Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of Treatments for Systemic Sclerosis-Related Interstitial Lung Disease: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
- Participants: females and males aged ≥18 years. Diagnosis of SSc-ILD according to validated criteria.
- Interventions and comparisons: various pharmacological interventions, alone or in combination, and placebo
- Outcome measures: (a) mean change in “FVC % of predicted” from baseline to 12 months; (b) mean change in “DLCO % of predicted” from baseline to 12 months; (c) number of patients with SAEs; (d) number of patients discontinuing treatment due to AEs; (e) mortality. Outcome measures collected at different follow-up timepoints were pooled at annual intervals, plus or minus six months, with the primary analysis covering the first 12 months.
- Study design: RCTs.
2.2. Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Information Sources and Searches
2.4. Data Extraction and Summary Measures
2.5. Risk of Bias (RoB)
2.6. Assessment of Reporting Bias and Sensitivity Analysis
2.7. GRADE Quality Assessment
2.8. Network Meta-Analysis
3. Results
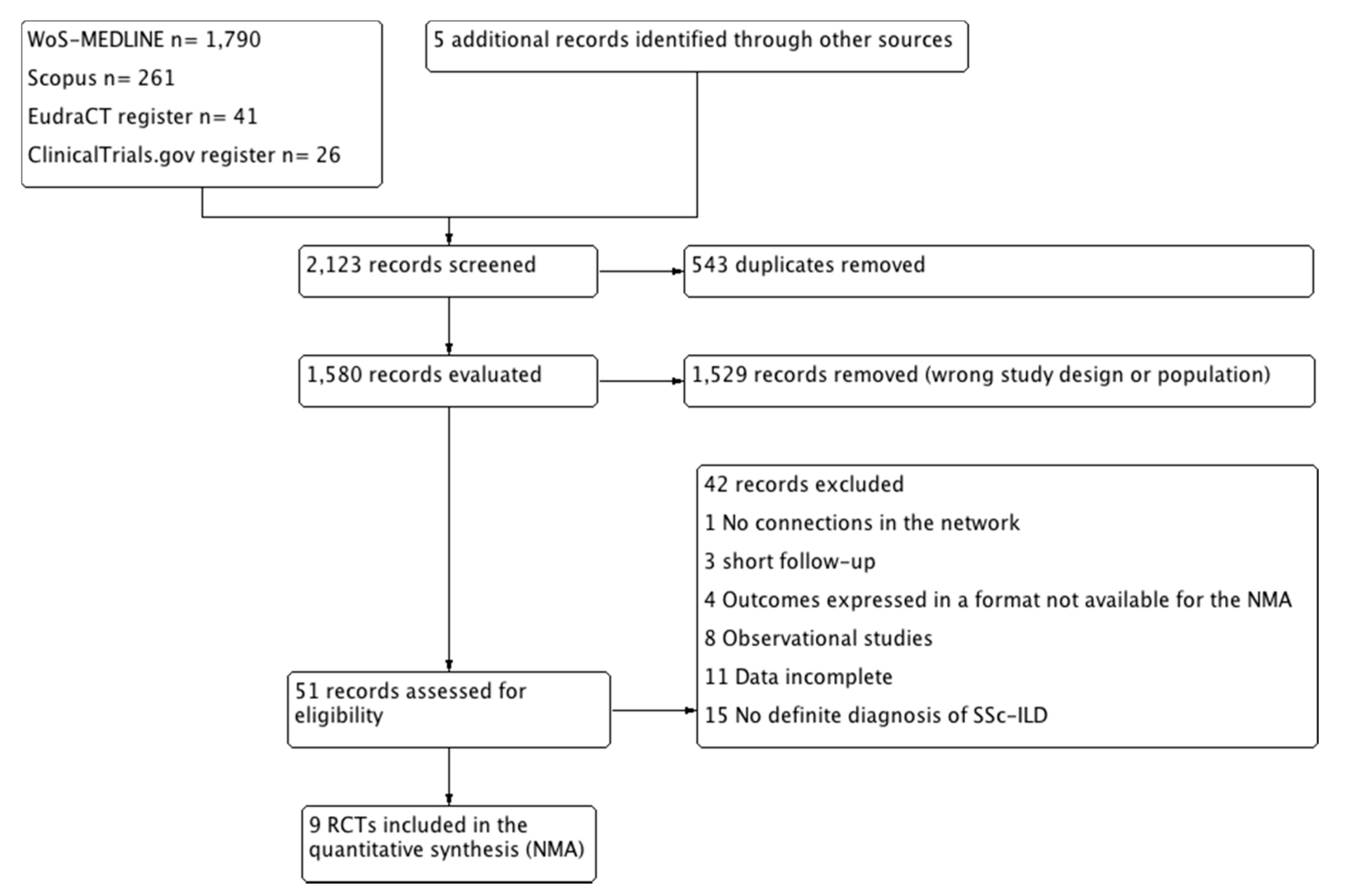
3.1. Search Results
3.2. Included Studies
3.3. Excluded Studies
3.4. Quality Assessment
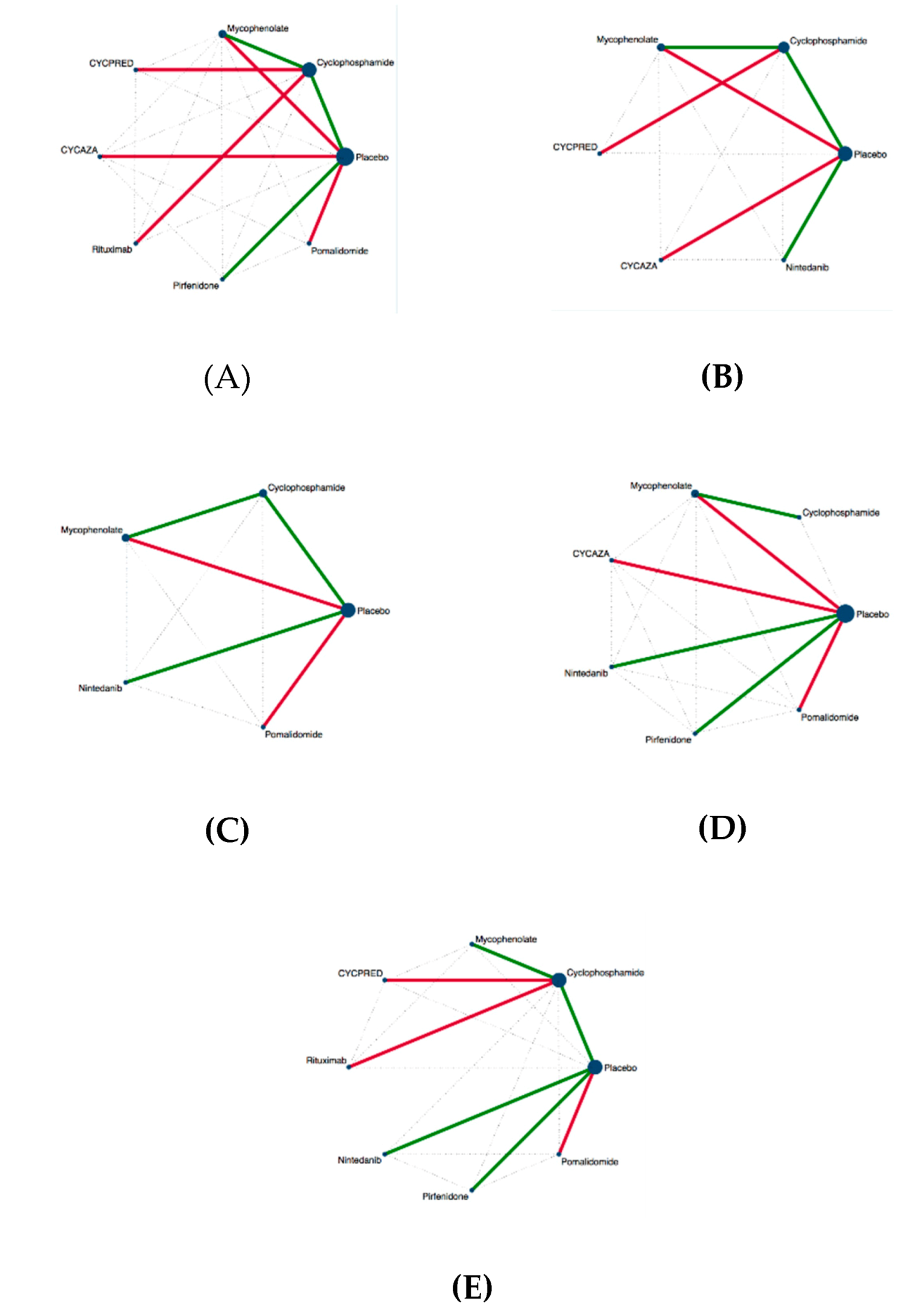
