sheen, I.-S.; Chien, R.-N.; Chu, C.-M.; Liaw, Y.-F. Long-term beneficial effect of interferon therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 1999, 29, 971–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.-M.; Yu, M.-L.; Lee, C.-M.; Chien, R.-N.; Sheen, I.-S.; Chu, C.-M.; Liaw, Y.-F. Interferon therapy in HBeAg positive chronic hepatitis reduces progression to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2007, 46, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liaw, Y.-F.; Sung, J.J.; Chow, W.C.; Farrell, G.; Lee, C.-Z.; Yuen, H.; Tanwandee, T.; Tao, Q.-M.; Shue, K.; Keene, O.N.; et al. Lamivudine for Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B and Advanced Liver Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eun, J.R.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, T.N.; Lee, K.S. Risk assessment for the development of hepatocellular carcinoma: According to on-treatment viral response during long-term lamivudine therapy in hepatitis B virus-related liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2010, 53, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papatheodoridis, G.V.; Lampertico, P.; Manolakopoulos, S.; Lok, A. Incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B patients receiving nucleos(t)ide therapy: A systematic review. J. Hepatol. 2010, 53, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Webster, D.P.; Klenerman, P.; Dusheiko, G.M. Hepatitis C. Lancet 2015, 385, 1124–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morgan, R.L.; Baack, B.; Smith, B.D.; Yartel, A.; Pitasi, M.; Falck-Ytter, Y. Eradication of Hepatitis C Virus Infection and the Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guarino, M.; Sessa, A.; Cossiga, V.; Morando, F.; Caporaso, N.; Morisco, F. Direct-acting antivirals and hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis C: A few lights and many shadows. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 2582–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearlman, B.L.; Traub, N. Sustained Virologic Response to Antiviral Therapy for Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection: A Cure and So Much More. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 889–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janjua, N.Z.; Wong, S.; Darvishian, M.; Butt, Z.A.; Yu, A.; Binka, M.; Alvarez, M.; Woods, R.; Yoshida, E.M.; Ramji, A.; et al. The impact of SVR from direct-acting antiviral- and interferon-based treatments for HCV on hepatocellular carcinoma risk. J. Viral Hepat. 2020, 27, 781–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ioannou, G.N.; Green, P.K.; Berry, K. HCV eradication induced by direct-acting antiviral agents reduces the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, G.N.; Beste, L.A.; Green, P.K.; Singal, A.G.; Tapper, E.B.; Waljee, A.K.; Sterling, R.K.; Feld, J.J.; Kaplan, D.E.; Taddei, T.H.; et al. Increased Risk for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Persists Up to 10 Years after HCV Eradication in Patients with Baseline Cirrhosis or High FIB-4 Scores. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 1264–1278.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamdane, N.; Jühling, F.; Crouchet, E.; El Saghire, H.; Thumann, C.; Oudot, M.A.; Bandiera, S.; Saviano, A.; Ponsolles, C.; Suarez, A.A.R.; et al. HCV-Induced Epigenetic Changes Associated with Liver Cancer Risk Persist After Sustained Virologic Response. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 2313–2329.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Volk, M.L.; Tocco, R.; Saini, S.; Lok, A.S.-F. Public health impact of antiviral therapy for hepatitis C in the United States. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1750–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, C.E.; Fried, M.W. Barriers to hepatitis C treatment. Liver Int. 2012, 32, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crowley, D.; Cullen, W.; Laird, E.; Lambert, J.S.; Mc Hugh, T.; Murphy, C.; Van Hout, M.C. Exploring patient characteristics and barriers to Hepatitis C treatment in patients on opioid substitution treatment attending a community based fibro-scanning clinic. J. Transl. Intern. Med. 2017, 5, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romero-Gómez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Trenell, M. Treatment of NAFLD with diet, physical activity and exercise. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 829–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pälve, K.; Pahkala, K.; Suomela, E.; Aatola, H.; Hulkkonen, J.; Juonala, M.; Lehtimäki, T.; Rönnemaa, T.; Viikari, J.S.A.; Kähönen, M.; et al. Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Risk of Fatty Liver. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2017, 49, 1834–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. EASL–EASD–EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Is universal screening appropriate? Diabetologia 2016, 59, 1141–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; LaVine, J.E.; Charlton, M.; Cusi, K.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 67, 328–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piguet, A.-C.; Saran, U.; Simillion, C.A.M.; Keller, I.; Terracciano, L.; Reeves, H.L.; Dufour, J.-F.F. Regular exercise decreases liver tumors development in hepatocyte-specific PTEN-deficient mice independently of steatosis. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 1296–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lassailly, G.; Caiazzo, R.; Buob, D.; Pigeyre, M.; Verkindt, H.; Labreuche, J.; Raverdy, V.; Leteurtre, E.; Dharancy, S.; Louvet, A.; et al. Bariatric Surgery Reduces Features of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Morbidly Obese Patients. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mummadi, R.R.; Kasturi, K.S.; Chennareddygari, S.; Sood, G.K. Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 6, 1396–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, M.; Mehaffey, J.H.; Hawkins, R.B.; Hsu, A.; Schirmer, B.; Hallowell, P.T. Bariatric surgery is associated with reduction in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma: A propensity matched analysis. Am. J. Surg. 2020, 219, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.K.; Das, B.K.; Choudhary, S.; Gupta, D.; Patil, U.K. Diabetes and hepatocellular carcinoma: A pathophysiological link and pharmacological management. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 991–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.K.; Ho, L.T.; Ting, L.P.; Hu, C.P.; Su, T.S.; Chang, W.C.; Suen, C.S.; Huang, M.Y.; Chang, C.M. Selective suppression of insulin-induced proliferation of cultured human hepatoma cells by somatostatin. J. Clin. Investig. 1987, 79, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, V.; Perlemuter, G.; Bonvoust, F.; Dargere, D.; Parfait, B.; Vidaud, M.; Conti, M.; Huet, S.; Bâ, N.; Buffet, C.; et al. High glucose and hyperinsulinemia stimulate connective tissue growth factor expression: A potential mechanism involved in progression to fibrosis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2001, 34, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, J.M.; Donnelly, L.A.; Emslie-Smith, A.M.; Alessi, D.R.; Morris, A.D. Metformin and reduced risk of cancer in diabetic patients. BMJ 2005, 330, 1304–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tseng, C.-H. Metformin and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with type 2 diabetes. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 2018–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Myers, R.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shen, X.; Fenyk-Melody, J.; Wu, M.; Ventre, J.; Doebber, T.; Fujii, N.; et al. Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Yang, W.; Wu, F.; Wang, C.; Yu, L.; Tang, L.; Qiu, B.; Li, Y.; Guo, L.; Wu, M.; et al. Prognostic Significance of AMPK Activation and Therapeutic Effects of Metformin in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5372–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deperalta, D.K.; Wei, L.; Ghoshal, S.; Schmidt, B.; Lauwers, G.Y.; Lanuti, M.; Chung, R.T.; Tanabe, K.K.; Fuchs, B.C. Metformin prevents hepatocellular carcinoma development by suppressing hepatic progenitor cell activation in a rat model of cirrhosis. Cancer 2016, 122, 1216–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cusi, K.; Orsak, B.; Bril, F.; Lomonaco, R.; Hecht, J.; Ortiz-Lopez, C.; Tio, F.; Hardies, J.; Darland, C.; Musi, N.; et al. Long-Term Pioglitazone Treatment for Patients with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Prediabetes or Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Ann. Intern. Med. 2016, 165, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ghoshal, S.; Sojoodi, M.; Arora, G.; Masia, R.; Erstad, D.J.; Lanuti, M.; Hoshida, Y.; Baumert, T.F.; Tanabe, K.K.; et al. Pioglitazone Reduces Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development in Two Rodent Models of Cirrhosis. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2018, 23, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, M.-Y.; Chung, C.-H.; Chang, W.-K.; Lin, C.-S.; Chen, K.-W.; Hsieh, T.-Y.; Chien, W.-C.; Lin, H.-H. The role of thiazolidinediones in hepatocellular carcinoma risk reduction: A population-based cohort study in Taiwan. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 7, 1606–1616. