Hepatitis C Virus: Evading the Intracellular Innate Immunity
Abstract
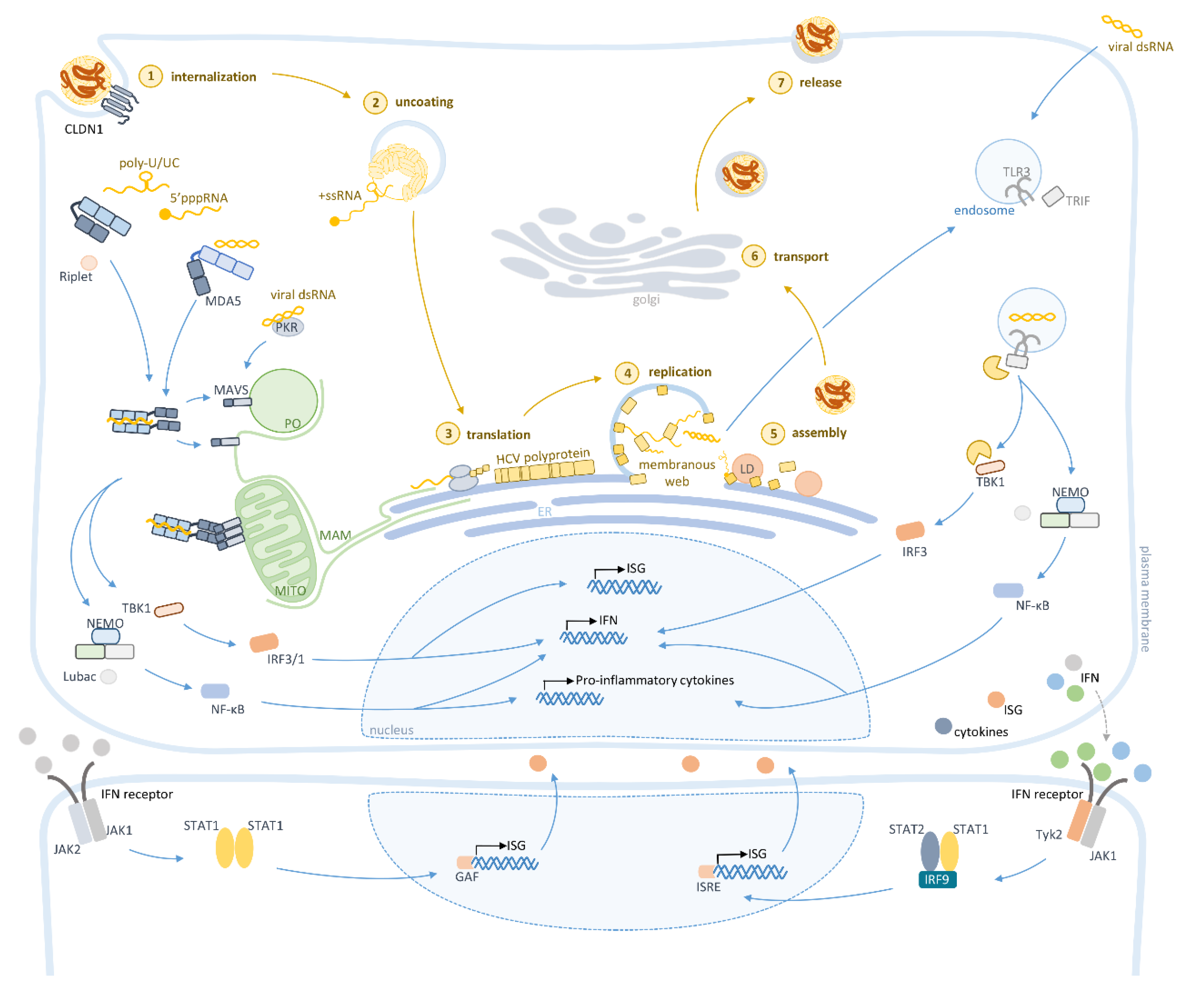
:1. Introduction
2. Hepatitis C Virus
3. Activation of the Intracellular Innate Immunity by HCV
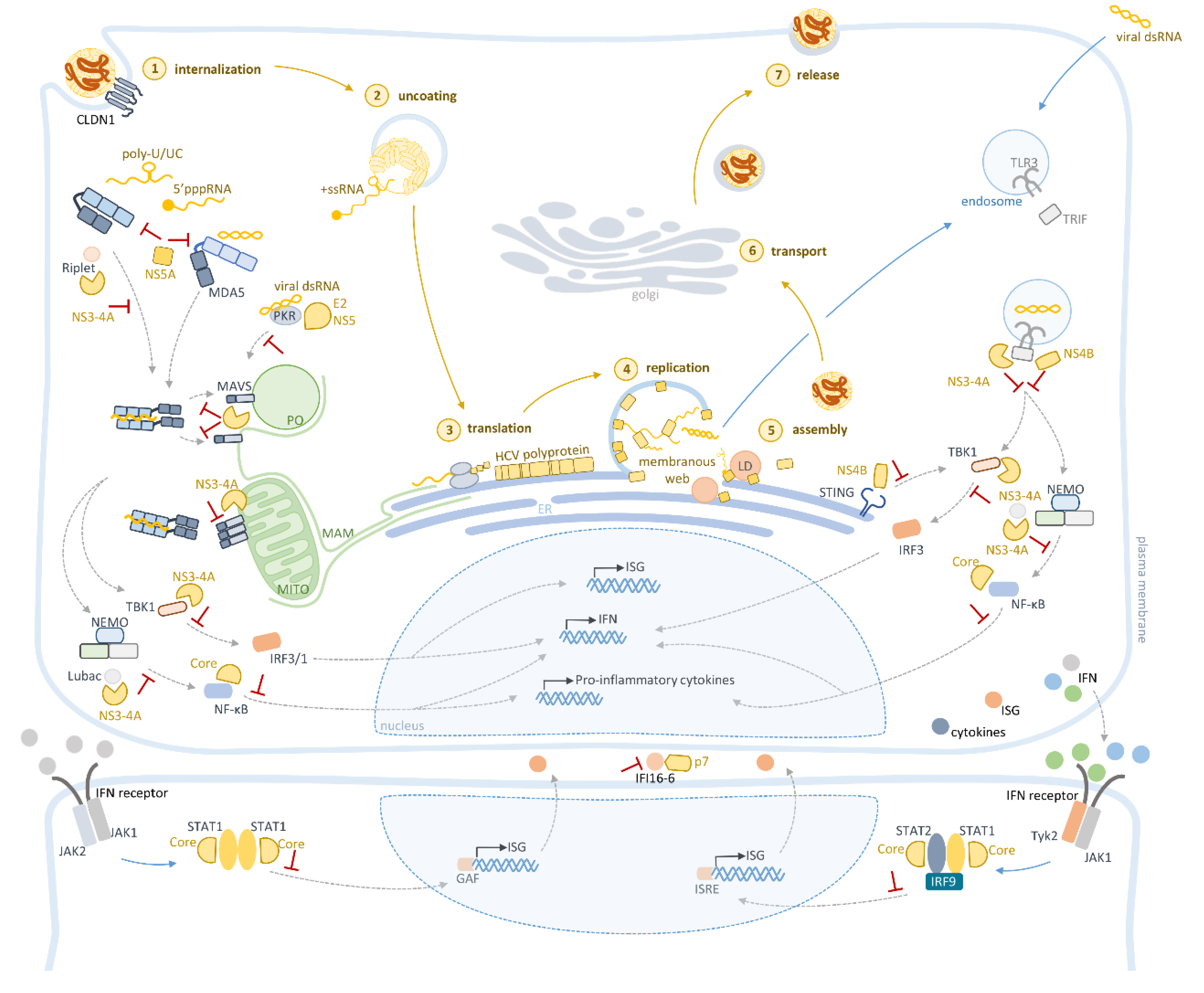
4. Innate Immune Evasion Mediated by HCV
4.1. NS3-4A
4.2. NS4B
4.3. NS5A and E2
4.4. Core
4.5. p7
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spearman, C.W.; Dusheiko, G.M.; Hellard, M.; Sonderup, M. Hepatitis C. Lancet 2019, 394, 1451–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization—WHO. Global Hepatitis Report 2017; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization Hepatitis C. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-c (accessed on 29 February 2020).
