Ischemic Stroke among the Symptoms Caused by the COVID-19 Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Thrombosis and COVID-19
3. Ischemic Stroke
3.1. Epidemiology of Stroke
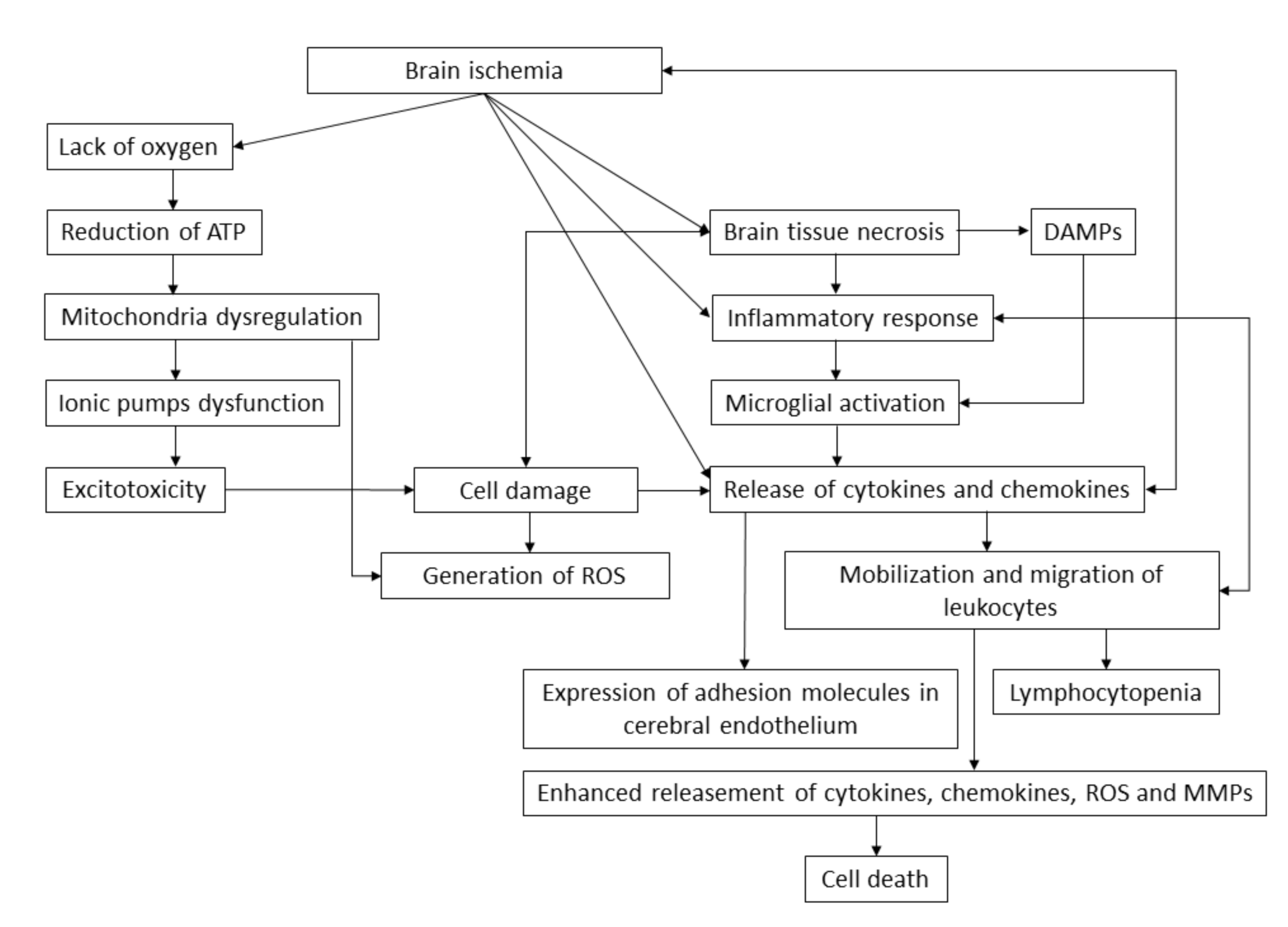
3.2. Molecular Pathophysiology of Ischemic Stroke
4. The Association between COVID-19 and Ischemic Stroke
4.1. The Clinical Characteristics of COVID-19 Patients
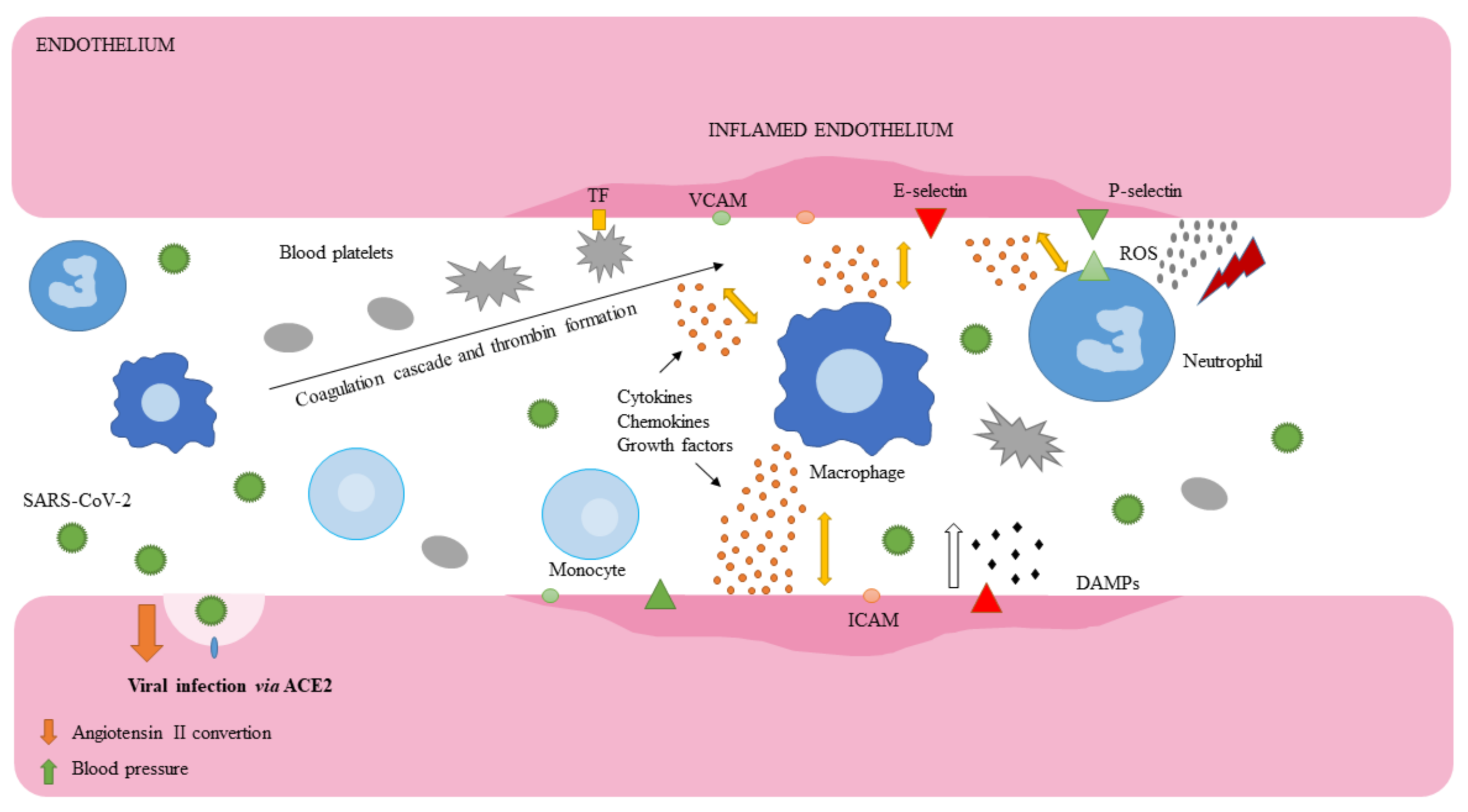
4.2. Molecular Association between SARS-CoV-2 and Ischemic Stroke
4.3. Endothelial Cells
4.4. Leukocytes and Macrophages
4.5. Blood Platelets and Coagulation Cascade
5. Pharmacological Treatment
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.; Liu, S.-M.; Yu, X.-H.; Tang, S.-L.; Tang, C.-K. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Current status and future perspectives. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuki, K.; Fujiogi, M.; Koutsogiannaki, S. COVID-19 pathophysiology: A review. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 215, 108427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J. SARS-CoV-2: An emerging coronavirus that causes a global threat. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 1678–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Q&A on Coronaviruses (COVID-19). Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/question-and-answers-hub/q-a-detail/q-a-coronaviruses#:~:text=symptoms (accessed on 18 June 2020).
