Cuffless Single-Site Photoplethysmography for Blood Pressure Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
Plethysmography as A Continuous, Non-Invasive Approach to BP Measurement
2. Methods
2.1. Database and MeSH Terms
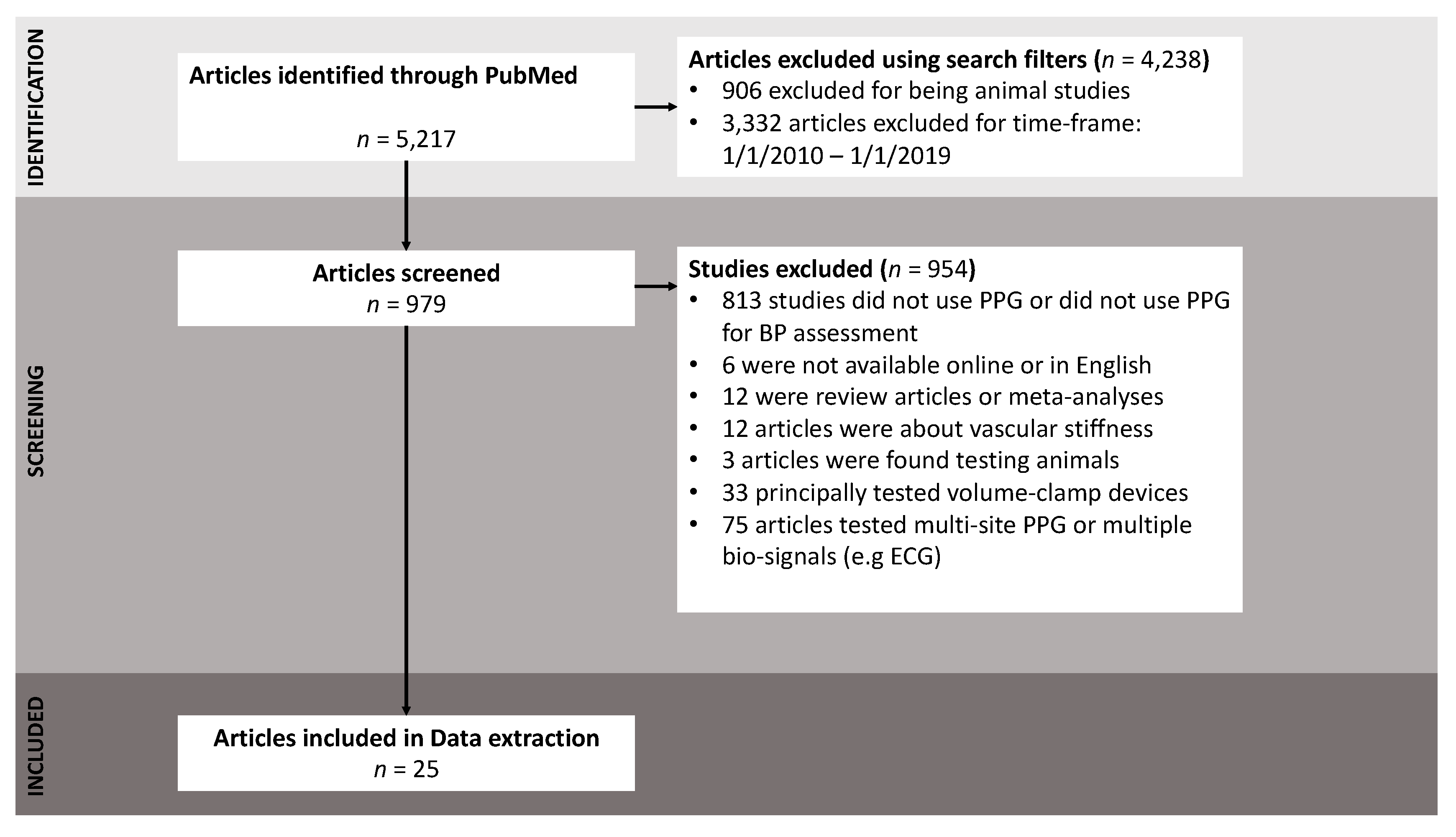
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
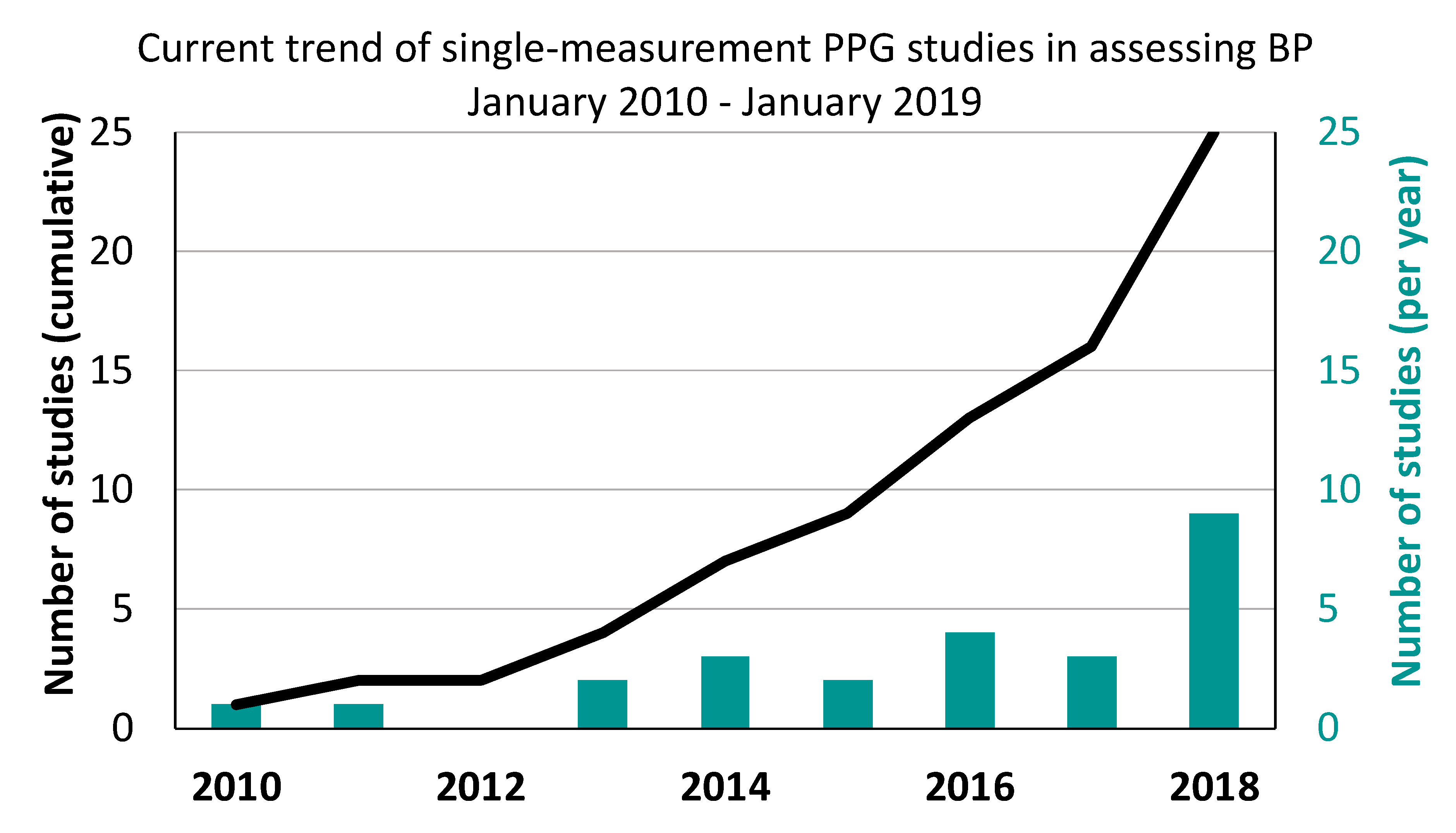
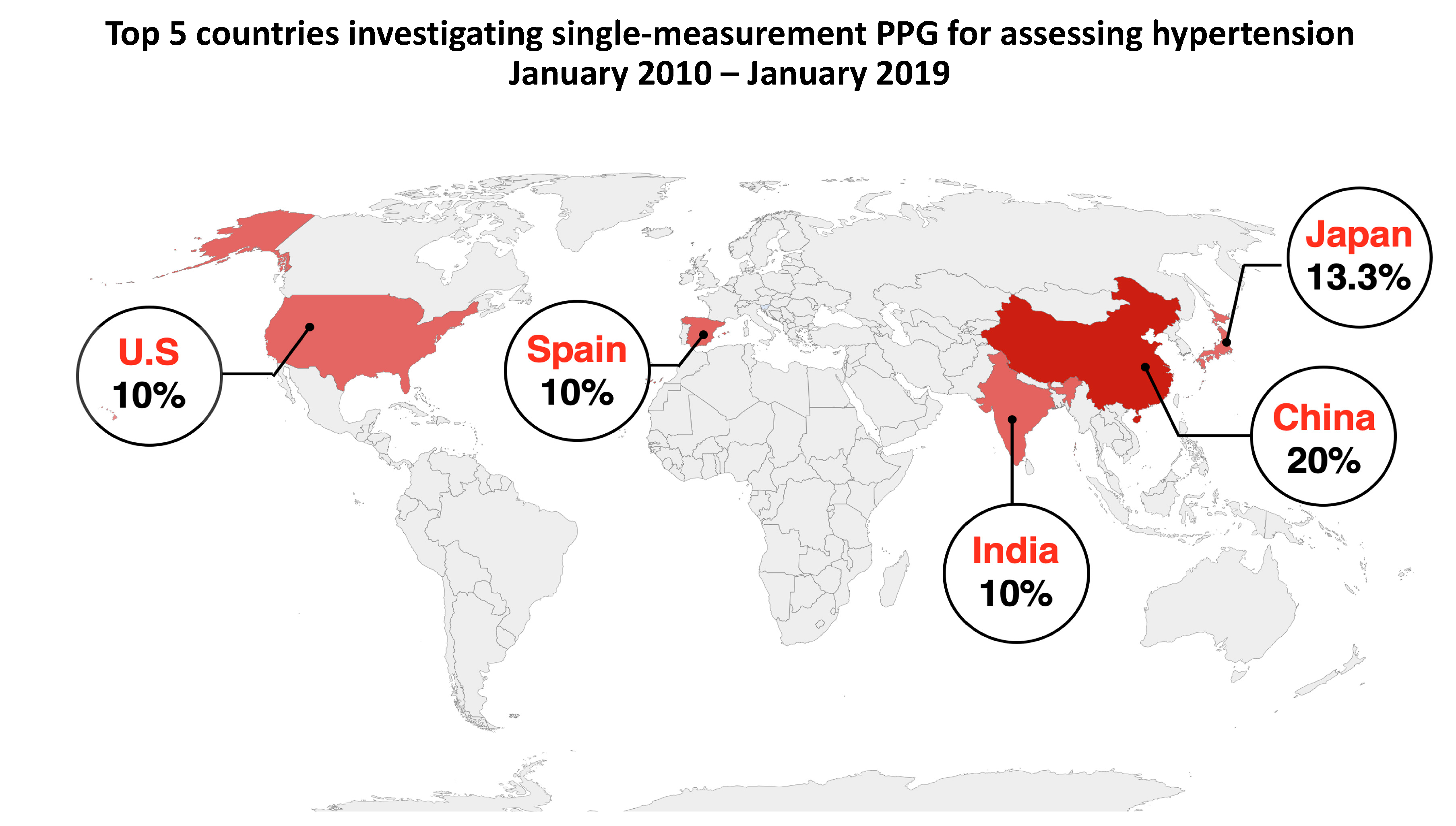
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Anatomical Site of PPG Measurement
4.2. Integration of Single PPG into Smartphone Applications
4.3. Varying Study Sample Sizes
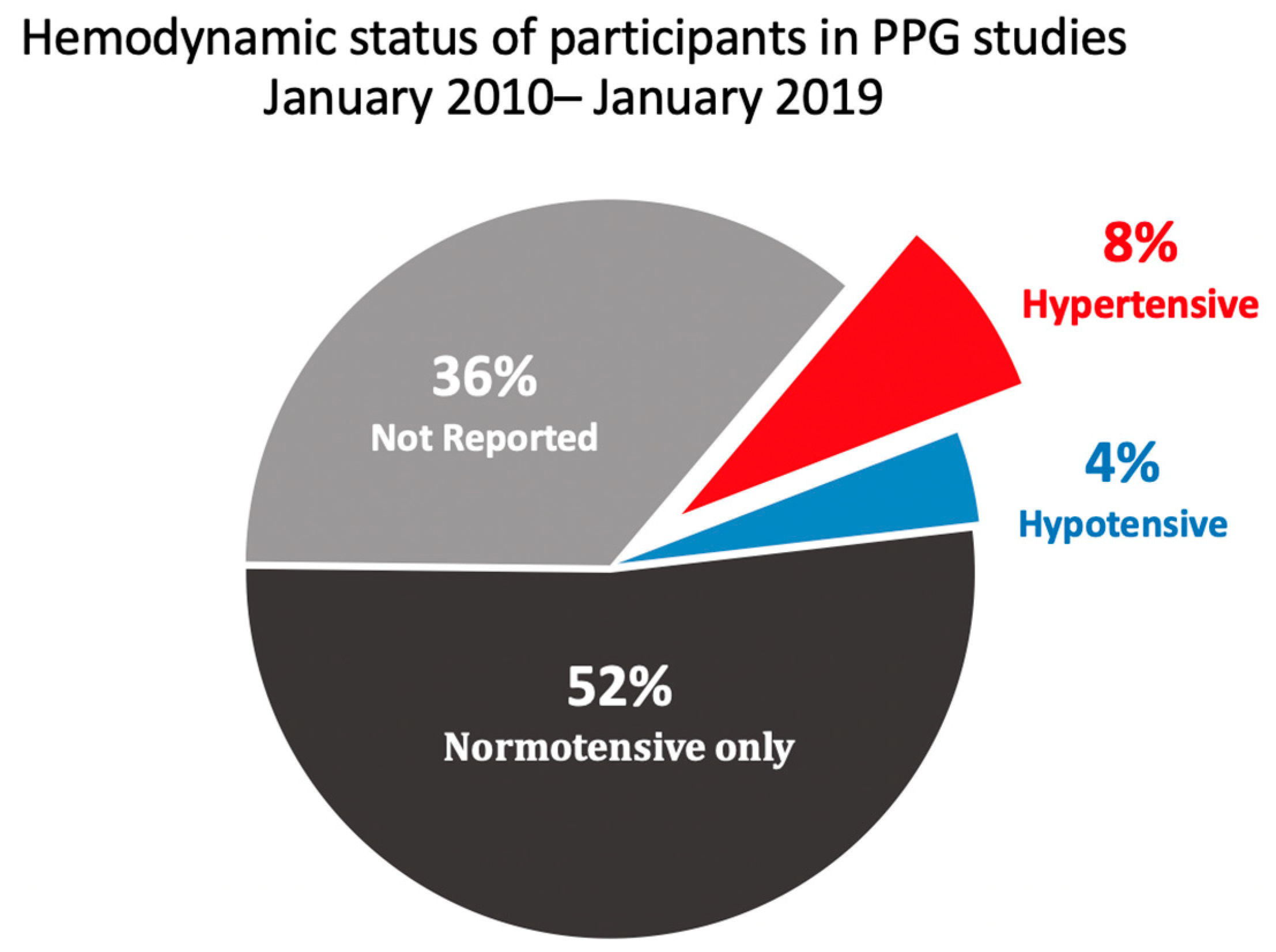
4.4. Use of Normotensive or Hypertensive Subjects
4.5. Gold Standard Method of BP Measurement
4.6. Studies that Included Pregnant Women
4.7. Clinical Practice
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| R | Pearson’s correlation coefficient |
| MAE | mean absolute error (systolic or diastolic) |
| MB | mean bias (calculated using Bland–Altman method) |
| PPG | Photoplethysmogram signal |
| APG ABP | acceleration PPG automated blood pressure measurement |
| RMSE | root mean square error (systolic or diastolic) |
| PE | precision error (systolic or diastolic) |
| Ra | correlation coefficient between PPG feature with measured BP |
| Rb | correlation coefficient between estimated BP and measured BP |
| N/R | not reported |
References
- Kearney, P.M.; Whelton, M.; Reynolds, K.; Muntner, P.; Whelton, P.K.; He, J. Global burden of hypertension: Analysis of worldwide data. Lancet 2005, 365, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxi, D.; Redoute, J.-M.; Yuce, M.R. A survey on signals and systems in ambulatory blood pressure monitoring using pulse transit time. Physiol. Meas. 2015, 36, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.M.; Leopold, D.; Campbell, K.; Mulligan, J.; Grudic, G.Z.; Moulton, S.L. Noninvasive monitoring of physiologic compromise in acute appendicitis: New insight into an old disease. J. Pediatric Surg. 2018, 53, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.R.; Zhao, N.; Yang, G.Z.; Pettigrew, R.I.; Lo, B.; Miao, F.