Rituximab Use in Warm and Cold Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. AIHA Pathophysiology
3. Rituximab Mechanism of Action
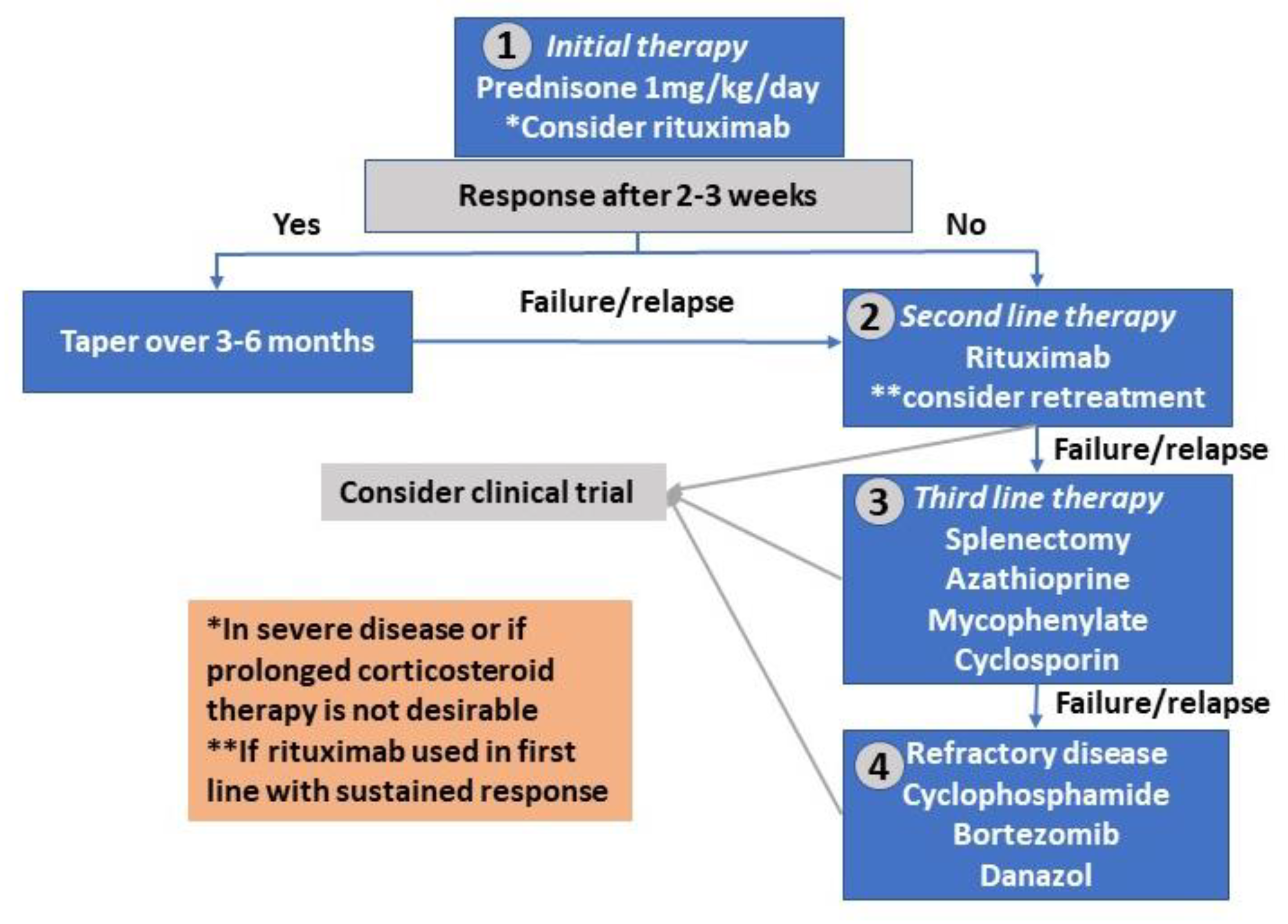
4. Treatment of Warm Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia
5. Rituximab in Warm Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia
5.1. Relapsed/Refractory wAIHA
5.2. Rituximab as First Line Therapy of wAIHA
5.3. Rituximab Combination Therapy
5.4. Rituximab in Secondary wAIHA
6. Treatment of Cold Agglutinin Disease
Rituximab in Primary CAD
7. Rituximab Dose
8. Rituximab Toxicity
9. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Petz, L.D.; Garratty, G. Immune Hemolytic Anemias, 2nd ed.; Churchill Livingstone: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lechner, K.; Jager, U. How I treat autoimmune hemolytic anemias in adults. Blood 2010, 116, 1831–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehrs, B.C.; Friedberg, R.C. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Am. J. Hematol. 2002, 69, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barcellini, W. New Insights in the Pathogenesis of Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia. Transfus. Med. Hemother. 2015, 42, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sokol, R.J.; Hewitt, S.; Stamps, B.K. Autoimmune haemolysis: An 18-year study of 865 cases referred to a regional transfusion centre. Br. Med. J. (Clin. Res. Ed.) 1981, 282, 2023–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamesaki, T.; Kajii, E. A Comprehensive Diagnostic Algorithm for Direct Antiglobulin Test-Negative Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia Reveals the Relative Ratio of Three Mechanisms in a Single Laboratory. Acta Haematol. 2018, 140, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalfa, T.A. Warm antibody autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Hematology 2016, 2016, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.; Rose, E.L.; Singh, A.; Hussain, S.; Stagliano, N.E.; Parry, G.C.; Panicker, S. TNT003, an inhibitor of the serine protease C1s, prevents complement activation induced by cold agglutinins. Blood 2014, 123, 4015–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shanbhag, S.; Spivak, J. Paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 29, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berentsen, S.; Hill, A.; Hill, Q.A.; Tvedt, T.H.A.; Michel, M. Novel insights into the treatment of complement-mediated hemolytic anemias. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valent, P.; Lechner, K. Diagnosis and treatment of autoimmune haemolytic anaemias in adults: A clinical review. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2008, 120, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, W.; Abeywardane, A.; Adikarama, M.; McLornan, D.; Raj, K.; de Lavallade, H.; Devereux, S.; Mufti, G.J.; Pagliuca, A.; et al. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: Analysis of 533 adult patients who underwent transplantation at King’s College Hospital. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015, 21, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- González-Vicent, M.; Sanz, J.; Fuster, J.L.; Cid, J.; de Heredia, C.D.; Morillo, D.; Fernández, J.M.; Pascual, A.; Badell, I.; Serrano, D.; et al. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA) following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT): A retrospective analysis and a proposal of treatment on behalf of the Grupo Español De Trasplante de Medula Osea en Niños (GETMON) and the Grupo Español de Trasplante Hematopoyetico (GETH). Transfus. Med. Rev. 2018, 32, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcellini, W.; Fattizzo, B.; Zaninoni, A. Management of refractory autoimmune hemolytic anemia after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: Current perspectives. J. Blood Med. 2019, 10, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanios, G.E.; Doley, P.B.; Munker, R. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia associated with the use of immune checkpoint inhibitors for cancer: 68 cases from the Food and Drug Administration database and review. Eur. J. Haematol. 2019, 102, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiq, O.; Atiq, S.O.; Atiq, Z.O.; Patel, V.; Atiq, M.O.; Atiq, O.T. Pembrolizumab-Induced Cold Agglutinin Disease. Am. J. Case Rep. 2020, 21, e924283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcellini, W.; Fattizzo, B.; Zaninoni, A.; Radice, T.; Nichele, I.; Di Bona, E.; Lunghi, M.; Tassinari, C.; Alfinito, F.; Ferrari, A.; et al. Clinical heterogeneity and predictors of outcome in primary autoimmune hemolytic anemia: A GIMEMA study of 308 patients. Blood 2014, 124, 2930–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattizzo, B.; Michel, M.; Zaninoni, A.; Giannotta, J.; Guillet, S.; Frederiksen, H.; Vos, J.M.I.; Mauro, F.R.; Jilma, B.; Patriarca, A.; et al. Efficacy of recombinant erythropoietin in autoimmune haemolytic anaemia: A multicentre international study. Haematologica 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audia, S.; Bach, B.; Samson, M.; Lakomy, D.; Bour, J.B.; Burlet, B.; Guy, J.; Duvillard, L.; Branger, M.; Leguy-Seguin, V.; et al. Venous thromboembolic events during warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Broome, C.M.; Cunningham, J.M.; Mullins, M.; Jiang, X.; Bylsma, L.C.; Fryzek, J.P.; Rosenthal, A. Increased risk of thrombotic events in cold agglutinin disease: A 10-year retrospective analysis. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 4, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bylsma, L.C.; Gulbech Ording, A.; Rosenthal, A.; Öztürk, B.; Fryzek, J.P.; Arias, J.M.; Röth, A.; Berentsen, S. Occurrence, thromboembolic risk, and mortality in Danish patients with cold agglutinin disease. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 2980–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berentsen, S.; Ulvestad, E.; Langholm, R.; Beiske, K.; Hjorth-Hansen, H.; Ghanima, W.; Sørbø, J.H.; Tjønnfjord, G.E. Primary chronic cold agglutinin disease: A population based clinical study of 86 patients. Haematologica 2006, 91, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Berentsen, S.; Barcellini, W.; D’Sa, S.; Randen, U.; Tvedt, T.H.A.; Fattizzo, B.; Haukås, E.; Kell, M.; Brudevold, R.; Dahm, A.E.A.; et al. Cold agglutinin disease revisited: A multinational, observational study of 232 patients. Blood 2020, 136, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dierickx, D.; Kentos, A.; Delannoy, A. The role of rituximab in adults with warm antibody autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Blood 2015, 125, 3223–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, E.; Elgohary, T.; Ibrahim, H. Naturally occurring regulatory T cells and interleukins 10 and 12 in the pathogenesis of idiopathic warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 21, 297–304. [Google Scholar]
- Howie, H.L.; Hudson, K.E. Murine models of autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2018, 25, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, S.; Liu, X.; Fang, L.; Chen, X.; Guo, T.; Zhang, J. The cytokine milieu in the interplay of pathogenic Th1/Th17 cells and regulatory T cells in autoimmune disease. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 7, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcellini, W.; Clerici, G.; Montesano, R.; Taioli, E.; Morelati, F.; Rebulla, P.; Zanella, A. In vitro quantification of anti-red blood cell antibody production in idiopathic autoimmune haemolytic anaemia: Effect of mitogen and cytokine stimulation. Br. J. Haematol. 2000, 111, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noack, M.; Miossec, P. Th17 and regulatory T cell balance in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Jin, H.; Nan, D.; Yu, W.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Hou, R.; Qin, R.; Hao, H.; Sun, Y.; et al. The Role of T Follicular Helper Cells and T Follicular Regulatory Cells in the Pathogenesis of Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randen, U.; Trøen, G.; Tierens, A.; Steen, C.; Warsame, A.; Beiske, K.; Tjønnfjord, G.E.; Berentsen, S.; Delabie, J. Primary cold agglutinin-associated lymphoproliferative disease: A B-cell lymphoma of the bone marrow distinct from lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma. Haematologica 2014, 99, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Tute, R.; Rawstron, A.; Evans, P.; Owen, R. Cold agglutinin disease is a phenotypically distinct clonal B-cell disorder. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2015, 15 (Suppl. 3), e184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małecka, A.; Trøen, G.; Tierens, A.; Østlie, I.; Małecki, J.; Randen, U.; Berentsen, S.; Tjønnfjord, G.E.; Delabie, J.M. Immunoglobulin heavy and light chain gene features are correlated with primary cold agglutinin disease onset and activity. Haematologica 2016, 101, e361–e364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Małecka, A.; Delabie, J.; Østlie, I.; Tierens, A.; Randen, U.; Berentsen, S.; Tjønnfjord, G.E.; Trøen, G. Cold agglutinin-associated B-cell lymphoproliferative disease shows highly recurrent gains of chromosome 3 and 12 or 18. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 993–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Małecka, A.; Trøen, G.; Tierens, A.; Østlie, I.; Małecki, J.; Randen, U.; Wang, J.; Berentsen, S.; Tjønnfjord, G.E.; Delabie, J.M.A. Frequent somatic mutations of KMT2D (MLL2) and CARD11 genes in primary cold agglutinin disease. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 183, 838–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harboe, M.; van Furth, R.; Schubothe, H.; Lind, K.; Evans, R.S. Exclusive occurrence of K chains in isolated cold haemagglutinins. Scand. J. Haematol. 1965, 2, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulvestad, E.; Berentsen, S.; Bø, K.; Shammas, F.V. Clinical immunology of chronic cold agglutinin disease. Eur. J. Haematol. 