1. Introduction
Ewe production in Portugal has changed a lot in the last 20 years. Its numbers have consistently increased from Portugal’s entry into the EU in 1989 until 1998, from 3547 to 3590 thousand animals [
1]. However, from 1998 until 2018, the percentage of sheep has decreased almost 40%, reaching 2208 thousand animals by the end of this period. This decrease is felt in all Portuguese regions but is particularly noticeable in the south of the country. The Alentejo region concentrates 55% to 60% of the total sheep production and had a decrease from 1883 to 1305 thousand animals during this period, which means that in this region were lost around 42% of the animals lost [
2].
Even though we can find some milk ewe production systems in Alentejo, the region’s prime production is meat [
2]. The meat is raised in an extensive agro-silvo-pastoral system known as Montado, which is characteristic and cover c.a. 1.2 million ha of the south of Portugal, mainly used for extensive livestock grazing [
3]. In this multifunctional system, cork oaks (
Quercus suber) represent around 70% of the area and holm oaks (
Quercus ilex) 30%. The system as a whole represents 34% of the total national forest [
4].
The combination of a system that is progressively adapted from a natural ecosystem to a productive agro-silvo and pastoral land use system results in an almost perfect integration [
4]. The same authors [
5] state that this integration requires multiple levels of human intervention and that until 1960 and 1970, most of the work required by the system was done with manual labor. This reflected the property and social structure present in the region of Alentejo.
Teller, Mathy, and Jeffers [
6], who analyzed the Spanish Montado (known as Dehesa), also stated that in this system, until the 1970s, only shepherds, without the use of fences, supervised the animal herds. Moreover, any additional maintenance of clear areas and shrub species control were done manually, which was possible due to the extremely low salaries paid.
The maintenance of this labor-intensive system did not survive the increase of workforce salaries, which were not accompanied by the same increase on the value of the system’s products [
6]. Pinto Correia and Godinho [
5] state that in Portugal, the increase in labor, production costs, and mechanization as well as the change in the political Portuguese regime, the integration in the European Union and the general globalization of markets disrupted the formal balance on Montado management.
Policy also contributed to a latter change. Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) per head livestock payments led to grazing intensification and to failures in tree regeneration in some areas [
7]. Additionally, as payments for cattle have been considerably superior to those for sheep, producers changed their activity from sheep and goats to cattle grazing, even though sheep have a lower grazing impact, which contributes to the maintenance of the Montado balance [
5]. Finally, extensification or abandonment of less fertile areas and intensification in more fertile ones are now pressing the system [
8].
Fragoso et al. [
9] state that the resources’ allocation is determined by their marginal value or opportunity cost. The decoupling of payments reduces the land rental price and the earned income from farm production with some impacts occurring, as expected, on the allocation of resources, other than land, as labor and capital. Katranidis and Kotakou [
10] state that the decoupling of payments leads production decisions, so the allocation of resources tends to be more dependent on market prices and competitive advantages. The mix of coupled and decoupled payments also affects production decisions and resources’ allocation.
Due to changes in labor supply and policy shifts, animal production has shifted from sheep and goats to cattle grazing over the last 20 to 30 years, causing the decrease pointed to above.
Nevertheless, the maintenance of Montado balance is easier with sheep that have a lower grazing impact than cattle [
5]. For this reason, it is important to assess the competitiveness of sheep production in this system among other European Union sheep production systems.
The system is sustainable in the sense defined by Sassenrath et al. [
11] “an approach to producing food and fibre which is profitable, uses on-farm resources efficiently to minimize adverse effects on environment and people, preserves the natural productivity and quality of the land and water, and sustains vibrant rural communities”. Nevertheless, analyzing vulnerability in the South of Portugal, Máñez Costa et al. [
12] state that the future can unfold in many different ways and the pathway embraced by the region will reflect the prevailing socioeconomic and policy drivers.
For farmers, the competitiveness of the systems, at least among their peers, is an important issue. Pinto Correia and Godinho [
5] cite [
13], stating that studies on Alentejo have shown that land managers want to be seen as successful producers in order to keep their position within the farmers’ community and to perceive themselves as good farmers. This perception is strongly linked with the competitiveness and efficiency of their production system.
The objective of this paper is to analyze the ewe production systems in the Montado, using the agri benchmark database, and compare these systems with other European countries’ systems, ranking their competitiveness and efficiency among other systems in the European Union.
The paper is structured in five sections. Beside this Introduction, the Material and Methods present the main concepts underlying the agri benchmark network and make a brief presentation of the EU ewe farms considered in this network. The Results section presents the results of the applied methodology to the network ewe farms. During the Discussion section the results obtained are discussed, as well as the reasons behind them. The Conclusions section withdraws the main conclusion of this method application and suggestions are provided.
