The Impact of Dysphagia in Myositis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Review
2.1.1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria in the Review
- Cohort: the article had to report on dysphagia in at least one subject with IIM. If the cohort included less than five subjects, it had to be stated that diagnostic criteria of definitive or probable IIM according to either Bohan and Peter [8,9], Griggs [10], Needham and Mastaglia [11], the European Neuromuscular Center [12] or the ACR/EULAR criteria [3] were met. If this was not the case, articles were only included if based on the information provided the current ACR/EULAR criteria [3] for definitive or probable IIM were met or if the diagnosis was confirmed by muscle biopsy.
- Topic: the articles had to report on at least one of the following topics:
- Epidemiology or prevalence of dysphagia in a population with a minimum of five subjects;
- Pathophysiology of dysphagia;
- Outcome of a patient cohort with dysphagia;
- Therapeutic effects on dysphagia or swallowing.
- Patients had other diseases associated with dysphagia, e.g., myasthenia gravis. However, this exclusion criterion was not applied to diseases associated with IIM such as rheumatological diseases in case of overlap syndromes;
- They exclusively reported on gastroesophageal reflux as manifestation of dysphagia;
- Dysphagia was reported exclusively as manifestation of structures distal to the esophagus;
- Conflicting results were reported within the article (e.g., differing prevalence rates).
2.1.2. Search Strategy
2.2. Meta-Analysis
2.2.1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria in the Meta-Analysis
2.2.2. Bias Risk in Individual Studies
2.2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Review
3.1.1. Epidemiology
3.1.1.1. Dysphagia and Disease Course
3.1.1.2. Factors Associated with Dysphagia
3.1.2. Pathophysiology
Inflammation of Swallowing Muscles
Dysphagia Pathology
3.1.3. Outcome
3.1.4. Therapy
Immunomodulatory Therapy
Therapy of Malignancy
Non-Pharmacological Interventional Therapy
Behavioral Therapy
3.2. Meta-Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sasegbon, A.; Hamdy, S. The anatomy and physiology of normal and abnormal swallowing in oropharyngeal dysphagia. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, S.M.; Martino, R. The normal swallow: Muscular and neurophysiological control. Otolaryngol. Clin. North Am. 2013, 46, 937–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottai, M.; Tjarnlund, A.; Santoni, G.; Werth, V.P.; Pilkington, C.; de Visser, M.; Alfredsson, L.; Amato, A.A.; Barohn, R.J.; Liang, M.H.; et al. EULAR/ACR classification criteria for adult and juvenile idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and their major subgroups: A methodology report. RMD Open 2017, 3, e000507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dziewas, R.; auf dem Brinke, M.; Birkmann, U.; Bräuer, G.; Busch, K.; Cerra, F.; Damm-Lunau, R.; Dunkel, J.; Fellgiebel, A.; Garms, E.; et al. Safety and clinical impact of FEES – results of the FEES-registry. Neurol. Res. Pract. 2019, 1, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, R.; Dziewas, R.; Beck, A.M.; Clave, P.; Hamdy, S.; Heppner, H.J.; Langmore, S.; Leischker, A.H.; Martino, R.; Pluschinski, P.; et al. Oropharyngeal dysphagia in older persons-from pathophysiology to adequate intervention: A review and summary of an international expert meeting. Clin. Interv. Aging 2016, 11, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weitoft, T. Occurrence of polymyositis in the county of Gavleborg, Sweden. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 1997, 26, 104–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, K.-Y.; Kouda, K.; Tajima, F.; Kondo, T. A dysphagia study in patients with sporadic inclusion body myositis (s-IBM). Neurol. Sci. 2012, 33, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohan, A.; Peter, J.B. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (first of two parts). N. Engl. J. Med. 1975, 292, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohan, A.; Peter, J.B. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (second of two parts). N. Engl. J. Med. 1975, 292, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griggs, R.C.; Askanas, V.; DiMauro, S.; Engel, A.; Karpati, G.; Mendell, J.R.; Rowland, L.P. Inclusion body myositis and myopathies. Ann. Neurol. 1995, 38, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, M.; Mastaglia, F.L. Inclusion body myositis: Current pathogenetic concepts and diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, M.R. 188th ENMC International Workshop: Inclusion Body Myositis, 2–4 December 2011, Naarden, The Netherlands. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2013, 23, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, J.A.; van der Windt, D.A.; Cartwright, J.L.; Cote, P.; Bombardier, C. Assessing bias in studies of prognostic factors. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neyeloff, J.L.; Fuchs, S.C.; Moreira, L.B. Meta-analyses and Forest plots using a microsoft excel spreadsheet: Step-by-step guide focusing on descriptive data analysis. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Green, S. Cochrane Handbook of Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Wiley: Chichester, New Hampshire, 2008; ISBN 9780470699515. [Google Scholar]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Badrising, U.A.; Maat-Schieman, M.L.C.; van Houwelingen, J.C.; van Doorn, P.A.; van Duinen, S.G.; van Engelen, B.G.M.; Faber, C.G.; Hoogendijk, J.E.; de Jager, A.E.; Koehler, P.J.; et al. Inclusion body myositis. Clinical features and clinical course of the disease in 64 patients. J. Neurol. 2005, 252, 1448–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benveniste, O.; Guiguet, M.; Freebody, J.; Dubourg, O.; Squier, W.; Maisonobe, T.; Stojkovic, T.; Leite, M.I.; Allenbach, Y.; Herson, S.; et al. Long-term observational study of sporadic inclusion body myositis. Brain 2011, 134, 3176–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- 19. De Camargo, L.V.; de Carvalho, M.S.; Shinjo, S.K.; de Oliveira, A.S.B.; Zanoteli, E. Clinical, Histological, and Immunohistochemical Findings in Inclusion Body Myositis. Biomed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 5069042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, S.K.; Yang, Y.H.; Wang, L.C.; Chiang, B.L. Ten-year experience of juvenile dermatomyositis: A retrospective study. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2007, 40, 68–73. [Google Scholar]