1999, 63, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berentsen, S. Cold agglutinin disease. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2016, 2016, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, M.R. Rituximab (monoclonal anti-CD20 antibody): Mechanisms of action and resistance. Oncogene 2003, 22, 7359–7368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reff, M.E.; Carner, K.; Chambers, K.S.; Chinn, P.C.; Leonard, J.E.; Raab, R.; Newman, R.A.; Hanna, N.; Anderson, D.R. Depletion of B cells in vivo by a chimeric mouse human monoclonal antibody to CD20. Blood 1994, 83, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, S.B.; Emery, P.; Greenwald, M.W.; Dougados, M.; Furie, R.A.; Genovese, M.C.; Keystone, E.C.; Loveless, J.E.; Burmester, G.R.; Cravets, M.W.; et al. Rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy: Results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III trial evaluating primary efficacy and safety at twenty-four weeks. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 2793–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraoui, B.; Bokarewa, M.; Kallmeyer, I.; Bykerk, V.P.; RESET Investigators. Safety and effectiveness of rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis following an inadequate response to 1 prior tumor necrosis factor inhibitor: The RESET Trial. J. Rheumatol. 2011, 38, 2548–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dierickx, D.; Verhoef, G.; Van Hoof, A.; Mineur, P.; Roest, A.; Triffet, A.; Kentos, A.; Pierre, P.; Boulet, D.; Bries, G.; et al. Rituximab in auto-immune haemolytic anaemia and immune thrombocytopenic purpura: A Belgian retrospective multicentric study. J. Intern. Med. 2009, 266, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvey, B. Rituximab in the treatment of autoimmune haematological disorders. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 141, 149–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barcellini, W.; Zanella, A. Rituximab therapy for autoimmune haematological diseases. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2011, 22, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narat, S.; Gandla, J.; Hoffbrand, A.V.; Hughes, R.G.; Mehta, A.B. Rituximab in the treatment of refractory autoimmune cytopenias in adults. Haematologica 2005, 90, 1273–1274. [Google Scholar]
- D’Arena, G.; Califano, C.; Annunziata, M.; Tartarone, A.; Capalbo, S.; Villani, O.; Amendola, G.; Pietrantuono, G.; Ferrara, F.; Pinto, A.; et al. Rituximab for warm-type idiopathic autoimmune hemolytic anemia: A retrospective study of 11 adult patients. Eur. J. Haematol. 2007, 79, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussone, G.; Ribeiro, E.; Dechartres, A.; Viallard, J.F.; Bonnotte, B.; Fain, O.; Godeau, B.; Michel, M. Efficacy and safety of rituximab in adults’ warm antibody autoimmune haemolytic anemia: Retrospective analysis of 27 cases. Am. J. Hematol. 2009, 84, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñalver, F.J.; Alvarez-Larrán, A.; Díez-Martin, J.L.; Gallur, L.; Jarque, I.; Caballero, D.; Díaz-Mediavilla, J.; Bustelos, R.; Fernández-Aceñero, M.J.; Cabrera, J.R.; et al. Rituximab is an effective and safe therapeutic alternative in adults with refractory and severe autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Ann. Hematol. 2010, 89, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roumier, M.; Loustau, V.; Guillaud, C.; Languille, L.; Mahevas, M.; Khellaf, M.; Limal, N.; Noizat-Pirenne, F.; Godeau, B.; Michel, M. Characteristics and outcome of warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia in adults: New insights based on a single-center experience with 60 patients. Am. J. Hematol. 2014, 89, E150–E155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauswirth, A.W.; Skrabs, C.; Schützinger, C.; Gaiger, A.; Lechner, K.; Jäger, U. Autoimmune hemolytic anemias, Evans’ syndromes, and pure red cell aplasia in non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Leuk. Lymphoma 2007, 48, 1139–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaime-Pérez, J.C.; Aguilar-Calderón, P.; Salazar-Cavazos, L.; Gómez-De León, A.; Gómez-Almaguer, D. Treatment of autoimmune hemolytic anemia: Real world data from a reference center in Mexico. Blood Res. 2019, 54, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Arena, G.; Laurenti, L.; Capalbo, S.; D’Arco, A.M.; De Filippi, R.; Marcacci, G.; Di Renzo, N.; Storti, S.; Califano, C.; Vigliotti, M.L.; et al. Rituximab therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia-associated autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Am. J. Hematol. 