Role of Viral Infections in the Pathogenesis of Sjögren’s Syndrome: Different Characteristics of Epstein-Barr Virus and HTLV-1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Viral Infection and Autoimmune Diseases (AIDs)
2.1. Possible Mechanism Triggered by Viral Infection in AIDs
2.2. The Relationship between Autoimmune Conditions and Viral Infection
3. EBV Infection and Sjögren’s Syndrome
3.1. Characteristics of the Infection Mechanism in EBV
3.2. Chronological Changes in the Interpretations of EBV Infection in SS
3.3. The Reactivation and Detection of EBV in SS
3.4. EBV-Mediated Pathogenesis Observed in SS
4. HTLV-1 Infection and SS
4.1. Retrovirus Infection (Other Than HTLV-1 Infection) and SS
4.2. Clinical and Epidemiological Findings of HTLV-1 Infection in SS
4.3. The Detection of HTLV-1 Genes and Proteins in SGs in SS
4.4. The Mode of HTLV-1 Infection in SS Salivary Glands
4.5. Immunological Modulation of HTLV-1 Infection in SS
5. Overview of the Involvement of Viruses in SS
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AhR | aryl hydrocarbon receptor |
| AID | autoimmune disease |
| APS | anti-phospholipid syndrome |
| ATL | adult T-cell leukemia |
| BCA | B cell-attracting |
| BLEL | benign lymphoepithelial lesion |
| CAEBV | chronic active EBV |
| CMV | cytomegalovirus |
| CXCL | C-X-C motif chemokine ligand |
| DILS | diffuse infiltrative lymphocytosis syndrome |
| EA | early antigen |
| EBER | EB encoding region |
| EBNA | EB nuclear antigen |
| EBV | Epstein-Barr virus |
| EBVCA | EBV capsid antigen |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| ELS | ectopic lymphoid structures |
| ESSDAI | EULAR Sjögren’s Syndrome Disease Activity Index |
| FasL | Fas ligand |
| GC | germinal center |
| GBS | Guillain-Barré Syndrome |
| HAART | highly active anti-retroviral therapy |
| HHV | human herpes virus |
| HIV | human immunodeficiency virus |
| HLA | human leukocyte antigen |
| HRV | human retrovirus |
| HTLV-1 | human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 |
| HRES | human endogenous retroviral sequence |
| ICAM | intracellular adhesion molecule |
| IFN | interferon |
| IHC | immunohistochemistry |
| IL | interleukin |
| IP | interferon-γ-inducible 10-kD protein |
| IRF | IFN-regulatory factor |
| ISH | in situ hybridization |
| LFA | lymphocyte function-associated antigen |
| LG | lacrimal gland |
| LSG | labial salivary gland |
| LMP | latent membrane protein |
| LPD | lymphoproliferative disorder |
| MALT | mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues |
| MAPK | mitogen activated protein kinase |
| MDA | melanoma differentiation associated gene |
| MHC | major histocompatibility complex |
| MNC | mononuclear cell |
| MTX | methotrexate |
| MZL | marginal zone lymphoma |
| NHL | non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma |
| NOD | nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain |
| NLR | (NOD)-like receptor |
| PAMP | pathogen-associated molecular pattern |
| pDC | plasmatoid dendritic cell |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| PCs | plasma cells |
| PVL | proviral load |
| RA | rheumatoid arthritis |
| RANTES | regulated on activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted |
| RF | rheumatoid factor |
| RIG-I | retinoic acid inducible gene-I |
| RLR | RIG-I-like receptor |
| RNA | ribonucleic acid |
| SG | salivary gland |
| SGEC | SG epithelial cell |
| SLE | systemic lupus erythematosus |
| SLS | SS-like syndrome |
| SS | Sjögren’s syndrome |
| TCDD | tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin |
| TCR | T-cell receptor |
| TEC | thymic epithelial cell |
| Tg | transgenic |
| TLR | toll-like receptor |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| TRX | thioredoxin |
| TUNEL | terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling |
| XIAP | X-chromosome-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein |
| WKAH | Wistar-King-Aptekman-Hokudai |
References
- Karameris, A.; Gorgoulis, V.; Iliopoulos, A.; Frangia, C.; Kontomerkos, T.; Ioakeimidis, D.; Kalogeropoulos, N.; Sfikakis, P.; Kanavaros, P. Detection of the Epstein Barr viral genome by an in situ hybridization method in salivary gland biopsies from patients with secondary Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 1992, 10, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; Takahashi, Y.; Yamamoto-Fukuda, T.; Horai, Y.; Nakashima, Y.; Arima, K.; Nakamura, T.; Koji, T.; Kawakami, A. Direct infection of primary salivary gland epithelial cells by human T lymphotropic virus type I in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ice, J.A.; Li, H.; Adrianto, I.; Lin, P.C.; Kelly, J.A.; Montgomery, C.G.; Lessard, C.J.; Moser, K.L. Genetics of Sjögren’s syndrome in the genome-wide association era. J. Autoimmun. 2012, 39, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, K.; Chen, H.; Sun, F.; Xu, J.; Wu, Z.; Li, P.; Zhang, L.; Du, Y.; Luan, H.; et al. A genome-wide association study in Han Chinese identifies a susceptibility locus for primary Sjögren’s syndrome at 7q11.23. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1361–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariette, X.; Criswell, L.A. Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; Kawakami, A.; Eguchi, K. Mechanisms of autoantibody production and the relationship between autoantibodies and the clinical manifestations in Sjögren’s syndrome. Transl. Res. 2006, 148, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimaru, N.; Arakaki, R.; Watanabe, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Miyazaki, K.; Hayashi, Y. Development of autoimmune exocrinopathy resembling Sjögren’s syndrome in estrogen-deficient mice of healthy background. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.; Choi, S.H.; Yoon, C.H.; Kim, M.K. Gut dysbiosis is prevailing in Sjögren’s syndrome and is related to dry eye severity. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Nakamura, H.; Takatani, A.; Umeda, M.; Horai, Y.; Kurushima, S.; Michitsuji, T.; Nakashima, Y.; Kawakami, A. Activation of Toll-like receptor 7 signaling in labial salivary glands of primary Sjögren’s syndrome patients. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2019, 196, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brauner, S.; Folkersen, L.; Kvarnström, M.; Meisgen, S.; Petersen, S.; Franzén-Malmros, M.; Mofors, J.; Brokstad, K.A.; Klareskog, L.; Jonsson, R.; et al. H1N1 vaccination in Sjögren’s syndrome triggers polyclonal B cell activation and promotes autoantibody production. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1755–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, J.R. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) reactivation and therapeutic inhibitors. J. Clin. Pathol. 2019, 7, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, F.; Smith, K.D.; Ozinsky, A.; Hawn, T.R.; Yi, E.C.; Goodlett, D.R.; Eng, J.K.; Akira, S.; Underhill, D.M.; Aderem, A. The innate immune response to bacterial flagellin is mediated by Toll-like receptor 5. Nature 2001, 410, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akira, S.; Takeda, K.; Kaisho, T. Toll-like receptors: Critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochud, P.Y.; Bochud, M.; Telenti, A.; Calandra, T. Innate immunogenetics: A tool for exploring new frontiers of host defence. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2007, 7, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchjorsen, J.; Jensen, S.B.; Malmgaard, L.; Rasmussen, S.B.; Weber, F.; Bowie, A.G.; Matikainen, S.; Paludan, S.R. Activation of innate defense against a paramyxovirus is mediated by RIG-I and TLR7 and TLR8 in a cell-type-specific manner. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 12944–12951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lund, J.M.; Alexopoulou, L.; Sato, A.; Karow, M.; Adams, N.C.; Gale, N.W.; Iwasaki, A.; Flavell, R.A. Recognition of single-stranded RNA viruses by Toll-like receptor 7. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 5598–5603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maria, N.I.; Steenwijk, E.C.; IJpma, A.S.; van Helden-Meeuwsen, C.G.; Vogelsang, P.; Beumer, W.; Brkic, Z.; van Daele, P.L.; van Hagen, P.M.; van der Spek, P.J.; et al. Contrasting expression pattern of RNA-sensing receptors TLR7, RIG-I and MDA5 in interferon-positive and interferon-negative patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, J.; Casabonne, D.; Newton, R. Coxsackie B virus serology and Type 1 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review of published case-control studies. Diabet. Med. 2004, 21, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aida, K.; Nishida, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Maruyama, T.; Shimada, A.; Awata, T.; Suzuki, M.; Shimura, H.; Takizawa, S.; Ichijo, M.; et al. RIG-I- and MDA5-initiated innate immunity linked with adaptive immunity accelerates beta-cell death in fulminant type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2011, 60, 884–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogawara, K.; Kuwabara, S.; Koga, M.; Mori, M.; Yuki, N.; Hattori, T. Anti-GM1b IgG antibody is associated with acute motor axonal neuropathy and Campylobacter jejuni infection. J. Neurol. Sci. 2003, 210, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uncini, A.; González-Bravo, D.C.; Acosta-Ampudia, Y.Y.; Ojeda, E.C.; Rodríguez, Y.; Monsalve, D.M.; Ramírez-Santana, C.; Vega, D.A.; Paipilla, D.; Torres, L.; et al. Clinical and nerve conduction features in Guillain-Barré syndrome associated with Zika virus infection in Cúcuta, Colombia. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 25, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Illescas-Montes, R.; Corona-Castro, C.C.; Melguizo-Rodríguez, L.; Ruiz, C.; Costela-Ruiz, V.J. Infectious processes and systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunology 2019, 158, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hod, T.; Zandman-Goddard, G.; Langevitz, P.; Rudnic, H.; Grossman, Z.; Rotman-Pikielny, P.; Levy, Y. Does parvovirus infection have a role in systemic lupus erythematosus? Immunol. Res. 2017, 65, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, M.; Sauce, D.; Deback, C.; Arnaud, L.; Mathian, A.; Miyara, M.; Boutolleau, D.; Parizot, C.; Dorgham, K.; Papagno, L.; et al. Exhausted cytotoxic control of Epstein-Barr virus in human lupus. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørgensen, K.T.; Wiik, A.; Pedersen, M.; Hedegaard, C.J.; Vestergaard, B.F.; Gislefoss, R.E.; Kvien, T.K.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Bendtzen, K.; Frisch, M. Cytokines, autoantibodies and viral antibodies in premorbid and postdiagnostic sera from patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Case-control study nested in a cohort of Norwegian blood donors. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwakura, Y.; Tosu, M.; Yoshida, E.; Takiguchi, M.; Sato, K.; Kitajima, I.; Nishioka, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Takeda, T.; Hatanaka, M. Induction of inflammatory arthropathy resembling rheumatoid arthritis in mice transgenic for HTLV-I. Science 1991, 253, 1026–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Sekiguchi, T.; Itagaki, K.; Saijo, S.; Iwakura, Y. Inflammatory polyarthritis in mice transgenic for human T cell leukemia virus type I. Arthritis Rheum. 1993, 36, 1612–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, B.; Gay, R.E.; Huang, G.Q.; Fassbender, H.G.; Gay, S. Immunohistochemical localization of HTLV-I p19- and p24-related antigens in synovial joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Am. J. Pathol. 1989, 35, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Umekita, K.; Umeki, K.; Miyauchi, S.; Ueno, S.; Kubo, K.; Kusumoto, N.; Takajo, I.; Nagatomo, Y.; Okayama, A. Use of anti-tumor necrosis factor biologics in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis does not change human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 markers: A case series. Mod. Rheumatol. 2015, 25, 794–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Fukui, S.; Umekita, K.; Miyamoto, J.; Umeda, M.; Nishino, A.; Okada, A.; Koga, T.; Kawashiri, S.Y.; Iwamoto, N.; et al. Brief report: Attenuated effectiveness of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors for anti-human T lymphotropic virus type I antibody-positive rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, G.; Pearson, G.; Nadkarni, J.S.; Nadkarni, J.J.; Klein, E.; Henle, G.; Henle, W.; Clifford, P. Relation between Epstein-Barr viral and cell membrane immunofluorescence of Burkitt tumor cells. I. Dependence of cell membrane immunofluorescence on presence of EB virus. J. Exp. Med. 1968, 128, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lam, W.K.J.; Jiang, P.; Chan, K.C.A.; Cheng, S.H.; Zhang, H.; Peng, W.; Tse, O.Y.O.; Tong, Y.K.; Gai, W.; Zee, B.C.Y.; et al. Sequencing-based counting and size profiling of plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA enhance population screening of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rahman, M.A.; Kingsley, L.A.; Atchison, R.W.; Belle, S.; Breinig, M.C.; Ho, M.; Rinaldo, C.R., Jr. Reactivation of Epstein-Barr virus during early infection with human immunodeficiency virus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1991, 29, 1215–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meijer, E.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.C.; Thijsen, S.F.; Dekker, A.W.; Verdonck, L.F. Increased incidence of EBV-associated lymphoproliferative disorders after allogeneic stem cell transplantation from matched unrelated donors due to a change of T cell depletion technique. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2002, 29, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katsuyama, T.; Sada, K.E.; Yan, M.; Zeggar, S.; Hiramatsu, S.; Miyawaki, Y.; Ohashi, K.; Morishita, M.; Watanabe, H.; Katsuyama, E.; et al. Prognostic factors of methotrexate-associated lymphoproliferative disorders associated with rheumatoid arthritis and plausible application of biological agents. Mod. Rheumatol. 2017, 27, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dojcinov, S.D.; Fend, F.