Is There a Role for Spacer Exchange in Two-Stage Exchange Arthroplasty for Periprosthetic Joint Infection?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Spacers
Types of Spacers
3. Spacer Exchange
3.1. Reasons for Spacer Exchange
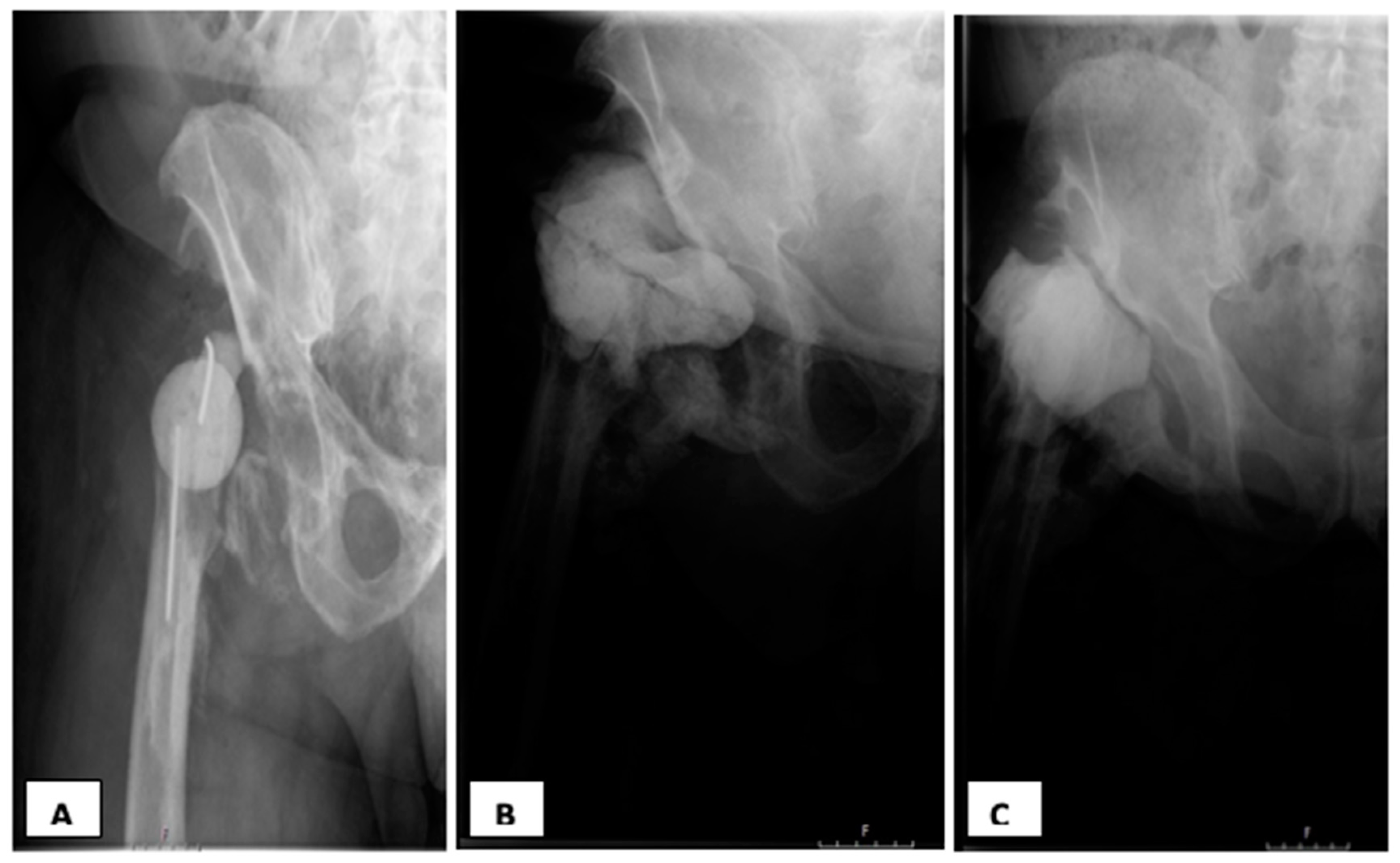
3.1.1. Mechanical Complications
3.1.2. Persistence of Infection
3.2. Spacer Exchange and Reimplantation
3.3. Impact of Spacer Exchange on the Success of Two-Stage Revision
3.3.1. Success of Two-Stage Revision
3.3.2. Spacer Exchange and the Success of Two-Stage Revision
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Namba, R.S.; Inacio, M.C.; Paxton, E.W. Risk Factors Associated with Deep Surgical Site Infections After Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2013, 95, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edwards, J.R.; Peterson, K.D.; Mu, Y.; Banerjee, S.; Allen-Bridson, K.; Morrell, G.; Dudeck, M.A.; Pollock, D.A.; Horan, T.C. National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) report: Data summary for 2006 through 2008, issued December 2009. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2009, 37, 783–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runner, R.P.; Mener, A.; Roberson, J.R.; Bradbury, T.L.; Guild, G.N.; Boden, S.D.; Erens, G.A. Prosthetic Joint Infection Trends at a Dedicated Orthopaedics Specialty Hospital. Adv. Orthop. 2019, 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.-D.; Wang, Y.-P.; Chen, C.-F.; Chen, H.-P. The incidence rate, trend and microbiological aetiology of prosthetic joint infection after total knee arthroplasty: A 13 years’ experience from a tertiary medical center in Taiwan. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2018, 51, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, M.; Premkumar, A.; Sheth, N.P. Projected Volume of Primary Total Joint Arthroplasty in the U.S., 2014 to 2030. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2018, 100, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmon, D.R.; Berbari, E.F.; Berendt, A.R.; Lew, D.; Zimmerli, W.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Rao, N.; Hanssen, A.; Wilson, W.R. Diagnosis and Management of Prosthetic Joint Infection: Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 56, e1–e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Urish, K.L.; Bullock, A.G.; Kreger, A.M.; Shah, N.B.; Jeong, K.; Rothenberger, S.D.; Infected Implant Consortium; Kreger, A. A Multicenter Study of Irrigation and Debridement in Total Knee Arthroplasty Periprosthetic Joint Infection: Treatment Failure Is High. J. Arthroplast. 2017, 33, 1154–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barberán, J.; Aguilar, L.; Carroquino, G.; Giménez, M.-J.; Artola, B.S.; Martinez, D.; Prieto, J. Conservative Treatment of Staphylococcal Prosthetic Joint Infections in Elderly Patients. Am. J. Med. 2006, 119, 993.e7–993.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, E.J.; Woodson, C.; Holtom, P.; Roidis, N.; Shufelt, C.; Patzakis, M. Periprosthetic Total Hip Infection. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2002, 403, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelli, C.C.; Gotti, V.; Ferrari, R. Two-stage treatment of infected total knee arthroplasty: Two to thirteen year experience using an articulating preformed spacer. Int. Orthop. 2014, 38, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooper, H.J.; Della Valle, C.J. The two-stage standard in revision total hip replacement. Bone Jt. J. 2013, 95-B, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanem, E.; Azzam, K.; Seeley, M.; Joshi, A.; Parvizi, J. Staged Revision for Knee Arthroplasty Infection: What Is the Role of Serologic Tests Before Reimplantation? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2009, 467, 1699–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bejon, P.; Berendt, A.; Atkins, B.L.; Green, N.; Parry, H.; Masters, S.; McLardy-Smith, P.; Gundle, R.; Byren, I. Two-stage revision for prosthetic joint infection: Predictors of outcome and the role of reimplantation microbiology. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Engesæter, L.B.; Dale, H.; Schrama, J.C.; Hallan, G.; Lie, S.A. Surgical procedures in the treatment of 784 infected THAs reported to the Norwegian Arthroplasty Register. Acta Orthop. 2011, 82, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, M.; Clar, H.; Friesenbichler, J.; Schwantzer, G.; Bernhardt, G.; Gruber, G.; Glehr, M.; Leithner, A.; Sadoghi, P. Prosthetic joint infection following total hip replacement: Results of one-stage versus two-stage exchange. Int. Orthop. 2014, 38, 1363–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Angelo, F.; Negri, L.; Binda, T.; Zatti, G.; Cherubino, P. The use of a preformed spacer in two-stage revision of infected hip arthroplasties. Musculoskelet. Surg. 2011, 95, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-H.; Kim, J.-S.; Park, J.-W.; Joo, J.-H. Cementless revision for infected total hip replacements. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 2011, 93, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, F.S.; Muirhead-Allwood, S.K.; Manktelow, A.R.J.; Bacarese-Hamilton, I. Two-stage uncemented revision hip arthroplasty for infection. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 2000, 82, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.S.; Raja, S.; Khan, M.A.; Haddad, F.S. A multidisciplinary team approach to two-stage revision for the infected hip replacement. Bone Jt. J. 2014, 96, 1312–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, K.H.; Yang, J.-W.; Cho, S.-H.; Song, H.-R.; Park, H.-B.; Ha, Y.-C.; Chang, J.-D.; Kim, S.-Y.; Kim, Y.-H. Impregnation of vancomycin, gentamicin, and cefotaxime in a cement spacer for two-stage cementless reconstruction in infected total hip arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2001, 16, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.; Miller, E.M.; Curtis, G.L.; Klika, A.; Barsoum, W.K.; Mont, M.A.; Higuera, C.A. Success of Two-Stage Reimplantation in Patients Requiring an Interim Spacer Exchange. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, S228–S232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, T.L.; Goswami, K.; Kheir, M.M.; Xu, C.; Wang, Q.; Parvizi, J. Surgical Treatment of Chronic Periprosthetic Joint Infection: Fate of Spacer Exchanges. J. Arthroplast. 2019, 34, 2085–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukeik, M. Two-stage procedure in the treatment of late chronic hip infections - spacer implantation. Int. J. Med Sci. 2009, 6, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charette, R.S.; Melnic, C.M. Two-Stage Revision Arthroplasty for the Treatment of Prosthetic Joint Infection. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2018, 11, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, E.K.; Seon, J.K.; Jeong, M.S. Delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction to piperacillin/tazobactam in a patient with an infected total knee replacement. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 2010, 92, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, B.; Hanson, A.; Sha, B. Diffuse Desquamating Rash Following Exposure to Vancomycin-Impregnated Bone Cement. Ann. Pharmacother. 