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, T.; Yoneda, M.; Nakamura, K.; Makino, I.; Terano, A. Plasma transforming growth factor-β1 level and efficacy of α-tocopherol in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A pilot study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 15, 1667–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kugelmas, M.; Hill, D.B.; Vivian, B.; Marsano, L.; McClain, C.J. Cytokines and NASH: A pilot study of the effects of lifestyle modification and vitamin E. Hepatology 2003, 38, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vajro, P.; Mandato, C.; Franzese, A.; Ciccimarra, E.; Lucariello, S.; Savoia, M.; Capuano, G.; Migliaro, F. Vitamin E Treatment in Pediatric Obesity-Related Liver Disease: A Randomized Study. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2004, 38, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanyal, A.J.; Chalasani, N.; Kowdley, K.V.; McCullough, A.; Diehl, A.M.; Bass, N.M.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; LaVine, J.E.; Tonascia, J.; Unalp, A.; et al. Pioglitazone, Vitamin E, or Placebo for Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1675–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, E.R.; Pastor-Barriuso, R.; Dalal, D.; Riemersma, R.A.; Appel, L.J.; Guallar, E. Meta-analysis: High-dosage vitamin E supplementation may increase all-cause mortality. Ann. Intern. Med. 2005, 142, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klein, E.A.; Thompson, I.M.; Tangen, C.M.; Crowley, J.J.; Lucia, M.S.; Goodman, P.J.; Minasian, L.M.; Ford, L.G.; Parnes, H.L.; Gaziano, J.M.; et al. Vitamin E and the Risk of Prostate Cancer: The selenium and vitamin e cancer prevention trial (SELECT). JAMA 2011, 306, 1549–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testino, G.; Leone, S.; Borro, P. Alcohol and hepatocellular carcinoma: A review and a point of view. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 15943–15954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addolorato, G.; Mirijello, A.; Barrio, P.; Gual, A. Treatment of alcohol use disorders in patients with alcoholic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 618–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, W.R.; Walters, S.T.; Bennett, M.E. How effective is alcoholism treatment in the United States? J. Stud. Alcohol. 2001, 62, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, K.V.N.; Gores, G.J.; Shah, V.H. Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Alcoholic Liver Disease. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2001, 76, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Humphreys, K.; Blodgett, J.C.; Wagner, T.H. Estimating the Efficacy of Alcoholics Anonymous without Self-Selection Bias: An Instrumental Variables Re-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2014, 38, 2688–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McHugh, R.K.; Hearon, B.A.; Otto, M.W. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Substance Use Disorders. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 33, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrison, S.A.; Torgerson, S.; Hayashi, P.; Ward, J.; Schenker, S. Vitamin E and vitamin C treatment improves fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 98, 2485–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, C.H.; Pedersen, B.; Tønnesen, H. The Efficacy of Disulfiram for the Treatment of Alcohol Use Disorder. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2011, 35, 1749–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, D.; Grant, E.R.; Pohorecky, L.A. Naltrexone reverses ethanol-induced dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens in awake, freely moving rats. Brain Res. 1993, 621, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, R.F.; O’Malley, S.S.; Ciraulo, D.A.; Cisler, R.A.; Couper, D.; Donovan, D.M.; Gastfriend, D.R.; Hosking, J.D.; Johnson, B.A.; LoCastro, J.S.; et al. Combined Pharmacotherapies and Behavioral Interventions for Alcohol Dependence. JAMA 2006, 295, 2003–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cholesterol Treatment Trialists’ (CTT) Collaboration Efficacy and safety of more intensive lowering of LDL cholesterol: A meta-analysis of data from 170,000 participants in 26 randomised trials. Lancet 2010, 376, 1670–1681. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poynter, J.N.; Gruber, S.B.; Higgins, P.D.; Almog, R.; Bonner, J.D.; Rennert, H.S.; Low, M.; Greenson, J.K.; Rennert, G. Statins and the risk of colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 2184–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campbell, M.J.; Esserman, L.J.; Zhou, Y.; Shoemaker, M.; Lobo, M.; Borman, E.; Baehner, F.; Kumar, A.S.; Adduci, K.; Marx, C.; et al. Breast Cancer Growth Prevention by Statins. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 8707–8714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shannon, J.; Tewoderos, S.; Garzotto, M.; Beer, T.M.; Derenick, R.; Palma, A.; Farris, P.E. Statins and Prostate Cancer Risk: A Case-Control Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 162, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyogo, H.; Tazuma, S.; Arihiro, K.; Iwamoto, K.; Nabeshima, Y.; Inoue, M.; Ishitobi, T.; Nonaka, M.; Chayama, K. Efficacy of atorvastatin for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with dyslipidemia. Metabolism 2008, 57, 1711–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athyros, V.; Alexandrides, T.K.; Bilianou, H.; Cholongitas, E.; Doumas, M.; Ganotakis, E.; Goudevenos, J.; Elisaf, M.S.; Germanidis, G.; Giouleme, O.; et al. The use of statins alone, or in combination with pioglitazone and other drugs, for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease/non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and related cardiovascular risk. An Expert Panel Statement. Metabolism 2017, 71, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsan, Y.-T.; Lee, C.-H.; Wang, J.-D.; Chen, P.-C. Statins and the Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Hepatitis B Virus Infection. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butt, A.A.; Yan, P.; Bonilla, H.; Abou-Samra, A.B.; Shaikh, O.S.; Simon, T.G.; Chung, R.T.; Rogal, S.S.; ERCHIVES (Electronically Retrieved Cohort of HCV Infected Veterans) Study Team. Effect of addition of statins to antiviral therapy in hepatitis C virus-infected persons: Results from ERCHIVES. Hepatology 2015, 62, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, Y.; Sakamoto, Y.; Ito, D.; Ito, K.; Arita, J.; Akamatsu, N.; Kaneko, J.; Hasegawa, K.; Moriya, K.; Kokudo, N. Statin use is associated with a reduced risk of hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence after initial liver resection. Biosci. Trends 2017, 11, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Z.; Fan-Minogue, H.; Bellovin, D.I.; Yevtodiyenko, A.; Arzeno, J.; Yang, Q.; Gambhir, S.S.; Felsher, D.W. MYC phosphorylation, activation, and tumorigenic potential in hepatocellular carcinoma are regulated by HMG-CoA reductase. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 2286–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roudier, E.; Mistafa, O.; Stenius, U. Statins induce mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-mediated inhibition of Akt signaling and sensitize p53-deficient cells to cytostatic drugs. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2006, 5, 2706–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghalali, A.; Martin-Renedo, J.; Högberg, J.; Stenius, U. Atorvastatin Decreases HBx-Induced Phospho-Akt in Hepatocytes via P2X Receptors. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Tokoro, T.; Higa, S.; Kitajima, I. Anti-inflammatory Effect of Pitavastatin on NF-κB Activated by TNF-α in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marinho, T.D.S.; Kawasaki, A.; Bryntesson, M.; Souza-Mello, V.; Barbosa-Da-Silva, S.; Aguila, M.B.; Mandarim-De-Lacerda, C.A. Rosuvastatin limits the activation of hepatic stellate cells in diet-induced obese mice. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 47, 928–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uschner, F.E.; Ranabhat, G.; Choi, S.S.; Granzow, M.; Klein, S.; Schierwagen, R.; Raskopf, E.; Gautsch, S.; Van Der Ven, P.F.M.; Fürst, D.O.; et al. Statins activate the canonical hedgehog-signaling and aggravate non-cirrhotic portal hypertension, but inhibit the non-canonical hedgehog signaling and cirrhotic portal hypertension. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pikarsky, E.; Porat, R.M.; Stein, I.; Abramovitch, R.; Amit, S.; Kasem, S.; Gutkovich-Pyest, E.; Urieli-Shoval, S.; Galun, E.; Ben-Neriah, Y. NF-κB functions as a tumour promoter in inflammation-associated cancer. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 431, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.; Karin, M. NF-κB and STAT3—Key players in liver inflammation and cancer. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sahasrabuddhe, V.V.; Gunja, M.Z.; Graubard, B.I.; Trabert, B.; Schwartz, L.M.; Park, Y.; Hollenbeck, A.R.; Freedman, N.D.; McGlynn, K.A. Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drug Use, Chronic Liver Disease, and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2012, 104, 1808–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Cai, W.; Chu, E.S.H.; Tang, J.; Wong, C.