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L. EBV-positive lymphoproliferations of B- T- and NK-cell derivation in non-immunocompromised hosts. Pathogens 2018, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, A.G.; Gaffy, C.B.; Weseli, J.R.; Gorres, K.L. Inhibition of Epstein-Barr virus lytic reactivation by the atypical antipsychotic drug clozapine. Viruses 2019, 11, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Gregory, C.; Sample, C.; Rowe, M.; Liebowitz, D.; Murray, R.; Rickinson, A.; Kieff, E. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein (LMP1) and nuclear proteins 2 and 3C are effectors of phenotypic changes in B lymphocytes: EBNA-2 and LMP1 cooperatively induce CD23. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 2309–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murata, T.; Sato, Y.; Kimura, H. Modes of infection and oncogenesis by the Epstein-Barr virus. Rev. Med. Virol. 2014, 24, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawandar, D.M.; Ohashi, M.; Djavadian, R.; Barlow, E.; Makielski, K.; Ali, A.; Lee, D.; Lambert, P.F.; Johannsen, E.; Kenney, S.C. Differentiation-dependent LMP1 expression is required for efficient lytic Epstein-Barr virus reactivation in epithelial cells. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e02438-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venables, P.J.; Ross, M.G.; Charles, P.J.; Melsom, R.D.; Griffiths, P.D.; Maini, R.N. A seroepidemiological study of cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus in rheumatoid arthritis and sicca syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1985, 44, 742–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fox, R.I.; Pearson, G.; Vaughan, J.H. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus-associated antigens and DNA in salivary gland biopsies from patients with Sjogren’s syndrome. J. Immunol. 1986, 137, 3162–3168. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaoka, K.; Miyasaka, N.; Yamamoto, K. Possible involvement of Epstein-Barr virus in polyclonal B cell activation in Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1988, 31, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, I.; Servenius, B.; Compton, T.; Fox, R.I. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus DNA by polymerase chain reaction in blood and tissue biopsies from patients with Sjogren’s syndrome. J. Exp. Med. 1989, 169, 2191–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Venables, P.J.; Teo, C.G.; Baboonian, C.; Griffin, B.E.; Hughes, R.A. Persistence of Epstein-Barr virus in salivary gland biopsies from healthy individuals and patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1989, 75, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mariette, X.; Gozlan, J.; Clerc, D.; Bisson, M.; Morinet, F. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus DNA by in situ hybridization and polymerase chain reaction in salivary gland biopsy specimens from patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Am. J. Med. 1991, 90, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflugfelder, S.C.; Tseng, S.C.; Pepose, J.S.; Fletcher, M.A.; Klimas, N.; Feuer, W. Epstein-Barr virus infection and immunologic dysfunction in patients with aqueous tear deficiency. Ophthalmology 1990, 97, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, I.; Shimuta, M.; Terauchi, K.; Tsubota, K.; Yodoi, J.; Miyasaka, N. Increased expression of human thioredoxin/adult T cell leukemia-derived factor in Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1996, 39, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitland, N.; Flint, S.; Scully, C.; Crean, S.J. Detection of cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus in labial salivary glands in Sjogren’s syndrome and non-specific sialadenitis. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 1995, 24, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haneji, N.; Nakamura, T.; Takio, K.; Yanagi, K.; Higashiyama, H.; Saito, I.; Noji, S.; Sugino, H.; Hayashi, Y. Identification of alpha-fodrin as a candidate autoantigen in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Science 1997, 276, 604–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiuchi, M.; Yamano, S.; Inoue, H.; Ishii, J.; Nagata, Y.; Adachi, H.; Ono, M.; Renard, J.N.; Mizuno, F.; Hayashi, Y.; et al. Possible involvement of IL-12 expression by Epstein-Barr virus in Sjögren syndrome. J. Clin. Pathol. 1999, 52, 833–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Royer, B.; Cazals-Hatem, D.; Sibilia, J.; Agbalika, F.; Cayuela, J.M.; Soussi, T.; Maloisel, F.; Clauvel, J.P.; Brouet, J.C.; Mariette, X. Lymphomas in patients with Sjogren’s syndrome are marginal zone B-cell neoplasms, arise in diverse extranodal and nodal sites, and are not associated with viruses. Blood 1997, 90, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pasoto, S.G.; Natalino, R.R.; Chakkour, H.P.; Viana Vdos, S.; Bueno, C.; Leon, E.P.; Vendramini, M.B.; Neto, M.L.; Bonfa, E. EBV reactivation serological profile in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: An underlying trigger of active articular involvement? Rheumatol. Int. 2013, 33, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, H.; Mishima, K.; Yamamoto-Yoshida, S.; Ushikoshi-Nakayama, R.; Nakagawa, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Ryo, K.; Ide, F.; Saito, I. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated induction of EBV reactivation as a risk factor for Sjögren’s syndrome. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 4654–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fox, R.I.; Chilton, T.; Scott, S.; Benton, L.; Howell, F.V.; Vaughan, J.H. Potential role of Epstein-Barr virus in Sjögren’s syndrome. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 1987, 13, 275–292. [Google Scholar]
- Origgi, L.; Hu, C.; Bertetti, E.; Asero, R.; D’Agostino, P.; Radelli, L.; Riboldi, P. Antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus in primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Boll. Ist. Sieroter. Milan. 1988, 67, 265–274. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, N.; Harada, S.; Miyasaka, N.; Oya, A.; Yanagi, K. Analysis of antibody titers to Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigens in sera of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome and with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Infect. Dis. 1991, 164, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiGiuseppe, J.A.; Wu, T.C.; Corio, R.L. Analysis of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNA 1 expression in benign lymphoepithelial salivary gland lesions. Mod. Pathol. 1994, 7, 555–559. [Google Scholar]
