FOXA1 Gene Expression for Defining Molecular Subtypes of Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer after Radical Cystectomy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Population and Histological Assessment
2.2. Assessment of mRNA Expression by RT-qPCR
2.3. Statistical Methods
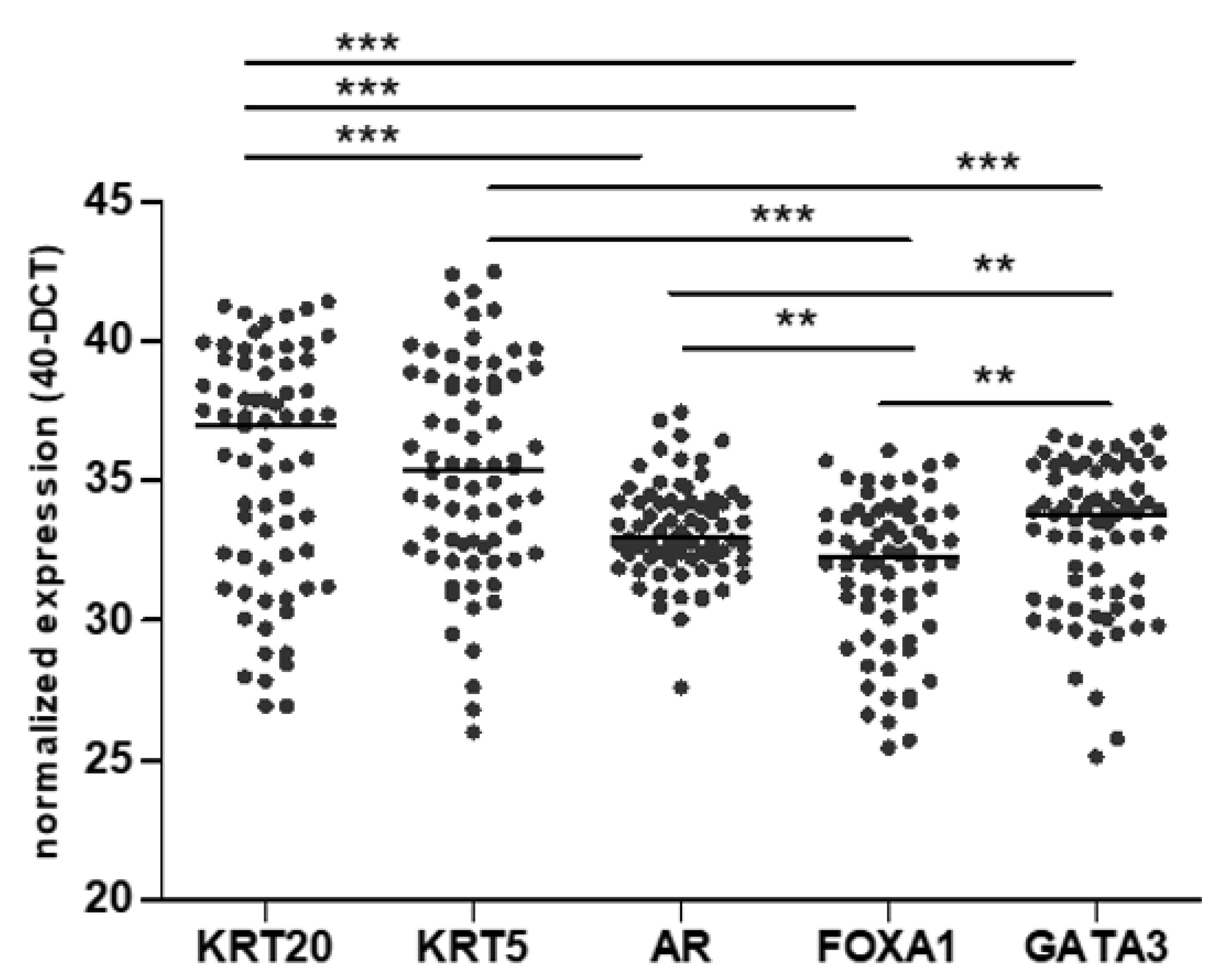
3. Results
3.1. Association of the Surrogate Markers with Clinicopathological Features
3.2. Association of the Surrogate Markers with Survival
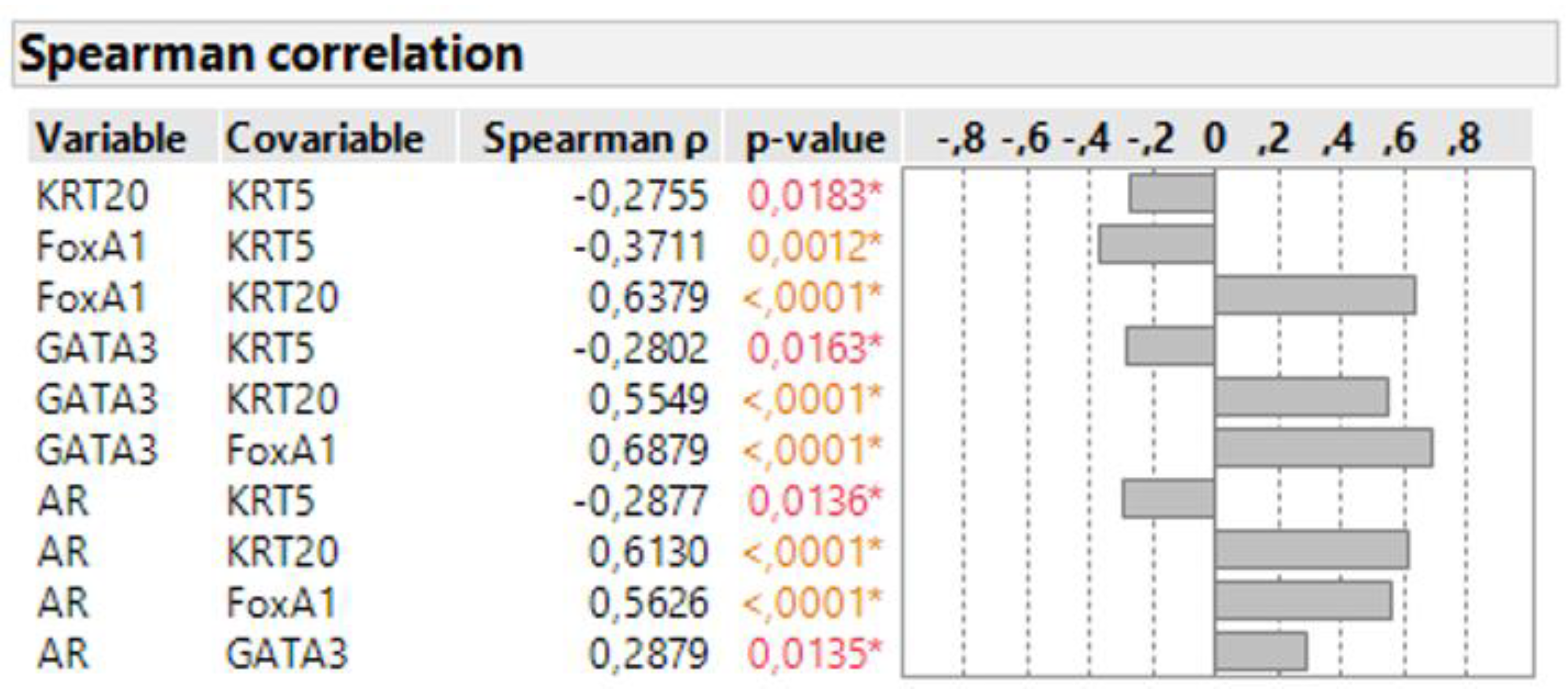
3.3. Correlation of Surrogate Markers with Molecular Subtypes Defined by Multigene Panels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burger, M.; Catto, J.W.; Dalbagni, G.; Grossman, H.B.; Herr, H.; Karakiewicz, P.; Kassouf, W.; Kiemeney, L.A.; La Vecchia, C.; Shariat, S.; et al. Epidemiology and risk factors of urothelial bladder cancer. Eur. Urol. 2013, 63, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfred Witjes, J.; Lebret, T.; Comperat, E.M.; Cowan, N.C.; De Santis, M.; Bruins, H.M.; Hernandez, V.; Espinos, E.L.; Dunn, J.; Rouanne, M.; et al. Updated 2016 EAU Guidelines on Muscle-invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 462–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babjuk, M.; Bohle, A.; Burger, M.; Capoun, O.; Cohen, D.; Comperat, E.M.; Hernandez, V.; Kaasinen, E.; Palou, J.; Roupret, M.; et al. EAU Guidelines on Non-Muscle-invasive Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder: Update 2016. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 447–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, A.; Gierth, M.; Rink, M.; Schmid, M.; Chun, F.K.; Dahlem, R.; Roghmann, F.; Palisaar, R.J.; Noldus, J.; Ellinger, J.; et al. Optimizing outcome reporting after radical cystectomy for organ-confined urothelial carcinoma of the bladder using oncological trifecta and pentafecta. World J. Urol. 2015, 33, 1945–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donat, S.M. Staged based directed surveillance of invasive bladder cancer following radical cystectomy: Valuable and effective? World J. Urol. 2006, 24, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, J.M.; Cookson, M.S.; Smith, J.A., Jr.; Chang, S.S. Patterns of initial transitional cell recurrence in patients after cystectomy. J. Urol. 2006, 175, 2054–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.H.; Kim, H.; Kwak, C.; Kim, H.H.; Jung, J.H.; Ku, J.H. Late Recurrence of Bladder Cancer following Radical Cystectomy: Characteristics and Outcomes. Urol. Int. 2019, 103, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svatek, R.S.; Hollenbeck, B.K.; Holmang, S.; Lee, R.; Kim, S.P.; Stenzl, A.; Lotan, Y. The economics of bladder cancer: Costs and considerations of caring for this disease. Eur. Urol. 2014, 66, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botteman, M.F.; Pashos, C.L.; Redaelli, A.; Laskin, B.; Hauser, R. The health economics of bladder cancer: A comprehensive review of the published literature. PharmacoEconomics 2003, 21, 1315–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, J.L.; Gilbert, S.M. Improving bladder cancer patient care: A pharmacoeconomic perspective. Expert Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2013, 13, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Porten, S.; Kim, S.; Willis, D.; Plimack, E.R.; Hoffman-Censits, J.; Roth, B.; Cheng, T.; Tran, M.; Lee, I.-L.; et al. Identification of distinct basal and luminal subtypes of muscle-invasive bladder cancer with different sensitivities to frontline chemotherapy. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sjödahl, G.; Lauss, M.; Lövgren, K.; Chebil, G.; Gudjonsson, S.; Veerla, S.; Patschan, O.; Aine, M.; Fernö, M.; Ringnér, M.; et al. A molecular taxonomy for urothelial carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 3377–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Network, C.G.A.R. Comprehensive molecular characterization of urothelial bladder carcinoma. Nature 2014, 507, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, W.; Czerniak, B.; Ochoa, A.; Su, X.; Siefker-Radtke, A.; Dinney, C.; McConkey, D.J. Intrinsic basal and luminal subtypes of muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2014, 11, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damrauer, J.S.; Hoadley, K.A.; Chism, D.D.; Fan, C.; Tiganelli, C.J.; Wobker, S.E.; Yeh, J.J.; Milowsky, M.I.; Iyer, G.; Parker, J.S.; et al. Intrinsic subtypes of high-grade bladder cancer reflect the hallmarks of breast cancer biology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3110–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seiler, R.; Ashab, H.A.D.; Erho, N.; van Rhijn, B.W.G.; Winters, B.; Douglas, J.; Van Kessel, K.E.; Fransen van de Putte, E.E.; Sommerlad, M.; Wang, N.Q.; et al. Impact of Molecular Subtypes in Muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer on Predicting Response and Survival after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Eur. Urol. 2017, 72, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldhirsch, A.; Wood, W.C.; Coates, A.S.; Gelber, R.D.; Thurlimann, B.; Senn, H.J.; Panel, M. Strategies