3.5. Inconsistency in NMA
3.6. Similarities Between Studies
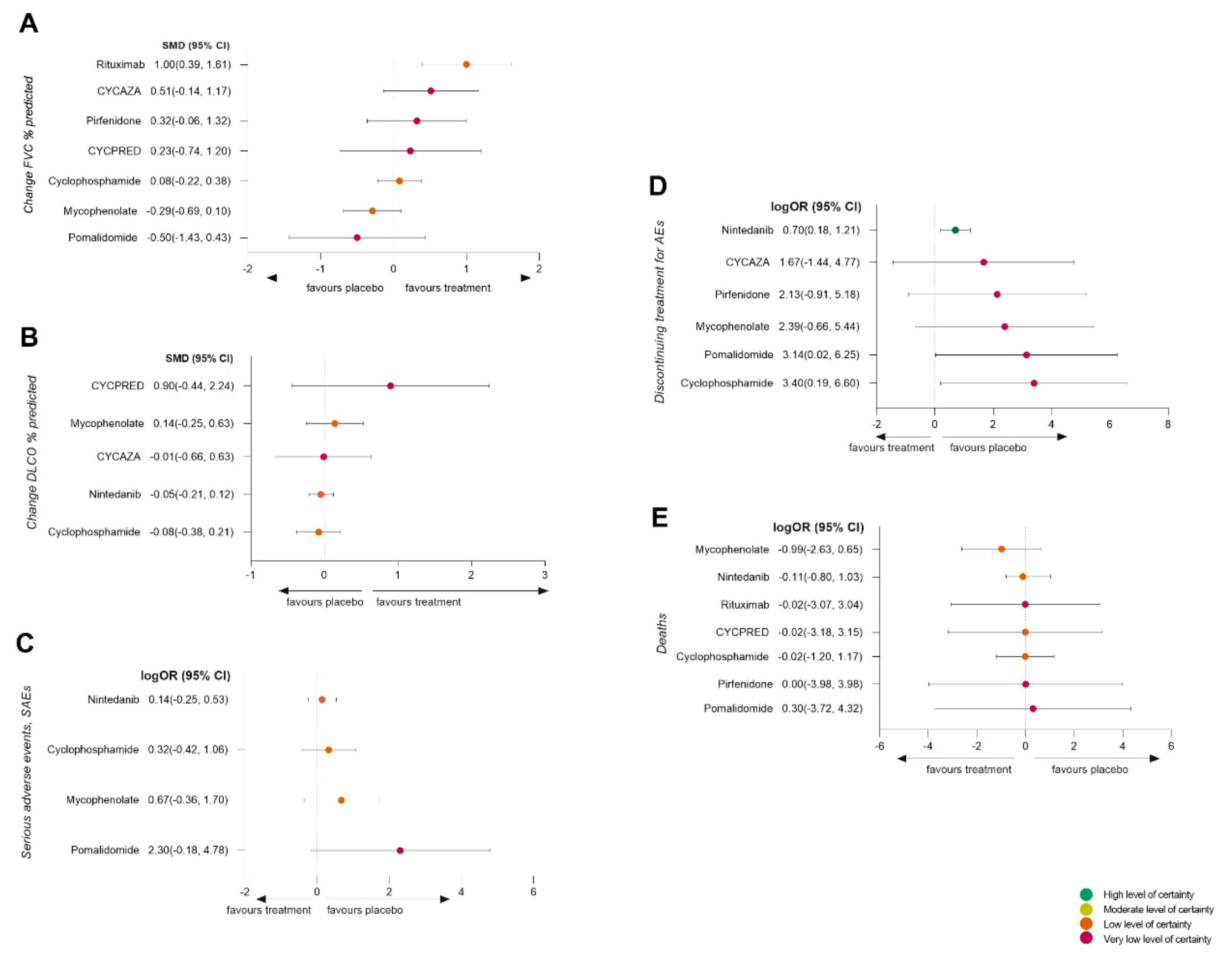
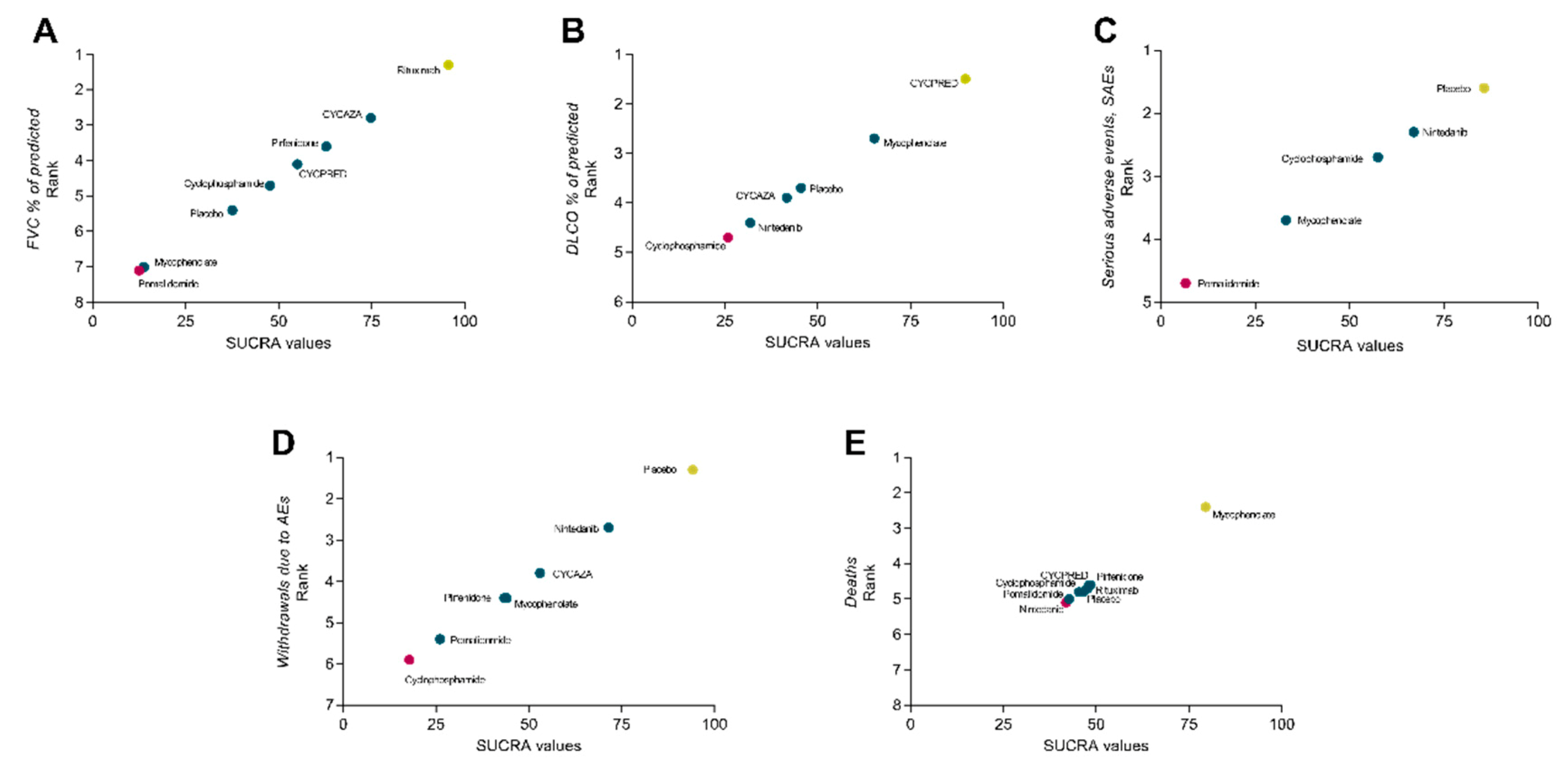
3.7. Efficacy Analysis
3.8. Safety Analysis
3.9. Tolerability Analysis
3.10. Mortality Analysis
3.11. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Denton, C.P.; Khanna, D. Systemic sclerosis. Lancet 2017, 390, 1685–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhai, M.; Meune, C.; Boubaya, M.; Avouac, J.; Hachulla, E.; Balbir-Gurman, A.; Riemekasten, G.; Airò, P.; Joven, B.; Vettori, S.; et al. Mapping and predicting mortality from systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Distler, O.; Volkmann, E.R.; Hoffmann-Vold, A.M.; Maher, T.M. Current and future perspectives on management of systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 15, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyndall, A.J.; Bannert, B.; Vonk, M.; Airò, P.; Cozzi, F.; Carreira, P.E.; Bancel, D.F.; Allanore, Y.; Müller-Ladner, U.; Distler, O.; et al. Causes and risk factors for death in systemic sclerosis: A study from the EULAR Scleroderma Trials and Research (EUSTAR) database. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1809–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolb, M.; Bondue, B.; Pesci, A.; Miyazaki, Y.; Song, J.W.; Bhatt, N.Y.; Huggins, J.T.; Oldham, J.M.; Padilla, M.L.; Roman, J.; et al. Acute exacerbations of progressive-fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2018, 27, 180071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowal-Bielecka, O.; Fransen, J.; Avouac, J.; Becker, M.; Kulak, A.; Allanore, Y.; Distler, O.; Clements, P.; Cutolo, M.; Czirjak, L.; et al. Update of EULAR recommendations for the treatment of systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1327–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashkin, D.P.; Roth, M.D.; Clements, P.J.; Furst, D.E.; Khanna, D.; Kleerup, E.C.; Goldin, J.; Arriola, E.; Volkmann, E.R.; Kafaja, S.; et al. Mycophenolate Mofetil versus Oral Cyclophosphamide in Scleroderma-related Interstitial Lung Disease: Scleroderma Lung Study II (SLS-II), a double-blind, parallel group, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 4, 708–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashkin, D.P.; Elashoff, R.; Clements, P.J.; Goldin, J.; Roth, M.D.; Furst, D.E.; Arriola, E.; Silver, R.; Strange, C.; Bolster, M.; et al. Cyclophosphamide versus placebo in scleroderma lung disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2655–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacchi, C.; Sebastiani, M.; Cassone, G.; Cerri, S.; Casa, G.D.; Salvarani, C.; Manfredi, A. Therapeutic Options for the Treatment of Interstitial Lung Disease Related to Connective Tissue Diseases. A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distler, O.; Highland, K.B.; Gahlemann, M.; Azuma, A.; Fischer, A.; Mayes, M.D.; Raghu, G.; Sauter, W.; Girard, M.; Alves, M.; et al. Nintedanib for systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2518–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.N.; Yang, Q.R.; Zhu, G.Q.; Pan, L.; Xia, J.X.; Wang, Q. Comparative efficacy and safety of immunosuppressive therapies for systemic sclerosis related interstitial lung disease: A Bayesian network analysis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2019, 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutton, B.; Salanti, G.; Caldwell, D.M.; Chaimani, A.; Schmid, C.H.; Cameron, C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Straus, S.; Thorlund, K.; Jansen, J.P.; et al. The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: Checklist and explanations. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions/Cochrane Training. Available online: https://training.cochrane.org/handbook#how-to-cite (accessed on 18 April 2020).