2006, 81, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maloney, D.G.; Liles, T.M.; Czerwinski, D.K.; Waldichuk, C.; Rosenberg, J.; Grillo-Lopez, A.; Levy, R. Phase I clinical trial using escalating single-dose infusion of chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (IDEC-C2B8) in patients with recurrent B-cell lymphoma. Blood 1994, 84, 2457–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tamimoto, Y.; Horiuchi, T.; Tsukamoto, H.; Otsuka, J.; Mitoma, H.; Kimoto, Y.; Nakashima, H.; Muta, K.; Abe, Y.; Kiyohara, C.; et al. A dose-escalation study of rituximab for treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus and Evans’ syndrome: Immunological analysis of B cells, T cells and cytokines. Rheumatology 2008, 47, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stasi, R. Rituximab in autoimmune hematologic diseases: Not just a matter of B cells. Semin. Hematol. 2010, 47, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Mou, W.; Lu, G.; Cao, J.; He, X.; Pan, X.; Xu, K. Low-dose rituximab combined with short-term glucocorticoids up-regulates Treg cell levels in patients with immune thrombocytopenia. Int. J. Hematol. 2011, 93, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasi, R.; Del Poeta, G.; Stipa, E.; Evangelista, M.L.; Trawinska, M.M.; Cooper, N.; Amadori, S. Response to B-cell depleting therapy with rituximab reverts the abnormalities of T-cell subsets in patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2007, 110, 2924–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasi, R.; Cooper, N.; Del Poeta, G.; Stipa, E.; Laura Evangelista, M.; Abruzzese, E.; Amadori, S. Analysis of regulatory T-cell changes in patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura receiving B cell-depleting therapy with rituximab. Blood 2008, 112, 1147–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhatia, D.; Sinha, A.; Hari, P.; Sopory, S.; Saini, S.; Puraswani, M.; Saini, H.; Mitra, D.K.; Bagga, A. Rituximab modulates T- and B-lymphocyte subsets and urinary CD80 excretion in patients with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr. Res. 2018, 84, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcellini, W.; Zaja, F.; Zaninoni, A.; Imperiali, F.G.; Battista, M.L.; Di Bona, E.; Fattizzo, B.; Consonni, D.; Cortelezzi, A.; Fanin, R.; et al. Low-dose rituximab in adult patients with idiopathic autoimmune hemolytic anemia: Clinical efficacy and biologic studies. Blood 2012, 119, 3691–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanella, A.; Barcellini, W. Treatment of autoimmune hemolytic anemias. Haematologica 2014, 99, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allgood, J.W.; Chaplin, H., Jr. Idiopathic acquired autoimmune hemolytic anemia. A review of forty-seven cases treated from 1955 through 1965. Am. J. Med. 1967, 43, 254–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulpa, J.; Skrabs, C.; Simanek, R.; Valent, P.; Panzer, S.; Lechner, K.; Sillaber, C.; Jäger, U. Probability of remaining in unsustained complete remission after steroid therapy withdrawal in patients with primary warm-antibody reactive autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2016, 128, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coon, W.W. Splenectomy in the treatment of hemolytic anemia. Arch. Surg. 1985, 120, 625–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.Y.; Chilsen, A.M.; Mathiason, M.A.; Kallies, K.J.; Bottner, W.A. Outcomes and complications after splenectomy for hematologic disorders. Am. J. Surg. 2012, 204, 1014–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akpek, G.; McAneny, D.; Weintraub, L. Comparative response to splenectomy in Coombs-positive autoimmune hemolytic anemia with or without associated disease. Am. J. Hematol. 1999, 61, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balagué, C.; Targarona, E.M.; Cerdán, G.; Novell, J.; Montero, O.; Bendahan, G.; García, A.; Pey, A.; Vela, S.; Diaz, M.; et al. Long-term outcome after laparoscopic splenectomy related to hematologic diagnosis. Surg. Endosc. 2004, 18, 1283–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisharat, N.; Omari, H.; Lavi, I.; Raz, R. Risk of infection and death among post-splenectomy patients. J. Infect. 2001, 43, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, R.W.; Schoonen, W.M.; Farkas, D.K.; Riis, A.; Jacobsen, J.; Fryzek, J.P.; Sørensen, H.T. Risk for hospital contact with infection in patients with splenectomy: A population-based cohort study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, R.W.; Schoonen, W.M.; Farkas, D.K.; Riis, A.; Fryzek, J.P.; Sørensen, H.T. Risk of venous thromboembolism in splenectomized patients compared with the general population and appendectomized patients: A 10-year nationwide cohort study. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 1413–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepke-Zaba, J.; Delcroix, M.; Lang, I.; Mayer, E.; Jansa, P.; Ambroz, D.; Treacy, C.; D’Armini, A.M.; Morsolini, M.; Snijder, R.; et al. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH): Results from an international prospective registry. Circulation 2011, 124, 1973–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barcellini, W.; Fattizzo, B.; Zaninoni, A. Current and emerging treatment options for autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 14, 857–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, Q.A.; Stamps, R.; Massey, E.; Grainger, J.D.; Provan, D.; Hill, A.; British Society for Haematology. The diagnosis and management of primary autoimmune haemolytic anaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 176, 395–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, Q.A.; Stamps, R.; Massey, E.; Grainger, J.D.; Provan, D.; Hill, A.; British Society for Haematology Guidelines. Guidelines on the management of drug-induced immune and secondary autoimmune, haemolytic anaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 177, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Go, R.S.; Winters, J.L.; Kay, N.E. How I treat autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Blood 2017, 129, 2971–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jäger, U.; Barcellini, W.; Broome, C.M.; Gertz, M.A.; Hill, A.; Hill, Q.A.; Jilma, B.; Kuter, D.J.; Michel, M.; Montillo, M.; et al. Diagnosis and treatment of autoimmune hemolytic anemia in adults: Recommendations from the First International Consensus Meeting. Blood Rev. 2020, 41, 100648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, J. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Review of 200 cases studied in a period of 20 years (1970–1989). Sangre 1992, 37, 265–274. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, Y.S. Efficacy of danazol in hematologic disorders. Acta Haematol. 1990, 84, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Safety and Efficacy Study of R935788 in the Treatment of Warm Antibody Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (AIHA) (SOAR). Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02612558 (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Momenta Pharmaceuticals. Efficacy and Safety of M281 in Adults with Warm Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia: A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Study. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04119050 (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Immunovant Sciences GmbH. To Assess the Efficacy and Safety of RVT-1401 in the Treatment of Warm Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (ASCEND-WAIHA). (ASCEND-WAIHA). Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04253236 (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Ibrutinib in Steroid Refractory Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (ISRAEL). Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03827603 (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- A Phase II, Single-Center, Open-label Trial to Determine the Safety and Efficacy of Ibrutinib in Refractory/Relapsed Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04398459 (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Zecca, M.; Nobili, B.; Ramenghi, U.; Perrotta, S.; Amendola, G.; Rosito, P.; Jankovic, M.; Pierani, P.; De Stefano, P.; Bonora, M.R.; et al. Rituximab for the treatment of refractory autoimmune hemolytic anemia in children. Blood 2003, 101, 3857–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maung, S.W.; Leahy, M.; O’Leary, H.M.; Khan, I.; Cahill, M.R.; Gilligan, O.; Murphy, P.; McPherson, S.; Jackson, F.; Hennessy, B.; et al. A multi-centre retrospective study of rituximab use in the treatment of relapsed or resistant warm autoimmune haemolytic anaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 163, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynaud, Q.; Durieu, I.; Dutertre, M.; Ledochowski, S.; Durupt, S.; Michallet, A.S.; Durand, D.V.; Lega, J.C. Efficacy and safety of rituximab in auto-immune hemolytic anemia: A meta-analysis of 21 studies. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birgens, H.; Frederiksen, H.; Hasselbalch, H.C.; Rasmussen, I.H.; Nielsen, O.J.; Kjeldsen, L.; Larsen, H.; Mourits-Andersen, T.; Plesner, T.; Rønnov-Jessen, D.; et al. A phase III randomized trial comparing glucocorticoid monotherapy versus glucocorticoid and rituximab in patients with autoimmune haemolytic anaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 163, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, M.; Terriou, L.; Roudot-Thoraval, F.; Hamidou, M.; Ebbo, M.; Le Guenno, G.; Galicier, L.; Audia, S.; Royer, B.; Morin, A.S.; et al. A randomized and double-blind controlled trial evaluating the safety and efficacy of rituximab for warm auto-immune hemolytic anemia in adults (the RAIHA study). Am. J. Hematol. 