for subtypes--dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: Highlights of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 1736–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, S.P.; McConkey, D.J.; Hoadley, K.A.; Chan, K.S.; Kim, W.Y.; Radvanyi, F.; Hoglund, M.; Real, F.X. Bladder Cancer Molecular Taxonomy: Summary from a Consensus Meeting. Bladder Cancer 2016, 2, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warrick, J.I.; Kaag, M.; Raman, J.D.; Chan, W.; Tran, T.; Kunchala, S.; Shuman, L.; DeGraff, D.; Chen, G. FOXA1 and CK14 as markers of luminal and basal subtypes in histologic variants of bladder cancer and their associated conventional urothelial carcinoma. Virchows Arch. Int. J. Pathol. 2017, 471, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldetti, S.; Rempel, E.; Worst, T.S.; Eckstein, M.; Steidler, A.; Weiss, C.A.; Bolenz, C.; Hartmann, A.; Erben, P. Subclassification, survival prediction and drug target analyses of chemotherapy-naive muscle-invasive bladder cancer with a molecular screening. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 25935–25945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eckstein, M.; Wirtz, R.M.; Gross-Weege, M.; Breyer, J.; Otto, W.; Stoehr, R.; Sikic, D.; Keck, B.; Eidt, S.; Burger, M.; et al. mRNA-Expression of KRT5 and KRT20 Defines Distinct Prognostic Subgroups of Muscle-Invasive Urothelial Bladder Cancer Correlating with Histological Variants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Breyer, J.; Wirtz, R.M.; Otto, W.; Erben, P.; Kriegmair, M.C.; Stoehr, R.; Eckstein, M.; Eidt, S.; Denzinger, S.; Burger, M.; et al. In stage pT1 non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC), high KRT20 and low KRT5 mRNA expression identify the luminal subtype and predict recurrence and survival. Virchows Arch. Int. J. Pathol. 2017, 470, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, A.G.; Kim, J.; Al-Ahmadie, H.; Bellmunt, J.; Guo, G.; Cherniack, A.D.; Hinoue, T.; Laird, P.W.; Hoadley, K.A.; Akbani, R.; et al. Comprehensive Molecular Characterization of Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. Cell 2017, 171, 540–556.e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breyer, J.; Otto, W.; Wirtz, R.M.; Wullich, B.; Keck, B.; Erben, P.; Kriegmair, M.C.; Stoehr, R.; Eckstein, M.; Laible, M.; et al. ERBB2 Expression as Potential Risk-Stratification for Early Cystectomy in Patients with pT1 Bladder Cancer and Concomitant Carcinoma in situ. Urol. Int. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perou, C.M.; Sorlie, T.; Eisen, M.B.; van de Rijn, M.; Jeffrey, S.S.; Rees, C.A.; Pollack, J.R.; Ross, D.T.; Johnsen, H.; Akslen, L.A.; et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2000, 406, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leapman, M.S.; Nguyen, H.G.; Cowan, J.E.; Xue, L.; Stohr, B.; Simko, J.; Cooperberg, M.R.; Carroll, P.R. Comparing Prognostic Utility of a Single-marker Immunohistochemistry Approach with Commercial Gene Expression Profiling Following Radical Prostatectomy. Eur. Urol. 2018, 74, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikic, D.; Wirtz, R.M.; Wach, S.; Dyrskjot, L.; Erben, P.; Bolenz, C.; Breyer, J.; Otto, W.; Hoadley, K.A.; Lerner, S.P.; et al. Androgen Receptor mRNA Expression in Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder: A Retrospective Analysis of Two Independent Cohorts. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 12, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeGraff, D.J.; Clark, P.E.; Cates, J.M.; Yamashita, H.; Robinson, V.L.; Yu, X.; Smolkin, M.E.; Chang, S.S.; Cookson, M.S.; Herrick, M.K.; et al. Loss of the urothelial differentiation marker FOXA1 is associated with high grade, late stage bladder cancer and increased tumor proliferation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuk, H.D.; Jeong, C.W.; Kwak, C.; Kim, H.H.; Moon, K.C.; Ku, J.H. Clinical outcomes of muscle invasive bladder Cancer according to the BASQ classification. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez-Beltran, A.; Henriques, V.; Montironi, R. Variants and new entities of bladder cancer. Histopathology 2019, 74, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Christoph, F.; Muller, M.; Schostak, M.; Soong, R.; Tabiti, K.; Miller, K. Quantitative detection of cytokeratin 20 mRNA expression in bladder carcinoma by real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. Urology 2004, 64, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazquez, C.; Ribal, M.J.; Marin-Aguilera, M.; Kayed, H.; Fernandez, P.L.; Mengual, L.; Alcaraz, A. Biomarkers vs conventional histological analysis to detect lymph node micrometastases in bladder cancer: A real improvement? BJU Int. 2012, 110, 1310–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, M.B.H.; Nordentoft, I.; Lamy, P.; Vang, S.; Reinert, L.; Mapendano, C.K.; Hoyer, S. Comprehensive multiregional analysis of molecular heterogeneity in bladder cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sjodahl, G.; Eriksson, P.; Liedberg, F.; Hoglund, M. Molecular classification of urothelial carcinoma: Global mRNA classification versus tumour-cell phenotype classification. J. Pathol. 2017, 242, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Patient Characteristic | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Tumor stage | |
