Treatment of Overlap Syndromes in Autoimmune Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection Criteria
2.2. Data Sources and Search Strategy
2.3. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Quality of Evidence
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Included Studies
3.2. Quality of Included Studies
3.3. Clinical Outcomes
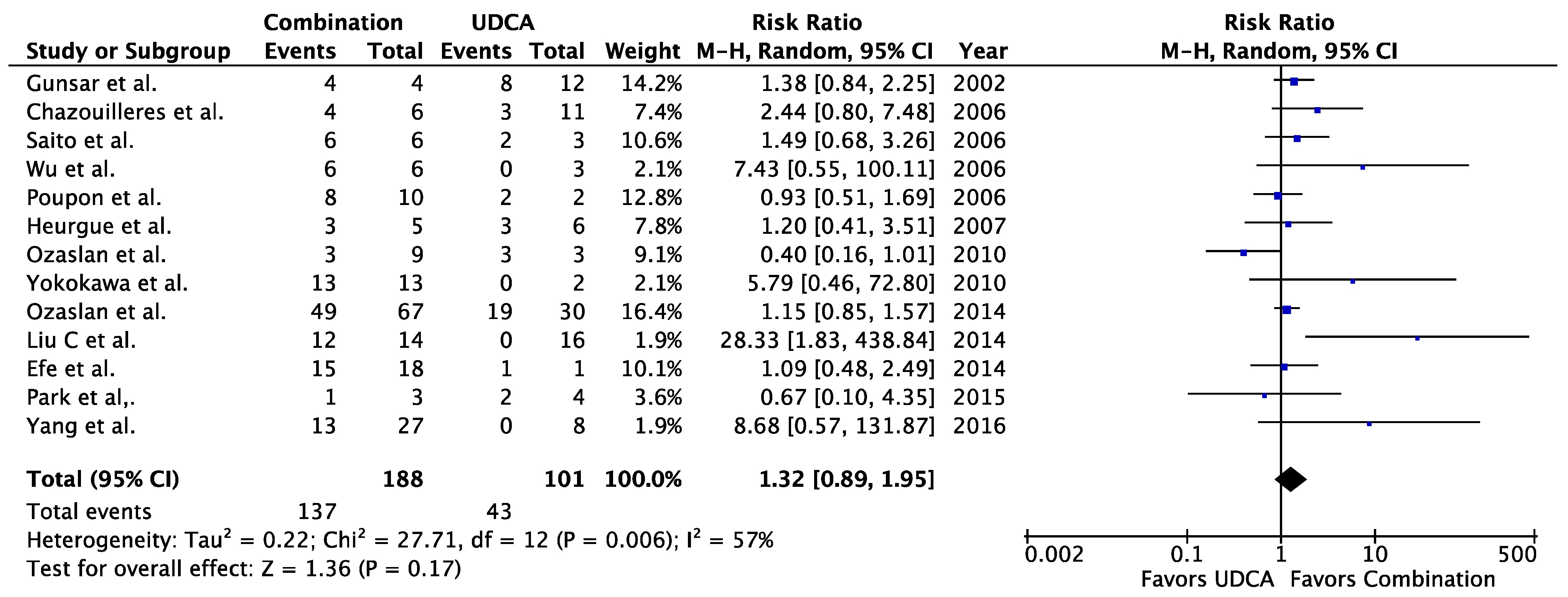
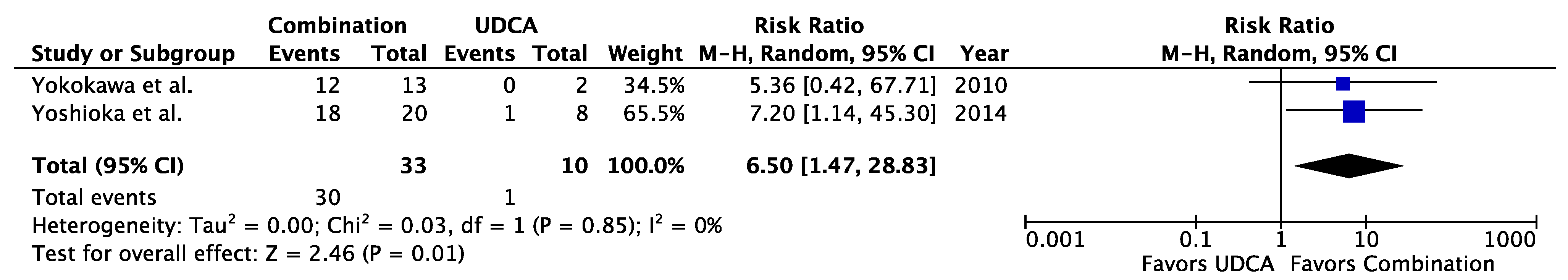
3.3.1. AIH-PBC
3.3.2. AIH-PSC
3.3.3. AIC
3.3.4. ASC
3.4. Quality of Evidence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Database | Time Span | Filters | Search Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| PubMed | Searched on 30 September 2019 | None | (overlap syndrome[Title/Abstract] AND (“hepatitis, autoimmune”[MeSH Terms] OR autoimmune hepatitis[Title/Abstract] OR autoimmune liver disease[Title/Abstract] OR “liver cirrhosis, biliary”[MeSH Terms] OR primary biliary cirrhosis[Title/Abstract] OR primary biliary cholangitis[Title/Abstract] OR “cholangitis, sclerosing”[MeSH Terms] OR primary sclerosing cholangitis[Title/Abstract])) OR ((“hepatitis, autoimmune”[MeSH Terms] OR autoimmune hepatitis[Title/Abstract]) AND (“liver cirrhosis, biliary”[MeSH Terms] OR primary biliary cirrhosis[Title/Abstract] OR primary biliary cholangitis[Title/Abstract])) OR ((“hepatitis, autoimmune”[MeSH Terms] OR autoimmune hepatitis[Title/Abstract]) AND (“cholangitis, sclerosing”[MeSH Terms] OR primary sclerosing cholangitis[Title/Abstract])) OR ((“liver cirrhosis, biliary”[MeSH Terms] OR primary biliary cirrhosis[Title/Abstract] OR primary biliary cholangitis[Title/Abstract]) AND (“cholangitis, sclerosing”[MeSH Terms] OR primary sclerosing cholangitis[Title/Abstract])) OR Autoimmune cholangitis[Title/Abstract] OR Autoimmune sclerosing cholangitis[Title/Abstract] |
| EMBASE | Searched on 30 September 2019 | Publication type restricted to articles, articles in press, or conference papers | ((‘overlap syndrome’/exp OR ‘overlap syndrome’:ab,ti) AND (‘autoimmune hepatitis’/exp OR ‘autoimmune hepatitis’:ab,ti OR ‘autoimmune liver disease’/exp OR ‘autoimmune liver disease’:ab,ti OR ‘primary biliary cirrhosis’/exp OR ‘primary biliary cirrhosis’:ab,ti OR ‘primary biliary cholangitis’:ab,ti OR ‘primary sclerosing cholangitis’/exp OR ‘primary sclerosing cholangitis’:ab,ti)) OR ((‘autoimmune hepatitis’/exp OR ‘autoimmune hepatitis’:ab,ti) AND (‘primary biliary cirrhosis’/exp OR ‘primary biliary cirrhosis’:ab,ti OR ‘primary biliary cholangitis’:ab,ti)) OR ((‘autoimmune hepatitis’/exp OR ‘autoimmune hepatitis’:ab,ti) AND (‘primary sclerosing cholangitis’/exp OR ‘primary sclerosing cholangitis’:ab,ti)) OR ((‘primary biliary cirrhosis’/exp OR ‘primary biliary cirrhosis’:ab,ti OR ‘primary biliary cholangitis’:ab,ti) AND (‘primary sclerosing cholangitis’/exp OR ‘primary sclerosing cholangitis’:ab,ti)) OR ‘Autoimmune cholangitis’/exp OR ‘autoimmune cholangitis’:ab,ti OR ‘Autoimmune sclerosing cholangitis’/exp OR ‘autoimmune sclerosing cholangitis’:ab,ti |
| Cochrane Library | Searched on 30 September 2019 | Study type restricted to clinical trials | (“overlap syndrome”:ab,ti AND (mh“autoimmune hepatitis” OR “autoimmune hepatitis”:ab,ti OR “autoimmune liver disease”:ab,ti OR mh“primary biliary cirrhosis” OR “primary biliary cirrhosis”:ab,ti OR “primary biliary cholangitis”:ab,ti OR mh“primary sclerosing cholangitis” OR “primary sclerosing cholangitis”:ab,ti)) OR ((mh“autoimmune hepatitis” OR “autoimmune hepatitis”:ab,ti) AND (mh“primary biliary cirrhosis” OR “primary biliary cirrhosis”:ab,ti OR “primary biliary cholangitis”:ab,ti)) OR ((mh“autoimmune hepatitis” OR “autoimmune hepatitis”:ab,ti) AND (mh“primary sclerosing cholangitis” OR “primary sclerosing cholangitis”:ab,ti)) OR ((mh“primary biliary cirrhosis” OR “primary biliary cirrhosis”:ab,ti OR “primary biliary cholangitis”:ab,ti) AND (mh“primary sclerosing cholangitis” OR “primary sclerosing cholangitis”:ab,ti)) OR “autoimmune cholangitis”:ab,ti OR “autoimmune sclerosing cholangitis”:ab,ti |
| Web of Science | Searched on 30 September 2019 | Restricted to articles, clinical trials, data sets, data studies, “early access”, unspecified, or “other” | (TS = (“overlap syndrome”) AND (TS = (“autoimmune hepatitis”) OR TS = (“autoimmune liver disease”) OR TS = (“primary biliary cirrhosis”) OR TS = (“primary biliary cholangitis”) OR TS = (“primary sclerosing cholangitis”))) OR (TS = (“autoimmune hepatitis”) AND (TS = (“primary biliary cirrhosis”) OR TS = (“primary biliary cholangitis”))) OR (TS = (“autoimmune hepatitis”) AND TS = (“primary sclerosing cholangitis”)) OR ((TS = (“primary biliary cirrhosis”) OR TS = (“primary biliary cholangitis”)) AND TS = (“primary sclerosing cholangitis”)) OR TS = (“Autoimmune cholangitis”) OR TS = (“Autoimmune sclerosing cholangitis”) |



References
