The Role of Bone Scintigraphy with SPECT/CT in the Characterization and Early Diagnosis of Stage 0 Charcot Neuroarthropathy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography/Computed Tomography (SPECT/CT) Scan
2.3. Assessment of Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography/Computed Tomography (SPECT/CT) Imaging & Outcome Analysis
2.4. Clinical Management
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients & Demographics
3.2. Results of Bone Scans with Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography/Computed Tomography (SPECT/CT)
3.2.1. Group 1: Patients with Fracture(s) on CT and Focal Uptake of Tracer on Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT)/) (Table 1)
3.2.2. Group 2: Patients with Bony Abnormalities Apart from Fracture on CT and Focal Uptake of Tracer on SPECT (Table 2)
3.2.3. Group 3: Patients with Normal CT Findings But Focal Uptake of Tracer on SPECT (Table 3)
4. Clinical Outcome
5. Discussion
6. Limitations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rogers, L.C.; Frykberg, R.G.; Armstrong, D.G.; Boulton, A.J.M.; Edmonds, M.; Van, G.H.; Hartemann, A.; Game, F.; Jeffcoate, W.; Jirkovska, A.; et al. The Charcot Foot in Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 2123–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rizzo, P.; Pitocco, D.; Zaccardi, F.; Di Stasio, E.; Strollo, R.; Rizzi, A.; Scavone, G.; Costantini, F.; Galli, M.; Tinelli, G.; et al. Autoantibodies to post-translationally modified type I and II collagen in Charcot neuroarthropathy in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes/Metabolism Res. Rev. 2016, 33, e2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chantelau, E. The perils of procrastination: Effects of early vs. delayed detection and treatment of incipient Charcot fracture. Diabet. Med. 2005, 22, 1707–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chantelau, E.; Poll, L.W. Evaluation of the Diabetic Charcot Foot by MR Imaging or Plain Radiography - an Observational Study. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2006, 114, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, T.; Tada, K.; Hashizume, C. The results of arthrodesis of the ankle for leprotic neuroarthropathy. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 1990, 72, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sella, E.J.; Barrette, C. Staging of Charcot neuroarthropathy along the medial column of the foot in the diabetic patient. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 1999, 38, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruotolo, V.; Di Pietro, B.; Giurato, L.; Masala, S.; Meloni, M.; Schillaci, O.; Bergamini, A.; Uccioli, L. A New Natural History of Charcot Foot. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2013, 38, 506–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonds, M.E.; Petrova, N.L.; Elias, D. The earliest magnetic resonance imaging sign of mid-foot Charcot osteoarthropathy is oedema of subchondral (subarticular) bone marrow which needs prompt therapeutic offloading. Diabet Med. 2005, 22, 93. [Google Scholar]
- Beeve, A.T.; Brazill, J.M.; Scheller, E.L. Peripheral neuropathy as a component of skeletal disease in diabetes. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2019, 17, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serino, J.; Kunze, K.N.; Jacobsen, S.K.; Morash, J.G.; Holmes, G.B.; Lin, J.; Lee, S.; Hamid, K.S.; Bohl, D.D. Nuclear Medicine for the Orthopedic Foot and Ankle Surgeon. Foot Ankle Int. 2020, 41, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Burke, C.J.; Desai, A.; Vijayanathan, S.; Gnanasegaran, G. SPECT-CT: Applications in musculoskeletal radiology. Br. J. Radiol. 2013, 86, 20120519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- NICE Clinical Guideline 10: Type 2 diabetes foot problems: Prevention and management of foot problems of the National Institute for Clinical Excellence (NICE). Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/Guidance/CG10 (accessed on 28 January 2004).