| T2 | 18 (24.7) |
| T3 | 43 (58.9) |
| T4 | 12 (16.4) |
| Nodal status | |
| N0 | 44 (60.3) |
| N positive | 29 (39.7) |
| Sex | |
| male | 54 (74.0) |
| female | 19 (26.0) |
| Grade (WHO 1973) | |
| G2 | 15 (20.5) |
| G3 | 58 (79.5) |
| Age | |
| <70 | 47 (64.4) |
| ≥70 | 26 (35.6) |
| Histology | |
| Pure urothelial carcinoma | 43 (58.9) |
| Histologic variants | 30 (41.1) |
| Squamous cell | 10 (13.7) |
| Sarcomatoid | 7 (9.6) |
| Micropapillary | 5 (6.9) |
| Small cell | 3 (4.1) |
| Adenocarcinoma | 2 (2.7) |
| Neuroendocrine | 1 (1.4) |
| Nested | 1 (1.4) |
| Plasmacytoid | 1 (1.4) |
| Parameter | Univariable | Multivariable | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Ratio | p-Value | Hazard Ratio | p-Value | |
| Tumor stage | ||||
| T3/4 vs. | 1.6203 | 0.2156 | ||
| T2 | ||||
| Nodal status | ||||
| N+ vs. | 2.8737 | 0.0027 | 2.4330 | 0.0146 |
| N0 | ||||
| Sex | ||||
| male vs. | 1.0155 | 0.9698 | ||
| female | ||||
| Grade (WHO 1973) | ||||
| G2 vs. | 0.4709 | 0.8186 | ||
| G3 | ||||
| Age | ||||
| <70 vs. | 0.8428 | 0.6454 | ||
| ≥70 | ||||
| KRT5 | ||||
| >median vs. | 0.5081 | 0.0513 | ||
| <median | ||||
| KRT20 | ||||
| >median vs. | 2.1233 | 0.0317 | 1.2927 | 0.5083 |
| <median | ||||
| FOXA1 | ||||
| >median vs. | 2.7209 | 0.0048 | 2.2670 | 0.0310 |
| <median | ||||
| GATA3 | ||||
| >median vs. | 1.9211 | 0.0629 | ||
| <median | ||||
| AR | ||||
| >median vs. | 1.6121 | 0.1670 | ||
| <median | ||||
| Parameter | Univariable | Multivariable | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Ratio | p-Value | Hazard Ratio | p-Value | |
| Tumor stage | ||||
| T3/4 vs. | 2.0330 | 0.0926 | ||
| T2 | ||||
| Nodal status | ||||
| N+ vs. | 2.7727 | 0.0044 | 2.6057 | 0.0077 |
| N0 | ||||
| Sex | ||||
| male vs. | 1.5435 | 0.2715 | ||
| female | ||||
| Grade (WHO 1973) | ||||
| G2 | 1.1484 | 0.7558 | ||
| G3 | ||||
| Age | ||||
| <70 | 0.8833 | 0.7404 | ||
| ≥70 | ||||
| KRT5 | ||||
| >median vs. | 0.6999 | 0.3072 | ||
| <median | ||||
| KRT20 | ||||
| >median vs. | 1.3249 | 0.4235 | ||
| <median | ||||
| FOXA1 | ||||
| >median vs. | 2.3617 | 0.0186 | 2.1946 | 0.0333 |
| <median | ||||
| GATA3 | ||||
| >median vs. | 1.2429 | 0.5359 | ||
| <median | ||||
| AR | ||||
| >median vs. | 1.3717 | 0.3670 | ||
| <median | ||||