2017, 92, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossignol, J.; Michallet, A.S.; Oberic, L.; Picard, M.; Garon, A.; Willekens, C.; Dulery, R.; Leleu, X.; Cazin, B.; Ysebaert, L. Rituximab-cyclophosphamide-dexamethasone combination in the management of autoimmune cytopenias associated with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2011, 25, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaufman, M.; Limaye, S.A.; Driscoll, N.; Johnson, C.; Caramanica, A.; Lebowicz, Y.; Patel, D.; Kohn, N.; Rai, K. A combination of rituximab, cyclophosphamide and dexamethasone effectively treats immune cytopenias of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2009, 50, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocian, H.; Piatek, C.; Liebman, H.A.; O’Connell, C.L.; Weitz, I.C.; Johnson, C.S. Combination treatment of rituximab, cyclophosphamide, and dexamethasone for warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Blood 2016, 128, 4802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piatek, C.I.; Bocian, H.; Algaze, S.; Weitz, I.C.; O’Connell, C.; Liebman, H.A. A Retrospective Study of the Combination of Rituximab, Cyclophosphamide and Dexamethasone for the Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Warm Antibody Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia. Acta Haematol. 2020, 143, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, D.A.; Call, T.G.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Kay, N.E.; Schwager, S.M.; Reinalda, M.S.; Rabe, K.G.; Slager, S.L.; Zent, C.S. Treatment of autoimmune cytopenia complicating progressive chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone. Leuk. Lymphoma 2010, 51, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quinquenel, A.; Willekens, C.; Dupuis, J.; Royer, B.; Ysebaert, L.; De Guibert, S.; Michallet, A.S.; Feugier, P.; Guieze, R.; Levy, V.; et al. Bendamustine and rituximab combination in the management of chronic lymphocytic leukemia-associated autoimmune hemolytic anemia: A multicentric retrospective study of the French CLL intergroup (GCFLLC/MW and GOELAMS). Am. J. Hematol. 2015, 90, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serris, A.; Amoura, Z.; Canouï-Poitrine, F.; Terrier, B.; Hachulla, E.; Costedoat-Chalumeau, N.; Papo, T.; Lambotte, O.; Saadoun, D.; Blanche, P.; et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab for systemic lupus erythematosus-associated immune cytopenias: A multicenter retrospective cohort study of 71 adults. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gobert, D.; Bussel, J.B.; Cunningham-Rundles, C.; Galicier, L.; Dechartres, A.; Berezne, A.; Bonnotte, B.; DeRevel, T.; Auzary, C.; Jaussaud, R.; et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab in common variable immunodeficiency-associated immune cytopenias: A retrospective multicentre study on 33 patients. Br. J. Haematol. 2011, 155, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanz, J.; Arango, M.; Carpio, N.; Montesinos, P.; Moscardó, F.; Martín, G.; López, F.; Jarque, I.; Lorenzo, I.; De La Rubia, J.; et al. Autoimmune cytopenias after umbilical cord blood transplantation in adults with hematological malignancies: A single-center experience. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Faraci, M.; Zecca, M.; Pillon, M.; Rovelli, A.; Menconi, M.C.; Ripaldi, M.; Fagioli, F.; Rabusin, M.; Ziino, O.; Lanino, E.; et al. Autoimmune hematological diseases after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children: An Italian multicenter experience. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014, 20, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schreiber, A.D.; Herskovitz, B.S.; Goldwein, M. Low-titer cold-hemagglutinin disease. Mechanism of hemolysis and response to corticosteroids. N. Engl. J. Med. 1977, 296, 1490–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hippe, E.; Jensen, K.B.; Olesen, H.; Lind, K.; Thomsen, P.E. Chlorambucil treatment of patients with cold agglutinin syndrome. Blood 1970, 35, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berentsen, S. New Insights in the Pathogenesis and Therapy of Cold Agglutinin-Mediated Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.; Gramegna, D.; Paoloni, F.; Fattizzo, B.; Binda, F.; D’Adda, M.; Farina, M.; Lucchini, E.; Mauro, F.R.; Salvi, F.; et al. Short course of bortezomib in anemic patients with relapsed cold agglutinin disease: A phase 2 prospective GIMEMA study. Blood 2018, 132, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röth, A.; Bommer, M.; Hüttmann, A.; Herich-Terhürne, D.; Kuklik, N.; Rekowski, J.; Lenz, V.; Schrezenmeier, H.; Dührsen, U. Eculizumab in cold agglutinin disease (DECADE): An open-label, prospective, bicentric, nonrandomized phase 2 trial. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 2543–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grossi, F.; Shum, M.K.; Gertz, M.A.; Roman, E.; Deschatelets, P.; Hamdani, M.; Stout, F.; Francois, C.G. Inhibition of C3 with APL-2 results in normalisation of markers of intravascular and extravascular hemolysis in patients with autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA). Blood 2018, 132 (Suppl. 1), 3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röth, A.; Barcellini, W.; D’Sa, S.; Miyakawa, Y.; Broome, C.M.; Michel, M.; Kuter, D.J.; Jilma, B.; Tvedt, T.H.A.; Lin, S.; et al. Inhibition of Complement C1s with Sutimlimab in Patients with Cold Agglutinin Disease (CAD): Results from the Phase 3 Cardinal Study. Blood 2019, 134 (Suppl. 