Inter- and Intrarater Agreement of Spot Sign and Noncontrast CT Markers for Early Intracerebral Hemorrhage Expansion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Image Acquisitions
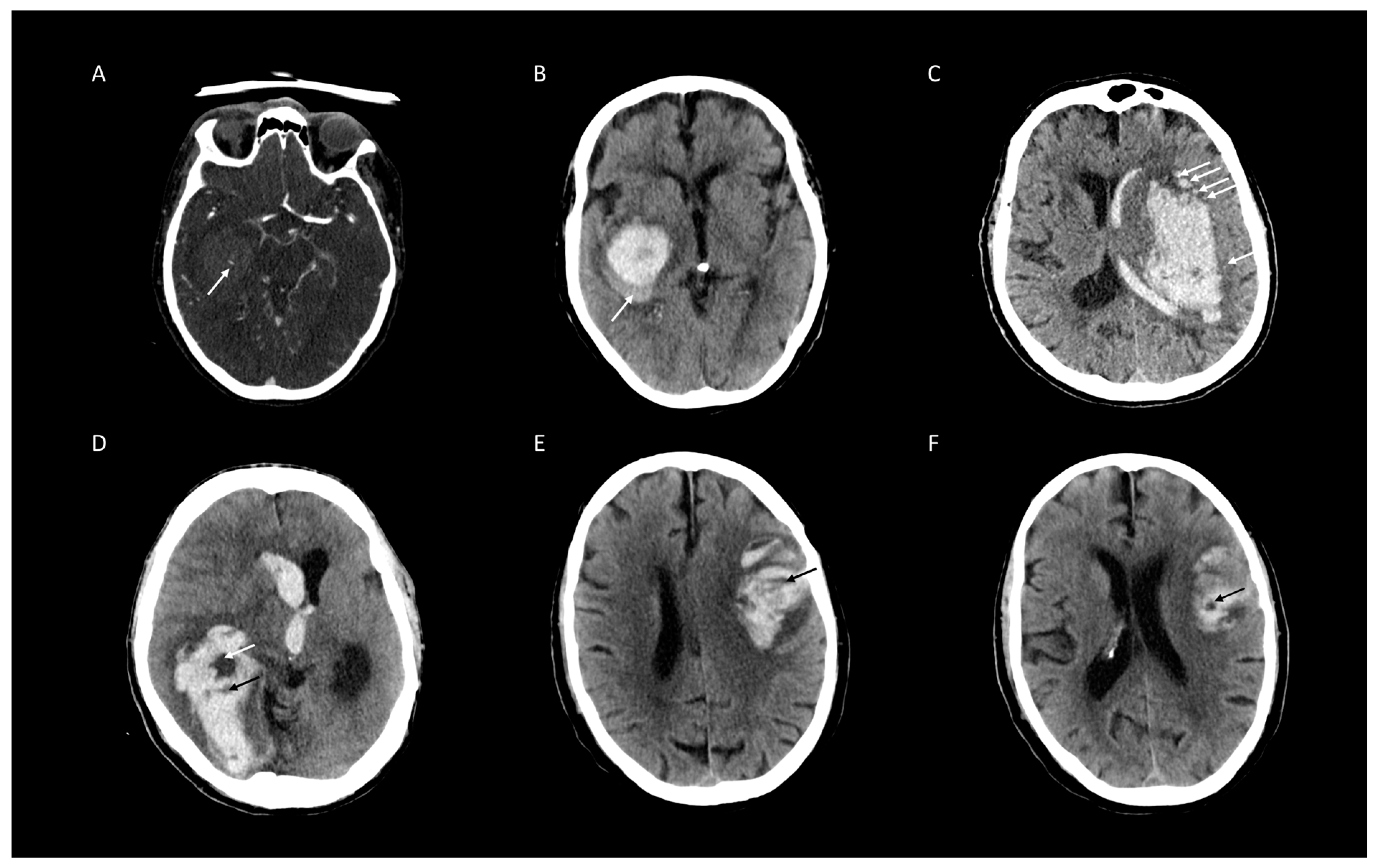
2.3. Image Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sporns, P.B.; Kemmling, A.; Schwake, M.; Minnerup, J.; Nawabi, J.; Broocks, G.; Wildgruber, M.; Fiehler, J.; Heindel, W.; Hanning, U. Triage of 5 Noncontrast Computed Tomography Markers and Spot Sign for Outcome Prediction After Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stroke 2018, 49, 2317–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drury, I.; Whisnant, J.P.; Garraway, W.M. Primary intracerebral hemorrhage: Impact of CT on incidence. Neurology 1984, 34, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubovic, R.; Aviv, R.I. Intracerebral hemorrhage: Toward physiological imaging of hemorrhage risk in acute and chronic bleeding. Front. Neurol. 2012, 3, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broderick, J.P.; Brott, T.; Duldner, J.E.; Tomsick, T.; Huster, G. Volume of intracerebral hemorrhage. A powerful and easy-to-use predictor of 30-day mortality. Stroke 1993, 24, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, S.A.; Sacco, R.L.; Shi, T.; Mohr, J. Neurologic deterioration in noncomatose patients with supratentorial intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurology 1994, 44, 1379–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morotti, A.; Boulouis, G.; Dowlatshahi, D.; Li, Q.; Barras, C.D.; Delcourt, C.; Yu, Z.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, Z.; Aviv, R.I.; et al. Standards for Detecting, Interpreting, and Reporting Noncontrast Computed Tomographic Markers of Intracerebral Hemorrhage Expansion. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 86, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brott, T.; Broderick, J.; Kothari, R.; Barsan, W.; Tomsick, T.; Sauerbeck, L.; Spilker, J.; Duldner, J.; Khoury, J. Early Hemorrhage Growth in Patients with Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stroke 1997, 28, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhao, B.; Wang, W.; Shi, L.; Reis, C.; Zhang, J. Predictors of hematoma expansion predictors after intracerebral hemorrhage. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 89348–89363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, T.; Bösel, J. Options to Restrict Hematoma Expansion after Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stroke 2010, 41, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, T.; Salman, R.A.