Complement Inhibition Therapy and Dialytic Strategies in Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria: The Nephrologist’s Opinion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. PNH Etiopathology, Laboratory Findings and Clinical Manifestations
2.1. PNH Genetic Mutation
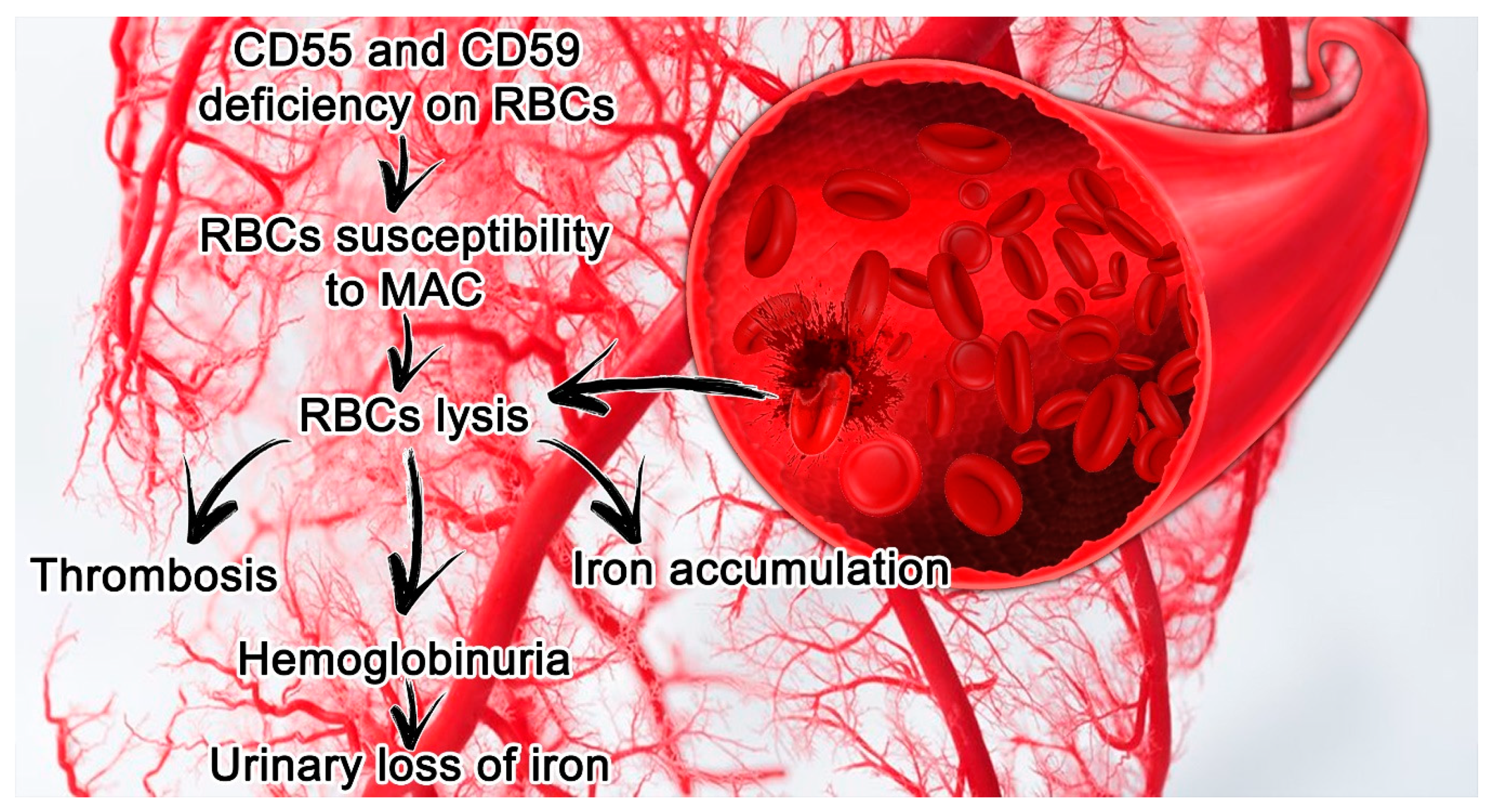
2.2. PNH Laboratory Findings and Clinical Manifestations
3. PNH and Kidney Diseases
3.1. PNH and Chronic Kidney Failure
3.2. Renal Hemosiderosis in the Course of PNH
3.3. PNH and Renal Tubulopathies
3.4. Glomerular Damage in the Course of PNH
3.5. Renal Compliance in the Course of PNH Therapy
4. Acute Kidney Injury
4.1. Acute Kidney Injury and Dialysis Choices in PNH—A Nephrologist’s Opinion
4.2. Dialysis Strategies for AKI in PNH Patients
5. PNH: Current and Future Perspectives of Complement Inhibition Therapy
5.1. The Role of the Complement System
5.2. C5 Inhibitors
5.3. C3 Inhibitors
5.4. Factor D Inhibitors
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKI | acute kidney injury |
| AKIN | acute kidney injury network |
| ATN | acute tubular necrosis |
| CF | concentration in the filtrate |
| CP | concentration in plasma water |
| CPFA | coupled plasma filtration adsorption |
| CRRT | Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy |
| CVVH | continuous veno-venous hemofiltration |
| CVVHDF | continuous veno-venous hemodiafiltration |
| DFO | deferoxamine |
| FD | protease factor D |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| GalNAc | N-acetylgalactosamine |
| GPI | glycosyl phosphatidylinositol |
| HD | hemodialysis |
| KDIGO | Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcome |
| MAC | membrane attack complex |
| LDH | lactate dehydrogenase |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| Chronic Kidney Disease | chronic kidney disease |
| HB | hemoglobin |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor kappa B |
| MN | Membranous Nephropathy |
| MW | molecular weights |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| Nrf2 | nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 |
| HO-1 | Heme oxygenase 1 |
| PIG-A | phosphatidylinositol glycan class A |
| PNH | Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria |
| PTECs | proximal tubular epithelial cells |
| RIFLE | risk, injury, failure, loss, end-stage kidney disease |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| NaHCO3 | sodium bicarbonate |
| RRT | renal replacement therapy |
| THP | Tamm Horsfall protein |
References
- Hill, A.; Platts, P.J.; Smith, A.; Richards, S.J.; Cullen, M.J.; Hill, Q.A.; Roman, E.; Hillmen, P. The incidence and prevalence of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) and survival of patients in Yorkshire. Blood 2006, 108, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodsky, R.A. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood 2014, 124, 2804–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arruda, M.M.; Rodrigues, C.A.; Yamamoto, M.; Figueiredo, M.S. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: From physiopathology to treatment. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2010, 56, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hillmen, P.; Lewis, S.M.; Bessler, M.; Luzzatto, L.; Dacie, J.V. Natural history of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 1253–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patriquin, C.J.; Kuo, K.H.M. Eculizumab and Beyond: The Past, Present, and Future of Complement Therapeutics. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2019, 33, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, R.M.; Connell, N.T. Ravulizumab: A novel C5 inhibitor for the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, N.; Schmidt, C.Q.; Schlapschy, M.; Skerra, A. PASylated Coversin, a C5-Specific Complement Inhibitor with Extended Pharmacokinetics, Shows Enhanced Anti-Hemolytic Activity in Vitro. Bioconjug. Chem. 2016, 27, 2359–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindorfer, M.A.; Pawluczkowycz, A.W.; Peek, E.M.; Hickman, K.; Taylor, R.P.; Parker, C.J. A novel approach to preventing the hemolysis of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: Both complement-mediated cytolysis and C3 deposition are blocked by a monoclonal antibody specific for the alternative pathway of complement. Blood 2010, 115, 2283–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorthiois, E.; Anderson, K.; Vulpetti, A.; Rogel, O.; Cumin, F.; Ostermann, N.; Steinbacher, S.; Mac Sweeney, A.; Delgado, O.; Liao, S.M.; et al. Discovery of Highly Potent and Selective Small-Molecule Reversible Factor D Inhibitors Demonstrating Alternative Complement Pathway Inhibition in Vivo. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 5717–5735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzzatto, L. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: An acquired X-linked genetic disease with somatic-cell mosaicism. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2006, 16, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, J.J.; Gropman, A.L.; Sapp, J.C.; Teer, J.K.; Martin, J.M.; Liu, C.F.; Yuan, X.; Ye, Z.; Cheng, L.; Brodsky, R.A.; et al. The phenotype of a germline mutation in PIGA: The gene somatically mutated in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 90, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brodsky, R.A. Advances in the diagnosis and therapy of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood Rev. 2008, 22, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kinoshita, T.; Inoue, N. Dissecting and manipulating the pathway for glycosylphos-phatidylinositol-anchor biosynthesis. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2000, 4, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, T. Biosynthesis and deficiencies of glycosylphosphatidylinositol. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2014, 90, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parker, C.J. Williams Hematology, 9th ed; Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 571–582. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, A.; DeZern, A.E.; Kinoshita, T.; Brodsky, R.A. Paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2017, 3, 17028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Armstrong, C.; Schubert, J.; Ueda, E.; Knez, J.J.; Gelperin, D.; Hirose, S.; Silber, R.; Hollan, S.; Schmidt, R.E.; Medof, M.E. Affected paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria T lymphocytes harbor a common defect in assembly of N-acetyl-d-glucosamine inositol phospholipid corresponding to that in class A Thy-1- murine lymphoma mutants. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 25347–25351. [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka, M.; Nagakura, S.; Horikawa, K.; Kawaguchi, T.; Iwamotot, N.; Kagimoto, T.; Takatsuki, K.; Nakakuma, H. Impaired glycosylation of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchor synthesis in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria leukocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 191, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgkins, S.R. 21-Intrinsic defects leading to increased erythrocyte destruction. In Rodak’s Hematology, 6th ed.; Keohane, E.M., Otto, C.N., Walenga, J.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 336–362. [Google Scholar]