2), LBA-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Study to Assess the Efficacy and Safety of BIVV009 (Sutimlimab) in Participants With Primary Cold Agglutinin Disease Without A Recent History of Blood Transfusion (Cadenza). Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03347422 (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- A Study to Assess the Efficacy and Safety of BIVV009 (Sutimlimab) in Participants With Primary Cold Agglutinin Disease Who Have a Recent History of Blood Transfusion (Cardinal Study). Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03347396 (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Jäger, U.; D’Sa, S.; Schörgenhofer, C.; Bartko, J.; Derhaschnig, U.; Sillaber, C.; Jilma-Stohlawetz, P.; Fillitz, M.; Schenk, T.; Patou, G.; et al. Inhibition of complement C1s improves severe hemolytic anemia in cold agglutinin disease: A first-in-human trial. Blood 2019, 133, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelbenegger, G.; Schoergenhofer, C.; Derhaschnig, U.; Buchtele, N.; Sillaber, C.; Fillitz, M.; Schenk, T.M.; D’Sa, S.; Cartwright, R.; Gilbert, J.C.; et al. Inhibition of complement C1s in patients with cold agglutinin disease: Lessons learned from a named patient program. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Phase 2, Open-Label Study of INCB050465 in Participants with Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03538041 (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Jalink, M.; Berentsen, S.; Castillo, J.J.; Treon, S.; Fattizzo, B.; Cassin, R.; De Haas, M.; Patriarca, A.; D’Sa, S.; Josephine, M.I.V. Effective Treatment of Cold Agglutinin Disease/Cold Agglutinin Syndrome with Ibrutinib: An International Case Series. 62nd Annual Meeting of the American Society of Hematology 2020. Abstract 1678. Available online: https://ash.confex.com/ash/2020/webprogram/Paper139131.html (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Schöllkopf, C.; Kjeldsen, L.; Bjerrum, O.W.; Mourits-Andersen, H.T.; Nielsen, J.L.; Christensen, B.E.; Jensen, B.A.; Pedersen, B.B.; Taaning, E.B.; Klausen, T.W.; et al. Rituximab in chronic cold agglutinin disease: A prospective study of 20 patients. Leuk. Lymphoma 2006, 47, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berentsen, S.; Ulvestad, E.; Gjertsen, B.T.; Hjorth-Hansen, H.; Langholm, R.; Knutsen, H.; Ghanima, W.; Shammas, F.V.; Tjønnfjord, G.E. Rituximab for primary chronic cold agglutinin disease: A prospective study of 37 courses of therapy in 27 patients. Blood 2004, 103, 2925–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berentsen, S.; Randen, U.; Vågan, A.M.; Hjorth-Hansen, H.; Vik, A.; Dalgaard, J.; Jacobsen, E.M.; Thoresen, A.S.; Beiske, K.; Tjønnfjord, G.E. High response rate and durable remissions following fludarabine and rituximab combination therapy for chronic cold agglutinin disease. Blood 2010, 116, 3180–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berentsen, S.; Randen, U.; Oksman, M.; Birgens, H.; Tvedt, T.H.A.; Dalgaard, J.; Galteland, E.; Haukås, E.; Brudevold, R.; Sørbø, J.H.; et al. Bendamustine plus rituximab for chronic cold agglutinin disease: Results of a Nordic prospective multicenter trial. Blood 2017, 130, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Provan, D.; Butler, T.; Evangelista, M.L.; Amadori, S.; Newland, A.C.; Stasi, R. Activity and safety profile of low-dose rituximab for the treatment of autoimmune cytopenias in adults. Haematologica 2007, 92, 1695–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mariette, X.; Rouanet, S.; Sibilia, J.; Combe, B.; Le Loët, X.; Tebib, J.; Jourdan, R.; Dougados, M. Evaluation of low-dose rituximab for the retreatment of patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: A non-inferiority randomised controlled trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1508–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaja, F.; Vianelli, N.; Volpetti, S.; Battista, M.L.; Defina, M.; Palmieri, S.; Bocchia, M.; Medeot, M.; De Luca, S.; Ferrara, F.; et al. Low-dose rituximab in adult patients with primary immune thrombocytopenia. Eur. J. Haematol. 2010, 85, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Almaguer, D.; Solano-Genesta, M.; Tarín-Arzaga, L.; Herrera-Garza, J.L.; Cantú-Rodríguez, O.G.; Gutiérrez-Aguirre, C.H.; Jaime-Pérez, J.C. Low-dose rituximab and alemtuzumab combination therapy for patients with steroid-refractory autoimmune cytopenias. Blood 2010, 116, 4783–4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcellini, W.; Zaja, F.; Zaninoni, A.; Imperiali, F.G.; Di Bona, E.; Fattizzo, B.; Consonni, D.; Cortelezzi, A.; Zanella, A. Sustained response to low-dose rituximab in idiopathic autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Eur. J. Haematol. 2013, 91, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattizzo, B.; Zaninoni, A.; Pettine, L.; Cavallaro, F.; Di Bona, E.; Barcellini, W. Low-dose rituximab in autoimmune hemolytic anemia: 10 years after. Blood 2019, 133, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kimby, E. Tolerability and safety of rituximab (MabThera). Cancer Treat. Rev. 2005, 31, 456–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gea-Banacloche, J.C. Rituximab-associated infections. Semin. Hematol. 