-S.; Beer, R.; Christensen, H.; Cordonnier, C.; Csiba, L.; Forsting, M.; Harnof, S.; Klijn, C.; Krieger, D.; et al. European Stroke Organisation (ESO) Guidelines for the Management of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Int. J. Stroke 2014, 9, 840–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, G.; Huang, Y.-J.; Dong, M.-X.; Lv, F.-J.; Wei, X.; Chen, J.-J.; Zhang, L.-J.; Qin, X.; Xie, P. Blend Sign on Computed Tomography. Stroke 2015, 46, 2119–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, G.; Xiong, X.; Wang, X.-C.; Yang, W.-S.; Li, K.-W.; Wei, X.; Xie, P. Black Hole Sign. Stroke 2016, 47, 1777–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.; Li, Q.; Yang, W.-S.; Wei, X.; Hu, X.; Wang, X.-C.; Zhu, D.; Li, R.; Cao, D.; Xie, P. Comparison of Swirl Sign and Black Hole Sign in Predicting Early Hematoma Growth in Patients with Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, Q.-J.; Yang, W.-S.; Wang, X.-C.; Zhao, L.-B.; Xiong, X.; Li, R.; Cao, D.; Zhu, D.; Wei, X.; et al. Island Sign. Stroke 2017, 48, 3019–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morotti, A.; Dowlatshahi, D.; Boulouis, G.; Al-Ajlan, F.; Demchuk, A.M.; Aviv, R.I.; Yu, L.; Schwab, K.; Romero, J.M.; Gurol, M.E.; et al. Predicting Intracerebral Hemorrhage Expansion With Noncontrast Computed Tomography: The BAT Score. Stroke 2018, 49, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, T.J.; Demchuk, A.M.; Dowlatshahi, D.; Gladstone, D.; Krischek, Ö.; Kiss, A.; Hill, M.D.; Molina, C.A.; Rodriguez-Luna, D.; Dzialowski, I.; et al. Spot Sign Number Is the Most Important Spot Sign Characteristic for Predicting Hematoma Expansion Using First-Pass Computed Tomography Angiography: Analysis From the PREDICT Study. Stroke 2013, 44, 972–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwers, H.B.; Goldstein, J.N.; Romero, J.M.; Rosand, J. Clinical applications of the computed tomography angiography spot sign in acute intracerebral hemorrhage: A review. Stroke 2012, 43, 3427–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brady, A.; Laoide, R.Ó.; McCarthy, P.; McDermott, R. Discrepancy and Error in Radiology: Concepts, Causes and Consequences. Ulst. Med. J. 2012, 81, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Dowlatshahi, D.; Morotti, A.; Al-Ajlan, F.S.; Boulouis, G.; Warren, A.D.; Petrcich, W.; Aviv, R.I.; Demchuk, A.M.; Goldstein, J.N. Interrater and Intrarater Measurement Reliability of Noncontrast Computed Tomography Predictors of Intracerebral Hemorrhage Expansion. Stroke 2019, 50, 1260–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, R.; Aviv, R.; Fox, A.J.; Sahlas, D.J.; Gladstone, D.; Tomlinson, G.; Symons, S.P. CT Angiography “Spot Sign” Predicts Hematoma Expansion in Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stroke 2007, 38, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporns, P.B.; Schwake, M.; Kemmling, A.; Minnerup, J.; Schwindt, W.; Niederstadt, T.; Schmidt, R.; Hanning, U. Comparison of Spot Sign, Blend Sign and Black Hole Sign for Outcome Prediction in Patients with Intracerebral Hemorrhage. J. Stroke 2017, 19, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulouis, G.; Morotti, A.; Brouwers, H.B.; Charidimou, A.; Jessel, M.J.; Auriel, E.; Pontes-Neto, O.; Ayres, A.; Vashkevich, A.; Schwab, K.M.; et al. Association Between Hypodensities Detected by Computed Tomography and Hematoma Expansion in Patients With Intracerebral Hemorrhage. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, F.-Z.; Jiang, R.; Gu, M.; He, C.; Guan, J. The Accuracy of Spot Sign in Predicting Hematoma Expansion after Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sporns, P.B.; Schwake, M.; Schmidt, R.; Kemmling, A.; Minnerup, J.; Schwindt, W.; Cnyrim, C.; Zoubi, T.; Heindel, W.; Niederstadt, T.; et al. Computed Tomographic Blend Sign Is Associated With Computed Tomographic Angiography Spot Sign and Predicts Secondary Neurological Deterioration After Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stroke 2017, 48, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHugh, M.L. Interrater reliability: The kappa statistic. Biochem. Med. 2012, 22, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangaraju, S.; Haussen, D.C.; Nogueira, R.G.; Nahab, F.; Frankel, M. Comparison of 3-Month Stroke Disability and Quality of Life across Modified Rankin Scale Categories. Interv. Neurol. 2016, 6, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salman, R.A.-S.; Frantzias, J.; Lee, R.J.; Lyden, P.D.; Battey, T.W.K.; Ayres, A.M.; Goldstein, J.N.; Mayer, S.A.; Steiner, T.; Wang, X.; et al. Absolute risk and predictors of the growth of acute spontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage: A systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Bae, H.-J. Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Management. J. Stroke 2017, 19, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, H.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, T.; Sheng, W.; Huang, Q.; Song, J.; Huang, D.; Lan, L.; Li, Y.; et al. Prediction of hematoma expansion in spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage using support vector machine. EBioMedicine 2019, 43, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
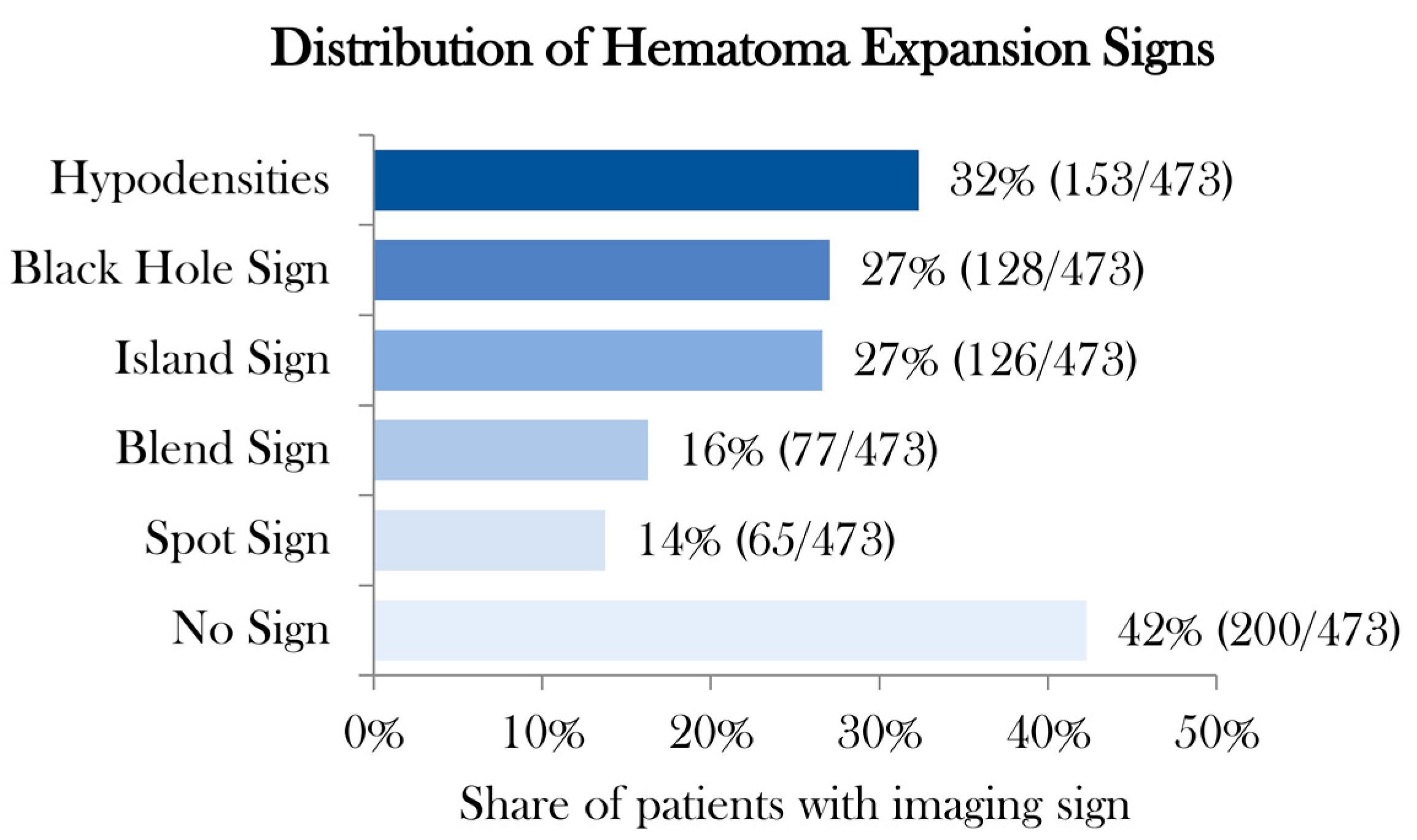


| Baseline Clinical and Imaging Characteristics | All (n= 473) |
|---|---|