- Furukawa, T.A.; Salanti, G.; Atkinson, L.Z.; Leucht, S.; Ruhe, H.G.; Turner, E.H.; Chaimani, A.; Ogawa, Y.; Takeshima, N.; Hayasaka, Y.; et al. Comparative efficacy and acceptability of first-generation and second-generation antidepressants in the acute treatment of major depression: Protocol for a network meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2016, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipriani, A.; Furukawa, T.A.; Salanti, G.; Chaimani, A.; Atkinson, L.Z.; Ogawa, Y.; Leucht, S.; Ruhe, H.G.; Turner, E.H.; Higgins, J.P.T.; et al. Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 21 antidepressant drugs for the acute treatment of adults with major depressive disorder: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet 2018, 391, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salanti, G.; Del Giovane, C.; Chaimani, A.; Caldwell, D.M.; Higgins, J.P. Evaluating the quality of evidence from a network meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puhan, M.A.; Schünemann, H.J.; Murad, M.H.; Li, T.; Brignardello-Petersen, R.; Singh, J.A.; Kessels, A.G.; Guyatt, G.H. A GRADE Working Group approach for rating the quality of treatment effect estimates from network meta-analysis. BMJ 2014, 349, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salanti, G. Indirect and mixed-treatment comparison, network, or multiple-treatments meta-analysis: Many names, many benefits, many concerns for the next generation evidence synthesis tool. Res. Synth. Methods 2012, 3, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, I.R. Network meta-analysis. Stata J. 2015, 951–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaimani, A.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Mavridis, D.; Spyridonos, P.; Salanti, G. Graphical Tools for Network Meta-Analysis in STATA. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, S.; Welton, N.J.; Caldwell, D.M.; Ades, A.E. Checking consistency in mixed treatment comparison meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2010, 29, 932–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, I.R.; Barrett, J.K.; Jackson, D.; Higgins, J.P.T. Consistency and inconsistency in network meta-analysis: Model estimation using multivariate meta-regression. Res. Synth. Methods 2012, 3, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domiciano, D.S.; Bonfá, E.; Borges, C.T.L.; Kairalla, R.A.; Capelozzi, V.L.; Parra, E.; Christmann, R.B. A long-term prospective randomized controlled study of non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) treatment in scleroderma. Clin. Rheumatol. 2011, 30, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyles, R.K.; Ellis, R.W.; Wellsbury, J.; Lees, B.; Newlands, P.; Goh, N.S.L.; Roberts, C.; Desai, S.; Herrick, A.L.; McHugh, N.J.; et al. A multicenter, prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of corticosteroids and intravenous cyclophosphamide followed by oral azathioprine for the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis in scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 3962–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidu, G.S.R.S.N.K.; Sharma, S.K.; Adarsh, M.B.; Dhir, V.; Sinha, A.; Dhooria, S.; Jain, S. Effect of mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) on systemic sclerosis-related interstitial lung disease with mildly impaired lung function: A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial. Rheumatol. Int. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sircar, G.; Goswami, R.P.; Sircar, D.; Ghosh, A.; Ghosh, P. Intravenous cyclophosphamide vs rituximab for the treatment of early diffuse scleroderma lung disease: Open label, randomized, controlled trial. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 2106–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, N.; Sharma, S.K.; Mishra, D.; Dhooria, S.; Dhir, V.; Jain, S. Efficacy and safety of pirfenidone in systemic sclerosis-related interstitial lung disease—A randomised controlled trial. Rheumatol. Int. 2020, 40, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, V.M.; Denton, C.P.; Domsic, R.T.; Furst, D.E.; Rischmueller, M.; Stanislav, M.; Steen, V.D.; Distler, J.H.W.; Korish, S.; Cooper, A.; et al. Pomalidomide in patients with interstitial lung disease due to systemic sclerosis: A phase II, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study. J. Rheumatol. 2018, 45, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Raya, A.; Abou-Raya, S.; Helmii, M. OP0038 Effects of Angiotensin II Receptor Blockade in Systemic Sclerosis: Randomized Controlled Trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, A61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allanore, Y.; Distler, O.; Jagerschmidt, A.; Illiano, S.; Ledein, L.; Boitier, E.; Agueusop, I.; Denton, C.P.; Khanna, D. Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 1 Antagonist SAR100842 for Patients With Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Eight-Week Placebo-Controlled Study Followed by a Sixteen-Week Open-Label Extension Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 1634–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allanore, Y.; Denton, C.; Khanna, D.; Soubrane, C.; Esperet, C. Efficacy and Safety of Romilkimab in Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis (dcSSc): A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, 24-week, Proof of Concept Study. In Proceedings of the 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting, Atlanta, GA, USA, 8–13 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- NCT02161406. A Study of Subcutaneous Abatacept to Treat Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis (ASSET). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02161406 (accessed on 30 June 2020).