- Luzzatto, L.; Gianfaldoni, G. Recent advances in biological and clinical aspects of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Int. J. Hematol. 2006, 84, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socie, G.; Mary, J.Y.; de Gramont, A.; Rio, B.; Leporrier, M.; Rose, C.; Heudier, P.; Rochant, H.; Cahn JYGluckman, E. Paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria: Long-term follow-up and prognostic factors. French Society of Haematology. Lancet 1996, 348, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, J.; Kanakura, Y.; Ware, R.E.; Shichishima, T.; Nakakuma, H.; Ninomiya, H.; Decastro, C.M.; Hall, S.; Kanamaru, A.; Sullivan, K.M.; et al. Clinical course and flow cytometric analysis of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria in the United States and Japan. Medicine (Baltimore) 2004, 83, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosse, W.F. Evolution of clinical understanding: Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria as a paradigm. Am. J. Hematol. 1993, 42, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couturier, C.; Haeffner-Cavaillon, N.; Caroff, M.; Kazatchkine, M.D. Binding sites for endotoxins (lipopolysaccharides) on human monocytes. J. Immunol. 1991, 147, 1899–1904. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Simmons, D.L.; Tan, S.; Tenen, D.G.; Nicholson-Weller, A.; Seed, B. Monocyte antigen CD14 is a phospholipid anchored membrane protein. Blood 1989, 73, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rachidi, S.; Musallam, K.M.; Taher, A.T. A closer look at paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2010, 21, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, R.S. Black mornings, yellow sunsets--a day with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 537–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bijnen, S.T.; Van Heerde, W.L.; Muus, P. Mechanisms and clinical implications of thrombosis in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.; Kelly, R.J.; Hillmen, P. Thrombosis in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood 2013, 121, 4985–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ziakas, P.D.; Poulou, L.S.; Rokas, G.I.; Bartzoudis, D.; Voulgarelis, M. Thrombosis in Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria: Sites, risks, outcome. An Overview. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 642–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, T.; Suzuki, K.; Sumi, M.; Yanaka, K.; Kojima, H.; Matsumura, A. Cerebral embolism as a complication of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Eur. Neurol. 2005, 53, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploug, M.; Plesner, T.; Ronne, E.; Ellis, V.; Høyer-Hansen, G.; Hansen, N.E.; Danø, K. The receptor for urokinase-type plasminogen activator is deficient on peripheral blood leukocytes in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood 1992, 79, 1447–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weitz, I.C. Thrombosis in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2011, 37, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziakas, P.D.; Poulou, L.S.; Pomoni, A. Thrombosis in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria at a glance: A clinical review. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2008, 6, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, C.; Omine, M.; Richards, S.; Nishimura, J.; Bessler, M.; Ware, R.; Hillmen, P.; Luzzatto, L.; Young, N.; Kinoshita, T. Diagnosis and management of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood 2005, 106, 3699–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brodsky, R.A. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice, 7th ed.; Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 415–424. [Google Scholar]
- De Latour, R.P.; Mary, J.Y.; Salanoubat, C.; Terriou, L.; Etienne, G.; Mohty, M.; Roth, S.; de Guibert, S.; Maury, S.; Cahn, J.Y. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: Natural history of disease subcategories. Blood 2008, 112, 3099–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillmen, P.; Elebute, M.; Kelly, R.; Urbano-Ispizua, A.; Hill, A.; Rother, R.P.; Khursigara, G.; Fu, C.L.; Omine, M.; Browne, P. Long-term effect of the complement inhibitor eculizumab on kidney function in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Am. J. Hematol. 2010, 85, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.S.; Cheong, J.W.; Mun, Y.C.; Jang, J.H.; Jo, D.Y.; Lee, J.W.; Aplastic Anemia Working Party of the Korean Society of Hematology. Clinical implication of renal dysfunction during the clinical course in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: A longitudinal analysis. Ann. Hematol. 2019, 98, 2273–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas, A.; Núñez, R.R.; Gaya, A.; Cuevas-Ruiz, M.V.; Bosch, J.M.; Carral, A.; Arrizabalaga, B.; Gomez-Roncero, M.I.; Mora, A.; Bravo, P.; et al. Presence of acute and chronic renal failure in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: Results of a retrospective analysis from the Spanish PNH registry. Ann. Hematol. 2017, 96, 1727–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachee, P.; Henckens, M.; Van Damme, B.; Boogaerts, M.A.; Rigauts, H.; Verberckmoes, R.K. Chronic renal failure due to renal hemosiderosis in a patient with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Clin. Nephrol. 1993, 39, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Preece, N.E.; Evans, P.F.; Howarth, J.A.; King, L.J.; Parker, D.V. The induction of autooxidative tissue damage by iron nitrilotriacetate in rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1988, 93, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.J.; Laszik, Z.; Wang, X.Q.; Silva, F.G.; Vaziri, N.D. Association of renal injury with increased oxygen free radical activity and altered nitric oxide metabolism in chronic experimental hemosiderosis. Lab. Investig. 2000, 80, 1905–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rubio-Navarro, A.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Guerrero-Hue, M.; García-Caballero, C.; Gutiérrez, E.; Yuste, C.; Sevillano, Á.; Praga, M.; Egea, J.; Román, E.; et al. Podocytes are new cellular targets of haemoglobin-mediated renal damage. J. Pathol. 2018, 244, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrakka, J.; Tryggvason, K. New insights into the role of podocytes in proteinuria. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2009, 5, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, G.I.; Saleem, M.A. Nephrin-signature molecule of the glomerular podocyte? J. Pathol. 