| Clinical Characteristics | |
| Age at admission [years], median (IQR) | 69.25 (67.9–70.6) |
| Female, n (%) | 252 (53.3) |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 326 (69.1) |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 65 (13.8) |
| Imaging Characteristics | |
| Bleeding location, n (%) | |
| • Deep | 206 (43.6) |
| • Lobar | 210 (44.4) |
| • Brain Stem, Pons | 17 (3.6) |
| • Cerebellum | 40 (8.5) |
| Intraventricular hemorrhage, n (%) | 248 (52.5) |
| Surgery procedures | |
| Supratentorial Craniectomy, n (%) | 110 (23.3) |
| Infratentorial Craniectomy, n (%) | 5 (1.1) |
| Clinical outcome, n (%) | |
| mRS ≤ 3 | 147 (31.1) |
| mRS > 3 | 326 (68.9) |
| Imaging Signs for ICH Expansion | Presence | mRS [median] | mRS > 3 [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| All NCCT Signs and Spot Sign on CTA | no | 3.3 | 47% |
| yes | 4.8 | 85% | |
| Black Hole Sign | no | 3.8 | 59% |
| yes | 5.4 | 95% | |
| Blend Sign | no | 4.1 | 65% |
| yes | 4.9 | 92% | |
| Hypodensities | no | 4.1 | 65% |
| yes | 4.5 | 77% | |
| Island Sign | no | 3.9 | 61% |
| yes | 5.2 | 92% | |
| Spot Sign | no | 4.1 | 65% |
| yes | 5.1 | 95% |
| Number of Imaging Signs | Number of Patients | mRS [median] | mRS > 3 [%] | Black Hole | Blend Sign | Island Sign | Hypodensities | Spot Sign |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 185 | 3 | 45% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| 1 | 129 | 4 | 74% | 27% | 15% | 11% | 39% | 9% |
| 2 | 92 | 5 | 89% | 51% | 20% | 63% | 51% | 15% |
| 3 | 42 | 6 | 98% | 62% | 40% | 79% | 74% | 45% |
| 4 | 15 | 5 | 87% | 67% | 87% | 73% | 100% | 73% |
| 5 | 10 | 5 | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Total | 473 | 4 | 69% | 27% | 16% | 27% | 32% | 14% |
| Rater 1 | Rater 2 | Level Agreement | Cohen’s kappa * | 95% Lower CI | 95% Upper CI | z-Statistic | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Rating | |||||||
| Black Hole | Black Hole | 98.7% | 0.97 | 0.94 | 0.99 | 21.0 | <0.001 |
| Spot Sign | Spot Sign | 98.5% | 0.93 | 0.88 | 0.98 | 20.3 | <0.001 |
| Hypodensities | Hypodensities | 96.2% | 0.91 | 0.87 | 0.95 | 19.8 | <0.001 |
| Island Sign | Island Sign | 96.4% | 0.90 | 0.86 | 0.95 | 19.7 | <0.001 |
| Blend Sign | Blend Sign | 96.0% | 0.85 | 0.78 | 0.91 | 18.4 | <0.001 |
| 2nd Rating | |||||||
| Black Hole | Black Hole | 98.1% | 0.95 | 0.92 | 0.98 | 20.7 | <0.001 |
| Spot Sign | Spot Sign | 98.3% | 0.93 | 0.87 | 0.98 | 20.2 | <0.001 |
| Hypodensities | Hypodensities | 97.3% | 0.94 | 0.90 | 0.97 | 20.4 | <0.001 |
| Island Sign | Island Sign | 97.0% | 0.92 | 0.88 | 0.96 | 20.1 | <0.001 |
| Blend Sign | Blend Sign | 97.0% | 0.89 | 0.83 | 0.95 | 19.3 | <0.001 |