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.T. Continuous blood pressure measurement from invasive to unobtrusive: Celebration of 200th birth anniversary of Carl Ludwig. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2016, 20, 1455–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Elgendi, M.; Chen, Z.; Ward, R. An optimal filter for short photoplethysmogram signals. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgendi, M.; Fletcher, R.; Liang, Y.; Howard, N.; Lovell, N.H.; Abbott, D.; Lim, K.; Ward, R. The use of photoplethysmography for assessing hypertension. Npj Digit. Med. 2019, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, G.; Cooper, R.; Hosanee, M.; Welykholowa, K.; Kyriacou, P.A.; Zheng, D.; Allen, J.; Abbott, D.; Lovell, N.H.; Fletcher, R.; et al. Multi-Site Photoplethysmography Technology for Blood Pressure Assessment: Challenges and Recommendations. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penaz, J. Photoelectric measurement of blood pressure and flow in the finger. In The Digest of 10th Inernational Conference of Medical Biological Engineering, Dresden, GDR, Germany, 13–17 August, 1973; Albert, R., Vogt, W., Helbig, W., Eds.; The Conference Committee: Bernburg, Germany, 1973; Volume 104. [Google Scholar]
- Raichle, C.J.; Eckstein, J.; Lapaire, O.; Leonardi, L.; Brasier, N.; Vischer, A.S.; Burkard, T. Performance of a blood pressure smartphone app in pregnant women: The iPARR Trial (iPhone app compared with standard RR measurement). Hypertension 2018, 71, 1164–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.-C.; Wu, H.-T.; Sun, C.-K. Assessment of subtle changes in diabetes-associated arteriosclerosis using photoplethysmographic pulse wave from index finger. J. Med Syst. 2018, 42, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alex, R.M.; Zhang, R.; Watenpaugh, D.E.; Behbehani, K. Mathematical Modeling of Arterial Blood Pressure Using Photo-Plethysmography Signal in Breath-hold Maneuver. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 July 2018; pp. 2711–2714. [Google Scholar]