- Petrova, N.L.; Moniz, C.; Elias, D.A.; Buxton, T.M.; Bates, M.; Edmonds, M.E. Is there a systemic inflammatory response in the acute charcot foot? Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 997–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Intenzo, C.M.; Wapner, K.L.; Park, C.H.; Kim, S.M. Evaluation of Plantar Fasciitis by Three-phase Bone Scintigraphy. Clin. Nucl. Med. 1991, 16, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clohisy, D.R.; Thompson, R.C. Fractures associated with neuropathiarthropathy in adults who have juvenile-onset diabetes. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1988, 70, 1192–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuto, G.; Richelme, E.; Cermolacce, C.; Nicaud, M.; Puech, B. Bone SPECT/CT of Ankle and Foot Originally published in French: Tomoscintigraphie osseous de la cheville et du pied by Guillaume Chuto et al.; Springer Nature (Switzerland): Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Softcover ISBN 978-3-319-90810-6, eBook ISBN 978-3-319-90811-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Haga, N. Skeletal complications in congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis: A case series of 14 patients and review of articles published in Japanese. J. Orthop. Sci. 2014, 19, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Kwon, Y.-W.; Sim, Y.-S.; Kim, T.H.; Song, D.; Lee, S. Achilles tenodesis for calcaneal insufficiency avulsion fractures associated with diabetes mellitus. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2017, 12, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kathol, M.H.; El-Khoury, G.Y.; Moore, T.E.; Marsh, J.L. Calcaneal insufficiency avulsion fractures in patients with diabetes mellitus. Radiol. 1991, 180, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, D.R.; Parsons, N.; Shaw, E.; Kulikov, Y.; Hutchinson, C.; Thorogood, M.; Lamb, S.E.; for the UK Heel Fracture Trial (UK HeFT) investigators. Operative versus non-operative treatment for closed, displaced, intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus: Randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2014, 349, g4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mortada, M.; Ezzeldin, N.; Hammad, M. Ultrasonographic features of acute Charcot neuroarthropathy of the foot: A pilot study. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 3787–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berli, M.; Higashigaito, K.; Götschi, T.; Pfirrmann, C.W.A.; Sutter, R.; Rosskopf, A.B. The “Balgrist Score” for evaluation of Charcot foot: A predictive value for duration of off-loading treatment. Skelet. Radiol. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonds, M.; Edmonds, A.; Petrova, N.L.; Edmonds, A.E. What happens to the initial bone marrow oedema in the natural history of Charcot osteoarthropathy? Diabetology 2006, 49, 684. [Google Scholar]