| Parameter | Univariable | Multivariable | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Ratio | p-Value | Hazard Ratio | p-Value | |
| Tumor stage | ||||
| T3/4 vs. | 2.0601 | 0.0048 | 1.7819 | 0.1251 |
| T2 | ||||
| Nodal status | ||||
| N+ vs. | 2.2720 | 0.0086 | 2.0806 | 0.0206 |
| N0 | ||||
| Sex | ||||
| male vs. | 1.3586 | 0.3820 | ||
| female | ||||
| Grade (WHO 1973) | ||||
| G2 vs. | 0.7678 | 0.4590 | ||
| G3 | ||||
| Age | ||||
| <70 vs. | 0.8253 | 0.5544 | ||
| ≥70 | ||||
| KRT5 | ||||
| >median vs. | 0.7012 | 0.2408 | ||
| <median | ||||
| KRT20 | ||||
| >median vs. | 1.1560 | 0.6334 | ||
| <median | ||||
| FOXA1 | ||||
| >median vs. | 1.7986 | 0.0580 | ||
| <median | ||||
| GATA3 | ||||
| >median vs. | 1.0844 | 0.7800 | ||
| <median | ||||
| AR | ||||
| >median vs. | 1.3104 | 0.3728 | ||
| <median | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sikic, D.; Eckstein, M.; Wirtz, R.M.; Jarczyk, J.; Worst, T.S.; Porubsky, S.; Keck, B.; Kunath, F.; Weyerer, V.; Breyer, J.; et al. FOXA1 Gene Expression for Defining Molecular Subtypes of Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer after Radical Cystectomy. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 994. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9040994
Sikic D, Eckstein M, Wirtz RM, Jarczyk J, Worst TS, Porubsky S, Keck B, Kunath F, Weyerer V, Breyer J, et al. FOXA1 Gene Expression for Defining Molecular Subtypes of Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer after Radical Cystectomy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(4):994. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9040994
Chicago/Turabian StyleSikic, Danijel, Markus Eckstein, Ralph M. Wirtz, Jonas Jarczyk, Thomas S. Worst, Stefan Porubsky, Bastian Keck, Frank Kunath, Veronika Weyerer, Johannes Breyer, and et al. 2020. "FOXA1 Gene Expression for Defining Molecular Subtypes of Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer after Radical Cystectomy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 4: 994. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9040994
APA StyleSikic, D., Eckstein, M., Wirtz, R. M., Jarczyk, J., Worst, T. S., Porubsky, S., Keck, B., Kunath, F., Weyerer, V., Breyer, J., Otto, W., Rinaldetti, S., Bolenz, C., Hartmann, A., Wullich, B., & Erben, P., on behalf of the BRIDGE Consortium e.V., Germany. (2020). FOXA1 Gene Expression for Defining Molecular Subtypes of Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer after Radical Cystectomy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(4), 994. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9040994