- Zadi, A.S.; Alex, R.; Zhang, R.; Watenpaugh, D.E.; Behbehani, K. Arterial blood pressure feature estimation using photoplethysmography. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 102, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.H.; Wang, H.; Samuel, O.W.; Liu, G.; Huang, Z.; Li, G. New photoplethysmogram indicators for improving cuffless and continuous blood pressure estimation accuracy. Physiol. Meas. 2018, 39, 025005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekhar, A.; Kim, C.S.; Naji, M.; Natarajan, K.; Hahn, J.O.; Mukkamala, R. Smartphone-based blood pressure monitoring via the oscillometric finger-pressing method. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaap8674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, J.; Gaurav, A.; Tiwari, V.N. InstaBP: Cuff-less Blood Pressure Monitoring on Smartphone using Single PPG Sensor. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 July 2018; pp. 5002–5005. [Google Scholar]
- Acciaroli, G.; Facchinetti, A.; Pillonetto, G.; Sparacino, G. Non-Invasive Continuous-Time Blood Pressure Estimation from a Single Channel PPG Signal using Regularized ARX Models. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 July 2018; pp. 3630–3633. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, H.; Min, S.D. Feasibility study for the non-invasive blood pressure estimation based on ppg morphology: Normotensive subject study. Biomed. Eng. Online 2017, 16, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Cheng, S.; Wang, T.; Ma, T. Novel blood pressure estimation method using single photoplethysmography feature. In Proceedings of the 2017 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Seogwipo, Korea, 11–15 July 2017; pp. 1712–1715. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.C.; Wittek, P.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, W.J. Data-driven estimation of blood pressure using photoplethysmographic signals. In Proceedings of the 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; pp. 766–769. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Bezemer, R.; Long, X.; Muehlsteff, J.; Aarts, R. Systolic blood pressure estimation using PPG and ECG during physical exercise. Physiol. Meas. 2016, 37, 2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A. Inverse-model-based cuffless blood pressure estimation using a single photoplethysmography sensor. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2015, 229, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.Q.; Fan, J.; Wang, Y.T. Toe photoplethysmographic monitor, a promising noninvasive technique for tracking systolic blood pressure trends beat-to-beat. Blood Press. Monit. 2014, 19, 246–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, R.; Bhuiyan, M.S.; Kawanaka, H.; Oguri, K. Separate estimation of long- and short-term systolic blood pressure variability from photoplethysmograph. In Proceedings of the 2014 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Chicago, IL, USA, 26–30 August 2014; pp. 1851–1854. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Rodríguez, J.C.; Ruiz-Sanmartín, A.; Ribas, V.; Caballero, J.; García-Roche, A.; Riera, J.; Nuvials, X.; de Nadal, M.; de Sola-Morales, O.; Serra, J.; et al. Innovative continuous non-invasive cuffless blood pressure monitoring based on photoplethysmography technology. Intensive Care Med. 2013, 39, 1618–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, H.; Kawanaka, H.; Bhuiyan, M.S.; Oguri, K. Cuffless Blood Pressure Estimation Using Only Photoplethysmography based On Cardiovascular Parameters. In Proceedings of the 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 2132–2135. [Google Scholar]