- Chwalinska-Sadowska, H.; Maldykowa, H. Polymyositis-dermatomyositis—A 25-year follow-up of 50 patients (analysis of clinical symptoms and signs and results of laboratory tests). Mater. Med. Pol. 1990, 22, 205–212. [Google Scholar]
- Dobloug, C.; Garen, T.; Bitter, H.; Stjarne, J.; Stenseth, G.; Grovle, L.; Sem, M.; Gran, J.T.; Molberg, O. Prevalence and clinical characteristics of adult polymyositis and dermatomyositis; data from a large and unselected Norwegian cohort. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1551–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lotz, B.P.; Engel, A.G.; Nishino, H.; Stevens, J.C.; Litchy, W.J. Inclusion body myositis. Observations in 40 patients. Brain 1989, 112 Pt 3, 727–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, I.; Menard, J.-F.; Hatron, P.Y.; Hachulla, E.; Mouthon, L.; Tiev, K.; Ducrotte, P.; Cherin, P. Intravenous immunoglobulins for steroid-refractory esophageal involvement related to polymyositis and dermatomyositis: A series of 73 patients. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2010, 62, 1748–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maugars, Y.M.; Berthelot, J.M.; Abbas, A.A.; Mussini, J.M.; Nguyen, J.M.; Prost, A.M. Long-term prognosis of 69 patients with dermatomyositis or polymyositis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 1996, 14, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Needham, M.; James, I.; Corbett, A.; Day, T.; Christiansen, F.; Phillips, B.; Mastaglia, F.L. Sporadic inclusion body myositis: Phenotypic variability and influence of HLA-DR3 in a cohort of 57 Australian cases. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2008, 79, 1056–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, F.M.; Verschuuren, J.J.; Verbist, B.M.; Niks, E.H.; Wintzen, A.R.; Badrising, U.A. Detecting dysphagia in inclusion body myositis. J. Neurol. 2009, 256, 2009–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lynn, S.J.; Sawyers, S.M.; Moller, P.W.; O’Donnell, J.L.; Chapman, P.T. Adult-onset inflammatory myopathy: North Canterbury experience 1989-2001. Intern. Med. J. 2005, 35, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, T.H.; Brumfield, K.A.; Hoskin, T.L.; Kasperbauer, J.L.; Basford, J.R. Dysphagia in inclusion body myositis: Clinical features, management, and clinical outcome. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2008, 87, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, T.H.; Brumfield, K.A.; Hoskin, T.L.; Stolp, K.A.; Murray, J.A.; Bassford, J.R. Dysphagia in inflammatory myopathy: Clinical characteristics, treatment strategies, and outcome in 62 patients. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2007, 82, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riminton, D.S.; Chambers, S.T.; Parkin, P.J.; Pollock, M.; Donaldson, I.M. Inclusion body myositis presenting solely as dysphagia. Neurology 1993, 43, 1241–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.B.; Grehan, M.J.; Hersch, M.; Andre, J.; Cook, I.J. Biomechanics, diagnosis, and treatment outcome in inflammatory myopathy presenting as oropharyngeal dysphagia. Gut 2003, 52, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labeit, B.; Muhle, P.; Suntrup-Krueger, S.; Ahring, S.; Ruck, T.; Dziewas, R.; Warnecke, T. Dysphagia as Isolated Manifestation of Jo-1 Associated Myositis? Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Danko, K.; Ponyi, A.; Constantin, T.; Borgulya, G.; Szegedi, G. Long-term survival of patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies according to clinical features: A longitudinal study of 162 cases. Medicine (Baltim.) 2004, 83, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galindo-Feria, A.S.; Rojas-Serrano, J.; Hinojosa-Azaola, A. Clinical and Prognostic Factors Associated With Survival in Mexican Patients with Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 22, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scola, R.H.; Werneck, L.C.; Prevedello, D.M.; Toderke, E.L.; Iwamoto, F.M. Diagnosis of dermatomyositis and polymyositis: A study of 102 cases. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2000, 58, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- So, M.W.; Koo, B.S.; Kim, Y.-G.; Lee, C.-K.; Yoo, B. Idiopathic inflammatory myopathy associated with malignancy: A retrospective cohort of 151 Korean patients with dermatomyositis and polymyositis. J. Rheumatol. 2011, 38, 2432–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casal-Dominguez, M.; Pinal-Fernandez, I.; Mego, M.; Accarino, A.; Jubany, L.; Azpiroz, F.; Selva-O’callaghan, A. High-resolution manometry in patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathy: Elevated prevalence of esophageal involvement and differences according to autoantibody status and clinical subset. Muscle Nerve 2017, 56, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilleker, J.B.; Vencovsky, J.; Wang, G.; Wedderburn, L.R.; Diederichsen, L.P.; Schmidt, J.; Oakley, P.; Benveniste, O.; Danieli, M.G.; Danko, K.; et al. The EuroMyositis registry: An international collaborative tool to facilitate myositis research. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azuma, K.; Yamada, H.; Ohkubo, M.; Yamasaki, Y.; Yamasaki, M.; Mizushima, M.; Ozaki, S. Incidence and predictive factors for malignancies in 136 Japanese patients with dermatomyositis, polymyositis and clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2011, 21, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Yuan, S.; Wu, X.; Li, H.; Qiu, Q.; Zhan, Z.; Ye, Y.; Lian, F.; Liang, L.; Xu, H.; et al. Incidence and predictive factors for malignancies with dermatomyositis: A cohort from southern China. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2014, 32, 615–621. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.-F.; Wu, Y.-J.J.; Kuo, C.-F.; Luo, S.-F.; Yu, K.-H. Malignancy in dermatomyositis and polymyositis: Analysis of 192 patients. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 35, 1977–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.H.; Lee, S.J.; Ascherman, D.P.