2. Material and Methods
As no previous research had been carried on to assess the competitiveness of sheep production in the Montado silvo-pastoral agro-ecosystem among other European Union sheep production systems, this study was exploratory in nature and was conducted to have a better understanding of the existing phenomenon [
14]. In addition, this is a research that allows answering an unknown problem precisely enough [
15].
The method of collection, analysis, and data interpretation in our study was based on secondary information. This systematic method with procedural and evaluative steps, in our study included two steps. The first step involved past data collection, embracing literature review and statistical data, accessible via various online and offline resources. This step aimed to specify how these past data contribute to our current research. The second step was focused on the agri benchmark database and its data availability and analysis methodology.
Agri benchmark is a global, non-profit network of agricultural economists, advisors, producers and specialists in key sectors of agricultural and horticultural value chains. It uses internationally standardized methods to analyze farms, production systems, and their profitability. The farm-level knowledge provided by partners world-wide is combined with an analysis of international commodity markets and value chains. This allows the provision of scientifically consistent and soundly based answers on strategic issues to decision-makers in policy, agriculture and agribusiness [
16].
The Portuguese ewe farms presented in the agri benchmark database are Montado farms. The agri benchmark database includes typical farms, which are defined as [
17]: (1) being an existing farm or a data set describing a farm; (2) being in a specific region which represents a major share of output for the product considered; (3) running the prevailing production system for the product considered; (4) reflecting the prevailing combination of enterprises as well as land and capital resources; and, (5) reflecting the prevailing type of labor organization.
As averages do not provide consistent production system data sets, the typical farms are not averages but rather the result of a panel meeting with four to six farmers and an advisor, where each figure is obtained in a consensus and/or based on individual farms which were ‘typified’ by replacing farm individual particularities by prevailing characteristics, figures, technologies, and procedures [
18].
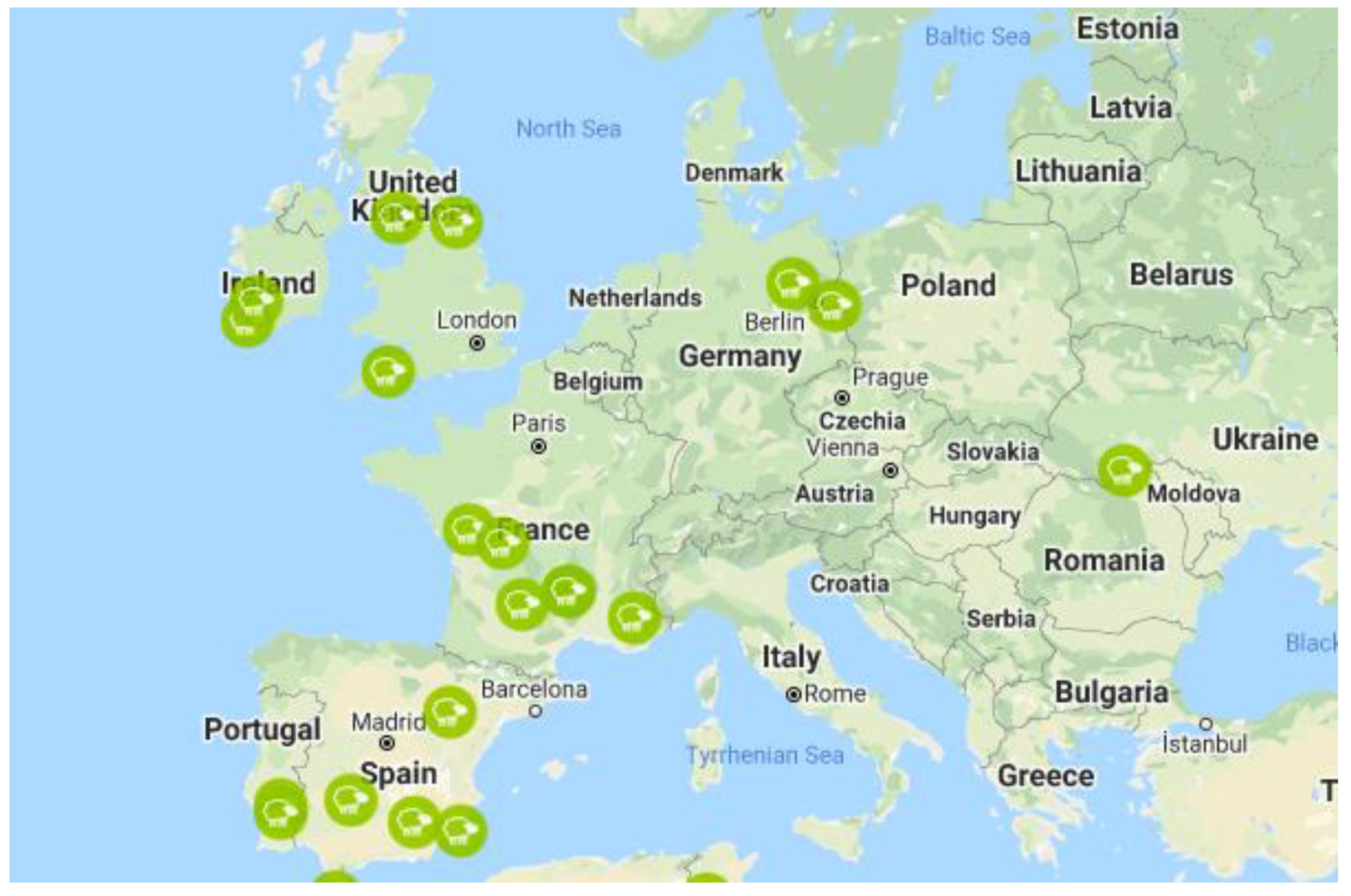
The EU ewe farms in the database are presented in
Figure 1. We still use the UK ewe farms for the comparison because the data that we have until this moment corresponds to farms that follow the CAP guidelines as EU farms. The data presented in the figures refers to the year 2018.