- Monte-Moreno, E. Non-invasive estimate of blood glucose and blood pressure from a photoplethysmograph by means of machine learning techniques. Artif. Intell. Med. 2011, 53, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, E.C.-P.; Redmond, S.J.; McDarby, G.; Heneghan, C. Towards using photo-plethysmogram amplitude to measure blood pressure during sleep. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 38, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atomi, K.; Kawanaka, H.; Bhuiyan, M.; Oguri, K. Cuffless blood pressure estimation based on data-oriented continuous health monitoring system. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2017, 2017, 1803485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, E.; Sohani, V.; Ali, M.; Chellappan, K.; Beng, G.K. Experimental feasibility study of estimation of the normalized central blood pressure waveform from radial photoplethysmogram. J. Healthc. Eng. 2015, 6, 121–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ward, R.; Elgendi, M. Photoplethysmography and deep learning: Enhancing hypertension risk stratification. Biosensors 2018, 8, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, K.; Qian, Z.; Atef, M.; Wang, G. A feature exploration methodology for learning based cuffless blood pressure measurement using photoplethysmography. In Proceedings of the 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; pp. 6385–6388. [Google Scholar]
- Gaurav, A.; Maheedhar, M.; Tiwari, V.N.; Narayanan, R. Cuff-less PPG based continuous blood pressure monitoring: A smartphone based approach. In Proceedings of the 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; pp. 607–610. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhury, A.D.; Banerjee, R.; Sinha, A.; Kundu, S. Estimating blood pressure using Windkessel model on photoplethysmogram. In Proceedings of the 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Chicago, IL, USA, 26–30 August 2014; pp. 4567–4570. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Yang, D.; Barszczyk, A.; Vempala, N.; Wei, J.; Wu, S.J.; Zheng, P.P.; Fu, G.; Lee, K.; Feng, Z.P. Smartphone-based blood pressure measurement using transdermal optical imaging technology. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, e008857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodore, A.C.; Gilles Clermont, M.; Dalton, A.; Finlay, G. Indications, interpretation, and techniques for arterial catheterization for invasive monitoring. UptoDate 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.M.; Arakawa, K.; Bliss, J. Arterial cannulation: Factors in the development of occlusion. Anesth. Analg. 1975, 54, 836–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutcheon, J.A.; Lisonkova, S.; Joseph, K.S. Epidemiology of pre-eclampsia and the other hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2011, 25, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.B.; Berson, A.S.; Robbins, C.; Jamieson, M.J.; Prisant, L.M.; Roccella, E.; Sheps, S.G. National standard for measurement of resting and ambulatory blood pressures with automated sphygmomanometers. Hypertension 1993, 21, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
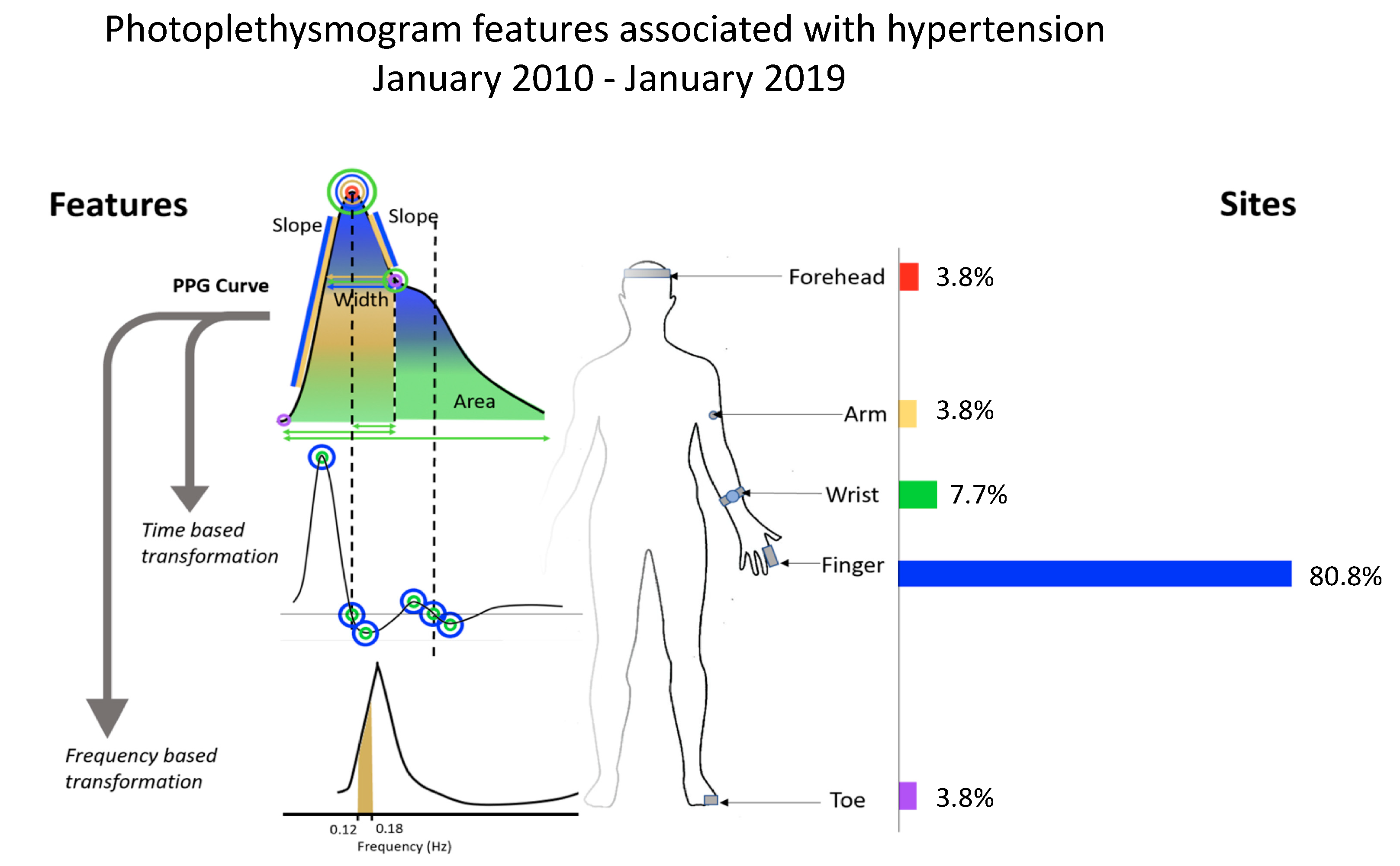

| Location | Study | Participants | Age | Gold Standard | Signal type (Number of Features) | Error (mmHg) | Correlation Co-Efficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Finger | Raichle et al. (2018) [9] | 32 (all F, pregnant) | ABP | PPG (N/R) | MBs = 5 ± 15 | Rs = 0.401 b | |
| Hsu et al.(2018) [10] | 94 (45:M, 49:F) | N/R | PPG (2) | N/R | Rs = 0.354 a | ||
| Alex et al.(2018) [11] | 7 (3:M, 4:F) | Volume clamp | PPG (2) | RMSES < 7 | N/R | ||
| Zadi et al.(2018) [12] | 15 (8:M, 7:F) | Volume clamp | PPG (2) | RMSES < 8 | N/R | ||
| Lin et al.(2018) [13] | 22 | Volume clamp | PPG (5) + VPG (8) + APG (6) | MBs = 4 ± 9 MBD = 4 ± 5 | N/R | ||