- Baumhauer, J.F.; O’Keefe, R.J.; Schon, L.C.; Pinzur, M.S. Cytokine-induced osteoclastic bone resorption in charcot arthropathy: An immunohistochemical study. Foot Ankle Int. 2006, 27, 797–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrova, N.L.; Dew, T.K.; Musto, R.L.; Sherwood, R.A.; Bates, M.; Moniz, C.; Edmonds, M.E. Inflammatory and bone turnover markers in a cross-sectional and prospective study of acute Charcot osteoarthropathy. Diabet. Med. 2014, 32, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrova, N.L.; Edmonds, M.E. Acute Charcot neuro-osteoarthropathy. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2016, 32, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantelau, E.A.; Richter, A. The acute diabetic Charcot foot managed on the basis of magnetic resonance imaging-A review of 71 cases. Swiss Med. Wkly 2013, 143, 13831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wukich, D.K.; Sung, W.; Wipf, S.A.M.; Armstrong, D.G. The consequences of complacency: Managing the effects of unrecognized Charcot feet. Diabet. Med. 2011, 28, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

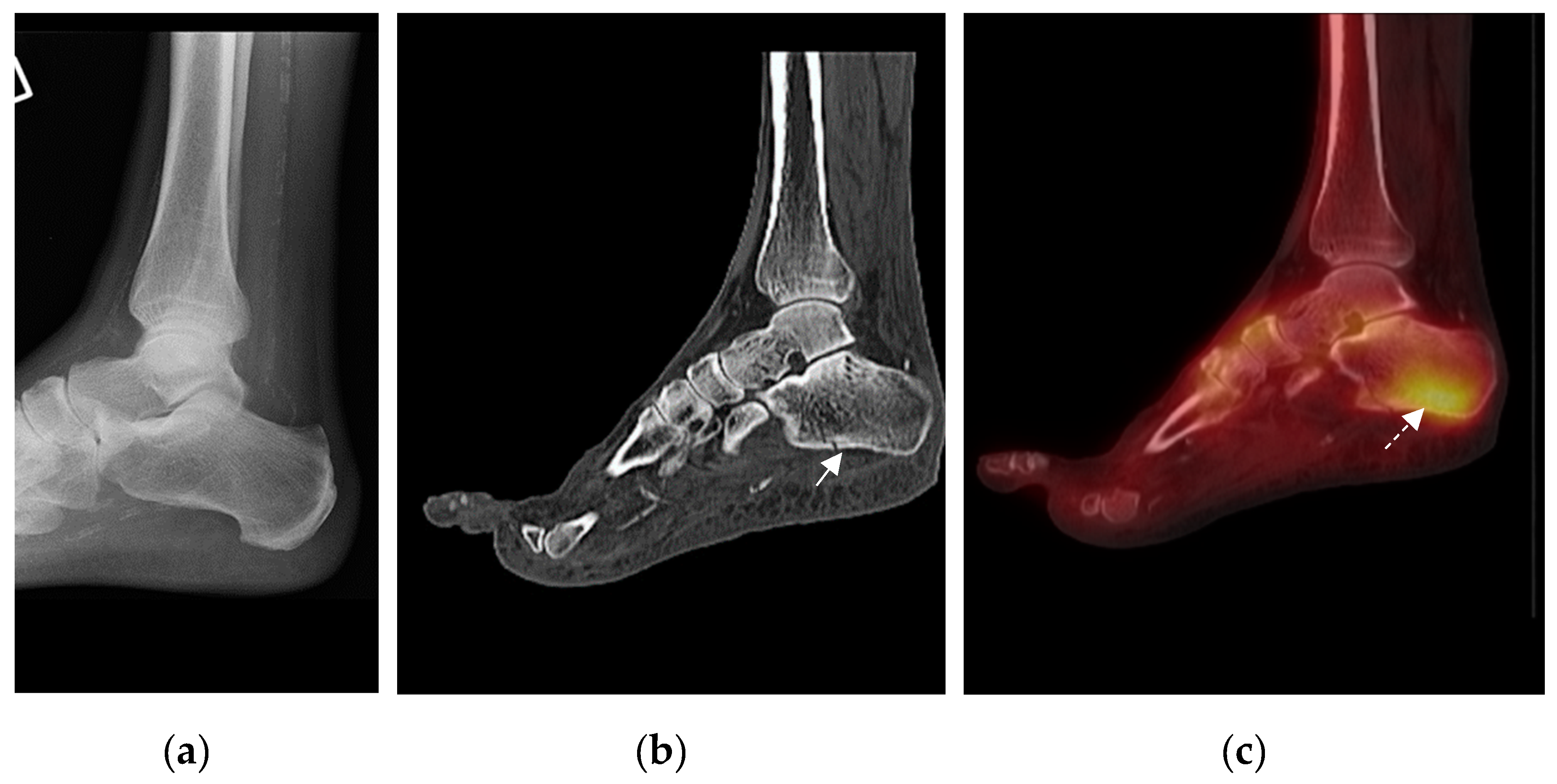
| Patient Number | Blood Flow | Blood Pool | Delayed Phase | SPECT (Areas of Increased Uptake) | CT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Medial and middle cuneiforms and navicular and proximal phalanx 1st ray | Fracture proximal phalanx and fracture 1st metatarsal head |
| 2 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Medial forefoot, mid-foot, dome of the medial talus and 1st metatarsal head | Fracture talus and a uni-cortical fracture 1st metatarsal head |
| 3 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Head of talus and body of navicular, (talo-navicular joint) and lateral cuneiform, 4th and 5th metatarsal bases | Fracture (avulsion) distal lateral cuneiform, and fracture base of 5th metatarsal |
| 4 | −ve | +ve | +ve | Head of 1st metatarsal 5th metatarsal base | Lucency 1st metatarsal head and fracture base of 5th metatarsal |
| 5 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Heads of 1st, 2nd and 3rd metatarsals (1st, 2nd and 3rd metatarsal-phalangeal joints) | Fracture head of 1st metatarsal with subarticular lucency and uni-cortical fractures 2nd and 3rd metatarsal heads and bases |
| 6 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Neck and body of talus | Fracture (avulsion) talar neck and subarticular fracture of posterior talar dome |
| 7 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Dome of talus, sustentaculum tali, navicular, fibula, and medial cuneiform | Fracture navicular and cyst fracture, multiple subarticular cysts of navicular |
| 8 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Calcaneum and cuboid, (calcaneo-cuboid joint), navicular, medial cuneiform, Base of 1st metatarsal (tarso-metatarsal joint), and base of 2nd metatarsal | Uni-cortical fracture (avulsion) navicular, and subarticular cyst of navicular |
| 9 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Inferior and medial aspect of medial cuneiform | Uni-cortical fracture (avulsion) medial cuneiform, subarticular cysts of navicular |
| 10 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Head and base of 1st metatarsal | Fractures head and base of 1st metatarsal |
| 11 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Medial cuneiform | Fracture 3rd toe and subarticular cyst medial cuneiform |
| 12 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Distal and middle phalanx of 1st toe | Uni-cortical fracture (avulsion) dorsal proximal phalanx and fragmentation |
| 13 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Navicular and medial cuneiform | Uni-cortical fracture (avulsion) navicular and periarticular cysts navicular |
