Effect of Intraoperative Sedation with Dexmedetomidine Versus Propofol on Acute Postoperative Pain Following Major Foot Surgery under Popliteal Sciatic Nerve Block: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
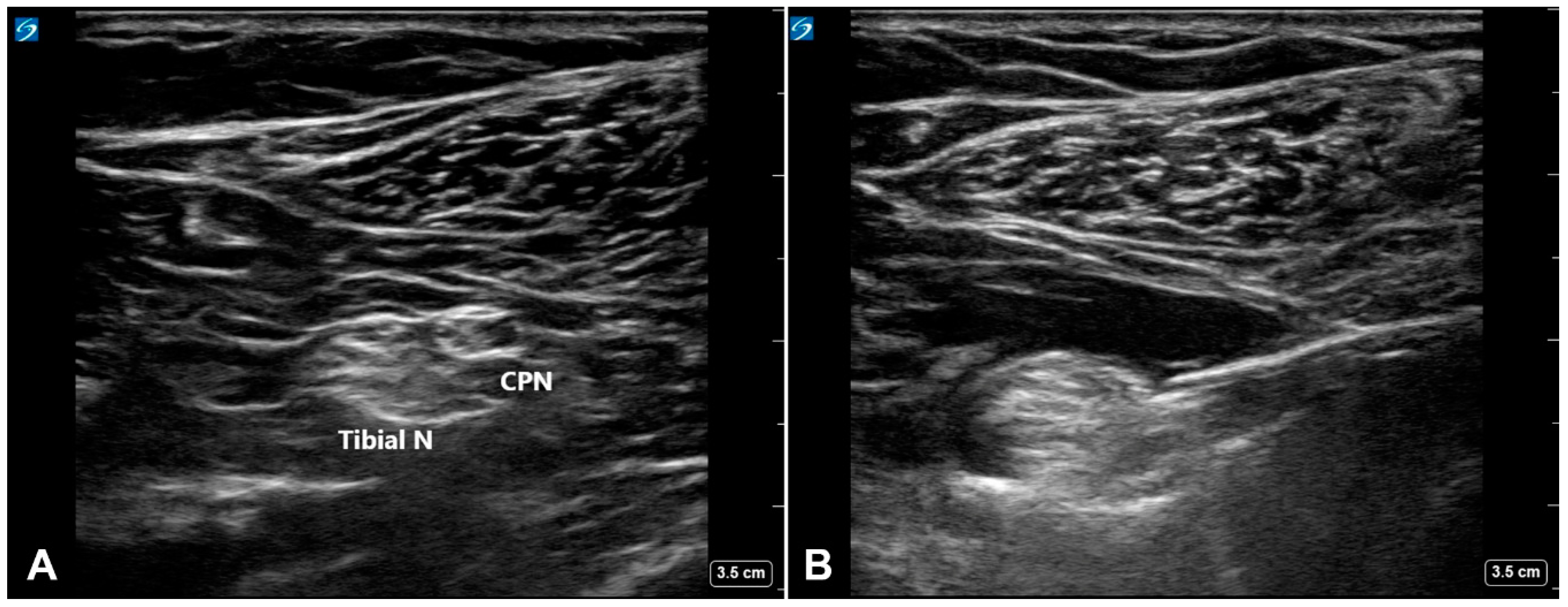
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Study Participants
3.2. Perioperative Parameters
3.3. Study Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chou, L.B.; Wagner, D.; Witten, D.M.; Martinez-Diaz, G.J.; Brook, N.S.; Toussaint, M.; Carroll, I.R. Postoperative Pain Following Foot and Ankle Surgery: A Prospective Study. Foot Ankle Int. 2008, 29, 1063–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ilfeld, B.M.; Morey, T.E.; Wang, R.D.; Enneking, F.K. Continuous Popliteal Sciatic Nerve Block for Postoperative Pain Control at Home: A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Study. Anesthesiology 2002, 97, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.F.; Issioui, T.; Skrivanek, G.D.; Early, J.S.; Wakefield, C. The Use of a Continuous Popliteal Sciatic Nerve Block After Surgery Involving the Foot and Ankle: Does it Improve the Quality of Recovery? Anesth. Analg. 2003, 97, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilfeld, B.M.; Thannikary, L.J.; Morey, T.E.; Vander Griend, R.A.; Enneking, F.K. Popliteal Sciatic Perineural Local Anesthetic Infusion: A Comparison of Three Dosing Regimens for Postoperative Analgesia. Anesthesiology 2004, 101, 970–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvarda, P.; Hagemeijer, N.C.; Waryasz, G.; Guss, D.; DiGiovanni, C.W.; Johnson, A.H. Opioid Consumption Rate Following Foot and Ankle Surgery. Foot Ankle Int. 2019, 40, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerink, M.A.; Struys, M.M.; Hannivoort, L.N.; Barends, C.R.; Absalom, A.R.; Colin, P. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Dexmedetomidine. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 56, 893–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.K.; Lee, J.H.; Yoo, S.; Kim, W.H.; Lim, Y.J.; Bahk, J.H.; Kim, J.T. Comparison of bupivacaine plus intrathecal fentanyl and bupivacaine alone for spinal anesthesia with intravenous dexmedetomidine sedation: a randomized, double-blind, noninferiority trial. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2019, 44, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.J.; Do, S.H.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, T.K.; Na, H.S. Comparison of Intraoperative Sedation With Dexmedetomidine Versus Propofol on Acute Postoperative Pain in Total Knee Arthroplasty Under Spinal Anesthesia: A Randomized Trial. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 129, 1512–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Jeong, J.S.; Park, H.; Sung, K.S.; Choi, S.J.; Gwak, M.S.; Kim, G.S.; Hahm, T.S.; Ko, J.S. Postoperative pain control after the use of dexmedetomidine and propofol to sedate patients undergoing ankle surgery under spinal anesthesia: a randomized controlled trial. J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Sedation and Analgesia by Non-Anesthesiologists. Practice Guidelines for Sedation and Analgesia by Non-Anesthesiologists. Anesthesiology 2002, 96, 1004–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldrete, J.A. The post-anesthesia recovery score revisited. J. Clin. Anesth. 1995, 7, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, S.M.; Ballantyne, J.C.; Rathmell, J.P. Opioid analgesics. In Bonica’s Management of Pain, 4th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (LWW): Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2010; pp. 1172–1187. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, R.A.; Jeong, J.S.; Yoo, J.C.; Lee, J.H.; Gwak, M.S.; Choi, S.J.; Hahm, T.S.; Cho, H.S.; Ko, J.S. Improvement in postoperative pain control by combined use of intravenous dexamethasone with intravenous dexmedetomidine after interscalene brachial plexus block for arthroscopic shoulder surgery: A randomised controlled trial. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2019, 36, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, R.; Jeong, J.S.; Yoo, J.C.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, S.J.; Gwak, M.S.; Hahm, T.S.; Huh, J.; Ko, J.S. Effective Dose of Intravenous Dexmedetomidine to Prolong the Analgesic Duration of Interscalene Brachial Plexus Block: A Single-Center, Prospective, Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Trial. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2018, 43, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, D.J.; Qi, B.; Tang, G.; Li, J.Y. Intraoperative Dexmedetomidine Promotes Postoperative Analgesia and Recovery in Patients after abdominal colectomy: A CONSORT-Prospective, Randomized, Controlled Clinical Trial. Medicine (Baltimore) 2015, 94, e1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, T.Z.; Jiang, J.Y.; Buttermann, A.E.; Maze, M. Dexmedetomidine injection into the locus ceruleus produces antinociception. Anesthesiology 1996, 84, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, F.; Li, C.; Kong, M.; Liu, H.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, S.; Cao, J.; Zhang, L.; Ma, H. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Analgesic Property of Intrathecal Dexmedetomidine and Its Neurotoxicity Evaluation: An In Vivo and In Vitro Experimental Study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaakola, M.L.; Salonen, M.; Lehtinen, R.; Scheinin, H. The analgesic action of dexmedetomidine—a novel alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist—in healthy volunteers. Pain 1991, 46, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, M.S.; Ramaswamy, B.; Davies, M.F.; Maze, M. Comparative Analgesic and Mental Effects of Increasing Plasma Concentrations of Dexmedetomidine and Alfentanil in Humans. Anesthesiology 2004, 101, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortinez, L.I.; Hsu, Y.W.; Sum-Ping, S.T.; Young, C.; Keifer, J.C.; Macleod, D.; Robertson, K.M.; Wright, D.R.; Moretti, E.W.; Somma, J. Dexmedetomidine pharmacodynamics: Part II: Crossover comparison of the analgesic effect of dexmedetomidine and remifentanil in healthy volunteers. Anesthesiology 2004, 101, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte-Uentrop, L.; Goepfert, M.S. Anaesthesia or sedation for MRI in children. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2010, 23, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belleville, J.P.; Ward, D.S.; Bloor, B.C.; Maze, M. Effects of intravenous dexmedetomidine in humans. I. Sedation, ventilation, and metabolic rate. Anesthesiology 1992, 77, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arain, S.R.; Ebert, T.J. The Efficacy, Side Effects, and Recovery Characteristics of Dexmedetomidine Versus Propofol When Used for Intraoperative Sedation. Anesth. Analg. 2002, 95, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bloor, B.C.; Ward, D.S.; Belleville, J.P.; Maze, M. Effects of intravenous dexmedetomidine in humans. II. Hemodynamic changes. Anesthesiology. 1992, 77, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, J.E.; Uhrich, T.D.; Barney, J.A.; Arain, S.R.; Ebert, T.J. Sedative, Amnestic, and Analgesic Properties of Small-Dose Dexmedetomidine Infusions. Anesth. Analg. 2000, 90, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasuya, Y.; Govinda, R.; Rauch, S.; Mascha, E.J.; Sessler, D.I.; Turan, A. The Correlation Between Bispectral Index and Observational Sedation Scale in Volunteers Sedated with Dexmedetomidine and Propofol. Anesth. Analg. 2009, 109, 1811–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Parameter | Propofol (n = 19) | Dexmedetomidine (n = 20) | * p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 53.6 ± 12.7 | 49.8 ± 15.8 | 0.410 |
| Sex (male/female) | 3/16 | 4/16 | >0.99 |