| Chandrasekhar et al. (2018) [14] | 35 | ABP | PPG (4) | MBs = 9 MBD = 8 | Rs = 0.76 b RD = 0.79 b | ||
| Dey et al.(2018) [15] | 205 (90:M, 115:F) | Manual | PPG/VPG/APG (233) + Demographics (3) | MAEs = 7 ± 9 MAED = 5 ± 6 | N/R | ||
| Acciaroli et al. (2018) [16] | 8 (7:M, 1:F) | 20–40 | Invasive | PPG (10) | RMSE = 7 ± 2 | N/R | |
| Shin et al. (2017) [17] | 25 (9:M, 16:F) | ABP | APG (8) + VPG (4) | N/R | Rs = 0.83 a RD = 0.12 a | ||
| Chen et al. (2017) [18] | 10 (5:M, 5:F) | Volume clamp | PPG (1) | MEs = −1 ± 4 MED = 0 ± 3 | N/R | ||
| Gao et al. (2016) [19] | 65 (40:M, 25:F) | ABP | PPG (22) + Demographics (2) | MEs = 5 ± 4 MED = 4 ± 4 | N/R | ||
| Sun et al. (2016) [20] | 19 (14:M, 5:F) | Volume clamp | PPG (10) + VPG (4) + APG (4) | RMSES = 9 | Rs = 0.85 b | ||
| Suzuki et al. (2015) [21] | 50 (20:M, 30:F) | 20–70 | ABP | VPG (2) + APG (3) | MAES = 8 | N/R | |
| Fu et al. (2014) [22] | 1 (M) | 54 | ABP | PPG (1) | N/R | N/R | |
| Kondo et al. (2014) [23] | 9 (5:M, 4:F) | Manual | PPG (5) + APG (25) | MEs = 6 | RS = 0.67 b | ||
| Ruiz-Rodríguez et al. (2013) [24] | 572(329:M, 243:F) | Invasive | PPG (N/R) | MBs = −3 ± 19 MBD = −4 ± 9 | N/R | ||
| Fukushima et al. (2013) [25] | 5 (2:M, 3:F) | Volume clamp | APG (6) | N/R | R = 0.71 b | ||
| Monte-Moreno et al. (2011) [26] | 410 (213:M, 197:F) | 9–80 | Manual | PPG (N/R) | N/R | RS = 0.954 b RD = 0.94 b | |
| Chua et al. (2010) [27] | 18 (14:M, 4:F) | Volume clamp | PPG (1) | N/R | RS = 0.73 a | ||
| Wrist | Atomi et al. (2017) [28] | 25 | Manual | PPG (1) + APG (15) + Demographics (4) | MES = 2 ± 9 | Rs = 0.80 b | |
| Zahedi et al. (2015) [29] | 1 (M) | 25 | ABP | PPG (1) | N/R | N/R | |
| Chua et al. (2010) [27] | 18 (14:M, 4:F) | Volume clamp | PPG (1) | N/R | RS = 0.40 a | ||
| Arm | Acciaroli et al. (2018) [16] | 8 (7:M, 1:F) | 20–40 | Invasive | PPG (10) | RMSE = 7 ± 2 | N/R |
| Toe | Fu et al. (2014) [22] | 1 (M) | 54 | ABP | PPG (1) | N/R | N/R |