- Czaja, A.J.; Carpenter, H.A. Autoimmune Hepatitis Overlap Syndromes and Liver Pathology. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 46, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonder, A.; Retana, A.; Winston, D.M.; Leung, J.; Kaplan, M. Prevalence of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis–Autoimmune Hepatitis Overlap Syndrome. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 9, 609–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czaja, A.J. Frequency and nature of the variant syndromes of autoimmune liver disease. Hepatology 1998, 28, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chazouillères, O.; Wendum, D.; Serfaty, L.; Montembault, S.; Rosmorduc, O.; Poupon, R. Primary biliary cirrhosis-autoimmune hepatitis overlap syndrome: Clinical features and response to therapy. Hepatology 1998, 28, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohse, A.W.; Büschenfelde, K.-H.M.Z.; Franz, B.; Kanzler, S.; Gerken, G.; Dienes, H.P. Characterization of the overlap syndrome of primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) and autoimmune hepatitis: Evidence for it being a hepatitic form of PBC in genetically susceptible individuals. Hepatology 1999, 29, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazouilleres, O.; Wendum, M.; Serfaty, L.; Rosmorduc, O.; Poupon, R. Long term outcome and response to therapy of primary biliary cirrhosis—Autoimmune hepatitis overlap syndrome. J. Hepatol. 2006, 44, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poupon, R.; Chazouilleres, O.; Corpechot, C.; Chrétien, Y. Development of autoimmune hepatitis in patients with typical primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology 2006, 44, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heurgué, A.; Vitry, F.; Diebold, M.-D.; Yaziji, N.; Bernard-Chabert, B.; Pennaforte, J.-L.; Picot, R.; Louvet, H.; Frémond, L.; Geoffroy, P.; et al. Overlap syndrome of primary biliary cirrhosis and autoimmune hepatitis: A retrospective study of 115 cases of autoimmune liver disease. Gastroentérologie Clin. Biol. 2007, 31, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratori, P.; Granito, A.; Pappas, G.; Pendino, G.M.; Quarneti, C.; Cicola, R.; Menichella, R.; Ferri, S.; Cassani, F.; Bianchi, F.B.; et al. The Serological Profile of the Autoimmune Hepatitis/Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Overlap Syndrome. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 1420–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaslan, E.; Efe, C.; Heurgué–Berlot, A.; Kav, T.; Masi, C.; Purnak, T.; Muratori, L.; Üstündağ, Y.; Bresson-Hadni, S.; Thiefin, G.; et al. Factors Associated With Response to Therapy and Outcome of Patients With Primary Biliary Cirrhosis With Features of Autoimmune Hepatitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Miao, Q.; Xiao, X.; Tang, R.; Chen, X.; Bian, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; et al. The Natural History and Prognosis of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis with Clinical Features of Autoimmune Hepatitis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2015, 50, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J.; Zhu, R.; Zheng, Y.; Dai, W.; Wang, F.; Chen, K.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; et al. Combination therapy of ursodeoxycholic acid and budesonide for PBC–AIH overlap syndrome: A meta-analysis. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joshi, S.; Cauch-Dudek, K.; Wanless, I.R.; Jorgensen, R.; Batts, K.; Heathcote, E.J.; Lindor, K.D. Primary biliary cirrhosis with additional features of autoimmune hepatitis: Response to therapy with ursodeoxycholic acid. Hepatology 2002, 35, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Ari, Z.; Dhillon, A.P.; Sherlock, S. Autoimmune cholangiopathy: Part of the spectrum of autoimmune chronic active hepatitis. Hepatology 1993, 18, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, D.C.; Bojito, L.; Facciuto, M.; Lebovics, E. Mycophenolate Mofetil for Autoimmune Hepatitis: A Single Practice Experience. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2008, 54, 2519–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baven-Pronk, A.M.C.; Coenraad, M.J.; Van Buuren, H.R.; De Man, R.A.; Van Erpecum, K.J.; Lamers, M.M.H.; Drenth, J.P.H.; Berg, A.P.V.D.; Beuers, U.H.; Ouden, J.D.; et al. The role of mycophenolate mofetil in the management of autoimmune hepatitis and overlap syndromes. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 34, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duclos-Vallée, J.C.; Hadengue, A.; Ganne-Carrié, N.; Robin, E.; Degott, C.; Erlinger, S. Primary biliary cirrhosis-autoimmune hepatitis overlap syndrome. Corticoresistance and effective treatment by cyclosporine A. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1995, 40, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhauser, M.; Bjornsson, E.; Treeprasertsuk, S.; Enders, F.; Silveira, M.; Talwalkar, J.; Lindor, K. Autoimmune Hepatitis–PBC Overlap Syndrome: A Simplified Scoring System May Assist in the Diagnosis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez Casas, O.Y.; Diaz Ramirez, G.S.; Marin Zuluaga, J.I.; Santos, O.; Munoz Maya, O.; Donado Gomez, J.H.; Restrepo Gutierrez, J.C. Autoimmune hepatitis—Primary biliary cholangitis overlap syndrome. Long-term outcomes of a retrospective cohort in a university hospital. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 41, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, M.G.; Talwalkar, J.A.; Angulo, P.; Lindor, K.D. Overlap of Autoimmune Hepatitis and Primary Biliary Cirrhosis: Long-Term Outcomes. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 102, 1244–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuiper, E.M.; Zondervan, P.E.; Van Buuren, H.R. Paris Criteria Are Effective in Diagnosis of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis and Autoimmune Hepatitis Overlap Syndrome. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 8, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindgren, S.; Glaumann, H.; Almer, S.; Bergquist, A.; Björnsson, E.; Broomé, U.; Danielsson, Å.; Lebrun, B.; Prytz, H.; Olsson, R. Transitions between variant forms of primary biliary cirrhosis during long-term follow-up. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2009, 20, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, S.; Gomes, D.; Cipriano, M.A.; Sofia, C. The clinical extremes of autoimmune cholangitis. Rev. Española Enferm. Dig. 2017, 109, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Czaja, A.J.; Carpenter, H.A.; Santrach, P.J.; Moore, S.B. Autoimmune cholangitis within the spectrum of autoimmune liver disease. Hepatology 2000, 31, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozaslan, E.; Efe, C.; Akbulut, S.; Purnak, T.; Savas, B.; Erden, E.; Altiparmak, E. Therapy response and outcome of overlap syndromes: Autoimmune hepatitis and primary biliary cirrhosis compared to autoimmune hepatitis and autoimmune cholangitis. Hepatogastroenterology 2010, 57, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Johnson, P.J.; McFarlane, I.G. Meeting report: International autoimmune hepatitis group. Hepatology 1993, 18, 998–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, F.; Berg, P.; Bianchi, F.; Bianchi, L.; Burroughs, A.; Cançado, E.L.R.; Chapman, R.; Cooksley, W.; Czaja, A.; Desmet, V.; et al. International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group Report: Review of criteria for diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 1999, 31, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennes, E.M.; Zeniya, M.; Czaja, A.J.; Parés, A.; Dalekos, G.N.; Krawitt, E.L.; Bittencourt, P.L.; Porta, G.; Boberg, K.M.; Hofer, H.; et al. Simplified criteria for the diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology 2008, 48, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, R.; Fevery, J.; Kalloo, A.; Nagorney, D.M.; Boberg, K.M.; Shneider, B.; Gores, G.J. Diagnosis and management of primary sclerosing cholangitis. Hepatology 2009, 51, 660–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manns, M.P.; Czaja, A.J.; Gorham, J.D.; Krawitt, E.L.; Mieli-Vergani, G.; Vergani, D.; Ling, S.C. Diagnosis and management of autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology 2010, 51, 2193–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Autoimmune hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 971–1004. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gohlke, F.; Lohse, A.W.; Dienes, H.P.; Löhr, H.; Märker-Hermann, E.; Gerken, G.; Büschenfelde, K.-H.M.Z. Evidence for an overlap syndrome of autoimmune hepatitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis. J. Hepatol. 1996, 24, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorio, G.; Portmann, B.; Karani, J.; Harrison, P.; Donaldson, P.T.; Vergani, D.; Mieli-Vergani, G. Autoimmune hepatitis/sclerosing cholangitis overlap syndrome in childhood: A 16-year prospective study. Hepatology 2001, 33, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floreani, A.; Rizzotto, E.R.; Ferrara, F.; Carderi, I.; Caroli, D.; Blasone, L.; Baldo, V. Clinical Course and Outcome of Autoimmune Hepatitis/Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Overlap Syndrome. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 100, 1516–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüth, S.; Kanzler, S.; Frenzel, C.; Kasper, H.U.; Dienes, H.P.; Schramm, C.; Galle, P.R.; Herkel, J.; Lohse, A.W. Characteristics and Long-term Prognosis of the Autoimmune Hepatitis/Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Overlap Syndrome. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2009, 43, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.T.; Liu, P.M.F.; Fagundes, E.D.T.; Queiroz, T.C.N.; Barbosa, P.D.S.H.; Silva, S.L.C.; Silva, A.C.S.; Miranda, D.M.; Ferreira, A.R.; Alberti, L.R. Clinical Characteristics and Prognosis in Children and Adolescents With Autoimmune Hepatitis and Overlap Syndrome. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2016, 63, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, G.; Endo, T.; Mikami, K.; Sawada, N.; Satake, R.; Ohta, R.; Sakamoto, J.; Yoshimura, T.; Kurose, A.; Kijima, H.; et al. Two Cases of Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Overlapping with Autoimmune Hepatitis in Adults. Intern. Med. 2017, 56, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lian, M.; Li, B.; Xiao, X.