2010, 220, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nath, K.A.; Vercellotti, G.M.; Grande, J.P.; Miyoshi, H.; Paya, C.V.; Manivel, J.C.; Haggard, J.J.; Croatt, A.J.; Payne, W.D.; Alam, J. Heme protein-induced chronic renal inflammation: Suppressive effect of induced heme oxygenase-1. Kidney Int. 2001, 59, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimizu, H.; Takahashi, T.; Suzuki, T.; Yamasaki, A.; Fujiwara, T.; Odaka, Y.; Hirakawa, M.; Fujita, H.; Akagi, R. Protective effect of heme oxygenase induction in ischemic acute renal failure. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 28, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryter, S.W.; Alam, J.; Choi, A.M. Heme oxygenase-1/carbon monoxide: From basic science to therapeutic applications. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 583–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitti, M.; Piras, S.; Marinari, U.M.; Moretta, L.; Pronzato, M.A.; Furfaro, A.L. HO-1 induction in cancer progression: A matter of cell adaptation. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, A.L.; Ryan, L.M.; Roth, D.A. Renal proximal tubular dysfunction and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Am. J. Med. 1977, 62, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kümpers, P.; Herrmann, A.; Lotz, J.; Mengel, M.; Schwarz, A. A blue kidney—Chronic renal failure as a consequence of siderosis in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria? Clin. Nephrol. 2006, 66, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moumas, E.; Bridoux, F.; Leroy, F.; Belmouaz, S.; Randriamalala, E.; Desport, E.; Dreyfus, B.; Delbès, S.; Quellard, N.; Touchard, G. Fanconi syndrome and chronic kidney disease in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: Effect of eculizumab therapy. Clin. Nephrol. 2012, 78, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, P.J.; Wang, S.C.; Wen, M.C.; Diang, L.K.; Lin, S.H. Fanconi syndrome and CKD in a patient with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria and hemosiderosis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2010, 55, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshbach, M.L.; Kaur, A.; Rbaibi, Y.; Tejero, J.; Weisz, O.A. Hemoglobin inhibits albumin uptake by proximal tubule cells: Implications for sickle cell disease. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2017, 312, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, D.E.; Ihekwaba, A.E.; Elliott, M.; Johnson, J.R.; Gibney, C.A.; Foreman, B.E.; Nelson, G.; See, V.; Horton, C.A.; Spiller, D.G. Oscillations in NF-kappaB signaling control the dynamics of gene expression. Science 2004, 306, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andrade-Oliveira, V.; Foresto-Neto, O.; Watanabe, I.K.M.; Zatz, R.; Câmara, N.O.S. Inflammation in Renal Diseases: New and Old Players. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, V.; Gandhi, A.; Sharma, S. Renal Biopsy in Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria: An Insight into the Spectrum of Morphologic Changes. Indian J. Nephrol. 2017, 27, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, R.K.; Khaira, A.; Sharma, A.; Mahajan, S.; Dinda, A.K. Spectrum of renal involvement in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: Report of three cases and a brief review of the literature. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2008, 40, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Q.; Nath, K.A.; Wu, Y.; Daoud, T.M.; Sethi, S. Hemolysis and acute kidney failure. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2010, 56, 780–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clark, D.A.; Butler, S.A.; Braren, V.; Hartmann, R.C.; Jenkins, D.E., Jr. The kidneys in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood 1981, 57, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zettl, J.; Mirgaine, P.; Aymard, B.; Valla, M.; Rahmati, M.; Tubail, Z.; Flechon-Meibody, F.; Savenkoff, B. Renal hemosiderosis following mechanical hemolysis: An original case report. Nephrol. Ther. 2019, 15, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asim, M.; Iqbal, Z.; Mujeeb, I.B. Blue kidney in a pale patient-a case for a causal association between renal haemosiderosis in paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria and chronic kidney disease. NDT Plus. 2009, 2, 365–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, R.; Sharma, A.; Agarwal, S.K.; Dinda, A.K. C1q nephropathy and isolated CD59 deficiency manifesting as necrotizing crescentic glomerulonephritis: A rare association of two diseases. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 2015, 26, 1274–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boqari, D.T.; Al Faraj, S.; Arafah, M.; Aloudah, N.; Alkhairy, K.S.; Alsuhaibani, A.; Alsaad, K.O. Herb-induced acute bone marrow intoxication and interstitial nephritis superimposing glomerular C1q deposition in a patient with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 2015, 26, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eggleton, P.; Bremer, E.; Dudek, E.; Michalak, M. Calreticulin, a therapeutic target? Expert Opin. Ther. Targets. 2016, 20, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, S.K.; Wong, P.N.; Lee, K.F.; Fung, L.H.; Wong, A.K. IgA nephropathy in a patient with paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1995, 10, 2126–2129. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kat, K.; Shibata, T.; Mukai, K.; Kitazawa, K.; Sugisaki, T. Case of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria complicated with IgA nephropathy who developed acute renal failure induced by hemolytic crisis. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 2005, 47, 540–546. [Google Scholar]
- Kuto, F.; Sakaguchi, T.; Horasawa, Y.; Hayashi, M.; Hirasawa, Y.; Tokuhiro, H. Total hemiatrophy. Association with localized scleroderma, Schönlein-Henoch nephritis, and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Arch. Intern. Med. 1985, 145, 731–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzi, F.; Botsios, C.; Ostuni, P.; Sfriso, P.; Piva, E.; Marson, P.; Punzi, L.; Todesco, S. Adult Henoch-Schönlein purpura with glomerulonephritis and paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria: An uncommon association. Clin. Rheumatol. 2002, 21, 408–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Yoshimura, A.; Inoue, Y.; Takahashi, N.; Sugenoya, Y.; Morita, H.; Kinugasa, E.; Ideura, T. A case of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria combined with focal segmental glomerular sclerosis. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 2001, 43, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, G.W.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.B.; Yu, E.S.; Lee, J.L.; Ryu, M.H.; Kim, E.; Choi, S.J.; Kim, W.K.; Lee, J.S.; et al. Membranous glomerulopathy as a manifestation of chronic graft-versus-host-disease after non-myeloablative stem cell transplantation in a patient with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2003, 18, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poggiali, E.; Cassinerio, E.; Zanaboni, L.; Cappellini, M.D. An update on iron chelation therapy. Blood Transfus. 2012, 10, 411–422. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, J.L.; Kizhakkedathu, J.N. Polymeric nanocarriers for the treatment of systemic iron overload. Mol. Cell. Ther. 2015, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, H.; Han, M.; Xue, J.; Baek, Y.; Chang, J.; Hu, S.; Nam, H.; Jo, M.J.; El Fakhri, G.; Hutchens, M.P.; et al. Renal clearable nanochelators for iron overload therapy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hillmen, P.; Hall, C.; Marsh, J.C.; Elebute, M.; Bombara, M.P.; Petro, B.E.; Cullen, M.J.; Richards, S.J.; Rollins, S.A.; Mojcik, C.F.; et al. Effect of eculizumab on hemolysis and transfusion requirements in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 350, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keating, G.M.; Lyseng-Williamson, K.A.; McKeage, K. Eculizumab: A guide to its use in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. BioDrugs 2012, 26, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risitano, A.M.; Rotoli, B. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: Pathophysiology, natural history and treatment options in the era of biological agents. Biologics 2008, 2, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanakura, Y.; Ohyashiki, K.; Shichishima, T.; Okamoto, S.; Ando, K.; Ninomiya, H.; Kawaguchi, T.; Nakao, S.; Nakakuma, H.; Nishimura, J.; et al. Safety and efficacy of the terminal complement inhibitor eculizumab in Japanese patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: The AEGIS clinical trial. Int. J. Hematol. 2011, 93, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, Ê.S.; Parente Filho, S.L.A.; Pro, J.D.Z.; Rolim, V.M.; Primo, G.A.S.; Brunetta, D.M.; Silva, H.F.D.; Meneses, G.C.; Barroso-Duarte, F.; Daher, E.F. Renal involvement in paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria: A brief review of the literature. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. (1992) 2018, 64, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, R.; Adiraju, K.P.; Gudithi, S.; Dakshinamurty, K.V. Renal Manifestations in Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria. Indian J. Nephrol. 2017, 27, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Qureshi, A.; Kazi, J. Renal involvement in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2013, 123, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, D.P.; Anderson, M.D.; Sutton, T.A. Pathophysiology of acute kidney injury. Compr. Physiol. 2012, 2, 1303–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Working Group. Definition and classification of acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2012, 2, 19–36. [Google Scholar]
- Koza, Y. Acute kidney injury: Current concepts and new insights. J. Inj. Violence Res. 2016, 8, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellomo, R.; Ronco, C.; Kellum, J.A.; Mehta, R.L.; Palevsky, P.; Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative Workgroup. Acute renal failure-definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: The Second International Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) Group. Crit. Care 2004, 8, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mehta, R.L.; Kellum, J.A.; Shah, S.V.; Molitoris, B.A.; Ronco, C.; Warnock, D.G.; Levin, A. Acute Kidney Injury Network: Report of an initiative to improve outcomes in acute kidney injury. Crit Care 2007, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dvanajscak, Z.; Walker, P.D.; Cossey, L.N.; Messias, N.C.; Boils, C.L.; Kuperman, M.B.; Larsen, C.P. Hemolysis-associated hemoglobin cast nephropathy results from a range of clinicopathologic disorders. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 1400–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abou Arkoub, R.; Wang, D.; Zimmerman, D. A Rare Cause of Reversible Renal Hemosiderosis. Case Rep. Nephrol. 2015, 2015, 464059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, K.; Zhang, X.-G.; Liu, S.-W.; Yin, Z.; Chen, X.-M.; Wu, D. Reversible acute kidney injury caused by paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2011, 341, 68–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalighi, M.A.; Henriksen, K.J.; Chang, A.; Meehan, S.M. Intratubular hemoglobin casts in hemolysis-associated acute kidney injury. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 65, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.H.; Li, K.J.; Yu, C.L.; Tsai, C.Y. Tamm-Horsfall Protein is a Potent Immunomodulatory Molecule and a Disease Biomarker in the Urinary System. Molecules 2018, 23, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shachner, M.S.; Miniter, P.M.; Mayer, A.R.; Andriole, V.T. Interaction of Tamm-Horsfall proteins with bacterial extracts. Kidney Int. 1987, 31, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pak, J.; Pu, Y.; Zhang, Z.-T.; Hasty, D.L.; Wu, X.-R. Tamm-Horsfall protein binds to type 1 fimbriated Escherichia coli and prevents E. coli from binding to uroplakin Ia and Ib receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 9924–9930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heyman, S.N.; Fuchs, S.; Brezis, M. The role of medullary ischemia in acute renal failure. New Horiz. 1995, 3, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kato, G.J.; Taylor, J.G., 6th. Pleiotropic effects of intravascular haemolysis on vascular homeostasis. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 148, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ballarín, J.; Arce, Y.; Torra Balcells, R.; Diaz Encarnación, M.; Manzarbeitia, F.; Ortiz, A.; Egido, J.; Moreno, J.A. Acute renal failure associated to paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria leads to intratubular haemosiderin accumulation and CD163 expression. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 3408–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Etzerodt, A.; Moestrup, S.K. CD163 and inflammation: Biological, diagnostic, and therapeutic aspects. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 2352–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Philippidis, P.; Mason, J.C.; Evans, B.J.; Nadra, I.; Taylor, K.M.; Haskard, D.O.; Landis, R.C. Hemoglobin scavenger receptor CD163 mediates interleukin-10 release and heme oxygenase-1 synthesis: Antiinflammatory monocyte-macrophage responses in vitro, in resolving skin blisters in vivo, and after cardiopulmonary bypass surgery. Circ. Res. 2004, 94, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gill, P.S.; Wilcox, C.S. NADPH oxidases in the kidney. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2006, 8, 1597–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-W.; Wu, V.-C.; Lin, W.-C.; Huang, J.-W.; Wu, M.-S. Acute renal failure in a patient with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Kidney Int. 2007, 71, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakthiswary, R.; Das, S.; Fadilah, S.A. Successful treatment of acute kidney injury secondary to haeme nephropathy in paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria with alkaline diuresis. EXCLI J. 2012, 11, 198–203. [Google Scholar]
- Real Academia Nacional De Medicina De Espana. Available online: https://analesranm.es/wp-content/uploads/primera-epoca/numero_133/2016-02.pdf (accessed on 2 February 2020).