- Merne, M.E.; Syrjänen, S.M. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus in salivary gland specimens from Sjögren’s syndrome patients. Laryngoscope 1996, 106, 1534–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croia, C.; Astorri, E.; Murray-Brown, W.; Willis, A.; Brokstad, K.A.; Sutcliffe, N.; Piper, K.; Jonsson, R.; Tappuni, A.R.; Pitzalis, C.; et al. Implication of Epstein-Barr virus infection in disease-specific autoreactive B cell activation in ectopic lymphoid structures of Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 2545–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackrides, N.; Campuzano-Zuluaga, G.; Maque-Acosta, Y.; Moul, A.; Hijazi, N.; Ikpatt, F.O.; Levy, R.; Verdun, R.E.; Kunkalla, K.; Natkunam, Y.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus-positive follicular lymphoma. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 30, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fox, R.I.; Howell, F.V. Reactivation of Epstein-Barr virus in Sjögren’s syndrome. Ric. Clin. Lab. 1987, 17, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fox, R.I.; Saito, I.; Chan, E.K.; Josephs, S.; Salahuddin, S.Z.; Ahlashi, D.V.; Staal, F.W.; Gallo, R.; Pei-Ping, H.; Le, C.S. Viral genomes in lymphomas of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. J. Autoimmun. 1989, 2, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.A.; Lamey, P.J.; Jarrett, R.F.; Onions, D.E. A model to study viral and cytokine involvement in Sjögren’s syndrome. Autoimmunity 1994, 18, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newkirk, M.M.; Shiroky, J.B.; Johnson, N.; Danoff, D.; Isenberg, D.A.; Shustik, C.; Pearson, G.R. Rheumatic disease patients, prone to Sjögren’s syndrome and/or lymphoma, mount an antibody response to BHRF1, the Epstein-Barr viral homologue of BCL-2. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1996, 35, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whittingham, S.; McNeilage, L.J.; Mackay, I.R. Epstein-Barr virus as an etiological agent in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Med. Hypotheses. 1987, 22, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venables, P.J.; Baboonian, C.; Maini, R.N. Normal serologic response to Epstein-Barr virus in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1989, 32, 811–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagasaki, M.; Morikawa, S.; Harada, T.; Miyasaka, N. A novel EBV-related nucleo-cytoplasmic antigen in a null cell-line (HLN-STL-C) reactive to antibodies in the sera from patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. J. Autoimmun. 1989, 2, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateishi, M.; Saito, I.; Yamamoto, K.; Miyasaka, N. Spontaneous production of Epstein-Barr virus by B lymphoblastoid cell lines obtained from patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Possible involvement of a novel strain of Epstein-Barr virus in disease pathogenesis. Arthritis Rheum. 1993, 36, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyasaka, N.; Saito, I.; Haruta, J. Possible involvement of Epstein-Barr virus in the pathogenesis of Sjogren’s syndrome. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1994, 72, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, H.; Tsubota, K.; Ono, M.; Kizu, Y.; Mizuno, F.; Takada, K.; Yamada, K.; Yanagi, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Saito, I. Possible involvement of EBV-mediated alpha-fodrin cleavage for organ-specific autoantigen in Sjogren’s syndrome. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 5801–5809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang’ondu, R.; Teal, S.; Park, R.; Heston, L.; Delecluse, H.; Miller, G. DNA damage signaling is induced in the absence of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) lytic DNA replication and in response to expression of ZEBRA. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, Y.; Inoue, H.; Yamada, K.; Higashiyama, H.; Mishima, K.; Kizu, Y.; Takeda, I.; Mizuno, F.; Hayashi, Y.; Saito, I. Activation of Epstein-Barr virus by saliva from Sjogren’s syndrome patients. Immunology 2004, 111, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomonsson, S.; Jonsson, M.V.; Skarstein, K.; Brokstad, K.A.; Hjelmström, P.; Wahren-Herlenius, M.; Jonsson, R. Cellular basis of ectopic germinal center formation and autoantibody production in the target organ of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 3187–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sène, D.; Ismael, S.; Forien, M.; Charlotte, F.; Kaci, R.; Cacoub, P.; Diallo, A.; Dieudé, P.; Lioté, F. Ectopic germinal center-like structures in minor salivary gland biopsy tissue predict lymphoma occurrence in patients with primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiødt, M.; Greenspan, D.; Daniels, T.E.; Nelson, J.; Leggott, P.J.; Wara, D.W.; Greenspan, J.S. Parotid gland enlargement and xerostomia associated with labial sialadenitis in HIV-infected patients. J. Autoimmun. 1989, 2, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garry, R.F.; Fermin, C.D.; Hart, D.J.; Alexander, S.S.; Donehower, L.A.; Luo-Zhang, H. Detection of a human intracisternal A-type retroviral particle antigenically related to HIV. Science 1990, 250, 1127–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talal, N.; Dauphinée, M.J.; Dang, H.; Alexander, S.S.; Hart, D.J.; Garry, R.F. Detection of serum antibodies to retroviral proteins in patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome (autoimmune exocrinopathy). Arthritis Rheum. 1990, 33, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talal, N. Immunologic and viral factors in Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 1990, 8, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Itescu, S.; Brancato, L.J.; Buxbaum, J.; Gregersen, P.K.; Rizk, C.C.; Croxson, T.S.; Solomon, G.E.; Winchester, R. A diffuse infiltrative CD8 lymphocytosis syndrome in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection: A host immune response associated with HLA-DR5. Ann. Intern. Med. 1990, 112, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itescu, S. Diffuse infiltrative lymphocytosis syndrome in human immunodeficiency virus infection—A Sjögren’s-like disease. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 1991, 17, 99–115. [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer, E.; Itescu, S.; Winchester, R. Characterization of the primary structure of T cell receptor beta chains in cells infiltrating the salivary gland in the sicca syndrome of HIV-1 infection. Evidence of antigen-driven clonal selection suggested by restricted combinations of V beta J beta gene segment usage and shared somatically encoded amino acid residues. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 92, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kordossis, T.; Paikos, S.; Aroni, K.; Kitsanta, P.; Dimitrakopoulos, A.; Kavouklis, E.; Alevizou, V.; Kyriaki, P.; Skopouli, F.N.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Prevalence of Sjögren’s-like syndrome in a cohort of HIV-1-positive patients: Descriptive pathology and immunopathology. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1998, 37, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, F.M.; Cohen, P.R.; Jumshyd, J.; Reveille, J.D.; Williams, F.M.; Cohen, P.R.; Jumshyd, J.; Reveille, J.D. Prevalence of the diffuse infiltrative lymphocytosis syndrome among human immunodeficiency virus type 1-positive outpatients. Arthritis Rheum. 1998, 41, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamano, S.; Renard, J.N.; Mizuno, F.; Narita, Y.; Uchida, Y.; Higashiyama, H.; Sakurai, H.; Saito, I. Retrovirus in salivary glands from patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. J. Clin. Pathol. 