- Burt, R.K.; Shah, S.J.; Dill, K.; Grant, T.; Gheorghiade, M.; Schroeder, J.; Craig, R.; Hirano, I.; Marshall, K.; Ruderman, E.; et al. Autologous non-myeloablative haemopoietic stem-cell transplantation compared with pulse cyclophosphamide once per month for systemic sclerosis ( ASSIST): An open-label, randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet 2011, 378, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonstra, M.; Meijs, J.; Dorjée, A.L.; Marsan, N.A.; Schouffoer, A.; Ninaber, M.K.; Quint, K.D.; Bonte-Mineur, F.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Scherer, H.U.; et al. Rituximab in early systemic sclerosis. RMD Open 2017, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakravarty, E.F.; Martyanov, V.; Fiorentino, D.; Wood, T.A.; Haddon, D.J.; Jarrell, J.A.; Utz, P.J.; Genovese, M.C.; Whitfield, M.L.; Chung, L. Gene expression changes reflect clinical response in a placebo-controlled randomized trial of abatacept in patients with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daoussis, D.; Liossis, S.N.C.; Tsamandas, A.C.; Kalogeropoulou, C.; Kazantzi, A.; Sirinian, C.; Karampetsou, M.; Yiannopoulos, G.; Andonopoulos, A.P. Experience with rituximab in scleroderma: Results from a 1-year, proof-of-principle study. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daoussis, D.; Liossis, S.N.C.; Tsamandas, A.C.; Kalogeropoulou, C.; Paliogianni, F.; Sirinian, C.; Yiannopoulos, G.; Andonopoulos, A.P. Effect of long-term treatment with rituximab on pulmonary function and skin fibrosis in patients with diffuse systemic sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2012, 30, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Daoussis, D.; Melissaropoulos, K.; Sakellaropoulos, G.; Antonopoulos, I.; Markatseli, T.E.; Simopoulou, T.; Georgiou, P.; Andonopoulos, A.P.; Drosos, A.A.; Sakkas, L.; et al. A multicenter, open-label, comparative study of B-cell depletion therapy with Rituximab for systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2017, 46, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denton, C.P.; Merkel, P.A.; Furst, D.E.; Khanna, D.; Emery, P.; Hsu, V.M.; Silliman, N.; Streisand, J.; Powell, J.; Åkesson, A.; et al. Recombinant human anti-transforming growth factor β1 antibody therapy in systemic sclerosis: A multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled phase I/II trial of CAT-192. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Z.; Marra, A.M.; Benjamin, N.; Eichstaedt, C.A.; Blank, N.; Bossone, E.; Cittadini, A.; Coghlan, G.; Denton, C.P.; Distler, O.; et al. Early treatment with ambrisentan of mildly elevated mean pulmonary arterial pressure associated with systemic sclerosis: A randomized, controlled, double-blind, parallel group study (EDITA study). Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, D.; Denton, C.P.; Jahreis, A.; van Laar, J.M.; Frech, T.M.; Anderson, M.E.; Baron, M.; Chung, L.; Fierlbeck, G.; Lakshminarayanan, S.; et al. Safety and efficacy of subcutaneous tocilizumab in adults with systemic sclerosis (faSScinate): A phase 2, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 2630–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCT02453256. A Study of the Efficacy and Safety of Tocilizumab in Participants With Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) [focuSSced]. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02453256 (accessed on 30 June 2020).
- Gordon, J.K.; Martyanov, V.; Franks, J.M.; Bernstein, E.J.; Szymonifka, J.; Magro, C.; Wildman, H.F.; Wood, T.A.; Whitfield, M.L.; Spiera, R.F. Belimumab for the Treatment of Early Diffuse Systemic Sclerosis: Results of a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Pilot Trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, B.L.; Kaufman, L.D. A double-blind randomized controlled trial of ketotifen versus placebo in early diffuse scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 1991, 34, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillevin, L.; Chouvet, B.; Mery, C.; Thivolet, J.; Godeau, P.; Delbarre, F. Traitement de la scl’erodermie. Cah. Coll. Med. Hop. Paris 1982, 3, 273–277. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.H.; Tu, W.Z.; Chen, D.D.; Sun, J.Y.; Shi, M. Therapeutic effects on systemic scleroderma of integrated therapy of Traditional Chinese Medicine with penicillamine. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2008, 37, 464–466. [Google Scholar]
- Henes, J.; Oliveira, M.C.; Labopin, M.; Badoglio, M.; Scherer, H.U.; Del Papa, N.; Daikeler, T.; Schmalzing, M.; Schroers, R.; Martin, T.; et al. Autologous stem cell transplantation for progressive systemic sclerosis: A prospective non-interventional study from the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation Autoimmune Disease Working Party. Haematologica 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrick, A.L.; Pan, X.; Peytrignet, S.; Lunt, M.; Hesselstrand, R.; Mouthon, L.; Silman, A.; Brown, E.; Czirják, L.; Distler, J.H.W.; et al. Treatment outcome in early diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis: The European Scleroderma Observational Study (ESOS). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1207–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann-Vold, A.; Fretheim, H.; Chung, B.; Didriksen, H.; Bækkevold, E.; Midtvedt, Ø.; Brunborg, C.; Garen, T.; Midtvedt, T.; Hov, J.; et al. OP0327 Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Systemic Sclerosis: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Randomized Pilot Trial. BJM J. 2019, 16, 246–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, D.; Clements, P.J.; Furst, D.E.; Korn, J.H.; Ellman, M.; Rothfield, N.; Wigley, F.M.; Moreland, L.W.; Silver, R.; Kim, Y.H.; et al. Recombinant human relaxin in the treatment of systemic sclerosis with diffuse cutaneous involvement: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1102–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabi, S.; Moradi, M.M.; Khodamoradi, Z.; Nazarinia, M.A. Effects of N-acetylcysteine on Pulmonary Functions in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: A double blind, placebo controlled study. Curr. Rheumatol. Rev. 2019, 15, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadashkevich, O.; Davis, P.; Fritzler, M.; Kovalenko, W. A randomized unblinded trial of cyclophosphamide versus azathioprine in the treatment of systemic sclerosis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2006, 25, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distler, O.; Pope, J.; Denton, C.; Allanore, Y.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; de Oliveira Pena, J.; Khanna, D. RISE-SSc: Riociguat in diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis. Respir. Med. 2017, 122, S14–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- NCT02465437. Safety, Tolerability, Efficacy, and Pharmacokinetics of JBT-101 in Systemic Sclerosis. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02465437 (accessed on 30 June 2020).