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, P.; Yan, L.; Sun, C.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Comparative clinical characteristics and natural history of three variants of sclerosing cholangitis: IgG4-related SC, PSC/AIH and PSC alone. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, A. Evolution of autoimmune hepatitis to primary sclerosing cholangitis: A sequential syndrome. Hepatology 2002, 36, 1393–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, R.; Glaumann, H.; Almer, S.; Broomé, U.; Lebrun, B.; Bergquist, A.; Björnsson, E.; Prytz, H.; Åke, D.; Lindgren, S. High prevalence of small duct primary sclerosing cholangitis among patients with overlapping autoimmune hepatitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2009, 20, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNair, A.N.; Moloney, M.; Portmann, B.C.; Williams, R.; McFarlane, I.G. Autoimmune hepatitis overlapping with primary sclerosing cholangitis in five cases. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1998, 93, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Buuren, H.R.; van Hoogstraten, H.J.E.; Terkivatan, T.; Schalm, S.W.; Vleggaar, F.P. High prevalence of autoimmune hepatitis among patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis. J. Hepatol. 2000, 33, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, F.; Ranucci, G.; Aloi, M.; Della Volpe, L.; Viola, F.; Miele, E.; Cucchiara, S.; Iorio, R. A promising medium-term follow-up of pediatric sclerosing cholangitis: Mild phenotype or early diagnosis? Hepatol. Res. 2018, 48, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolka, V.; Karaskova, E.; Tkachyk, O.; Aiglova, K.; Ehrmann, J.; Michalkova, K.; Konecny, M.; Volejnikova, J. Long-term follow-up of children and adolescents with primary sclerosing cholangitis and autoimmune sclerosing cholangitis. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis. Int. 2016, 15, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aw, M.M.; Dhawan, A.; Samyn, M.; Bargiota, A.; Mieli-Vergani, G. Mycophenolate mofetil as rescue treatment for autoimmune liver disease in children: A 5-year follow-up. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Chalabi, T.; Portmann, B.C.; Bernal, W.; McFarlane, I.G.; Heneghan, M.A. Autoimmune hepatitis overlap syndromes: An evaluation of treatment response, long-term outcome and survival. Aliment. Pharm. Ther. 2008, 28, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burak, K.; Urbanski, S.J.; Swain, M.G. CASE REPORT: A Case of Coexisting Primary Biliary Cirrhosis and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis: A New Overlap of Autoimmune Liver Diseases. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2001, 46, 2043–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floreani, A.; Motta, R.; Cazzagon, N.; Franceschet, I.; Roncalli, M.; Del Ross, T.; Rosina, F.; Lleo, A.; Mescoli, C.; Colloredo, G.; et al. The overlap syndrome between primary biliary cirrhosis and primary sclerosing cholangitis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2015, 47, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeevagan, A. Overlap of primary biliary cirrhosis and primary sclerosing cholangitis—A rare coincidence or a new syndrome. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2010, 3, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kingham, J.G.; Abbasi, A. Co-existence of primary biliary cirrhosis and primary sclerosing cholangitis: A rare overlap syndrome put in perspective. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 17, 1077–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandolesi, D.; Lenzi, M.; D’Errico, A.; Festi, D.; Bazzoli, F.; Colecchia, A. Primary biliary cholangitis–primary sclerosing cholangitis in an evolving overlap syndrome: A case report. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 40, 669–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, E.M.G.; Oliveira, P.M.; Becker, V.; Dellavance, A.; Andrade, L.E.C.; Lanzoni, V.; Silva, A.E.B.; Ferraz, M.L.G. Overlapping of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis and Small Duct Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis: First Case Report. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2012, 4, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaram, S.; Shankar, K.; Mazumdar, S.; Shukla, A. Overlap Syndrome between Primary Biliary Cholangitis and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis. ACG Case Rep. J. 2018, 5, e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, W.; Qumosani, K. A195 triple overlap syndrome? A rare case of aih, pbc and psc overlap. J. Can. Assoc. Gastroenterol. 2018, 1, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, S.J.; Xu, Y.; Bao, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.M.; Hua, J. Diagnosis and Treatment of Trigeminy Overlap Syndrome of Autoimmune Liver Disease. World Chin. J. Dig. 2016, 24, 293–298. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, J.; Dai, W.; Wang, F.; Shen, M.; Yang, J.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, H.; Chen, K.; Cheng, P.; et al. Combination Therapy of Ursodeoxycholic Acid and Corticosteroids for Primary Biliary Cirrhosis with Features of Autoimmune Hepatitis: A Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2013, 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günsar, F.; Akarca, U.S.; Ersöz, G.; Karasu, Z.; Yüce, G.; Batur, Y. Clinical and biochemical features and therapy responses in primary biliary cirrhosis and primary biliary cirrhosis-autoimmune hepatitis overlap syndrome. Hepatogastroenterology 2002, 49, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, A.; Harada, K.; Ebinuma, H.; Komori, A.; Yokokawa, J.; Yoshizawa, K.; Abe, M.; Miyake, Y.; Kikuchi, K.; Ohira, H.; et al. Primary biliary cirrhosis—Autoimmune hepatitis overlap syndrome: A rationale for corticosteroids use based on a nation-wide retrospective study in Japan. Hepatol. Res. 2011, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschfield, G.; Beuers, U.; Corpechot, C.; Invernizzi, P.; Jones, D.; Marzioni, M.; Schramm, C. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: The diagnosis and management of patients with primary biliary cholangitis. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 145–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindor, K.D.; Bowlus, C.L.; Boyer, J.; Levy, C.; Mayo, M. Primary Biliary Cholangitis: 2018 Practice Guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Clin. Liver Dis. 2020, 15, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wells, G.A.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (Nos) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies in Metaanalyses. Available online: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 1 November 2019).
- Schünemann, H.; Brożek, J.; Guyatt, G.; Oxman, A. GRADE Handbook. Available online: https://gdt.gradepro.org/app/handbook/handbook.html (accessed on 24 March 2020).
- Cheikh, I.; Said, Y.; Chaabouni, H.; Ouerghi, H.; Ben Ammar, A. Primary biliary cirrhosis and autoimmune hepatitis overlap syndrome: Therapeutic features in 5 patients. Ann. Med. Interne 2003, 154, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Efe, C.; Ozaslan, E.; Heurgue-Berlot, A.; Kav, T.; Masi, C.; Purnak, T.; Torgutalp, M.; Muratori, L.; Bresson-Hadni, S.; Thiefin, G.; et al. Sequential presentation of primary biliary cirrhosis and autoimmune hepatitis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 26, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Zhu, Y.; Men, R.; Wen, M.; Shen, Y.; Lu, C.; Yang, L. Efficacy and Safety of Immunosuppressive Therapy for PBC–AIH Overlap Syndrome Accompanied by Decompensated Cirrhosis: A Real-World Study. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, C.; Naik, J.; Giordano, C.; Mandalia, A.; O’Brien, C.; Bhamidimarri, K.R.; Schiff, E.R.; Martin, P. Hispanics With Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Are More Likely to Have Features of Autoimmune Hepatitis and Reduced Response to Ursodeoxycholic Acid Than Non-Hispanics. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 1398–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Xu, C.; Li, G.; Chi, B. Analysis of clinical features of patients with autoimmune hepatitis/primary biliary cirrhosis overlap syndrome. J. Jilin Univ. Med. 2014, 40, 646–649. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Pan, Z.G.; Ye, J.; Xu, N.; Guo, H.; Li, G.P.; Xu, K.S.; Hou, X.H.; Song, Y. Primary biliary cirrhosis-autoimmune hepatitis overlap syndrome: Simplified criteria may be effective in the diagnosis in Chinese patients. J. Dig. Dis. 2014, 15, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Cho, Y.; Cho, E.J.; Kim, Y.J. Retrospective analysis of autoimmune hepatitis-primary biliary cirrhosis overlap syndrome in Korea: Characteristics, treatments, and outcomes. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2015, 21, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saito, H.; Rai, T.; Takahashi, A.; Kanno, Y.; Monoe, K.; Irisawa, A.; Ohira, H. Clinicolaboratory Characteristics of Japanese Patients with Primary Biliary Cirrhosis-Autoimmune Hepatitis Overlap. Fukushima J. Med Sci. 2006, 52, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serghini, M.; Haddad, W.; Karoui, S.; Ben Mustapha, N.; Kallel, L.; Fekih, M.; Boubaker, J.; Filali, A. Overlap syndrome of primary biliary cirrhosis and autoimmune hepatitis. La Tunis. Medicale 2012, 90, 741–743. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.-H.; Wang, Q.-H.; Tian, G.-S.; Xu, X.-Y.; Yu, Y.-Y.; Wang, G.-Q. Clinical features of the overlap syndrome of autoimmune hepatitis and primary biliary cirrhosis: Retrospective study. Chin. Med. J. 2006, 119, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokokawa, J.; Saito, H.; Kanno, Y.; Honma, F.; Monoe, K.; Sakamoto, N.; Abe, K.; Takahashi, A.; Yokokawa, H.; Ohira, H. Overlap of primary biliary cirrhosis and autoimmune hepatitis: Characteristics, therapy, and long term outcomes. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 25, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshioka, Y.; Taniai, M.; Hashimoto, E.; Haruta, I.; Shiratori, K. Clinical profile of primary biliary cirrhosis with features of autoimmune hepatitis: Importance of corticosteroid therapy. Hepatol. Res. 2013, 44, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efe, C.; Ozaslan, E.; Kav, T.; Purnak, T.; Shorbagi, A.; Ozkayar, O.; Berlot, A.H.; Sokmensuer, C.; Muratori, P. Liver fibrosis may reduce the efficacy of budesonide in the treatment of autoimmune hepatitis and overlap syndrome. Autoimmun. Rev. 2012, 11, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heathcote, E.J. Management of primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology 2000, 31, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, J.; Czaja, A.J.; Dickson, E.R.; LaRusso, N.F.; Wiesner, R.H. Manifestations of nonsuppurative cholangitis in chronic hepatobiliary diseases: Morphologic spectrum, clinical correlations and terminology. Liver 1984, 4, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batts, K.P.; Ludwig, J. An Update on Terminology and Reporting. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1995, 19, 1409–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaja, A.J. Diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of classical autoimmune chronic active hepatitis. In Autoimmune Liver Disease; Raven: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 143–166. [Google Scholar]
- Ishak, K.; Baptista, A.; Bianchi, L.; Callea, F.; De Groote, J.; Gudat, F.; Denk, H.; Desmet, V.; Korb, G.; Macsween, R.N.; et al. Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 1995, 22, 696–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mileti, E.; Rosenthal, P.; Peters, M.G. Validation and Modification of Simplified Diagnostic Criteria for Autoimmune Hepatitis in Children. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 10, 417–421.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bedossa, P.; Poynard, T. An algorithm for the grading of activity in chronic hepatitis C. The METAVIR Cooperative Study Group. Hepatology 1996, 24, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Danford, C.J.; Trivedi, H.D.; Tapper, E.B.; Patwardhan, V.R.; Bonder, A. Treatment of Fatigue in Primary Biliary Cholangitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 64, 2338–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











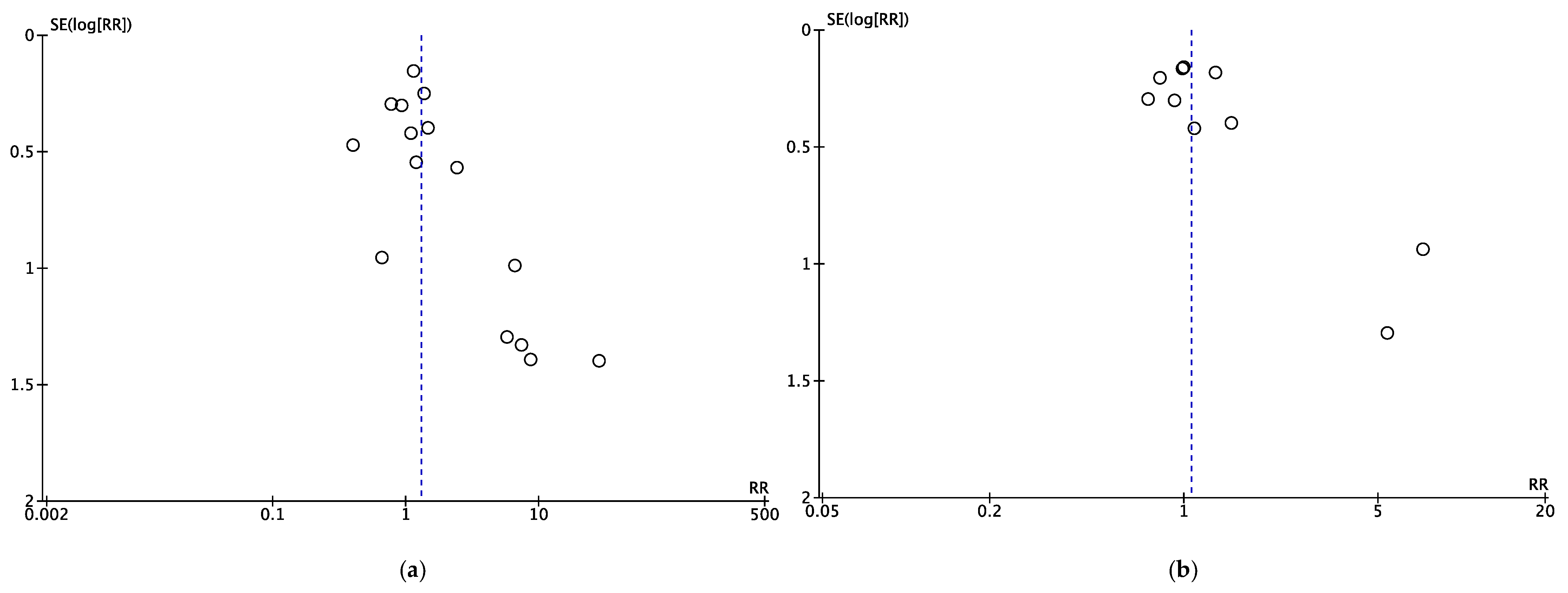
| Study | Design | Population | N | Treatments | Outcomes | Follow-Up (months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AIH-PBC | ||||||
| Chazouillères 2006 [6] | Retrospective cohort study | AIH-PBC (Paris criteria) [4]. Median age 41; 88% female | 17 |
| Complete biochemical response (ALT < 2× ULN, IgG < 16g/L); improved histologic activity; fibrosis non-progression; TFS | Median 90 |
| Efe 2014 [65] | Retrospective cohort study | AIH-PBC (Paris criteria) [4]. Mean age 50; 89% female | 19 |
| Biochemical remission (normalization or >40% reduction in AP at 1 year, normalization of transaminases); TFS | Mean 50 |
| Fan 2018 [66] | Prospective cohort study | AIH-PBC (Paris criteria) [4]. Median age 60 (UDCA group), 48 (combination therapy group); 89% female | 28 |
| Symptomatic improvement; biochemical remission of AIH features (normalization of ALT, AST, and IgG at 1 year); TFS | Median 18 |
| Gunsar 2002 [57] | Retrospective cohort study | AIH-PBC (histologic, serologic, and biochemical features of both diseases). Median age 44 years, 90% female | 16 * |
| Biochemical improvement † (Significant decrease in ALT, AST, AP, and globulin levels); improved histologic activity; TFS | Median 28 |
| Heurgue 2007 [8] | Retrospective cohort study | AIH-PBC (Paris criteria) [4]. Median age 44; 87% female | 15 |
| Complete biochemical response (ALT decreased to <2× ULN, AP, and GGT normalized); TFS | Median 60 |
| Joshi 2002 [8] | Retrospective cohort study | AIH-PBC (Paris criteria) [4]. Median age 46; 94% female | 16 |
| Improved histologic activity (“standardized scoring system for lobular inflammation”, not otherwise specified) | Median 84 |
| Levy 2014 [67] | Retrospective cohort study | AIH-PBC (Paris criteria) [4]. Median age 50–55; 92% female | 39 |
| Complete biochemical response † (“normalization of liver biochemistries”, not otherwise specified) | Median 38 |
| Lindgren 2009 [22] | Retrospective cohort study | AIH-PBC (AIH—IAIHG revised score [27]; PBC—histology, AMA+). Mean age 56; 88% female | 25 |
| Biochemical remission (normalization of transaminases) | Mean 168 |
| Liu 2014 [69] | Retrospective cohort study | AIH-PBC (AIH—IAIHG simplified score [28]; PBC—Paris criteria) [4]. Median age 53; 86% female | 7 § |
| “Complete response” = histologic improvement or biochemical response (ALT < 2× ULN, IgG < 15.6 g/L) | Range 9–48 |
| Ozaslan 2010 [25] | Retrospective cohort study | AIH-PBC (Paris criteria) [4]. Median age 44; 92% female | 12 |
| Symptom resolution; complete biochemical remission (ALT and AST < 2× ULN, Tbili, and gamma globulin normalization); TFS | Median 32 |