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, E.Y.; Lee, E.B.; Song, Y.W. Temporal relationship between cancer and myositis identifies two distinctive subgroups of cancers: Impact on cancer risk and survival in patients with myositis. Rheumatology (Oxf.) 2016, 55, 1631–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mugii, N.; Hasegawa, M.; Matsushita, T.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Oohata, S.; Okita, H.; Yahata, T.; Someya, F.; Inoue, K.; Murono, S.; et al. Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Dermatomyositis: Associations with Clinical and Laboratory Features Including Autoantibodies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neri, R.; Barsotti, S.; Iacopetti, V.; Iacopetti, G.; Pepe, P.; d’Ascanio, A.; Tavoni, A.G.; Mosca, M.; Bombardieri, S. Cancer-associated myositis: A 35-year retrospective study of a monocentric cohort. Rheumatol. Int. 2014, 34, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albayda, J.; Pinal-Fernandez, I.; Huang, W.; Parks, C.; Paik, J.; Casciola-Rosen, L.; Danoff, S.K.; Johnson, C.; Christopher-Stine, L.; Mammen, A.L. Antinuclear Matrix Protein 2 Autoantibodies and Edema, Muscle Disease, and Malignancy Risk in Dermatomyositis Patients. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2017, 69, 1771–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ge, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, T.; Zheng, X.; Peng, Q.; Lu, X.; Wang, G. The spectrum and clinical significance of myositis-specific autoantibodies in Chinese patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 2171–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, A.; Chung, L.; Li, S.; Casciola-Rosen, L.; Fiorentino, D.F. Cutaneous and Systemic Findings Associated With Nuclear Matrix Protein 2 Antibodies in Adult Dermatomyositis Patients. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2017, 69, 1909–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rider, L.G.; Shah, M.; Mamyrova, G.; Huber, A.M.; Rice, M.M.; Targoff, I.N.; Miller, F.W. The myositis autoantibody phenotypes of the juvenile idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Medicine (Baltim.) 2013, 92, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, I.; Wick, C.; Hallgren, A.; Tjarnlund, A.; Nagaraju, K.; Andrade, F.; Thompson, K.; Coley, W.; Phadke, A.; Diaz-Gallo, L.-M.; et al. Development of autoantibodies against muscle-specific FHL1 in severe inflammatory myopathies. J. Clin. Invest. 2015, 125, 4612–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, Y.; Lu, X.; Shu, X.; Peng, Q.; Wang, G. Clinical characteristics of anti-SAE antibodies in Chinese patients with dermatomyositis in comparison with different patient cohorts. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, Y.; Lu, X.; Peng, Q.; Shu, X.; Wang, G. Clinical Characteristics of Anti-3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl Coenzyme A Reductase Antibodies in Chinese Patients with Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, N.A.; Cash, T.M.; Alam, U.; Enam, S.; Tierney, P.; Araujo, N.; Mozaffar, F.H.; Pestronk, A.; Mozaffar, T. Seropositivity for NT5c1A antibody in sporadic inclusion body myositis predicts more severe motor, bulbar and respiratory involvement. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2016, 87, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengstman, G.J.D.; ter Laak, H.J.; Vree Egberts, W.T.M.; Lundberg, I.E.; Moutsopoulos, H.M.; Vencovsky, J.; Doria, A.; Mosca, M.; van Venrooij, W.J.; van Engelen, B.G.M. Anti-signal recognition particle autoantibodies: Marker of a necrotising myopathy. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2006, 65, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, Y.; Uruha, A.; Suzuki, S.; Nakahara, J.; Hamanaka, K.; Takayama, K.; Suzuki, N.; Nishino, I. Clinical features and prognosis in anti-SRP and anti-HMGCR necrotising myopathy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2016, 87, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, E.; Uruha, A.; Suzuki, S.; Hamanaka, K.; Ohnuki, Y.; Tsugawa, J.; Watanabe, Y.; Nakahara, J.; Shiina, T.; Suzuki, N.; et al. Skeletal Muscle Involvement in Antisynthetase Syndrome. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoesly, P.M.; Sluzevich, J.C.; Jambusaria-Pahlajani, A.; Lesser, E.R.; Heckman, M.G.; Abril, A. Association of antinuclear antibody status with clinical features and malignancy risk in adult-onset dermatomyositis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 1364–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azola, A.; Mulheren, R.; Mckeon, G.; Lloyd, T.; Christopher-Stine, L.; Palmer, J.; Chung, T.H. Dysphagia in myositis: A study of the structural and physiologic changes resulting in disordered swallowing. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Cochicho, J.; Madaleno, J.; Louro, E.; Simao, A.; Carvalho, A. Polymyositis and the Spectrum of Scleroderma Disorders. Eur. J. Case Rep. Intern. Med. 2016, 3, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malandraki, G.A.; Kaufman, A.; Hind, J.; Ennis, S.; Gangnon, R.; Waclawik, A.; Robbins, J. The effects of lingual intervention in a patient with inclusion body myositis and Sjogren’s syndrome: A longitudinal case study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 93, 1469–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.W.C.; Tarnopolsky, M.; Armstrong, D. Injection of botulinum toxin A to the upper esophageal sphincter for oropharyngeal dysphagia in two patients with inclusion body myositis. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 18, 397–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korn, J.H.; Mauiyyedi, S. Case 26-2001. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 596–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darrow, D.H.; Hoffman, H.T.; Barnes, G.J.; Wiley, C.A. Management of dysphagia in inclusion body myositis. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1992, 118, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierney, D.; Jirjis, J.N. A woman with difficulty swallowing. Tenn. Med. 1997, 90, 462–463. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takamiya, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Morimoto, M.; Morimoto, N.; Yamashita, S.; Abe, K. Effect of intravenous immunoglobulin therapy on anti-NT5C1A antibody-positive inclusion body myositis after successful treatment of hepatitis C: A case report. eNeurologicalSci 2019, 16, 100204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, S.; Izumi, R.; Hara, T.; Ohshima, R.; Nakamura, N.; Suzuki, N.; Kato, K.; Katori, Y.; Tateyama, M.; Kuroda, H.; et al. Five-year history of dysphagia as a sole initial symptom in inclusion body myositis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 381, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofori, E.; Ramai, D.; Ona, M.; Reddy, M. Paraneoplastic Dermatomyositis Syndrome Presenting as Dysphagia. Gastroenterology Res. 2017, 10, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schrey, A.; Airas, L.; Jokela, M.; Pulkkinen, J. Botulinum toxin alleviates dysphagia of patients with inclusion body myositis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 380, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, M.; Macchia, L.; Amati, A.; Lia, A.; Girolamo, F.; D’Abbicco, D.; Trojano, M.; Iannone, F. A rare association of anti-alanine-transfer RNA synthetase (anti-PL12) syndrome and sporadic inclusion body myositis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2018, 47, 336–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, Z.; Patel, L.; Das, M.K.; Mecoli, C.A.; Ramji, A. NXP-2 Positive Dermatomyositis: A Unique Clinical Presentation. Case Rep. Rheumatol. 2017, 2017, 4817275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olthoff, A.; Carstens, P.-O.; Zhang, S.; von Fintel, E.; Friede, T.; Lotz, J.; Frahm, J.; Schmidt, J. Evaluation of dysphagia by novel real-time MRI. Neurology 2016, 87, 2132–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pede, C.; Masiero, S.; Bonsangue, V.; Ragona, R.M.; Del Felice, A. Botulinum toxin and rehabilitation treatment in inclusion body myositis for severe oropharyngeal dysphagia. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 37, 1743–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannone, F.; Giannini, M.; Lapadula, G. Recovery of barium swallow radiographic abnormalities in a patient with dermatomyositis and severe dysphagia after high-dose intravenous immunoglobulins. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2015, 21, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eura, N.; Sugie, K.; Kiriyama, T.; Ueno, S. Characteristic dysphagia as a manifestation of dermatomyositis on oropharyngeal muscle imaging. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2015, 21, 105–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, E.H.; Rubin, A.D. Dysphagia due to inclusion body myositis: Case presentation and review of the literature. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2014, 123, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagan, A.; Markovits, D.; Braun-Moscovici, Y.; Rozin, A.; Toledano, K.; Balbir-Gurman, A. Life-threatening oropharyngeal aphagia as the major manifestation of dermatomyositis. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2013, 15, 453–455. [Google Scholar]
- Langdon, P.C.; Mulcahy, K.; Shepherd, K.L.; Low, V.H.; Mastaglia, F.L. Pharyngeal dysphagia in inflammatory muscle diseases resulting from impaired suprahyoid musculature. Dysphagia 2012, 27, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, K.-Y.; Kouda, K.; Tajima, F.; Kondo, T. Balloon dilation in sporadic inclusion body myositis patients with Dysphagia. Clin. Med. Insights Case Rep. 2013, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakovic, Z.; Vesic, S.; Tomovic, M.; Vukovic, J. Oropharyngeal dysphagia as dominant and life-threatening symptom in dermatomyositis. Vojnosanit. Pregl. 2009, 66, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, H.; Yoshifuku, K.; Kurono, Y. Polymyositis with dysphagia treated with endoscopic balloon dilatation. Auris Nasus Larynx 2009, 36, 705–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafejee, A.; Coulson, I.H. Dysphagia in dermatomyositis secondary to bladder cancer: Rapid response to combined immunoglobulin and methylprednisolone. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2005, 30, 93–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertekin, C.; Secil, Y.; Yuceyar, N.; Aydogdu, I. Oropharyngeal dysphagia in polymyositis/dermatomyositis. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2004, 107, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, R.B.; Swash, M. Pharyngeal Dysphagia in dermatomyositis: Responsive to cyclophosphamide. J. Clin. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2004, 5, 166–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, A.; Nor, A.M.; Costigan, D.; Foley-Nolan, D.; El-Rafie, A.; Farrell, M.A.; Hardiman, O. Polymyositis masquerading as motor neuron disease. Arch. Neurol. 2003, 60, 1001–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cherin, P.; Pelletier, S.; Teixeira, A.; Laforet, P.; Simon, A.; Herson, S.; Eymard, B. Intravenous immunoglobulin for dysphagia of inclusion body myositis. Neurology 2002, 58, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, G.; Streppel, M.; Krug, B.; Neuen-Jacob, E. Cricopharyngeal muscle hypertrophy associated with florid myositis. Dysphagia 2001, 16, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, K.M.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, Y.H. A case report of life-threatening acute dysphagia in dermatomyositis: Challenges in diagnosis and treatment. Medicine (Baltim.) 2018, 97, e0508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelik, O.; Almoznino-Sarafian, D.; Alon, I.; Rapoport, M.J.; Goltsman, G.; Herbert, M.; Modai, D.; Cohen, N. Acute inflammatory myopathy with severe subcutaneous edema, a new variant? Report of two cases and review of the literature. Rheumatol. Int. 2001, 20, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrera, P.; den Broeder, A.A.; van den Hoogen, F.H.; van Engelen, B.G.; van de Putte, L.B. Postural changes, dysphagia, and systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1998, 57, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caramaschi, P.; Blasi, D.; Carletto, A.; Randon, M.; Bambara, L.M. Megaoesophagus in a patient affected by dermatomyositis. Clin. Rheumatol. 1997, 16, 106–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, J.; Martin, S.; DeGirolami, U.; Goyal, R. Inflammatory myopathy causing pharyngeal dysphagia: A new entity. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1996, 105, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St Guily, J.L.; Perie, S.; Willig, T.N.; Chaussade, S.; Eymard, B.; Angelard, B. Swallowing disorders in muscular diseases: Functional assessment and indications of cricopharyngeal myotomy. Ear Nose Throat J. 1994, 73, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.R.; McKenzie, S.W. Kinematic pharyngeal transit times in myopathy: Evaluation for dysphagia. Dysphagia 1993, 8, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.; Bradley, W.G.; Adesina, A.M.; Sofferman, R.; Pendlebury, W.W. Inclusion body myositis with cricopharyngeus muscle involvement and severe dysphagia. Muscle Nerve 1991, 14, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danon, M.J.; Friedman, M. Inclusion body myositis associated with progressive dysphagia: Treatment with cricopharyngeal myotomy. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 1989, 16, 436–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wintzen, A.R.; Bots, G.T.; de Bakker, H.M.; Hulshof, J.H.; Padberg, G.W. Dysphagia in inclusion body myositis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1988, 51, 1542–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kagen, L.J.; Hochman, R.B.; Strong, E.W. Cricopharyngeal obstruction in inflammatory myopathy (polymyositis/dermatomyositis). Report of three cases and review of the literature. Arthritis Rheum. 1985, 28, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, H.; Berkowitz, D.; McDonald, E.; Bernstein, L.H.; Beneventano, T. The esophageal motility disorder of polymyositis. A prospective study. Arch. Intern. Med. 1983, 143, 2262–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Merieux, P.; Verity, M.A.; Clements, P.J.; Paulus, H.E. Esophageal abnormalities and dysphagia in polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Arthritis Rheum. 1983, 26, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, F.; Logeman, J.A.; Sahgal, V.; Schmid, F.R. Cricopharyngeal muscle dysfunction in the differential diagnosis of dysphagia in polymyositis. Arthritis Rheum. 1980, 23, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metheny, J.A. Dermatomyositis: A vocal and swallowing disease entity. Laryngoscope 1978, 88, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porubsky, E.S.; Murray, J.P.; Pratt, L.L. Cricopharyngeal achalasia in dermatomyositis. Arch. Otolaryngol. 1973, 98, 428–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, F.B.; LeBauer, S.; Greenberger, N.J. Polymyositis masquerading as carcinoma of the cervical esophagus. Arch. Intern. Med. 1972, 129, 984–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Hara, J.M.; Szemes, G.; Lowman, R.M. The esophageal lesions in dermatomyositis. A correlation of radiologic and pathologic findings. Radiology 1967, 89, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoghue, F.E.; Winkelmann, R.K.; Moersch, H.J. Esophageal defects in dermatomyositis. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1960, 69, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felice, K.J.; North, W.A. Inclusion body myositis in Connecticut: Observations in 35 patients during an 8-year period. Medicine (Baltim.) 2001, 80, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paik, N.-J.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Jeon, J.Y.; Lim, J.-Y.; Han, T.R. Movement of the hyoid bone and the epiglottis during swallowing in patients with dysphagia from different etiologies. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2008, 18, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vencovsky, J.; Rehak, F.; Pafko, P.; Jirasek, A.; Valesova, M.; Alusik, S.; Trnavsky, K. Acute cricopharyngeal obstruction in dermatomyositis. J. Rheumatol. 1988, 15, 1016–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Porkodi, R.; Shanmuganandan, K.; Parthiban, M.; Madhavan, R.; Rajendran, P. Clinical spectrum of inflammatory myositis in South India—A ten year study. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2002, 50, 1255–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Houser, S.M.; Calabrese, L.H.; Strome, M. Dysphagia in patients with inclusion body myositis. Laryngoscope 1998, 108, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palace, J.; Losseff, N.; Clough, C. Isolated dysphagia due to polymyositis. Muscle Nerve 1993, 16, 680–681. [Google Scholar]
- Margulis, A.R.; Koehler, R.E. Radiologic diagnosis of disordered esophageal motility: A unified physiologic approach. Radiol. Clin. North Am. 1976, 14, 429–439. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, J.D., Jr.; Lowry, L.D. Head and neck manifestations of dermatomyositis-polymyositis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1985, 93, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marie, I.; Hachulla, E.; Levesque, H.; Reumont, G.; Ducrotte, P.; Cailleux, N.; Hatron, P.Y.; Devulder, B.; Courtois, H. Intravenous immunoglobulins as treatment of life threatening esophageal involvement in polymyositis and dermatomyositis. J. Rheumatol. 1999, 26, 2706–2709. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kleine-Natrop, H.E.; Engel, S. Participation of smooth muscles in dermatomyositis. I. Arch. Klin. Exp. Dermatol. 1967, 228, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degos, R.; Civatte, J.; Belaich, S.; Delarue, A. The prognosis of adult dermatomyositis. Trans. St Johns. Hosp. Dermatol. Soc. 1971, 57, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Sousa Gameiro, R.; Reis, A.I.A.; Grilo, A.C.; Noronha, C. Following leads: Connecting dysphagia to mixed connective tissue disease. BMJ Case Rep. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyorffy, J.B.; Marowske, J.; Gancayco, J. A Rare Cause of Dysphagia and Weight Loss. Case Rep. Gastroenterol. 2018, 12, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Xiong, W.; Yu, T.; Wang, M.; Zhang, G.; Lin, L. Eosinophilic Esophageal Myositis a Plausible Cause of Histological Changes of Primary Jackhammer Esophagus: A Case Report. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 150–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobloug, G.C.; Antal, E.A.; Sveberg, L.; Garen, T.; Bitter, H.; Stjarne, J.; Grovle, L.; Gran, J.T.; Molberg, O. High prevalence of inclusion body myositis in Norway; a population-based clinical epidemiology study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2015, 22, 672-e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobloug, C.; Walle-Hansen, R.; Gran, J.T.; Molberg, O. Long-term follow-up of sporadic inclusion body myositis treated with intravenous immunoglobulin: A retrospective study of 16 patients. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2012, 30, 838–842. [Google Scholar]