- Tu, Y.F.; Chien, C.S.; Yarmishyn, A.A.; Lin, Y.Y.; Luo, Y.H.; Lin, Y.T.; Lai, W.Y.; Yang, D.M.; Chou, S.J.; Yang, Y.P.; et al. A review of SARS-CoV-2 and the ongoing clinical trials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gandhi, M.; Yokoe, D.S.; Havlir, D.V. Asymptomatic transmission, the Achilles’ Heel of current strategies to control Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2158–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadyen James, D.; Stevens, H.; Peter, K. The emerging threat of (Micro)Thrombosis in COVID-19 and its therapeutic implications. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 571–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oklu, R. Thrombosis. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2017, 7, S131–S133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, J.M.; Levy, J.H. COVID-19 and its implications for thrombosis and anticoagulation. Blood 2020, 135, 2033–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Jin, H.; Wang, M.; Hu, Y.; Chen, S.; He, Q.; Chang, J.; Hong, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, D.; et al. Neurologic manifestations of hospitalized patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Wuhan, China. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, Z.; Duan, J.; Hashimoto, K.; Yang, L.; Liu, C.; Yang, C. Nervous system involvement after infection with COVID-19 and other coronaviruses. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 87, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gorp, E.C.M.; Suharti, C.; ten Cate, H.; Dolmans, W.M.V.; van der Meer, J.W.M.; ten Cate, J.W.; Brandjes, D.P.M. Review: Infectious diseases and coagulation disorders. J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 180, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venugopal, A. Disseminated intravascular coagulation. Indian J. Anaesth. 2014, 58, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Li, D.; Wang, X.; Sun, Z. Abnormal coagulation parameters are associated with poor prognosis in patients with novel coronavirus pneumonia. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 844–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lippi, G.; Plebani, M.; Henry, B.M. Thrombocytopenia is associated with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infections: A meta-analysis. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2020, 506, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyrouti, R.; Adams, M.E.; Benjamin, L.; Cohen, H.; Farmer, S.F.; Goh, Y.Y.; Humphries, F.; Jäger, H.R.; Losseff, N.A.; Perry, R.J.; et al. Characteristics of ischaemic stroke associated with COVID-19. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, F.L.; Vogler, T.O.; Moore, E.E.; Moore, H.B.; Wohlauer, M.V.; Urban, S.; Nydam, T.L.; Moore, P.K.; McIntyre, R.C. Fibrinolysis shutdown correlates to thromboembolic events in severe COVID-19 infection. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranucci, M.; Ballotta, A.; Di Dedda, U.; Bayshnikova, E.; Dei Poli, M.; Resta, M.; Falco, M.; Albano, G.; Menicanti, L. The procoagulant pattern of patients with COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1747–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magro, C.; Mulvey, J.J.; Berlin, D.; Nuovo, G.; Salvatore, S.; Harp, J.; Baxter-Stoltzfus, A.; Laurence, J. Complement associated microvascular injury and thrombosis in the pathogenesis of severe COVID-19 infection: A report of five cases. Transl. Res. 2020, 220, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carsana, L.; Sonzogni, A.; Nasr, A.; Rossi, R.; Pellegrinelli, A.; Zerbi, P.; Rech, R.; Colombo, R.; Antinori, S.; Corbellino, M.; et al. Pulmonary post-mortem findings in a large series of COVID-19 cases from Northern Italy. MedRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frizzell, J.P. Acute stroke: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. AACN Clin. Issues 2005, 16, 421–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donkor, E.S. Stroke in the 21(st) Century: A snapshot of the burden, epidemiology, and quality of life. Stroke Res. Treat. 2018, 2018, 3238165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hankey, G.J. Stroke. Lancet 2017, 389, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehme, A.K.; Esenwa, C.; Elkind, M.S.V. Stroke risk factors, genetics, and prevention. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 472–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musuka, T.D.; Wilton, S.B.; Traboulsi, M.; Hill, M.D. Diagnosis and management of acute ischemic stroke: Speed is critical. CMAJ Can. Med. Assoc. J./J. De L’association Med. Can. 2015, 187, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donkel, S.J.; Benaddi, B.; Dippel, D.W.J.; Ten Cate, H.; de Maat, M.P.M. Prognostic hemostasis biomarkers in acute ischemic stroke. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanyal, N. The science of ischemic stroke: Pathophysiology and pharmacological treatment. Int. J. Pharma Res. Rev. 2015, 4, 65–84. [Google Scholar]