| Ozaslan 2014 [25] | Retrospective cohort study | AIH-PBC (Paris criteria) [4]. Median age 48; 84% female | 88 |
| Biochemical remission (normalization or >40% reduction in AP at 1 year, normalization of transaminases); fibrosis non-progression | Mean 66 |
| Park 2015 [10] | Retrospective cohort study | AIH-PBC (Paris criteria) [4]. Median age 49; 100% female | 7 ** |
| Biochemical remission (For UDCA + corticosteroid group: Normalization of transaminases, Tbili, IgG. For UDCA group: AP < 3× ULN, AST < 2× ULN, Tbili ≤ 1 mg/dL within 1 year) | Median 70 |
| Poupon 2006 [70] | Retrospective cohort study | AIH-PBC (Paris criteria) [4]. Mean age 46; 100% female | 12 |
| Sustained biochemical remission (ALT ≤ 2× ULN, Tbili < 20 mol/L); TFS | Not reported |
| Saito 2006 [71] | Retrospective cohort study | AIH-PBC (Paris criteria) [4]. Median age 55; 80% female | 10 |
| Biochemical response † (ALT < 2× ULN); TFS | Median 84 |
| Wu 2006 [73] | Retrospective cohort study | AIH-PBC (AIH—IAIHG revised score [27]; PBC—AASLD guidelines) [77]. Mean age 51; gender not reported | 12 |
| Complete biochemical remission † (transaminases < 2× ULN, significant decrease in AP and GGT) | Not reported |
| Yang 2016 [73] | Retrospective cohort study | AIH-PBC (AIH—Paris criteria [4]; PBC—histologic, serologic, and biochemical features). Mean age 46; 85% female †† | 35 ‡‡ |
| Biochemical remission (Paris-I criteria: AP < 3× ULN, AST < 2× ULN, Tbili normalization) | Median 38 |
| Yokokawa 2010 [74] | Retrospective cohort study | AIH-PBC (Paris criteria) [4]. Mean age 56; 88% female | 16 |
| Biochemical remission † (normalization of ALT, AP); TFS | Median 119 |
| Yoshioka 2014 [75] | Retrospective cohort study | AIH-PBC (biochemical, serologic, and histologic features of both diseases) [75]. Median age 55; 93% female | 28 |
| Biochemical remission (normalization of transaminases); improved histologic activity (Ludwig) [78]; improved piecemeal necrosis (undefined); fibrosis non-progression; TFS | Median 94 |
| Liu 2014 [68] | Prospective cohort study | AIH-PBC (biochemical & histologic features of both diseases). Mean age 56; 33% female | 43 |
| Complete biochemical remission † (undefined) | Mean 10 |
| Cheikh 2003 [64] | Retrospective cohort study | AIH-PBC (Paris criteria) [4]. Median age 38; 100% female | 5 |
| Symptomatic improvement; complete biochemical response (normalization of ALT, AP, GGT, and Tbili); improved histologic activity; fibrosis non-progression | Mean 17 |
| Serghini 2012 [72] | Retrospective cohort study | AIH-PBC (Paris criteria) [4]. Mean age 53; 100% female | 5 |
| Complete biochemical response (ALT < 2× ULN, normalization of AP and GGT) | Median 11 |
| Luth 2009 [35] | Retrospective cohort study | AIH-PSC (AIH—IAHG revised score [27]; PSC—histologic or cholangiographic features). Mean age 34; 19% female | 16 |
| Biochemical response † (Improvement in ALT at 6 months) | Median 144 |
| McNair 1998 [41] | Prospective cohort study | AIH-PSC (AIH—definite by original IAIHG score [26]; PSC—positive cholangiogram). Median age 20; 20% female | 5 |
| Symptomatic improvement; improved histologic activity; fibrosis non-progression (Batts & Ludwig) [79] | Median 84 |
| AIC | ||||||
| Czaja 2000 [24] | Prospective cohort study | AIC (serologic and biochemical features of AIH; biochemical or histologic features of PBC but AMA). Mean age 46; 85% female | 20 |
| Biochemical remission (per Czaja 1991) [80]; improved histologic activity (criteria by Ishak et al.) [81] | Not reported |
| Campos 2017 [23] | Prospective cohort study | AIC (biochemical features of AIH and PBC, histologic features of PBC, AMA-). Mean age 28.5; 100% female | 2 |
| Symptomatic improvement; biochemical remission † (normalization of ALT, AST, AP, and GGT); TFS | Not reported |
| Lindgren 2009 [22] | Retrospective cohort study | AIC (biochemical & histologic features of PBC, ANA, or ASMA+, AMA-). Mean age 51; 88% female | 4 §§ |
| Biochemical remission (normalization of transaminases) | Mean 127 |
| Smolka 2016 [44] | Retrospective cohort study | ASC (probable or definite AIH by simplified IAIHG score modified for children [82]; positive cholangiogram). Median age 14; 55% female | 11 |
| Biochemical remission † (undefined); TFS | Median 144 |
| Ferrari 2018 [43] | Retrospective cohort study | ASC (biochemical and histologic and/or cholangiographic features of PSC; AIH features on IAIHG revised score) [27]. Mean age 9.9; gender not reported | 14 ¶¶ |
| Biochemical remission † (undefined) | Median 79 |
| Gregorio 2001 [33] | Prospective cohort study | ASC (probable or definite AIH by IAIHG revised score [27]; positive cholangiogram. Median age 11.8; 56% female | 26 ## |
| Biochemical remission † (normalization of liver function tests); improved histologic activity (inflammatory activity index scored 0–12, Incorporating portal tract inflammation, lobular activity, and piecemeal necrosis) [33] | Median 72 |
