Relationship between Tube Parameters and Corneal Endothelial Cell Damage after Ahmed Glaucoma Valve Implantation: A Comparative Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Corneal Specular Microscopy
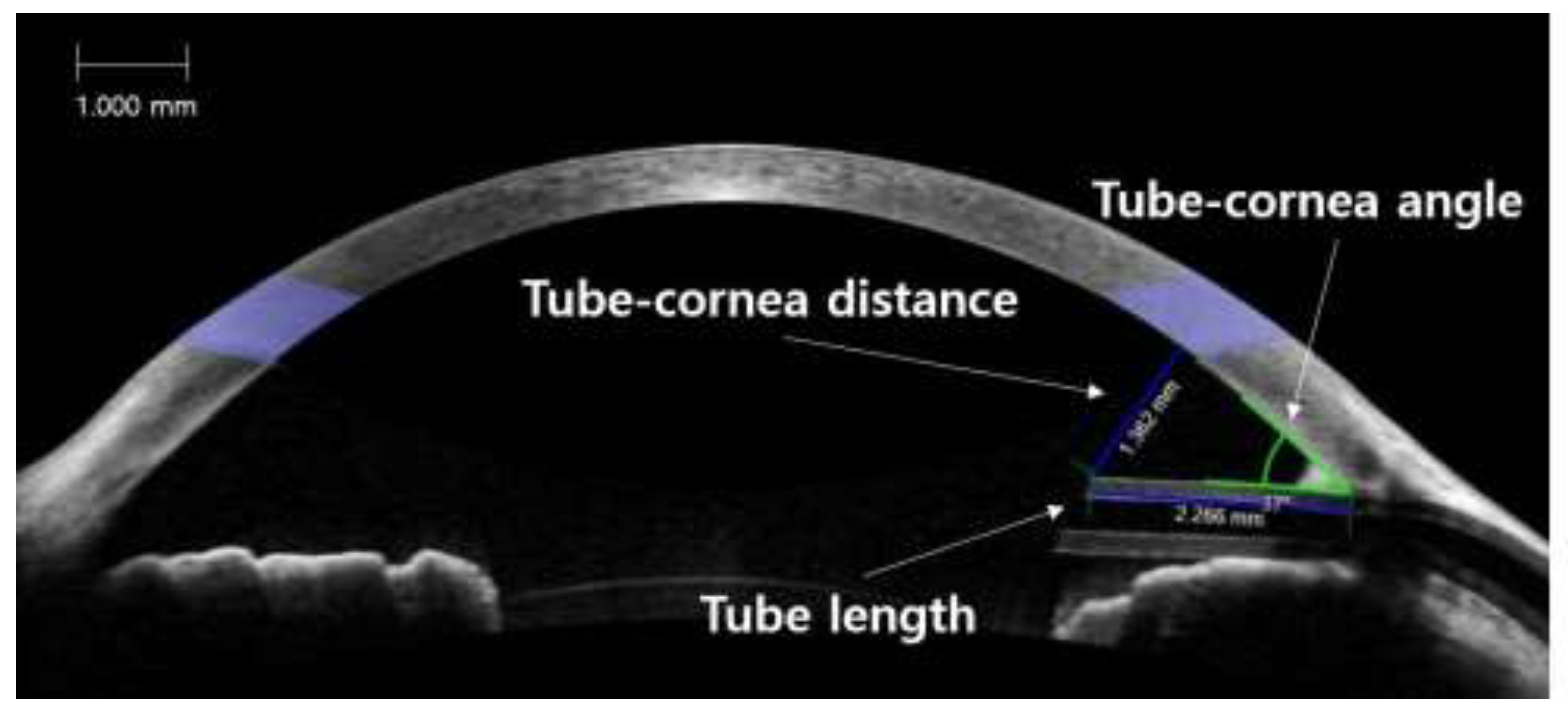
2.3. Anterior Segment Optical Coherence Tomography
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
Demographics
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arora, K.S.; Robin, A.L.; Corcoran, K.J.; Corcoran, S.L.; Ramulu, P.Y. Use of Various Glaucoma Surgeries and Procedures in Medicare Beneficiaries from 1994 to 2012. Ophthalmology 2015, 122, 1615–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, M.R.; Mendis, U.; Paliwal, A.; Haynatzka, V. Long-term follow-up of primary glaucoma surgery with Ahmed glaucoma valve implant versus trabeculectomy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2003, 136, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allingham, R.R.; Damji, K.F.; Freedman, S.F.; Moroi, S.E.; Rhee, D.J.; Shields, M.B. Shields Textbook of Glaucoma; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gedde, S.J.; Schiffman, J.C.; Feuer, W.J.; Herndon, L.W.; Brandt, J.D.; Budenz, D.L. Treatment Outcomes in the Tube Versus Trabeculectomy (TVT) Study After Five Years of Follow-up. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 153, 789–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taglia, D.P.; Perkins, T.W.; Gangnon, R.; Heatley, G.A.; Kaufman, P.L. Comparison of the Ahmed Glaucoma Valve, the Krupin Eye Valve with Disk, and the Double-plate Molteno Implant. J. Glaucoma 2002, 11, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDermott, M.L.; Swendris, R.P.; Shin, D.H.; Juzych, M.S.; Cowden, J.W. Corneal Endothelial Cell Counts After Molteno Implantation. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1993, 115, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topouzis, F.; Coleman, A.L.; Choplin, N.; Bethlem, M.M.; Hill, R.; Yu, F.; Panek, W.C.; Wilson, M.R. Follow-up of the original cohort with the Ahmed glaucoma valve implant. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1999, 128, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.S.; Yim, J.H.; Lee, E.K.; Lee, N.H. Changes in corneal endothelial cell density and morphology after Ahmed glaucoma valve implantation during the first year of follow up. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2008, 36, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minckler, D.S.; Francis, B.A.; Hodapp, E.A.; Jampel, H.D.; Lin, S.C.; Samples, J.R.; Smith, S.D.; Singh, K. Aqueous Shunts in Glaucoma: a report by the American Academy of Ophthalmology. Ophthalmology 2008, 115, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.-K.; Yun, Y.-J.; Lee, J.-E.; Yim, J.-H.; Kim, C.-S. Changes in Corneal Endothelial Cells after Ahmed Glaucoma Valve Implantation: 2-Year Follow-up. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 148, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.N.; Lee, S.B.; Lee, Y.-H.; Lee, J.J.; Bin Lim, H.; Kim, C.S. Changes in corneal endothelial cell density and the cumulative risk of corneal decompensation after Ahmed glaucoma valve implantation. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 100, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, A.P.; Barton, K.; Konstas, A.G. Corneal Edema After Aqueous Drainage Device Implantation. J. Glaucoma 2007, 16, 388–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiore, P.M.; Richter, C.U.; Arzeno, G.; Arrigg, C.A.; Shingleton, B.J.; Bellows, A.R.; Hutchinson, B.T. The Effect of Anterior Chamber Depth on Endothelial Cell Count After Filtration Surgery. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1989, 107, 1609–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarodia, U.; Sharkawi, E.; Hau, S.; Barton, K. Visualization of Aqueous Shunt Position and Patency Using Anterior Segment Optical Coherence Tomography. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 143, 1054–1056.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendrinos, E.; Dosso, A.; Sommerhalder, J.; Shaarawy, T. Coupling of HRT II and AS-OCT to evaluate corneal endothelial cell loss and in vivo visualization of the Ahmed glaucoma valve implant. Eye 2008, 23, 1836–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koo, E.B.; Hou, J.; Han, Y.; Keenan, J.D.; Stamper, R.L.; Jeng, B.H. Effect of Glaucoma Tube Shunt Parameters on Cornea Endothelial Cells in Patients With Ahmed Valve Implants. Cornea 2015, 34, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, A.N.; Webers, C.A.B.; Berendschot, T.T.J.M.; De Brabander, J.; De Witte, P.M.; Nuijts, R.M.M.A.; Schouten, J.; Beckers, H.J.M. Corneal endothelial cell loss after Baerveldt glaucoma drainage device implantation in the anterior chamber. Acta Ophthalmol. 2016, 95, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Console, J.W.; Sakata, L.M.; Aung, T.; Friedman, D.S.; He, M. Quantitative analysis of anterior segment optical coherence tomography images: the Zhongshan Angle Assessment Program. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2008, 92, 1612–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanaswamy, A.; Sakata, L.M.; He, M.; Friedman, D.; Chan, Y.-H.; Lavanya, R.; Baskaran, M.; Foster, P.J.; Aung, T. Diagnostic Performance of Anterior Chamber Angle Measurements for Detecting Eyes With Narrow Angles: an anterior segment OCT study. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2010, 128, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kee, C. Prevention of Early Postoperative Hypotony by Partial Ligation of Silicone Tube in Ahmed Glaucoma Valve Implantation. J. Glaucoma 2001, 10, 466–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.S.; Lee, M.W. Usefulness of opening pressure grading just prior to Ahmed glaucoma valve implantation to predict early postoperative hypotony. Acta Ophthalmol. 