| 14 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Left 5th toe | Fracture proximal third of 5th toe |
| 15 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Calcaneal body | Fracture calcaneum |
| 16 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Medial cuneiform | Fracture (avulsion) medial cuneiform, degenerative change 1st metatarsal-phalangeal joint |
| 17 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Fibula, posterior talus and distal tibia (tibio-talar joint) | Fracture fibula and associated cortical fragmentation of distal third fibula |
| 18 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Osteophyte from medial cuneiform to middle cuneiform | Fracture of cuneiform bridging osteophyte |
| 19 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Proximal 4th phalanx, 4th and 5th metatarsals and dorsal talar neck | Fracture proximal third 4th phalanx |
| 20 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Posterior third of calcaneum | Fracture posterior calcaneum |
| 21 | −ve | +ve | +ve | Base of 5th metatarsal | Uni-cortical fracture base 5th metatarsal Cystic change in lateral cuneiform, irregularity talo-calcaneal joint, and anterior talar lip fragmentation |
| 22 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Cuboid and posterior talus | Fracture superior articular surface of cuboid, degenerative change 1st metatarsal head and osteophytes |
| 23 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Distal calcaneum, posterior talus and fibula | Fragmentation of cuboid, and fracture (avulsion) distal third fibula |
| 24 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Anterior facet of calcaneum and proximal cuboid (calcaneo-cuboid joint) | Left calcaneal anterior process fracture |
| 25 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Navicular and middle cuneiform | Uni-cortical fracture and fragmentation of the middle cuneiform |
| 26 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Lateral malleolus (Fibula) | Fracture (avulsion) distal fibula |
| 27 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Posterior calcaneum at the insertion of Achilles tendon | Fracture (avulsion) of posterior third of calcaneum |
| Patient Number | Blood Flow | Blood Pool | Delayed Phase | SPECT (Areas of Increased Uptake) | CT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | +ve | +ve | +ve | 1st, 2nd and 3rd Metatarsal bases Medial, middle and lateral cuneiforms, (1st, 2nd and 3rd tarso-metatarsal joints), talus, and calcaneum | Erosions medial cuneiform |
| 2 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Base of 5th metatarsal | Navicular cyst |
| 3 | −ve | +ve | +ve | Medial cuneiform, 2nd and 3rd metatarsal bases | Cyst middle cuneiform and 2nd metatarsal and subarticular cystic lesions medial cuneiform |
| 4 | +ve | +ve | +ve | 1st Metatarsal head | Lucency 1st metatarsal head |
| 5 | +ve | −ve | +ve | 1st Metatarsal head | Cyst 1st metatarsal head |
| 6 | +ve | +ve | +ve | 1st Metatarsal base and medial cuneiform | Erosions 1st metatarsal base and medial cuneiform and Erosions in 1st metatarsal head |
| 7 | +ve | −ve | +ve | Medial cuneiform,1st and 2nd metatarsal bases | Erosions medial cuneiform and 1st and 2nd metatarsal bases |
| 8 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Base of cuboid and distal anterior calcaneum (calcaneo-cuboid joint) | Subarticular cysts base of cuboid |