- Gottwein, J.M.; Bukh, J. Cutting the Gordian Knot-Development and Biological Relevance of Hepatitis C Virus Cell Culture Systems. Adv. Virus Res. 2008, 71, 51–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgia, S.M.; Hedskog, C.; Parhy, B.; Hyland, R.H.; Stamm, L.M.; Brainard, D.M.; Subramanian, M.G.; McHutchison, J.G.; Mo, H.; Svarovskaia, E.; et al. Identification of a Novel Hepatitis C Virus Genotype From Punjab, India: Expanding Classification of Hepatitis C Virus Into 8 Genotypes. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 1722–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, E.; Feld, J.J.; Li, Q.; Hu, Z.; Fried, M.W.; Liang, T.J. Ribavirin potentiates interferon action by augmenting interferon-stimulated gene induction in hepatitis C virus cell culture models. Hepatology 2011, 53, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spengler, U. Direct antiviral agents (DAAs)—A new age in the treatment of hepatitis C virus infection. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 183, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levrero, M. Viral hepatitis and liver cancer: The case of hepatitis C. Oncogene 2006, 25, 3834–3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medzhitov, R.; Janeway, C.A. Innate Immunity: The Virtues of a Nonclonal System of Recognition. Cell 1997, 91, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janeway, C.A.; Medzhitov, R. Innate Immune Recognition. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 20, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, B.; Jeong, W.-I.; Tian, Z. Liver: An organ with predominant innate immunity. Hepatology 2008, 47, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.R.; Kaminski, J.J.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Fitzgerald, K.A. Pattern recognition receptors and the innate immune response to viral infection. Viruses 2011, 3, 920–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moradpour, D.; Penin, F.; Rice, C.M. Replication of hepatitis C virus. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, M.; Masumi, A.; Mochida, K.; Kukihara, H.; Moriishi, K.; Matsuura, Y.; Yamaguchi, K.; Mizuochi, T. Peripheral B Cells May Serve as a Reservoir for Persistent Hepatitis C Virus Infection. J. Innate Immun. 2010, 2, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, D.; Wölk, B.; Gosert, R.; Bianchi, L.; Blum, H.E.; Moradpour, D.; Bienz, K.; Bianchi, L. Expression of hepatitis C virus proteins induces distinct membrane alterations including a candidate viral replication complex. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 5974–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gosert, R.; Egger, D.; Lohmann, V.; Bartenschlager, R.; Blum, H.E.; Bienz, K.; Moradpour, D. Identification of the Hepatitis C Virus RNA Replication Complex in Huh-7 Cells Harboring Subgenomic Replicons. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 5487–5492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartenschlager, R.; Lohmann, V. Replication of hepatitis C virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 1631–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enomoto, N.; Sato, C. Hepatitis C virus quasispecies populations during chronic hepatitis C infection. Trends Microbiol. 1995, 3, 445–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukiyama-Kohara, K.; Kohara, M. Hepatitis C Virus: Viral Quasispecies and Genotypes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartenschlager, R.; Penin, F.; Lohmann, V.; André, P. Assembly of infectious hepatitis C virus particles. Trends Microbiol. 2011, 19, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulant, S.; Douglas, M.W.; Moody, L.; Budkowska, A.; Targett-Adams, P.; McLauchlan, J. Hepatitis C virus core protein induces lipid droplet redistribution in a microtubule- and dynein-dependent manner. Traffic 2008, 9, 1268–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T. Assembly of hepatitis C virus particles. Microbiol. Immunol. 2011, 55, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tews, B.A.; Popescu, C.-I.; Dubuisson, J. Last stop before exit—Hepatitis C assembly and release as antiviral drug targets. Viruses 2010, 2, 1782–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.M.; McLauchlan, J. Hepatitis C virus: Assembly and release of virus particles. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 22733–22739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindenbach, B.D.; Rice, C.M. The ins and outs of hepatitis C virus entry and assembly. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 688–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saito, T.; Owen, D.M.; Jiang, F.; Marcotrigiano, J.; Gale, M. Innate immunity induced by composition-dependent RIG-I recognition of hepatitis C virus RNA. Nature 2008, 454, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoneyama, M.; Onomoto, K.; Jogi, M.; Akaboshi, T.; Fujita, T. Viral RNA detection by RIG-I-like receptors. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2015, 32, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Liang, Y.; Devaraj, S.; Wang, J.; Lemon, S.M.; Li, K. Toll-Like Receptor 3 Mediates Establishment of an Antiviral State against Hepatitis C Virus in Hepatoma Cells. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 9824–9834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, K.; Li, N.L.; Wei, D.; Pfeffer, S.R.; Fan, M.; Pfeffer, L.M. Activation of chemokine and inflammatory cytokine response in hepatitis C virus-infected hepatocytes depends on toll-like receptor 3 sensing of hepatitis C virus double-stranded RNA intermediates. Hepatology 2012, 55, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Pathogen recognition by the innate immune system. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 30, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, Y.-M.; Owen, D.M.; Li, K.; Erickson, A.K.; Johnson, C.L.; Fish, P.M.; Carney, D.S.; Wang, T.; Ishida, H.; Yoneyama, M.; et al. Viral and therapeutic control of IFN-beta promoter stimulator 1 during hepatitis C virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 6001–6006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, X.; Ding, Q.; Lu, J.; Tao, W.; Huang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Niu, J.; Liu, Y.-J.; Zhong, J. MDA5 Plays a Critical Role in Interferon Response during Hepatitis C Virus Infection. J. Hepatol. 2014, 62, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiet, M.-S.; Bauhofer, O.; Zayas, M.; Roth, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Schirmacher, P.; Willemsen, J.; Grünvogel, O.; Bender, S.; Binder, M.; et al. Control of temporal activation of hepatitis C virus-induced interferon response by domain 2 of nonstructural protein 5A. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, X.; Kinch, L.N.; Brautigam, C.A.; Chen, X.; Du, F.; Grishin, N.V.; Chen, Z.J. Ubiquitin-induced oligomerization of the RNA sensors RIG-I and MDA5 activates antiviral innate immune response. Immunity 2012, 36, 959–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kowalinski, E.; Lunardi, T.; McCarthy, A.A.; Louber, J.; Brunel, J.; Grigorov, B.; Gerlier, D.; Cusack, S. Structural basis for the activation of innate immune pattern-recognition receptor RIG-I by viral RNA. Cell 2011, 147, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seth, R.B.; Sun, L.; Ea, C.-K.; Chen, Z.J. Identification and Characterization of MAVS, a Mitochondrial Antiviral Signaling Protein that Activates NF-κB and IRF3. Cell 2005, 122, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meylan, E.; Curran, J.; Hofmann, K.; Moradpour, D.; Binder, M.; Bartenschlager, R.; Tschopp, J. Cardif is an adaptor protein in the RIG-I antiviral pathway and is targeted by hepatitis C virus. Nature 2005, 437, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.-G.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Han, K.-J.; Li, L.-Y.; Zhai, Z.; Shu, H.-B. VISA is an adapter protein required for virus-triggered IFN-beta signaling. Mol. Cell 2005, 19, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Takahashi, K.; Sato, S.; Coban, C.; Kumar, H.; Kato, H.; Ishii, K.J.; Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. IPS-1, an adaptor triggering RIG-I- and Mda5-mediated type I interferon induction. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, F.; Sun, L.; Zheng, H.; Skaug, B.; Jiang, Q.-X.; Chen, Z.J. MAVS forms functional prion-like aggregates to activate and propagate antiviral innate immune response. Cell 2011, 146, 448–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; He, X.; Zheng, H.; Huang, L.J.; Hou, F.; Yu, Z.; de la Cruz, M.J.; Borkowski, B.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.J.; et al. Structural basis for the prion-like MAVS filaments in antiviral innate immunity. Elife 2014, 3, e01489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chen, J.; Cai, X.; Wu, J.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.-T.; Sun, L.; Chen, Z.J. MAVS recruits multiple ubiquitin E3 ligases to activate antiviral signaling cascades. Elife 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M. Role of Adaptor TRIF in the MyD88-Independent Toll-Like Receptor Signaling Pathway. Science 2003, 301, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, E.; Kagan, J.C. Intracellular Pathogen Detection by RIG-I-Like Receptors. Adv. Immunol. 2013, 117, 99–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoneyama, M.; Kikuchi, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Imaizumi, T.; Miyagishi, M.; Taira, K.; Foy, E.; Loo, Y.-M.; Gale, M., Jr.; Akira, S.; et al. Shared and Unique Functions of the DExD/H-Box Helicases RIG-I, MDA5, and LGP2 in Antiviral Innate Immunity. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 2851–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leung, D.W.; Basler, C.F.; Amarasinghe, G.K. Molecular mechanisms of viral inhibitors of RIG-I-like receptors. Trends Microbiol. 2012, 20, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majoros, A.; Platanitis, E.; Kernbauer-Hölzl, E.; Rosebrock, F.; Müller, M.; Decker, T. Canonical and non-canonical aspects of JAK-STAT signaling: Lessons from interferons for cytokine responses. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Xu, L.; Su, J.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Pan, Q. Transcriptional Regulation of Antiviral Interferon-Stimulated Genes. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Dong, H.; Eksioglu, E.; Hemming, A.; Cao, M.; Crawford, J.M.; Nelson, D.R.; Liu, C. Hepatitis C Virus Triggers Apoptosis of a Newly Developed Hepatoma Cell Line Through Antiviral Defense System. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 1649–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, K.; Lange, C.M.; Gouttenoire, J.; Meylan, E.; Brass, V.; Penin, F.; Moradpour, D. Nonstructural protein 3-4A: The Swiss army knife of hepatitis C virus. J. Viral Hepat. 2011, 18, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradpour, D.; Penin, F. Hepatitis C virus: From structure to Function. In Hepatitis C Virus: From Molecular Virology to Antiviral Therapy; Bartenschlager, R., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 113–142. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.; Kim, S.S.; Yeung, E.; Kamegaya, Y.; Blackard, J.T.; Kim, K.A.; Holtzman, M.J.; Chung, R.T. Hepatitis C Virus Core Protein Blocks Interferon Signaling by Interaction with the STAT1 SH2 Domain. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 9226–9235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, A.R.; Magalhães, A.C.; Camões, F.; Gouveia, A.; Vieira, M.; Kagan, J.C.; Ribeiro, D. Hepatitis C virus NS3-4A inhibits the peroxisomal MAVS-dependent antiviral signalling response. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, S.; Reuter, A.; Eberle, F.; Einhorn, E.; Binder, M.; Bartenschlager, R. Activation of Type I and III Interferon Response by Mitochondrial and Peroxisomal MAVS and Inhibition by Hepatitis C Virus. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horner, S.M.; Liu, H.M.; Park, H.S.; Briley, J.; Gale, M. Mitochondial-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes (MAM) form innate immune synapses and are targeted by hepatitis C virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14590–14595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.-D.; Sun, L.; Seth, R.B.; Pineda, G.; Chen, Z.J. Hepatitis C virus protease NS3/4A cleaves mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein off the mitochondria to evade innate immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 17717–17722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bellecave, P.; Sarasin-Filipowicz, M.; Sarasin-Filipowicz, O.D.; Kennel, A.; Gouttenoire, J.J.; Meylan, E.; Terracciano, L.; Tschopp, J.; Sarrazin, C.; Berg, T.; et al. Cleavage of mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein in the liver of patients with chronic hepatitis c correlates with a reduced activation of the endogenous interferon system. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Foy, E.; Ferreon, J.C.; Nakamura, M.; Ferreon, A.C.M.; Ikeda, M.; Ray, S.C.; Gale, M.; Lemon, S.M. Immune evasion by hepatitis C virus NS3/4A protease-mediated cleavage of the Toll-like receptor 3 adaptor protein TRIF. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 2992–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fitzgerald, K.A.; McWhirter, S.M.; Faia, K.L.; Rowe, D.C.; Latz, E.; Golenbock, D.T.; Coyle, A.J.; Liao, S.M.; Maniatis, T. IKKE and TBKI are essential components of the IRF3 signalling pathway. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; TenOever, B.R.; Grandvaux, N.; Zhou, G.P.; Lin, R.; Hiscott, J. Triggering the interferon antiviral response through an IKK-related pathway. Science 2003, 300, 1148–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, M.; Kato, N.; Moriyama, M.; Taniguchi, H.; Wang, Y.; Dharel, N.; Kawabe, T.; Omata, M. Interaction between the HCV NS3 protein and the host TBK1 protein leads to inhibition of cellular antiviral responses. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshiumi, H.; Miyashita, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Seya, T. A Distinct Role of Riplet-Mediated K63-Linked Polyubiquitination of the RIG-I Repressor Domain in Human Antiviral Innate Immune Responses. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vazquez, C.; Tan, C.Y.; Horner, S.M. Hepatitis C virus infection is inhibited by a non-canonical antiviral signaling pathway targeted by NS3-NS4A. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00725-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kang, W.; Ryu, S.W.; Kim, W.I.; Chang, D.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Park, D.Y.; Choi, Y.H.; Choi, K.; Shin, E.C.; et al. Hepatitis C virus infection enhances TNFα-induced cell death via suppression of NF-κB. Hepatology 2012, 56, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasarte, J.J.; Sarobe, P.; Boya, P.; Casares, N.; Arribillaga, L.; López-Díaz de Cerio, A.; Gorraiz, M.; Borrás-Cuesta, F.; Prieto, J. A recombinant adenovirus encoding hepatitis C virus core and E1 proteins protects mice against cytokine-induced liver damage. Hepatology 2003, 37, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; He, L.; Peng, Y.; Shi, X.; Chen, J.; Zhong, J.; Chen, X.; Cheng, G.; Deng, H. The hepatitis C virus protein NS3 suppresses TNF-α-stimulated activation of NF-κB by targeting LUBAC. Sci. Signal. 2015, 8, RA118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Choe, W.H.; Hiasa, Y.; Kamegaya, Y.; Blackard, J.T.; Schmidt, E.V.; Chung, R.T. Hepatitis C virus expression suppresses interferon signaling by degrading STAT1. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Cao, X.; Ding, Q.; Zhao, Y.; He, Z.; Zhong, J. Hepatitis C virus NS4B induces the degradation of TRIF to inhibit TLR3-mediated interferon signaling pathway. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitta, S.; Sakamoto, N.; Nakagawa, M.; Kakinuma, S.; Mishima, K.; Kusano-Kitazume, A.; Kiyohashi, K.; Murakawa, M.; Nishimura-Sakurai, Y.; Azuma, S.; et al. Hepatitis C virus NS4B protein targets STING and abrogates RIG-I-mediated type I interferon-dependent innate immunity. Hepatology 2013, 57, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Cao, X.; Lu, J.; Huang, B.; Liu, Y.-J.; Kato, N.; Shu, H.-B.; Zhong, J. Hepatitis C virus NS4B blocks the interaction of STING and TBK1 to evade host innate immunity. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, H.; Barber, G.N. STING is an endoplasmic reticulum adaptor that facilitates innate immune signalling. Nature 2008, 455, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Waterman, P.M.; Jonscher, K.R.; Short, C.M.; Reisdorph, N.A.; Cambier, J.C. MPYS, a novel membrane tetraspanner, is associated with major histocompatibility complex class II and mediates transduction of apoptotic signals. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 5014–5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, H.; You, F.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhai, Z.; Chen, D.; Jiang, Z. ERIS, an endoplasmic reticulum IFN stimulator, activates innate immune signaling through dimerization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 8653–8658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, B.; Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Li, Y.; Diao, F.; Lei, C.; He, X.; Zhang, L.; Tien, P.; et al. The Adaptor Protein MITA Links Virus-Sensing Receptors to IRF3 Transcription Factor Activation. Immunity 2008, 29, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paludan, S.R.; Bowie, A.G. Immune sensing of DNA. Immunity 2013, 38, 870–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yi, G.; Wen, Y.; Shu, C.; Han, Q.; Konan, K.V.; Li, P.; Kao, C.C. The Hepatitis C Virus NS4B Can Suppress STING Accumulation to Evade Innate Immune Responses. J. Virol. 2015, 90, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, C.Y.; Chang, T.H.; Liang, J.J.; Chiang, R.L.; Lee, Y.L.; Liao, C.L.; Lin, Y.L. Dengue virus targets the adaptor protein MITA to subvert host innate immunity. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, C.K.; Rahbek, S.H.; Gad, H.H.; Bak, R.O.; Jakobsen, M.R.; Jiang, Z.; Hansen, A.L.; Jensen, S.K.; Sun, C.; Thomsen, M.K.; et al. Influenza A virus targets a cGAS-independent STING pathway that controls enveloped RNA viruses. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, S.; Maestre, A.M.; Pagni, S.; Patel, J.R.; Savage, T.; Gutman, D.; Maringer, K.; Bernal-Rubio, D.; Shabman, R.S.; Simon, V.; et al. DENV Inhibits Type I IFN Production in Infected Cells by Cleaving Human STING. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Goulet, M.-L.; Sze, A.; Hadj, S.B.; Belgnaoui, S.M.; Lababidi, R.R.; Zheng, C.; Fritz, J.H.; Olagnier, D.; Lin, R. RIG-I-Mediated STING Upregulation Restricts Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Infection. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 9406–9419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marques, M.; Ferreira, A.R.; Ribeiro, D. The Interplay between Human Cytomegalovirus and Pathogen Recognition Receptor Signaling. Viruses 2018, 10, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, A.; Yang, Y.L.; Flati, V.; Der, S.; Kadereit, S.; Deb, A.; Haque, J.; Reis, L.; Weissmann, C.; Williams, B.R.G. Deficient cytokine signaling in mouse embryo fibroblasts with a targeted deletion in the PKR gene: Role of IRF-1 and NF-κB. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McAllister, C.S.; Samuel, C.E. The RNA-activated protein kinase enhances the induction of interferon-β and apoptosis mediated by cytoplasmic RNA sensors. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 1644–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arnaud, N.; Dabo, S.; Akazawa, D.; Fukasawa, M.; Shinkai-Ouchi, F.; Hugon, J.; Wakita, T.; Meurs, E.F. Hepatitis C virus reveals a novel early control in acute immune response. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pindel, A.; Sadler, A. The role of protein kinase R in the interferon response. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2011, 31, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garaigorta, U.; Chisari, F.V. Hepatitis C virus blocks interferon effector function by inducing protein kinase R phosphorylation. Cell Host Microbe 2009, 6, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arnaud, N.; Dabo, S.; Maillard, P.; Budkowska, A.; Kalliampakou, K.I. Hepatitis C Virus Controls Interferon Production through PKR Activation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gale, M.J.; Korth, M.J.; Tang, N.M.; Tan, S.L.; Hopkins, D.A.; Dever, T.E.; Polyak, S.J.; Gretch, D.R.; Katze, M.G. Evidence that hepatitis C virus resistance to interferon is mediated through repression of the PKR protein kinase by the nonstructural 5A protein. Virology 1997, 230, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, D.R.; Shi, S.T.; Romano, P.R.; Barber, G.N.; Lai, M.M.C. Inhibition of the interferon-inducible protein kinase PKR by HCV E2 protein. Science 1999, 285, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Satoh, S.; Noshi, T.; Hatada, E.; Fukuda, R.; Kawai, A.; Ikeda, S.; Hijikata, M.; Shimotohno, K. Effects of Mutation in Hepatitis C Virus Nonstructural Protein 5A on Interferon Resistance Mediated by Inhibition of PKR Kinase Activity in Mammalian Cells. Microbiol. Immunol. 