As shown in
Table 1, the feeding system in all typologies of enterprises in Portugal is based on grazing (PT_600 and PT_700). The first of these farms (PT_600) will be referred, from now on, as the bigger farm, since it represents a more extensive system based in a big extension of land. In opposition, the other farm (PT_700) will be referred as the smaller farm. In Spain ewe enterprises, the feeding system is based on grains, concentrates, and forages (ES_600, ES_800, ES_900, ES_1400, ES_2650). French ewe enterprises have different feeding systems, based on grazing (FR_460, FR_860) or based on grains, concentrates and forages (FR_470, FR_500, FR_750). In Germany, the feeding systems of ewe enterprises are based on grazing (DE_500, DE_1000) as well as in Ireland (IE_230, IE_300) and UK (UK_500, UK_700).
The competitiveness of these systems will be assessed using standard economic indicators, both on the structure of the farm (whole farm figures) and on the economic viability of the productions (enterprise figures).
Whole-farm figures
Return structure—this indicator weights the different farm activities on the farm returns.
Percentage composition of whole farm returns—this indicator shows, on a percentage basis, where the whole farm returns come from.
Whole farm costs—this indicator details the farms’ cost structure.
Whole farm profitability.
Enterprise figures
The efficiency of the production and the resources’ use will be assessed using standard indicators that compare production efficiency regardless of mother’s weight or race:
The economic indicator chosen, which can be expressed per animal, per ha and per 100 kg live weight sold, is:
Productivity figures are:
Economic labor productivity.
Physical labor productivity.
Cash and non-cash costs, returns, and profitability.
Profitability with variations in opportunity costs.
4. Discussion
Typically, the Montado silvo-pastoral agro-ecosystem is related to low intensity, low inputs, and high structural diversity [
19]. In this grazed Mediterranean open woodland, acorn and semi-natural vegetation are the alimentary basis of the sheep, Iberian pigs, and cattle explored in these livestock farming systems [
20].
Ewe production systems in the Montado area have two different orientations: specialized ewe production farms; or complementary ewes to cow-calf production assuring the most efficient use of pasture and a risk diversification. In both cases the competitiveness of the system is important. However, when ewes complement cow-calf, the farm economic returns are mainly from cow-calf instead of ewes. Cattle production means higher returns, though they are more demanding in terms of fodder intake and have greater impacts on the soil and trees’ roots [
19]. According to these authors, sheep are less demanding in fodder and have a lesser impact on the soil. Indeed, sheep are better adapted to an extensive governance model which relies on grazing in natural pastures, thus requiring very little investment in pasture improvement or fodder production [
19].
The Portuguese ewe typical farms on agri benchmark are managed extensively, with very low levels of capital input. The use of labour is low and although its physical productivity is poor, particularly in the most extensive farms, the economic efficiency of labour is very good in both cases.
For both systems, most of the returns that do not come from the market come from decoupled payments. The market returns and decoupled payments assure 92% of farm returns for the ewe specialized farm, and 79% for the farm combining suckler cows and ewes. The discussion about competitiveness must not ignore government payments that assure the human presence in the man-made ecosystem of the Montado. Concerning competitiveness, the main question is whether or not the resulting structure assures that decision-making is linked to market prices and competitive advantages of ewe production, which is clearly the case. Thus, it is important that market values sheep products.