- Almodovar, R.; Lindo, D.P.; Martin, H.; Mazzuchelli, R.; Pardo, J.; Quiros, F.J.; Zarco, P. Dermatomyositis and meningioma in the same patient. Reumatol. Clin. 2012, 8, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mii, S.; Niiyama, S.; Kusunoki, M.; Arai, S.; Katsuoka, K. Cyclosporine A as treatment of esophageal involvement in dermatomyositis. Rheumatol. Int. 2006, 27, 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, J.; Uerlich, M.; Gerdsen, R.; Bieber, T.; Boehm, I. Association of inclusion body myositis with subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol. Int. 2001, 21, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uthman, I.; Vazquez-Abad, D.; Senecal, J.L. Distinctive features of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies in French Canadians. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 1996, 26, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, H.W.; Sanghera, K.; Goldberg, N.; Pechman, D.; Kamer, R.; Duray, P.; Weinstein, A. Dermatomyositis associated with Lyme disease: Case report and review of Lyme myositis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1994, 18, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, M.; McNeil, J.D.; Maddern, G.J.; Collins, P.J.; Shearman, D.J. Abnormalities of gastric and esophageal emptying in polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Gastroenterology 1986, 90, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.B.; Hookman, P.; Siegel, C.I.; Esterly, J.R.; Shulman, L.E.; Hendrix, T.R. Aperistalsis of the esophagus in patients with connective-tissue disorders and raynaud’s phenomenon. N. Engl. J. Med. 1964, 270, 1218–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marie, I.; Hatron, P.Y.; Levesque, H.; Hachulla, E.; Hellot, M.F.; Michon-Pasturel, U.; Courtois, H.; Devulder, B. Influence of age on characteristics of polymyositis and dermatomyositis in adults. Medicine (Baltim.) 1999, 78, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, I.; Hachulla, E.; Hatron, P.Y.; Hellot, M.F.; Levesque, H.; Devulder, B.; Courtois, H. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis: Short term and longterm outcome, and predictive factors of prognosis. J. Rheumatol. 2001, 28, 2230–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, I.P.; Wang, J.; Tsang, Y.M.; Hsiao, C.H. Focal myositis of esophagus: A distinct inflammatory pseudotumor mimicking esophageal malignancy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1997, 92, 174–175. [Google Scholar]
- Laurikainen, E.; Aitasalo, K.; Halonen, P.; Falck, B.; Kalimo, H. Muscle pathology in idiopathic cricopharyngeal dysphagia. Enzyme histochemical and electron microscopic findings. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 1992, 249, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolman, L.; Darke, C.S.; Young, A. The larynx in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Laryngol. Otol. 1965, 79, 403–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otao, G.; Yamashita, S.-I.; Kyoraku, I.; Shiomi, K.; Nakazato, M. Dysphagia due to inflammation of oral muscles as the first symptom of dermatomyositis. Intern. Med. 2007, 46, 923–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Curiel, R.V.; Brindle, K.A.; Kressel, B.R.; Katz, J.D. Dysphagia after testicular cancer. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuber, M.A.; Kouba, M.; Rudolph, S.E.; Weller, M.; Hrdlicka, P. Severe dysphagia and erythrodermia in a 59-year-old man. Internist (Berl.) 2013, 54, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Han, T.R.; Jeong, S.J.; Beom, J.W. Comparison between swallowing-related and limb muscle involvement in dermatomyositis patients. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 39, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, L.J.; Garay, S.M.; Ryan, M.M.; Harris, R.; Riley, P.; Pilkington, C.A. Oropharyngeal dysphagia in juvenile dermatomyositis (JDM): An evaluation of videofluoroscopy swallow study (VFSS) changes in relation to clinical symptoms and objective muscle scores. Rheumatology (Oxf.) 2007, 46, 1363–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, T.; Park, J.H.; Sohn, C.; Yoon, K.J.; Lee, Y.-T.; Park, J.H.; Jung, I.S. Failed Deglutitive Upper Esophageal Sphincter Relaxation Is a Risk Factor for Aspiration in Stroke Patients with Oropharyngeal Dysphagia. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 23, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertekin, C.; Aydogdu, I.; Yuceyar, N. Piecemeal deglutition and dysphagia limit in normal subjects and in patients with swallowing disorders. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1996, 61, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pearson, W.G.J.R.; Hindson, D.F.; Langmore, S.E.; Zumwalt, A.C. Evaluating swallowing muscles essential for hyolaryngeal elevation by using muscle functional magnetic resonance imaging. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 85, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelly, J.H. Management of upper esophageal sphincter disorders: Indications and complications of myotomy. Am. J. Med. 2000, 108 (Suppl. 4a), 43S–46S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa-Momohara, M.; Muro, Y.; Kono, M.; Akiyama, M. Prognosis of dysphagia in dermatomyositis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2019, 37, 165. [Google Scholar]