- Tseng, M.F.; Chou, C.L.; Chung, C.H.; Chien, W.C.; Chenk, Y.K.; Yang, H.C.; Liao, C.Y.; Wei, K.Y.; Wu, C.C. Continuous veno-venous hemofiltration yields better renal outcomes than intermittent hemodialysis among traumatic intracranial hemorrhage patients with acute kidney injury: A nationwide population-based retrospective study in Taiwan. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajehdehi, P. Reversible acute renal failure with prolonged oliguria and gross hematuria in a case of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Scand. J. Urol. Nephrol. 2000, 34, 284–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balwani, M.R.; Kute, V.B.; Shah, P.R.; Shah, M.; Varyani, U.; Trivedi, H.L. Manifestation of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria as repeated acute kidney injury. J. Nephropharmacol. 2015, 5, 116–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kirsch, A.H.; Pollheimer, M.J.; Troppan, K.; Horina, J.H.; Rosenkranz, A.R.; Eller, K. The Case|Acute kidney injury and hemolysis in a 58-year-old woman. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 993–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimoto, M.; Matsui, M.; Tsushima, H.; Tanabe, K.; Tagawa, M.; Samejima, K.I.; Akai, Y.; Saito, Y. Acute kidney injury in a postpartum woman with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: A case report and literature review. Hemodial. Int. 2018, 22, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masakane, I.; Sakurai, K. Current approaches to middle molecule removal: Room for innovation. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33 (Suppl. 3), 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bowry, S.K. Membrane requirements for high-flux and convective therapies. Contrib. Nephrol. 2011, 175, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanholder, R.; De Smet, R.; Glorieux, G.; Argilés, A.; Baurmeister, U.; Brunet, P.; Clark, W.; Cohen, G.; De Deyn, P.P.; Deppisch, R.; et al. Review on uremic toxins: Classification, concentration, and interindividual variability. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 1934–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henderson, L.W.; Besarab, A.; Michaels, A.; Bluemle, L.W., Jr. Blood purification by ultrafiltration and fluid replacement (diafiltration). Trans. Am. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs 1967, 17, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, W.R.; Gao, D.; Neri, M.; Ronco, C. Solute Transport in Hemodialysis: Advances and Limitations of Current Membrane Technology. Contrib. Nephrol. 2017, 191, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronco, C.; Ghezzi, P.M.; Brendolan, A.; Crepaldi, C.; La Greca, G. The haemodialysis system: Basic mechanisms of water and solute transport in extracorporeal renal replacement therapies. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1998, 13 (Suppl. 6), 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ISO. BS EN ISO 8637:2014. Cardiovascular Implants and Extracorporeal Systems. Haemodialysers, Haemodiafilters, Haemofilters and Haemoconcentrators. 2014. Available online: https://shop.bsigroup.com/ProductDetail/?pid=000000000030280719 (accessed on 10 October 2017).
- British Standards Institution. Haemodialysers, Haemodiafilters, Haemofilters, Haemoconcentrators and Their Extracorporeal Circuits (BS EN 1283:1996). 1996. Available online: http://shop.bsigroup.com/ProductDetail/?pid=000000000000875837 (accessed on 10 October 2017).
- Huang, Z.; Gao, D.; Letteri, J.J.; Clark, W.R. Blood-membrane interactions during dialysis. Semin. Dial. 2009, 22, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiore, G.B.; Guadagni, G.; Lupi, A.; Ricci, Z.; Ronco, C. A new semiempirical mathematical model for prediction of internal filtration in hollow fiber hemodialyzers. Blood Purif. 2006, 24, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangel, A.V.; Kim, J.C.; Kaushik, M.; Garzotto, F.; Neri, M.; Cruz, D.N.; Ronco, C. Backfiltration: Past, present, and future. Contrib. Nephrol. 2011, 175, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ronco, C.; Clark, W.R. Haemodialysis membranes. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 394–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronco, C. The Rise of Expanded Hemodialysis. Blood Purif. 2017, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boschetti-de-Fierro, A.; Voigt, M.; Hulko, M.; Storr, M.; Krause, B. Enhanced HD membrane reaches equivalent performance as HDF. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 234–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boschetti-de-Fierro, A.; Voigt, M.; Hulko, M.; Storr, M.; Krause, B. MCO ® Dialyzers: Enhanced Selectivity High-flux; Abstract #SAT-481. In Proceedings of the World Congress of Nephrology, Cape Town, South Africa, 13–17 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Storr, M.; Boschetti-de-Fierro, A.; Krause, B.; Hulko, M.; Leypoldt, K.; Girndt, M.; Fiedler, R.; Zickler, D.; Schindler, R. Efficient removal of polyclonal free light chains (FLC) by hemodialysis using medium cut-off membranes: In vitro and in vivo studies. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voigt, M.; Boschetti-de-Fierro, A.; Haug, U.; Hulko, M.; Storr, M.; Krause, B. Changes in coagulation factors and inhibitors during simulated HD with the novel MCO high flux membrane. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Storr, M.; Boschetti-de-Fierro, A.; Voigt, M.; Hulko, M.; Krause, B. MCO dialyzer: Enhanced high-flux membrane with expanded toxin removal. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 313. [Google Scholar]
- Boschetti-de-Fierro, A.; Voigt, M.; Hulko, M.; Storr, M.; Krause, B. Improved clearance of middle molecules with high-flux hemodialysis membrane. Hemodial. Int. 2015, 19, S26. [Google Scholar]
- Gebert, M.; Schmidt, C.; Hodler, J.; Voigt, M.; Boschetti-de-Fierro, A.; Hulko, M.; Krause, B. Removal of drugs beneficial to patients by various high-flux membranes. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2016, 39, 378. [Google Scholar]