Sheep production has to increase certified products (per example, biological production, for which the Alentejo region has the biggest share in the country) especially if it is to reach external markets. The non-differentiation of sheep products induces several constraints in per capita consumption and imports. Producers should invest in this approach so that the productions can increase not just in number but also in market dimension. Better assistance to producers and an increase in their levels of schooling is necessary so that there will be more innovation and more productivity.
Additionally, Pinto Correia and Breman [
21] stated that the diversification to other income sources, such as hunting or green/environmental tourism, is most likely a good option for the future of these farms. This diversification will improve the balance between costs from Profit and Loss, account, and returns.
Nevertheless, there is a great need to support producer’s sustainability, reducing the gap between producer prices and transformation/distribution prices. In addition, the increase of short chains and the creation of partnerships with local restaurants, where producers can sell their products directly without needing transformation or distribution channels. Such can be appealing to new consumers and increase the willingness to pay for the product.
The Montado systems are classified as extensive systems, mostly meaning an extensive use of land. Our results show that ewe Montado systems are also not capital intensive. Labor seem to remain an important resource, which is also true in most of the EU and UK production systems. Albeit to a lesser degree than in the past, the Montado systems are still dependent on work, especially the most extensive ones, as capital resources are mostly linked with fences, feeders and other livestock handling equipment. Such emphasizes the social importance of the Montado in rural areas.
With this background, it is important to analyze the production efficiency of these systems among EU and UK ewe production systems.
The Portuguese ewe specialized farm is one of the most efficient farms analyzed when concerning the weaned lambs per 100 ewes a year. In fact, it belongs to the top 22% more productive farms in the sample. This result is most likely a consequence of the crossbreed choice that profits from a more productive breed on crosses.
The efficiency measured through the total LW sold per kg of breeding ewe also showed that Portuguese farms are the most efficient. This can be seen as a proxy for the current and future competitiveness of this production.
In what concerns cash and non-cash costs, returns, and profitability, it is possible to state that for the smaller Portuguese farm (PT_700) an increase on productivity or a reduction on cash costs would easily assure the long term economic sustainability of this farm, for which the returns pay already 95% of all costs. Nevertheless, managers have to be aware of the rationale behind every investment, so that those investments likely to raise fixed costs can be kept as low as possible. For the bigger Portuguese farm, returns pay cash costs, depreciation, and part of the opportunity costs that come from land. It can be argued that this farm could improve its long-term economic sustainability by a) improving the total LW sold per ewe that, as seen in
Figure 6, is low or by b) reducing the cash costs per kg of LW sold. However, the true question that should be raised is whether there is an opportunity for this land outside the system. The profitability with variations on opportunity costs shows clearly that, in this case, not considering the opportunity cost of land will considerably improve the farms’ profitability, meaning that in the long term the system is only profitable for landowners that have no other alternatives for land. The eco-labels and the geographic indications of origin can be one of the most suitable and profitable options for the ewe systems context in future [
22].
Like many other sectors, sheep production depends on several factors, both internal and external, and has many challenges ahead. Pinto Correia and Godinho [
5] stated that, when talking about preservation of the system or landscape, the question lies in which future pathways the land managers take. In addition, these traditional systems centered on one dominant tree species may be at risk under changing climatic conditions [
23]. So, we believe that the bigger challenge is dealing with a new green economy, with probable new functions and new opportunities for land. Will the land management take ownership of new functions that may support high environmental quality and be a source of economic returns, but depend on the existence of the agro-silvo-pastoral system? Or, particularly in the bigger and more extensive farms, will new needs within the bioeconomy create new opportunities for land, and therefore pressure these systems’ maintenance?
5. Conclusions
The objective of this paper was to analyze the ewe production systems in the Montado, using the agri benchmark database and quantitative standard analysis methodology, and compare these systems with other European countries’ systems, ranking their competitiveness and efficiency among other systems in the European Union. We concluded that this methodology facilitated an in-depth understanding not only of the competitiveness and efficiency of ewe production systems in Portugal but also of their positioning regarding other systems in the European Union.
A green economy is one that provides economic opportunities and improved human well-being as well as sustainable management of natural resources, with multiple forms of locally specific green-economy activity. If the key principle of the green economy is about seeking economic opportunities from socially and environmentally sustainable practices, the ewe production systems analyzed follow this principle. However, making the transition to the green economy in rural areas requires political will, technological developments, and encouragement from market pressures. In practice, transition is likely to take place through a sequence of progressive steps.
Emerging from the study is the fact that, on the one side, farms are competitive because they are depending on the market for their decisions and, on the other side, that the diversification to other income sources would be a good option for the future sustainability of these farms. Thus, one recommendation is that the impact of market changes in decision-making process and consequently in competitiveness of sheep production systems should be examined. Other suggestions for future research is to study the impact of diversification alternatives in order to improve the balance between cost and returns and/or in the pattern of returns and the sheep production systems competitive position.