- Pawluk, H.; Woźniak, A.; Grześk, G.; Kołodziejska, R.; Kozakiewicz, M.; Kopkowska, E.; Grzechowiak, E.; Kozera, G. The role of selected pro-inflammatory cytokines in pathogenesis of ischemic stroke. Clin. Interv. Aging 2020, 15, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strecker, J.-K.; Schmidt, A.; Schäbitz, W.-R.; Minnerup, J. Neutrophil granulocytes in cerebral ischemia—Evolution from killers to key players. Neurochem. Int. 2017, 107, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, R.; Yang, G.; Li, G. Inflammatory mechanisms in ischemic stroke: Role of inflammatory cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 87, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bobryshev, Y.V. Monocyte recruitment and foam cell formation in atherosclerosis. Micron 2006, 37, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsberg Perttu, J.; Grau Armin, J. Inflammation and infections as risk factors for ischemic stroke. Stroke 2003, 34, 2518–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawabori, M.; Yenari, M.A. Inflammatory responses in brain ischemia. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 1258–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rezaei, O.; Pakdaman, H.; Gharehgozli, K.; Simani, L.; Vahedian-Azimi, A.; Asaadi, S.; Sahraei, Z.; Hajiesmaeili, M. S100 B: A new concept in neurocritical care. Iran. J. Neurol. 2017, 16, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bharosay, A.; Bharosay, V.V.; Varma, M.; Saxena, K.; Sodani, A.; Saxena, R. Correlation of Brain Biomarker Neuron Specific Enolase (NSE) with degree of disability and neurological worsening in cerebrovascular stroke. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. IJCB 2012, 27, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oxley, T.J.; Mocco, J.; Majidi, S.; Kellner, C.P.; Shoirah, H.; Singh, I.P.; De Leacy, R.A.; Shigematsu, T.; Ladner, T.R.; Yaeger, K.A.; et al. Large-vessel stroke as a presenting feature of Covid-19 in the young. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkler, A.E.; Parikh, N.S.; Mir, S.; Gupta, A.; Kamel, H.; Lin, E.; Lantos, J.; Schenck, E.J.; Goyal, P.; Bruce, S.S.; et al. Risk of ischemic stroke in patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) vs Patients with influenza. JAMA Neurol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klok, F.A.; Kruip, M.J.H.A.; van der Meer, N.J.M.; Arbous, M.S.; Gommers, D.A.M.P.J.; Kant, K.M.; Kaptein, F.H.J.; van Paassen, J.; Stals, M.A.M.; Huisman, M.V.; et al. Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19. Thromb. Res. 2020, 191, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodigiani, C.; Iapichino, G.; Carenzo, L.; Cecconi, M.; Ferrazzi, P.; Sebastian, T.; Kucher, N.; Studt, J.-D.; Sacco, C.; Alexia, B.; et al. Venous and arterial thromboembolic complications in COVID-19 patients admitted to an academic hospital in Milan, Italy. Thromb. Res. 2020, 191, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghi, S.; Ishida, K.; Torres, J.; Mac Grory, B.; Raz, E.; Humbert, K.; Henninger, N.; Trivedi, T.; Lillemoe, K.; Alam, S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 and stroke in a New York Healthcare System. Stroke 2020, 51, 2002–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Zhou, L.; Hu, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhang, S.; Chen, M.; Yu, H.; Tian, D.-S.; Wang, W. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of COVID-19 patients with a history of stroke in Wuhan, China. Stroke 2020, 51, 2219–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corman, V.M.; Lienau, J.; Witzenrath, M. Coronaviruses as the cause of respiratory infections. Internist 2019, 60, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mousavizadeh, L.; Ghasemi, S. Genotype and phenotype of COVID-19: Their roles in pathogenesis. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-C.; Bai, W.