- Boschetti-de-Fierro, A.; Beck, W.; Hildwein, H.; Krause, B.; Storr, M.; Zweigart, C. Membrane Innovation in Dialysis. Contrib. Nephrol. 2017, 191, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Manna, G.; Donati, G. Coupled Plasma Filtration Adsorption: A Multipurpose Extracorporeal Detoxification Therapy. Blood Purif. 2018, 46, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formica, M.; Inguaggiato, P.; Bainotti, S.; Wratten, M.L. Coupled plasma filtration adsorption. Contrib. Nephrol. 2007, 156, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finazzi, S.; Garbero, E.; Trussardi, G.; Bertolini, G. The Hematocrit Affects the Volume of Plasma Treated With Coupled Plasma Filtration and Adsorption With Predilution. Artif. Organs 2017, 41, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalesso, F. Plasma filtration adsorption dialysis (PFAD): A new technology for blood purification. Int. J. Artif. Organs. 2005, 28, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetta, C.; Cavaillon, J.M.; Schulze, M.; Ronco, C.; Ghezzi, P.M.; Camussi, G.; Serra, A.M.; Curti, F.; Lonnemann, G. Removal of cytokines and activated complement components in an experimental model of continuous plasma filtration coupled with sorbent adsorption. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1998, 13, 1458–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; Guo, Q.; Zhou, J. Plasmapheresis Combined with Continuous Plasma Filtration Adsorption Rescues Severe Acute Liver Failure in Wilson’s Disease before Liver Transplantation. Blood Purif. 2019, 47, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, R.; Scarrone, S.; Pizzi, B.; Bonato, V.; Vivaldi, N. Coupled plasma filtration-adsorption in Weil’s syndrome: Case report. Minerva Anestesiol. 2011, 77, 846–849. [Google Scholar]
- Pezzi, M.; Renda, S.; Giglio, A.M.; Scozzafava, A.M.; Tiburzi, S.P.; Casella, P.; Iannelli, F.; Verre, M. The Use of Coupled Plasma Filtration Adsorption in Traumatic Rhabdomyolysis. Case Rep. Crit. Care 2017, 2017, 5764961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vignesh, P.; Rawat, A.; Sharma, M.; Singh, S. Complement in autoimmune diseases. Clin. Chim. Acta 2017, 465, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricklin, D.; Hajishengallis, G.; Yang, K.; Lambris, J.D. Complement: A key system for immune surveillance and homeostasis. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Merle, N.S.; Noe, R.; Halbwachs-Mecarelli, L.; Fremeaux- Bacchi, V.; Roumenina, L.T. Complement system Part II: Role in immunity. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zewde, N.; Gorham, R.D., Jr.; Dorado, A.; Morikis, D. Quantitative Modeling of the Alternative Pathway of the Complement System. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luzzatto, L. Recent Advances in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria. F1000Res 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jore, M.M.; Johnson, S.; Sheppard, D.; Barber, N.M.; Li, Y.I.; Nunn, M.A.; Elmlund, H.; Lea, S.M. Structural basis for therapeutic inhibition of complement C5. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schatz-Jakobsen, J.A.; Zhang, Y.; Johnson, K.; Neill, A.; Sheridan, D.; Andersen, G.R. Structural Basis for Eculizumab-Mediated Inhibition of the Complement Terminal Pathway. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hillmen, P.; Young, N.S.; Schubert, J.; Brodsky, R.A.; Socié, G.; Muus, P.; Röth, A.; Szer, J.; Elebute, M.O.; Nakamura, R.; et al. The complement inhibitor eculizumab in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodsky, R.A.; Young, N.S.; Antonioli, E.; Risitano, A.M.; Schrezenmeier, H.; Schubert, J.; Gaya, A.; Coyle, L.; de Castro, C.; Fu, C.L.; et al. Multicenter phase III study of the complement inhibitor eculizumab for the treatment of patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood 2008, 111, 1840–1847. [Google Scholar]
- Risitano, A.M. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria in the era of complement inhibition. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 359–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rother, R.P.; Rollins, S.A.; Mojcik, C.F.; Brodsky, R.A.; Bell, L. Discovery and development of the complement inhibitor eculizumab for the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1256–1264, Erratum in: 2007, 25, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, R.J.; Hill, A.; Arnold, L.M.; Brooksbank, G.L.; Richards, S.J.; Cullen, M.; Mitchell, L.D.; Cohen, D.R.; Gregory, W.M.; Hillmen, P. Long-term treatment with eculizumab in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: Sustained efficacy and improved survival. Blood 2011, 117, 6786–6792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Sicre Fontbrune, F.; de Peffault Latour, R. Ten Years of Clinical ExperienceWith Eculizumab in Patients with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria. Semin. Hematol. 2018, 55, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loschi, M.; Porcher, R.; Barraco, F.; Terriou, L.; Mohty, M.; de Guibert, S.; Mahe, B.; Lemal, R.; Dumas, P.Y.; Etienne, G.; et al. Impact of eculizumab treatment on paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: A treatment versus no-treatment study. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA Approves Ravulizumab-cwvz for Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria. Available online: www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-ravulizumab-cwvz-paroxysmal-nocturnal-hemoglobinuria (accessed on 2 February 2020).
- European Medicines Agency. Ultomiris, Authorisation Details. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/ultomiris (accessed on 4 February 2020).
- Röth, A.; Rottinghaus, S.T.; Hill, A.; Bachman, E.S.; Kim, J.S.; Schrezenmeier, H.; Terriou, L.; Urbano-Ispizua, Á.; Wells, R.A.; Jang, J.H.; et al. Ravulizumab (ALXN1210) in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: Results of 2 phase 1b/2 studies. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 2176–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheridan, D.; Yu, Z.X.; Zhang, Y.; Patel, R.; Sun, F.; Lasaro, M.A.; Bouchard, K.; Andrien, B.; Marozsan, A.; Wang, Y.; et al. Design and preclinical characterization of ALXN1210: A novel anti-C5 antibody with extended duration of action. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.W.; Sicre de Fontbrune, F.; Wong Lee Lee, L.; Pessoa, V.; Gualandro, S.; Füreder, W.; Ptushkin, V.; Rottinghaus, S.T.; Volles, L.; Shafner, L.; et al. Ravulizumab (ALXN1210) vs eculizumab in adult patients with PNH naive to complement inhibitors: The 301 study. Blood 2019, 133, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulasekararaj, A.G.; Hill, A.; Rottinghaus, S.T.; Langemeijer, S.; Wells, R.; Gonzalez-Fernandez, F.A.; Gaya, A.; Lee, J.W.; Gutierrez, E.O.; Piatek, C.I.; et al. Ravulizumab (ALXN1210) vs eculizumab in C5-inhibitor-experienced adult patients with PNH: The 302 study. Blood 2019, 133, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeage, K. Ravulizumab: First Global Approval. Drugs 2019, 79, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexion Reports Second Quarter 2018 Results. Available online: https://ir.alexion.com/news-releases/news-release-details/alexion-reports-second-quarter-2018-results (accessed on 4 February 2020).