| Forehead | Sun et al. (2016) [20] | 19 (14:M, 5:F) | Volume clamp | PPG (10) + VPG (4) + APG (4) | RMSES = 9 | Rs = 0.85 b | |
| N/R | Liang et al. (2018) [30] | 121 | N/R | Invasive | PPG (N/R) | N/R | N/R |
| Duan et al. (2016) [31] | 32 | N/R | N/R | PPG (15) | MAEs = 5 ± 8 MAED = 4 ± 6 | N/R | |
| Gaurav et al. (2016) [32] | 3000 | N/R | Invasive | PPG (12) + APG (23) | MEs = 0.2 ± 7 MED = 0 ± 5 | N/R | |
| Choudhury et al. (2014) [33] | 32 | N/R | N/R | PPG (4) | MBs = 1 ± 13 MBD = 1 ± 10 | N/R |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hosanee, M.; Chan, G.; Welykholowa, K.; Cooper, R.; Kyriacou, P.A.; Zheng, D.; Allen, J.; Abbott, D.; Menon, C.; Lovell, N.H.; et al. Cuffless Single-Site Photoplethysmography for Blood Pressure Monitoring. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9030723
Hosanee M, Chan G, Welykholowa K, Cooper R, Kyriacou PA, Zheng D, Allen J, Abbott D, Menon C, Lovell NH, et al. Cuffless Single-Site Photoplethysmography for Blood Pressure Monitoring. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(3):723. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9030723
Chicago/Turabian StyleHosanee, Manish, Gabriel Chan, Kaylie Welykholowa, Rachel Cooper, Panayiotis A. Kyriacou, Dingchang Zheng, John Allen, Derek Abbott, Carlo Menon, Nigel H. Lovell, and et al. 2020. "Cuffless Single-Site Photoplethysmography for Blood Pressure Monitoring" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 3: 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9030723
APA StyleHosanee, M., Chan, G., Welykholowa, K., Cooper, R., Kyriacou, P. A., Zheng, D., Allen, J., Abbott, D., Menon, C., Lovell, N. H., Howard, N., Chan, W.-S., Lim, K., Fletcher, R., Ward, R., & Elgendi, M. (2020). Cuffless Single-Site Photoplethysmography for Blood Pressure Monitoring. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(3), 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9030723