- NCT02745145. Abituzumab in SSc-ILD. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02745145 (accessed on 30 June 2020).
- Pakas, I.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Malagari, K.; Skopouli, F.N.; Moutsopoulos, H.M.; Vlachoyiannopoulos, P.G. Cyclophosphamide with low or high dose prednisolone for systemic sclerosis lung disease. J. Rheumatol. 2002, 29, 298–304. [Google Scholar]
- Panopoulos, S.T.; Bournia, V.K.; Trakada, G.; Giavri, I.; Kostopoulos, C.; Sfikakis, P.P. Mycophenolate versus cyclophosphamide for progressive interstitial lung disease associated with systemic sclerosis: A 2-year case control study. Lung 2013, 191, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poormoghim, H.; Rezaei, N.; Sheidaie, Z.; Almasi, A.R.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; Almasi, S.; Andalib, E. Systemic sclerosis: Comparison of efficacy of oral cyclophosphamide and azathioprine on skin score and pulmonary involvement—A retrospective study. Rheumatol. Int. 2014, 34, 1691–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, J.E.; Bellamy, N.; Seibold, J.R.; Baron, M.; Ellman, M.; Carette, S.; Smith, C.D.; Chalmers, I.M.; Hong, P.; O’Hanlon, D.; et al. A randomized, controlled trial of methotrexate versus placebo in early diffuse scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prey, S.; Ezzedine, K.; Doussau, A.; Grandoulier, A.S.; Barcat, D.; Chatelus, E.; Diot, E.; Durant, C.; Hachulla, E.; De Korwin-Krokowski, J.D.; et al. Imatinib mesylate in scleroderma-associated diffuse skin fibrosis: A phase II multicentre randomized double-blinded controlled trial. Br. J. Dermatol. 2012, 167, 1138–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quillinan, N.P.; McIntosh, D.; Vernes, J.; Haq, S.; Denton, C.P. Treatment of diffuse systemic sclerosis with hyperimmune caprine serum (AIMSPRO): A phase II double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiopu, E.; Chatterjee, S.; Hsu, V.; Flor, A.; Cimbora, D.; Patra, K.; Yao, W.; Li, J.; Streicher, K.; McKeever, K.; et al. Safety and tolerability of an anti-CD19 monoclonal antibody, MEDI-551, in subjects with systemic sclerosis: A phase I, randomized, placebo-controlled, escalating single-dose study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EudraCT 2014-001101-40 Sclero XIII: A phase II, Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Study to Investigate the Pharmacokinetics, Safety and Efficacy of Intravenous Factor XIII Treatment in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/search?query=Sclero+XIII (accessed on 30 June 2020).
- Seibold, J.R.; Korn, J.H.; Simms, R.; Clements, P.J.; Moreland, L.W.; Mayes, M.D.; Furst, D.E.; Rothfield, N.; Steen, V.; Weisman, M.; et al. Recombinant human relaxin in the treatment of scleroderma. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2000, 132, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibold, J.R.; Denton, C.P.; Furst, D.E.; Guillevin, L.; Rubin, L.J.; Wells, A.; Matucci Cerinic, M.; Riemekasten, G.; Emery, P.; Chadha-Boreham, H.; et al. Randomized, prospective, placebo-controlled trial of bosentan in interstitial lung disease secondary to systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2101–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.I.K.; Khanna, D.; Furst, D.E.; Danovitch, G.; Burger, C.; Maranian, P.; Clements, P.J. Rapamycin versus methotrexate in early diffuse systemic sclerosis: Results from a randomized, single-blind pilot study. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 3821–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, K.M.; Majhail, N.S.; Bredeson, C.; Carpenter, P.A.; Chatterjee, S.; Crofford, L.J.; Georges, G.E.; Nash, R.A.; Pasquini, M.C.; Sarantopoulos, S.; et al. Systemic Sclerosis as an Indication for Autologous Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: Position Statement from the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 2018, 24, 1961–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Hoogen, F.H.J.; Boerbooms, A.M.T.; Swaak, A.J.G.; Rasker, J.J.; Van Lier, H.J.J.; Van De Putte, L.B.A. Comparison of methotrexate with placebo in the treatment of systemic sclerosis: A 24 week randomized double-blind trial, followed by a 24 week observational trial. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1996, 35, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Laar, J.M.; Farge, D.; Sont, J.K.; Naraghi, K.; Marjanovic, Z.; Larghero, J.; Schuerwegh, A.J.; Marijt, E.W.A.; Vonk, M.C.; Schattenberg, A.V.; et al. Autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation vs intravenous pulse cyclophosphamide in diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA-J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2014, 311, 2490–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellan, M.; Patrucco, F.; Barone-Adesi, F.; Gavelli, F.; Castello, L.M.; Nerviani, A.; Andreoli, L.; Cavagna, L.; Pirisi, M.; Sainaghi, P.P. Targeting CD20 in the treatment of interstitial lung diseases related to connective tissue diseases: A systematic review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 102453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosello, S.L.; De Luca, G.; Rucco, M.; Berardi, G.; Falcione, M.; Danza, F.M.; Pirronti, T.; Ferraccioli, G. Long-term efficacy of B cell depletion therapy on lung and skin involvement in diffuse systemic sclerosis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2015, 44, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosello, S.; De Santis, M.; Lama, G.; Spanò, C.; Angelucci, C.; Tolusso, B.; Sica, G.; Ferraccioli, G. B cell depletion in diffuse progressive systemic sclerosis: Safety, skin score modification and IL-6 modulation in an up to thirty-six months follow-up open-label trial. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafyatis, R.; Kissin, E.; York, M.; Farina, G.; Viger, K.; Fritzler, M.J.; Merkel, P.A.; Simms, R.W. B cell depletion with rituximab in patients with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhai, M.; Boubaya, M.; Distler, O.; Smith, V.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Alegre Sancho, J.J.; Truchetet, M.E.; Braun-Moscovici, Y.; Iannone, F.; Novikov, P.I.; et al. Outcomes of patients with systemic sclerosis treated with rituximab in contemporary practice: A prospective cohort study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, P.; Tsipouri, V.; Keir, G.J.; Ashby, D.; Flather, M.D.; Parfrey, H.; Babalis, D.; Renzoni, E.A.; Denton, C.P.; Wells, A.U.; et al. Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide for the treatment of connective tissue diseaseassociated interstitial lung disease (RECITAL): Study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials 2017, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, S.; Huscher, D.; Siegert, E.; Allanore, Y.; Czirják, L.; DelGaldo, F.; Denton, C.P.; Distler, O.; Frerix, M.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; et al. Systemic sclerosis associated interstitial lung disease—Individualized immunosuppressive therapy and course of lung function: Results of the EUSTAR group. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, M.D.; Tseng, C.H.; Clements, P.J.; Furst, D.E.; Tashkin, D.P.; Goldin, J.G.; Khanna, D.; Kleerup, E.C.; Li, N.; Elashoff, D.; et al. Predicting Treatment Outcomes and Responder Subsets in Scleroderma-related Interstitial Lung Disease. Arthritis Rheum 2011, 63, 2797–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, H.; Holland, A.E.; Westall, G.P.; Goh, N.S.L.; Glaspole, I.N. Cyclophosphamide for connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broad, K.; Pope, J. The efficacy of treatment for systemic sclerosis interstitial lung disease: Results from a meta-analysis. Case Rep. Clin. Pract. Rev. 2010, 16, 187–190. [Google Scholar]
- Nannini, C.; West, C.P.; Erwin, P.J.; Matteson, E.L. Effects of cyclophosphamide on pulmonary function in patients with scleroderma and interstitial lung disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and observational prospective cohort studies. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2008, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkmann, E.R.; Tashkin, D.P.; Li, N.; Roth, M.D.; Khanna, D.; Hoffmann-Vold, A.M.; Kim, G.; Goldin, J.; Clements, P.J.; Furst, D.E.; et al. Mycophenolate Mofetil Versus Placebo for Systemic Sclerosis–Related Interstitial Lung Disease: An Analysis of Scleroderma Lung Studies I and II. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, A.U.; Hirani, N. Interstitial lung disease guideline: The British Thoracic Society in collaboration with the Thoracic Society of Australia and New Zealand and the Irish Thoracic Society. Thorax 2008, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Erre, G.L.; Sebastiani, M.; Fenu, M.A.; Zinellu, A.; Floris, A.; Cavagna, L.; Renzoni, E.; Manfredi, A.; Passiu, G.; Woodman, R.J.; et al. Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of Treatments for Systemic Sclerosis-Related Interstitial Lung Disease: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9082560
Erre GL, Sebastiani M, Fenu MA, Zinellu A, Floris A, Cavagna L, Renzoni E, Manfredi A, Passiu G, Woodman RJ, et al. Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of Treatments for Systemic Sclerosis-Related Interstitial Lung Disease: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(8):2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9082560
Chicago/Turabian StyleErre, Gian Luca, Marco Sebastiani, Maria Antonietta Fenu, Angelo Zinellu, Alberto Floris, Lorenzo Cavagna, Elisabetta Renzoni, Andreina Manfredi, Giuseppe Passiu, Richard John Woodman, and et al. 2020. "Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of Treatments for Systemic Sclerosis-Related Interstitial Lung Disease: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 8: 2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9082560
APA StyleErre, G. L., Sebastiani, M., Fenu, M. A., Zinellu, A., Floris, A., Cavagna, L., Renzoni, E., Manfredi, A., Passiu, G., Woodman, R. J., & Mangoni, A. A. (2020). Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of Treatments for Systemic Sclerosis-Related Interstitial Lung Disease: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(8), 2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9082560