2016, 94, e514–e515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hau, S.; Scott, A.; Bunce, C.; Barton, K. Corneal Endothelial Morphology in Eyes Implanted With Anterior Chamber Aqueous Shunts. Cornea 2011, 30, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourne, W.M.; Nelson, L.R.; Hodge, D.O. Central corneal endothelial cell changes over a ten-year period. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1997, 38, 779–782. [Google Scholar]
- Gedde, S.J. Results from the tube versus trabeculectomy study. Middle East Afr. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 16, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gedde, S.J.; Schiffman, J.C.; Feuer, W.J.; Herndon, L.W.; Brandt, J.D.; Budenz, N.L. Three-Year Follow-up of the Tube Versus Trabeculectomy Study. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 148, 670–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadaki, T.G.; Zacharopoulos, I.P.; Pasquale, L.R.; Christen, W.B.; Netland, P.A.; Foster, C.S. Long-term Results of Ahmed Glaucoma Valve Implantation for Uveitic Glaucoma. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 144, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.C.; Netland, P.A.; Coleman, A.L.; Siegner, S.W.; Moster, M.R.; Hill, R.A. Intermediate-term clinical experience with the Ahmed Glaucoma Valve implant. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1999, 127, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.P.; Yamamoto, T.; Sawada, A.; Parrish, R.K., 2nd; Kitazawa, Y. Use of Antifibrosis Agents and Glaucoma Drainage Devices in the American and Japanese Glaucoma Societies. J. Glaucoma 1997, 6, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, N.C. Proliferative capacity of the corneal endothelium. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2003, 22, 359–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-Y.L.; Jung, K.I.; Park, C.K. Serial intracameral visualization of the Ahmed glaucoma valve tube by anterior segment optical coherence tomography. Eye 2012, 26, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, W.H.; Kim, T.-W.; Park, K.H.; Kim, D.M. Location of the Tube Tip in the Anterior Chamber and Change in Corneal Endothelium after Ahmed Valve Implantation. J. Korean Ophthalmol. Soc. 2013, 54, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Characteristics | Patients with ECD Damage (Group 1, n = 30) | Patients without ECD Damage (Group 2, n = 63) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years, mean ± SD) | 64.60 ± 11.63 | 60.41 ± 13.58 | 0.150 |
| Sex (M/F) | 24/6 | 42/21 | 0.227 |