-C.; Wong, S.H.; Sun, W.; Liang, Q.; Fang, J.; Sun, Z.; et al. Hepatic cyclooxygenase-2 overexpression induced spontaneous hepatocellular carcinoma formation in mice. Oncogene 2017, 36, 4415–4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leng, J.; Han, C.; Demetris, A.J.; Michalopoulos, G.K.; Wu, T. Cyclooxygenase-2 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth through Akt activation: Evidence for Akt inhibition in celecoxib-induced apoptosis. Hepatology 2003, 38, 756–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, T.G.; Ma, Y.; Ludvigsson, J.F.; Chong, D.Q.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Fuchs, C.S.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Corey, K.E.; Chung, R.T.; Zhang, X.; et al. Association Between Aspirin Use and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1683–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Funaki, M.; Kitabayashi, J.; Shimakami, T.; Nagata, N.; Kai, T.; Takegoshi, K.; Okada, H.; Murai, K.; Shirasaki, T.; Oyama, T.; et al. Peretinoin, an acyclic retinoid, inhibits hepatocarcinogenesis by suppressing sphingosine kinase 1 expression in vitro and in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malehmir, M.; Pfister, D.; Gallage, S.; Szydlowska, M.; Inverso, D.; Kotsiliti, E.; Leone, V.; Peiseler, M.; Surewaard, B.G.J.; Rath, D.; et al. Platelet GPIbα is a mediator and potential interventional target for NASH and subsequent liver cancer. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Fu, X.; Jin, T.; Zhang, L.; Liu, B.; Wu, Y.; Xu, F.; Wang, X.; Ye, K.; Zhang, W.; et al. Aspirin targets P4HA2 through inhibiting NF-κB and LMCD1-AS1/let-7g to inhibit tumour growth and collagen deposition in hepatocellular carcinoma. EBioMedicine 2019, 45, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roehlen, N.; Baumert, T.F. Uncovering the mechanism of action of aspirin in HCC chemoprevention. EBioMedicine 2019, 46, 21–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simon, T.G.; Henson, J.; Osganian, S.; Masia, R.; Chan, A.T.; Chung, R.T.; Corey, K.E. Daily Aspirin Use Associated with Reduced Risk For Fibrosis Progression In Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 2776–2784.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sakurai, T.; Kudo, M. Molecular Link between Liver Fibrosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2013, 2, 365–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loomba, R.; Lawitz, E.; Mantry, P.S.; Jayakumar, S.; Caldwell, S.H.; Arnold, H.; Diehl, A.M.; Djedjos, C.S.; Han, L.; Myers, R.P.; et al. The ASK1 inhibitor selonsertib in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A randomized, phase 2 trial. Hepatology 2018, 67, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratziu, V.; Harrison, S.A.; Francque, S.; Bedossa, P.; Lehert, P.; Serfaty, L.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Boursier, J.; Abdelmalek, M.; Caldwell, S.; et al. Elafibranor, an Agonist of the Peroxisome Proliferator−Activated Receptor−α and −δ, Induces Resolution of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis without Fibrosis Worsening. Gastroenterol. 2016, 150, 1147–1159.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumada, H. Long-term treatment of chronic hepatitis C with glycyrrhizin [stronger neo-minophagen C (SNMC)] for preventing liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology 2002, 62, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arase, Y.; Ikeda, K.; Murashima, N.; Chayama, K.; Tsubota, A.; Koida, I.; Suzuki, Y.; Saitoh, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Kumada, H. The long term efficacy of glycyrrhizin in chronic hepatitis C patients. Cancer 1997, 79, 1494–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rossum, T.G.J.; Vulto, A.G.; De Man, R.A.; Brouwer, J.T.; Schalm, S.W. glycyrrhizin as a potential treatment for chronic hepatitis C. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1998, 12, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiota, G.; Harada, K.-I.; Ishida, M.; Tomie, Y.; Okubo, M.; Katayama, S.; Ito, H.; Kawasaki, H. Inhibition of hepatocellular carcinoma by glycyrrhizin in diethylnitrosamine-treated mice. Carcinogenesis 1999, 20, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oka, H.; Yamamoto, S.; Kuroki, T.; Harihara, S.; Marumo, T.; Kim, S.R.; Monna, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Tango, T. Prospective study of chemoprevention of hepatocellular carcinoma with sho-saiko-to (TJ-9). Cancer 1995, 76, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishayee, A.; Chatterjee, M.; Chatterjee, M. Further Evidence for Chemopreventive Potential of β-Carotene Against Experimental Carcinogenesis: Diethylnitrosamine-Initiated and Phenobarbital-Promoted Hepatocarcinogenesis Is Prevented More Effectively by β-Carotene Than by Retinoic Acid. Nutr. Cancer 2000, 37, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, C.D.; Neal, C.P.; Garcea, G.; Manson, M.M.; Dennison, A.R.; Berry, D.P. Phytochemicals as potential chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic agents in hepatocarcinogenesis. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2009, 18, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Ning, Y.; Lotlikar, P.D. Chemoprevention of Aflatoxin B1-Initiated and Carbon Tetrachloride-Promoted Hepatocarcinogenesis in the Rat by Green Tea. Nutr. Cancer 2000, 38, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Tang, L.; Tang, M.; Billam, M.; Huang, T.; Yu, J.; Wei, Z.; Liang, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Z.-Q.; et al. Phase IIa chemoprevention trial of green tea polyphenols in high-risk individuals of liver cancer: Modulation of urinary excretion of green tea polyphenols and 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine. Carcinogenesis 2005, 27, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sojoodi, M.; Wei, L.; Erstad, D.J.; Yamada, S.; Fujii, T.; Hirschfield, H.; Kim, R.S.; Lauwers, G.Y.; Lanuti, M.; Hoshida, Y.; et al. Epigallocatechin Gallate Induces Hepatic Stellate Cell Senescence and Attenuates Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Prev. Res. 2020, 13, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavin, C.; Holzhäuser, D.; Constable, A.; Huggett, A.C.; Schilter, B. The coffee-specific diterpenes cafestol and kahweol protect against aflatoxin B1-induced genotoxicity through a dual mechanism. Carcinogenesis 1998, 19, 1369–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, G.L.H.; Chan, H.L.-Y.; Chan, H.-Y.; Tse, C.-H.; Chim, A.M.-L.; Lo, A.O.-S.; Wong, V.W.-S. Adverse Effects of Vitamin D Deficiency on Outcomes of Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 783–790.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedirko, V.; Duarte-Salles, T.; Bamia, C.; Trichopoulou, A.; Aleksandrova, K.; Trichopoulos, D.; Trepo, E.; Tjønneland, A.; Olsen, A.; Overvad, K.; et al. Prediagnostic circulating vitamin D levels and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in European populations: A nested case-control study. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1222–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.-J.; Won, Y.-S.; Suh, H.-W.; Jeon, J.-H.; Shao, Y.; Yoon, S.-R.; Chung, J.-W.; Kim, T.-D.; Kim, H.-M.; Nam, K.-H.; et al. Vitamin D3 Upregulated Protein 1 Suppresses TNF-α–Induced NF-κB Activation in Hepatocarcinogenesis. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 3980–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cha, J.H.; Bae, S.H.; Kim, H.L.; Park, N.R.; Choi, E.S.; Jung, E.S.; Choi, J.Y.; Yoon, S.K. Branched-Chain Amino Acids Ameliorate Fibrosis and Suppress Tumor Growth in a Rat Model of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Liver Cirrhosis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, T.; Shiraishi, K.; Ito, T.; Suzuki, K.; Koreeda, C.; Ohtake, T.; Iwasa, M.; Tokumoto, Y.; Endo, R.; Kawamura, N.; et al. Branched-Chain Amino Acids Prevent Hepatocarcinogenesis and Prolong Survival of Patients with Cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 1012–1018.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Sun, K.; Guo, M.; Gao, H.; Liu, K.; Yang, C.; Li, S.; Liu, N. Fish consumption and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Causes Control. 2014, 26, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, N.; Inoue, M.; Iwasaki, M.; Sasazuki, S.; Shimazu, T.; Yamaji, T.; Takachi, R.; Tanaka, Y.; Mizokami, M.; Tsugane, S. Consumption of n-3 Fatty Acids and Fish Reduces Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1468–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebig, M.; Dannenberger, D.; Vollmar, B.; Abshagen, K. n-3 PUFAs reduce tumor load and improve survival in a NASH-tumor mouse model. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2019, 10, 2040622319872118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.; Yang, W.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Simon, T.G.; Sui, J.; Wu, K.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Chan, A.T.; Zhang, X. Meat intake and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in two large US prospective cohorts of women and men. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 48, 1863–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briske-Anderson, M.J.; Finley, J.W.; Newman, S.M. The Influence of Culture Time and Passage Number on the Morphological and Physiological Development of Caco-2 Cells. Exp. Biol. Med. 1997, 214, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartung, T. Food for thought look back in anger–What clinical studies tell us about preclinical work. Altex 2013, 30, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.; Sirota, M.; Fan-Minogue, H.; Hadley, D.; Butte, A.J. Relating hepatocellular carcinoma tumor samples and cell lines using gene expression data in translational research. BMC Med. Genom. 2015, 8, S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gillet, J.-P.; Calcagno, A.M.; Varma, S.; Marino, M.; Green, L.J.; Vora, M.I.; Patel, C.; Orina, J.N.; Eliseeva, T.A.; Singal, V.; et al. Redefining the relevance of established cancer cell lines to the study of mechanisms of clinical anti-cancer drug resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 18708–18713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moon, H.; Ju, H.-L.; Chung, S.I.; Cho, K.J.; Eun, J.W.; Nam, S.W.; Han, K.-H.; Calvisi, D.F.; Ro, S.W. Transforming Growth Factor-β Promotes Liver Tumorigenesis in Mice via Up-regulation of Snail. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 1378–1391.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Qi, X.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Xu, Q.; Shen, C.; Zhou, G.; Yang, S.; et al. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated p53 and Pten dual mutation accelerates hepatocarcinogenesis in adult hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Recknagel, R.O.; Glende, E.A.; Dolak, J.A.; Waller, R.L. Mechanisms of carbon tetrachloride toxicity. Pharmacol. Ther. 1989, 43, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.N.; Badawi, A.F.; O’Connor, P.J.; Saffhill, R. The detection of alkylation damage in the DNA of human gastrointestinal tissues. Br. J. Cancer 1991, 64, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallace, M.; Hamesch, K.; Lunova, M.; Kim, Y.; Weiskirchen, R.; Strnad, P.; Friedman, S.L. Standard Operating Procedures in Experimental Liver Research: Thioacetamide model in mice and rats. Lab. Anim. 2015, 49, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kushida, M.; Kamendulis, L.M.; Peat, T.J.; Klaunig, J.E. Dose-Related Induction of Hepatic Preneoplastic Lesions by Diethylnitrosamine in C57BL/6 Mice. Toxicol. Pathol. 2011, 39, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Norman, G.A. Phase II Trials in Drug Development and Adaptive Trial Design. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2019, 4, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebholz, C.E.; Swiss Paediatric Oncology Group (SPOG); Rueegg, C.S.; Michel, G.; Ammann, R.A.; Von Der Weid, N.X.; Kuehni, C.E.; Spycher, B.D. Clustering of health behaviours in adult survivors of childhood cancer and the general population. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perrone, J.; Phillips, C.; Gaieski, D. Occult Metformin Toxicity in Three Patients with Profound Lactic Acidosis. J. Emerg. Med. 2011, 40, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Saviano, A.; Erstad, D.J.; Hoshida, Y.; Fuchs, B.C.; Baumert, T.; Tanabe, K.K. Risk Factors, Pathogenesis, and Strategies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Prevention: Emphasis on Secondary Prevention and Its Translational Challenges. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3817. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9123817
Li S, Saviano A, Erstad DJ, Hoshida Y, Fuchs BC, Baumert T, Tanabe KK. Risk Factors, Pathogenesis, and Strategies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Prevention: Emphasis on Secondary Prevention and Its Translational Challenges. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(12):3817. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9123817
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shen, Antonio Saviano, Derek J. Erstad, Yujin Hoshida, Bryan C. Fuchs, Thomas Baumert, and Kenneth K. Tanabe. 2020. "Risk Factors, Pathogenesis, and Strategies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Prevention: Emphasis on Secondary Prevention and Its Translational Challenges" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 12: 3817. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9123817
APA StyleLi, S., Saviano, A., Erstad, D. J., Hoshida, Y., Fuchs, B. C., Baumert, T., & Tanabe, K. K. (2020). Risk Factors, Pathogenesis, and Strategies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Prevention: Emphasis on Secondary Prevention and Its Translational Challenges. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(12), 3817. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9123817