2010, 47, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carson, K.R.; Evens, A.M.; Richey, E.A.; Habermann, T.M.; Focosi, D.; Seymour, J.F.; Laubach, J.; Bawn, S.D.; Gordon, L.I.; Winter, J.N.; et al. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy after rituximab therapy in HIV-negative patients: A report of 57 cases from the Research on Adverse Drug Events and Reports project. Blood 2009, 113, 4834–4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Focosi, D.; Tuccori, M.; Maggi, F. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies: What do we know after 20 years of rituximab. Rev. Med. Virol. 2019, 29, e2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evens, A.M.; Jovanovic, B.D.; Su, Y.C.; Raisch, D.W.; Ganger, D.; Belknap, S.M.; Dai, M.S.; Chiu, B.C.; Fintel, B.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Rituximab-associated hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation in lymphoproliferative diseases: Meta-analysis and examination of FDA safety reports. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 1170–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien, Y.C.; Yen, H.H.; Chiu, Y.M. Incidence and clinical characteristics of hepatitis B virus reactivation in HBsAg-negative/HBcAb-positive patients receiving rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017, 35, 831–836. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.M.; Chen, H.H.; Huang, W.N.; Chen, Y.H.; Hsieh, T.Y.; Yang, S.S.; Lan, J.L.; Chen, D.Y. Reactivation of hepatitis B virus infection following rituximab treatment in HBsAg-negative, HBcAb-positive rheumatoid arthritis patients: A long-term, real-world observation. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 22, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| First Author (Year) | Number of Patients | Splenectomy (N) | ORR/CR (%) | Duration of Response (mo) | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Narat (2005) [46] | 11 | 5 | 64/27 | 2–20 (median 11) | |
| D’Arena (2007) [47] | 11 | 1 | 100/73 | 1–96+ | All primary AIHA, 2 patients received 3 additional monthly doses of maintenance R; additional patient had Rituxan retreatment for ITP |
| Bussone (2009) [48] | 27 | 6 | 93/30 | NR | 5 (18% relapses) after median f/u 20.9 mo, 3 retreated with R and responded |
| Dierickx (2009) [43] | 36 | 10 | 83/50 | 1yr PFS 72% 2yr PFS 56% | |
| Peñalver (2010) [49] | 27 | 13 | 77/61 | Duration of response > 6mo in patients in CR | |
| Maung (2013) [86] | 34 | 3 | 71/27 | 9–60 | 50% relapse; median time to next treatment 16.5mo 28.5% maintained response at 3 years |
| Roumier (2014) [50] | 25 | 2 | 80/NR | 50% relapse after a mean of 14 ± 8 | 62% secondary wAIHA |
| Barcellini (2014) [17] | 32 | NR | 81/56 | Primary AIHA only low dose R | |
| Jaime-Pérez (2019) [52] First-line Relapsed | 18 8 | N/A 7 | 100/83 100/63 | Median 16.5 Mean maintained response 82 ± 18 | Low dose R + high dose dexamethasone (40 mg/day) for 4 days |
| Underlying Condition | First Author (Year) | Regimen | Number of Patients | ORR/CR (%) | Duration of Response (mo) | Line of Therapy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLL | D’Arena (2006) [53] | R 375 mg/m2 × 4 | 14 | 72/22 | NR | R/R |
| CLL | Rossignol (2011) [90] | rituximab, cyclophosphamide, and dexamethasone (RCD) | 26 | 89.5/81 | 24 | R/R (including R-refractory |
| CLL | Kaufman (2009) [91] | RCD | 7 13 | 100/85 | 22 | 1st line R/R |
| CLL | Bowen (2010) [94] | R-CVP | 17 | 100/82 | 21.7 | R/R (including R-refractory |
| CLL | Quinquenel (2015) [95] | R-bendamustine | 25 1 | 81/31 | 28 | 1st line R/R |
| non-CLL LPD | Hauswirth (2007) [51] | R, R-chemo | 7 | 100/100 | NR | R/R |
| SLE | Serris (2018) [96] | R, R-immunosuppression | 16 | 87.5/75 | RFS 62.5% at 2 years | R/R |
| CVID | Gobert (2011) [97] | R | 5 AIHA 5 AIHA/ITP | 80/80 80/40 | NR | R/R |
| Transplant associated | Faraci (2014) [99] | R, immunosuppression | 7 | 100/100 | NR | R/R |
| Transplant associated | Sanz (2014) [98] | R, immunosuppression | 4 4 | 75/50% 50%/0 | NR | 1st line R/R |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Murakhovskaya, I. Rituximab Use in Warm and Cold Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 4034. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9124034
Murakhovskaya I. Rituximab Use in Warm and Cold Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(12):4034. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9124034
Chicago/Turabian StyleMurakhovskaya, Irina. 2020. "Rituximab Use in Warm and Cold Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 12: 4034. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9124034
APA StyleMurakhovskaya, I. (2020). Rituximab Use in Warm and Cold Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(12), 4034. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9124034