| Laterality (R/L) | 15/15 | 31/32 | 1.000 |
| Systemic disease, n (%) | |||
| DM | 10 (33.33) | 26 (41.27) | 0.503 |
| HTN | 14 (46.67) | 30 (47.62) | 1.000 |
| CVA | 1 (3.33) | 1 (1.59) | 0.543 |
| Axial length (mm) | 24.58 ± 2.06 | 24.37 ± 2.12 | 0.641 |
| Anterior chamber depth (mm) | 4.06 ± 0.96 | 3.81 ± 0.86 | 0.238 |
| Baseline ECD (cells/mm2) | |||
| Average * | 2194.03 ± 572.08 | 2324.19 ± 510.16 | 0.272 |
| Center | 2182.03 ± 569.97 | 2320.33 ± 500.55 | 0.237 |
| Superior-temporal | 2184.60 ± 574.20 | 2311.90 ± 532.75 | 0.296 |
| Diagnosis, n (%) | 0.275 † | ||
| Neovascular glaucoma | 10 (33.33) | 30 (47.62) | |
| Primary open-angle glaucoma | 9 (30.00) | 11 (17.46) | |
| Uveitic glaucoma | 5 (16.67) | 11 (17.46) | |
| Chronic angle-closure glaucoma | 3 (10.00) | 1 (1.59) | |
| Pseudoexfoliation glaucoma | 1 (3.33) | 2 (3.17) | |
| Steroid induced glaucoma | 1 (3.33) | 1 (1.59) | |
| Other secondary glaucoma | 1 (3.33) | 7 (11.11) | |
| Preoperative IOP (mmHg) | 36.63 ± 9.76 | 38.97 ± 11.76 | 0.234 |
| Postoperative mean IOP (mmHg) | 18.27 ± 4.25 | 19.13 ± 5.27 | 0.489 |
| Final IOP (mmHg) | 16.35 ± 3.45 | 15.71 ± 4.34 | 0.561 |
| Follow-up period (months) | 29.30 ± 14.67 | 27.75 ± 11.63 | 0.582 |
| Postoperative topical CAI | 15 (50.00) | 35 (53.85) | 0.661 † |
| Tube Parameters | Patients with ECD Damage (Group 1, n = 30) | Patients without ECD Damage (Group 2, n = 63) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tube length (mm) | 2.21 ± 0.70 | 2.21 ± 0.69 | 0.989 |
| Tube-cornea distance (mm) | 0.98 ± 0.38 | 1.26 ± 0.39 | 0.002 |
| Tube-cornea angle (degree) | 28.67 ± 7.79 | 36.35 ± 5.35 | <0.001 |
| Corneal Area | Patients with ECD Damage (Group 1, n = 30) | p-Value | Patients without ECD Damage (Group 2, n = 63) | p-Value | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average † | −18.82 ± 22.97 (412.91 ± 503.96) | <0.001 | 2.14 ± 2.93 (49.74 ± 68.10) | 0.342 | <0.001 |
| Center | −17.82 ± 25.01 (388.84 ± 545.73) | <0.001 | 1.95 ± 3.06 (45.25 ± 71.00) | 0.612 | <0.001 |
| Superior temporal (ST) | −30.38 ± 26.18 (663.68 ± 571.93) | <0.001 | 2.56 ± 4.21 (59.18 ± 97.33) | 0.440 | <0.001 |
| Difference between ST and center | −12.56 ± 17.01 (274.84 ± 371.50) | <0.001 ‡ | 0.61 ± 3.26 (14.10 ± 75.34) | 0.145 ‡ | <0.001 |
| Characteristics | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β (95% CI) | p-Value | β (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Age (years, mean ± SD) | −0.067 (−0.324 to 0.190) | 0.611 | ||
| Sex (male) | −6.329 (−13.599 to 0.941) | 0.091 | −4.506 (−10.274 to 1.262) | 0.129 |
| Laterality (right) | −0.577 (−7.282 to 6.128) | 0.866 | ||
| Systemic disease | ||||
| DM | 1.270 (−5.608 to 8.148) | 0.718 | ||
| HTN | 3.743 (−2.927 to 10.413) | 0.274 | ||
| CVA | 3.390 (−19.711 to 26.491) | 0.774 | ||
| Axial length (mm) | −0.554 (−2.161 to 1.053) | 0.501 | ||