| 1st Rating | 2nd Rating | Level of Agreement | Cohen’s kappa * | 95% Lower CI | 95% Upper CI | z-Statistic | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rater 1 | |||||||
| Black Hole | Black Hole | 100% | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 21.75 | <0.001 |
| Island Sign | Island Sign | 97.9% | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.98 | 20.50 | <0.001 |
| Hypodensities | Hypodensities | 97.3% | 0.93 | 0.90 | 0.97 | 20.34 | <0.001 |
| Spot Sign | Spot Sign | 99.2% | 0.96 | 0.92 | 1.00 | 20.92 | <0.001 |
| Blend Sign | Blend Sign | 96.0% | 0.85 | 0.78 | 0.91 | 18.44 | <0.001 |
| Rater 2 | |||||||
| Black Hole | Black Hole | 99.4% | 0.98 | 0.97 | 1.00 | 21.40 | <0.001 |
| Island Sign | Island Sign | 98.5% | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.99 | 20.93 | <0.001 |
| Hypodensities | Hypodensities | 98.3% | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.99 | 20.91 | <0.001 |
| Spot Sign | Spot Sign | 98.9% | 0.95 | 0.91 | 0.99 | 20.77 | <0.001 |
| Blend Sign | Blend Sign | 97.0% | 0.89 | 0.83 | 0.95 | 19.33 | <0.001 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nawabi, J.; Elsayed, S.; Kniep, H.; Sporns, P.; Schlunk, F.; McDonough, R.; Broocks, G.; Dührsen, L.; Schön, G.; Götz, T.; et al. Inter- and Intrarater Agreement of Spot Sign and Noncontrast CT Markers for Early Intracerebral Hemorrhage Expansion. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9041020
Nawabi J, Elsayed S, Kniep H, Sporns P, Schlunk F, McDonough R, Broocks G, Dührsen L, Schön G, Götz T, et al. Inter- and Intrarater Agreement of Spot Sign and Noncontrast CT Markers for Early Intracerebral Hemorrhage Expansion. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(4):1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9041020
Chicago/Turabian StyleNawabi, Jawed, Sarah Elsayed, Helge Kniep, Peter Sporns, Frieder Schlunk, Rosalie McDonough, Gabriel Broocks, Lasse Dührsen, Gerhard Schön, Thomalla Götz, and et al. 2020. "Inter- and Intrarater Agreement of Spot Sign and Noncontrast CT Markers for Early Intracerebral Hemorrhage Expansion" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 4: 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9041020
APA StyleNawabi, J., Elsayed, S., Kniep, H., Sporns, P., Schlunk, F., McDonough, R., Broocks, G., Dührsen, L., Schön, G., Götz, T., Fiehler, J., & Hanning, U. (2020). Inter- and Intrarater Agreement of Spot Sign and Noncontrast CT Markers for Early Intracerebral Hemorrhage Expansion. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(4), 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9041020