2014, 48, 1061–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aeng, E.S.Y.; Shalansky, K.; Lau, T.T.Y.; Zalunardo, N.; Li, G.; Bowie, W.R.; Duncan, C.P. Acute Kidney Injury With Tobramycin-Impregnated Bone Cement Spacers in Prosthetic Joint Infections. Ann. Pharmacother. 2015, 49, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menge, T.J.; Koethe, J.; Jenkins, C.A.; Wright, P.W.; Shinar, A.A.; Miller, G.G.; Holt, G.E. Acute Kidney Injury After Placement of an Antibiotic-Impregnated Cement Spacer During Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2012, 27, 1221.e2–1227.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citak, M.; Masri, B.A.; Springer, B.; Argenson, J.-N.; Kendoff, D.O. Are Preformed Articulating Spacers Superior To Surgeon-Made Articulating Spacers in the Treatment Of PJI in THA? A Literature Review. Open Orthop. J. 2015, 9, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voleti, P.B.; Baldwin, K.D.; Lee, G.-C. Use of Static or Articulating Spacers for Infection Following Total Knee Arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2013, 95, 1594–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahhas, C.R.; Chalmers, P.N.; Parvizi, J.; Sporer, S.M.; Berend, K.R.; Moric, M.; Chen, A.F.; Austin, M.S.; Deirmengian, G.K.; Morris, M.J.; et al. A Randomized Trial of Static and Articulating Spacers for the Treatment of Infection Following Total Knee Arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2020, 102, 778–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emerson, R.H., Jr.; Muncie, M.; Tarbox, T.R.; Higgins, L.L. Comparison of a Static with a Mobile Spacer in Total Knee Infection. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2002, 404, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, P.-H.; Shih, C.-H.; Chang, Y.; Lee, M.S.; Shih, H.-N.; Yang, W.-E. Two-stage revision hip arthroplasty for infection: Comparison between the interim use of antibiotic-loaded cement beads and a spacer prosthesis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2004, 86, 1989–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzucchelli, L.; Rosso, F.; Marmotti, A.; Bonasia, D.E.; Bruzzone, M.; Rossi, R. The use of spacers (static and mobile) in infection knee arthroplasty. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2015, 8, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mariconda, M.; Ascione, T.; Balato, G.; Rotondo, R.; Smeraglia, F.; Costa, G.G.; Conte, M. Sonication of antibiotic-loaded cement spacers in a two-stage revision protocol for infected joint arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2013, 14, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, N.; Shanks, R.M.Q.; Davis, C.M.; Craft, D.W.; Wood, T.K.; Hamlin, B.R.; Urish, K.L. Viable bacteria persist on antibiotic spacers following two-stage revision for periprosthetic joint infection. J. Orthop. Res. 2017, 36, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sigmund, I.K.; Winkler, T.; Önder, N.; Perka, C.; Renz, N.; Trampuz, A. Complications of Resection Arthroplasty in Two-Stage Revision for the Treatment of Periprosthetic Hip Joint Infection. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Struelens, B.; Claes, S.; Bellemans, J. Spacer-related problems in two-stage revision knee arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. Belg. 2013, 79, 422–426. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, J. Complications after spacer implantation in the treatment of hip joint infections. Int. J. Med Sci. 2009, 6, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lau, A.C.; Howard, J.L.; Macdonald, S.J.; Teeter, M.G.; Lanting, B.A.; Information, P.E.K.F.C. The Effect of Subluxation of Articulating Antibiotic Spacers on Bone Defects and Degree of Constraint in Revision Knee Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2016, 31, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Diemen, M.P.; Colen, S.; Dalemans, A.A.; Stuyck, J.; Mulier, M. Two-Stage Revision of an Infected Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Follow-up of 136 Patients. HIP Int. 2013, 23, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel, M.P.; Barreira, P.; Battenberg, A.; Berry, D.J.; Blevins, K.; Font-Vizcarra, L.; Frommelt, L.; Goswami, K.; Greiner, J.; Janz, V.; et al. Hip and Knee Section, Treatment, Two-Stage Exchange Spacer-Related: Proceedings of International Consensus on Orthopedic Infections. J. Arthroplast. 2019, 34, S427–S438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Ledezma, C.; Higuera, C.A.; Parvizi, J. Success After Treatment of Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Delphi-based International Multidisciplinary Consensus. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2013, 471, 2374–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parvizi, J.; Zmistowski, B.; Berbari, E.F.; Bauer, T.W.; Springer, B.D.; Della Valle, C.J.; Garvin, K.L.; Mont, M.A.; Wongworawat, M.D.; Zalavras, C.G. New Definition for Periprosthetic Joint Infection: From the Workgroup of the Musculoskeletal Infection Society. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2011, 469, 2992–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parvizi, J.; Tan, T.L.; Goswami, K.; Higuera, C.; Della Valle, C.; Chen, A.F.; Shohat, N.; Tan, T. The 2018 Definition of Periprosthetic Hip and Knee Infection: An Evidence-Based and Validated Criteria. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 1309.e2–1314.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, W.-S.; Byun, S.-E.; Cho, W.-J.; Yoon, Y.-S.; Dhurve, K. Polymorphonuclear Cell Count on Frozen Section Is Not an Absolute Index of Reimplantation in Infected Total Knee Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2013, 28, 1874–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.; Kwiecien, G.; Klika, A.; Ramanathan, D.; Bauer, T.W.; Barsoum, W.K.; Higuera, C.A. Are Frozen Sections and MSIS Criteria Reliable at the Time of Reimplantation of Two-stage Revision Arthroplasty? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2016, 474, 1619–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zmistowski, B.M.; Clyde, C.T.; Ghanem, E.; Gotoff, J.R.; Deirmengian, C.; Parvizi, J. Utility of Synovial White Blood Cell Count and Differential Before Reimplantation Surgery. J. Arthroplast. 2017, 32, 2820–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusuma, S.K.; Ward, J.; Jacofsky, M.; Sporer, S.M.; Della Valle, C.J. What is the Role of Serological Testing Between Stages of Two-stage Reconstruction of the Infected Prosthetic Knee? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2010, 469, 1002–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samuel, L.T.; Sultan, A.A.; Kheir, M.; Villa, J.; Patel, P.; Parvizi, J.; Higuera, C.A. Positive Alpha-defensin at Reimplantation of a Two-stage Revision Arthroplasty Is Not Associated with Infection at 1 Year. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2019, 477, 1615–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, A.; Kheir, M.M.; Tarabichi, M.; Hosseinzadeh, H.R.; Tan, T.L.; Parvizi, J. Serum D-Dimer Test Is Promising for the Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection and Timing of Reimplantation. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2017, 99, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Meng, Z.; Pan, L.; Liu, H.; Yang, X.; Yongping, C.; Hao, W.; Zhichao, M.; Liping, P.; Heng, L.; et al. Plasma Fibrinogen Performs Better Than Plasma d-Dimer and Fibrin Degradation Product in the Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection and Determination of Reimplantation Timing. J. Arthroplast. 2020, 35, 2230–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babis, G.C.; Sakellariou, V.I.; Pantos, P.G.; Sasalos, G.G.; Stavropoulos, N.A. Two-Stage Revision Protocol in Multidrug Resistant Periprosthetic Infection Following Total Hip Arthroplasty Using a Long Interval Between Stages. J. Arthroplast. 2015, 30, 1602–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, A.A.; Goswami, K.; Shohat, N.; Tokarski, A.T.; White, A.E.; Parvizi, J. Time to Reimplantation: Waiting Longer Confers No Added Benefit. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 1850–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabry, F.Y.; Buller, L.; Ahmed, S.; Klika, A.K.; Barsoum, W.K. Preoperative Prediction of Failure Following Two-Stage Revision for Knee Prosthetic Joint Infections. J. Arthroplast. 2014, 29, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, S.M.J.; Vegari, D.; Ho, A.; Zmistowski, B.; Parvizi, J. Two-stage Exchange Arthroplasty for Infected Total Knee Arthroplasty: Predictors of Failure. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2011, 469, 3049–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomez, M.M.; Tan, T.L.; Manrique, J.; Deirmengian, G.K.; Parvizi, J. The Fate of Spacers in the Treatment of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2015, 97, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Goswami, K.; Kuo, F.-C.; Xu, C.; Tan, T.L.; Parvizi, J. Two-Stage Exchange Arthroplasty for Periprosthetic Joint Infection: The Rate and Reason for the Attrition After the First Stage. J. Arthroplast. 2019, 34, 2749–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, M.K.; Damsgaard, C.; Wadibia, J.; Wong, G.; Lazar, D.; Smith, E.; Talmo, C.; Bedair, H. Laboratory Tests for Diagnosis of Chronic Periprosthetic Joint Infection Can Help Predict Outcomes of Two-Stage Exchange. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2018, 100, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillingham, Y.A.; Della Valle, C.J.; Suleiman, L.I.; Springer, B.D.; Gehrke, T.; Bini, S.A.; Segreti, J.; Chen, A.F.; Goswami, K.; Tan, T.L.; et al. Definition of Successful Infection Management and Guidelines for Reporting of Outcomes After Surgical Treatment of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2019, 101, e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kozaily, E.; Chisari, E.; Parvizi, J. Is There a Role for Spacer Exchange in Two-Stage Exchange Arthroplasty for Periprosthetic Joint Infection? J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092901
Kozaily E, Chisari E, Parvizi J. Is There a Role for Spacer Exchange in Two-Stage Exchange Arthroplasty for Periprosthetic Joint Infection? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(9):2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092901
Chicago/Turabian StyleKozaily, Elie, Emanuele Chisari, and Javad Parvizi. 2020. "Is There a Role for Spacer Exchange in Two-Stage Exchange Arthroplasty for Periprosthetic Joint Infection?" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 9: 2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092901
APA StyleKozaily, E., Chisari, E., & Parvizi, J. (2020). Is There a Role for Spacer Exchange in Two-Stage Exchange Arthroplasty for Periprosthetic Joint Infection? Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(9), 2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092901