| Study | Selection | Comparability | Exposure | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Represent-Ativeness of Exposed Cohort | Selection of Non-Exposed Cohort | Ascertainment of Exposure | Demonstration that Outcomes of Interest Were not Present at Start of Study | Comparability of Cohorts on Basis of Design or Analysis * | Assessment of Outcomes | Length of Follow-Up † | Adequacy of Follow-Up ‡ | Total | |
| Campos 2017 [23] | * | * | * | * | * | * | 6 | ||
| Chazouillères 2006 [6] | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| Cheikh 2003 [64] | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| Czaja 2000 [24] | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| Efe 2014 [65] | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| Fan 2018 [66] | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| Ferrari 2018 [43] | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| Gregorio 2001 [33] | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| Gunsar 2002 [57] | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| Heurgue 2007 [8] | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| Joshi 2002 [8] | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 8 |
| Levy 2014 [67] | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| Lindgren 2009 [22] | |||||||||
| AIH-PBC | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| AIC | * | * | * | * | * | * | 6 | ||
| Liu 2014 [69] | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| Liu 2014 [68] | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| Luth 2009 [35] | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| McNair 1998 [41] | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| Ozaslan 2010 [25] | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| Ozaslan 2014 [25] | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| Park 2015 [10] | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| Poupon 2006 [70] | * | * | * | * | * | * § | * | 7 | |
| Saito 2006 [71] | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| Serghini 2012 [72] | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| Smolka 2016 [44] | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| Wu 2006 [73] | * | * | * | * | * | * § | * | 7 | |
| Yang 2016 [73] | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| Yokokawa 2010 [74] | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| Yoshioka 2014 [75] | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 |
| Study | Treatments Compared | Symptom Improvement | Biochemical Improvement | Improved Histologic Activity | Fibrosis Non-Progression | Transplant-Free Survival | Reason for Exclusion from Meta-Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AIH-PBC | |||||||
| Joshi 2002 [8] | UDCA | — | — | 3/9 | — | — * | Only study comparing UDCA to placebo |
| Placebo | — | — | 0/2 | — | — * | ||
| Lindgren 2009 [22] | UDCA | — | 3/18 | — | — | — | Overlapping treatment groups (see Table 1) |
| Corticosteroids | — | 5/15 | — | — | — | ||
| Liu 2014 [69] | UDCA | — | 0/6 | — | — | — | No endpoints reached in either treatment group |
| UDCA + prednisone± | — | 0/1 | — | — | — | ||
| Serghini 2012 [72] | UDCA + corticosteroids + AZA | — | 0/4 | — | — | — | No endpoints reached in either treatment group |
| Corticosteroids + AZA | — | 0/1 | — | — | — | ||
| AIH-PSC | |||||||
| Luth 2009 [35] | Corticosteroids± | — | 9/10 | — | — | — | No comparator study for biochemical improvement (see below) |
| UDCA + corticosteroids ± AZA | — | 6/6 | — | — | — | ||
| McNair 1998 [41] | Prednisolone + AZA | 2/3 | 0/3 | 2/3 | 2/3 | 2/3 | No biochemical endpoints reached in either group |
| UDCA + prednisolone + AZA | 2/2 | 0/2 | 0/1 † | 1/1 † | 2/2 | ||
| AIC | |||||||
| Campos 2017 [23] | Prednisolone, then UDCA, cholestyramine, rifampicin, naltrexone, sertraline, hydroxyzine, amitriptyline, phototherapy, molecular adsorbent recirculating system, prednisolone, budesonide, AZA, MMF | — | 1/1 | — | — | 1/1 | No comparator studies with similar treatment groups |
| 0/1 | 0/1 | — | — | 1/1 | |||
| ASC | |||||||
| Gregorio 2001 [33] | UDCA | — | — | 3/3 | — | — | No endpoint is reported for both treatment groups |
| Prednisolone ± UDCA ± AZA | — | 20/23 | — | — | — |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Freedman, B.L.; Danford, C.J.; Patwardhan, V.; Bonder, A. Treatment of Overlap Syndromes in Autoimmune Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051449
Freedman BL, Danford CJ, Patwardhan V, Bonder A. Treatment of Overlap Syndromes in Autoimmune Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(5):1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051449
Chicago/Turabian StyleFreedman, Benjamin L., Christopher J. Danford, Vilas Patwardhan, and Alan Bonder. 2020. "Treatment of Overlap Syndromes in Autoimmune Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 5: 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051449
APA StyleFreedman, B. L., Danford, C. J., Patwardhan, V., & Bonder, A. (2020). Treatment of Overlap Syndromes in Autoimmune Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(5), 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051449