- Sampei, Z.; Haraya, K.; Tachibana, T.; Fukuzawa, T.; Shida-Kawazoe, M.; Gan, S.W.; Shimizu, Y.; Ruike, Y.; Feng, S.; Kuramochi, T.; et al. Antibody engineering to generate SKY59, a long-acting anti-C5 recycling antibody. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0209509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukuzawa, T.; Sampei, Z.; Haraya, K.; Ruike, Y.; Shida-Kawazoe, M.; Shimizu, Y.; Gan, S.W.; Irie, M.; Tsuboi, Y.; Tai, H.; et al. Long lasting neutralization of C5 by SKY59, a novel recycling antibody, is a potential therapy for complement-mediated diseases. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proof of Concept Study to Assess. The Efficacy Safety and Pharmacokinetics of LFG316 in Patients with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria. ClinicalTrials.gov. A Service of the U.S. National Institutes of Health. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02534909 (accessed on 6 February 2020).
- Weyne, N.Y.J.; DelGizzi, R.; Godin, S.; Morton, L.; Prasad, S.; Rankin, A.J.; Simek-Lemos, M.; Wang, M.D.; Rippley, R.; Harari, O. A Randomized, Double -Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 1 Study of the Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of REGN3918, a Human Antibody Against Complement Factor C5, in Healthy Volunteers. Blood 2018, 132, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeth, Z.N.A.; Egyed, M.; Winter, E.; Hsu, J.; Dieckmann, A.; Anzures -Cabrera, J.; Mannino, M.; Fernandez, E.; Jordan, G.; Klughammer, B.; et al. The SMART-IgG Anti -hC5 Antibody (SKY59/RO7112689) Has Favorable PK, PD, Subcutaneous Bioavailability, and Safety Profile in Phase I HV Study. Blood 2017, 130, 4750. [Google Scholar]
- A Randomized, Double-Blind, Active-Controlled Phase 3 Study Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of ABP 959 Compared with Eculizumab in Adult Subjects with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT03818607 (accessed on 2 February 2020).
- A Phase III Randomised, Double-Blind, Multicentre Study to Compare the Efficacy, Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Immunogenicity Between SB12 (Proposed Eculizumab Biosimilar) and Soliris® in Subjects with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Haemoglobinuria. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT04058158 (accessed on 3 February 2020).
- Weston-Davies, W.H.; Nunn, M.A.; Pinto, F.O.; Mackie, I.; Richards, S.J.; Machin, S.J.; Prudo, R.; Hillmen, P. Clinical and Immunological Characterisation of Coversin, a Novel Small Protein Inhibitor of Complement C5 with Potential as a Therapeutic Agent in PNH and Other Complement Mediated Disorders. Blood 2014, 124, 4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.; Kulasekararaj, A.; Windyga, J.; Robak, T.; Hellman, A.; Weston-Davies, W.; Griffin, M.; Munir, T.; Szmigielska-Kaplon, A.; Piekarska, A.; et al. Results of COBALT, a Phase II clinical trial of Coversin in PNH 2018. In Proceedings of the 23rd Congress of EHA, Stockholm, Sweden, 14–17 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ra Pharmaceuticals. Ra Pharmaceuticals Announces Positive Top-Line Data from Phase 2 Trial of Zilucoplan in Patients with Generalized Myasthenia Gravis. 2018. Available online: https://rapharma.gcs-web.com/news-releases/news-release-details/ra-pharmaceuticals-announces-positive-top-line-data-phase-2. (accessed on 15 December 2019).
- Hill, A.; Schrezenmeier, H.; Hillmen, P.; Szer, H.P.J.; Spearing, R.; Forsyth, C.; Armstrong, E.; Patriquin, C.; Weitz, I.; Shen, Y.M.; et al. RA101495, a Subcutaneoulsy-Administered Peptide Inhibitor of Complement Component C5, for the Treatment of Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria: Phase 2 Results; European Hematology Association: Stockholm, Sweden, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Phase 2 Multicenter, Open-Label, Uncontrolled Study to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability, Efficacy, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of RA101495 in Subjects with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT03078582 (accessed on 5 February 2020).
- Kusner, L.L.; Yucius, K.; Sengupta, M.; Sprague, A.G.; Desai, D.; Nguyen, T.; Charisse, K.; Kuchimanchi, S.; Kallanthottathil, R.; Fitzgerald, K.; et al. Investigational RNAi Therapeutic Targeting C5 Is Efficacious in Pre-clinical Models of Myasthenia Gravis. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2019, 13, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- A Phase 2 Open-Label Single Dose Study of Subcutaneously Administered ALN-CC5 in Patients with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria Who Are Inadequate Responders to Eculizumab. EU Clinical Trials Register. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/search?query=2016–002943-40 (accessed on 3 February 2020).
- Alnylam Pharmaceuticals. A Phase 2, Open-Label, Single Dose, Study of Subcutaneously Administered ALN-CC5 in Patients with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria Who Are Inadequate Responders to Eculizumab. 2017. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/trial/2016-002943-40/ES (accessed on 5 February 2020).
- Mastellos, D.C.; Reis, E.S.; Yancopoulou, D.; Risitano, A.M.; Lambris, J.D. Expanding Complement Therapeutics for the Treatment of Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria. Semin. Hematol. 2018, 55, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.; Kay, B.K.; Lambris, J.D. Inhibition of human complement by a C3-binding peptide isolated from a phage displayed random peptide library. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 884–891. [Google Scholar]
- Fiane, A.E.; Mollnes, T.E.; Videm, V.; Hovig, T.; Høgåsen, K.; Mellbye, O.J.; Spruce, L.; Moore, W.T.; Sahu, A.; Lambris, J.D. Compstatin, a peptide inhibitor of C3, prolongs survival of ex vivo perfused pig xenografts. Xenotransplantation 1999, 6, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, E.S.; DeAngelis, R.A.; Chen, H.; Resuello, R.R.; Ricklin, D.; Lambris, J.D. Therapeutic C3 inhibitor Cp40 abrogates complement activation induced by modern hemodialysis filters. Immunobiology 2015, 220, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Risitano, A.M.; Ricklin, D.; Huang, Y.; Reis, E.S.; Chen, H.; Ricci, P.; Lin, Z.; Pascariello, C.; Raia, M.; Sica, M.; et al. Peptide inhibitors of C3 activation as a novel strategy of complement inhibition for the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood. 2014, 123, 2094–2101, Erratum in 2007, 129, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, B.J.; Halff, E.F.; Lambris, J.D.; Gros, P. Structure of compstatin in complex with complement component C3c reveals a new mechanism of complement inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 29241–29247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Z.; Schmidt, C.Q.; Koutsogiannaki, S.; Ricci, P.; Risitano, A.M.; Lambris, J.D.; Ricklin, D. Complement C3dg-mediated erythrophagocytosis: Implications for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood 2015, 126, 891–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murphy, K.; Weaver, C. Innate immunity: The first lines of defense. In Janeway’s Immunobiology, 9th ed.; Garland Science: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Risitano, A.M.; Notaro, R.; Marando, L.; Serio, B.; Ranaldi, D.; Seneca, E.; Ricci, P.; Alfinito, F.; Camera, A.; Gianfaldoni, G.; et al. Complement fraction 3 binding on erythrocytes as additional mechanism of disease in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria patients treated by [a C5 inhibitor]. Blood 2009, 113, 4094–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Phase Ib, Open Label, Multiple Ascending Dose, Pilot Study to Assess the Safety, Preliminary Efficacy and Pharmacokinetics of Subcutaneously Administered APL-2 in Subjects with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02588833 (accessed on 9 February 2020).