2001, 45, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çevik, R.E.; Cesarec, M.; Da, A.; Filipe, S.; Licastro, D.; Mclauchlan, J.; Marcello, A. Hepatitis C Virus NS5A Targets Nucleosome Assembly Protein NAP1L1 To Control the Innate Cellular Response. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00880-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, H.; Mudryj, M.; Guadalupe, M.; Dandekar, S. Hepatitis C virus core protein expression leads to biphasic regulation of the p21 cdk inhibitor and modulation of hepatocyte cell cycle. Virology 2003, 312, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, W.; Lo, S.Y.; Chen, M.; Wu, K.J.; Fung, Y.K.T.; Ou, J.H. Activation of p53 tumor suppressor by hepatitis C virus core protein. Virology 1999, 264, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ray, R.B.; Martin Lagging, L.; Meyer, K.; Steele, R.; Ray, R. Transcriptional regulation of cellular and viral promoters by the hepatitis C virus core protein. Virus Res. 1995, 37, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Yang, S.H.; Cho, Y.G.; Hwang, S.B.; Hahn, Y.S.; Sung, Y.C. Hepatitis C virus core from two different genotypes has an oncogenic potential but is not sufficient for transforming primary rat embryo fibroblasts in cooperation with the H-ras oncogene. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 3060–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moriya, K.; Fujie, H.; Shintani, Y.; Yotsuyanagi, H.; Tsutsumi, T.; Ishibashi, K.; Matsuuras, Y.; Kimura, S.; Miyamura, T.; Koike, K. The core protein of hepatitis C virus induces hepatocellular carcinoma in transgenic mice. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 1065–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, R.B.; Lagging, L.M.; Meyer, K.; Ray, R. Hepatitis C virus core protein cooperates with ras and transforms primary rat embryo fibroblasts to tumorigenic phenotype. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 4438–4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shrivastava, A.; Manna, S.K.; Ray, R.; Aggarwal, B.B. Ectopic Expression of Hepatitis C Virus Core Protein Differentially Regulates Nuclear Transcription Factors. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 9722–9728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, H.; Sankaran, S.; Dandekar, S. Hepatitis C virus core protein induces expression of genes regulating immune evasion and anti-apoptosis in hepatocytes. Virology 2006, 354, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, H.; Kato, N.; Shiratori, Y.; Otsuka, M.; Maeda, S.; Kato, J.; Omata, M. Hepatitis C virus core protein activates nuclear factor b-dependent signaling through tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 16399–16405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- You, L.R.; Chen, C.M.; Lee, Y.H. Hepatitis C virus core protein enhances NF-kappaB signal pathway triggering by lymphotoxin-beta receptor ligand and tumor necrosis factor alpha. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 1672–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marusawa, H.; Hijikata, M.; Chiba, T.; Shimotohno, K. Hepatitis C virus core protein inhibits Fas- and tumor necrosis factor alpha-mediated apoptosis via NF-kappaB activation. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 4713–4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kato, N.; Yoshida, H.; Kioko Ono-nita, S.; Kato, J.; Goto, T.; Otsuka, M.; Lan, K.; Matsushima, K.; Shiratori, Y.; Omata, M. Activation of intracellular signaling by hepatitis B and C viruses: C-viral core is the most potent signal inducer. Hepatology 2000, 32, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Meyer, K.; Ray, R.B.; Ray, R. Hepatitis C virus core protein modulates the interferon-induced transacting factors of Jak/Stat signaling pathway but does not affect the activation of downstream IRF-1 or 561 gene. Virology 2001, 288, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heim, M.H.; Moradpour, D.; Blum, H.E. Expression of Hepatitis C Virus Proteins Inhibits Signal Transduction through the Jak-STAT Pathway. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 8469–8475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blindenbacher, A.; Duong, F.H.T.; Hunziker, L.; Stutvoet, S.T.D.; Wang, X.; Terracciano, L.; Moradpour, D.; Blum, H.E.; Alonzi, T.; Tripodi, M.; et al. Expression of hepatitis C virus proteins inhibits interferon α signaling in the liver of transgenic mice. Gastroenterology 2003, 124, 1465–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, F.H.T.; Filipowicz, M.; Tripodi, M.; La Monica, N.; Heim, M.H. Hepatitis C Virus Inhibits Interferon Signaling through Up-regulation of Protein Phosphatase 2A. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong, F.H.T.; Christen, V.; Berke, J.M.; Penna, S.H.; Moradpour, D.; Heim, M.H. Upregulation of Protein Phosphatase 2Ac by Hepatitis C Virus Modulates NS3 Helicase Activity through Inhibition of Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 1. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 15342–15350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Lucas, S.; Bartolomé, J.; Carreño, V. Hepatitis C Virus Core Protein Down-Regulates Transcription of Interferon-Induced Antiviral Genes. JID 2005, 191, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luquin, E.; Larrea, E.; Civeira, M.P.; Prieto, J.; Aldabe, R. HCV structural proteins interfere with interferon-alpha Jak/STAT signalling pathway. Antivir. Res. 2007, 76, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosui, A.; Ohkawa, K.; Ishida, H.; Sato, A.; Nakanishi, F.; Ueda, K.; Takehara, T.; Kasahara, A.; Sasaki, Y.; Hori, M.; et al. Hepatitis C Virus Core Protein Differently Regulates the JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway under Interleukin-6 and Interferon-Stimuli* Downloaded from. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 28562–28571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larrea, E.; Aldabe, R.; Molano, E.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, C.M.; Ametzazurra, A.; Civeira, M.P.; Prieto, J. Altered expression and activation of signal transducers and activators of transcription (STATs) in hepatitis C virus infection: In vivo and in vitro studies. Gut 2006, 55, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T. Morphogenesis of infectious hepatitis C virus particles. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, H.; Chu, V.; Wu, N.C.; Chen, Z.; Truong, S.; Brar, G.; Su, S.Y.; Du, Y.; Arumugaswami, V.; Olson, C.A.; et al. Systematic identification of anti-interferon function on hepatitis C virus genome reveals p7 as an immune evasion protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 2018–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Jiang, J.-D.; Peng, Z.-G. MicroRNA-mediated interactions between host and hepatitis C virus. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 1487–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcfarland, A.P.; Horner, S.M.; Jarret, A.; Joslyn, R.C.; Bindewald, E.; Shapiro, B.A.; Delker, D.A.; Hagedorn, C.; Carrington, M.; Gale, M.; et al. IFNL3 (IL28B) favorable genotype escapes hepatitis C virus-induced microRNAs and mRNA decay HHS Public Access Author manuscript. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grünvogel, O.; Colasanti, O.; Lee, J.Y.; Klöss, V.; Belouzard, S.; Reustle, A.; Esser-Nobis, K.; Hesebeck-Brinckmann, J.; Mutz, P.; Hoffmann, K.; et al. Secretion of Hepatitis C Virus Replication Intermediates Reduces Activation of Toll-Like Receptor 3 in Hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 2237–2251.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Viral Factor | Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| N3-4A | cleaves MAVS, to impair production of IFNs and proinflammatory cytokines | [31,37,52,53,54,55,57] |
| cleaves TRIF, to impair production of IFNs and proinflammatory cytokines | [28,58] | |
| inactivates Riplet, inhibiting RIG-I and IRF3 activation | [62,63] | |
| binds to LUBAC, impairing the polyubiquitynation of NEMO required for NF-κB activation | [66] | |
| induces degradation of STAT1, impairing the expression of antiviral effectors | [67] | |
| binds to TBK1, impairing IRF3 activation | [59,60,61] | |
| Core | blocks NF-κB, to suppress inflammatory response | [98,99] |
| targets JAK/STAT pathway by targeting STAT1 and STAT2, inhibiting the production of ISGs | [52,67,104,105,106,107,108,110,111,112] | |
| E2 | interacts with PKR, repressing its antiviral effects | [89] |
| NS5A | interacts with PKR, repressing its antiviral effects | [88,90] |
| induces NAP1L1 degradation, inhibiting gene transcription essential for RIG-I- and TLR3-mediated responses | [91] | |
| impedes RIG-I- and MDA5 activation, impairing IFNs expression | [33] | |
| NS4B | downregulates TRIF protein, inhibiting TLR3 signaling | [68] |
| interacts with STING, inhibiting the production of IFNs | [69,70] | |
| p7 | interacts with IFI16-16, inhibiting its antiviral function | [114] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferreira, A.R.; Ramos, B.; Nunes, A.; Ribeiro, D. Hepatitis C Virus: Evading the Intracellular Innate Immunity. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9030790
Ferreira AR, Ramos B, Nunes A, Ribeiro D. Hepatitis C Virus: Evading the Intracellular Innate Immunity. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(3):790. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9030790
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerreira, Ana Rita, Bruno Ramos, Alexandre Nunes, and Daniela Ribeiro. 2020. "Hepatitis C Virus: Evading the Intracellular Innate Immunity" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 3: 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9030790
APA StyleFerreira, A. R., Ramos, B., Nunes, A., & Ribeiro, D. (2020). Hepatitis C Virus: Evading the Intracellular Innate Immunity. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(3), 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9030790