1997, 50, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rigby, S.P.; Griffiths, D.J.; Weiss, R.A.; Venables, P.J. Human retrovirus-5 proviral DNA is rarely detected in salivary gland biopsy tissues from patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40, 2016–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panayiotakopoulos, G.D.; Aroni, K.; Kyriaki, D.; Paikos, S.; Vouyioukas, N.; Vlachos, A.; Kontos, A.N.; Kordossis, T. Paucity of Sjogren-like syndrome in a cohort of HIV-1-positive patients in the HAART era. Part II. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2003, 42, 1164–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vitali, C.; Bombardieri, S.; Jonsson, R.; Moutsopoulos, H.M.; Alexander, E.L.; Carsons, S.E.; Daniels, T.E.; Fox, P.C.; Fox, R.I.; Kassan, S.S.; et al. Classification criteria for Sjögren’s syndrome: A revised version of the European criteria proposed by the American-European Consensus Group. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2002, 61, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, M.; Inoue, J.; Fujisawa, J.; Seiki, M. Molecular mechanisms of regulation of HTLV-1 gene expression and its association with leukemogenesis. Genome 1989, 31, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takatsuki, K. Discovery of adult T-cell leukemia. Retrovirology 2005, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, M.; Miyoshi, I.; Hinuma, Y. Isolation and characterization of retrovirus from cell lines of human adult T-cell leukemia and its implication in the disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 2031–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeang, K.T.; Widen, S.G.; Semmes, O.J., 4th; Wilson, S.H. HTLV-I trans-activator protein, tax, is a trans-repressor of the human beta-polymerase gene. Science 1990, 247, 1082–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osame, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Usuku, K.; Izumo, S.; Ijichi, N.; Amitani, H.; Tara, M.; Igata, A. Chronic progressive myelopathy associated with elevated antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type I and adult T-cell leukemialike cells. Ann. Neurol. 1987, 21, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izumo, S.; Umehara, F.; Osame, M. HTLV-I-associated myelopathy. Neuropathology 2000, 20, S65–S68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamoi, K.; Mochizuki, M. HTLV infection and the eye. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2012, 23, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, A.; Ikeda, E.; Mochizuki, M.; Matsuoka, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Sawada, T.; Yamane, S.; Tokudome, S.; Watanabe, T. Provirus load in patients with human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 uveitis correlates with precedent Graves’ disease and disease activities. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1998, 89, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, M.; Kitaichi, M.; Ikeda, A.; Nagai, S.; Izumi, T. Chronic bronchioloalveolitis associated with human T-cell lymphotrophic virus type I infection. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 1998, 4, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto-Taguchi, N.; Satou, Y.; Miyazato, P.; Ohshima, K.; Nakagawa, M.; Katagiri, K.; Kinashi, T.; Matsuoka, M. HTLV-1 bZIP factor induces inflammation through labile Foxp3 expression. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, H.; Kawakami, A.; Tominaga, M.; Hida, A.; Yamasaki, S.; Migita, K.; Kawabe, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Eguchi, K. Relationship between Sjögren’s syndrome and human T-lymphotropic virus type I infection: Follow-up study of 83 patients. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 2000, 135, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, M.; Nakamura, H.; Nakamura, T.; Eguchi, K.; Nakamura, T. Sjögren’s syndrome (SS) in patients with human T cell leukemia virus I associated myelopathy: Paradoxical features of the major salivary glands compared to classical SS. J. Rheumatol. 1999, 26, 2609–2614. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, H.; Takagi, Y.; Kawakami, A.; Ida, H.; Nakamura, T.; Nakamura, T.; Eguchi, K. HTLV-I infection results in resistance toward salivary gland destruction of Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2008, 26, 653–655. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cruz, B.A.; Catalan-Soares, B.; Proietti, F. Higher prevalence of fibromyalgia in patients infected with human T cell lymphotropic virus type, I.J. Rheumatol. 2006, 33, 2300–2303. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, C.; Thoma-Kress, A.K. Molecular Mechanisms of HTLV-1 Cell-to-Cell Transmission. Viruses 2016, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, C.M.; Santos, S.; Dourado, A.; Carvalho, N.B.; Bittencourt, V.; Lessa, M.M.; Siqueira, I.; Carvalho, E.M. Association of sicca syndrome with proviral load and proinflammatory cytokines in HTLV-1 infection. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 8402059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kakugawa, T.; Sakamoto, N.; Ishimoto, H.; Shimizu, T.; Nakamura, H.; Nawata, A.; Ito, C.; Sato, S.; Hanaka, T.; Oda, K.; et al. Lymphocytic focus score is positively related to airway and interstitial lung diseases in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Respir. Med. 2018, 137, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shattles, W.G.; Brookes, S.M.; Venables, P.J.; Clark, D.A.; Maini, R.N. Expression of antigen reactive with a monoclonal antibody to HTLV-1 P19 in salivary glands in Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1992, 89, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariette, X.; Agbalika, F.; Daniel, M.T.; Bisson, M.; Lagrange, P.; Brouet, J.C.; Morinet, F. Detection of human T lymphotropic virus type I tax gene in salivary gland epithelium from two patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1993, 36, 1423–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumida, T.; Yonaha, F.; Maeda, T.; Kita, Y.; Iwamoto, I.; Koike, T.; Yoshida, S. Expression of sequences homologous to HTLV-I tax gene in the labial salivary glands of Japanese patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1994, 37, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amft, N.; Bowman, S.J. Chemokines and cell trafficking in Sjögren’s syndrome. Scand. J. Immunol. 2001, 54, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terada, K.; Katamine, S.; Eguchi, K.; Moriuchi, R.; Kita, M.; Shimada, H.; Yamashita, I.; Iwata, K.; Tsuji, Y.; Nagataki, S. Antibodies to HTLV-I in Sjögren’s syndrome. Lancet 1994, 344, 1116–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satou, Y.; Yasunaga, J.; Zhao, T.; Yoshida, M.; Miyazato, P.; Takai, K.; Shimizu, K.; Ohshima, K.; Green, P.L.; Ohkura, N.; et al. HTLV-1 bZIP factor induces T-cell lymphoma and systemic inflammation in vivo. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1001274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchi, N.; Miura, K.; Tsukiyama, T.; Sasaki, D.; Ishihara, K.; Tsuruda, K.; Hasegawa, H.; Miura, S.; Yanagihara, K.; Masuzaki, H. Natural course of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 proviral DNA levels in carriers during pregnancy. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 217, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguchi, K.; Matsuoka, N.; Ida, H.; Nakashima, M.; Sakai, M.; Sakito, S.; Kawakami, A.; Terada, K.; Shimada, H.; Kawabe, Y.; et al. Primary Sjögren’s syndrome with antibodies to HTLV-I: Clinical and laboratory features. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1992, 51, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartier, L.; Castillo, J.L.; Cea, J.G.; Villagra, R. Chronic dacryosialadenitis in HTLV I associated myelopathy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1995, 58, 244–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, H.; Eguchi, K.; Nakamura, T.; Mizokami, A.; Shirabe, S.; Kawakami, A.; Matsuoka, N.; Migita, K.; Kawabe, Y.; Nagataki, S. High prevalence of Sjögren’s syndrome in patients with HTLV-I associated myelopathy. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1997, 56, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hida, A.; Imaizumi, M.; Sera, N.; Akahoshi, M.; Soda, M.; Maeda, R.; Nakashima, E.; Nakamura, H.; Ida, H.; Kawakami, A.; et al. Association of human T lymphotropic virus type I with Sjogren syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 2056–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, H.; Shimizu, T.; Takagi, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Horai, Y.; Nakashima, Y.; Sato, S.; Shiraishi, H.; Nakamura, T.; Fukuoka, J.; et al. Reevaluation for clinical manifestations of HTLV-I-seropositive patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2015, 16, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Tadokoro, K. Current prevalence of HTLV-1 in Japan as determined by screening of blood donors. J. Med. Virol. 2012, 84, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, M.; Iwanaga, M.; Sagara, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Okuma, K.; Hamaguchi, I. Incidence of human T-lymphotropic virus 1 infection in adolescent and adult blood donors in Japan: A nationwide retrospective cohort analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, D.A.D.; Casseb, J.; de Oliveira, A.C.P.; Bussoloti Filho, I.; de Sousa, S.C.O.M.; Ortega, K.L. Prevalence of Sjögren’s syndrome in Brazilian patients infected with human T-cell lymphotropic virus. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2017, 46, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigby, S.P.; Cooke, S.P.; Weerasinghe, D.; Venables, P.J. Absence of HTLV-1 tax in Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1996, 39, 1609–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohyama, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Hara, H.; Shinohara, M.; Sasaki, M.; Ikebe-Hiroki, A.; Mouri, T.; Tsunawaki, S.; Abe, K.; Shirasuna, K.; et al. Accumulation of human T lymphotropic virus type I-infected T cells in the salivary glands of patients with human T lymphotropic virus type I-associated Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1998, 41, 1972–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizokami, A.; Eguchi, K.; Moriuchi, R.; Futsuki, Y.; Terada, K.; Nakamura, H.; Miyamoto, T.; Katamine, S. Low copy numbers of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) tax-like DNA detected in the salivary gland of seronegative patients with Sjögren’s syndrome in an HTLV-I endemic area. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 1998, 27, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangy, F.; Ossondo, M.; Vernant, J.C.; Smadja, D.; Blétry, O.; Baglin, A.C.; Ozden, S. Human T cell leukemia virus type I expression in salivary glands of infected patients. J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 179, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, M.; Nakamura, S.; Ohyama, Y.; Shinohara, M.; Ezaki, I.; Hara, H.; Kadena, T.; Kishihara, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Nomoto, K.; et al. Accumulation of common T cell clonotypes in the salivary glands of patients with human T lymphotropic virus type I-associated and idiopathic Sjögren’s syndrome. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 2823–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mariette, X.; Agbalika, F.; Zucker-Franklin, D.; Clerc, D.; Janin, A.; Cherot, P.; Brouet, J.C. Detection of the tax gene of HTLV-I in labial salivary glands from patients with Sjögren’s syndrome and other diseases of the oral cavity. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2000, 18, 341–347. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.J.; Lee, J.S.; Shin, M.G.; Tanaka, Y.; Park, D.J.; Kim, T.J.; Park, Y.W.; Lee, S.S. Detection of HTLV-1 in the labial salivary glands of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome: A distinct clinical subgroup? J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Hasegawa, H.; Sasaki, D.; Takatani, A.; Shimizu, T.; Kurushima, S.; Horai, Y.; Nakashima, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Fukuoka, J.; et al. Detection of human T lymphotropic virus type-I bZIP factor and tax in the salivary glands of Sjögren’s syndrome patients. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2018, 36 (Suppl. 112), 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Igakura, T.; Stinchcombe, J.C.; Goon, P.K.; Taylor, G.P.; Weber, J.N.; Griffiths, G.M.; Tanaka, Y.; Osame, M.; Bangham, C.R. Spread of HTLV-I between lymphocytes by virus-induced polarization of the cytoskeleton. Science 2003, 299, 1713–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pais-Correia, A.M.; Sachse, M.; Guadagnini, S.; Robbiati, V.; Lasserre, R.; Gessain, A.; Gout, O.; Alcover, A.; Thoulouze, M.I. Biofilm-like extracellular viral assemblies mediate HTLV-1 cell-to-cell transmission at virological synapses. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoulouze, M.I.; Alcover, A. Can viruses form biofilms? Trends Microbiol. 2011, 19, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Prooyen, N.; Gold, H.; Andresen, V.; Schwartz, O.; Jones, K.; Ruscetti, F.; Lockett, S.; Gudla, P.; Venzon, D.; Franchini, G. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 p8 protein increases cellular conduits and virus transmission. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 20738–20743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malbec, M.; Roesch, F.; Schwartz, O. A new role for the HTLV-1 p8 protein: Increasing intercellular conduits and viral cell-to-cell transmission. Viruses 2011, 3, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, H.; Shimizu, T.; Takatani, A.; Suematsu, T.; Nakamura, T.; Kawakami, A. Initial human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 infection of the salivary gland epithelial cells requires a biofilm-like structure. Virus Res. 2019, 269, 197643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J.E.; Hinrichs, S.H.; Vogel, J.; Jay, G. Exocrinopathy resembling Sjögren’s syndrome in HTLV-1 tax transgenic mice. Nature 1989, 341, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, H.; Ikeda, H.; Ishizu, A.; Nakamaru, Y.; Sugaya, T.; Kikuchi, K.; Yamada, S.; Wakisaka, A.; Kasai, N.; Koike, T.; et al. A wide spectrum of collagen vascular and autoimmune diseases in transgenic rats carrying the env-pX gene of human T lymphocyte virus type, I. Int. Immunol. 1997, 9, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshiki, T.; Ikeda, H.; Tomaru, U.; Ohya, O.; Kasai, T.; Yamashita, I.; Morita, K.; Yamazaki, H.; Ishizu, A.; Nakamaru, Y.; et al. Models of HTLV-I-induced diseases. Infectious transmission of HTLV-I in inbred rats and HTVL-I env-pX transgenic rats. Leukemia 1997, 11 (Suppl. 3), 245–246. [Google Scholar]