- An Open Label, Single and Multiple Ascending Dose Study to Assess the Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of APL-2 as an Add-On to Standard of Care in Subjects with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02264639 (accessed on 9 February 2020).
- Mastellos, D.C.; Yancopoulou, D.; Kokkinos, P.; Huber-Lang, M.; Hajishengallis, G.; Biglarnia, A.R.; Lupu, F.; Nilsson, B.; Risitano, A.M.; Ricklin, D.; et al. Compstatin: A C3-targeted complement inhibitor reaching its prime for bedside intervention. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 45, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricklin, D.; Lambris, J.D. Complement therapeutics. Semin. Immunol. 2016, 28, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maibaum, J.; Liao, S.M.; Vulpetti, A.; Ostermann, N.; Randl, S.; Rüdisser, S.; Lorthiois, E.; Erbel, P.; Kinzel, B.; Kolb, F.A.; et al. Small-molecule factor D inhibitors targeting the alternative complement pathway. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An Open Label, Single Arm, Multiple Dose Study to Assess Efficacy, Safety, Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of LNP023 When Administered in Addition to Standard of Care (SoC) in Patients With Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH) with Signs of Active Hemolysis. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT03439839 (accessed on 4 February 2020).
- Risitano, A.M.; Lee, J.W.; Notaro, R.; Brodsky, R.A.; Kulasekararaj, A.; Maciejewski, J.P.; Huang, M.; Geffner, M.; Browett, P. Mechanistic Evaluation of Efficacy Using Biomarkers of the Oral, Small Molecule Factor D Inhibitor, Danicopan (ACH-4471), in Untreated Patients with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH). Blood 2019, 134 (Suppl. 1), 2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achillion Reports Positive Interim Data for ACH-4471 Phase 2 Combination Trial with Eculizumab at the New Era of Aplastic Anemia and PNH Meeting. Available online: https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2019/05/17/1826802/0/en/Achillion-Reports-Positive-Interim-Data-for-ACH-4471-Phase-2-Combination-Trial-with-Eculizumab-at-The-New-Era-of-Aplastic-Anemia-and-PNH-Meeting.html (accessed on 2 February 2020).
- A Treatment Study of ACH-0144471 in Patients with Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH) with Inadequate Response to Eculizumab. ClinicalTrials.gov. A Service of the U.S. National Institutes of Health. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03472885 (accessed on 2 February 2020).
| Initiation Phase | Extension Phase | Maintenance Phase | Recovery Phase |
|---|---|---|---|
| Renal tubular epithelial cell injury | Prolonged hypoxia consecutive to the initial ischemic event | Cells go through repair mechanisms, migration, apoptosis and proliferation with the intent to restore cellular and tubule integrity | Cellular differentiation continues |
| Renal ischemia | Continued inflammatory response | Epithelial cells provide intracellular and intercellular homeostasis | |
| Changes in structural and functional alterations in renal PTECs | Cells continue to go through damage and death with both necrosis and apoptosis, principally in the outer medulla | Slowly improving cellular and organ function | Epithelial polarity is reestablished |
| Alteration of the regular framework of filamentous actin in the cell | The proximal tubule cells in the outer cortex undergo cellular repair and improve morphologically | Blood flow returns toward normal | |
| Ischemic injury to vascular smooth muscles cells and endothelial cells | GFR continues to fall | GFR is stable at a degree influenced by the severity of the initial event | Normal cellular and organ function is restored. Renal function can be directly linked with the mechanisms of cell injury and recovery |
| Up-regulation of chemokines and cytokines triggering the inflammatory cascade | Continuous generation and release of chemokines and cytokines |
| Phase 1 | Phase 2 | Phase 3 | Phase 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initiation (Fluid Phase) | Amplification | Termination | Regulation |
| Tick-over consists of the hydrolysis of C3 into C3a and C3b in fluid phase, with the activation of the alternative pathway. | C3b molecules can indiscriminately bind to host damaged cells or pathogen surfaces and form C3 convertase that amplifies C3 deposition and initiates a set of cascade reactions. | C3b molecules on the surface of a pathogen lead to opsonization, a process stimulating phagocytosis by macrophages. C3b also binds C3 convertase to form C5 convertase (C3b2Bb) of the alternative pathway. This protein complex cleaves C5, resulting in C5a and C5b. C5b initiates the assembly of membrane attack complex (MAC), a pore responsible for cell lysis. | Complement amplification is regulated through the inhibition of convertase formation, dissociation of existing convertases, cleavage of C3b into iC3b and subsequent cleavage of iC3b to C3dg. The terminal pathway is regulated by soluble vitronectin and clusterin, and CD59 complement regulators. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gembillo, G.; Siligato, R.; Cernaro, V.; Santoro, D. Complement Inhibition Therapy and Dialytic Strategies in Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria: The Nephrologist’s Opinion. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1261. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051261
Gembillo G, Siligato R, Cernaro V, Santoro D. Complement Inhibition Therapy and Dialytic Strategies in Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria: The Nephrologist’s Opinion. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(5):1261. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051261
Chicago/Turabian StyleGembillo, Guido, Rossella Siligato, Valeria Cernaro, and Domenico Santoro. 2020. "Complement Inhibition Therapy and Dialytic Strategies in Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria: The Nephrologist’s Opinion" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 5: 1261. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051261
APA StyleGembillo, G., Siligato, R., Cernaro, V., & Santoro, D. (2020). Complement Inhibition Therapy and Dialytic Strategies in Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria: The Nephrologist’s Opinion. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(5), 1261. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051261