-Z.; Hashikawa, T. The neuroinvasive potential of SARS-CoV2 may play a role in the respiratory failure of COVID-19 patients. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 552–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamming, I.; Timens, W.; Bulthuis, M.L.C.; Lely, A.T.; Navis, G.J.; van Goor, H. Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis. J. Pathol. 2004, 203, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; He, L.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Z.; Che, X.; Hou, J.; Wang, H.; Shen, H.; Qiu, L.; Li, Z.; et al. Organ distribution of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) associated coronavirus (SARS-CoV) in SARS patients: Implications for pathogenesis and virus transmission pathways. J. Pathol. 2004, 203, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Gong, E.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, J.; Gao, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Zou, W.; Zhan, J.; Wang, S.; Xie, Z.; et al. Multiple organ infection and the pathogenesis of SARS. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhong, S.; Liu, J.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Li, Z.; Deng, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, N.; et al. Detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus in the brain: Potential role of the chemokine MiG in pathogenesis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Netland, J.; Meyerholz, D.K.; Moore, S.; Cassell, M.; Perlman, S. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection causes neuronal death in the absence of encephalitis in mice transgenic for human ACE2. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 7264–7275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verdecchia, P.; Cavallini, C.; Spanevello, A.; Angeli, F. The pivotal link between ACE2 deficiency and SARS-CoV-2 infection. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 76, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Lazartigues, E. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: Central regulator for cardiovascular function. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2010, 12, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zhou, M.; Dong, X.; Qu, J.; Gong, F.; Han, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. Lancet 2020, 395, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalrymple, N.A.; Mackow, E.R. Virus interactions with endothelial cell receptors: Implications for viral pathogenesis. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2014, 7, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Hinsbergh, V.W.M. Endothelium—Role in regulation of coagulation and inflammation. Semin. Immunopathol. 2012, 34, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cotran, R.S.; Pober, J.S. Effects of cytokines on vascular endothelium: Their role in vascular and immune injury. Kidney Int. 1989, 35, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doll, D.N.; Barr, T.L.; Simpkins, J.W. Cytokines: Their role in stroke and potential use as biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Aging Dis. 2014, 5, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javanmard, S.H.; Nasim, D. The effect of interferon γ on endothelial cell nitric oxide production and apoptosis. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2012, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyer, K.K.; Dooms, H.; Barron, L.; Abbas, A.K. Interleukin-2 in the development and control of inflammatory disease. Immunol. Rev. 2008, 226, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Paul, A.; Ko, K.W.S.; Sheldon, M.; Rich, B.E.; Terashima, T.; Dieker, C.; Cormier, S.; Li, L.; Nour, E.A.; et al. Interleukin-7 induces recruitment of monocytes/macrophages to endothelium. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 3114–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmane, S.L.; Kremlev, S.; Amini, S.; Sawaya, B.E. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1): An overview. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009, 29, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menten, P.; Wuyts, A.; Van Damme, J. Macrophage inflammatory protein-1. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2002, 13, 455–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Guo, S.; Hibbert, J.M.; Jain, V.; Singh, N.; Wilson, N.O.; Stiles, J.K. CXCL10/IP-10 in infectious diseases pathogenesis and potential therapeutic implications. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2011, 22, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, D.; Li, P.; Gong, K.; Yang, Z.; Yu, H.; Hage, F.G.; Oparil, S.; Chen, Y.-F. Endothelial cells overexpressing interleukin-8 receptors reduce inflammatory and neointimal responses to arterial injury. Circulation 2012, 125, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas-Zuleta, W.G.; Sanchez, E. IL-9: Function, sources, and detection. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1585, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, A.; Han, J.; Kim, S.O. The multifaceted effects of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in immunomodulation and potential roles in intestinal immune homeostasis. IUBMB Life 2010, 62, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mostafa Mtairag, E.; Chollet-Martin, S.; Oudghiri, M.; Laquay, N.; Jacob, M.-P.; Michel, J.-B.; Feldman, L.J. Effects of interleukin-10 on monocyte/endothelial cell adhesion and MMP-9/TIMP-1 secretion. Cardiovasc. Res. 2001, 49, 882–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamilos, M.; Petousis, S.; Parthenakis, F. Interaction between platelets and endothelium: From pathophysiology to new therapeutic options. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2018, 8, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, A.J. Continuing education course #2: Current understanding of hemostasis. Toxicol. Pathol. 2011, 39, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Meyer, S.F.; Denorme, F.; Langhauser, F.; Geuss, E.; Fluri, F.; Kleinschnitz, C. Thromboinflammation in stroke brain damage. Stroke 2016, 47, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ed Rainger, G.; Chimen, M.; Harrison, M.J.; Yates, C.M.; Harrison, P.; Watson, S.P.; Lordkipanidzé, M.; Nash, G.B. The role of platelets in the recruitment of leukocytes during vascular disease. Platelets 2015, 26, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szelenberger, R.; Kostka, J.; Saluk-Bijak, J.; Miller, E. Pharmacological interventions and rehabilitation approach for enhancing brain self-repair and stroke recovery. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2020, 18, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers William, J.; Rabinstein Alejandro, A.; Ackerson, T.; Adeoye Opeolu, M.; Bambakidis Nicholas, C.; Becker, K.; Biller, J.; Brown, M.; Demaerschalk Bart, M.; Hoh, B.; et al. 2018 Guidelines for the Early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: A guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2018, 49, e46–e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines. National Institutes of Health. Available online: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/ (accessed on 10 August 2020).
| Remdesivir | Intravenous prodrug responsible for inhibiting viral replication via binding to the viral RNA polymerase. |
| Chloroquine/Hydroxychloroquine | Antimalarial drug, which inhibits the fusion of virus with host cell membranes. In vitro studies showed that both drugs may block the viral transport from endosomes to endolysosomes, thus regulating the releasement of viral genome. Chloroquine has an ability to inhibits glycosylation of ACE2 receptor, thus interfering the viral linkage. |
| Lopinavir/Ritonavir | Lopinavir/Ritonavir inhibits the activity of proteases responsible for replication of SARS-CoV-2. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szelenberger, R.; Saluk-Bijak, J.; Bijak, M. Ischemic Stroke among the Symptoms Caused by the COVID-19 Infection. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2688. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092688
Szelenberger R, Saluk-Bijak J, Bijak M. Ischemic Stroke among the Symptoms Caused by the COVID-19 Infection. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(9):2688. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092688
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzelenberger, Rafal, Joanna Saluk-Bijak, and Michal Bijak. 2020. "Ischemic Stroke among the Symptoms Caused by the COVID-19 Infection" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 9: 2688. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092688
APA StyleSzelenberger, R., Saluk-Bijak, J., & Bijak, M. (2020). Ischemic Stroke among the Symptoms Caused by the COVID-19 Infection. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(9), 2688. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092688