- Gavrieli, Y.; Sherman, Y.; Ben-Sasson, S.A. Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J. Cell Biol. 1992, 119, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, N.; Yonehara, S.; Ishii, A.; Yonehara, M.; Mizushima, S.; Sameshima, M.; Hase, A.; Seto, Y.; Nagata, S. The polypeptide encoded by the cDNA for human cell surface antigen Fas can mediate apoptosis. Cell 1991, 66, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, T.; Nagata, S. Purification and characterization of the Fas-ligand that induces apoptosis. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 179, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Horai, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Kawakami, A. Modulation of apoptosis by cytotoxic mediators and cell-survival molecules in Sjögren’s syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, H.; Kawakami, A.; Tominaga, M.; Migita, K.; Kawabe, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Eguchi, K. Expression of CD40/CD40 ligand and Bcl-2 family proteins in labial salivary glands of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Lab. Investig. 1999, 79, 261–269. [Google Scholar]
- Tsukahara, T.; Kannagi, M.; Ohashi, T.; Kato, H.; Arai, M.; Nunez, G.; Iwanaga, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Ohtani, K.; Nakamura, M.; et al. Induction of Bcl-x(L) expression by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax through NF-kappaB in apoptosis-resistant T-cell transfectants with Tax. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 7981–7987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawakami, A.; Nakashima, T.; Sakai, H.; Urayama, S.; Yamasaki, S.; Hida, A.; Tsuboi, M.; Nakamura, H.; Ida, H.; Migita, K.; et al. Inhibition of caspase cascade by HTLV-I tax through induction of NF-kappaB nuclear translocation. Blood 1999, 94, 3847–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; Kawakami, A.; Yamasaki, S.; Kawabe, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Eguchi, K. Expression of mitogen activated protein kinases in labial salivary glands of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1999, 58, 382–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Kawakami, A.; Yamasaki, S.; Nakashima, T.; Kamachi, M.; Migita, K.; Kawabe, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Koji, T.; Hayashi, Y.; et al. Expression and function of X chromosome-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein in Sjögren’s syndrome. Lab. Investig. 2000, 80, 1421–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bohnhorst, J.Ø.; Bjørgan, M.B.; Thoen, J.E.; Natvig, J.B.; Thompson, K.M. Bm1-Bm5 classification of peripheral blood B cells reveals circulating germinal center founder cells in healthy individuals and disturbance in the B cell subpopulations in patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 3610–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legler, D.F.; Loetscher, M.; Roos, R.S.; Clark-Lewis, I.; Baggiolini, M.; Moser, B. B cell-attracting chemokine 1, a human CXC chemokine expressed in lymphoid tissues, selectively attracts B lymphocytes via BLR1/CXCR5. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 187, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghrenassia, E.; Martis, N.; Boyer, J.; Burel-Vandenbos, F.; Mekinian, A.; Coppo, P. The diffuse infiltrative lymphocytosis syndrome (DILS). A comprehensive review. J. Autoimmun. 2015, 59, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Iwamoto, N.; Horai, Y.; Takagi, Y.; Ichinose, K.; Kawashiri, S.Y.; Taguchi, J.; Hayashi, T.; Nakamura, T.; Kawakami, A. A case of adult T-cell leukemia presenting primary Sjögren’s syndrome-like symptoms. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 16, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shiboski, C.H.; Shiboski, S.C.; Seror, R.; Criswell, L.A.; Labetoulle, M.; Lietman, T.M.; Rasmussen, A.; Scofield, H.; Vitali, C.; Bowman, S.J.; et al. 2016 American College of Rheumatology/European League against Rheumatism Classification Criteria for Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: A consensus and data-driven methodology involving three international patient cohorts. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Ito, K.; Moritoyo, T.; Fujino, Y.; Masuda, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Mochizuki, M.; Izumo, S.; Osame, M.; Watanabe, T. Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 can infect primary rat retinal glial cells and induce gene expression of inflammatory cytokines. Curr. Eye Res 1997, 16, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, M.; Eguchi, K.; Terada, K.; Nakashima, M.; Yamashita, I.; Ida, H.; Kawabe, Y.; Aoyagi, T.; Takino, H.; Nakamura, T. Infection of human synovial cells by human T cell lymphotropic virus type I. Proliferation and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor production by synovial cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 92, 1957–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carvalho Barros, L.R.; Linhares-Lacerda, L.; Moreira-Ramos, K.; Ribeiro-Alves, M.; Machado Motta, M.C.; Bou-Habib, D.C.; Savino, W. HTLV-1-infected thymic epithelial cells convey the virus to CD4+ T lymphocytes. Immunobiology 2017, 222, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
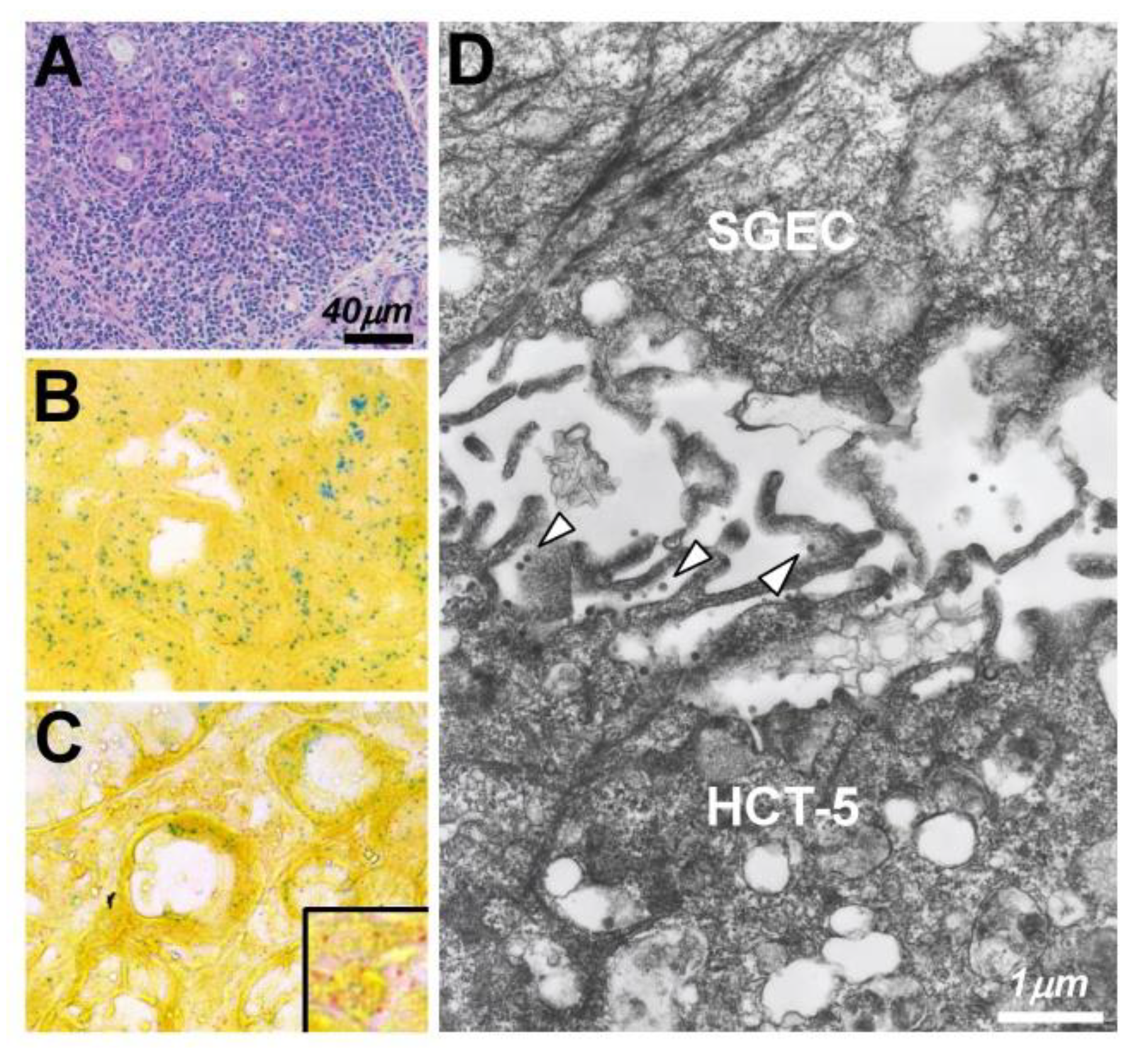
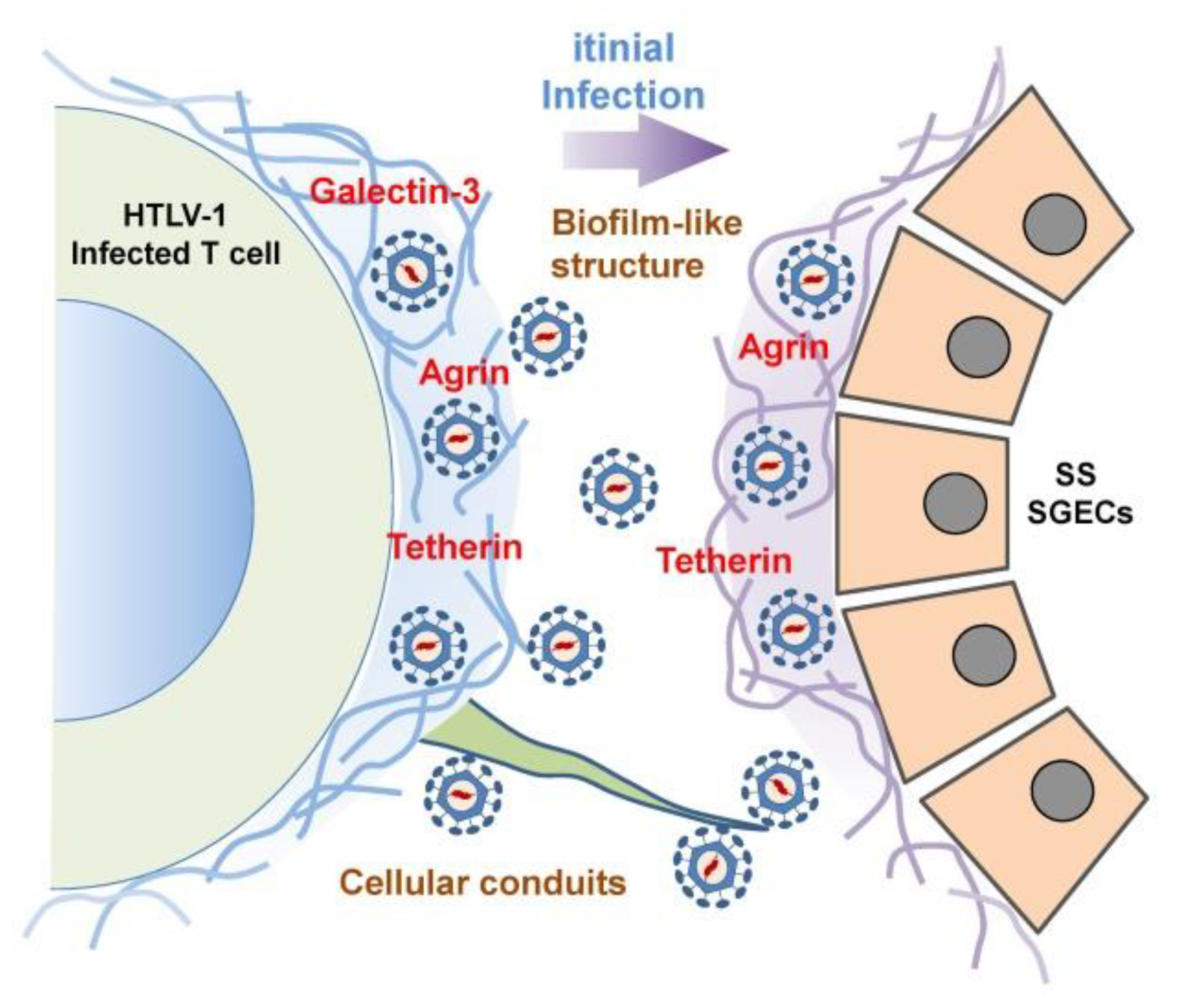
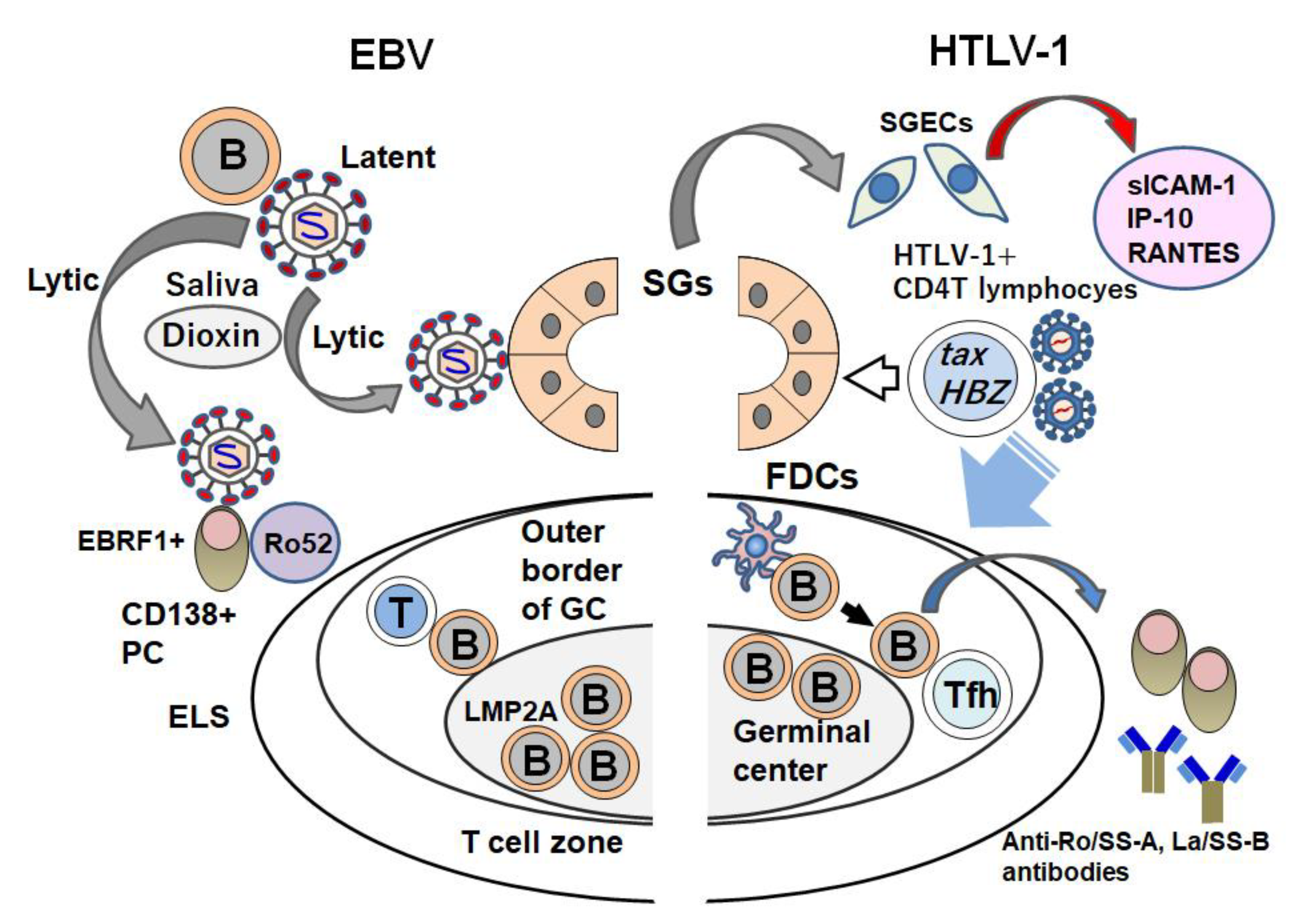
| Authors [Ref.] | Origin | Year | Detection | Key Points |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Venables [40] | UK | 1985 | Indirect IF | IgG antibody against EBVCA was detected in sicca syndrome patients, RA patients, and healthy subjects. |
| Fox [41] | USA | 1986 | Immunostaining, IB, slot hybridization | EA-D was detected in 8 of 14 SGs and EBVDNA was detected in 8 of 20 saliva samples from SS patients. |
| Yamaoka [42] | Japan | 1988 | Indirect IF | IgG and IgM antibodies against EBV capsid antigen and EBV excretion from the oropharynx were observed in SS patients. |
| Saito [43] | USA | 1989 | PCR | The usefulness of PCR was shown, revealing viral DNA in SG epithelial cells from SS patients. |
| Venables [44] | UK | 1989 | ISH, IF, immunostaining | EBVDNA was detected in SGs from 60% of healthy subjects and 17% of SS patients. |
| Mariette [45] | France | 1991 | ISH, PCR | A combination of ISH and PCR was introduced, showing a high positive rate in patients with SS. |
| Inoue [46] | Japan | 1991 | ELISA, IB | Elevated IgG antibody against EBNA antigens was detected in sera from SS patients. |
| Fox [45] | USA | 1989 | RFLP | Two SS patients with B-cell lymphoma showed an unusual RFLP pattern. |
| Tateishi [47] | Japan | 1993 | FCM, PCR | Massive EBV production was confirmed in an SS PBMC-derived B-cell line. |