| Anterior chamber depth (mm) | 1.544 (−6.735 to 9.823) | 0.716 | ||
| Baseline ECD (cells/mm2) | ||||
| Average * | 0.006 (0.001 to 0.012) | 0.068 | 0.003 (−0.001 to 0.007) | 0.266 |
| Center | 0.006 (0.001 to 0.012) | 0.059 | ||
| Superior temporal | 0.006 (0.001 to 0.012) | 0.074 | ||
| Diagnosis | ||||
| Neovascular glaucoma | 4.710 (−1.991 to 11.411) | 0.172 | ||
| Primary open-angle glaucoma | 2.816 (−5.324 to 10.956) | 0.499 | ||
| Uveitic glaucoma | −12.178 (−20.702 to −3.654) | 0.006 | −5.150 (−12.188 to 1.888) | 0.155 |
| Chronic angle-closure glaucoma | 1.462 (−15.061 to 17.985) | 0.863 | ||
| Pseudoexfoliation glaucoma | 3.123 (−15.842 to 22.088) | 0.748 | ||
| Steroid induced glaucoma | −3.738 (−26.837 to 19.361) | 0.752 | ||
| Other secondary glaucoma | 0.328 (−11.628 to 12.284) | 0.957 | ||
| Preoperative IOP (mmHg) | 0.104 (−0.180 to 0.388) | 0.306 | ||
| Postoperative mean IOP (mmHg) | 1.155(0.285 to 2.025) | 0.011 | 0.547 (−0.163 to 1.257) | 0.135 |
| Final IOP (mmHg) | 0.514 (−0.223 to 0.251) | 0.467 | ||
| Follow-up (months) | 0.252 (−0.011 to 0.515) | 0.063 | 0.189 (−0.021 to 0.399) | 0.081 |
| Postoperative topical CAI | 0.056 (−4.246 to 4.358) | 0.542 | ||
| AS-OCT parameters | ||||
| Tube length (mm) | −2.088 (−6.949 to 2.773) | 0.402 | ||
| Tube-cornea distance (mm) | 14.493 (6.786 to 22.200) | <0.001 | 0.744 (−7.515 to 9.003) | 0.860 |
| Tube-cornea angle (degree) | 1.427 (1.060 to 1.794) | <0.001 | 1.254 (0.776 to 1.732) | <0.001 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.M.; Kim, K.N.; Park, K.S.; Lee, N.H.; Lee, S.B.; Kim, C.-S. Relationship between Tube Parameters and Corneal Endothelial Cell Damage after Ahmed Glaucoma Valve Implantation: A Comparative Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9082546
Lee HM, Kim KN, Park KS, Lee NH, Lee SB, Kim C-S. Relationship between Tube Parameters and Corneal Endothelial Cell Damage after Ahmed Glaucoma Valve Implantation: A Comparative Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(8):2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9082546
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Han Min, Kyoung Nam Kim, Kee Sup Park, Nam Ho Lee, Sung Bok Lee, and Chang-Sik Kim. 2020. "Relationship between Tube Parameters and Corneal Endothelial Cell Damage after Ahmed Glaucoma Valve Implantation: A Comparative Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 8: 2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9082546
APA StyleLee, H. M., Kim, K. N., Park, K. S., Lee, N. H., Lee, S. B., & Kim, C.-S. (2020). Relationship between Tube Parameters and Corneal Endothelial Cell Damage after Ahmed Glaucoma Valve Implantation: A Comparative Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(8), 2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9082546