- Medsger, T.A.J.R.; Robinson, H.; Masi, A.T. Factors affecting survivorship in polymyositis. A life-table study of 124 patients. Arthritis Rheum. 1971, 14, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, J.R.; Bunch, T.W.; Engel, A.G.; O’Brien, P.C. Survival in polymyositis: Corticosteroids and risk factors. J. Rheumatol. 1977, 4, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Capkun, G.; Callan, A.; Tian, H.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, C.; Agashivala, N.; Barghout, V. Burden of illness and healthcare resource use in United States patients with sporadic inclusion body myositis. Muscle Nerve 2017, 56, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, A.; Koffman, B.M.; Malley, J.D.; Dalakas, M.C. Disease progression in sporadic inclusion body myositis: Observations in 78 patients. Neurology 2000, 55, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.A.; Barghout, V.; Benveniste, O.; Christopher-Stine, L.; Corbett, A.; de Visser, M.; Hilton-Jones, D.; Kissel, J.T.; Lloyd, T.E.; Lundberg, I.E.; et al. Mortality and Causes of Death in Patients with Sporadic Inclusion Body Myositis: Survey Study Based on the Clinical Experience of Specialists in Australia, Europe and the USA. J. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2016, 3, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benbassat, J.; Gefel, D.; Larholt, K.; Sukenik, S.; Morgenstern, V.; Zlotnick, A. Prognostic factors in polymyositis/dermatomyositis. A computer-assisted analysis of ninety-two cases. Arthritis Rheum. 1985, 28, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochberg, M.C.; Feldman, D.; Stevens, M.B. Adult onset polymyositis/dermatomyositis: An analysis of clinical and laboratory features and survival in 76 patients with a review of the literature. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 1986, 15, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challa, D.; Crowson, C.S.; Niewold, T.B.; Reed, A.M. Predictors of changes in disease activity among children with juvenile dermatomyositis enrolled in the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance (CARRA) Legacy Registry. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Nishikawa, A.; Kuwana, M.; Nishimura, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Nakahara, J.; Hayashi, Y.K.; Suzuki, N.; Nishino, I. Inflammatory myopathy with anti-signal recognition particle antibodies: Case series of 100 patients. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2015, 10, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, S.; Higuchi, K.; Tamaki, H.; Wada, Y.; Wada, N.; Kubo, M.; Koike, Y.; Nagata, M.; Tatsuzawa, O.; Fujikawa, S. Characteristics of juvenile dermatomyositis in Japan. Acta Paediatr. Jpn. 1997, 39, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cnop, K.; Martinez, B.; Austad, K.E. Resistant dermatomyositis in a rural indigenous Maya woman. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinniah, K.J.; Mody, G.M. Recovery from severe dysphagia in systemic sclerosis-myositis overlap: A case report. Afr. Health Sci. 2017, 17, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raghu, P.; Manadan, A.M.; Schmukler, J.; Mathur, T.; Block, J.A. Pulse Dose Methylprednisolone Therapy for Adult Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathy. Am. J. Ther. 2015, 22, 244–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonin, C.C.; Santos Pires da Silva, B.; Mota, L.M.; de Carvalho, J.F. Severe and refractory myositis in mixed connective tissue disease: A description of a rare case. Lupus 2010, 19, 1659–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateyama, M.; Saito, N.; Fujihara, K.; Shiga, Y.; Takeda, A.; Narikawa, K.; Hasegawa, T.; Taguchi, Y.; Sakuma, R.; Onodera, Y.; et al. Familial inclusion body myositis: A report on two Japanese sisters. Intern. Med. 2003, 42, 1035–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Mayouf, S.; Al-Mazyed, A.; Bahabri, S. Efficacy of early treatment of severe juvenile dermatomyositis with intravenous methylprednisolone and methotrexate. Clin. Rheumatol. 2000, 19, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarlane, L.; Osman, N.; Ritter, S.; Miller, A.L.; Loscalzo, J. Clinical Problem-Solving. Eye of the Beholder. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1774–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnayake, S.K.; Blumbergs, P.; Tan, J.A.; Roberts-Thompson, P.J.; Limaye, V. Inflammatory myopathy with anti-SRP antibodies: Case series of a South Australian cohort. Clin. Rheumatol. 2015, 34, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Natsuga, K.; Arita, K.; Abe, R.; Shimizu, H. Generalized acute subcutaneous edema as a rare cutaneous manifestation of severe dermatomyositis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2016, 30, e151–e152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zedan, M.; El-Ayouty, M.; Abdel-Hady, H.; Shouman, B.; El-Assmy, M.; Fouda, A. Anasarca: Not a nephrotic syndrome but dermatomyositis. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2008, 167, 831–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Pu, C.; Shi, Q.; Wang, Q.; Cong, L.; Liu, J.; Luo, H.; Fei, L.; Tang, W.; Yu, S. Chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia with inflammatory myopathy. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 8887–8892. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Black, M.; Marshman, G. Dermatomyositis and pemphigus vulgaris: Association or coincidence? Australas. J. Dermatol. 2011, 52, e11–e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, H.; Kai, C.; Deng, J. Polymyositis associated with hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism: Two cases and review of the literature. Clin. Rheumatol. 2011, 30, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noda, S.; Umezaki, H.; Itoh, H.; Hiromatsu, K.; Yamamoto, T. Chronic focal polymyositis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1988, 51, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milisenda, J.C.; Doti, P.I.; Prieto-Gonzalez, S.; Grau, J.M. Dermatomyositis presenting with severe subcutaneous edema: Five additional cases and review of the literature. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2014, 44, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitzia, C.; Sansone, V.A.; Corsi Romanelli, M.M. Creatine kinase elevation: A neglected clue to the diagnosis of polymyositis. A case report. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2019, 57, e149–e151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqatari, S.; Riddell, P.; Harney, S.; Henry, M.; Murphy, G. MDA-5 associated rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease with recurrent Pneumothoraces: A case report. BMC Pulm. Med. 2018, 18, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prossliner, V.; Philipp, M.; Moosbrugger, V.; Poewe, W.; Zangerle, R.; Wanschitz, J.; Schmuth, M. Severe dysphagia, myalgia, and rash in a 55-year-old man. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2016, 14, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, N.; Asano, T.; Sato, S.; Sasajima, T.; Fujita, Y.; Temmoku, J.; Yashiro Furuya, M.; Matsumoto, H.; Suzuki, E.; Kobayashi, H.; et al. A case of dermatomyositis complicated with pleural effusion and massive ascites. Fukushima J. Med. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pars, K.; Garde, N.; Skripuletz, T.; Pul, R.; Dengler, R.; Stangel, M. Subcutaneous immunoglobulin treatment of inclusion-body myositis stabilizes dysphagia. Muscle Nerve 2013, 48, 838–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, D.; Mahmood, R.; Williams, P.; Kitchen, P. Dysphagia secondary to dermatomyositis treated successfully with intravenous immunoglobulin: A case report. Int. Arch. Med. 2008, 1, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.-H.; Lim, S.-R.; Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, K.-J.; Myung, D.-S.; Jeong, H.-C.; Yoon, W.; Lee, S.-S.; Park, Y.-W. Acute dermatomyositis associated with generalized subcutaneous edema. Rheumatol. Int. 2008, 28, 797–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalakas, M.C.; Sonies, B.; Dambrosia, J.; Sekul, E.; Cupler, E.; Sivakumar, K. Treatment of inclusion-body myositis with IVIg: A double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Neurology 1997, 48, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherin, P.; Delain, J.-C.; de Jaeger, C.; Crave, J.-C. Subcutaneous Immunoglobulin Use in Inclusion Body Myositis: A Review of 6 Cases. Case Rep. Neurol. 2015, 7, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, C.; Jean-Christophe, D.; Jean-Charles, C.; Odile, C. High-dose subcutaneous immunoglobulins for the treatment of severe treatment-resistant polymyositis. Case Rep. Rheumatol. 2014, 2014, 458231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, P.M.; Zhou, L.; Motiwala, R.; Kerr, L.D.; Shin, S.C. Immune Myopathy With Perimysial Pathology Associated With Interstitial Lung Disease and Anti-EJ Antibodies. J. Clin. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2017, 18, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakonstantinou, E.; Kapp, A.; Raap, U. A mild form of dermatomyositis as a prodromal sign of lung adenocarcinoma: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2016, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dias, L.P.N.; Faria, A.L.A.; Scandiuzzi, M.M.; dos Santos Inhaia, C.L.; Shida, J.Y.; Gebrim, L.H. A rare case of severe myositis as paraneoplastic syndrome on breast cancer. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venhuizen, A.C.; Martens, J.E.; van der Linden, P.J. Dermatomyositis as first presentation of ovarian cancer. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2006, 85, 1271–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshie, H.; Nakazawa, R.; Usuba, W.; Kudo, H.; Sato, Y.; Sasaki, H.; Chikaraishi, T. Paraneoplastic Dermatomyositis Associated with Metastatic Seminoma. Case Rep. Urol. 2016, 2016, 7050981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagano, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Shimura, T.; Fujikawa, H.; Okugawa, Y.; Hiro, J.; Toiyama, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Mohri, Y.; Kusunoki, M. Exacerbation of Dermatomyositis with Recurrence of Rectal Cancer: A Case Report. Case Rep. Oncol. 2015, 8, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenzi, F.M. Myositis Specific Autoantibodies: A Clinical Perspective. Open Access Rheumatol. 2020, 12, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Huang, L.; Yang, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, K.; Liu, M.; Xiao, Y.; Luo, H.; Zuo, X.; et al. Calcinosis and malignancy are rare in Chinese adult patients with myositis and nuclear matrix protein 2 antibodies identified by an unlabeled immunoprecipitation assay. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.M.S.; Dumitrascu, O.M.; Gordon, L.K. Orbital myositis: Diagnosis and management. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2009, 9, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalf, J.G.; de Swart, B.J.M.; Bloem, B.R.; Munneke, M. Prevalence of oropharyngeal dysphagia in Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2012, 18, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leder, S.B.; Espinosa, J.F. Aspiration risk after acute stroke: Comparison of clinical examination and fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing. Dysphagia 2002, 17, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
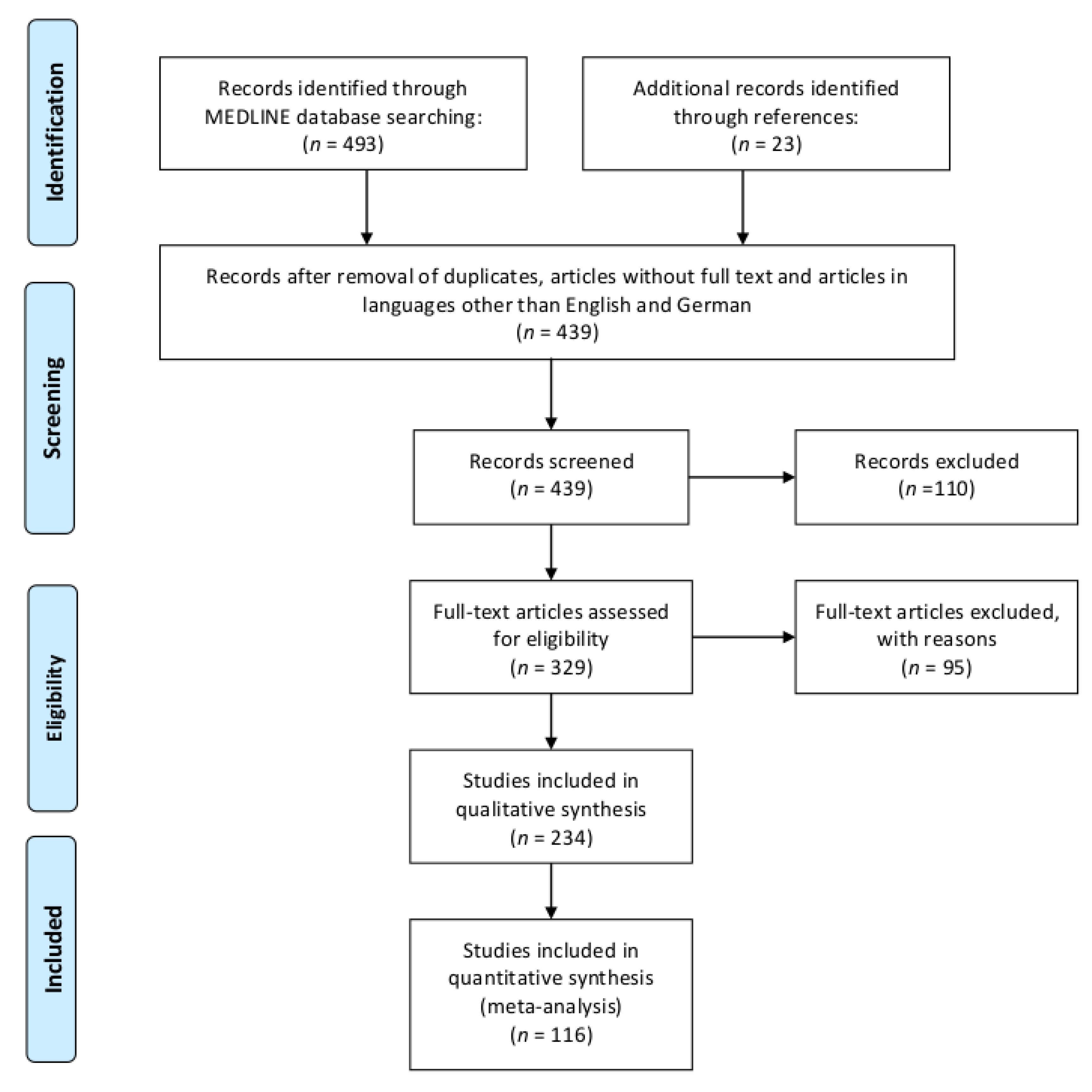




| Patient Group | n, Studies | n, Subjects | Prevalence | CI Lower | CI Upper | I-Squared | p-Value Egger’s Test | Low Bias Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| total cohort | 109 | 10382 | 36% | 33% | 40% | 87% | >0.01 * | 6% |
| PM | 21 | 882 | 23% | 18% | 27% | 52% | 0.03 * | 5% |
| DM | 49 | 3274 | 31% | 26% | 35% | 80% | >0.01 * | 2% |
| IBM | 23 | 1352 | 56% | 47% | 65% | 76% | >0.01 * | 22% |
| low bias risk | 6 | 115 | 82% | 65% | 98% | 0% | 0.70 | 100% |
| malignancy+ | 13 | 271 | 51% | 43% | 60% | 0% | 0.39 | 0% |
| malignancy− | 13 | 1120 | 23% | 17% | 30% | 85% | 0.02 * | 0% |
| NXP2+ | 5 | 196 | 56% | 45% | 66% | 0% | 0.42 | 0% |
| NXP2− | 5 | 1188 | 33% | 28% | 37% | 42% | 0.22 | 0% |
| MDA5+ | 3 | 89 | 12% | 0% | 23% | 61% | 0.13 | 0% |
| MDA5− | 3 | 538 | 21% | 10% | 32% | 86% | 0.22 | 0% |
| SEA+ | 2 | 17 | 76% | 35% | 100% | 0% | n.a. | 0% |
| SEA− | 2 | 589 | 35% | 20% | 49% | 81% | n.a. | 0% |
| SRP+ | 3 | 51 | 62% | 40% | 84% | 0% | 0.69 | 0% |
| SRP− | 3 | 943 | 36% | 26% | 45% | 81% | 0.15 | 0% |
| TIF1y+ | 3 | 103 | 45% | 32% | 58% | 0% | 0.67 | 0% |
| TIF1y− | 3 | 519 | 23% | 0% | 48% | 98% | 0.12 | 0% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Labeit, B.; Pawlitzki, M.; Ruck, T.; Muhle, P.; Claus, I.; Suntrup-Krueger, S.; Warnecke, T.; Meuth, S.G.; Wiendl, H.; Dziewas, R. The Impact of Dysphagia in Myositis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2150. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072150
Labeit B, Pawlitzki M, Ruck T, Muhle P, Claus I, Suntrup-Krueger S, Warnecke T, Meuth SG, Wiendl H, Dziewas R. The Impact of Dysphagia in Myositis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(7):2150. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072150
Chicago/Turabian StyleLabeit, Bendix, Marc Pawlitzki, Tobias Ruck, Paul Muhle, Inga Claus, Sonja Suntrup-Krueger, Tobias Warnecke, Sven G. Meuth, Heinz Wiendl, and Rainer Dziewas. 2020. "The Impact of Dysphagia in Myositis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 7: 2150. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072150





