- Article
Characterization of CircRNA Expression Profiles and ceRNA Networks in Mongolian Sheep Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Metabolism During Growth
- Yunfei Han,
- Lu Chen and
- Gerelt Borjigin
- + 3 authors
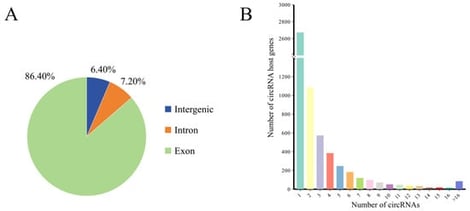
While circular RNAs (circRNAs) are known to play crucial roles in adipose tissue metabolism, their regulatory mechanisms in naturally grazing Mongolian sheep remain poorly understood. This study characterized the circRNA expression profiles in the subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT) of castrated rams (Mongolian sheep) at 6, 18, and 30 months after of birth (n = 3). A total of 18,581 circRNAs were identified in the SAT of these sheep, among which 203 were differentially expressed (DE) across different growth stages, including circRNA7989, circRNA2263, circRNA4685, and circRNA4786. The host genes of DE circRNAs were enriched in lipid metabolism, amino acid metabolism, and glucose metabolism. Moreover, competing endogenous RNA network analysis combining miRNA and mRNA data revealed that circRNA4744, circRNA12148, circRNA10725, and circRNA4895 potentially modulate adipocyte hyperplasia, TG synthesis, and fat deposition by regulating miRNAs that target PDPN, CYP26B1, COL24A1, and SCD. The results of the present study suggest that circRNAs and the ceRNA network play a critical role in SAT metabolism during the growth of naturally grazing sheep, offering a theoretical foundation for breeding strategies and meat quality regulation, for example, by modulating key genes such as circRNA4744, circRNA12148, circRNA10725, and circRNA4895.
9 February 2026



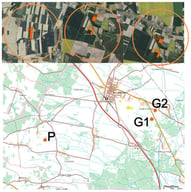
![Distribution and coverage of the IDs in Sinaloa Mexico: (a) geographic location of the study area at the national and continental scale; (b) spatial distribution of the irrigation districts in Sinaloa, including district boundaries, and main rivers. Source: prepared by the authors using CONAGUA data [45].](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/agriculture/agriculture-16-00399/article_deploy/html/images/agriculture-16-00399-g001-550.jpg)