| Newkirk [48] | Canada | 1996 | ELISA | Antibodies against early EBV peptides such as BHRF1 were detected in SS patients. |
| Merne [49] | Finland | 1996 | ISH, PCR | ISH detected EBVDNA in SGs from 19% of SS patients and 3% of controls. |
| Inoue [50] | Japan | 2001 | IF, RT-PCR, IB | ZEBRA mRNA in SGs from SS patients was observed, and EBV-activated lymphocyte mediated the production of 120-kDa alpha-fodrin. |
| Inoue [51] | Japan | 2012 | Luciferase assay | With the use of saliva from SS patients, dioxin augmented the transcription of BZLF1that stimulated conversion to the lytic phase in EBV. |
| Pasoto [52] | Brazil | 2013 | ELISA | Frequent anti-EA-D antibodies were observed in SS patients. |
| Croia [53] | UK | 2014 | RT-PCR, ISH, immunostaining | Affinity of lytic phase EBV toward PCs in ELS was shown. Perifollicular PCs showed reactivity toward Ro52. |
| Author [Ref. No] | Origin | Year | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Schiødt [75] | USA | 1989 | 9 patients with HIV-SGD showed parotid gland enlargement and 11 patients with xerostomia. CD8 T cells showed in LSGs. No EBV and CMV was detected. |
| Garry [76] | USA | 1990 | Particles of human intracisternal A-type retrovirus that were similar to HIV were observed in LSGs of SS patients. |
| Talal [77,78] | USA | 1990 | Antibodies against HIV-1 were detected in 30% of SS patients and 1 among 120 normal subjects. Seropositive SS patients reacted p24 (gag) only. |
| Itescu [79] | USA | 1990 | Among 17 HIV patients showed, 14 patients had xerostomia and 11 patients had abnormal Gallium uptake. CD8 cells in LSGs and HLA-DR5 were associated with these patients. |
| Itescu [80] | USA | 1991 | Concept of diffuse infiltrative lymphocytosis syndrome (DILS) in patients with HIV was released. CD8 T cell infiltration and involvement of exocrine glands and other tissues were shown. |
| Dwyer [81] | USA | 1993 | Sharing of the sequences of 59 beta-chains in 5 DILS patients was shown. Additionally, appearance of certain common V beta and J beta gene segments was found. Usage of TCR beta chains was different from primary SS patients. |
| Kordossis [82] | Greece | 1998 | The prevalence of SLS in HIV-1-positive patients was 7.79%, in which 6 out of 14 patients showed sialadenitis with CD8 T cell dominancy. These patients had no anti-Ro/SS-A and La/SS-B antibodies but had hypergammaglobulinemia. |
| Williams [83] | USA | 1998 | Among 523 patients with HIV, 15 patients (3%) showed DILS with racial differences. DILS patients had high CD8 counts and clinical stage of DILS patients was less than non-DILS patients. |
| Yamano S [84] | Japan | 1997 | Sera from 33% SS patients reacted against p24 (gag) and LSGs from 47% SS patients reacted against anti-p24 monoclonal antibody. Additionally, A-type-like retroviral particles were detected by electron microscopy in LSGs from SS patients. |
| Rigby [85] | UK | 1997 | By nested PCR, 1 non-SS patient and 1 secondary SS patient showed positive for human retrovirus-5 (HRV-5) among 92 samples. Three different sequences of HRV-5 were 98% identical to originally detected sequence. |
| Panayiotakopoulos [86] | Greece | 2001 | Reduced prevalence of SLS after introduction of the highly active anti-retroviral therapy (HAART) was detected with only 2 positive findings among 17 SGs biopsy. Prevalence of 7.8% in pre-HAART period disappeared after execution of HAART. |
| Authors [Ref.] | Origin | Year | Detection | Key Points |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green [98] | USA | 1989 | IB, IHC | Tax protein expression was detected in SGs and muscle of tax transgenic mice as a first mouse model of SS. |
| Shattles [99] | UK | 1992 | Indirect IF | HTLV-1 p19 was detected in 31% of epithelial cytoplasm of SS patients by using a monoclonal antibody specific for retrovirus. |
| Mariette [100] | France | 1993 | ISH, PCR | tax gene only was detected in 2/9 LSGs from SS patients, although these patients did not react to anti-HTLV-1 antibodies. |
| Sumida [101] | Japan | 1994 | RT-PCR | tax gene only was detected in 4 of 14 LSGs from Japanese SS patients. The pXIV region sequence had homology to MT-2 cells. |
| Terada [102] | Japan | 1994 | IB, PCR | Salivary IgA antibodies to SS patients with anti-HTLV-1 antibody and high prevalence of HTLV-1 in SS patients were observed. |
| Yamazaki [103] | Japan | 1997 | RT-PCR | Transgenic rats with env-pX gene showed chronic sialadenitis as well as arthritis, vasculitis, and polymyositis. |
| Ohyama [104] | Japan | 1998 | PCR, in situ PCR hybridization | Extracted DNA from HTLV-1 seropositive SS contained full proviral DNA. Infiltrating T cells had proviral DNA in the nucleus. |
| Tangy [105] | France | 1999 | PCR, ISH | Expression of tax was observed in SGs of HTLV-1-seropositive SS and HTLV-1-seronegative SS patients and sicca subjects. |
| Sasaki [106] | Japan | 2000 | PCR, SSCP, sequencing of cDNA | Use of TCR Vβ5.2, 6, and 7 in LSGs from HTLV-1-seropositive SS patients. Vβ7 with conserved AA motif was observed in these patients. |
| Mariette [107] | France | 2000 | PCR | tax gene was detected in LSGs from 30% of SS patients, 28% of patients with inflammatory diseases, and 4% of healthy subjects. |
| Lee [108] | Korea | 2012 | PCR, nested PCR, IHC | tax gene but not pX, p19 or pol was observed in PBMCs from 3.8% of SS patients. p19 and Tax were expressed in LSGs. |
| Nakamura [109] | Japan | 2015 | In situ PCR, IF | Expressions of proviral DNA, Gag, and chemokines were observed on SGECs co-cultured with a HTLV-1-positive cell line. |
| Nakamura [110] | Japan | 2018 | Real-time PCR, ISH, IHC | In LSGs of HAM-SS, dominant tax and HBZ was observed with the expression of Foxp3 in LSGs from HAM-SS and ATL patients. |
| Nakamura [111] | Japan | 2019 | IF, EM | A biofilm-like structure but not virus synapses was involved in the transmission of HTLV-1 virions from HTLV-1-positive cells to SGECs. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakamura, H.; Shimizu, T.; Kawakami, A. Role of Viral Infections in the Pathogenesis of Sjögren’s Syndrome: Different Characteristics of Epstein-Barr Virus and HTLV-1. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1459. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051459
Nakamura H, Shimizu T, Kawakami A. Role of Viral Infections in the Pathogenesis of Sjögren’s Syndrome: Different Characteristics of Epstein-Barr Virus and HTLV-1. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(5):1459. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051459
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakamura, Hideki, Toshimasa Shimizu, and Atsushi Kawakami. 2020. "Role of Viral Infections in the Pathogenesis of Sjögren’s Syndrome: Different Characteristics of Epstein-Barr Virus and HTLV-1" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 5: 1459. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051459
APA StyleNakamura, H., Shimizu, T., & Kawakami, A. (2020). Role of Viral Infections in the Pathogenesis of Sjögren’s Syndrome: Different Characteristics of Epstein-Barr Virus and HTLV-1. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(5), 1459. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051459