| Height (cm) | 160.1 ± 6.8 | 160.6 ± 9.2 | 0.846 |
| Weight (kg) | 60.1 ± 10.9 | 62.4 ± 12.4 | 0.540 |
| ASA physical status (I/II) | 8/11 | 13/7 | 0.205 |
| Type of surgery | 0.532 | ||
| Hallux valgus osteotomy | 16 | 16 | |
| 1st toe bunion correction operation | 2 | 1 | |
| 1st metacarpophalangeal joint fusion | 1 | 3 |
| Parameters | Propofol (n = 19) | Dexmedetomidine (n = 20) | * p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| In operating room | |||
| Total infused amount of study drug | 211.6 ± 77.1 mg | 103.7 ± 37.6 µg | N/A |
| Requirement for additional midazolam, n | 0 | 16 (80%) | <0.001 |
| Dose of midazolam, mg | 0 | 1.1 ± 0.7 | <0.001 |
| Respiratory depression, n | 0 | 0 | >0.99 |
| Hypotension (requiring ephedrine treatment), n | 1 | 1 | >0.99 |
| Bradycardia, n | 1 | 1 | >0.99 |
| Mean intraoperative blood pressure, mm Hg | 77.9 ± 11.0 | 78.0 ± 7.9 | 0.978 |
| Mean intraoperative heart rate, beats per minute | 75.7 ± 10.7 | 72.0 ± 11.5 | 0.309 |
| Duration of surgery (minutes) | 59.6 ± 19.5 | 58.8 ± 23.3 | 0.899 |
| In PACU | |||
| Static pain score at PACU, (0–10) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0.607 |
| OAA/S score | 5 (5–5) | 5 (5–5) | 0.411 |
| Nausea/vomiting, n | 0 | 0 | N/A |
| Pruritus, n | 0 | 0 | N/A |
| Duration of PACU stay (minutes) | 48.6 ± 11.6 | 46.9 ± 7.6 | 0.595 |
| Outcomes | Propofol (n = 19) | Dexmedetomidine (n = 20) | * p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary outcome | |||
| Cumulative opioid consumption at 24 h: converted to IV morphine equivalent, mg | 17.5 (15–25) | 15 (7.5–16.9) | 0.019 |
| Secondary outcomes | |||
| Time to first rescue analgesic request, h | 10.0 ± 2.7 | 11.8 ± 2.2 | 0.030 |
| Time to first toe movement, h | 11.2 ± 2.5 | 12.1 ± 2.9 | 0.321 |
| Static pain score at 24 h, (0-10) | 3.5 (2–5) | 3 (2–4.8) | 0.607 |
| PCRA consumption at 24 h, mL | 143.2 ± 64.5 | 115.8 ± 40.6 | 0.125 |
| Nausea within 24 h, n | 13 (68.4%) | 7 (35%) | 0.056 |
| Mild/moderate/severe | 10/0/3 | 6/0/1 | 0.065 |
| Vomiting within 24 h, n | 5 (26.3%) | 1 (5%) | 0.091 |
| Pruritus within 24 h, n | 0 | 0 | N/A |
| Quality of sleep on the first night († Likert scale; 1 to 5) | 1 (1–2) | 2 (1.3–3) | 0.019 |
| Patient satisfaction with pain relief at 24 h († Likert scale; 1 to 5) | 2 (1–3) | 3 (2–3) | 0.050 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, R.; Choi, J.W.; Sung, K.-S.; Wi, W.; Hahm, T.S.; Cho, H.S.; Yang, M.K.; Ko, J.S. Effect of Intraoperative Sedation with Dexmedetomidine Versus Propofol on Acute Postoperative Pain Following Major Foot Surgery under Popliteal Sciatic Nerve Block: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9030654
Kang R, Choi JW, Sung K-S, Wi W, Hahm TS, Cho HS, Yang MK, Ko JS. Effect of Intraoperative Sedation with Dexmedetomidine Versus Propofol on Acute Postoperative Pain Following Major Foot Surgery under Popliteal Sciatic Nerve Block: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(3):654. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9030654
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, RyungA, Ji Won Choi, Ki-Sun Sung, Wongook Wi, Tae Soo Hahm, Hyun Sung Cho, Mi Kyung Yang, and Justin Sangwook Ko. 2020. "Effect of Intraoperative Sedation with Dexmedetomidine Versus Propofol on Acute Postoperative Pain Following Major Foot Surgery under Popliteal Sciatic Nerve Block: A Randomized Controlled Trial" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 3: 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9030654
APA StyleKang, R., Choi, J. W., Sung, K.-S., Wi, W., Hahm, T. S., Cho, H. S., Yang, M. K., & Ko, J. S. (2020). Effect of Intraoperative Sedation with Dexmedetomidine Versus Propofol on Acute Postoperative Pain Following Major Foot Surgery under Popliteal Sciatic Nerve Block: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(3), 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9030654