| 9 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Middle cuneiform and navicular, 3rd metatarsal | Lucency middle cuneiform, degenerative change 1st metatarsal-phalangeal joint |
| Patient Number | Blood Flow | Blood Pool | Delayed Phase | SPECT (Areas of Increased Uptake) | CT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Navicular, calcaneo-talar, tibio-talar, and medial cuneiform | −ve |
| 2 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Base of 1st and 2nd metatarsals, medial cuneiform and distal part of middle cuneiform | −ve |
| 3 | −ve | +ve | +ve | 2nd, 3rd, 4th and 5th metatarsal bases and medial, middle and lateral cuneiforms and cuboid (2nd, 3rd, 4th and 5th tarso-metatarsal joints) | −ve |
| 4 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Lateral cuneiform | −ve |
| 5 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Superior calcaneum and tibial deltoid insertion | −ve |
| 6 | +ve | +ve | −ve | Navicular, medial cuneiform, middle cuneiform and 1st metatarsal base and sesamoids | −ve |
| 7 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Bases of 1st, 2nd and 3rd metatarsals and medial, middle and lateral cuneiforms (1st, 2nd and 3rd tarso-metatarsal joints) | −ve |
| 8 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Navicular, medial and middle cuneiforms, and insertion of plantar fascia | −ve |
| 9 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Insertion of Achilles tendon at calcaneum and 2nd metatarsal head | −ve |
| 10 | +ve | +ve | +ve | Insertion of Achilles tendon at calcaneum and insertion of plantar fascia | −ve |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahluwalia, R.; Bilal, A.; Petrova, N.; Boddhu, K.; Manu, C.; Vas, P.; Bates, M.; Corcoran, B.; Reichert, I.; Mulholland, N.; et al. The Role of Bone Scintigraphy with SPECT/CT in the Characterization and Early Diagnosis of Stage 0 Charcot Neuroarthropathy. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 4123. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9124123
Ahluwalia R, Bilal A, Petrova N, Boddhu K, Manu C, Vas P, Bates M, Corcoran B, Reichert I, Mulholland N, et al. The Role of Bone Scintigraphy with SPECT/CT in the Characterization and Early Diagnosis of Stage 0 Charcot Neuroarthropathy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(12):4123. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9124123
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhluwalia, Raju, Ahmad Bilal, Nina Petrova, Krishna Boddhu, Chris Manu, Prashanth Vas, Maureen Bates, Ben Corcoran, Ines Reichert, Nicola Mulholland, and et al. 2020. "The Role of Bone Scintigraphy with SPECT/CT in the Characterization and Early Diagnosis of Stage 0 Charcot Neuroarthropathy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 12: 4123. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9124123
APA StyleAhluwalia, R., Bilal, A., Petrova, N., Boddhu, K., Manu, C., Vas, P., Bates, M., Corcoran, B., Reichert, I., Mulholland, N., Kavarthapu, V., Vivian, G., & Edmonds, M. (2020). The Role of Bone Scintigraphy with SPECT/CT in the Characterization and Early Diagnosis of Stage 0 Charcot Neuroarthropathy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(12), 4123. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9124123





